
Two Dimensional Sediment Transport Simulation around Kamijoro
Intake, Yogyakarta, Indonesia
Pradipta Nandi Wardhana and Rizki Budiman
Civil Engineering Department, Universitas Islam Indonesia, Jalan Kaliurang Km 14.5, Yogyakarta, Indonesia
Keywords: Sediment Transport, 2 Dimensional Model Simulation, Nays2DH.
Abstract: Kamijoro Intake is irrigation water intake structure located in Progo River. The Kamijoro Intake is irrigation
water source for 2,365 hectares of irrigation area in Bantul, Yogyakarta, Indonesia. In the operational phase,
the Kamijoro Intake cannot operate optimally because of sediment deposition around the intake structure.
Thus, the sediment deposition behavior led to conduct research regarding flow pattern and sedimentation
characteristic around the intake structure. Two-dimensional mathematical simulation was conducted by using
Nays2DH solver provided by iRIC software. This work simulated two hydraulic conditions to enhance
understanding of hydraulic and sediment transport behavior under high discharge and low discharge. The
simulations result showed that high discharge scenario produced higher value on flow parameter such as water
depth, velocity, and shear stress than low discharge scenario. Furthermore, high discharge generated higher
value of sediment transport parameter than the low discharge such as river bed deformation, river bed
elevation development and bed load parameter. Findings also revealed that immense sediment deposition
around Kamijoro Intake is most influenced by small value of river slope.
1 INTRODUCTION
Kamijoro Intake is located at Kamijoro Village,
Pajangan Subdistrict, Bantul District, Daerah
Istimewa Yogyakarta, Indonesia. The structure is
utilized as irrigation water intake for 2,365 hectares
of irrigation area. Kamijoro Intake was built in year
1924. In order to be located at free sediment
deposition area, Kamijoro Intake positioned at outer
section of river bend (see Figure 1). Despite of
located at outer river reach bend, sometime Kamijoro
Intake cannot operate properly because of sediment
deposition flowing inside the intake. The main factor
influencing Kamijoro Intake performance in
supplying irrigation water is the intake structure
location at the Progo River reach having small river
slope. Small river slope around Kamijoro Intake
generates sediment deposition that must be removed
regularly. Progo River sediment source is Merapi
Mount. Merapi Mount is one of the active volcanoes
in the world.
International River Interface Cooperation (iRIC)
is international group consisted of scientist and
engineers who want to provide access of state-of-the-
art mathematic model software for undergraduate and
graduate student to enhance understanding of
morphodynamics. Furthermore, the research group
released package software consisted of several
mathematical solver modules by using similar name
as iRIC (Nelson, 2016).
Nays2DH is two dimensional, depth averaged,
unsteady, coupled flow, and sediment transport solver
provided by iRIC (Kinze, 2015). Nays2DH has
capabilities to simulate river flow, sediment transport,
and river bed geomorphology.
There are wide range of researches regarding
sediment transport and morphological development
simulation. Norman (2017) assessed hydraulic and
transport sediment behaviour of ephermal stream for
restoration purpose, Wickham (2015) found that grain
size heterogeneity influences bed load transport,
while bed roughness variability do not generated
impact in sediment transport, Wongsa (2016)
simulated breach morphological development of
earthen embankment, and Sarkawt (2017) simulated
hydro morphology response of Sandy River in
Oregon toward flood occurrence.
Moreover, Ali (2017) demonstrated Nays2DH
ability to simulate flow pattern around single groyne
with several angles toward approaching flow. The
hydraulic simulation also could produce secondary
flow well at the downstream of installed groyne.
590
Wardana, P. and Budiman, R.
Two Dimensional Sediment Transport Simulation Around Kamijoro Intake, Yogyakarta, Indonesia.
DOI: 10.5220/0010371305900595
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference of Computer, Environment, Agriculture, Social Science, Health Science, Engineering and Technology (ICEST 2018), pages 590-595
ISBN: 978-989-758-496-1
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
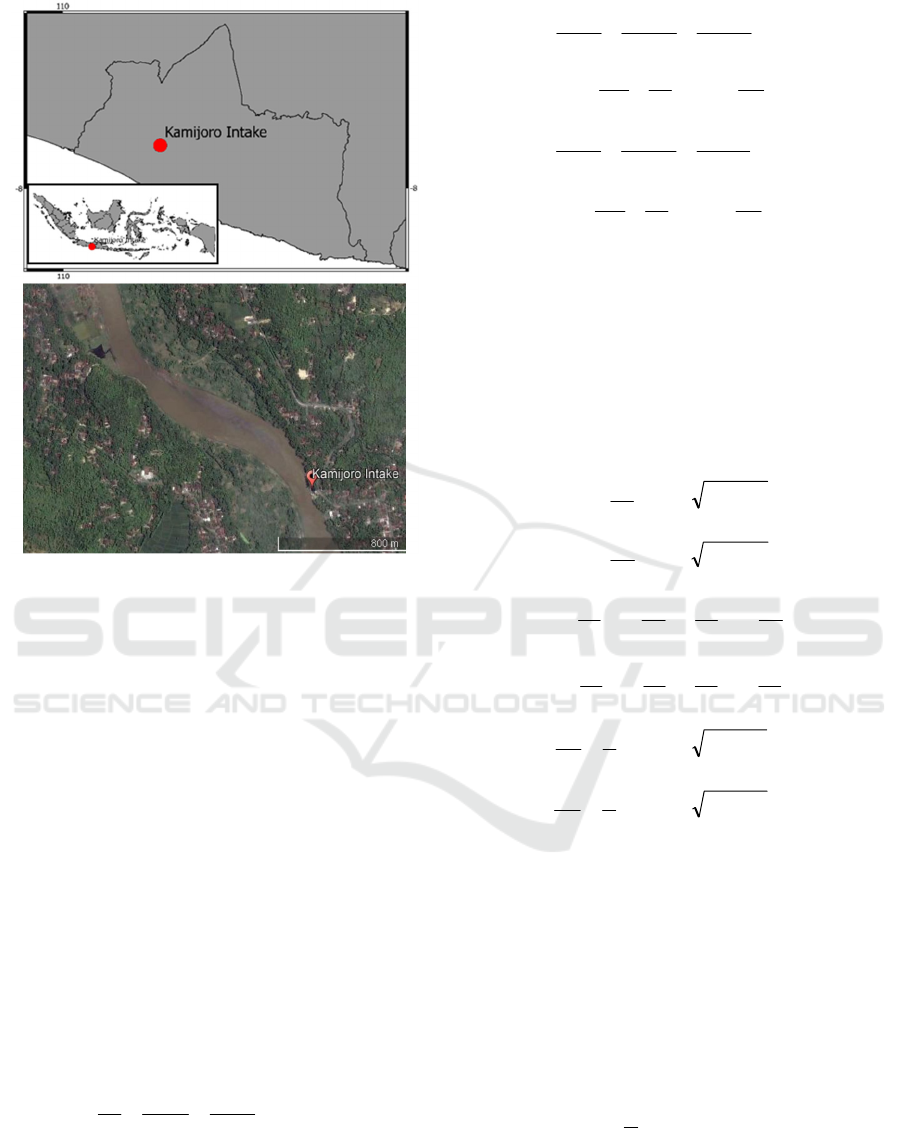
Figure 1: An overview of study area.
2 THEORIETICAL
CONSIDERATION
Nays2DH is mathematic two-dimensional model for
simulation of flow, sediment transport, riverbed
morphology change, and riverbank. The model is
consisted of Nays2D and Morpho2D. The Nays2D is
developed by Dr Yasuyuki Shimizu from Hokkaido
University and Dr. Hiroshi Takebayashi from Kyoto
University Shimizu (2014).
2.1 Basic Equation
Below are continuity equation (1) and momentum
equation ((2) and (3)) used by Nays2DH solver in
orthogonal coordinate. Nays2DH solver uses
following equations in general coordinate in order to
be used in irregular mesh shape.
0
y
hv
x
hu
t
h
(1)
x
x
x
F
D
x
H
gh
y
huv
x
hu
t
uh
2
(2)
y
y
y
F
D
x
H
gh
y
hv
x
huv
t
vh
2
(3)
Where h is water depth, t is time, u is velocity in
x direction, v is velocity in y direction, g is
gravitational acceleration, H is water depth, τ is shear
stress, and F is drag force caused by vegetation.
Moreover, shear stress (τ) calculation involves
riverbed drag coefficient (C
f
) that can be determined
by (4) and (5). Whereas, the diffusion parameter are
calculated as (6) and (7), and drag force influenced by
vegetation equation are shown as (8) and (9).
22
vuuC
f
x
(4)
22
vuuC
f
y
(5)
y
u
hv
yx
u
hv
x
D
tt
x
(6)
y
v
hv
yx
v
hv
x
D
tt
y
(7)
22
2
1
vuuhaC
F
vsD
x
(8)
22
2
1
vuuhaC
F
vsD
y
(9)
2.2 Turbulence Model
Turbulence simulation employs turbulent zero-
equation model shown by (10).
hauv
t *
(10)
Where ν
t
is eddy viscosity coefficient, a is 0,07,
and
*
u
is bed shear velocity. The eddy viscosity can
expressed as (11) below.
eet
BhuA
k
v
*
6
(11)
Where k is von Karman coefficient (0,4), A
e
is
eddy viscosity parameter, and B
e
is eddy viscosity
parameter.
Two Dimensional Sediment Transport Simulation Around Kamijoro Intake, Yogyakarta, Indonesia
591
2.3 River Bed Friction Coefficient
River bed friction coefficient is calculated based on
Manning roughness value. The river bed friction
coefficient can be computed by using (12), whereas
Manning roughness value is expressed by (13).
3
1
2
h
gn
C
m
f
(12)
g
k
n
s
m
66.7
6
1
(13)
Where
C
f
is river bed friction coefficient, g is
gravitational acceleration, and n
m
is Manning
roughness value. Furthermore, the Manning
roughness value is calculated based on Strickler
roughness value.
2.4 Shields Number
Shields number is non dimensional river bed stress
used to determine initial sediment movement. Shield
number is calculated by using (14) and (15) below.
ds
hI
g
e
(14)
3
1
22
2
dhs
Vn
dgs
VC
g
m
g
f
(15)
22
vuV
(16)
Where
σ
*
is Shields number, I
e
is energy slope, s
σ
is specific weight of bed material in fluid,
d is
sediment diameter, V is composite velocity, u is
velocity toward
x direction, v is velocity toward y
direction. The composite velocity is analyzed by
using (16).
2.5 Bed Load Transport
Equation (17) shows Meyer-Peter Muller equation to
calculate bed load transport.
bg
c
b
rgdsq
3
5.1
8
(17)
1
b
r
besd
EE
(18)
be
b
b
E
E
r
besd
EE
(19)
Where
q
b
is bed load transport,
σ
*c
is critical
Shields number,
r
b
is exchange layer thickness,E
sd
is
sediment layer thickness on fixed bed, E
be
is
equilibrium bed load layer thickness, and E
b
is bed
load layer thickness. Exchange layer thickness is
determined by using (18) or (19).
2.6 Velocity near River Bed
Relation of velocity near river bed with respect to
mean velocity is stated by (20) below.
Vu
s
b
~
(20)
3
1
3
(21)
1
3
0
k
(22)
u
V
0
(23)
Where
s
b
u
~
is velocity near river bed,
and
Ø
0
is
velocity coefficient.
3 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
Boundary conditions used to simulate hydraulic
condition around Kamijoro Intake were discharge
record obtained from Sapon AWLR station for
upstream boundary condition (see Figure 2) and water
elevation stage at the downstream of Kamijoro Intake
as downstream boundary condition. The elevation
stages were analyzed by steady state one dimensional
simulation using HEC-RAS.
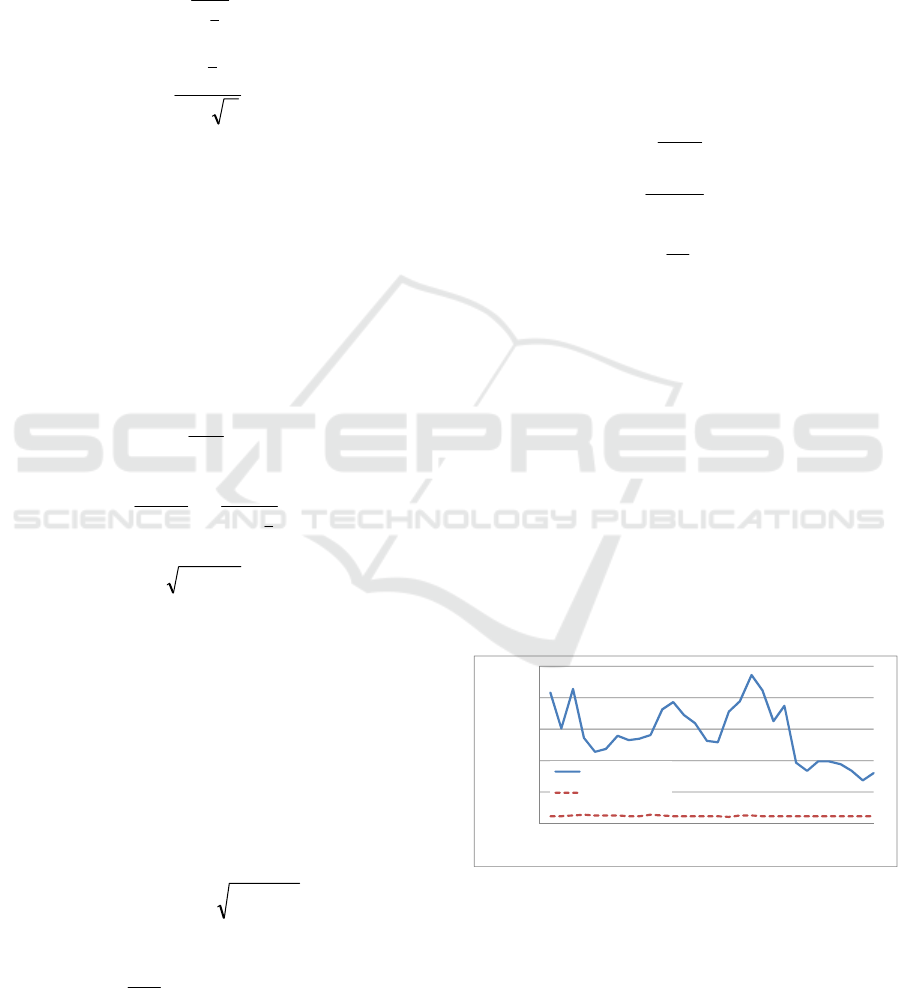
Figure 2 : Discharge data used for simulation.
The mathematical simulation was conducted in
two scenarios. The scenarios were high discharge and
low discharge in order to analyze the difference
hydraulic characteristic between wet season and dry
season respectively. Both scenarios were selected in
order to investigate hydraulic and sediment transport
characteristic near Kamijoro Intake. The hydraulic
0
50
100
150
200
250
0 5 10 15 20 25 30
Discharge (m3/s)
Days
High Discharge
Low Discharge
ICEST 2018 - 3rd International Conference of Computer, Environment, Agriculture, Social Science, Health Science, Engineering and
Technology
592

characteristic around Kamijoro Intake was simulated
in unsteady condition and the simulation length for
each simulation was 30 days.
Figure 3 below is overview of topographic model
used to conduct the simulation hydraulics and
sediment transport behaviour near Kamijoro Intake.
Figure 3: Topographic overview of Kamijoro Intake.
Figure 4 : Grain size distribution.
Figure 4 above shows grain size distribution of
Progo River used for this work. Moreover, sediment
specific gravity is 2.65 and d
50
size is 1.01 mm.
4 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
Simulation result will be discussed to compare
hydraulic and sediment transport condition at peak
discharge and end of simulation for both simulation
scenarios. Result analysis of the end of simulation is
intended to compare hydraulic and sediment transport
characteristic as result of geomorphology
development.
4.1 Velocity
Magnitude and velocity vectors around Kamijoro
Intake can be seen at Simulation results express that
velocity magnitude at around Kamijoro Intake
generated by high discharge is higher than velocity
obtained from low discharge. Moreover, the velocity
vectors show that high velocity vectors occupy area
at the edge of river flow and the velocity flow vectors
direction are downstream direction. Although,
velocity near Kamijoro Intake has high value but the
flow direction does not lead into Kamijoro Intake.
Hence, river water condition inside the intake
structure is calm. Whereas, velocity vectors generated
by low discharge show random direction and occupy
area at the middle of river cross section. High value
of velocity parameter at outer river bend is similar
with the river flow velocity characteristic.
4.2 Water Depth
Simulation results yielded by high discharge show
that river water inundated Kamijoro Intake with
approximately 2 m (see
Figure
7: Shear stress distribution around Kamijoro Intake.
). While in dry season, the water depth is low. Low
water depth on Kamijoro Intake causes the intake
structure cannot operate normally. Furthermore,
water depth will influences shear stress analyses.
Moreover, the bigger water depth will produce higher
hydrodynamic pressure that can seize bed load
sediment.
4.3 Shear Stress
Shear stress distribution around Kamijoro Intake
indicates that high value shear stress only generates
by high discharge. The high value shear stress occupy
area outer river bend. The phenomenon is similar with
river velocity characteristic. In the river bend, the
high flow velocity occupies outer bend area. Other
three simulation results express that shear stress
occurred around Kamijoro Intake is low therefore
there will be sediment deposition around Kamijoro
Intake. Low value of shear stress can be yielded by
small value of river slope.
4.4 Bed Load Flux
Bed load flux distributions show that significant bed
load flux is generated by peak of high discharge
UPSTREAM
DOWNSTREAM
N
↑
Two Dimensional Sediment Transport Simulation Around Kamijoro Intake, Yogyakarta, Indonesia
593
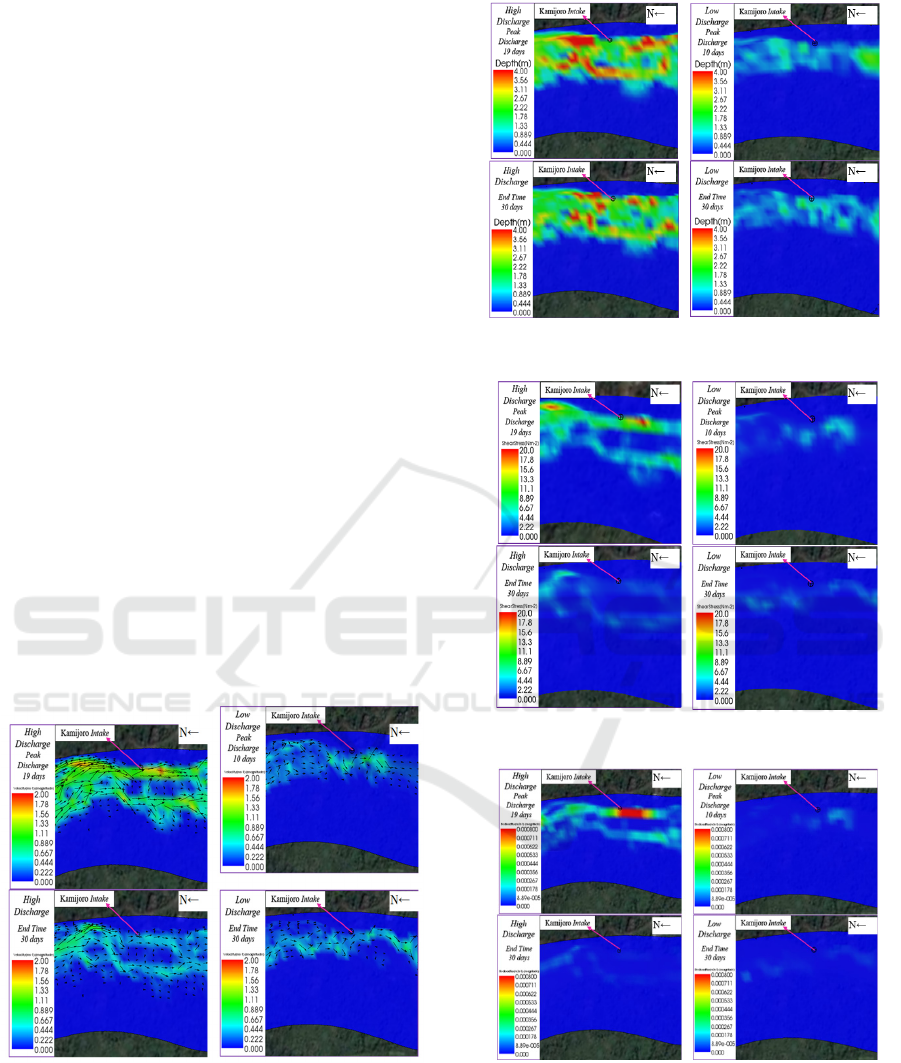
scenario. The highest bed load flux occupies edge
area of river cross section. The significant bed load
flux location is similar with finding showed by shear
stress parameter, and flow velocity result. All of the
simulation result distributions show occurrence of
high value of each parameter at the outer of river
reach.
4.5 Bed Elevation Change
Elevation change parameter reveals two possibilities.
Positive value means sediment deposition, while
negative value means sediment aggradations.
High discharge scenario generates more positive
elevation change rather than negative elevation
change. It means that sediment deposition will
occupy in most area than sediment aggradations. The
high positive bed elevation change is distributed at
the centre of river reach. While at the edge of river
reach is occupied by low bed elevation change.
4.6 Bed Elevation Development
This work indicates that there is sediment deposition
on both scenarios particulary at the area near with
Kamijoro Intake. The sediment deposition around
intake structure causes river water unable to flow into
Kamijoro Intake. The simulation results also
represent that high discharge scenario generates
higher river bed levation than low discharge scenario.
Figure 5: Velocity magnitude and velocity Vector around
Kamijoro Intake.
Figure 6: Water depth distribution around Kamijoro Intake.
Figure 7: Shear stress distribution around Kamijoro Intake.
Figure 8: Bed load flux distribution around Kamijoro
Intake.
ICEST 2018 - 3rd International Conference of Computer, Environment, Agriculture, Social Science, Health Science, Engineering and
Technology
594

Figure 9: Bed elevation change distribution around
Kamijoro Intake.
Figure 10: Bed elevation development distribution around
Kamijoro Intake.
5 CONCLUSION
This work shows that sediment deposition near
Kamijoro Intake is influenced mostly by small value
of river slope. Either flow velocity and water depth
cannot produce enough shear stress to entrain bed
load at location near Kamijoro Intake. Based on
elevation change distribution produced by high
discharge scenario, Kamijoro Intake will be
surrounded by high sediment deposition. Thus, river
water cannot flow into Kamijoro Intake.
REFERENCES
Ali, M.S., Hasan, M.M., Haque, M., 2017. Two-
Dimensional Simulation of Flows in an Open Channel
with Groin-Like Structures by iRIC
Nays2DH.Mathematical Problems in Engineering,
Kinzel, P.J., Logan, B.L., and Nelson, J.M., 2015. Effects
of Upstream Sediment Supply and Flow Rate on The
Initiation and Topographic Evolution of Sandbars in
Laboratory and Numerical Channels. Proceedings of
the Joint 10th Federal Interagency Sedimentation
Conference and 5th Federal Interagency Hydrologic
Modeling Conference.
Muhammad, S. H., 2017. Application of Numerical
Modeling to Study River Dynamics: Hydro-
Geomorphological Evolution Due to Extreme Events in
the Sandy River, Oregon. Dissertations and Theses
Portland State University
Nelson, J.M., Shimizu, Y., Abe, T., Asahi, K., Gamou, M.,
Inoue, T., Iwasaki, T., Kakinuma, T., Kawamura, S.,
Kimura, I., Kyua, T., McDonald, R.R., Nabi, M.,
Nakatsugawa, M., Simões, F.R., Takebayashi, H., &
Watanabe, Y. 2015. The International River Interface
Cooperative: Public Domain Flow and
Morphodynamics Software For Education and
Applications. Advances in Water Resources.
Norman, L. M., Sankey, J. B., Dean, D. J., Caster, J.,
DeLong, S. B., DeLong, W. M., & Pelletier, J., 2017.
Quantifying Geomorphic Change at Ephemeral Stream
Restoration Sites Using a Coupled-model Approach.
Geomorphology
Shimizu, Y., H. Takebayashi, T. Inoue, M. Hamaki, T.
Iwasaki, and N. Mohamed., 2014. Nays2DH Solver
Manual, International River Interface Cooperation
Wickham, R.S., 2015. The Effects of Grain Size
Heterogeneity on Sediment Transport Modelling.
Dissertations and Theses Washington State University
Wongsa, S., 2016. Physical and Numerical Modelling of
Overtopping Erosion and Earthen Embankment
Breach. International Journal of Advances in
Mechanical and Civil Engineering.
Two Dimensional Sediment Transport Simulation Around Kamijoro Intake, Yogyakarta, Indonesia
595
