
Clinical Pharmacy Services in Community Pharmacies at Medan City
Indonesia
Wiryanto
1
, H. R. Tanjung
1
and R. A. Dalimunthe
2
1
Pharmacist Education Program, Pharmacy Faculty, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Medan, Indonesia
2
Bachelor of Pharmacy Program,
Pharmacy Faculty, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Medan, Indonesia
Keywords: Clinical pharmacy services, Community pharmacies.
Abstract: Clinical Pharmacy is the practice of pharmacy as part of a multidisciplinary healthcare team directed at
achieving quality use of medicines. The standards of pharmaceutical services in community pharmacies
No.73/2016 consists of two areas; standards of pharmacies management and clinical pharmacy services. The
aim of this study was to describe the level of implementation of clinical pharmacy services in community
pharmacies at Medan city, Indonesia. This pilot study was a descriptive research that used a cross-sectional
survey methodology. The level of implementation of clinical pharmacy services in community pharmacies
obtained by direct survey to selected pharmacies. The clinical pharmacy services implementation level was
obtained from 99 community pharmacies. Overall, the data revealed that the average score of total score from
99 community pharmacies was 6.65±3.25. The highest level of clinical pharmacy services implementation
was fair (42.42%) followed by bad (33.33%) and good (14.14%). The data above showed that the clinical
pharmacy services implementation in community pharmacy still in the fair level (score 6-10).
1 INTRODUCTION
The Ministry of Health of Republic of Indonesia
published the act of Ministry of Health No. 1027 in
September 2004 for standards of pharmaceutical
services in community pharmacies even though the
concept of Pharmaceutical Care in Indonesia was
introduced since the late of 1990’s (Ministry of health
of RI, 2004). Finally, the Government issued the
government regulation No.51/2009 on
pharmaceutical practice as law standards of pharmacy
practice in Indonesia and the most recent Act of
Ministry of Health No. 73/2016 as the up-dated rule
on the standards of pharmaceutical services in
community pharmacies. (Ministry of health of RI,
2016). The standards of pharmaceutical services in
community pharmacies No.73/2016 consists of two
areas; standards of pharmacies management and
clinical pharmacy services. All of the regulations was
the government policy to back up the implementation
of Pharmaceutical Care practice in Indonesia.
Pharmacists can apply their expertise of drug
knowledge to help identify, solve and prevent
medication related problems and increase patient
safety by working with other health professionals
(SHPA, 2005).
Pharmacists administer drug review of
prescription to assess the drug appropriateness and
identify actual or potential drug related problems after
a prescription prescribed. Pharmacists determine
patients accept the most appropriate medicine,
regimen dose and dosage form for their medical
complain and drug related problems are minimized.
Pharmacists contact the physician if there are any
incompatibility/mistake. Pharmacists also have an
obligation to counsel the patients about the drug
information and education to optimize the safe and
appropriate use of medicines (Shah, 2009).
However, until now, there is no data about the
implementation of standards of clinical pharmacy
services in community pharmacies at Medan city
even though the rules were already published by the
Ministry of health years ago. The aim of this study
was to describe the level of implementation of clinical
pharmacy services in community pharmacies at
Medan city, Indonesia
.
Wiryanto, ., Tanjung, H. and Dalimunthe, R.
Clinical Pharmacy Services in Community Pharmacies at Meda City Indonesia.
DOI: 10.5220/0010093508410844
In Proceedings of the International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches (ICOSTEERR 2018) - Research in Industry 4.0, pages
841-844
ISBN: 978-989-758-449-7
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
841
2 METHODS
This pilot study was a descriptive research that used
a cross-sectional survey methodology. The level of
implementation of clinical pharmacy services in
community pharmacies obtained by direct survey to
the selected community pharmacy at Medan city.
The selection of community pharmacy was done
by purposive random sampling method. Researcher
was offered the pharmacists joined the study by a
whatsapp and facebook app groups and until the date
line time there were 99 pharmacists that joined the
study. The study was conducted on July 2018.
The professional pharmacists in selected
community pharmacy was asked to fill the
questioners that developed according to the standards
of clinical pharmacy services that stated in the Act of
of Ministry of Health No. 73/2016.
The questioners consists of 7 (seven) element of
clinical pharmacy services; the assessment and
prescription services, drug dispensing, drug
information services, drug counselling, home
pharmacy care, medication therapy review, drug’s
side effect monitoring. The pharmacists was asked to
choose the answer about the implementation of the 7
(seven) element in 3 (three) level implementation;
done and documented (score 2), done but not
documented (score 1), not implemented (score 0).
The total score obtained by summed the score of
every element. The score will range from 0 to 14 for
every community pharmacy. The level of
implementation were divided in three levels based on
total score; good (total score 11-14), fair (total score
6-10) and bad (total score 0-5).
3 RESULTS
99 pharmacists of community pharmacies located in
some district at Medan city was filled out the
questioners of the implementation of clinical
pharmacy services in community pharmacies at
Medan City.
3.1 Clinical Pharmacy Services
Implementation
The clinical pharmacy services implementation level
was obtained from 99 community pharmacies.
Overall, the data revealed that the average score of
total score from 99 community pharmacies was
6.65±3.25 as mention in Table 1.
Table 1: Clinical pharmacy services implementation
(n=99)
No. of CP Average score Highest
Score
Lowest
score
99 6.65±3.25 14 1
The data showed that the clinical pharmacy
services implementation in community pharmacy still
in the fair level (score 6-10). The highest score was
14 and the lowest score was 1. This study also
categorized all of 99 community pharmacies based on
its own total score in to three level; good, fair and bad
as mention in Table 2.
Table 2: Clinical pharmacy services implementation level
categorization (n=99)
No Level Frequency Percentage
1 Good 14 14.14
2 Fair 42 42.42
3 Bad 33 33.33
Total 99 100
The highest level of clinical pharmacy services
implementation was fair (42.42%) followed by bad
(33.33%) and good (14.14%).
3.2 Seven Element of Clinical Pharmacy
Services Implementation
The standards of clinical pharmacy stated in Act of
Ministry of health No.73/2016 was consists of 7
elements. The data obtained from this study revealed
that there were three element that still had low
implementation as mention in Table 3.
The three elements with high no implementation
level were the home pharmacy care (62.62%),
followed by the drug’s side effect monitoring
(50.50%) and the medication therapy review
(44.44%).
4 DISCUSSIONS
4.1 Clinical Pharmacy Services
Implementation
This study revealed that the the clinical pharmacy
services implementation in community pharmacy still
in the fair level (score 6-10). This study also showed
ICOSTEERR 2018 - International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches
842

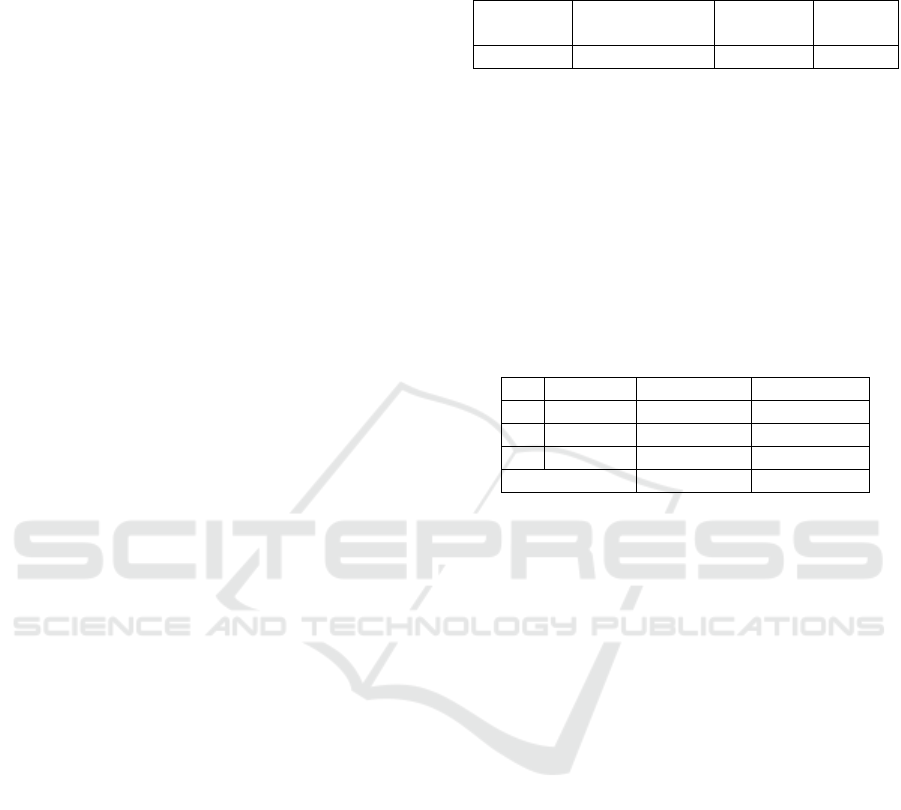
Table 3: Seven element of clinical pharmacy services implementation (n=99)
No. Element of CP services Done and documented
(%)
Done, not documented
(%)
No Implementation
(%)
1 The assessment and prescription
services
33.33 53.53.5 13.13
2 The drug dispensing 35.35 56.56 9.09
3 The drug information services 25.25 65.65 8.08
4 The drug counselling 26.26 65.65 8.08
5 The home pharmacy care 11.11 26.26 62.62
6 The medication therapy review 14.14 41.41 44.44
7 The drug’s side effect monitoring 13.13 36.36 50.50
that some community pharmacies have only score 1
(one) in
implement the clinical pharmacy services.
This condition are becoming important problem
that must be resolved together by the government,
pharmacists professional organization, and other part
of society in order to ensure the providing of the safe,
qualified, and effective pharmaceutical services to the
society.
4.2 Seven Element of Clinical Pharmacy
Services Implementation
The data obtained from this study showed the three
elements that have low implementation level. The
first elements with the highest percentage (62.62%)
of no implementation is the home pharmacy care.
This services were asked the pharmacists to
provide the pharmaceutical services with home visit
session, especially for the old age patients and
patients with chronic diseases. The two others
elements were the drug’s side effect monitoring
(50.50%) and the medication therapy review
(44.44%).
The pharmacists that want to provide this three
elements services must understand and possess the
pharmaceutical care concept and clinical pharmacy
skills. A study revealed that lack of training, lack of
knowledge and confidence, poor understanding about
pharmacist’s role as the barriers towards extended
services in clinical pharmacy services (Nordin, et al,
2017; Cordina, et al, 2008).
This research also revealed that the
implementation of clinical pharmacy services
categorization was predominantly by “done, not
documented”. This condition was far from ideal
condition of clinical pharmacy services. The primary
outcome of documenting clinical pharmacy activities
is to improve the quality of each patient’s care.
Documentation is also an instrument that can be used
to evaluate the accountability of the pharmacist’s and
the evidence of impact of the pharmacist’s services
(SHPA, 2013). Another benefit of pharmacists
documentation were accurate and timely
communication of medication therapy
recommendation, helps to ensure continuity of care,
illustrates the role of the pharmacists in patients care
(Dunkin and Dumont, 2013). Further research is
needed to reveal the barriers of implementation of
clinical pharmacy services in community pharmacies
at Medan city.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The data above showed that the clinical pharmacy
services implementation in community pharmacy at
Medan city was still in the fair level (score 6-10). This
condition must be resolved together by the
government, pharmacist professional organization,
and other part of society in order to ensure the
providing of the safe, qualified, and effective
pharmaceutical services to the society.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors acknowledge that the research was
supported by Rector of the University of Sumatera
Utara. The support is under the research grant
TALENTA USU of year 2018 contract number
2590/UN5.1.R/PPM/2018.
REFERENCES
Cordina, M., Safta, V., Ciobanu, A., Sautenkova, N., 2008.
An assessment of community pharmacists’ attitudes
towards professional practice in the Republic of
Moldova. Pharmacy Practice, Jan-Mar; 6(1):1-8.
Indonesian Ministry of Health., 2004. Act of RI Ministry of
Clinical Pharmacy Services in Community Pharmacies at Meda City Indonesia
843

Health No.1176/Menkes/SK/X/2004.
Indonesian Ministry of Health. (2017). Act of RI Ministry
of Health No.73/Menkes/SK/X/2017.
Dunkin, J and Dumont Z, 2013. Documenting pharmacy
interventions in a busy dispensary. Pharmacy practice
webinar of Canadian Pharmacists Association.
Nordin, et al., 2017. Actual or potential extended services
performed by malaysian community pharmacists,
perceptions and barriers towards it’s performance: a
systematic review. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci, Vol 9, Issue
10, 13-20.
Shah, A. (2009). Pharmacy Intervention in The Medication-
use Process: the role of pharmacists in improving
patient safety. Internship with International
Pharmaceutical Federation (FIP). Netherland: Den
Haag.
Society of Hospital Pharmacist of Australia (SHPA). 2005.
SHPA Standards of Practice for Clinical Pharmacy.
Journal of Pharmaceutical Practice Res. 35(2), 122-46.
Society of Hospital Pharmacist of Australia (SHPA). 2013.
Documenting Clinical Activities. Journal of Pharmacy
Practice and Research. 43(2), Suppl.
ICOSTEERR 2018 - International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches
844
