
Effect of Physical Activity on Fasting Blood Sugar Level, HbA1c and
Total Cholesterol among Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients in Medan
City, Indonesia
Rina Amelia
1
, Juliandi Harahap
1
, Aznan Lelo
2,
Reni Asmara Ariga
3
, and Novita Sari Harahap
4
1
Department of Community Medicine/Public Health, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Jl. dr. Mansyur
No.5 Kampus USU Medan 20155, Indonesia
2
Department of Pharmacology and Therapeutics, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Jl. dr. Mansyur No.5
Kampus USU Medan 20155, Indonesia
3
Faculty of Nursing, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Jl. Prof. Maas No. 3 Kampus USU Medan 20155, Indonesia
4
Faculty of Sport Sciences, State University of Medan, Jl. Wilem Iskandar Medan , Indonesia
Keywords: Physical activity, Type 2 Diabetes Meletus, Fasting Blood Glucose level, HbA1C, Total Cholesterol.
Abstract: Physical activity is an important role in diabetic patients. Physical activity done regularly and enough will
help patients to blood sugar control and prevent complications and control the body weight. The aim of this
study was to analyze the effect of physical activity on Fasting Blood Sugar Level, Hba1c and Total
Cholesterol among Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) patients in Medan City. The study design was analytic
with cross sectional approach. The study population was T2DM patients in Medan City with the number of
samples is 87 people who have fulfilled the inclusion and exclusion criteria. Data collection is done by
interviewing and patient blood test. Assessment of physical activity of diabetic patients using a global
questionnaire physical activity instrument that is a valid and reliable questionnaire. Fasting Blood Glucose
Level and Total Cholesterol examination done by Spectrophotometer Colorimeter + Full Automatic and
HbA1c examination using Doronad affinity + Modified HPLC method. The data analyzed using one way
ANOVA statistic test and processed data using SPSS. The results showed there was a relationship of physical
activity to fasting BGL, HbA1C levels and Total cholesterol of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 patients in Medan
City.
1 INTRODUCTION
The increased prevalence of diabetes mellitus has
influenced by changes in lifestyle and lack of physical
activity. Adults who have less physical activity will
experience an increased risk of death by 20-30%
compared with people who perform enough physical
activity or routine each week (Ricther and
Hargreaves, 2013). Physical exercise is any body
movement produced by skeletal muscle contraction
that increases energy expenditure above the basal
level (Centre for Disease Control and Prevention,
2011). Physical activity is a movement of the body
due to skeletal muscle activity resulting in energy
expenditure, including activities while working,
playing, doing housework, travel, and recreation.
Physical activity is not the same as exercise or
physical exercise, where exercise is a subcategory of
planned, structured, a repetitive physical exercise to
improve and to maintain physical fitness (World
Health Organization, 2015)
Physical activity together with diet and drug
modifications has recommended one of four
components for diabetes therapy, in which the study
found that exercise can reduce hyperglycemia and
body fat and increase protection against the
development of cardiovascular complications
(Indonesia, 2015). Regular physical exercise reduces
dyslipidemia and increases insulin sensitivity. By
increasing the concentration of GLUT-4 receptors on
the plasma membrane or sarcolemma, insulin
resistance affects the transport of glucose into cells.
The glycemic control reduced visceral fat and
decreased plasma triglycerides can be achieved
528
Amelia, R., Harahap, J., Lelo, A., Ariga, R. and Harahap, N.
Effect of Physical Activity on Fasting Blood Sugar Level, HbA1c and Total Cholesterol among Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients in Medan City, Indonesia.
DOI: 10.5220/0010077205280533
In Proceedings of the International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches (ICOSTEERR 2018) - Research in Industry 4.0, pages
528-533
ISBN: 978-989-758-449-7
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

without loss of body weight (Kennedy et. al., 2012;
Amelia, 2017). Aerobic exercise increases glucose
uptake of muscle by up to five times through an
insulin-independent mechanism. After exercise,
glucose uptake continues to increase with an insulin-
independent mechanism for 2 hours and insulin-
dependent for up to 48 hours if prolonged exercise
(Colberg et al., 2010; Paramitha, 2014; Ramadhanisa,
2013; Amelia et al., 2017). Structured physical
activity like aerobic exercise, resistance training, or a
combination of both has been shown to decrease
HbA1c levels in diabetic patients; besides, moderate
intensity exercise for more than 150 minutes per week
is also closely related to decreased HbA1c (Cavero-
Redondo et al., 2017). Regular exercise of mild
intensity for more than 150 minutes per week proved
to be more effective than those who exercised less
than 150 minutes per week. This situation is indeed in
line with the theory since HbA1c is a valid glycemic
blood marker in the last three months. Regular
exercise of mild intensity for more than 150 minutes
per week proved to be more effective than those who
exercised less than 150 minutes per week (Cavero-
Redondo et al., 2018; Boniol et al., 2017; Amelia et
al., 2018; Harahap et al., 2018). The aim of this study
was to analyze the effect of physical activity on
glycemic control (FBGL and HbA1C and Total
Cholesterol) of T2DM patients in Medan City.
2 MATERIAL AND METHOD
The study design was analytic with a cross-sectional
approach, in which the assessment of physical activity
and glycemic control has performed at one time only.
After the collection of observational data on diabetes
patients continue to assess the complications
experienced by patients. The conducted data has done
in April-May 2018. The study population was DM
Type 2 patient in Medan City. Sampling is type2
Diabetic patients from several community health
centers in Medan City and General Practice doctors
serving outpatient diabetes patients. Determination of
the sample size done by using the formula of
population proportion estimation by using a single
simple formula for the proportion of population
hypothesis so that the number of samples is 85 people
who have fulfilled the inclusion and exclusion
criteria. The inclusion criteria in this study were:
Patients DMT2 aged 35-55 years, had no
contraindication to doing physical exercise, willing to
follow the research and the patient came
independently to the place of service and independent
in performing daily activities. While Exclusion
Criteria are: Patients with severe complications, type
1 Diabetes mellitus patients, another type, and
gestational, type 2 diabetes mellitus patients
accompanied by other comorbidities.
Data collection is done by interviewing and taking
blood. Before the research, this research protocol has
been approved by the research ethics committee at the
Faculty of Medicine Universitas Sumatera Utara, and
all participants who are willing to participate in the
research have signed written informed consent. The
source of research data is primary data, namely
patient characteristics data, nutritional status, data
physical activity and glycemic control data.
Assessment of the physical activity of diabetic
patients using a global physical activity questionnaire
instrument that is a valid and reliable questionnaire,
for each patient answer will get a predetermined
score, physical activity in diabetes patients divide to
three categories, namely physical activity is less/low,
enough/ excellent and high/excessive. Assessment of
glycemic control includes fasting blood glucose level,
hbA1C levels and Total cholesterol by direct blood
venous removal from diabetes patients. Fasting blood
glucose level ad Total Cholesterol examinations were
done by Spectrophotometer Colorimeter + Full
Automatic and HbA1c examination using Doronad
affinity + Modified HPLC method. After the data
collected then analyzed by using one way ANOVA
statistical test and processed data using SPSS.
3 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Baseline Characteristics of T2DM
Patients in Medan City
Table 1: Basic Characteristics of T2DM patients in Medan
City
Characteristics
Frequency
(n)
Percentage
(%)
Gender
Man 16 18.8
Woman 69 81.2
Age Group
Late adolescent (36-
45 years old)
12 14.1
Early elderly (46-55
years old)
73 85.9
Ethnic
Batak 4 4.7
Mandailing 8 9.4
Padang 10 11.8
Jawa 52 61.2
Effect of Physical Activity on Fasting Blood Sugar Level, HbA1c and Total Cholesterol among Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients in Medan
City, Indonesia
529
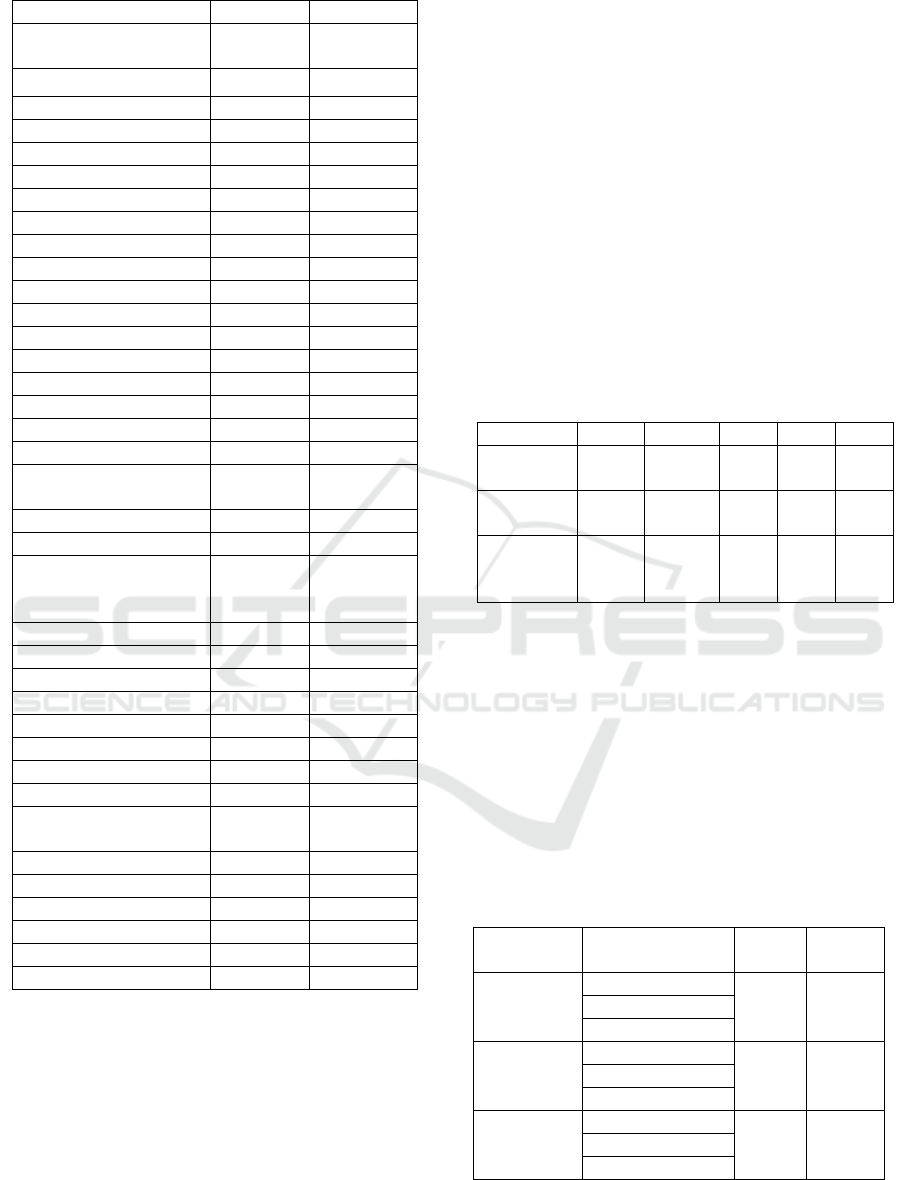
Melayu 10 11.8
Banjar 1 1.2
Work
Civil Servants 7 8.2
Private Servants 23 27.1
Retired 3 3.5
Policemen 2 2.4
Entrepreneurs 8 9.4
Housewives 42 49.4
Duration of Illness
1-5 years 52 61.2
6-10 years 20 23.5
11-15 years 11 12.9
˃ 15 years 2 2.4
Diabetes History
Father 15 17.6
Mother 15 17.6
Father and Mother 8 9.4
No one 47 55.3
Use of Anti-Diabetic
Drugs
Glibenclamide 68 80.0
Metformin 7 8.2
Combination
(Glikenklamid+
Metformin)
5 5.9
Traditional drug 3 3.5
Use of Insulin
Present 2 2.4
Not Present 83 97.6
BMI
Less Weight 8 9.4
Normal Weight 43 50.6
Obesity 34 40
Blood Pressure
Hypertension 68 80.0
Not Hypertension 17 20.0
Physical Activity (PA)
High PA 19 22.4
Medium PA 13 15.3
Low PA 53 62.4
Table 1 explains that based on gender it is known that
most patients are women (81.2%), based on age
known to most elderly patients are Early elderly (46-
55 years old) (85.9%). Based on the ethnic, majority
is Java as many as 52 people (61.2%). The most
patient work is a housewife as much as 42 people
(49.4%). Based on the duration of diabetes known to
the majority of diabetes for 1-5 years as many as 52
people (61.2%), most patients with diabetes. Based on
the family history known most diabetic patients have
a family history of diabetes suffered by the mother as
much as 47 people (55.3%). The majority of diabetic
patients consume glibenclamide as an anti-diabetic
drug as much as 68 people (80%) and only 2 people
who have a history of using insulin 83 people
(97.6%). Nutritional status of diabetes patients most
normal nutritional status as many as 43 people
(50.5%). The majority of patients experienced an
increase in blood pressure as much as 68 people
(80%). Based on physical activity it is known that the
majority of diabetic patients have a less physical
activity / low as much as 68 people (80%).
3.2 Fasting Blood Glucose Level,
HbA1C, and Total Cholesterol of
T2DM Patients in Medan City
Table 2: Glycemic and Total Cholesterol Control Data of
T2DM Patients
Parameter Mean Median SD Min Max
FBSL
(mg/dl)
249.9 245.0 109.
2
87.0 600.
0
HbA1C
(mg/dl)
9.4 9.1 2.8 6.0 15.8
Total
Kolesterol
(mg/dl)
232.5 229.0 196.
0
110.
0
456.
0
Results of Table 2 showed that mean of FBSL was
249.9 mg/dl, and the hbA1C level was 9.4 mg/dl and
the total cholesterol level was 232.5 mg/dl.
3.3 Relationship of Physical Activity
with Fasting Blood Glucose,
HbA1C, and Total Cholesterol in
T2DM Patients in Medan City
Table 3: Relation of Physical Activity with Fasting Blood
Glucose, HbA1C, and Total Cholesterol in T2DM Patients
in Medan City
Parameter Physical Activity
(PA)
F Sig
BGL
(mg/dl)
High PA 3.518
0.025
Medium PA
Low PA
HbA1C
(mg/dl)
High PA 3.403
0.038
Medium PA
Low PA
Total
Kolesterol
(mg/dl)
High PA 3.710 0.045
Medium PA
Low PA
Table 3 is the result of ANOVA test. The results of
table 2 show that there are differences in the average
ICOSTEERR 2018 - International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches
530

levels of FBGL, HBA1C, and total cholesterol based
on the physical activity of T2DM patients.
Diabetes is one of the metabolic diseases, in the
metabolic syndrome, regular physical exercise will
lower blood sugar, HbA1c, triglycerides, blood
pressure, and insulin resistance. Insulin work on the
muscles and the liver can be modified either by
physical exercise that is acute or physical exercise
regularly (Meenu and Jayendrasinh, 2013; Rusdiana
et al., 2018; Nurmawati and Kusmiyati, 2008).
Accordingly, aerobic exercise increases the uptake of
glucose up to five muscles fold through the insulin-
independent mechanism After exercise, and glucose
uptake continues to rise with a 2-hour insulin-
independent and insulin-dependent mechanism for up
to 48 hours if prolonged exercise (Colberg et al.,
2010). Improvement of insulin work can last up to 24
hours after a short physical exercise (about 20
minutes) if the intensity has increased close to the
maximum. Even low-intensity aerobic exercise can
improve insulin work in obese patients, and insulin
resistance for 24 hours. Increased entry of glucose
into muscle cells lasts for several hours after physical
exercise. Regular or regular physical exercise may
also increase prolonged insulin sensitivity (Guelfi et
al., 2007). During physical exercise, the entry of
glucose into the skeletal muscle will increase. This
situation is due to an increase in the number of
glucose transporters in the muscle cell membrane of
GLUT-4 (glucose transporters-4). In addition to being
found in muscle cells, GLUT-4 is also present in fatty
tissues and other tissues. Physical activity extends the
capillary collateral area of muscle and blood flow,
where the GLUT4 expression (skeletal muscle
glucose transporter protein 4) will increase as well;
increased glucose synthesis, reduced release as well
as increased clearance of free fatty acids. With the
least amount of blood glucose available, the process
of glucose binding to heteroprotein hemoglobin will
reduce so that HbA1c levels are also decreased
(Amelia et al., 2017; Cavero-Redondo et al., 2017;
Boniol and Dragomir, 2017; Amelia et al., 2018).
The rate of reduction of BGL, HbA1C, and Total
cholesterol depends on the type of physical activity
performed. The Surgeon General's Report on Physical
Activity and Health recommends that all adult
individuals should have the moderate physical
activity for at least 30 minutes almost every day of the
week) (Cavero-Redondo et al., 2017; Boniol and
Dragomir, 2017). In general, a physical activity
carried out is aerobic and nonaerobic (resistance
training) and mixed physical exercise between
aerobic and resistance training. Aerobics and
prisoners have their respective advantages and
disadvantages in maintaining BGL and HbA1c levels,
but by doing a combination of both types of physical
activity, it will get better results. One of the famous
trial studies in examining the relationship between
physical activity and HbA1c levels was a trial DARE
(The Diabetes Aerobic and Resistance Exercise
Study) examined and compared the effects of
physical exercise resistance training, aerobic, and a
combination of both for six months. Once examined,
the combination of physical exercise is the most
effective physical activity in controlling HbA1c
compared to a physical activity other singles: were
found to decrease by 0.46% larger in the couch
damping aerobic exercise alone and 0.59% greater
than the resistance exercise only. Besides, it can
presume that participants with baseline HbA1c lower
than 7.5% had only a 'down' effect through
combination physical exercise; participants with
HbA1c levels> 7.5% independent of the type of
physical activity selected, although combination
physical exercise provides more benefits (Byrne et
al., 2017). For good results, physical activity must
meet the requirements that are done at least 3 to 4
times a week with and at least 30 minutes in a
continuous activity for at least eight weeks. The
duration of physical activity affects the fraction of
BGL decrease, HbA1c, and Total Cholesterol.
A prospective study in 16 patients with T2DM
aged 50-54 who underwent aerobic physical exercise
for eight weeks obtained improved blood glucose
control with decreased fasting blood glucose levels
and significant HbA1c levels with value p <0.05
(Maiorana et al., 2001; Huang et al., 2014). In
moderate exercise intensity for more than 150
minutes per week proved to be more effective than
those who exercised less from 150 minutes per week.
HbA1c is a valid glycemic marker of blood in the last
three months. The authors themselves acknowledge
the variation of physical activity intervention is one
of the factors that trigger the variation in quality and
heterogeneity of data in this meta-analysis.
Another study showed that the mean decrease of
blood sugar, HbA1c, cholesterol, LDL, HDL, and
triglyceride levels were found in moderate physical
activity with duration ≥ 150 minutes/week. Besides,
mean BGL, HbA1c, cholesterol, LDL, HDL and
triglyceride levels were found to decrease in intensive
physical activity for ≥ 75 minutes/week and ≥ 150
minutes/week (Carral Fet al., 2013).
Effect of Physical Activity on Fasting Blood Sugar Level, HbA1c and Total Cholesterol among Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients in Medan
City, Indonesia
531

4 CONCLUSIONS
Physical activity has an essential role in controlling
BGL, HbA1 C and total cholesterol in addition to diet
and drug consumption. Education and motivation
need to be given to patients so they can perform the
regular physical activity and continue to avoid
complications of diabetes.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors gratefully acknowledge that the present
research was support by the Directorate of Research
and Community Service of the Directorate General
for Research and Development of the Ministry of
Research, Technology and Higher Education by the
agreement of Funding Research and Community
Service for the Fiscal Year 2018 with the contract
number: 117/UN5.2.3.1/PPM/KP-DRPM/2018
REFERENCES
Amelia, R., 2017. The Correlation Between Body Mass
Index and Self-Efficacy with Blood Glucose Level in
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Advanced Science
Letters, 23(4), pp.3606-3609.
Amelia, R., Damanik, H.A., Lindarto, D. and Mutiara, E.,
2017. The Correlation Between the Level of HbA1c
with Total Serum Cholesterol of Uncontrolled Type 2
Diabetes Mellitus Patients in Binjai, Sumatera
Utara. Advanced Science Letters, 23(4), pp.3610-3613.
Amelia, R., Lelo, A., Lindarto, D. and Mutiara, E., 2018,
March. Quality of life and glycemic profile of type 2
diabetes mellitus patients of Indonesian: a descriptive
study. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and
Environmental Science (Vol. 125, No. 1, p. 012171).
IOP Publishing.
Boniol, M., Dragomir, M., Autier, P. and Boyle, P., 2017.
Physical activity and change in fasting glucose and
HbA1c: a quantitative meta-analysis of randomized
trials. Acta diabetologica, 54(11), pp.983-991.
Byrne, H., Caulfield, B. and De Vito, G., 2017. Effects of
Self-directed Exercise Programmes on Individuals with
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review
Evaluating Their Effect on HbA 1c and Other Metabolic
Outcomes, Physical Characteristics, Cardiorespiratory
Fitness and Functional Outcomes. Sports
Medicine, 47(4), pp.717-733.
Carral, F., Gutiérrez, J.V., del Carmen Ayala, M., García,
G. and Aguilar, M., 2013. Intense physical activity is
associated with better metabolic control in patients with
type 1 diabetes. Diabetes research and clinical
practice, 101(1), pp.45-49.
Cavero-Redondo, I., Peleteiro, B., Álvarez-Bueno, C.,
Garrido-Miguel, M., Artero, E.G. and Martinez-
Vizcaino, V., 2017. The effects of physical activity
interventions on glycated haemoglobin A1c in non-
diabetic populations: a protocol for a systematic review
and meta-analysis. BMJ open, 7(7), p.e015801.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2011. National
diabetes fact sheet: national estimates and general
information on diabetes and prediabetes in the United
States, 2011. Atlanta, GA: US department of health and
human services, centers for disease control and
prevention, 201(1).
Colberg, S.R., Sigal, R.J., Fernhall, B., Regensteiner, J.G.,
Blissmer, B.J., Rubin, R.R., Chasan-Taber, L., Albright,
A.L. and Braun, B., 2010. Exercise and type 2 diabetes:
the American College of Sports Medicine and the
American Diabetes Association: joint position
statement. Diabetes care, 33(12), pp.e147-e167.
Guelfi, K.J., Ratnam, N., Smythe, G.A., Jones, T.W. and
Fournier, P.A., 2007. Effect of intermittent high-
intensity compared with continuous moderate exercise
on glucose production and utilization in individuals
with type 1 diabetes. American Journal of Physiology-
Endocrinology And Metabolism, 292(3), pp.E865-
E870.
Harahap, N.S., Lelo, A., Purba, A. and Diningrat, D.S.,
2018. Influence of combination of weight training with
sport massage on 200 meter runnners. Journal of
Medical Sciences, 18(02), pp.96-102.
Huang, J.H., Cheng, F.C., Tsai, L.C., Lee, N.Y. and Lu,
Y.F., 2014. Appropriate physical activity and dietary
intake achieve optimal metabolic control in older type 2
diabetes patients. Journal of diabetes
investigation, 5(4), pp.418-427.
Indonesia, P.E., 2015. Pengelolaan dan Pencegahan
Diabetes Melitus Tipe 2 di Indonesia. PB. PERKENI.
Kennedy JW, Michael F. Hirshman J, Ernest V. Diabetes:
Exercise and glut4 in human muscle. Missouri: Elsevier
Mosby, 2012; 292-326.
Maiorana, A., O'Driscoll, G., Goodman, C., Taylor, R. and
Green, D., 2002. Combined aerobic and resistance
exercise improves glycemic control and fitness in type
2 diabetes. Diabetes research and clinical
practice, 56(2), pp.115-123.
Meenu, J., Jadeja Jayendrasinh, M. and Neeta, M., 2013.
Correlation between HbA1c values and lipid profile in
type 2 diabetes mellitus. TC (mg/dl), 147(35.40).
Nurmawati, L. and Nurmawati, L., 2008. Hubungan
Asupan Lemak dan Aktivitas Fisik dengan Profil Lipid
Pada Pasien Diabetes Mellitus Tipe 2 di RSUD
dr. M. Ashari Pemalang(Doctoral dissertation, Program
Studi Ilmu Gizi).
Paramitha, G.M., 2014. Hubungan Aktivitas Fisik Dengan
Kadar Gula Darah Pada Pasien Diabetes Melitus Tipe
2 di Rumah Sakit Umum Daerah
ICOSTEERR 2018 - International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches
532

Karanganyar (Doctoral dissertation, Universitas
Muhammadiyah Surakarta).
Ramadhanisa, A., Larasati, T.A. and Mayasari, D., 2013.
Hubungan aktivitas fisik dengan kadar HbA1c pasien
diabetes melitus tipe 2 di laboratorium patologi klinik
RSUD dr. H. abdul moeloek Bandar lampung. Jurnal
Majority, 2(4).
Richter, E.A. and Hargreaves, M., 2013. Exercise, GLUT4,
and skeletal muscle glucose uptake. Physiological
reviews, 93(3), pp.993-1017.
Rusdiana, M.S. and Amelia, R., 2018. The Effect of
Diabetes Self-Management Education on Hba1c Level
and Fasting Blood Sugar in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Patients in Primary Health Care in Binjai City of North
Sumatera, Indonesia. Open access Macedonian journal
of medical sciences, 6(4), p.715.
World Health Organization, 2015. World report on ageing
and health. World Health Organization.
Effect of Physical Activity on Fasting Blood Sugar Level, HbA1c and Total Cholesterol among Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients in Medan
City, Indonesia
533
