
Formaldehyde Detection using Thin Film Sensor based on Chitosan
Crosslinked with Glutaraldehyde
I. Nainggolan
1
, P. Faradilla
1
, T. I. Nasution
2
, H. Agusnar
1
1
Chemistry Department, Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Science, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Medan 20155,
Sumatera Utara, Indonesia
2
Physics Department, Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Science, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Medan 20155, Sumatera
Utara, Indonesia
Keywords: Chitosan, Electrodeposition, Formaldehyde, Film, Sensor.
Abstract: In this study, chitosan was crosslinked with glutaraldehyde to fabricate a formaldehyde sensor. Chitosan based
sensor was used for formaldehyde detection in various concentration (1 ppm; 1,5 ppm; and 2 ppm). The sensor
fabrication was performed using electrodeposition method to form a film sensor. The cross-linking agent is
glutaraldehyde, the aim of adding glutaraldehyde is to enhance the sensing properties of chitosan sensor
especially the life time of the sensor. The existence of glutaraldehyde which was crosslinked with chitosan
has been proved by FTIR spectra. Formaldehyde was dropped onto chitosan film surface and the response of
the chitosan sensor towards formaldehyde was recorded as output voltage. The average of output voltage
values for three times measurements were within the range of 0,0143 V to 0,0286 V. Increasing concentration
of formaldehyde showed the increasing of output voltage value. The sensors showed good sensitivity and fast
response.
1 INTRODUCTION
In Indonesian traditional markets, the control of
government on utilization of prohibited and
dangerous substance in food, especially formalin, is
still weak. It emerges a fret as well as a worry to the
customer, which may cause harm to human health
(Noordiana, 2011). Although adding formalin to
foods is forbidden as stated in The Regulation of
Indonesian Minister of Health No.
1168 /
Menkes /PER/X/1999, some industries, especially
small/home scale industries still add it in foods and sell
them to traditional markets. The Indonesian Agency for
Drug and Food Control found that many testing samples
of food products of Small-Medium Industries are proven
to be positive containing formalin (Media Industry,
2006). According to WHO standard in 2002, the
maximum formalin content contained in food is 1 mg/l
equivalent to 1 ppm (WHO, 2002). Nowadays, the
common method to detect formalin in food is gas
chromatography-mass spectroscopy (GC-MS) but the
analysis tool is expensive and time consuming. It is
highly desirable to develop a sensitive, cheap and
easy-to-use method for formaldehyde detection.
Chitosan as a natural polymer is attractive
sensitive material with several plus properties.
Recently it has been found that chitosan can be
dramatically modified and blended to be used as an
effective sensitive material. It is of interest because
of the possibility to enhance sensitivity and
selectivity due to modification of chitosan structure,
excellent film-forming ability, high mechanical
strength, adhesive, high heat stability (Yang, 2013).
The high chitosan solubility in acidic media also
makes chitosan easily deposited to form film onto a
substrate (Sun,2011). The advantages of non-porous
film layers offer high permeability, mechanical
strength, and selectivity (Kanti, 2004).
Decreasing the mechanical properties of chitosan
in wet conditions can be reduced by the addition of
crosslinking. Cross-linking is the most effective
method for improving membrane properties.
Commonly used crosslinking agents are
glutaraldehyde, trisodium citrate, sulfuric acid, and
pentasodium tripolyphosphate (Safitri, 2016).
Nainggolan, I., Faradilla, P., Nasution, T. and Agusnar, H.
Formaldehyde Detection using Thin Film Sensor based on Chitosan Crosslinked with Glutaraldehyde.
DOI: 10.5220/0010096610391041
In Proceedings of the International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches (ICOSTEERR 2018) - Research in Industry 4.0, pages
1039-1041
ISBN: 978-989-758-449-7
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
1039

Utilization of chitosan as a sensitive sensor
material is rarely performed whereas chitosan has
amine (-NH
2) and hydroxyl (-OH) groups in its
molecular structure which enable chitosan as a
sensitive material. The high chitosan solubility in
acidic media also makes chitosan easily deposited in
the form of film onto a substrate (Sun, 2011). So,
chitosan is a potential sensitive material to be a
sensing material to detect formaldehyde.
2 MATERIALS AND METHOD
2.1 Materials and Instruments
Materials which were used in this experimental work
are chitosan with deacetylation degree 80% (medium
molecular weight), glutaraldehyde, CH3COOH 2%,
H2SO4, HNO3, CoCl2 0,01 M, KSCN 1 M, HCl 2 N
(Merck). Printed circuit board (PCB) was used as a
substrate of sensor. Vacuum oven, hot plate, magnetic
stirrer, centrifuge, ultrasonic were used to fabricate
the sensors. A set of FTIR Shimadzu IR prestige-21
was used to characterize the chitosan film and an
electronic set-up was used to test the sensor.
2.2 Preparation of Chitosan Solution
Chitosan powder was supplied by Sigma–Aldrich
(medium molecular weight), it was dissolved in acetic
acid 2% then stirred using a magnetic bar stirrer for
24 hours at room temperature to prepare the chitosan
solution gel.
2.3 Preparation of Chitosan Film
Sensor
Chitosan film was made by chitosan solution using
electrodeposition method. On this process, printed
circuit board (PCB) was used as a substrate of sensor.
The electrodeposition process of chitosan films
illustrates as in Figure 1. The supplied voltage was
fixed at 2,5 volts and left to dry for 5 minutes at 105
o
C
in oven. Chitosan film was cross-linked using
glutaraldehyde 25%. CoCl2 0,01 M was used as a
template, KSCN 1 M and HCl 2 N were used as
template remover during crosslinking process.
Formaldehyde solutions with various concentration
(1 ppm; 1,5 ppm; 2 ppm; 5 ppm; and 10 ppm) were
used to test the sensitivity of the chitosan film sensor.
Formaldehyde solution was dropped onto chitosan
film
sensors. Sensor testing was performed using
amperometric method, amperometric method is a
method for detecting analyte using amperometry and
the output was showed based on the characteristic of
sensor. The response of the chitosan sensor towards
formaldehyde was recorded as output voltage.
Figure 1: Deposition Process of Chitosan Film Sensor
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Chitosan is positively charged in acidic condition
thus it would assemble onto the PCB surface to form
a chitosan film sensor. Glutaraldehyde as a cross-
linking agent made the sensing properties of chitosan
high especially the shelf life of the sensor. The cross-
linked chitosan sensor gave response (output voltage)
to the formaldehyde in various concentration. The
cross-linked chitosan sensor showed good stability in
measurement, there is no any fluctuation in output
voltage. The measurements were repeated three
times. The output voltage values of chitosan sensor
when detecting formaldehyde for 1; 1,5 and 2 ppm
are reported in Table 1.
Table 1: The output voltage of chitosan sensor when
detecting formaldehyde.
Formaldeh
y
de Outpu
t
Concentration
Volta
g
e
(ppm)
Average
(V)
1
0,0143
1,5
0,0213
2
0,0286
Table 1 shows the output voltage of chitosan sensor
when its surface was dropped by formaldehyde
standard solution. The output voltage values show the
ICOSTEERR 2018 - International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches
1040
sensitivity of chitosan sensor during detecting various
concentration of formaldehyde. The average of output
voltage values for three times measurements were
within the range of 0,0143 V to 0,0286 V. The highest
output value (0,0286 V) was observed when chitosan
sensor detecting 2 ppm of formaldehyde, while the
lowest value (0,0143 V) was observed during the
sensor was dropped by 1 ppm of formaldehyde. As
shown by the table, increasing concentration of
formaldehyde shows the increasing in output value.
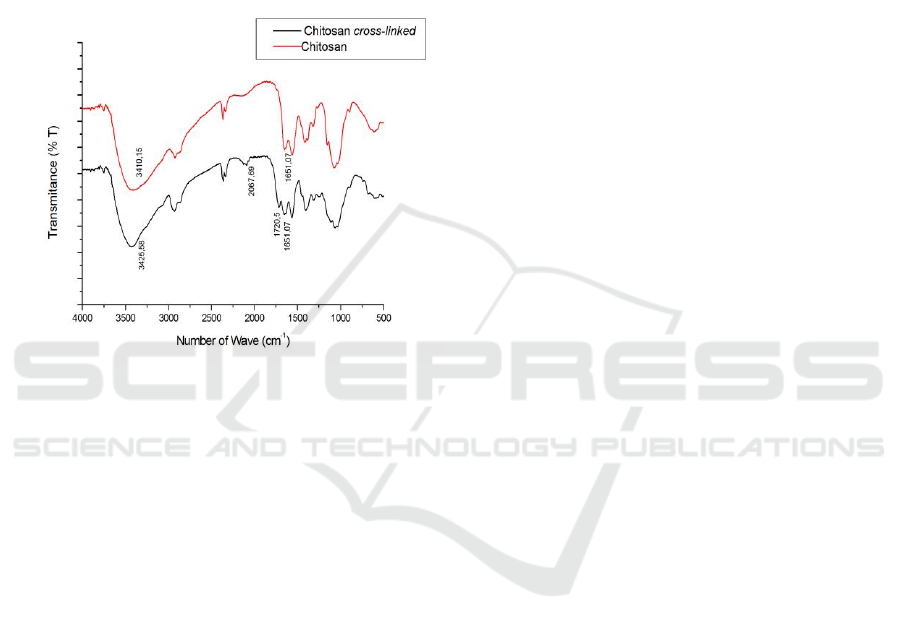
Figure 2: FTIR Spectra of Cross-linked Chitosan and
Chitosan Films
The cross-linked process of chitosan has been
done successfully. FT-IR was used to check the
existence of cross-linking based on functional groups
of chitosan. The spectrum of cross-linked chitosan
shows in Figure 2. The hydroxyl groups (O-H
vibration) are showed by band at 3425 cm
-1
for cross-
linked chitosan film and band at 3410 cm
-1
for
chitosan film. The presence of amine group is
strengthened in 1651 cm
-1
(chitosan cross-linked and
chitosan). From the FTIR spectrum, the cross-linking
has been showed at band 1720 cm
-1
for aldehyde
group.
4 CONCLUSIONS
The experimental results of chitosan sensor showed that
chitosan sensor was capable to detect formaldehyde in
various concentration. The chitosan sensor can
differentiate the various concentration of formaldehyde.
The sensitivity of chitosan sensors has been proven by
the different output voltage values which were showed
by the sensors during tested with different concentration
of formaldehyde. Increasing concentration of
formaldehyde showed the increasing on sensor output
voltage values. The highest sensor
output value
(0,0286 V) was showed during the sensor detecting 2
ppm of formaldehyde, while the lowest value (0,0143
V) was showed during the sensor detecting 1 ppm of
formaldehyde.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
This work was financially supported by TALENTA
USU research grant No. 2590/UN5.1.R/PPM/2018
REFERENCES
Noordiana, N., Fatimah, AB., Farhana, YCB. 2011. Int.
Food Res. J. 18: 125–136
Media
Industry Penyalahgunaan Formalin dan Peran
Pemerintah Media Ind., 2006. No. 21.III. 5–9.
World Health Organization (WHO)., 2002. Formaldehyde.
Concise International Chemical Assessment Document
40. Geneva; 48: 6-7
Yang, Y., Fang, G., Liu, G., Pan, M., Wang, X., Kong, L.,
2013. Biosens. Bioelectron. 47: 475–481.
Sun, K., Li, ZH., 2011. Express Polymer Letters 5(4): 342
- 361.
Kanti, P., Srigowri., Madhuri, J., Sridhar, S., 2004.
Separation and Purification Technology, 40 259-266
Safitri, A.G., Santoso, E., 2016. Sains and Arts Journals ITS
Vol. 5, No.1, 2337-3520
Formaldehyde Detection using Thin Film Sensor based on Chitosan Crosslinked with Glutaraldehyde
1041
