
The Rapid Extraction of Suspicious Traffic from Passive DNS
Wenbo Wang
1
, Tianning Zang
2
and Yuqing Lan
1
1
School of Computer Science and Engineering, Beihang University, China
2
National Internet Emergency Center, China
Keywords: DNS, Amplification Attack, Random Subdomain Attack, Domain Generation Algorithm, Malicious Domain
Name.
Abstract: The network traffic is filled with numerous malicious requests, most of which is generated by amplified at-
tacks, random subdomain name attacks and botnets. Through using DNS traffic for malicious behavior anal-
ysis, we often need to test each domain alone. Besides, the amount of data is very large and simple filtering
cannot quickly reduce the need to detect the number of domain names. As a result, it takes a lot of time to
calculate on the premise of limited resources. Therefore, this paper introduces a extraction scheme for DNS
traffic. We designed a simple and efficient method for extracting three kinds of attack traffic with the largest
proportion of traffic. Besides, the method of statistics and classification was used to deal with all the traffic.
We implemented a prototype system and evaluated it on real-world DNS traffic. In the meanwhile, as the
recall rate reached almost 100%, the number of secondary domain names to be detected was reduced to 8%
of the original quantity, and the DNS record to be detected was reduced to 1% of the original number.
1 INTRODUCTION
As a logical address to define a device in the network
location, IP address is provided by the IP protocol
digital unified address identification, With the grad-
ual increase in network equipment, memory difficul-
ties of IP address emerged. In 1983, Paul Mockapetris
proposed the architecture of DNS and proposed to im-
prove it into a distributed and dynamic database do-
main name system, which refers to the prototype of
the domain name system used today. As a tool, do-
main name brings us convenience, which simultane-
ously leads to corresponding security issues.
For these malicious behavior, there are blacklists
and the corresponding reputation systems such as
DGArchive (Plohmann et al., 2016), Notos (Antona-
kakis et al., 2010), DSBL (Serdar Argic, 2009). There
are some detection systems like Pleiades (Antona-ka-
kis et al, 2012), EXPOSURE (Bilge et al, 2011),
FluxBuster (Perdisci et al, 2012). Besides, there are
some systems using depth learning model to solve the
problem like LSTM (Woodbridge and Anderson,
2016), word2vec (Goldberg and Levy, 2014). When
dealing with passive DNS data from Shangxi and
Guangdong Telecom, the amount of data is too large
to easily complete processing of all data. If only the
white list is used to filter data, it leads to ignoring at-
tacks by benign domains or attacks against benign do-
mains. We hope to build an efficient model for mali-
cious traffic extraction by simplifying or referring to
these detection methods.
In this paper, we propose a malicious traffic loca-
tion model. Using some statistical characteristics and
pre-trained model, we can quickly locate suspicious
malicious traffic. This model is deployed in the local
server or recursive network edge node, and monitor
DNS request and response of the network, which can
analyze the data at regular intervals, and quickly lo-
cate the traffic containing malicious domain names
for further analysis and detection. According to the
report (Orthbandt, 2015), in the malicious traffic sta-
tistics, random subdomain names accounted for 80%,
amplification attacks accounted for 15% and C&C
traffic occupied 5%. Besides, our model will also ad-
dress these areas. Our model to locate malicious traf-
fic from massive data has a high recall rate. At the
same time, it can greatly reduce the detection of ma-
licious domain time spending. Because many inter-
ferences are removed, the effect of detection is greatly
improved. The experiments are carried out at differ-
ent time in Shanxi and Guangdong provinces, proving
that the model has good adaptability.
190
Wang, W., Zang, T. and Lan, Y.
The Rapid Extraction of Suspicious Traffic from Passive DNS.
DOI: 10.5220/0006543401900198
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy (ICISSP 2018), pages 190-198
ISBN: 978-989-758-282-0
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

This paper makes the following contributions:
▪ we propose a lightweight model for malicious
traffic extraction, which can effectively locate
malicious traffic in large-scale ISP (Internet
Service Provider) networks and rapidly reduce
the magnitude of further traffic detection;
▪ we provide the prototype implementation of the
model, and experiment in the network environ-
ment of different periods in the two provinces.
The result has excellent recall rate, reduced
traffic scale, and has high applicability;
The remainder of the paper is organized as fol-
lows. Section 2 introduces some background on DNS
and related works. We provide an overview of our
system in Section 3. Each part process is described in
Section 4. The experimental results are presented in
Section 5 and we discuss the limitations of our sys-
tems in Section 6. Section 7is the conclusion of the
paper in.
2 BACKGROUND AND RELATED
WORK
2.1 DNS Amplification Attack
DNS amplification attack uses the DNS server as a
springboard to amplify traffic. In the case of a normal
DNS query, the source IP address sends a DNS query
to the DNS server, and the source IP address is re-
turned. In addition, the attacker will attack the target
IP address forged as the source IP address and the
query results will return to the forged IP address. Usu-
ally, a DNS query packet size is about 60 bytes. If you
initiate a DNS query with a request type of ANY, it
indicates a request for all DNS resource records (in-
cluding A record, MX record, CNAME record, PTR
record, etc.). Then, the returned packets typically
reach hundreds of bytes to thousands of bytes. Aka-
mai researchers found a DNS amplification attack us-
ing TXT records in 2014 (Kovacs, 2014). An attacker
uses a tool named DNS Flooder to obtain a TXT rec-
ord by querying guessinfosys.com with an attack
peak of 4.3Gbps.
Tama et al used the method of anomaly detection
to model the network data stream according to the
header attribute, and adopted the naive Bayesian al-
gorithm to score each incoming data stream to evalu-
ate the rationality of the message (Tama and Rhee,
2015). Karnwal et al transformed the one-dimen-
sional timing into multidimensional AR model pa-
rameters through dimension transformation, and used
the support vector machine algorithm to study and
classify the data stream (Karnwal et al., 2013). Wang
et al have considered the use of anomaly detection
methods, who also use hidden Markov model to de-
scribe the change of data header in data stream (Wang
et al., 2015).
2.2 Random Subdomain Attack
Domains generated by random subdomain attack
(also known as Random subdomain DDoS or the
Random QNAME attack or the Nonsense Name at-
tack) (Liu, 2015) having the same SLD (second-level
domain name) or third-level domain name have nu-
merous different random subdomain names, and these
SLD is usually legal. This attack is a DDoS attack
against the domain name server, or even against the
root domain name server (VeriSign, 2015).
An attacker uses infected network devices to con-
struct DNS queries for a random subdomain based on
a legal SLD. These queries first arrive at the recursive
DNS server. Since the server does not have the corre-
sponding cache, these queries are propagated to the
top-level domain name server and the domain author-
itative server. These processes consume query re-
sources rather than bandwidth, yet will obviously
slow down or even prevent the domain name of the
normal query and cause over-loading of the server
(Rizzo et al., 2016).
There is no sophisticated and mature real-time de-
tection method for random subdomain attacks yet.
For example, the solution given by secure64 is to in-
crease memory, increase recursive complexity, and
automatically block IP with too many failed requests
(Andrew, 2015).
2.3 Botnet based on DGA
DGA (Domain generation algorithms) uses algo-
rithms to pseudo-randomly generate domain names.
These domain names are used to establish the connec-
tion between the infected host and the C&C servers
(command and control servers). The traditional botnet
uses a fixed IP or domain name to establish a connec-
tion with the C&C servers, which is poorly concealed
and easily found.Afterwards, there are P2P-based
botnets such as Nugache (Stover et al., 2007), Storm
(Wikipedia, 2010), Waledac (Williams, 2010), Zeus
(abuse.ch, 2011), etc. with good robustness and sta-
bility but also high difficulty of implementation and
maintenance costs. At present, most of the active bot-
nets use DGA, relying on the concentration of C&C
server. Compared with the first two, it is simpler
while considering the advantages of stability and con-
cealment.
The Rapid Extraction of Suspicious Traffic from Passive DNS
191

The detection of DGA algorithm mainly includes
black list, machine learning method and reverse engi-
neering. L.Bilge (Bilge et al, 2011) extracted a total
of 15 features from the DNS data based on time, DNS
response, TTL (Time to Live), domain name charac-
ters. The J48 decision tree is used to train the classi-
fier and make up for the inability to detect a malicious
domain name that has been used only once by an IP
address with the perfect feature selection. Besides,
they also set up the EXPOSURE system to conduct
extensive detection of malicious domain names. B.
Rahbarinia proposed a behaviour based system
named Segugio (Rahbarinia, 2016). Segugio effi-
ciently discovers the newly added malware-control
domain name by tracking DNS requests that are in-
fected by host malware in a large ISP network. Notos
(Antonakakis et al., 2010) and EXPOSURE establish
domain-IP mapping relationship model (using the
characteristics of the domain name string, the domain
name carries malicious content and other infor-
mation) without using the local DNS server down-
stream host request behaviours. Compared to these
two, Segugio monitors DNS user requests for DNS
requests, focusing on the precise "malware-only" do-
main name. J. Woodbridge (Woodbridge and Ander-
son, 2016) and other researchers use LSTM to predict
DGA-generated domain names that can be run in real
time and do not require artificially created features.
D. Plohmann, F. Fkie and others have conducted a lot
of detailed work on the DGA (Plohmann et al., 2016).
They conducted a comprehensive study of 43 DGA
malware families and variants, presented a taxonomy
for DGA, and used this to classify and compare the
studied DGA.
In general, the above-mentioned detection meth-
ods use the Alexa top domain name as a whitelist for
initial filtering, but the number of filtered domain
names is quite limited.
2.4 Related Work
The biggest difference between our work and the de-
tection model for traffic refers to that we do not focus
on false positives. We want to get the highest possible
recall rate, extraction rate and extraction efficiency.
Regarding the work of amplification attacks, the
most significant point is that we only need to use pas-
sive DNS rather than complete package. At first, we
attempted using logistic regression, hoping to achieve
binary classification with a small number of attrib-
utes. We try to modify the manual annotation to im-
prove the recall rate, but even if this is done, the dif-
ference between the number of positive cases and the
number of negative cases is still very large. As a re-
sult, we cannot get stable corresponding to the corre-
sponding weight of the various features. We consider
using more practical statistical methods and observa-
tion experience in the classification. Besides, we are
concerned about the proportion of TXT queries and
ANY queries. To save the additional text information
of the domain name TXT records are used and the
content is written in a certain format, like the SPF for-
mat. Additionally, this format is used to register a do-
main name for outgoing mail all the IP address. When
an attacker uses an TXT record to amplify an attack,
it uses the pre-registered domain name and sets the txt
record content of the domain name as long as possible
to increase the magnification. Any query will query
all the records of the domain name, so the attacker
chooses to use ANY query. Therefore, they can easily
get a lot of magnification. The only concern about the
proportion of TXT query and ANY query is to mini-
mize the extraction time, in the process of doing tra-
versal can record each domain name TXT query,
ANY query number, and the number of all inquiries.
The extraction of random sub domain attack traf-
fic has similarities with above method. We mainly fo-
cus on the number of sub domain names and domain
name query success rate. In the process of extracting,
the reverse domain name parsing record (suffix is
‘.in-addr.arpa’) and some misconfigured domain
names (suffix is usually '.localhost' or '.local') are
cleaned first, which will generate a large number of
subdomains and unresolvable records.
For the extraction of DGA domain, effect of only
using the blacklist filtering is poor. Simple use of sta-
tistical data for fitting leads to very low extraction
rates due to the diversity and complexity of the DGA
species. It takes too much time to build complex mod-
els and detection methods, so we choose to use black
and white list training model as well as select only the
domain name character.
3 SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
Our system aims to extract DNS traffic from amplifi-
cation attacks, random subdomain attacks and DGA.
Given a continuous flow of time, or even only one
hour of traffic data, we can initially determine the ma-
licious part. Intuitively, we can divide a batch of DNS
data into two parts, some of which only contain legit-
imate access, and the other part contains all the mali-
cious traffic. Our data source is passive DNS data in-
cluding the recursive domain name server response
history information. We collected recursive DNS
ICISSP 2018 - 4th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy
192
server data from Shanxi and Guangdong, with an av-
erage of 80 million data per hour in Shanxi and an
average of one hundred and seventy million data per
hour in Guangdong. During the process of extracting
DGA domain name traffic, we collected a blacklist
with a whitelist, where the blacklist came from the
360 netlab while the whitelist used alexa top 1 mil-
lion.
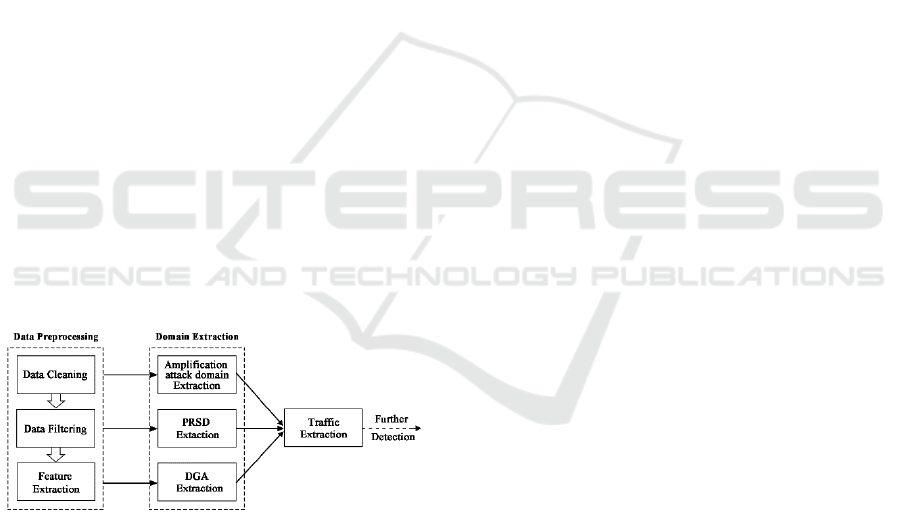
3.1 System Overview
In this section, we conduct a high-level overview of
our system. According to Figure 1, we divide the sys-
tem into two parts, respectively, the Passive DNS pre-
processing module and the traffic extraction module.
Besides, we will describe each module function and
discuss how to achieve the goal together as well as
maximize the recall rate and efficiency.
The process of pre-processing mainly achieves
three goals. One is to remove the DNS records con-
taining the wrong domain name, that is, to clean data.
For example, there are some illegal characters like ‘!’
and ‘_’ appeared in domain names. The second is to
eliminate unrelated traffic, which will not appear in
malicious traffic \, such as traffic of reverse DNS. On
the other, we will try to remove domain names that do
not appear in malicious traffic during a certain type of
traffic extraction process. For example, the domain
name in the whitelist can be removed during the ex-
traction of DGA traffic. The third is to calculate the
eigenvalues for the traffic extraction module, such as
the proportion of ANY queries for each domain name.
Figure 1: System Overview.
3.2 Statistical Features
This section will define key statistical features and in-
troduce the calculation method. We calculate nine
features for each domain name, namely, bigram, tri-
gram, fourgram, entropy, length, Qar (query ANY
record ratio), Qtr (query TXT record ratio), sdc (sub-
domain count), and nxdr (non-exist subdomain ratio).
3.2.1 Definitions and Notation
A domain name is consisted of two or more groups of
ASCII or language characters, each of which is sepa-
rated by ‘.’. The rightmost part is called a TLD (top-
level domain name). SLD (Second-level domain) re-
fers to the domain name under the top-level domain
name, which is registered by the domain name regis-
trant. Third-level domain name under the SLD, can
be called sub-domain name.
3.2.2 N-gram Features
SLDs are taken out of the domain name in the white-
list. Each of the SLDs is added with '^' at the begin-
ning and ended with the '$'. For example, there is a
domain, ‘www.buaa.edu.cn’ with SLD of ‘buaa’ and
becomes ‘^buaa&’. These SLDs are used as training
corpus to measure the N-gram frequency distribution,
where n = 2, 3, 4. Besides, given a domain name, we
can use their SLD respectively to obtain the corre-
sponding Bigram, Trigram and Fourgram features.
3.2.3 Entropy Features
Considering a domain name, we extract the SLD and
calculate its entropy according to equation 1, where
p(c) is the probability of occurrence of each character
in the SLD. Entropy can show the randomness of a
domain name.
(1)
3.2.4 Ratio-related Features
Some ratio-related features can be calculated through
the DNS record. These features are expressed by pro-
portion rather than absolute number, such as the pro-
portion of ANY type queries to the total number of
queries.
3.3 Data Preprocessing
The preprocessing module performs three layers of
raw data collected, respectively, data cleaning, data
filtering and feature extraction.
3.3.1 Data Cleaning
First, all the data is to be cleaned. A valid domain
name contains only 26 alphanumeric characters (in-
cluding uppercase and lowercase), numbers, dashes,
and points used to split each segment. It is easy to
clean up these data by building regular expressions.
Another part is domain names without TLD. There
The Rapid Extraction of Suspicious Traffic from Passive DNS
193

are many reasons for this situation, such as configu-
ration and human reasons.
3.3.2 Data Filtering
Secondly, the data filtering operation is carried out.
The first part is to filter the reverse domain name. In-
verse address resolution refers to the mapping from
IP address to domain name, which is mainly applied
by mail servers to prevent spam. The return packet is
small and is not suitable for use as a zoom attack.
Therefore, there is no behavior in the malicious traffic
that uses the reverse parsing record to attack. The sec-
ond part is to filter the domain name generated by the
configuration errors, which is quite common. Among
them, "local" and "localhost" as the suffix domain
name appears most. The third part is to filter IDNs
(Internationalized Domain Names). IDNs are a gen-
eral term for non-English-speaking countries to pro-
mote their own language domain name systems with
punycode encoding.
3.3.3 Feature Extraction
Another major function of the module is to convert
DNS records into corresponding feature vectors. DNS
records is divided by each hour to form a DNS re-
source records sequence, S = {rr
1
, rr
2
, ..., rr
m
}, where
each resource record contains the domain name,
source IP, request type, return type, rcode, timestamp,
and so on. Each of the SLDs under the TLD is an in-
dependent branch, which is managed by a different
domain name registrant. Therefore, our statistical fea-
tures are for the SLD. We count the number of queries
group by each SLD within a period as qc: the number
of queries which type is ANY as qac and the number
of queries which type is TXT as qtc. We set any query
ratio qar = qac / qc, txt record query ratio qtr = qtc /
qc. According to rcode to determine whether the do-
main name can be successfully resolved, we calculate
the proportion of non-existent domain name nxdr. We
count the number of sub-domain names for each SLD
in the time interval, named sdc. In this paper, we
choose the interval as one hour, which will be dis-
cussed in Section 4.2. Then, we calculate the entropy,
bigram, trigram, fourgram, length, and label whether
it is in alexatop 100 million white list based on these
SLD.
Eventually, we get each record for SLD, qar, qtr,
nxdr, sdc, entropy, bigram, trigram, fourgram, length,
and inwhite.
3.4 The Extraction of Domain Names
This module is to take advantage of the SLD and its
features, and extract the domain name which involves
malicious behaviours. The extraction process aims at
three types of attacks, namely, amplification attacks,
random subdomain attacks, and DGA domains.
3.4.1 Domains of Amplification Attack
This part is mainly to find the part of the domain that
acts as a springboard in the amplification attack. The
attacker uses these domains by using their TXT rec-
ords or ANY queries to return all the resource records
of the domain name. We use the qar and qtr obtained
in section 3.3. By formula 2, we set a parameter β.
When qar+qtr<=β, the result is 0. When qar+qtr>β,
the sum of qar and qtr was positively correlated with
S
1
. At the same time, we set threshold α, in which
S
1
>α, and identified as the suspected amplification at-
tack of traffic. Here the value of α is 0.1 and the value
of β is 0.05. The threshold value will be carefully dis-
cussed in the next chapter.
(2)
3.4.2 Domains of Random Subdomain Attack
This part aims to locate the domain name used by ran-
dom subdomain attacks. The attackers generate nu-
merous sub domains randomly under the SLD, and
these domain names do not exist. Therefore, we mul-
tiply sdc with nxdr to represent the possibility of ma-
licious use, and this value range is large. We use for-
mula 3 to change the result to between 0 and 1. Here,
we choose θ as 0.3.
3.4.3 Algorithmically-Generated Domains
ADGs (YADAV et al., 2010) means the domain name
generated by the DGA algorithm. The domain name
generated by DGA is second-level domain, so this
part of the extration is concerned with the SLD in the
traffic. Our model is trained with black and white
lists, and data sources are presented in section 4.1. We
extracted the SLD of each domain name in the list,
and calculated their length, entropy and n-gram re-
spectively, where n=2,3,4. We chose Random Forests
as classifiers. When each tree is trained, a data set of
the same size as N can be trained (bootstrap sampling)
(3)
ICISSP 2018 - 4th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy
194
from a full training sample (sample number N). Ran-
dom Forests are trained at a faster rate, which can bal-
ance errors.
We get the domain name from the previous mod-
ule. For each SLD, we first remove it if it is in the
white list, and then classify the remaining domains
into categories in turn to obtain the suspected ADGs.
3.5 The Extraction of Domain Names
Further detection often requires complete DNS re-
source record. Therefore, after obtaining the domain
name through Section 3.4, the module will restore this
set of secondary domain names to the corresponding
traffic, that is, the original DNS resource record. The
operation is very simple. This batch of secondary do-
main name after cleaning is listed. Then, the records
are retained which have the same SLDs.
4 EVALUATION
In this section, we report the results of the evaluation
of the entire system. First, we introduce the data we
use, and then discuss the parameters in section 4.2.
Finally, the results of traffic extraction are demon-
strated.
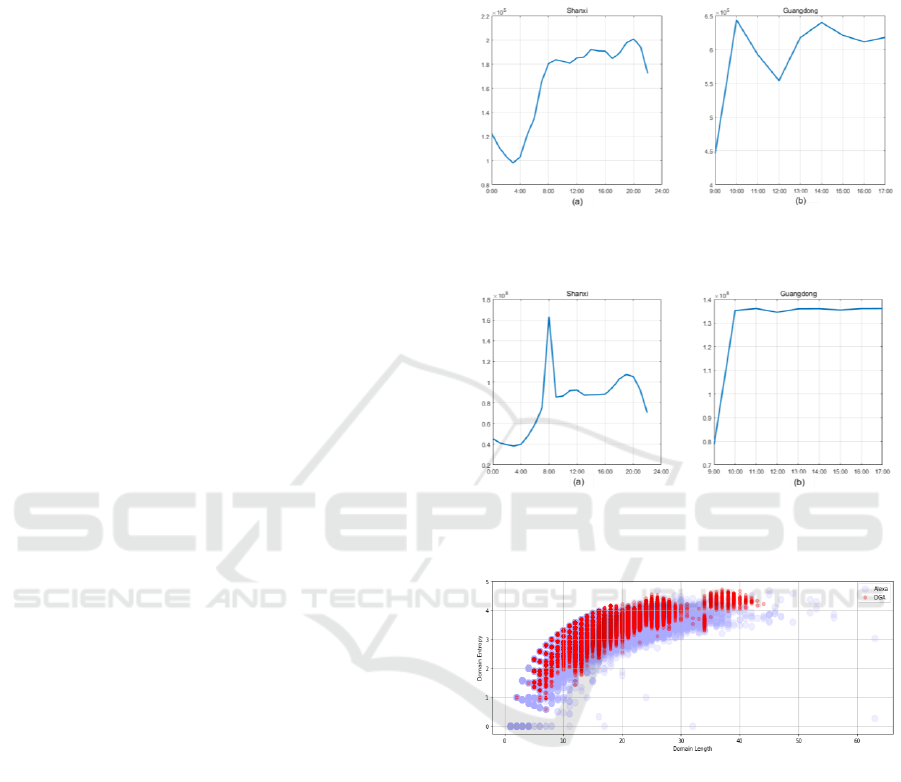
4.1 Datasets
Our data comes from CNCERT / CC including
Shanxi Telecom China Passive DNS data and Guang-
dong Telecom Passive DNS data. The data from
Shanxi Province is collected on October 15, 2015,
which contains 23 hours. According to figure 3(a), the
total amount of DNS records close to 2 billion. The
number of domain names that are not duplicated per
hour is between 100 thousand and 200 thousand. We
labelled 101 DDOS related malicious domain names
and 322 DGA related domain names. The data from
Guangdong province is collected on April 14, 2017,
which contains 9 o'clock to 16 o'clock a total of 9
hours of data. As shown in Figure 3(b), the total num-
ber of DNS records is more than 1.1 billion, and the
number of distinct secondary domain names per hour
is about 600,000. We labeled 163 DDOS related ma-
licious domain names and 265 DGA related domain
names.
In the extraction of DGA traffic, we use the alex-
atop100 million domain name list as a whitelist. Be-
sides, we downloaded the DGA blacklist from the 360
netlab as a blacklist containing 1037304 second level
domain names. Figure 4 presents the relationship be-
tween the length and the entropy of the secondary do-
main name from the blacklist and whitelist. When
consistent in length, the domain of DGA is often as-
sociated with a greater entropy value.
Figure 2: Number of distinct SLDs in Shanxi and Guang-
dong.
Figure 3: Number of DNS records in Shanxi and Guang-
dong.
Figure 4: The entropy changes with the length of the do-
main name.
4.2 Parameter Analysis
We first discuss the parameters appearing in the 3.4.1
section, where three parameters are involved, namely,
the time interval and the threshold value α to judge
whether the domain name is suspicious, and the pa-
rameter β in formula 2. The values of time interval are
10 minutes, 30 minutes, 60 minutes and 120 minutes,
and the values of alpha are 0, 0.05, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.5
and 0.6. Besides, the values of beta are 0.07, 0.1, 0.15
and 0.2. Figure 5 shows that the Z axis represents the
recall rate. When the time interval is 10 minutes, the
recall rate is always above 0.98. Additionally, the
maximum recall rate was 0.94 when the time interval
The Rapid Extraction of Suspicious Traffic from Passive DNS
195
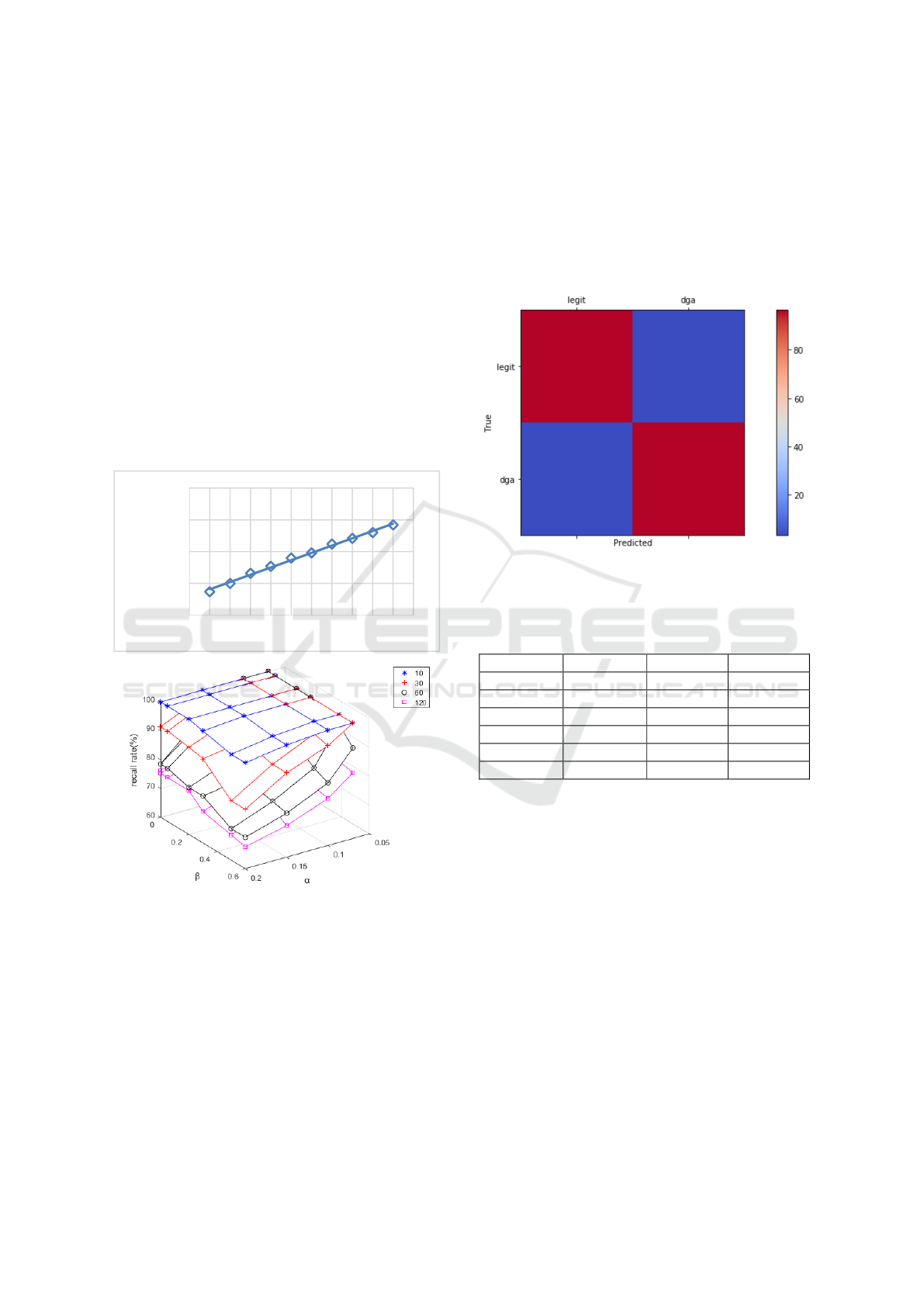
was 120. The two cases cannot be satisfied with the
values of α and β. Table 1 shows the relationship be-
tween the value of the different parameters and the
number of suspicious domains. Obviously, the time
interval selected as 30 minutes or 60 minutes can
achieve the effect of little difference. But the number
of executions of the former is twice that of the latter,
so we set the time interval to 60 minutes. To obtain as
few domain names as possible, we set α to 0.1 and β
to 0.05.
Another parameter that needs to be discussed is θ
in Equation 3 in Section 3.4.2. The smaller the value
of θ, the smoother the curve of this function. As
shown in Figure 6, the relation between the value of
θand the number of domains extracted is described.
When θwas 0.1, the recall rate was 50%. When θis
greater than 0.2, the recall rate is 100%.
Figure 5: The effect of different α, β, and time intervals on
the recall rate.
Figure 6: The relation between θ and the number of domain
names in domain names extraction of PRSD.
We discuss our choice of features in the pro-
cessing of the DGA domain name. On the one hand,
we cannot select too many features to ensure that the
training time and classification time of the model can-
not be too long. On the other, we cannot choose too
few characteristics, otherwise it is difficult to achieve
satisfactory recall rate. Finally, we select the SLD’s
length, entropy, and bigram, trigram, fourgram, these
five characteristics. In addition, we use random for-
ests as classifiers. As shown in Figure 7, we observe
the result through confusion matrices, with a recall
rate of more than 96%. Besides, we carried out ten-
fold cross validation, recall rates are above 85%, the
highest can reach more than 98%.
Figure 7: The effect of different α, β, and time intervals on
the recall rate.
Table 1: When the recall rate is 100%, the relationship be-
tween α, β and the number of suspected domain names.
α
β
30 mins
60 mins
0.07
0.05
784
764
0.07
0.1
779
758
0.07
0.2
768
749
0.07
0.3
762
738
0.1
0
751
731
0.1
0.05
750
730
4.3 The Effect of the Model
In Section 4.2, we use the data from Shanxi Province
to experiment with the relevant parameters, and the
results shown in Figure 8. In addition, we have also
experimented with the data in Guangdong using the
same parameters, which can be found in Figure 9. Be-
sides, Figure 8 (a) shows the trend of the number of
domain names involved in subdomain attacks and
amplification attacks. The peak value is about twice
that of the valley value. From Figure 8 (b), the change
trend is not the same as the change of the number of
domain names. The peak value is about 7 times that
of the valley, which is more likely to reflect an attack
of amplification attacks and random subdomain at-
tacks. Figure 8 (c) shows the trend of the number of
DGA domain extraction. Since we only judge by the
character of the domain name, the extracted domain
0
50
100
150
200
0 0,1 0,2 0,3 0,4 0,5 0,6 0,7 0,8 0,9 1 1,1
Domain Count
ICISSP 2018 - 4th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy
196
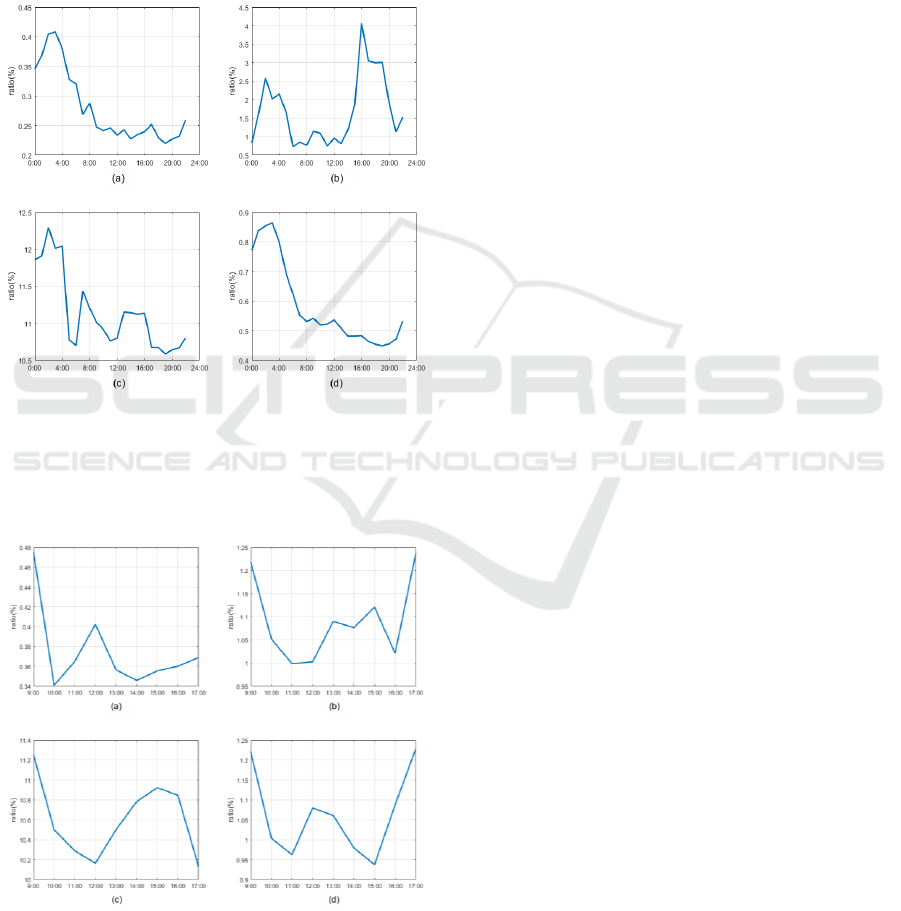
name contains numerous legitimate domain names.
Therefore, the number of DNS records does not really
reflect the size of the actual attack traffic. Moreover,
the recall rate of our DGA domain is 92% here.
In using the results of the experiment on the data
in Guangdong, the recall rate of the amplified attack
and the random subdomain attack was also 100%, but
the recall rate to the DGA was close to 90%. Regard-
ing how to further raise the recall rate, we have put
forward some ideas and discussed in Chapter 5.
Figure 8: The results of experiments using 23 hours of data
from Shanxi Province. (a) (b) are the ratio of number of
SLDs and DNS records extracted from PRSD and zoom at-
tacks in an interval. (c) (d) are the ratio of number of SLDs
and DNS records extracted from DGA in an interval.
Figure 9: The results of experiments using 23 hours of data
from Guangdong Province.
5 LIMITATION AND
DISCUSSION
In this paper, we build a malicious traffic extraction
system. It can quickly extract the DNS resource rec-
ords of zoom attacks, random subdomain attacks and
DGAs from passive DNS data, rather than just
through blacklist or more simple way to filter. Be-
sides, it can greatly reduce the amount of DNS data
that is further detected.
In addition, our system also has some limitations.
For example, due to the lack of continuous long-term
data sources, and the lack of sufficient historical data
support, we believe that the construction of data ware-
house by using some statistical characteristics of the
historical data, to determine whether the domain
name can be clearer. For example, the survival time
of DGA domains is usually well below 30 days, and
we can build corresponding features to record the
number of times over the past few days. Through us-
ing this feature, we can significantly identify domain
names. The same reason also caused us being unable
to explore the timeliness of the model, which also
cannot determine how long the parameters are valid.
However, we provide methods for exploring parame-
ters in this paper.
For the extraction of DGA traffic, the recall rate
has not reached 100%. Besides, we also have some
ideas on how to improve recall rates. Besides adding
feature mentioned in the previous paragraph, the
DGA is also divided into several categories. We need
to distinguish whether the DGA is generated using the
dictionary or hash, or according to the time pseudo-
randomly generated. Meanwhile, we also need to con-
sider the balance time and recall rate, and the closer it
is to a complete detection model, the more time it
takes, which is what we need to focus on.
In the extraction of DDOS traffic, our method can
only select the secondary domain names of the web-
site. When it is related to some of the higher traffic
flow of the site, we cannot distinguish between the
legitimate traffic and malicious traffic on the same
website when we change the domain name into the
actual traffic, which may reduce the efficiency of do-
main name extraction.
6 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, we propose a malicious traffic extrac-
tion model system. The system refers to the relevant
detection system, selects features, and preliminarily
filters the domain names and traffic related to some
The Rapid Extraction of Suspicious Traffic from Passive DNS
197

attacks. Compared with the simple pre-processing
process, the system can select the malicious traffic to
a smaller range, while ensuring the recall rate. How-
ever, it is also very fast to achieve their goals, which
is to narrow the range for further detection. Our eval-
uation uses real data from passive DNS data of pro-
vincial telecommunication at different times. Ampli-
fication attacks and random sub-domain name attacks
involved in the domain name recall rate reached
100%, DGA domain name recall rate of 90% or more.
REFERENCES
Antonakakis, M., Perdisci, R., Dagon, D., Lee, W., and
Feamster, N. (2010). Building a dynamic reputation
system for dns. InUsenix Security Symposium, Wash-
ington, Dc, Usa, August 11-13, 2010, Proceed-
ings,pages 273–290.
Antonakakis, M., Perdisci, R., Nadji, Y., Vasiloglou, N.,
Abu-Nimeh, S., Lee, W., and Dagon, D. (2012). From
throw-away traffic to bots: Detecting the rise of dga-
based malware. In Presented as part of the 21
st
USENIX
Security Symposium (USENIX Security 12), pages 491–
506, Bellevue, WA. USENIX.
Bilge, L., Kirda, E., Kruegel, C., and Balduzzi, M. (2011).
Exposure: Finding malicious domains using passive
dns analysis. InNetwork and Distributed System Secu-
rity Symposium, NDSS 2011, San Diego, California,
Usa, February - February.
Plohmann, D., Yakdan, K., Klatt, M., Bader, J., and Ger-
hards-Padilla, E. (2016). A comprehensive measure-
ment study of domain generating malware. In 25th
USENIX Security Symposium (USENIX Security 16),
pages 263–278, Austin, TX. USENIX Association.
Serdar Argic, Shane Atkinson, R. C. Dsbl. http://www.
dsbl.org/. A blocklist specialized in listing open relays
and open proxies.
Perdisci R, Corona I, Giacinto G. Early detection of mali-
cious flux networks via large-scale passive DNS traffic
analysis. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Se-
cure Computing, 2012, 9(5): 714–726.
Woodbridge J, Anderson H S, Ahuja A, et al.(2016). Pre-
dicting Domain Generation Algorithms with Long
Short-Term Memory Networks[J]..
Goldberg, Y., & Levy, O. (2014). Word2vec explained: de-
riving mikolov et al.'s negative-sampling word-embed-
ding method. Eprint Arxiv.
Thomas Orthbandt. (2015). Nominum. https://nomi-
num.com/press_item/sharp-rise-in-dns-based-ddos-
last-year-signals-larger-more-frequent-attacks-in-
2015/. DNS-based DDoS rise signals more attacks in
2015.
Tama, B. A., & Rhee, K. H. (2015). Data mining techniques
in DoS/DDoS attack detection: A literature review. In-
ternational Information Institute (Tokyo). Information,
18(8), 3739.
Karnwal, T., Sivakumar, T., & Aghila, G. (2013). A comber
approach to protect cloud computing against xml ddos
and http ddos attack, 182, 1-5.
Wang, B., Zheng, Y., Lou, W., & Hou, Y. T. (2015). Ddos
attack protection in the era of cloud computing and soft-
ware-defined networking. Computer Networks, 81(C),
308-319.
Eduard Kovacs. (2014). Large DNS Text Records Used to
Amplify DDoS Attacks: Akamai. http://www.securi-
tyweek.com/large-dns-text-records-used-amplify-
ddos-attacks-akamai.
C. Liu. A new kind of ddos threat: The â ˘ AIJnonsense
nameâ ˘ IA˙ attack. Network World, 2015. [Online;
posted 27-January-2015]
VeriSign, Verisign distributed denial of service trends re-
port q4 2015. https://www.verisign.com/assets/report-
ddos-trends-Q42015.pdf, 2015.
Rizzo, G., Van Erp, M., Plu, J., & Troncy, R. (2016). Mak-
ing sense of microposts (#Microposts2016) named en-
tity recognition and linking (NEEL) challenge. CEUR
Workshop Proceedings, 1691, 50–59. https://doi.org/
10.1145/1235.
Andrew. (2015). https://secure64.com/defenses-pseudo-
random-subdomain-attacks-prsd/. More Defenses
Against Pseudo Random Subdomain attacks (PRSD).
S. Stover, D. Dittrich, J. Hernandez, and S. Diet- rich. Anal-
ysis of the storm and nugache trojans: P2P is here. In
USENIX ;login:, vol. 32, no. 6, December 2007.
Wikipedia. The storm botnet. http://en. wikipe-
dia.org/wiki/Storm_botnet, 2010.
J.Williams. What we know (and learned) from the waledac
takedown. http://tinyurl.com/ 7apnn9b, 2010.
abuse.ch. ZeuS Gets More Sophisticated Using P2P Tech-
niques. http://www.abuse.ch/ ?p=3499, 2011.
Rahbarinia, B. (2016). Segugio:Efficient and Accurate Be-
havior-Based Tracking of Malware-Control Domains
in Large ISP Networks, 19(2). https://doi.org/
10.1145/2960409.
Yadav, S., Reddy, A. K. K., Reddy, A. N., and Ranjan, S.
Detecting Algorithmically Generated Malicious Do-
main Names. In Proceedings of the 10th ACM
SIGCOMM Conference on Internet Measurement
(2010), IMC ’10.
ICISSP 2018 - 4th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy
198
