
Predisposing Factor Associated with Community Action in
Terminating TB Transmission in KB Village 2018
S. M. Sarumpaet
1
and Syarifah
2
1
Department of Epidemiology FKM Universitas Sumatera Utara, Medan, 20155, Indonesia
2
Department of Health Education and Behavioural Science FKM Universitas Sumatera Utara, Medan, 20155, Indonesia
Keywords: KB Village, Pulmonary TB, Predisposing Factor, Action.
Abstract: The purpose of KB village is to improve the degree of public health. Pulmonary TB is a disease with high
prevalence and degrade the public health and welfare level. This study aims to analyze the relationship of
predisposing factor with knowledge, attitude, and community action in terminating pulmonary TB
transmission with cross-sectional design. The population is all households from two neighborhoods of KB
Village of 204 households. The sample is taken randomly from the list of households and got 132 respondents
and analyzed using independent t-test. The proportion of respondent’s factor was female (93.9%), age ≤ 50
years (71.2%), lower education (59.1%), unemployment (72.7%), and less dense population (65.9%). It is
obtained gender, age, and occupation are significantly related with knowledge (p<0.05). Only employed is
related with attitude (p<0.05) and gender is related with action (p<0.05). Intensive counseling is needed for
the people of KB Village to improve their attitude and action in effort of terminating pulmonary TB
transmission. The role of cadre in KB Village have to improve in order to give understandable counseling and
can be applied by the community, therefore an effective and efficient counseling method is being prepared by
utilizing poster and cadre’s book guideline.
1 INTRODUCTION
KB Village an area equivalent to hamlet/RW with
certain criteria in which there is an integrated
program of Population, Family Planning, and Family
Development, and the related sector development is
conducted systematically. The purpose of KB village
establishment is to improve the degree of public
health (BKKBN, 2016).
One of contagious disease with high prevalence
and can degrade the degree of public health as well
as welfare level is pulmonary TB disease, the
transmission can develop rapidly especially in slum
and dense populated area with low socio-economics.
There are six countries that contributing 60% of new
cases, there are India, Indonesia, China, Nigeria,
Pakistan, and South Africa (WHO, 2016).
The estimation of all cases of pulmonary TB
prevalence in Indonesia was 660,000 and the
estimation of incident was 430,000 of new cases per
year. The number of deaths from pulmonary TB was
estimated to be 61,000 per year. The number of
pulmonary TB new and relapsing cases notification
from 2000-2009 was increasing, then gradually
decreasing until 2013, but then increasing again until
2015. The notification number of new pulmonary TB
cases was 117 per 100,000 population (Kemenkes,
2016).
In 2015, in Sumatera Utara the prevalence rate of
pulmonary TB was 794/100,000 population, the
incident rate was 501/100,000 population and the
number of deaths from pulmonary TB was
41/100,000 population, with Case Detection Rate
(CDR) of all forms of 22,961 (33.3%). According to
the report of Integrated TB Information System
(SITT) in 2016, the rate incident was estimated to be
129 per 100,000 penduduk. Although the estimation
was still lower than it supposed to occur in the
community (Dinkes, 2013).
In the effort of increasing CDR of pulmonary TB
Kemenkes RI has launched a pulmonary TB
prevention program in Indonesia known as TOSS
Pulmonary TB (Temukan Obati Sampai Sembuh).
The success of this program is strongly influenced by
the level of knowledge, attitude, as well as the
community role in recognizing the early symptoms,
the transmission method, and the termination of
transmission, the treatment, and the prevention of
Sarumpaet, S. and Syarifah, .
Predisposing Factor Associated with Community Action in Terminating TB Transmission in KB Village 2018.
DOI: 10.5220/0010084106890693
In Proceedings of the International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches (ICOSTEERR 2018) - Research in Industry 4.0, pages
689-693
ISBN: 978-989-758-449-7
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
689

pulmonary TB. The effort of pulmonary TB
termination was adopted from Green’s theory of
health-seeking service by the community. Therefore,
the predisposing factor associated with knowledge,
attitude, and community action in terminating
pulmonary TB transmission in KB Village is needed
(Kemenkes, 2016).
2 RESEARCH METHOD
The research method is performed through cross-
sectional design with independent variable of
predisposing (sociodemography, knowledge, and
attitude) and dependent variable of the effort in
terminating pulmonary TB transmission.
Sociodemographic factor is age which grouped into
over ≤50 years old and >50 years old, education is
grouped into lower education level ( Elementary
School and Middle School graduates) and higher
education level (High School and University
graduates), occupation is grouped into
unemployment and employed, and population is
grouped into less dense population (≤5) and densely
populated (>5). Knowledge is categorized into less
with score of ≤20 and decent >20, attitude is
categorized into less with score of ≤54 and decent
>54, and action is categorized into less with score
of
≤13 and decent >13.
The population of this study is all of householders
within the area of KB Village in Titi Kuning Sub-
District Medan Johor District and Padang Bulan Sub-
District and Medan Baru District with total of 204
people. The amount of the sample is determined
based on Slovin formula with SE = 0.05 so the
sample obtained is 132 respondents. The sample is
randomly picked according to the list of households
within the two areas with inclusion criteria of the
head of the family is willing to be interviewed and
trained in recognizing pulmonary TB patient, the
prevention, and the transmission within the family.
Out of willingness it turns out most of housewives
were willing to participate in the research (124
people) and male only 8 people. The data collecting
technique is performed with interview using
questionnaires that have been tested and approved by
Ethical Commission with registered number:
1522/VI/SP/2018. Bivariate analysis is performed
with independent t-test.
3
RESULT AND DISCUSSION
3.1
Univariate Analysis
According to the result, the respondent’s
predisposing factor distribution can be seen in table
1.
Table 1: Distribution of KB Village Community’s
Predisposing Factor
Characteristic
f
%
Gender
Male
Female
8
124
6.1
93.9
Age
≤50years old 94 71.2
>50years old 38 28.8
Education
Lower Education Level 78 59.1
Higher Education Level 54 40.9
Occupation
Unemployment 96 72.7
Employed 36 27.3
Population
Less Dense Population 87 65.9
Densely Populated 45 34.1
Total 132 100.0
Table 1 shows respondent’s predisposing based
on gender, female is 124 people (93.9%). This
number is higher than male of 8 people (6.1%).
Based on age, the highest proportion is at age group
of ≤ 50 years old, which is 94 people (71.2%). Next,
the highest proportion of education is at the group of
lower education level (Elementary and Middle
School), which is 78 people (59.1%). Furthermore,
the highest proportion of occupation is at the group
of unemployment which is 96 people (72.7%). And
lastly, the highest proportion of population is at the
group of less dense population which is 87 people
(65.9%). This illustrates the characteristic of KB
Village in which the people is pre-prosperous and the
majority of them have lower education level and are
unemployed.
ICOSTEERR 2018 - International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches
690
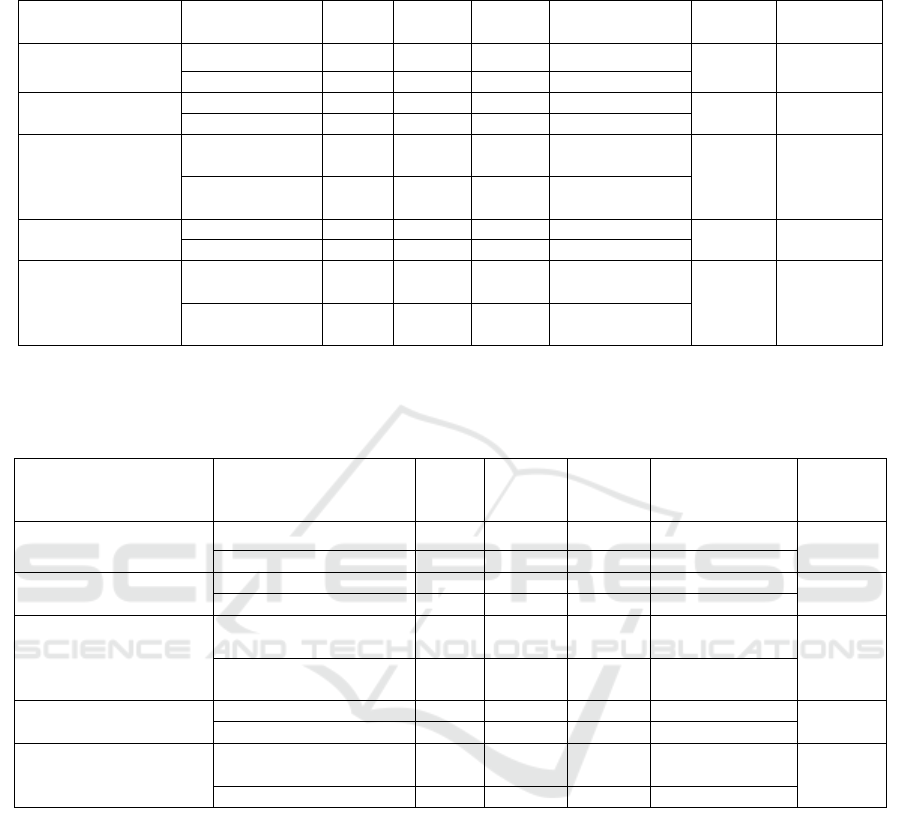
Table 2: The Association of Predisposing Factor with Respondent’s Knowledge in Terminating Pulmonary TB Transmission
in KB Village 2018
Characteristic Category
n
SD Mean Median
(min-max)
p 95% CI
Gender Male 8 8.418 14.50 13.50 (6-27) 0.003
-11.200- (-
2.284)
Female 124 6.025 21.24 21.50 (7-40)
Age
≤50 years ol
d
94 6.471 21.63 22.00 (6-40)
0.023
0.378-
5.140
>50 years ol
d
38 5.701 18.87 19.00 (7-32)
Education
Lower
Education Level
78 6.204 20.64 22.00 (6-40) 0.948
*
Higher
Education Level
54 6.632 21.11 19.50 (7-39)
Occupation
Unemployment 96 6.357 21.74 22.00 (6-40)
0.007 0.922-
0.5724
Employe
d
36 5.793 18.42 18.50 (6-30)
Population
Less Dense
Population
87 6.548 20.99 22.00 (6-39) 0.648
*
Densely
Populate
d
45 6.048 20.53 19.00 (6-40)
*switched to median due to the data is not normally distributed and the Mann-Whitney test is performed
Table 3: The Association of Predisposing Factor with Respondent’s Attitude in Terminating Pulmonary TB Transmission in
KB Village 2018
Characteristic Category
n
SD Mean Median
(min-
max)
p
Gender Male 8 1.581 52.25 52.00 (50-55) 0.088
*
Female 124 5.006 54.73 54.00 (40-66)
Age
≤ 50 years ol
d
94 5.171 54.19 53.00 (40-66)
0.147
*
> 50 years ol
d
38 4.058 55.55 55.00 (48-66)
Education
Lower Education
Level
78 4.552 54.56 54.00 (40-64) 0.987
*
Higher Education
Level
54 5.409 54.61 54.00 (41-66)
Occupation
Unemployment 96 4.951 55.10 55.00 (40-66)
0.010
*
Employe
d
36 4.541 53.19 52.00 (44-63)
Population
Less Dense
Population
87 5.025 54.67 54.00 (40-66) 0.954
Densely Populate
d
45 4.702 54.42 54.00 (41-66)
3.2
Bivariate Analysis
Based on the result, the association of predisposing
factor with knowledge, attitude, and respondent’s
action in terminating pulmonary TB transmission in
KB Village 2018 can be seen in the table 2 and 3.
Table 2 exhibits independent variables (gender,
age, and occupation) have significant relationship
with respondent’s knowledge in terminating TB
transmission (p<0.05) and independent variables
(education and population) do not have significant
relationship with respondent’s knowledge in
terminating TB transmission (p>0.05). The condition
above can be assumed is due to the majority of
respondents is at productive age (≤ 50 years old),
housewives, and unemployed. This group usually is
responsible for caring and maintaining the family’s
health, thus the curiosity on the disease is very high.
Predisposing Factor Associated with Community Action in Terminating TB Transmission in KB Village 2018
691

Table 4: The Association of Predisposing Factor with Respondent’s Action in Terminating Pulmonary TB Transmission in
KB Village 2018
Characteristic Category
n
SD Mean
Median
(min-maks)
p
Gender Male 8 2.615 10.62 11.50 (7-13) 0.003
*
Female 124 1.758 12.77 13.00 (7-14)
Age ≤ 50 years ol
d
94 1.697 12.85 13.00 (7-14) 0.127
*
> 50 years ol
d
38 2.203 12.11 13.00 (7-14)
Education
Lower
Education Level
78 1.744 12.71 13.00 (7-14) 0.873
*
Higher
Education Level
54 2.071 12.54 13.50 (7-14)
Occupation Unemployment 96 1.877 12.61 13.00 (7-14) 0.768
*
Employe
d
36 1.910 12.69 13.00 (7-14)
Population Less Dense
Population
87 1.885 12.52 13.00 (7-14)
0.138
*
Densely
Populated
45 1.866 12.87 14.00 (7-14)
*switched to median due to the data is not normally distributed and the Mann-Whitney test is performed
This is not in line with the study result of Gelaw
(2015) in which there is a significant relationship
between lower education level with pulmonary TB
knowledge, female with Adjusted Odd Ratio
(AOR)=1.95 and male=3.4, but in this study lower
education level is Elementary School graduates.
Table 3 showed independent variables (gender, age,
education, and population) do not have significant
relationship with respondent’s attitude in terminating
TB transmission (p>0.05) and only occupation has a
significant relationship with respondent’s attitude in
terminating TB transmission (p<0.05). This is line
with the relationship of characteristic with
knowledge in which unemployed respondents have
better knowledge, this also related with a better
attitude in terminating pulmonary TB transmission.
This is in line with a study of Rahmawati S.A (2017)
in which there is a significant relationship between
knowledge with the attitude in terminating
pulmonary TB transmission (p= 0.001).
Table 4 reveals independent variables (age,
education, occupation, and population) do not have
significant relationship with respondent’s action in
terminating pulmonary TB transmission (p>0.05)
and only gender has a significant relationship with
respondent’s action in terminating pulmonary TB
transmission (p<0.05).
It is in line with the relationship of characteristic
with knowledge and respondent’s attitude of female
is better and the proportion is more dominant
(93.9%), hence it also related with better action in
terminating pulmonary TB transmission. This is also
in line with a study from Wijaya MK dkk (2012) in
which showed there is a significant relationship
between knowledge and attitude in controlling TB
case in Buleleng District.
But the result of this study is not in accordance
with a study from Nasirudin (2014) which revealed
there is no relationship between knowledge (p=
0.448) and attitude (p= 1.000) in the prevention
action of TB transmission in the working area of
Puskesmas Ngemplak in Boyolali District.
According to the result an intensive counseling is
still required to be performed to the people of KB
Village to raise their attitude and action in the effort
of terminating pulmonary TB transmission. The role
of cadre in KB Village have to be improved in order
for them to give understandable counseling and can
be applied by the community, therefore an effective
and efficient counseling method is being prepared by
utilizing poster and cadre’s guideline.
4
CONCLUSIONS
The proportion of respondent’s factor was female
(93.9%), age ≤ 50 years (71.2%), lower education
(59.1%), unemployment (72.7%), and less dense
population (65.9%). It is obtained gender, age, and
occupation are significantly related with knowledge
(p<0.05). Only employed is related with attitude
(p<0.05) and gender is related with action (p<0.05).
Intensive counseling is needed for the people of KB
Village to improve their attitude and action in effort
of terminating pulmonary TB transmission.
ICOSTEERR 2018 - International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches
692

ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Thank you to the Research Institute of Universitas
Sumatera Utara as the source of Talenta research
fund with research scheme of Basic Research of
Fiscal Year 2018 Number86/UN5.2.3.1/PPM/KP-
TALENTA USU/2018 16
th
March 2018.
REFERENCES
BKKBN Kota Medan, 2016. Tentang Kampung KB.
Available from http://kampungkb.bkkbn.go.id
Dinas Kesehatan Provinsi Sumatera Utara, 2013. Profil
Kesehatan Sumatera Utara Tahun 2013. Available from
http://dinkes.sumutprov.go.id/editor/gambar/file/TAB
EL%20LAMPIRAN%20PROFIL%202013%20FINA
L.pdf
Gelaw, SM., 2015. Socioeconomic Factors Associated
with Knowledge on Tuberculosis among Adults in
Ethiopia. Available from
http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/6207457
Kemenkes, 2016. Infodatin Tuberkulosis. Available from
http://www.depkes.go.id/download.php?file=downloa
d/pusdatin/infodatin/InfoDatin-2016-TB.pdf
Nasirudin M.R., 2014. Hubungan Tingkat Pengetahuan dan
Sikap dengan Perilaku Pencegahan Penularan
Tuberkulosis (TB) di Wilayah Kerja Puskesmas
Ngemplak Kabupaten Boyolali. Available from
http://eprints.ums.ac.id/31050/
Rahmawati, S.A. 2017. Pengetahuan dan Sikap Akan
Meningkatkan Tindakan Pencegahan Tuberculosis
(TBC). Available from
http://digilib.unisayogya.ac.id/2640/1/NASKAH%20P
UBLIKASI.pdf
WHO, 2016. Global Tuberculosis Report. Available from
http://www.who.int/tb/publications/global_report/en/
WHO., 2016. Tuberculosis Country Profiles. Available
from http://www.who.int/tb/country/data/profiles/en/
Wijaya, MK., Murti, B., Suriyasa, P., 2013. Hubungan
Pengetahuan, Sikap, dan Motivasi Kader Kesehatan
dengan Aktivitasnya dalam Pengendalian Kasus
Tuberkulosis di Kabupaten Buleleng. Jurnal
Magister Kedokteran Keluarga Vol 1, No 1, 2013 (page
38-48)
Predisposing Factor Associated with Community Action in Terminating TB Transmission in KB Village 2018
693
