
Optimization of Polymer and Cross-linker Combination on the
Formation of Pectin Film Containing Metformin Hydrochloride
Mariadi
1,2
*, Bayu Eko Prasetyo
1,2
and Yade Metri Permata
3
1
Departement of Pharmaceutical Technology, Faculty of Pharmacy, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Medan, 20155, Indonesia
2
Nanomedicine Centre of Innovation, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Medan, 20155, Indonesia
3
Departement of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, Faculty of Pharmacy, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Medan, 20155, indonesia
Keywords: Pectin film, combination of polymers, cross-linker, metformin hydrochloride.
Abstract: Pectin has been developed as an edible film in drug delivery systems, however pectin has some disadvantages
such as rapid drug release, low mechanical strength, and low drug infusion efficiency. The purpose of this
study was to optimize the polymer and cross-linker combination on the formation of pectin film containing
metformin hydrochloride. The films were prepared using a single or combination of polymer as a matrix and
glycerin as a plasticizer. The homogenous mixture of pectin mucilage, alginate mucilage, hydroxyl-propyl
methylcellulose (HPMC) mucilage, ethyl-cellulose, glycerin, and metformin hydrochloride was flattened on
an object glass (2 cm x 5 cm) and then allowed to dry at room temperature. The all formula were evaluated
the capability of forming the membrane or film and elasticity properties. The pectin, alginate, HPMC, and
ethyl-cellulose polymer in single or two polymer combination cannot form a film with the addition of
metformin hydrochloride. The combination of three polymers of pectin, alginate, and ethyl-cellulose can form
a finer, smoother surface, more elastic, rolled and folded membrane/film. The combination of three polymers
of pectin, alginate, ethyl-cellulose and the addition of cross-linkers to a combination of pectin, alginate,
HPMC provides an optimal film for Drug Delivery System.
1 INTRODUCTION
Pectin is widely used in the pharmaceutical as an
ingredient for applications of Drug Delivery System
(DDS). Pectin has advantages as a non-toxic nature
polymers, low production cost, and high availability
(
Mishra, 2012). Edible films can be distinguished in
three categories based on the raw materials used i.e.
hydrocolloids, fats and mixtures of both. The
hydrocolloid groups can be prepared from
polysaccharides (cellulose, modified cellulose,
starch, agar, alginate, pectin, dextrin), proteins
(collagen, gelatin, egg white), and also lipids
(Omidian and Kinam, 2012).
Drug release from high methoxy pectin has been
studied in terms acrylamide grafted pectin was
characterized by FTIR, DSC and X-ray diffraction.
The polymer was cross-linked with glutaral dehyde
and tested for salicylic acid release using a Franz
diffusion cell. A grafted hydrogel displayed better
film-forming properties than pectin (Sutar, 2008).
Hydrogel membrane based on pectin and
polyvinylpyrrolidone have been prepared by physical
blending and conventional solution casting methods.
The release of salicylic acid was monitored at
different aqueous media using a UV Vis
spectrophotometer at 294 nm wavelength. The
presence of secondary amide, decrease in crystallinity
at higher PVP ratio (Mishra, 2008). Amidated pectin
complexes with calcium were used in preparation of
a multipar-ticulate system with the potential for site-
specific colon delivery (Munjeri, 1997).
In the manufacture of edible film from pectin as a
drug delivery system, pectin has several
disadvantages such as rapid drug release, low
mechanical strength, and low drug infusion
efficiency. The purpose of this study is the optimize
of polymer and cross-linker combination on the
formation of pectin film containing metformin
hydrochloride.
Mariadi, ., Prasetyo, B. and Permata, Y.
Optimization of Polymer and Cross-linker Combination on the Formation of Pectin Film Containing Metformin Hydrochloride.
DOI: 10.5220/0010093608450851
In Proceedings of the International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches (ICOSTEERR 2018) - Research in Industry 4.0, pages
845-851
ISBN: 978-989-758-449-7
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
845

2 METHODS
2.1 Materials
Metformin hydrochloride was obtained from Iol
Chemicals and Pharmaceuticals Ltd India. Sodium
Alginate 500~600 cP was the products of Wako Pure
Chemical Industries, Ltd Japan. Pectin was obtained
from Cargill Deutschland GmbH Germany, ethyl
cellulose was the products of Shanghai Honest Chem
Co., Ltd. China, and hydroxypropyl methylcel lulose
(HPMC) was the products of Wuhan Senwayer
Century Chemical Co., Ltd., China.
2.2 Preparation of Films Containing
Metformin Hydrochloride
The films were prepared using the single or
combination of polymer as a matrix and glycerin as a
plasticizer. The homogenous mixture of mucillage of
4% sodium alginate in water, mucillage of 10% pectin
in water, mucillage of 8% HPMC in water,
ethylcellulose, glycerin, and metformin
hydrochloride (Table 1) was flattened on a object
glass (2 cm x 5 cm) and then allowed to dry at room
temperature for 48 hours. The films formed were
removed carefully, and placed in desiccator.
3 EVALUATION
The formulas designed with various combinations of
polymers containing metformin hydrochloride (Table
1), the capability of the polymer in each formula to
form the membrane/film was observed visually and
the elasticity properties was evaluated by rolling or
folding the membrane/film.
4 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
4.1 The Film Properties of Single
Polymers without Metformin
Hydrochloride
The membrane/films of single polymers and
combinations without containing metformin
hydrochloride were prepared by dissolving the
polymers at concentrations which may form a gel.
The gel solution is then placed on the mold and dried
at room temperature. The gel solutions of the pectin,
alginate, HPMC and ethyl cellulose polymers all
demonstrate to form a films. The generally obtained
films have properties such as plastic, transparent,
thin, elastic to be rolled or folded, except for the films
of ethyl cellulose showed yellowish white film as
shown in Table 2 and Figure 1.
Based on the data in table 2, all of the polymers
have the ability to form a good film. Edible film
preparations can be distinguished based on the raw
materials used namely hydrocolloids, fats and
mixtures of both. Edible hydrocolloid group films can
be made from polysaccharides such as cellulose,
cellulose modification, starch, agar, alginate, pectin,
and dextrin (Omidian and Kinam, 2012).
The ability of these polymers to form films and
applications as matrices in drug delivery systems has
been reported in several studies i.e. combinations of
chitosan-alginic films containing antacids as the
gastroretentive drug delivery system (Mariadi, 2015),
the characterization of pectin/PVP hydrogel
membranes containing salicylic acid for drug
delivery system (Mishra, 2008), pectin-based
biodegradable hydrogels with potential biomedical
application as drug delivery system (Sadeghi, 2011),
and chitosan-alginate films prepared with chitosan of
different molecular weights (Yan, 2001).
Table 1: Formula of films containing metformin hydrochloride
No Polymers
Polymers
Ratio
Metformin
h
y
drochloride
Glycerin
1
Single of polymer without
containing metformin
hydrochloride
Pectin 10%
- - 2 drops
HPMC 8%
- - 2 drops
Etil Selulosa 8%
- - 2 drops
Alginate 4%
- - 2 drops
2
Single of polymer
containing metformin
hydrochloride
Pectin 10% - 500 mg 4 drops
HPMC 8% - 500 m
g
4 dro
p
s
Eth
y
l cellulose 8% - 500 m
g
4 dro
p
s
Sodium Al
g
inate 4% - 500 m
g
4 dro
p
s
3
Combination of two
polymer containing
metformin hydrochloride
Pectin + HPMC 1:1 500 mg 4 drops
Pectin + Ethyl cellulose 1:1 500 mg 4 drops
Pectin + Sodium Al
g
inate 1:1 500 m
g
4 dro
p
s
ICOSTEERR 2018 - International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches
846

Table 1: Formula of films containing metformin hydrochloride(cont.)
No Polymers
Polymers
Ratio
Metformin
hydrochloride
Glycerin
4
Combination of three
polymers containing
metformin hydrochloride
Pectin + Sodium Alginate +
Eth
y
l cellulose
1:1:1 500 mg 4 drops
Pectin + Sodium Algintae +
HPMC
1:1:1 500 mg 4 drops
Pectin + Ethyl cellulose +
HPMC
1:1:1 500 mg 4 drops
5
Combination of two and
three polymers with the
addition of Crosslinker
(CaCl
2
) containing
Metformin hydrochloride
Pectin + Alginate + CaCl
2
1%
+ metformin HCl
1:1 500 mg 4 drops
Pectin + Alginate + CaCl
2
2%
+ metformin HCl
1:1 500 mg 4 drops
Pectin+ Alginate + CaCl
2
3%
+ metformin HCl
1:1 500 mg 4 drops
Pectin + Alginate + Ethyl
cellulose + CaCl
2
1% +
Metformin HCl
1:1:1 500 mg 4 drops
Pectin + Alginate + HPMC +
CaCl
2
1% + Metformin HCl
1:1:1 500 mg 4 drops
Table 2: The properties of single polymer membrane/film
No Polymer
Thickness of the
membrane/fil
m
(
mm
)
Properties of Film
1 Pectin 10% 0.27±0.05 Transparent fil
m
: thin, elastic and roll able/foldable
2 HPMC 8% 0.14±0.01
Transparent film: thin, elastic and roll able/foldable
3
Ethyl Cellulose
8%
0.34±0.02
Yellowish white film: thin, elastic and roll able/foldable
4 Alginat 4 % 0.75±0.17
Transparent fil
m
: thin, elastic and roll able
/
foldable
Pectin HPMC Al
g
inate
Ethylcellulose
Figure 1: The Films of pectin, alginate, HPMC and ethyl cellulose polymer
4.2 The Membrane Properties of Single
Polymer Contains Metformin
Hydrochloride
The gel solution of the pectin, alginate, HPMC and
ethylcellulose polymers added with metformin HCl
respectively, indicates that this mixture can not form
the membrane/ film, but produces crystalline particles
of metformine HCl-coated polymer as shown in Table
3 and Figure 2.
From the obtained data, the membrane/film can not
be formed suspected that it is related to the water-
soluble nature of metformin HCl, so that when mixed
with the polymer gel solution dissolves between the
gel and metformin HCl. The gel solution breaks into
liquid and dilute, this is because the dissolved
metformin HCl can break the crosslinks in the
polymer chains of the gel. The breaking of crosslinks
of the gel preparations of these polymers results in the
loss of the gel properties, so that when the mixture is
dried it can not form membrane /films. In physical
gels, the nature of the crosslinking process is
physical. This is normally achieved via utilizing
physical processes such as association, aggregation,
crystal lization, complexation, and hydrogen
bonding. While physical hydrogels are reversible due
Optimization of Polymer and Cross-linker Combination on the Formation of Pectin Film Containing Metformin Hydrochloride
847

Table 3: The membrane properties of single polymer contains metformin hydrochloride
No Polymer
The resultin
g
film membrane
The result Pro
p
erties of membrane
1 Pectin 10% + Metformin HCl
Could not formed films Produce irregular crystals
2 HPMC 8% + Metformin HCl
Could not formed films Produce rod-shaped crystals
3 Alginate 4% + Metformin HCl
Could not formed films Produce irregular crystals
4 Ethyl cellulose 10% + Metformin HCl
Could not formed films Produce powder
Pectin + Metformin HCl HPMC + Metformin HCl
Alginate + Metformin
HCl
Ethylcellulose
+ Metformin HCl
Figure 2: Single polymer (pectin, alginate, HPMC and ethyl cellulose) can not form a film membranes with Metformin HCl
to the conformational changes. Hydrogels are also
classified as hydrogels responsive to changes in terms
of their interaction with the surrounding environment,
i.e., responses to the changes in pH, temperature, and
the composition of the surrounding liquid. Depending
on its structure, hydrogel can respond to
environmental changes by changing its size or shape
(Omidian and Kinam, 2012).
4.3 The Memran/Film Properties of
Pectin (two polymer combination)
That Contain Metformin HCl
The membrane/film properties of pectin (two
polymer combination) that contain metformin HCl
shows the same results as a single polymer that can
not form a film, as in the Table 4 and Figure 3.
Table 4: The film membrane properties of polymer (two
polymer combination) containing Metformin HCl
No Polymer The result
1
Pectin + HPMC
+ Metformin HCl
Could not formed films
2
Pectin
+ Ethylcellulose
+ Metformin HCl
Could not formed films
3
Pectin + Alginate
+ Metformin HCl
Could not formed films
4.4. The Membrane/Film Properties of
Pectin (three polymer combination)
Containing Metformin HCl
The properties of the pectin membranes/films (three
polymer combination) containing metformin HCl can
be seen in Table 5 and Figure 4, that the combination
of three polymers gives different results, some
formulas may form membranes/films and some other
can not. It will be dependent on combination of the
polymer from the formula.
The combination of pectin, alginate and
ethylcellulose polymer can form membran/film, but
combination with ethylcellulose powder provides
better membrane/film than mucilago ethyl cellulose,
which is obtained more smooth and flat surface
membrane, elastic, easily rolled and folded. It is
assumed that the ethyl cellulose powder as a
hydrophobic polymer covers/coats the metformin
HCl so it is not disturb the stability of the gel solution
of the hydrophilic pectin and alginate polymers and
capable to form a membrane/film.
ICOSTEERR 2018 - International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches
848
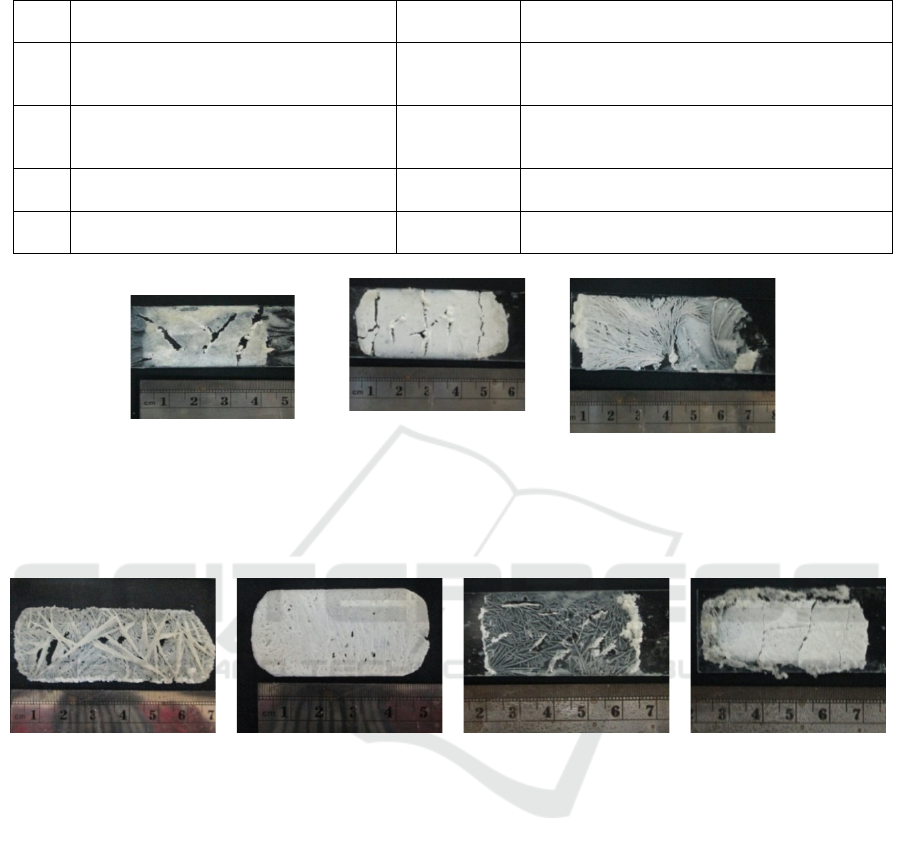
Table 5: The membrane film of polymer (three polymer combination) that contain metformin HCl
No Polymer
Thickness
(mm)
Properties of film
1
Pectin + Alginate + mucillage of ethyl
cellulose + Metformin HCl
0.96±0.02
Retrieved membranes/films with a rough surface
containing metformin HCl, uneven, and
p
erforated crystals
2
Pectin + Alginate + powder of ethyl
cellulose + Metformin HCl
0.71±0.04
Retrieved membranes /films with a smoother
and flat surface, elastic, easily rolled and folde
d
3
Pectin + Alginate + HPMC + Metformin
HCl
- Could not formed films
4
Pectin + HPMC + Ethyl cellulose
+ Metformin HCl
- Could not formed films
Figure 3: Polymers of pectin, alginate, HPMC and ethyl cellulose (two polymers combination) can not form film membranes
with Metformin HCl
Pectin + Alginate
+ mucillage of Ethyl
cellulose + Metformin HCl
Pectin + Alginate
+ powder of Ethyl cellulose
+MetforminHCl
Pectin + Alginate
+ HPMC + Metformin HCl
Pectin + HPMC
+ Ethylcellulose
+ Metformin HCl
Figure 4: Polymers of pectin, alginate, HPMC and ethyl cellulose (three polymer combination) containing Metformin HCl:
only a combination of pectin + alginate and powder of Ethyl cellulose are capable of forming a good film.
4.5 The Membrane/Film Properties of
Pectin (three polymer combination)
with the Addition of CaCl
2
Containing Metformin HCl
Interestingly, the addition of crosslinkers (CaCl
2
) to a
combination of polymers containing metformin HCl
is a combination of the polymer pectin, alginate and
HPMC in the previous data can not form
membrane/film, but the addition of CaCl
2
showed
different results, it is capable to form a thin films,
elastic, easily rolled and folded, as shown in Table 6
and Figure 5. It can be explained that one of the
properties of sodium alginate is having the ability to
form a gel by addition of a calcium salts and caused
by the occurrence of chelating between the L-
guluronic of alginate chains with calcium ions. This
gel is a cross link network composed of the calcium
alginate forming egg box conformation (
Morris,,
1978)
.
5 CONCLUSIONS
A single and combination of the polymers containing
metformin hydrochloride could not formed films. The
combination of pektin, alginat, and ethylcellulose
pectin and the addition of crosslinker (CaCl
2
) in
Pectin + HPMC
+ Metformin HCl
Pectin + Ethylcellulose
+ Metformin HCl
Pectin + Alginate +
Metformin HCl
Optimization of Polymer and Cross-linker Combination on the Formation of Pectin Film Containing Metformin Hydrochloride
849
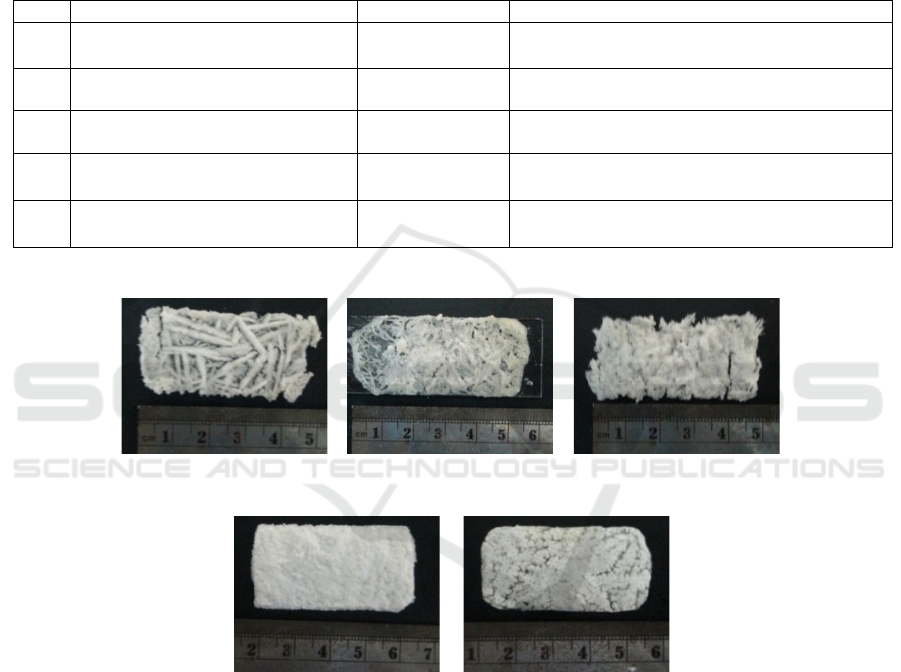
pectin alginate and HPMC polymer combination
capable to form an optimum membrane/film and
potential for drug delivery system.
ACKNOWLEDMENTS
This research is funded by Universitas Sumatera
Utara in accordance with the contract of TALENTA
research implementation of Universitas Sumatera
Utara for 2018 No: 2590 / UN.5.1.R / PPM / 2018
dated 16
th
March 2018.
Table 6: The membrane/film of pectin (three polymer combination) with the addition of CaCl
2
containing Metformin HCl
No Polyme
r
Thickness (mm) Properties of film
1
Pectin + Alginate + CaCl
2
1% +
metformin HCl
- Could not formed films
2
Pectin+ Alginate + CaCl
2
2% +
metformin HCl
- Could not formed films
3
Pectin+ Alginate + CaCl
2
3%
metformin HC
- Could not formed films
4
Pectin + Alginate + Ethyl cellulose
+ CaCl2 1 % Metformin HCl
1.32 ±0.03
Retrieved thin, rigid, non-rolled and folded film
membranes.
5
Pectin+Alginate + HPMC+ CaCl
2
1% + Metformin HCl
0.87±0.03
Retrieved thin, elastic, transparent, irregularly
shaped, easily rolled or folded film membranes.
Pectin + Alginate
+ CaCl
2
1%
+ metformin HCl
Pectin + Alginate
+ CaCl
2
2%
+ metformin HCl
Pectin + Alginate + CaCl
2
3% + metformin HCl
Pectin + Alginate Pectin + Alginate + HPMC
+ Ethyl cellulose + CaCl
2
1%
+ CaCl
2
1% + metformin HCl + metformin HCl
Figure 5: Pectin Membrane Film (three polymers combination) with addition (CaCl
2
) Containing Metformin HCl:
combination of pectin + alginate + powder of Ethyl cellulose and combination of pectin + alginate + HPMC capable to form
a film membrane.
REFERENCES
Mariadi, Bangun, H., and Karsono, 2015. Formulation and
In Vitro Evaluation of Gastroretentive Drug Delivery
System of Antacids Using Alginate-Chitosan Films.
International Journal of Pharm Tech Research. Vol.8,
No.9, pp 01-12.
Mishra, R.K., Banthia, A.K., Majeed, A.B.A., 2012. Pectin
Based Formulations for Biomedical Applications: A
Review, Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical
Research. Volume 5, 1-7.
Mishra, R.K., Datt M., Banthia, AK., 2008. Synthesis and
characterization of pectin/PVP hydrogel membranes for
drug delivery system. AAPS PharmSciTech 9(2):395–
403.
ICOSTEERR 2018 - International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches
850

Morris, E.R., Rees, D.A., and Thom, D., 1978. Chiroptical
and Stoichiometry Evidence of a Specific Primary
Dimerisation in Alginat Gelation. Carbohydrate
Research. 11(2): 272-277.
Munjeri O., Collett J.H., Fell J.T., 1997. Hydrogel beads
based on amidated pectins for colon-specific drug
delivery: the role of chitosan in modifying drug release.
J Control Release. 46 (3):273–278.
Omidian, H and Kinam P., 2012. Hydrogels. In: Siepmann,
J., Ronald, A., Michael J (Editors), Fundamentals and
Applications of Controlled Release Drug Delivery.
Springer New York Dordrecht Heidelberg. London. P.
76-78.
Sadeghi, M., 2011. Pectin-Based Biodegradable Hydrogels
with Potential Biomedical Application as Drug
Delivery System. Biomaterials and
Nanobiotechnology, 2, 36-40.
Sutar, P.B., 2008. Development of pH sensitive
polyacrylamide grafted pectin hydrogel for controlled
drug delivery system. J Mater Sci Mater Med
19(6):2247–2253.
Yan, X.L., Khor, E., Lim, L-Y., 2001. Chitosan-Alginate
Films Prepared With Chitosan Of Different Molecular
Weights. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research:
Applied Biomaterials. (4): 358-365.
Optimization of Polymer and Cross-linker Combination on the Formation of Pectin Film Containing Metformin Hydrochloride
851
