
Von Willebrand Factor Levels and Control Glycemic Type 2 Diabetes
Mellitus Patients
Rusdiana
1 *
,Maya Savira
2
, Sry Suryani Widjaja
1
,Muhammad Syahputra
1
1
Departement of Biochemistry, Medical Faculty, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Jl. dr. Mansur no.5,
Medan, Indonesia.
2
Departement of Physiology, Medical Faculty, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Jl. dr. Mansur
no.5,Medan, Indonesia.
Keywords: Diabetes mellitus type 2, Fasting Blood Sugar, Von Willebrand Factor
Abstract: Diabetes Mellituswas disorder metabolic syndrome, characterized by hyperglycemia, which was caused by
insulin secretion defect.The chronic hyperglicemia dan insulin resistence caused increasing blood vessel
permeability and endothelial cell damage. Von willebrand factor (vWF) was synthesized by endothelial
cell.The aim of the study was knowingassociation between von Willebrand factor (VWF) levels and control
glycemic base on Fasting Blood Sugar and Haemoglicosylate (Hba1c) at Type 2 diabetes mellituspatients.
The sutudy was cross-sectional design , was conducted on 40 type 2 Diabetes Mellitus patients who
attended Primary Health Care Clinic in Binjai city, Sumatera Utara, Indonesia.The inclusion criteteria of the
samples was patients with age > 40 years old, (both sexes). Body Mass Index, Blood Pressure,disease
history and socioeconomic status were recorded. The laboratory parameters including Hba1c, Fasting Blood
Sugar Levels. Examining Fasting Blood Sugar Levels by using portable measuring instrument, and Hba1c
was examined by Thamrin clinical laboratory. We found there was correlation significant between FBS with
Hba1c and correlation significant FBS and VWF.
1 INTRODUCTION
Diabetes Melitus (DM) was caused by the body’s
inability to produce the insulin as needed or because
of ineffective use of insulinor the both. This is
characterized by increasing blod sugar level or
hyperglycemia and the development of chronic
vascular complications (Perkeni,2011,IDF 5
th
).There
was an increasing the prevalence the diabetes
mellitus with type 2 the worldwide and it was
association with obesity. The number of diabetics in
Indonesia is 7 th in the world. The prevalence of
diabetes in Indonesia has been diagnosed 1,4%, this
will continue increasing (Rikesdas,2013).The
evidence of diabetes mellitus with a potent
cardiovascular risk factor have annual mean
mortality rate of 5.4% (Rikesdas,2013). Men with
diabetes have two-fold to three-fold increase in
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) compared with
non-diabetics (Donnelly R,et al, 2000). It affects
between 1% and 10% of most population, although
in some areas of the world up to 50% of the
population has diabetes (Vaccaro O et al,1998).
WHO estimated 21.527.000 Indonesia population
will suffer from diabetes mellitus in 2030
(WHO).As we know for many years that the
complication of diabetes mellitus associated with
cardiovascular, cerebrovascular and peripheral
vascular disease. Because of chronic hyperglycemic
and insulin resitance caused increasing permeability
of blood vessel and disorder endothelial cell. Type 2
diabetes patients have early development of
abnormal endothelial function, it caused
vasocontriction, inflammation cell
accumulated,migration of smooth muscle cell and
increased cytokine production,which results in
plaque development. And then it was caused platelet
hyperactivity, aggressive atherosclerosis,a
propensity for adverse arterial remodeling, enhanced
cellular and matrix proliferation after arterial injury
and impaired fibrinolysis with tendency for
thrombosis and inflammation. The earliest
manifestation of endothelial dysfunction was
profound arteriopathy the result of the diabetic state
(K.G.M.M. Alberti, 2013).
Rusdiana, ., Savira, M., Widjaja, S. and Syahputra, M.
Von Willebrand Factor Levelsand Control glycemic Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients.
DOI: 10.5220/0010067504030406
In Proceedings of the International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches (ICOSTEERR 2018) - Research in Industry 4.0, pages
403-406
ISBN: 978-989-758-449-7
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
403

Type 2 diabetes mellitus patients have a
higher incidence of thrombotic complications
(Beckman JA, 2002). Many factors that have been
proposed explaining the observed prothrombotic
state. In connection with prothrombotic state,
endothelial activation has been shown to occur in
patients suffering from type 2 diabetes (Frankel DS,
2008). Von Willebrand factor (vWF) is a large
glycoprotein produced by vascular endothelial cells
that mediates platelet adhesion to injured
endothelium, the first step in thrombus formation.
yWF also serves as the carrier protein for
coagulation factor VIII (Natali A, 2006).Given
essential role in thrombosis and is frequently used as
marker for endothelial activation and damage
(Sadler JE, 1991,Ruggeri ZM, 1999)
Recently many researches that was found that
Von Willebrand Factor has been associated with
insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes mellitus
(Blann AD, 2006, Meigs JB et al, 2006).The
previous study in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients it
was found the increased circulating levels of plasma
vWF, it have been attributed to enhanced endothelial
cell release from a potentially greater intracellular
storage pool and to increased endothelial synthesis
(Ostergard T et al, 2006, Porta M, 1982). The aim
of this study was to knowing association von
Willebrand factor levels and glycemic control at
type 2 diabetes mellitus
2 MATERIAL AND METHODS
In the study,a total of 72 patients with type 2
diabetes mellitus were recruited from Primary
Health Care in Binjai city, North Sumatera,
Indonesia. The number of the samples was
calculated using the formula n=N/1 +N (d
2
). This
was conducted from April to July 2018. In
accordance with the inclusion criteria which
are,aged > 40 years old and cooperative and have a
will to join this research and exclusion criteria which
are, using diuretic and the middle of cancer therapy.
This research was approved by Health Research
Ethical Committee, Medical Faculty of University
Sumatera Utara/H.Adam Malik General Hospital by
number 591/TGL/KEPK FK USU-RSUP HAM
/2018. Patients were informed with the detail of the
study and written consent was obtained from the
patients before they participated in the study.We
measured height and weight with the subjects
standing in light clothes . Body mass index was
calculated as the weight in kilograms divided by
square of the height in meters (kg/m
2
).We examine
the blood pressure values as mean of two
measurements after the subjects had been seated for
at least five minutes. The patients fasted overnight to
provide a blood specimen. Blood samples were
collected (using syringe) and transferred to Thamrin
clinical laboratory immediately to be conducted
glycosylated haemoglobin test by Alere Afinion as
100 Analyzer . We examined glycosylated
haemoglobin test for patients because of this
examination as gold standard for diabetes mellitus
patients. Fasting blood sugar of samples we
examined by using portable measuring instrument
(Gluco DR).We measured the Von Willebrand
Factor levels with an ELISA assay in laboratory in
Medical Faculty, Universitas Sumatera Utara.
The Examination Von Willebrand Factor levels
in the serum which allow samples to clot for 2 hours
at room temperature or overnight at 4
o
C before
centrifugation for 15 min at 1000x g g at 2-8
o
C. We
collect the supernatant to carry out the assay. We
used the blood collection tubes should be disposable
and be non-endotoxin. Average the duplicate
readings for each standard and samples, then
subtract the average zero standard optical density.
Plot a four parameter logistic curve on log-log graph
paper, with standard concentration on the x-axis and
Optical Density (OD) values on the y-axis. If the
samples have been diluted, the concentration
calculated from the standard curve must be
multiplied by dilution factor. If the OD of the
samples surpasses the upper limit of the standard
curve, we must do re-test it with an appropriate
dilution. The actual concentration is calculated
concentration multiplied by dilution factor. The
Optical Density (OD) was determined using a
microplate reader set to 450nm.
3 STASTICAL ANALYSIS
All data were presented by using SPSS software,
version 24.The continuous data was expressed as
mean ±standard deviation (SD). The correlation
were done by Pearson correlation analysis, using
correlation test, p-value < 0.05 was considered to be
statistically significant.
4 RESULT
Among 72 known type 2 Diabetes Mellitus patients
30 people were male (41.7%) and 42 people were
female (58.3%). The characteristic of the subjects of
ICOSTEERR 2018 - International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches
404
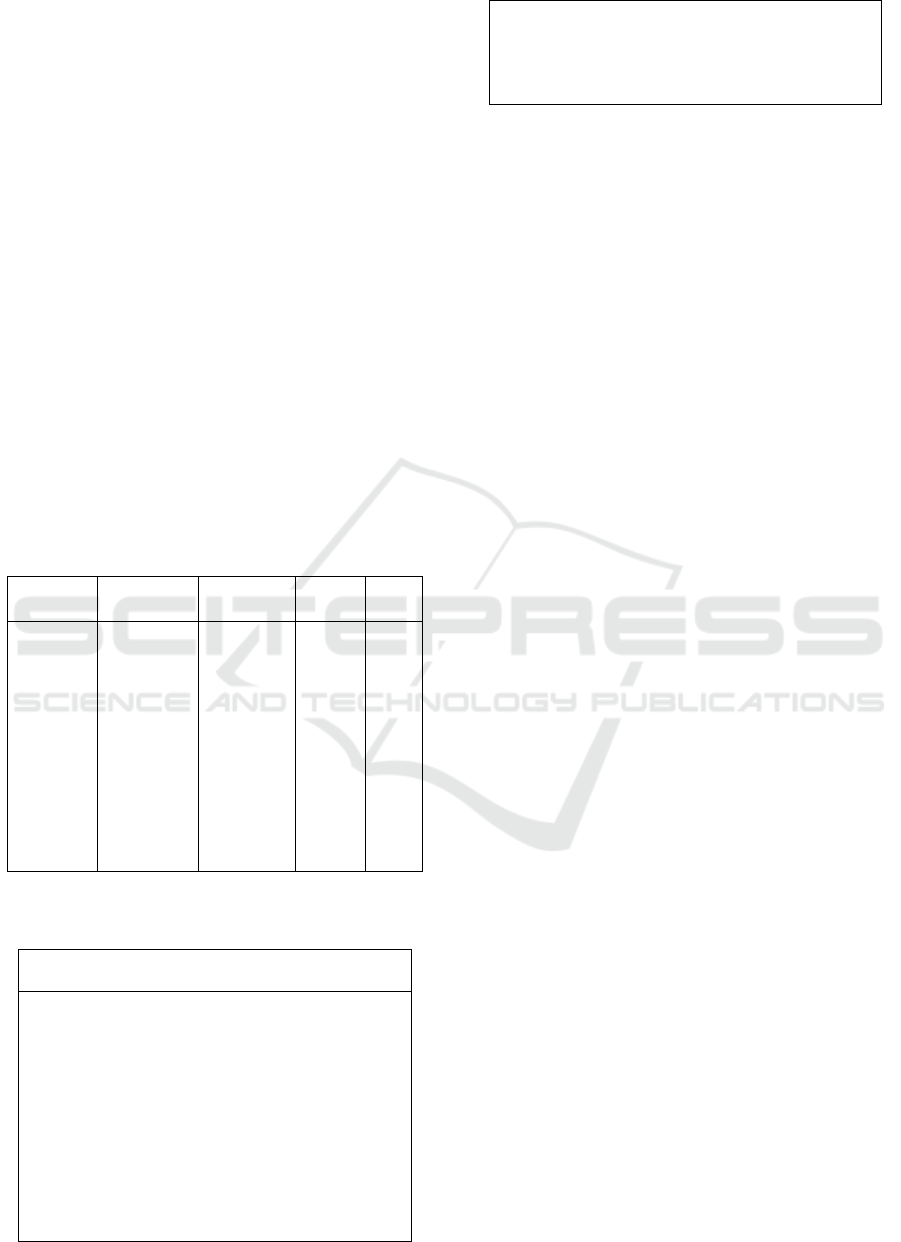
this study are shown in the table 1. Subjects in this
study were not bellow 40 years old. Maximum age
of the samples were 79 years old and minimum age
were 40 years old. Maximum of Body Mass Index of
the samples were 32.86 kg/m
2
and minimum were
16.02 kg/m
2
. Maximum of waist size of the samples
were 107 cm and minimum were 73 cm. Maximum
of the Fasting Blood Sugar (FBS) of the patients
were 600 mg/dL and Minimum were 85 mg/dL.
Maximum of the Hba1c of patients were 14% and
minimum were 6% and Maximum of the Von
Willebrand Factor Level of the patients were 35.10
ng/mL and minimum were 2.16 ng/mL. The range of
fasting plasma levels of vWF at baseline was from
0.64 to 5.35 U/ml.
The Pearson’s correlation coefficient for the
correlation between von Willebrand Factor levels
and and Hba1c showed a negative correlation but a
positive correlation between von Willebrand Factor
levels and fasting blood sugar levels and showed a
positive correlation between Fasting Blood Sugar
Levels and Hba1c (p<0.005.)
Table 1: Baseline characteristic of 72 patients type 2
diabetes mellitus
Minimum Maximum Mean SD
Age
(y.o)
BMI
(kg/m
2
)
Waist
size (cm)
FBS
(mg/dL)
Hba1C
(%)
VWF
(mg/dL)
40
16.02
73
85
6
2.16
79
32.86
107
600
14
35.10
58.31
24.33
91.32
243.0
1
9.501
11.14
8.82
2
3.34
8.18
102.
2
1.90
4
6.84
Table 2 : Pearson Correlation vWF and glycemic control
(Hba1c,FBS)
Hba1c
vWF FBS
Hba1c Pearson Correlation 1 0.002
389**
Sig.(2-tailed) 0.985
0.001
N 72 72
72
vWF Pearson Correlation 0.002 1
0.250*
Sig.(2-tailed) 985**
034
N 72 72
72
FBS Pearson Correlation 389**
250* 1
Sig.(2-tailed) 001 034
N 72 72
72
**.Correlation is significant at the 0.01 level (2-tailed).
*. Correlation is significant at the 0.05 level (2-tailed).
5 DISCUSSION
The aim of study was to knowing association
between von Willebrand factor levels and glycemic
control at type 2 diabetes mellitus. As we know that
von Willebrand factor was one of the marker for
endothelial dysfunction (Porta M, 2006).The
primary physiologic function of von Willebrand
factor is to maintain haemostatic balance in the
vasculature, but because the endothelium is a
primary source of von Willebrand factor elevated
levels reflect stimulation or injury to endothelial
cells (Goldberg RB et al, 2012).This research
showed that there was significant correlation
between vWF level with fasting blood sugar as
glycemic control, as we know that vWF were
significantly higher in patients with type 2 diabetes
mellitus. Another study by Umadevi B et al showed
that a significant increase in plasma levels of von
Willebrand factor (vWF) in patients with type 2 DM
compared to normal, which suggests that there is
significant endothelial injury in type 2 diabetes
mellitus patients (Tian J et al, 2012).And the present
study shows that type 2 diabetes mellitus patients
have significant endothelial injury as assessed by
increased levels of plasma von Willebrand Factor
(vWF) and these are probably at risk of developing
cardiovascular complications in the future.
6 CONCLUSION
There was significant correlation between vWF level
with fasting blood sugar at type 2 diabetes mellitus
patients.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors gratefully acknowledge that the present
research is supported by Ministry of Research and
Technology and Higher Education Republic
Indonesia. The support is under the research grant
TALENTA USU of Year 2018.
Von Willebrand Factor Levelsand Control glycemic Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients
405

REFFERENCES
Beckman JA, Creager MA, Libby P, Diabetes and
atherosclerosis epidemiology, pathophysiology, and
management. JAMA 2002;287 (19):2570- 81.
Blann AD,Plasma von Willebrand factor, thrombosis, and
the endothelium: the first 30 years. Thromb
Haemost,2006;95:49-55.
Donnelly R, Emslie-Smith AM, Gardner ID, et al.
Vascular complication of diabetes. BMJ
2000;320:1062-6.
Frankel DS, Meigs JB, Massaro JM, Wilson PW,
O’Donnell CJ, D’Agostino RB, Tofler GH, Von
Willebrand Factor, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and risk
of cardiovascular disease: the Framingham offspring
study. Circuation.2008;118:2533-2539.doi:
10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.792986.[PMC
free article] [Pubmed] [Cross Ref].
Goldberg RB. Cytokine and cytokine-like inflammation
markers, endothelial dysfunction and imbalanced
coagulation in development of diabetes and its
complications. J.Cin Endocrinol Metab
2009;(9):3171-82.
International diabetes Federation (IDF) atlas 5th edition.
Available from:
http://www.idf.org/diabetesatlas/5e/the-global-
burden
K.G.M.M. Alberti and P.Zimmet, “Epidemiology: global
burden of disease-where does diabetes mellitus fit
in?” Nature Reviews Endocrinology, vol.9,
no.5,pp.258-260,2013.View at Publisher . View at
Google Scholar . View at Scopus
Meigs JB, O’Donnell CJ, Tofler GH, Benjamin EJ, Fox
CS, Lipinska I, Nathan DM , Sullivan LM,
D’AGostino RB, Wilson PW. Haemostatic markers
of endothelial dysfunction and risk of incident type 2
diabetes , the Framingham Offspring
Study.Metabolism , 2006;55:1133-1140.
Natali A, Toschi E, Baldeweg S,et al. Clustering of insulin
resistance with vascular dysfunction and low-grade
inflammation in type 2 diabetes . Diabetes,
2006;55:1133-1140.
Ostergard T, Nyhol B, Hansen TK,Rasmussen LM,
Ingerslev J,Sorensen KE, Botker HE, Saltin B,
Schmitz O. Endothelial function and biochemical
vascular markers in first- degree relatives of type
diabetic patients: the effect of exercise training .
Metabolism, 2006;55:530-537.
PERKENI 2011. Konsensus pengelolaan dan pencegahan
diabetes melitus tipe 2.di indonesia, PB. PERKENI
Porta M. Availability of endothelial von Willebrand factor
and platelet function in diabetic patients infused with
a vasopressin analogue. Diabetologia.1982;23:452-
455.
Prevention of diabetes mellitus.Report of WHO study
group. World Health Organ Tech Rep Ser
1994;844:1-100.
Riskesdas 2013. Riset kesehatan dasar Riskesdas 2013.
Ruggeri ZM. Structure and function of von Willebrand
factor. Thromb Haemost 1999;82:576-84.
[PubMed:10605754].
Sadler JE, Von Willebrand factor. J Biol Chem.
1991;266:22777-22780
Tian J, Wangf J, Li Y, et al. Endothelial function in
patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes
receiving eary intensive insulin therapy . American
Journal of Hipertension 2012;25 (12):1242-8.
Umadevi B, Roopakala M.S, Wilma Delphine Silvia C.R,
Prasanna Kumar K.M. Role of Von Willebrand Factor In
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients. J.Evolution
Med.Dent.Sci 2016;5: 81.DOI:10.14260/jemds/20161372
Vaccaro O, Stamler J, Neaton JD. Sixteen- year coronary
mortality in black and white men with diabetes screened
for the multiple risk factor intervention trial (MRFIT).
Int.J.Epidemiol 1998;27 (4):636-41.
ICOSTEERR 2018 - International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches
406
