
Profile Women Pregnancy with HIV Infection in Clinic Voluntary
Counseling and Testing in Medan
Rahayu Lubis
1
, Jemadi
1
and Surya Utama
1
1
Faculty of Public Health, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Jalan Universitas No. 21, Medan, Indonesia
Keywords: HIV, AIDS, VCT, Pregnancy, Profile.
Abstract: There were 1.4 million women pregnancy with HIV in 2016 whole world. More than 90% HIV cases in
children get infection by mother to child transmission. In Indonesia, out of 43,264 pregnant women who
underwent HIV testing there were as many as 1,329 people (3.04%) positive HIV. The aim of study is to
describe the profile women pregnancy with HIV infection in clinic voluntary counselling and testing (VCT)
in Medan. This is the retrospective study. The Population is all pregnant women with HIV infection in clinic
VCT in Medan. The sample was pregnant women with HIV infection in 2015 to 2017. Data collection from
medical records. Analysis descriptive data was used and showed in table distribution and frequency. Total 92
respondents were studied. Majority of respondent in aged less than 35 years (75%), Bataknese (72.8%), have
more than 9 years attainment of education (77.2%) and spouse education (73.9%). There are (68.8%) don’t
have employment and their spouse (73.9%) work as non manual worker. They come to clinic in less than 6
month of pregnancy (64.1%), the CD4 less than 350 u/dl (65.2%), in late stadium (71.7%), receiving
antiretroviral therapy more than 6 month (73.9%) and don’t have opportunistic infection (53.3%).
1 INTRODUCTION
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) is still a
global problem. By 2016 about 36.7 million people
are infected with HIV in the world, 1.8 million of
whom are new HIV cases and about 1 million people
die from HIV (WHO, 2017). In the Asia and Pacific
region by 2016 there are 5.1 million people infected
with HIV. Approximately 270,000 people are new
infections of HIV, 15,000 new cases occur in children
and about 170,000 people die from HIV. The
country's highest HIV prevalence in Asia Pacific is
India, China, Indonesia and Pakistan, covering over
75% of new infections HIV in Asia Pacific. There are
more than 1.4 million (1.1 to 1.7 million) women
pregnancy with HIV infection by 2016. It is estimated
that 76% (66-88%) of women pregnancy with HIV
infection take antiretroviral drugs to prevent HIV
transmission to their babies because more than 90%
HIV cases in children get infection by mother to child
transmission (UNAIDS, 2017).
In Indonesia, HIV cases continue to increase and
have spread in 386 districts / cities. The cumulative
number of HIV patients from 1987-2016 was 232,323
people and the total cumulative AIDS sufferers were
86,725 people (Kemenkes RI, 2017). HIV infection
poses a threat to the development of human quality
and productivity in Indonesia. This is indicated by the
high rate of HIV transmission that occurs. HIV
transmission has begun to shift from predominantly
male-dominated, slowly increasing the number of
HIV-infected individuals in women (KPAN, 2010).
According to Ministry of Health Indonesia that from
86,780 people suffering from HIV, 56% of whom are
women and out of 43,264 pregnant women who
underwent HIV testing there were as many as 1,329
people (3.04%) positive HIV.
HIV-infected women are generally transmitted
from sexual partners, such as HIV-infected wives the
source of infection is HIV-infected husbands as well.
If the wife is pregnant then the risk of transmission
continues from the mother to the baby. The study in
the United States and Europe shows the magnitude of
the risk of perinatal HIV transmission in pregnant
women is 20-40%. The study in Samarinda reported
that the highest risk of HIV transmission in pregnant
women is transmitted from her husband as much as
77.3% (Abidah, 2017). Another study in Medan
showed the cumulative number of pregnant women
with HIV infection in Adam Malik Hospital from
period 2013 to2017 were 132 people (Anggreyani,
2015). Therefore, HIV infection in pregnant women
572
Lubis, R., Jemadi, . and Utama, S.
Profile Women Pregnancy with HIV Infection in Clinic Voluntary Counseling and Testing in Medan.
DOI: 10.5220/0010078605720574
In Proceedings of the International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches (ICOSTEERR 2018) - Research in Industry 4.0, pages
572-574
ISBN: 978-989-758-449-7
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
becomes very important because the consideration of
its effect on pregnancy and the baby. The aim of this
study is to know the profile of the incidence of women
pregnancy with HIV infection in VCT Clinic Medan
City.
2 METHODS
This is a retrospective study in clinic voluntary
counselling and testing in Medan. The Population is
all pregnant women with HIV infected patients in
clinic VCT in Medan. The sample was pregnant
women with HIV infected patient in clinic VCT
Medan during the period of 2015-2017. Data
collection from medical records at clinic VCT in
Medan. Analysis with descriptive data was used and
showed in table distribution and frequency.
3 RESULT AND DISCUSION
3.1 Sociodemographic Characteristic
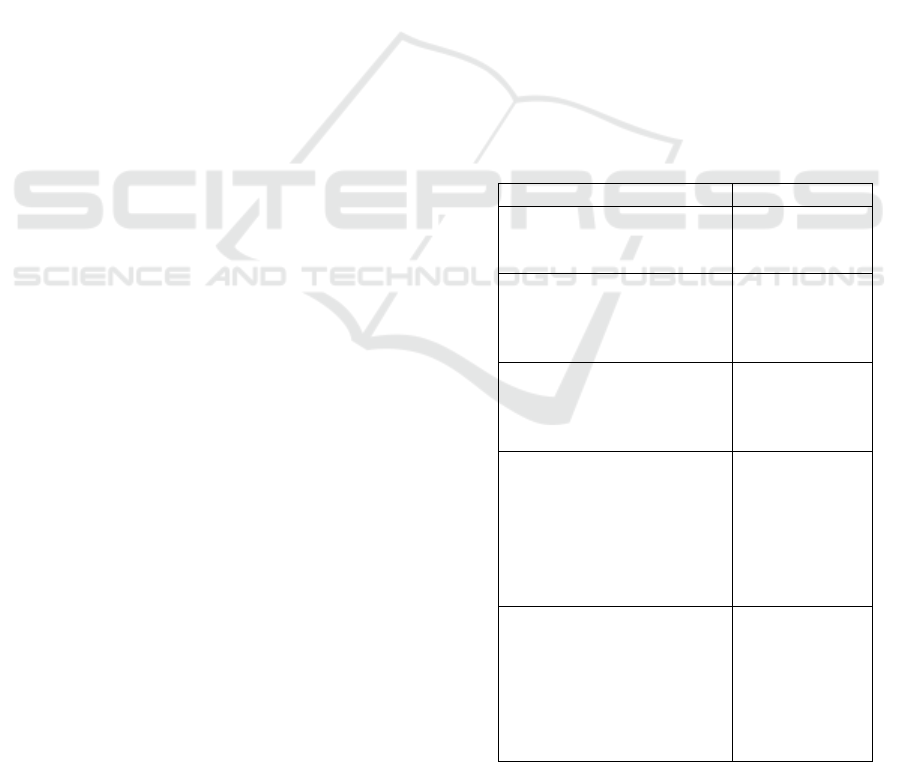
Totally 92 pregnant women with HIV infection
included in this study. Majority in aged less than 35
years old (75%), Bataknese (72.8%), with Christian
religion (51.1%). More than 9 years attainment of
respondent’s education (77.2%) and spouse education
(73.9%). There are (68.8%) of respondent don’t have
employment and their spouse (73.9%) as non manual
worker, such as government employees, private
employees, for more details can be seen in Table 1.
Similarity with this study in Africa reported that
elevated incidence of pregnant women with HIV
infection in younger women (less than 35 years old)
(Chetty, 2017). In this study the youngest age of
pregnant women with HIV is 21 years, and the oldest
age is 42 years. The largest proportion of pregnant
women with HIV occurs in the age less than 35 years.
The age group of 20-35 years is the age of active
reproduction and the best age for childbirth because
pregnancy in age above 35 years is high risk. Similar
with this study in Sanglah hospital in Bali found that
the largest proportion of pregnant women with HIV
occurred at the age of less than 35 years (Suherlim,
2015).
3.2 Clinical Condition
Regarding the clinical condition of respondent,
majority come to clinic with less than 6 month of a
pregnancy (64.1%) with the CD4 less than 350 u/dl
(65.2%), in late stadium of HIV (71.7%) and
receiving antiretroviral therapy more than 6 month
(73.9%). Haemoglobin level and body mass index
(BMI) not much difference between normal and
abnormal level. The respondent who don’t have
opportunistic infection (53.3%) and who have
opportunistic infection (46.7%). It can seen in Table
2. Similarity with this study in Brighton reported that
about 60% pregnant women with HIV infection
received ART (Salters, 2017). Pregnant women
received ART for prevention of mother to child
transmission as per protocol which varied during the
period of study (Dadhwal, 2017). In Africa, more than
half pregnant women with HIV infection come to
clinic with less immunity and there were association
between pregnancy and clinical (Wall, 2017). The
similar study showed that the respondent come to
clinic on average at 22 weeks gestation (range 6-34)
and most of patient with BMI more increased
(Floridia, 2017). Antiretroviral therapy can maintain
the condition of pregnant women with HIV.
Similarity with this study showed that ART can
extend the life expectancy of HIV patients (Lubis,
2014)
Table 1: Sociodemographic characteristic of respondent
Varibles f (%)
Aged (years old)
< 35
≥ 35
69 (75%)
23 (25%)
Ethnic
Bataknese
Javanese
Others
67 (72.8%)
16 (17.4%)
9 ( 9.8%)
Religion
Christian
Moeslem
Bhuddist
47 (51.1%)
44 (47.8%)
1 ( 1.1%)
Education of Pregnant
women
≥ 9 years attainment
< 9 years attainment
Education of Spouse
≥ 9 years attainment
< 9 years attainment
71 (77.2%)
21 (22.8%)
68 (73.9%)
24 (26.1%)
Occupotional of Pregnant
women
Not Employment
Employment
Occupotional of Spouse
Non manual worker
Manual worker
63 (68.5%)
29 (31.5%)
68 (73.9%)
24 (26.1%)
Profile Women Pregnancy with HIV Infection in Clinic Voluntary Counseling and Testing in Medan
573
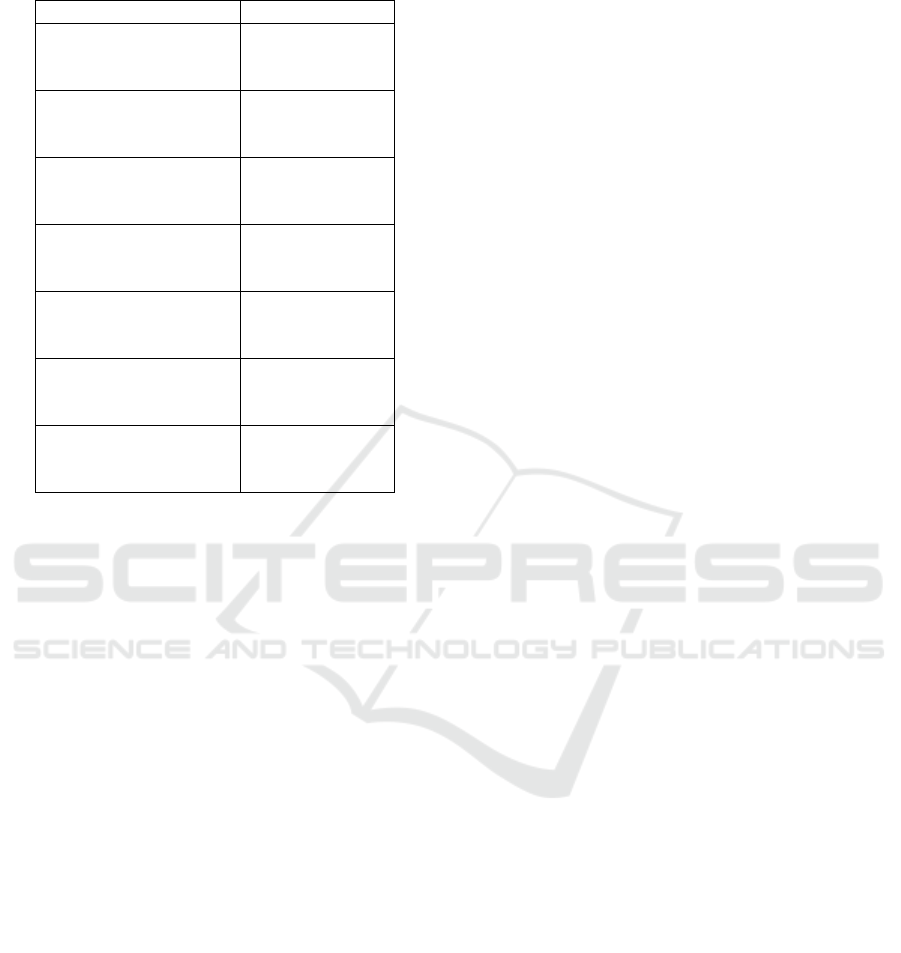
Table 2: Clinical condition of respondent
Varibles f (%)
Pregnancy
< 6 month
≥ 6 month
59 (64.1%)
33 (35.9%)
CD4 (u/dl)
≥ 350
< 350
32 (34.8%)
60 (65.2%)
BMI (kg/m
2
)
≥ 23
< 23
49 (53.3%)
43 (46.7%)
Hb (g%)
≥ 11
< 11
47 (51.1%)
45 (48.9%)
Stadium of HIV
Early
Late
26 (28.3%)
66 (71.7%)
Infeksi opportunistic
No
Yes
49 (53.3%)
43 (46.7%)
Antiretroviral therapy
≥ 6 month
< 6 month
68 (73.9%)
24 (26.1%)
4 CONCLUSIONS
The Majority of pregnant women in aged less than 35
years, Bataknese , Christian religion, have more than
9 years attainment of education for respondents and
their spouse, unemployment of respondent and their
spouse work as non manual worker. They come to
clinic in less than 6 month of pregnancy, the CD4 less
than 350 u/dl, in late stadium of HIV, receiving
antiretroviral therapy more than 6 month
Haemoglobin level and body mass index not much
difference between normal and abnormal level. The
respondent who don’t have opportunistic infection
more than who have opportunistic infection.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This study supported by TALENTA fund Universitas
Sumatera Utara (Basic Research Scheme) in 2018
based on contract number 185/UN5.2.3.1/PPM/KP-
TALENTA USU/2018.
REFERENCES
WHO, 2017. Treat all: Policy adoption and implementation
status in countries. Fact sheet. Link:
http://www.who.int/hiv/pub/progressreports/en/
UNAIDS, 2017. UNAIDS DATA 2017. Available in link:
http://www.unaids.org/en/resources/documents/2017/2
017_data_book
Kemenkes RI, 2017. Statistik kasus HIV/AIDS di Indonesia
dilapor s/d Desember 2016, Jakarta.
KPAN, 2010. Laporan Komisi Penanggulangan AIDS
Nasional tahun 2010. Kementrian Koordinator Bidang
Kesejahteraan Rakyat Republik Indonesia
Abidah Sholihatuz Zahro, et al, 2017. Gambaran
Karakteristik ibu Penderita HIV/AIDS Yang
Melahirkan Bayi Di RSUD Abdul Wahab Sjahranie
Samarinda. Jurnal Kebidanan Mutiara Mahakam V(1):
p. 1-10
Anggreyani, 2015. Gambaran Kasus HIV pada ibu hamil
dan luaran bayi di RSUP Haji Adam Malik Medan
tahun 2008-2015, in Fakultas Kesehatan Masyarakat.
2015, Universitas Sumatera Utara: Medan.
Chetty, T., et al, 2017. Incident HIV during pregnancy and
early postpartum period: a population-based cohort
study in a rural area in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa.
BMC Pregnancy Childbirth,. 17(1): p. 248
Suherlim Richard and AA Ngurah Sumbawa,2015.
Karakteristik Penderita Pada ibu Hamil di Klinik
Prevention Mother to Child Transmision (PMTCT) Poli
Kebidanan RSUP Sanglah Denpasar Periode Juli 2013-
Juni 2014. Jurnal Cerebellum Vol.1 No.3.
Salters, K., et al, 2017. Pregnancy incidence and intention
after HIV diagnosis among women living with HIV in
Canada. PLoS One, 12(7): p. e0180524
Dadhwal, V., et al, 2017. Pregnancy Outcomes in HIV-
Infected Women: Experience from a Tertiary Care
Center in India. Int J MCH AIDS, 6(1): p. 75-81
Wall, K.M., et al, 2017. Pregnancy and HIV Disease
Progression in an Early Infection Cohort from Five
African Countries. Epidemiology, 28(2): p. 224-232
Floridia, M., et al, 2017. Rate, correlates and outcomes of
repeat pregnancy in HIV-infected women. HIV Med,
18(6): p. 440-443
Lubis, R., & Bulgiba, A. M. (2014). Anti-retroviral therapy
of HIV infected patients. JUMMEC: Journal of Health
and Translational Medicine (Formerly known as
Journal of the University of Malaya Medical
Centre), 17(1), 18-22.
ICOSTEERR 2018 - International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches
574
