
Increasing Availability and Water Quality in Kampung Nelayan
Seberang Belawan, Medan City
I. Suryati
1
, N. Herlina
1
, M. Nasri Akbar
1
, R. Prayudhi Utama
1
, N. Latifah
1
and A. Muhammad Iman
1
1
Environmental Engineering, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Jl Almamater, Medan 20155, Indonesia
Keywords: availability, fishing villages, quantity, SDGs, water.
Abstract: The dominant coastal areas inhabited by the fishing villages are identical to slums. Slums can be seen from
scattered rubbish, toilet from latrines, and the lacking of clean water quality and quantity. Problems relating
to environmental sanitation in Kampung Nelayan Seberang Belawan are mainly caused by uneven
distribution of clean water and the quality of clean water that is physically cloudy and has a taste. Clean
water is needed in meeting the daily needs of fishing communities to drink, wash and bathe. The limited
resources and distribution of clean water in which the community of fishing villages has to take a long way
to get clean water and have to pay to get the clean water. The source of water which can be utilized in the
form of deep wells with a depth of ± 50 m - 80 m. The well is equipped with a suction pump. Meanwhile, to
improve the quality of water, was used simple a water filter tool in the form of slow sand filter with filter
media such as zeolite, silica sand, gravel and activated carbon. This slow sand filter media effectively
reduces Fe and Mn levels in clean water sources, especially ground water ranges from 33% - 96%.
1 INTRODUCTION
One of the goals of Sustainable Development Goals
(SDGs) is to ensure the availability, management of
clean water, and sustainable sanitation for all. In
achieving these objectives, the government sets
targets for 2019 outcome indicators such as 100%
access to drinking water services, 0% proportion of
inhabited households and inadequate slum
settlements in urban areas, as well as 100%
achievement of accessible sanitation services also
with the 100-0-100 program (Kementerian Pekerjaan
Umum, 2014).
Fulfilling the need for clean water is one of the
basic rights for every individual. The 1945
Constitution has mandated that every citizen of
Indonesia has the right to have a decent life. Water
as one of the fundamental human needs, not only in
terms of availability but also quality, accessibility
and affordability economically (Komisi Nasional
Hak Asasi Manusia, 2017).
Based on the global targets of sanitation and
clean water by 2030, is to achieve universal and
equitable access to safe and affordable drinking
water for all. Meanwhile, the national target is to
increase access to drinking water services, proper
sanitation, and sustainable. The national indicator to
achieve the target is the realization of 100% of
drinking water services, with 85% of the population
served by access to water in line with the 4K
principle (affordability, continuity, quality and
quantity) and the other 15% will be served in
accordance with basic service needs; (Baseline
2014: 70%, 2019 target: 100%) and access to
potable water (Komisi Nasional Hak Asasi Manusia,
2017;Badan Pusat Statisik, 2014).
Area with sanitary and clean water conditions
which is quite alarming in Indonesia is a coastal area
occupied by fishermen. Fishermen are a group of
people whose lives depend directly on seafood,
either by capture or cultivation. They generally live
on the beach, a neighborhood close to the location of
their activities (Mulyadi, 2007).
Geographically, the fishing community lives,
grows and develops in coastal areas, ie a transition
zone between land and sea (Kusnadi, 2009). The
potential of Indonesia's vast marine and fishery
resources can be considered to be the largest in the
world, very contradictory to the current reality
where 98.7% of Indonesian fishermen belong to the
category of small fishermen group and 25.14% of
Indonesia's poor communities are fishermen
(Surono, 2016).
Suryati, I., Herlina, N., Akbar, M., Latifah, N., Utama, R. and Iman, A.
Increasing Availability and Water Quality in Kampung Nelayan Seberang Belawan, Medan City.
DOI: 10.5220/0010067201570162
In Proceedings of the International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches (ICOSTEERR 2018) - Research in Industry 4.0, pages
157-162
ISBN: 978-989-758-449-7
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
157

The existence of the fishing village is close to the
poverty stigma. Viewed from the scope, the poverty
of fishermen consists of infrastructure and family
poverty. Infrastructure poverty can be indicated in
the inavailability of physical infrastructure in fishing
villages, which are generally very limited, such as
the absence of clean water, away from the market,
and lack of access to fuel at a standard price. Indirect
poverty of infrastructure also contributes to the
emergence of family poverty, infrastructure poverty
can also cause families in the near poor to decline
into poor families (Mulyadi, 2007).
One of the fishing village in Medan City is
Kampung Nelayan Seberang in Medan Belawan
Sub-district. Kampung Nelayan Seberang is located
on the outskirts of the river and sea. This condition
affects the water used by the community for daily
activities and water for consumption. Because the
quality of brackish water is not feasible for
consumption then the fulfillment of clean water
needs in Kampung Nelayan Seberang is to make
wells drilled either for private property or the
government whose water is used for consumption as
drinking water and for cooking. In addition, water
wells are also used by residents for MCK activities
(bathing, washing, and serving as a lavatory). The
condition of the clean water availability in Kampung
Nelayan Seberang can be seen in Figure 1.
Figure 1: Conditions of water supply in Kampung Nelayan
Seberang Belawan.
In Figure 1, there is a pump that people use to
supply clean water to houses. As for, the water
quality is physically quite good, but there are some
community wells whose water quality is poor as
cloudy and has a taste.
Based on a preliminary survey at Kampung
Nelayan Lingkungan XII, Belawan I Urban Village
Medan and Dusun XIV Paluh Kurau Village,
Hamparan Perak Subdistrict, Deli Serdang Regency,
it can be seen the limited water-related infrastructure
such as in Figure 2.
In Figure 2, there are 2 (two) water reservoirs to
hold clean water from wellbore. The condition of
one of the water reservoirs has been damaged and
cannot be longer utilized, while one holder of water
reservoir is not utilized optimally. There were also
some complaints from local residents related to the
continuity of water. Water obtained by communities
around Kampung Nelayan Seberang has not been
evenly distributed. Drill wells are only owned by
certain groups who are quite well-established
economically. Meanwhile, for people who do not
have a drilled well, they are charged a certain rate if
they connect the water source with pipes to their
homes. In addition, there is only 1 (one) refill depot
to meet the availability of drinking water for ± 500
households.
In addition to the problems of affordability and
continuity, some of the physical water quality of the
borehole in Kampung Nelayan Seberang is cloudy
and has sweet taste. In line with the target of SDGs,
it is necessary to improve the quantity and quality of
clean water service in Kampung Nelayan Seberang,
Medan Belawan Subdistrict. One of the programs
which can improve the clean water service in
Kampung Nelayan Seberang is through community
service program by University of Sumatera Utara.
Figure 2: Damaged water reservoir condition and unused
reservoir holder
2 IMPLEMENTATION METHOD
The implementation of community service starts
from the initial survey and identifying problems in
partner villages. To overcome the shortage of clean
water supply, the location of drilling well was
chosen. The location taken is near the residents’
houses which do not have a drilled well. Meanwhile,
for residents who already have drilled well but water
quality is not good then it was designed a simple
water purifier with slow sand filter method.
ICOSTEERR 2018 - International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches
158
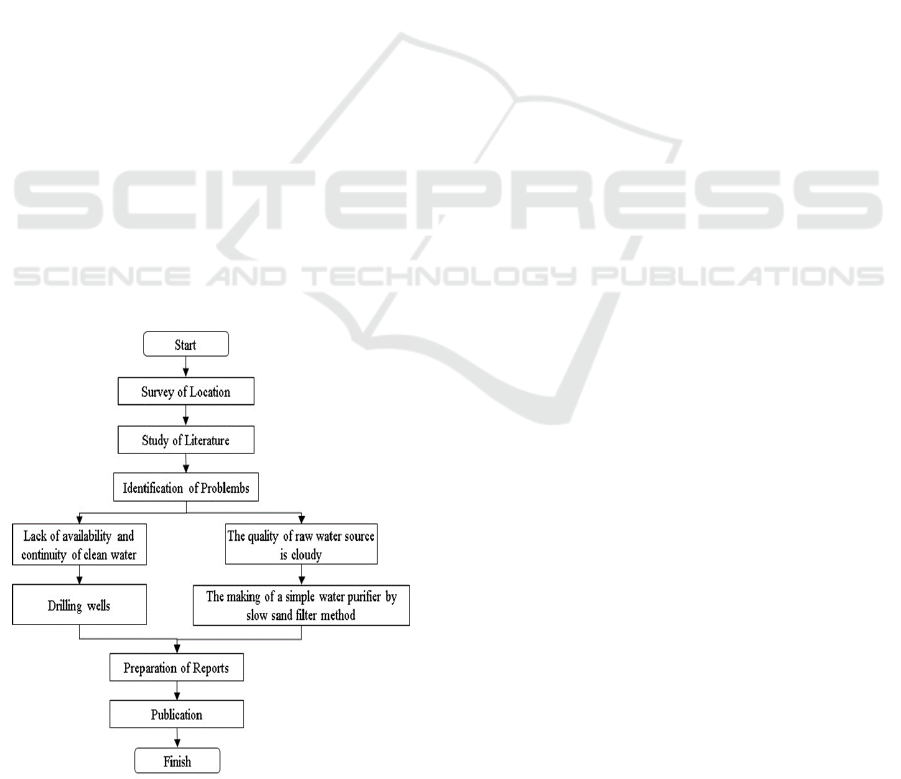
The implementation method is starting from the
determination of the location of the activity,
identification of partner problems, the drilling well
stage, the design stage of a simple water purifier, the
socialization stage of simple water purifier and
preparation of reports.
2.1 Location
The location of community service activity of Mono
Year scheme (Junior Lecturer) is at Kampung
Nelayan Lingkungan XII, Kelurahan Belawan I,
Medan City and Dusun XIV of Paluh Kurau Village,
Hamparan Perak Subdistrict, Deli Serdang Regency.
2.2 Stage of Activity
The activity begins with a literature study on
solutions to solve the problems of continuity,
availability, and quality of water in the region of the
coast. Afterward, surveying the location of
community service, identifying partner problems,
analyzing the situation and conditions, determining
solutions to solve partner problems, determining the
location of drilling wells, determine simple
technology in order to purify well water drilling,
preparing reports and publications. A flowchart of
stage of activity of increasing availability and
quality of clean water in Kampung Nelayan
Seberang can be seen in Figure 3.
Figure 3: Flow chart of activities to increase the
availability and quality of clean water in Kampung
Nelayan Seberang
2.3 Drilling Deep Well Method
Drill wells are usually drilled by professional driller
with experience and adequate equipment to obtain
ground water more depth than other wells. Various
well drilling methods have been developed
according to geological conditions ranging from
hard rock such as granite and dolomite to fully
consolidated sediments such as alluvial sand and
gravel. Certain drilling methods may be more
dominant in certain areas as they are most effective
in penetrating local aquifers, which can save costs
(Kementerian Pekerjaan Umum dan Perumahan
Rakyat, 2015).
The well construction usually consists of four or
five steps of work, namely: (a) drilling, (b)
installation of casing pipe and screen pipe, (c)
placement of filter packs or filters; (d) casting
grouting to provide contamination protection; e)
well testing to ensure water is free of sand and
maximum result (Kementerian Pekerjaan Umum dan
Perumahan Rakyat, 2015).
The tools and materials used in the manufacture
of deep wells are: (a) PVC pipe (length 4 m) of 16
pieces, (b) glue pipe as many as 1 bottle, (c) pipe
accessories in the form of shock as many as 10
pieces, (d) coating or casing (length 4 m) of 3
pieces, (e) pumps of 1 unit, (f) drill pipe for 1 unit,
(g) 1 freon / gas tube, (h) cement by ½ bag and (i) )
sand as many as 3 buckets.
The process of making a wellbore was starting
from (a) determining the location / point of drilling
of the borehole; (b) drilling and drilling wells depth
≥ 50 meters; (d) installing a water pumping machine,
LPG freon / gas and suction pipe installation at the
wellbore, (e) performing groundwater pumping tests
(Rahmansah, 2017). The drilling well was done for 3
(three) days.
2.4 Simple Water Purification Method
In order to improve the quality of clean water in
Kampung Nelayan Seberang, it was needed to
design a simple water purifier. One of the simplest
alternative technologies that can be applied is a slow
sand filter.
The slow sand filter system is a very simple
water treatment technology with good quality clean
water. Slide sand filter system has advantages
Increasing Availability and Water Quality in Kampung Nelayan Seberang Belawan, Medan City
159

including it does not require any chemical
substances (coagulant) (Idaman, 1999).
The filtration process in slow sand filters is done
physically and biologically. Physically, particles
present in a cloudy or dirty water source will be
retained by the sand layer present in the filter.
Biologically, the sieve will form a layer of bacteria.
The bacteria of the genus Pseudomonas and
Trichoderma will grow and multiply to form a
special coating. During the filtration process with
slow water discharge (100-200 liters / hour / m2 of
filter surface area), the pathogen retained by the
sieve will be destroyed by the bacteria (Satrio,
2018). The scheme of a simple water purifier with
slow sand filter can be seen in Figure 4.
Figure 4: Water Purification Scheme With Slow Sand
Filter (Satrio, 2018 modified)
3 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
The geographical condition of Kampung Nelayan
Seberang which is a coastal, in which the needs of
the water is constrained by the quantity and quality
of clean water. To obtain clean water with good
quality, it needs to be drilled deep well with depth ≥
50 m. Based on the observation, the availability of
clean water in Kampung Nelayan Seberang has not
been fulfilled 100%. Complaints from some
residents who do not have a drilled well is the cost
they must spend in buying water to residents who
have a large drill well. Therefore, in the program of
community service was given the help of making 1
(one) borehole that can serve for ± 10 households.
The initial stage of drilling this well is drilling by
drilling machine to find the raw water source of
clean water (see Figure 5a). Thereafter are the
installation of pipes, accessories ,pumps (see Figure
5b) and the last is to test the obtained water (see
Figure 5c).
Figure 5: (a) drilling, (b) plumbing and (c) testing of water
In addition to the problem of water availability
which is still lacking, the other residents’ problems
that the water is cloudy and has taste.The solution to
overcome this is to design a simple water purifier
such as a sketch in Figure 6.
Figure 6: Sketch of a simple water purifier (Sumardika,
2012 modified)
Based on the physical test, the water pH value in
Kampung Nelayan Seberang is 8.2 - 8.5. Meanwhile,
the Fe value was 0.1 mg / l and Mg of 0.03 mg / l.
To reduce the content of Fe and Mn from raw water
source, it can be used a simple technology, the slow
sand filter. The slow sand filter depends on the filter
media used. In the design of a simple water purifier
for the Kampung Nelayan Seberang, it was used a
gravel media, activated carbon, silica and zeolite.
Zeolite is a three-dimensional crystalline
alumina silica, and is formed from tetrahedral
alimina and silica with inner cavities containing
metal ions, usually alkaline or alkaline and freely
moving water molecules. Zeolite serves as an
adsorbent and molecular filter, as well as ion
exchanger in water treatment (Kusnaedi, 2010).
Activated carbon is a powder-shaped material
derived from carbon-containing material such as
coal and coconut shell. The activated charcoal can
ICOSTEERR 2018 - International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches
160

adsorb certain gases and chemical compounds or
selective adsorption properties (choosing),
depending on the size or volume of the pores and
surface area. The absorption capacity of activated
charcoal is very large, ie 25-100% to the weight of
activated charcoal. The usefulness of activated
charcoal is as a remover of cloudy, bad smell, and
resin in the water of households (Kumalasari, 2013).
Several previous studies have found the
effectiveness of a combination of filter media such
as zeolite, silica sand and active carbon can remove
Fe by 96% and Mn by 84.3% (Yudi, 2017).
Meanwhile, the results of the study (Syahputra,
2015) showed that the use of activated carbon could
remove Fe by 75%, Zn by 14.29% and Cu by
10.78%. The combination of zeolite, silica, active
carbon and gravel was effective to reduce Fe by 74%
and Mn by 33% (Rizki, 2013).
4 CONCLUSIONS
Community service in Kampung Nelayan Seberang
was conducted to overcome the problem of water
availability and water quality. The solution to
overcome water availability was done by providing
assistance to drill deep wells with a depth of ≥ 50 m.
Drilling wells were carried out for ± 3 days with
well drilling stages, pipes and accessories and water
testing. The water source in the form of a deep well
drill can serve for ± 10 households.
In the case of overcoming the muddy and bad
tasting water quality was done by using a simple
water purifier in the form of a slow sand filter. The
medium used is zeolite, silica, activated carbon and
gravel. The use of this medium can reduce Fe and
Mn levels in well water ranging from 33% - 96%.
The deep drill well is an alternative to fulfill the
water needs of fishermen living in the coastal area.
Another alternative that can be done next is to
process brackish water into a source of clean water
with membrane technology and desalination.
Intensive and unstructured deep groundwater intake
will have negative impacts such as decreasing
ground water levels, damaging the hydrological
cycle, and often the depletion of water reserves that
are useful for balancing ground surface pressure and
resulting in landslides and ground-level ambles. The
use of membrane technology and desalination can be
recommended to meet water quality and certainly
require high investment costs.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors gratefully acknowledge that the present
research was supported by Community Service
Institute of the University of Sumatera Utara. The
support is under the Mono Year (Junior Lecturer)
BPPTN.
REFERENCES
Badan Pusat Statistik (BPS). 2014. Kajian Indikator
Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Jakarta: BPS
Idaman, Said et al. 1999. Teknologi Pengolahan Air
Bersih dengan Proses Saringan Pasir Lambat “Up
Flow. Jakarta: Badan Pengkajian dan Penerapan
Teknologi (BPPT)
Kementerian Pekerjaan Umum. 2014. Pemukiman Layak
Huni dan Berkelanjutan dalam Kacamata 100-0-100.
Buletin Cipta Karya 7(XII), 6-8
Kementerian Pekerjaan Umum dan Perumahan Rakyat.
2015. Buku Manual Perencanaan dan Konstruksi
Sumur dan Sumur Bor. Jakarta: Pamsimas
Komisi Nasional Hak Asasi Manusia. 2017. Kerangka
Analisis untuk Mengintegrasikan Tujuan
Pembangunan Berkelanjutan (SDGs) dengan
Kewajiban Pemenuhan Hak-hak Asasi Manusia untuk
di Indonesia. Jakarta: Komnasham
Kumalasari, F dan Satoto, Y. 2011. Teknik Praktis
Mengolah Air Kotor Menjadi Air Bersih. Bekasi:
Laskar Aksara
Kusnadi. 2009. Keberdayaan Nelayan Dalam Dinamika
Ekonomi Pesisir. Yogyakarta : Ar- Ruzz Media
Kusnaedi. 2010. Mengolah Air Kotor untuk Air Minum.
Jakarta: Panebar Swadaya.
Mulyadi. 2007. Ekonomi Kelautan. Jakarta: Raja Grafindo
Persada
Rahmansah. 2017. Penerapan Sumur Bor Sistem Pipa
Konservasi Air Tanah (Pipa Imbuh). Prosiding
Seminar Nasional Fakultas Teknik Universitas Negeri
Makasar, 329-338
Rizki, J, Rudianto dan Risdiawan, H. 2013. Portable Alat
Penjernih Air dengan Sistem Filtrasi. Jurnal Riset
Daerah Edisi Khusus Tahun 2013. 89 -104
Satrio, Wibowo. Teknik Penjernihan
Air.http://aimyaya.com.id diakses pada tanggal 28
Juni 2018
Sumardika, H. 2012. Cara Membuat Filter Air Sendiri.
http://www.hrwaterfilter.com.diakses pada tanggal 28
Juni 2018
Surono, Ono. 2015. Koperasi Nelayan Pengelolaan
Sumber Daya Perikanan Tangkap Berbasis Ekonomi
Gotong Royong. Jakarta : PT. Wahana Semesta
Intermedia
Syahputra, A. Sugianto dan Riad, S. 2015. Rancang
Bangun Alat Penjernih Air yang Tercemar Logam
Berat Fe, Cu, Zn dalam Skala Laboratorium. Jurnal
JOM FMIPA Universitas Riau 2 (1), 86-92
Increasing Availability and Water Quality in Kampung Nelayan Seberang Belawan, Medan City
161

Yudi SU, Rizki. 2017. Studi Efektifitas Filter Penjernih
Air Menggunakan Media Zeolite, Karbon Aktif dan
Pasir Silika untuk Mengurangi Kadar Besi (Fe) dan
Mangan (Mn) dengan Variasi Sudut Kemiringan Pada
Alat Uji dan Penambahan Filter Keramik. Skripsi.
Malang : Teknik Pengairan, Universitas Brawijaya.
ICOSTEERR 2018 - International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches
162
