
CARS - A Spatio-temporal BDI Recommender System:
Time, Space and Uncertainty
Amel Ben Othmane
1
, Andrea Tettamanzi
2
, Serena Villata
2
and Nhan Le Thanh
2
1
Universit
´
e C
ˆ
ote d’Azur, ADEME, Inria, CNRS, I3S, France
2
Universit
´
e C
ˆ
ote d’Azur, CNRS, Inria, I3S, France
Keywords:
Region Connection Calculus, Allen’s Intervals, Fuzzy Sets.
Abstract:
Agent-based recommender systems have been exploited in the last years to provide informative suggestions
to users, showing the advantage of exploiting components like beliefs, goals and trust in the recommenda-
tions’ computation. However, many real-world scenarios, like the traffic one, require the additional feature of
representing and reasoning about spatial and temporal knowledge, considering also their vague connotation.
This paper tackles this challenge and introduces CARS, a spatio-temporal agent-based recommender system
based on the Belief-Desire-Intention (BDI) architecture. Our approach extends the BDI model with spatial
and temporal information to represent and reason about fuzzy beliefs and desires dynamics. An experimental
evaluation about spatio-temporal reasoning in the traffic domain is carried out using the NetLogo platform,
showing the improvements our recommender system introduces to support agents in achieving their goals.
1 INTRODUCTION
Agent-based recommender systems (Casali et al.,
2008a; Chen and Cheng, 2010; Batet et al., 2012;
Othmane et al., 2016b) have been proposed in the last
years in different scenarios, like tourism, health-care,
and traffic, to provide suggestions and support users
to achieve their goals. The advantage of such sys-
tems is that of encoding users’ beliefs and goals in
the system to return a recommendation which is as
close as possible to their needs, with the possibility to
include additional information like the confidence in
the source. In addition, several application scenarios
require to formalize knowledge about the time and the
location in which the action is taking place. This in-
formation often needs to be considered as a whole, as
in the case of the traffic scenario, where a traffic jam
is identified by its location and the time it is occurring
during the day, and require to encode a certain degree
of vagueness as well.
In this paper, we answer the following research
question:
• how to represent and reason about fuzzy spatial-
temporal knowledge to provide useful recommen-
dations?
To answer this question, we introduce CARS,
a spatio-temporal Cognitive Agent-based Recom-
mender System, extending with spatio-temporal in-
formation the system proposed by (Othmane et al.,
2016b). Based on the extension principle of fuzzy set
theory (Zadeh, 1975), we define a fuzzy counterpart
of Allen’s intervals (Allen, 1983) to model temporal
knowledge, while fuzzy topological relations are de-
fined in terms of a fuzzy extension of the region con-
nection calculus (Randell et al., 1992), whereby re-
gions are represented as fuzzy sets. These two com-
ponents, namely spatial and temporal information, are
combined together based on the assumption that the
degree to which a spatio-temporal belief is true is
the minimum between the confidence degrees of the
spatial belief and temporal one, respectively. Spatio-
temporal knowledge is thus exploited by agents to
update their beliefs following the other agents’ rec-
ommendations, with the aim to reach their goals. To
show the advantages of the proposed agent-based rec-
ommender system, we address an empirical evalua-
tion in a simulated environment using the NetLogo
platform. In particular, we consider the traffic sce-
nario, where the goal of the agents is to reach a cer-
tain point of interest in the fastest way as possible.
The results of the simulations show that CARS allows
agents to faster reach their own destinations with re-
spect to the baseline, where no recommendation to the
agents is provided.
To the best of our knowledge, CARS is the first
48
Othmane, A., Tettamanzi, A., Villata, S. and Thanh, N.
CARS - A Spatio-temporal BDI Recommender System: Time, Space and Uncertainty.
DOI: 10.5220/0006590700480057
In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2018) - Volume 1, pages 48-57
ISBN: 978-989-758-275-2
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
agent-based recommender system taking into account
at the some time i) spatial and temporal knowledge,
and ii) the vagueness and incompleteness typical of
these components. Related work considers either
spatial or temporal knowledge without providing a
unique reasoning model (Jarvis et al., 2005), or does
not take into account the fuzzy connotation of spatio-
temporal knowledge (Schuele and Karaenke, 2010;
Behzadi and Alesheikh, 2013).
The rest of the paper is organized as follows. After
some preliminaries, Section 3 formally introduces the
spatio-temporal fuzzy representation of the agents’
beliefs as well as their update mechanism. Section 4
describes the experimental setting and discusses the
results. The discussion of the related work and con-
clusions end the paper.
2 PRELIMINARIES
In this section, we provide some background about
the formalisms we adopt to introduce our spatio-
temporal fuzzy representation of beliefs and goals.
2.1 Region Connection Calculus
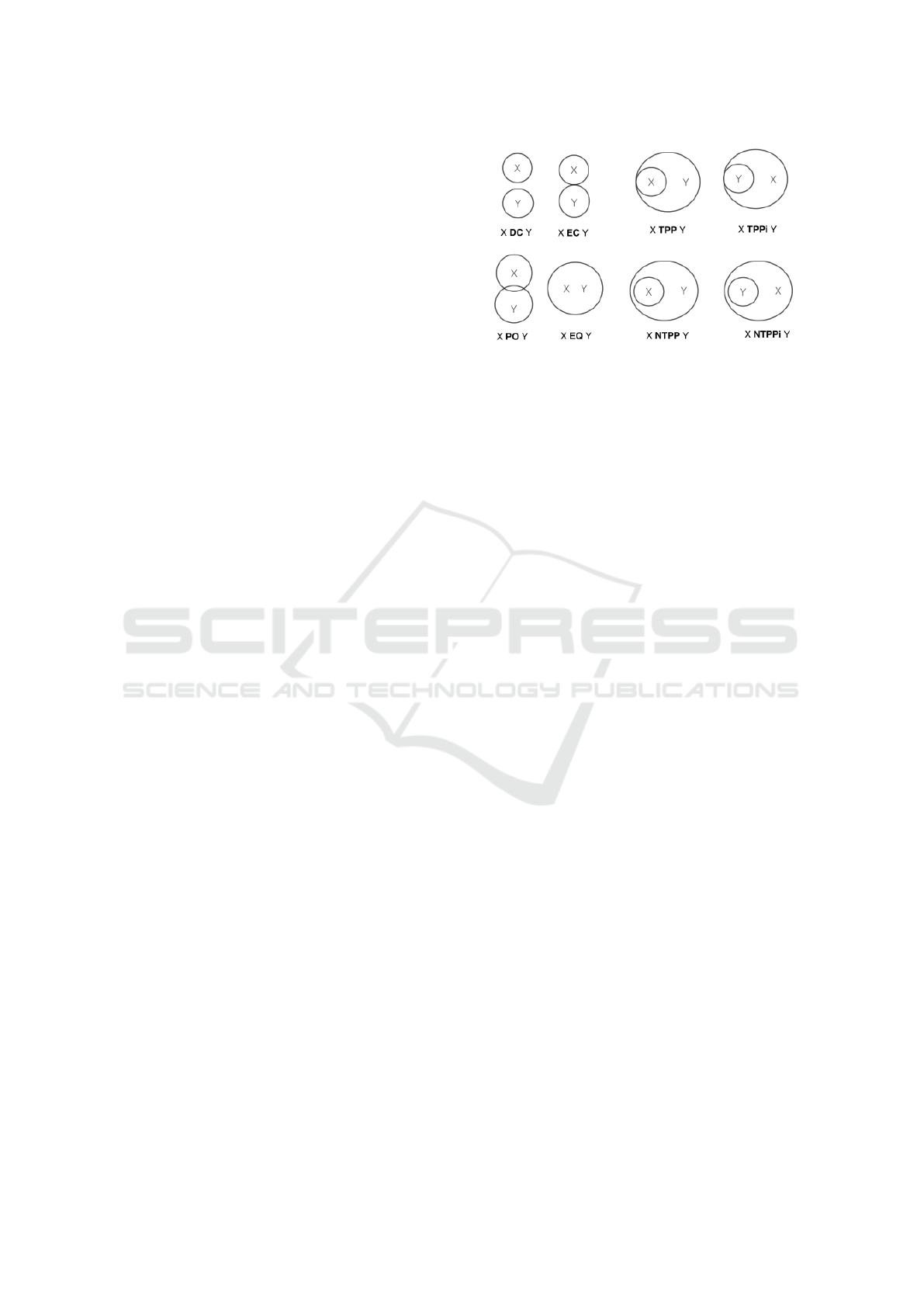
One of the most important formalisms for topologi-
cal relationships is the Region Connection Calculus
(RCC) (Randell et al., 1992). The RCC is an ax-
iomatization in first order logic of certain spatial con-
cepts and relations. The basic theory assumes just one
primitive dyadic relation: C(x,y), to be read as “x con-
nects with y”. RCC has eight basic relations (illus-
trated in Figure 1): DC (DisConnected), EC (Exter-
nally Connected), PO (Partial Overlap), EQ (EQual),
TPP (Tangential Proper Part), NTPP (Non Tangential
Proper Part) and their converse relations TPPi (TPP
inverse) and NTPPi (NTPP inverse). The formal def-
inition of the spatial relation entailed in the RCC is
given in Table 1 for reference. For further details
about RCC, we refer the reader to (Randell et al.,
1992).
2.2 Allen’s Intervals Algebra
Allen’s Interval Algebra (Allen, 1983) is an alge-
bra of binary relations on intervals for representing
and reasoning about qualitative temporal information.
Allen’s approach is based on the notion of time inter-
vals and binary relations among them. A time inter-
val X is an ordered pair hX
−
,X
+
i such that X
−
< X
+
,
where X
−
and X
+
are interpreted respectively as the
starting and ending points of the interval. Allen in-
troduces thirteen basic interval relations, illustrated in
Figure 1: The main RCC-8 relations.
Table 2: ≺ (before), m (meets), o (overlaps), d (dur-
ing), s (starts), f (finishes), their converse relations
(, m
i
, o
i
, d
i
, s
i
, f
i
), and = (equal), where each basic
relation can be defined in terms of relations involv-
ing its endpoints. For example, the interval relation-
ship X
d
Y (interval X occurs during interval Y) can be
expressed as (X
−
> Y
−
) ∧ (X
+
< Y
+
). We refer the
reader to (Allen, 1983) for a more detailed discussion.
2.3 Fuzzy set Theory
Fuzzy set theory (Zadeh, 1965) deals with sets or cat-
egories whose boundaries are blurred or gradual. A
fuzzy set is a set of objects whose membership to the
set takes a value between zero and one. Each fuzzy
object can have partial or multiple memberships. A
fuzzy set A in universe of discourse X is mathemati-
cally characterized by a membership function µ
A
(x),
which associates with each x in X a real number in the
interval [0,1], with the membership value at x repre-
senting the “degree of membership” of x in A.
Let X be a set of objects, called the the universe,
whose elements are denoted x. A membership in a
fuzzy subset A of X is defined by the membership
function µ
A
from A to {0,1} such that
µ
A
(x) =
1 iff x ∈ A
0 iff x /∈ A
The closer the value of µ
A
(x) is to 1, the more x
belongs to A. A is a subset of X that has no sharp
boundary and is characterized by a set of pairs A =
{(x,µ
A
(x)),x ∈ X }. When X is a finite set {x
1
,...,x
n
},
a fuzzy set is expressed as A =
n
∑
i=1
µ
A
(x
i
)/x
i
; when x
is not finite, we write A =
R
X
µ
A
(x)/x.
2.4 The Extension Principle
The extension principle (Zadeh, 1975) provides a way
to extend non-fuzzy mathematical concepts to deal
CARS - A Spatio-temporal BDI Recommender System: Time, Space and Uncertainty
49

Table 1: Definition of spatial relations entailed in the RCC. U is the universe of all regions; x and y are variables denoting
arbitrary elements of U, i.e. regions.
Name Relation Definition
Disconnected DC(x,y) ¬C(x,y)
Part P(x,y) ∀z ∈ U,C(z,x) → C(z,y)
Proper Part PP(x,y) P(x,y) ∧ ¬P(y,x)
Equals EQ(x,y) P(x,y) ∧ P(y,x)
Overlaps O(x,y) ∃z ∈ U, P(z, x) ∧ P(z,y)
Discrete DR(x,y) ¬O(x,y)
Partially Overlaps PO(x,y) O(x,y) ∧ ¬P(x, y) ∧ ¬P(y,x)
Externally connects EC(x,y) C(x, y) ∧ ¬O(x,y)
Tangential Proper Part T PP PP(x,y) ∧ (∃z ∈ U, EC(z, x) ∧ EC(z, y))
Non-Tangential Proper Part NT PP(x, y) PP(x, y) ∧ ¬(∃z ∈ U,EC(z,x) ∧ EC(z,y))
Table 2: Allen’s thirteen time relations.
Relation Converse Pictorial Example Endpoint Relations
X ≺ Y X Y X
+
< Y
−
XmY Xm
i
Y X
+
= Y
−
XoY Xo
i
Y X
−
< Y
−
, X
+
> Y
−
, X
+
< Y
+
XdY Xd
i
Y X
−
> Y
−
, X
+
< Y
+
XsY Xs
i
Y X
−
= Y
−
, X
+
< Y
+
X fY X f
i
Y X
−
< Y
−
, X
+
= Y
+
X = Y X = Y X
−
= Y
−
, X
+
= Y
+
with fuzzy quantities. It is defined by the following
equation:
µ
A∗B
(z) = sup
z=x∗y
min{µ
A
(x),µ
B
(y)} (1)
where ∀x,y ∈ X , µ
A
(x) ∈ [0,1] and µ
B
(y) ∈ [0,1] are
membership functions defining the degree of mem-
bership of the elements of X to the fuzzy subsets A
and B, respectively. Symbol ∗ denotes any crisp op-
erator. Some of the consequences of applying a fuzzy
function to logical operators are the following:
µ
X∧Y
= min(µ
X
,µ
Y
)
µ
X∨Y
= max(µ
X
,µ
Y
)
µ
¬X
= 1 − µ
X
The union ∪ and the intersection ∩ of ordinary subsets
of X can be extended such that:
∀x ∈ X , µ
A∪B
= max (µ
A
(x), µ
B
(x)) (2)
∀x ∈ X , µ
A∩B
= min (µ
A
(x), µ
B
(x)) (3)
where µ
A∪B
and µ
A∩B
are respectively the membership
functions of A ∪ B and A ∩ B.
2.5 T-Norms and T-Conorms
T-norms and T-conorms (Deschrijver et al., 2004) are
used to calculate the membership values of intersec-
tion and union of fuzzy sets, respectively. A T-norm
is a binary operation T : [0,1]
2
→ [0,1] satisfying the
following axioms for all x,y,z ∈ [0,1]:
(i) T (x, y) = T (y,x) (commutativity),
(ii) T (x, y) ≤ T (x,z),i f y ≤ z (monotonicity),
(iii) T (x, T (y, z)) = T (T (x, y), z) (associativity),
(iv) T (x,1) = x
Some common T-norms (and respectively, their cor-
responding T-conorms) are the minimum T
M
(S
M
), the
product T
P
(S
P
) and Łukasiewicz T
W
(S
W
), defined as
follows:
• T
M
(x,y) = min(x,y), S
M
(x,y) = max(x,y);
• T
P
(x,y) = x.y, S
M
(x,y) = x + y + xy;
• T
W
(x,y) = max(0,x + y − 1), S
W
(x,y) =
min(1,x + y).
Implicators generalize the logical implication to the
unit interval and are defined by I
S
(x,y) = S(1 − x, y)
for x and y in [0,1], e.g., the implicator for S
M
is de-
fined by I
S
M
(x,y) = max(1 − x,y). For more details,
we refer the reader to (Schweizer and Sklar, 1960;
Schweizer and Sklar, 1983).
ICAART 2018 - 10th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
50

3 SPATIO-TEMPORAL BELIEF
REPRESENTATION AND
REASONING
In this section, we describe the the main features of
our formal representation of fuzzy spatio-temporal
beliefs. Since we extend the multi-agent BDI recom-
mender systems proposed by (Othmane et al., 2016b;
Othmane et al., 2016a) with the formal representation
of fuzzy spatio-temporal information, we begin by re-
calling our multi-context framework, which handles
information uncertainty using possibility theory.
3.1 A Multi-Context Recommender
Agent
Using cognitive agents architecture such as the belief-
desire-intention model as a base of a recommender
system is relevant especially in real-world applica-
tions (Casali et al., 2008b). Casali et al. (Casali et al.,
2008a) and (Othmane et al., 2016b) proposed similar
multi-agent BDI recommender systems that handles
information uncertainty using possibility theory. We
decided to extend the approach proposed in (Othmane
et al., 2016b) because it proposes already a mecha-
nism for beliefs and intentions update compared to
(Casali et al., 2008a). In (Othmane et al., 2016b),
a BDI agent visualized in Figure 2 is defined using
multi-context systems (Parsons et al., 2002) as fol-
lows:
Ag = ({BC,DC,GC,SC,PC,IC,CC},∆
br
)
where BC, DC, GC represent respectively the Be-
lief Context, the Desire Context and the Goal Context
which model an agent mental attitude. PC, IC and CC
are functional contexts that represent respectively the
Planning Context, the Intention Context and the Com-
munication Context. SC is for the Social Context, and
it models social influence between agents. Authors
of (Othmane et al., 2016b) assume a trust relation-
ship between agents and trustworthiness of an agent
a
i
towards agent a
j
about an information φ is inter-
preted as a necessity measure τ ∈ [0,1]. The behavior
of these contexts is handled by means of internal de-
duction rules ∆
i
and axioms L
i
. The overall behavior
of the system is handled by bridge rules like Rule (2)
(shown in Figure 2) linking GC to DC, and expressed
as follows:
(2)GC : G(a
i
,φ) = δ
φ
→ DC : D
+
(a
i
,φ) = δ
φ
It can be read as follows: if an agent a
i
has as
goal φ with a satisfaction degree δ
φ
in a GC then it
positively desires φ with the same degree δ
φ
in a DC.
Figure 2: A global view of the multi-context agent compo-
nents.
For more details about this agent model, we refer the
reader to (Othmane et al., 2016b).
Indeed, the work of (Othmane et al., 2016b) has
shown how autonomous BDI agents (Othmane et al.,
2016a) can evolve and move within a dynamic envi-
ronment, this work lacks from a spatial and temporal
reasoning in order to match the needs of a real-world
application.
A spatio-temporal belief is an event defined as
a spatial relation holding in a temporal interval. A
spatio-temporal belief consists then of a sequence of
snapshots of an entity taken at specific time points:
b
1
at t
1
, b
2
at t
2
,..., b
n
at t
n
where t
1
,t
2
,...,t
n
∈ T and
b
1
,b
2
,...,b
n
are spatio-temporal beliefs concerning a
moving spatial object (e.g. car, moving person, etc..).
3.2 Fuzzy Sets for Representing
Imprecise Spatio-temporal Beliefs
Spatio-temporal data are often affected by impreci-
sion and uncertainty (Galton, 2009) due to several
reasons. Spatial uncertainty refers to positional ac-
curacy (e.g., location of an individual or a car). Tem-
poral uncertainty states whether temporal information
describes well a spatial phenomena. A fuzzy set, be-
cause of its ability to represent degrees of member-
ship, is more suitable for modeling geographical en-
tities. In a GIS database, real world objects can be
represented by the degrees of membership to multiple
classes or objects.
Representing only the spatial or the temporal di-
mension is not sufficient to model and analyze such
phenomena. Modeling change involves incorporat-
ing both dimensions simultaneously. In this work,
CARS - A Spatio-temporal BDI Recommender System: Time, Space and Uncertainty
51

Figure 3: Fuzzy time membership function.
we adopt a dual representation of dynamic spatial
information proposed by Bordogna et al. (Bordogna
et al., 2003). In this approach, they introduce two
representations: i) a precise spatial reference and in-
determinate or vague time reference (e.g., if I leave
home now, I should be at work around 8 pm), and
ii) a precise time reference and a fuzzy spatial one
(e.g., an accident has just occurred in between Route
A and Route B). According to (Bordogna et al.,
2003), a spatial dynamic object can be represented
in the first case as a set of pairs (τ
i
,o
i
): o
d
:=
{(τ
1
,o
1
),..,(τ
i
,o
i
),...,(τ
n
,o
n
)}, where τ
i
is the time
fuzzy validity range associated with the spatial object
o
i
. The semantics of τ
i
is defined by a triangular mem-
bership function centred in t
i
(see Figure 3). In the
same way, a spatial object with precise time reference
is defined by a set of pairs (t
i
,σ
i
), where σ
i
stands
for the spatial validity of the observed phenomenon at
time instant t
i
represented as a triangular membership
function. In order to reason about such information,
we need a mechanism to represent also qualitative re-
lationships between spatio-temporal entities. For this
reason, we propose a fuzzy RCC-8 and an extension
to Allen’s intervals to support fuzziness.
3.3 Fuzzy Allen’s Intervals
The twelve relations defined by Allen for simple time
intervals presented in Section 2.2 are generalized for
modeling fuzzy time relations. Each basic relation
can be defined in terms of endpoint relations defined
in Table 2. Using the extension principle, a fuzzy tem-
poral relation is defined. For example, the fuzzy rela-
tion d
f
is introduced for the simple temporal relation
d (during), as follows:
Xd
f
Y ⇔ (X
−
>
f
Y
−
) ∧ (X
+
<
f
Y
+
)
and the corresponding degree of confidence, using the
extension principle, can be expressed as:
µ
Xd
f
Y
= min(µ
X
−
>
f
Y
−
,µ
X
+
<
f
Y
+
)
All the values X and Y can be generalized to fuzzy
values and represented by fuzzy triangular numbers.
Based on the extension principle, we define first the
confidence degrees of the fuzzy relations ≥
f
and ≤
f
,
in order to deduce respectively the one of >
f
, <
f
and =
f
. Suppose we have two fuzzy intervals A and
B defined by triangular fuzzy functions as follows:
A = (a
1
,a
2
,a
3
) and B = (b
1
,b
2
,b
3
). By applying
the extension principle, we can deduce the following
fuzzy relations:
µ
A≤
f
B
=
0 if a
1
> b
3
b
3
−a
1
b
3
−a
1
+a
2
−b
2
if a
1
≤ b
3
,b
2
< a
2
1 if a
2
≤ b
2
(4)
µ
A≥
f
B
=
0 if b
1
> a
3
a
3
−b
1
a
3
−b
1
+b
2
−a
2
if b
1
≤ a
3
,b
2
> a
2
1 if b
2
≤ a
2
(5)
From Equations 4 and 5, we can deduce the
confidence degree of relations >
f
, <
f
and =
f
as
follows:
A <
f
B = A ≤
f
B ∧ ¬(A =
f
B)
A >
f
B = A ≥
f
B ∧ ¬(A =
f
B)
(A =
f
B) = A ≤
f
B ∧ A ≥
f
B
Let us consider, for instance, A = (8,9,10) and
B = (8.5,9.5,10.5) representing two fuzzy time-
points. We can compute the degree of confidence
of this fuzzy temporal relation “A occurs at ap-
proximately the same time as B” using Equation 4
and Equation 5 as follows: µ
A=
f
B
= µ
A≤
f
B∧A≥
f
B
=
min(µ
A≤
f
B
,µ
A≥
f
B
) = min(1,0.75) = 0.75.
3.4 Fuzzy Topological Relations
The eight binary topological predicates for simple
regions (Section 2.1) are generalized for modeling
fuzzy topological relations. Based on the approach
proposed by Schockaert et al. (Schockaert et al.,
2009) and the definition of the RCC relations in Ta-
ble 2, we present here an approach for modelling im-
precise spatial information when regions are repre-
sented as fuzzy sets. Let U be a nonempty set (rep-
resenting regions), and C a reflexive and symmetric
binary fuzzy relation on it modeling connection. Sev-
eral other topological relations can be defined based
on this relation. These include the RCC8 basic rela-
tions DC, EC, PO, EQ, TPP, NTPP, and the converses
of TPP and NTPP (see Table 3 for their definitions).
Note that we adopt, following (Schockaert et al.,
2006), the Łukasiewicz-norm T
w
and its correspond-
ing implicator I
T
w
to generalize the standard logical
conjunction and implication. In addition, we chose
this logic for its convenience, especially regarding
ICAART 2018 - 10th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
52

Table 3: Fuzzy RCC definitions
Name Definition Fuzzy Definition
DC(x,y) ¬C(x,y) 1 −C(x,y)
P(x,y) ∀z ∈ U,C(z,x) → C(z,y) inf
z∈U
I
W
(C(z, x),C(z,y))
PP(x,y) P(x,y) ∧ ¬P(y, x) min(P(x,y),1 − P(y,x))
EQ(x,y) P(x,y) ∧ P(y, x) min((P(x,y),P(y,x))
O(x,y) ∃z ∈ U, P(z, x) ∧ P(z,y) sup
z∈C
T
W
(P(z,x),P(z,y))
DR(x,y) ¬O(x,y) 1 − O(x, y)
PO(x,y) O(x,y) ∧ ¬P(x, y) ∧ ¬P(y,x) min (O(x,y),1 − P(x, y), 1 − P(y,x)))
EC(x,y) C(x, y) ∧ ¬O(x,y) min(C(x,y),1 − O(x,y))
NT P(x,y) ∀z ∈ U,C(z,x) → O(z,y) inf
t∈U
I
W
(C(z, x), O(z, y))
T PP(x, y) PP(x,y) ∧ ¬NT P(x, y) min(PP(x,y),1 − NT P(x, y))
NT PP(x,y) PP(x,y) ∧ NT P(x,y) min(1 − P(x, y), NT P(x, y))
the implication function. The implicator correspond-
ing to the Łukasiewicz t-norm is defined by: I
T
W
=
min(1,1 − x + y). In fact, the minimum operator does
not eliminate values arbitrarily, leaving thus more un-
certainty. For simplicity, we write I
W
instead of I
T
W
in
the remainder of the paper.
Using this formalism, we can, for example, calcu-
late a fuzzy spatial relation “p is precisely located far
from q”. Knowing the location of p and q, we can
calculate their fuzzy position using Equation 6. We
can then calculate the degree to which those two lo-
cations are connected, and consequently, their degree
of disconnection: DC(p,q) = 1 −C(p,q).
3.5 Fuzzy Spatio-temporal Belief
Representation and Reasoning
In order to represent an imprecise spatio-temporal be-
lief or desire such as “An accident occurred around 8
PM between road A and road B” or “I want to be at
work before 9 AM”, we combine the RCC spatial re-
lations with Allen’s temporal relations. The degree to
which this belief is true is computed using the mini-
mum between the degrees of confidence of the spatial
belief and the temporal one, respectively. For repre-
senting a spatio-temporal belief, we annotate spatial
formulas with temporal information, meaning that a
spatial formula is true during a time interval or at a
specific time point. In other words, it can be written
as follows:
XDC
I
Y,Y PO
J
Z
where X and Y represent two different regions or
moving objects, and I and J are time intervals. This
formula means that X is disconnected from Y during
time interval I, and Y is part of Z during time inter-
val J.
Let us consider again the belief “An accident (A)
occurred around 8 PM (t
1
) between road A (R
A
) and
road B (R
B
)”. This can be formalized as follows:
(A PO
t
1
R
A
) ∧ (A PO
t
1
R
B
).
Its degree of belief is:
B((A PO
t
1
R
A
) ∧ (A PO
t
1
R
B
)) =
= min{B(A PO
t
1
R
A
),B(A PO
t
1
R
B
)}.
Later, one can reason about temporal intervals or
time-points to infer relevant information such as be-
ing at the same time nearby the accident place. This
spatio-temporal belief is essential for an agent to de-
cide or not to reconsider its intention in case the de-
gree of confidence of this belief is high. However, this
belief is no longer useful after a certain time period,
or if the accident is not placed on the agent’s route
(i.e., intentions).
4 EVALUATION
In this section, we present the evaluation of the
CARS recommendation system equipped with the
fuzzy spatio-temporal belief representation. The pur-
pose of the evaluation is to quantify the gain of agents,
in terms of execution and limited waiting time, to
reach their goals, by exchanging spatio-temporal be-
liefs and desires. To this aim, we propose to test
the proposed model in a real-world scenario where
spatio-temporal knowledge represents a crucial factor
in the user decision making process. In this evalu-
ation, different agent’s strategies are considered, fol-
lowing the ideas proposed by (Othmane et al., 2016a):
• individual agent strategy: agents behave individ-
ually without taking into account any information
coming from other agents. Only information from
external resources are considered in this case, e.g.,
data from the Traffic Message Channel (TMC).
CARS - A Spatio-temporal BDI Recommender System: Time, Space and Uncertainty
53

• social agent strategy: agents are part of a social
network and communicate with the other agents
in the network by exchanging their own beliefs
and desires. Agents fully trust all other agents in
the network.
• social distrustful agent strategy: agents are part of
a social network, but they consider also the trust-
worthiness degree of the other agents, when they
exchange messages. Agents accept information
only from trustworthy agents. An agent is consid-
ered as deceitful if the information it provides is
repeatedly proven to be false.
4.1 Scenario
In order to evaluate the applicability of the proposed
model in a real-world application, we propose the fol-
lowing scenario. Agent a
1
uses an electric car, and
needs to reach an electric public charging point. Like
most road users, a
1
usually consults web-based or
mobile mapping services before the trip to determine
the nearest charging station and to avoid possible traf-
fic jams. Knowing where to get to and estimating the
time needed for the journey, a
1
can plan its trip. Thus,
it selects a course of actions that will result in reach-
ing its destination before the battery of its car goes
out of charge. It chooses a route to follow and a time
to leave so that it can arrive by a desired arrival time.
Once the trip is planned, it can be executed. As long
as a
1
has not found any obstacle within the journey, it
can keep executing its original plan. However, it just
found that a certain road on its route is closed due to
an accident (other city events such as soccer games
or music concerts can be considered as well). As a
1
is not able to drive through that road anymore, it has
to reconsider its options and find an alternative route
to reach its destination while taking into account its
battery life (hence its arrival time).
4.2 Implementation
In agent-based systems with spatial reasoning and so-
cial behavior, a visual output is needed to display the
agents’ movements and interactions in two- or three-
dimensional spaces. NetLogo
1
is a multi-agent pro-
gramming language and modeling environment for
simulating natural and social phenomena particularly
suited for modeling complex systems evolving over
time.
To implement our scenario, we decided to use
NetLogo, as it also provides support for the BDI ar-
chitecture and the FIPA Agent Communication Lan-
guage. The spatial module is implemented using the
1
https://ccl.northwestern.edu/netlogo/
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) extension for
Netlogo
2
. We used data about the road network and
Electric Vehicle (EV) charging points from the Nice
city open geographical database
3
in shapefile format
(i.e., the format supported by the GIS Netlogo exten-
sion). The resulting environment of agents is shown
in Figure 4.
In order to adapt a fuzzy topological relation to a
GIS vector data model, we assume that crisp regions
are a set of trapezoidal shapes containing a finite se-
quence of line segments. To simplify the representa-
tion, we use a Gaussian function distribution as an ap-
proximation of the trapezoidal distribution. Then, the
membership function µ(x,y) of a spatial object with
coordinates (x, y) is defined by the following equa-
tion:
µ
x,y
= e
−k
d
|(x−x
R
)+(y−y
R
|
2
, (6)
where x
R
and y
R
are the coordinates of a landmark
point, and k
d
corresponds to a flattening coefficient
defined according to the user description (d) of a be-
lief. We define then different coefficients for k
precisely
,
k
approximately
, k
near
, k
around
. An example of this distri-
bution run is visualized in Figure 5.
Figure 5: Example of the Gaussian distribution
Agents in this simulation are spatial entities (mov-
ing cars) in an environment (the road network of the
Nice city) which may change their location and at-
tributes as time goes by
4
. At the beginning of the
simulation, each agent has a desire. As defined in
our scenario, the desire of an agent is to go to the
nearest EV recharge point. A recommended plan is
proposed to the agent following the multi-context ap-
proach to the deliberation of agent behavior proposed
by (Othmane et al., 2016b; Othmane et al., 2016a).
2
https://ccl.northwestern.edu/netlogo/docs/gis.html
3
http://opendata.nicecotedazur.org/data/
4
The simulation code is available at this link:
http://modelingcommons.org/browse/one model/4832
#model tabs browse info.
ICAART 2018 - 10th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
54

Figure 4: The user interface of the agent-based simulation in NetLogo. The central part shows the agent’s environment
constituted of roads. Blue points represent Electric Vehicle charging stations. An agent is represented by a car. Red squares
represent accidents. Labels represent an agent intention, which consists of two elements: the name, mapped to a NetLogo
command, and a done-condition, mapped to a NetLogo reporter. Intentions are stored in a stack, and are popped out when
they are to be executed. If the done-condition is satisfied, the intention is removed and the next intention is popped out
consecutively. The figure shows also, on the right-hand side, how the graphs are updated dynamically as the program runs.
The left-hand pane shows some setup parameters.
Once the agent starts executing its plan, we trigger
at different random times in different random places
spatio-temporal events, i.e., accidents. If the agent re-
ceives information, it adds it to its belief base and, if
the accident is on its route, it updates its intentions,
if possible. Agents applying the individual strategy
have no knowledge from the other agents, thus they
update their route only when they encounter a closed
route in their plan.
4.3 Results and Discussion
The experiments were conducted as a version of the
scenario proposed in Section 4.1, with the adoption of
the three different strategies described in Section 4.
The scenario is executed with 10, 50, 100, and 150
agents as part of the environment in three different
experiments. We measured the time it took an agent
to reach its destination. Results of the average time
for agents to reach their destination for the different
cases are reported in Figure 6-[a]. The average time
for all agents to reach their destination increases as
the number of agents increases. This can be explained
by the traffic overload, which cannot be avoided due
the number of cars on the road network. However,
it is worth noticing that the time decreases when the
two social agent strategies are exploited, in contrast
to the individual agent strategy. Notice also that so-
cial agents using trust-based information to judge the
reliability of the recommendations they receive have
better performance than purely social ones. As a
conclusion, the results show that exchanging spatio-
temporal beliefs among agents enhances the overall
performance of the agent network.
It is worth observing that some agents adopting
the individual strategy do not even reach their desti-
nation (i.e., they cannot satisfy their goals). There-
fore, the average time reported in the diagrams keeps
rising indefinitely. In contrast, social agents always
achieve their goals and reach their destination, with
an even more limited time interval observed for those
agents exploiting trust-based information. These re-
sults show that exchanging fuzzy spatio-temporal be-
liefs helps agents to achieve their goals by anticipat-
ing the consequences of their intentions. In other
words, agents can anticipate and change their inten-
tions to avoid huge waiting time. Taking into account
spatio-temporal beliefs coming only from trustworthy
agents avoids agents to be mislead and hence to waste
time. Figure 6-[b] reports the average waiting time of
agents. Within social agents, results are slightly bet-
ter for those exploiting trust-based information, ex-
cept when the number of agents is 150. This is due
to the time required to process such information for
the whole agent network, as more processing time is
needed to verify agents’ reliability.
5 RELATED WORK
Few approaches exist to represent and reason about
spatio-temporal beliefs, desires and intentions’ dy-
CARS - A Spatio-temporal BDI Recommender System: Time, Space and Uncertainty
55

(a) (b)
Figure 6: Experimental results (selfish agents: blue, social agents: red, social distrustful agents: green): (a) average time
required by the agents to reach a destination, and (b) average waiting time for the agents.
namics. (Jonker et al., 2003) propose a formal spatio-
temporal state language to define the spatio-temporal
behavior of an agent in a dynamic environment. Al-
though their approach provides an interesting formal-
ism for predicting agent spatial behavior, many ques-
tions concerning beliefs, desires and intentions dy-
namics are left open. For example, no mechanism
for updating beliefs, desires and intentions in this for-
malism is presented. Male
ˇ
s and colleagues (Male
ˇ
s
and
ˇ
Zarni
´
c, 2011) use modal logic to define an agent
capable of updating its mental attitude according to
spatio-temporal relations considered as events. They
define a language for events in which spatio-temporal
knowledge is defined under the form of predicates,
with an example in the traffic scenario. Nevertheless,
the proposed framework is still in a preliminary stage
and presents some drawbacks, e.g., lack of a mech-
anism to update such spatio-temporal beliefs and de-
sires. (Schuele and Karaenke, 2010) propose a spatial
model to enable BDI agents to move autonomously
and collision-free in a spatial environment. Authors
assume that in a spatial context, the agents’ knowl-
edge about their environment is uncertain. However,
this problem is not handled through a qualitative ap-
proach for spatial reasoning. Time reasoning is not
handled neither. Other relevant approaches for spa-
tial reasoning in BDI models are discussed in (Vahid-
nia et al., 2015). However, none of them consider
the imprecision and vagueness that characterise spa-
tial knowledge. So far, to the best of our knowledge,
many approaches to reason about time in the BDI
agent model are proposed in the literature (among
them, see (Jarvis et al., 2005; Fisher, 2005; Sierra and
Sonenberg, 2005) but none of them deals with time
information imprecision. Unlike the aforementioned
approaches, our approach besides combining spatial
and temporal reasoning within the BDI model, it ad-
dresses the open challenge of spatio-temporal infor-
mation vagueness and fuzziness that strongly charac-
terizes such a kind of knowledge.
6 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, we have introduced and evaluated
the CARS agent-based recommender system, where
fuzzy spatio-temporal beliefs are formally repre-
sented and updated. Answering the need to represent
spatio-temporal information to provide recommenda-
tions in the traffic scenario, we define spatio-temporal
knowledge annotating spatial formulae (formalized
through fuzzy RCC) with temporal information (for-
malized through fuzzy Allen’s time intervals). The
goodness of the proposed formal framework is vali-
dated through an empirical evaluation simulating the
agents’ behaviour in the traffic scenario. Results show
that the time required by the agents to reach a certain
point of interest sensibly decreases when the CARS
model is applied.
Several open challenges have to be tackled as fu-
ture research. First of all, further qualitative relations
about directions should be introduced concerning spa-
tial reasoning to allow the representation of a model
closer to reality. Second, on the simulation side, ex-
tending the evaluation introducing new metrics to fur-
ther reduce the processing time is also part of our fu-
ture research.
ICAART 2018 - 10th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
56

REFERENCES
Allen, J. F. (1983). Maintaining knowledge about temporal
intervals. Communications of the ACM, 26(11):832–
843.
Batet, M., Moreno, A., S
´
anchez, D., Isern, D., and Valls, A.
(2012). Turist@: Agent-based personalised recom-
mendation of tourist activities. Expert Systems with
Applications, 39(8):7319–7329.
Behzadi, S. and Alesheikh, A. A. (2013). Introducing a
novel model of belief–desire–intention agent for ur-
ban land use planning. Engineering Applications of
Artificial Intelligence, 26(9):2028–2044.
Bordogna, G., Carrara, P., Chiesa, S., and Spaccapietra,
S. (2003). A dual representation of uncertain dy-
namic spatial information. In International Fuzzy
Systems Association World Congress, pages 652–659.
Springer.
Casali, A., Godo, L., and Sierra, C. (2008a). A tourism
recommender agent: from theory to practice. Revista
Iberoamericana de Inteligencia Artificial, 12(40):23–
38.
Casali, A., Godo, L., and Sierra, C. (2008b). Validation
and experimentation of a tourism recommender agent
based on a graded bdi model. In CCIA, pages 41–50.
Chen, B. and Cheng, H. (2010). A review of the applica-
tions of agent technology in traffic and transportation
systems. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Sys., 11(2):485–
497.
Deschrijver, G., Cornelis, C., and Kerre, E. E. (2004). On
the representation of intuitionistic fuzzy t-norms and
t-conorms. IEEE Tran. on fuzzy systems, 12(1):45–61.
Fisher, M. (2005). Temporal development methods for
agent-based. JAAMAS, 10(1):41–66.
Galton, A. (2009). Spatial and temporal knowledge repre-
sentation. Earth Science Informatics, 2(3):169–187.
Jarvis, B., Corbett, D., and Jain, L. C. (2005). Reason-
ing about time in a BDI architecture. In Int. Conf. on
Knowledge-Based and Intell. Inf. and Eng. Sys., pages
851–857.
Jonker, C. M., Terziyan, V., and Treur, J. (2003). Temporal
and spatial analysis to personalise an agents dynamic
belief, desire, and intention profiles. In Int. Work.
on Cooperative Information Agents, pages 298–315.
Springer.
Male
ˇ
s, L. and
ˇ
Zarni
´
c, B. (2011). A spatiotemporal model
of events within a bdi. In Int. Conf. on Computer as a
Tool, pages 1–4. IEEE.
Othmane, A. B., Tettamanzi, A., Villata, S., and Thanh,
N. L. (2016a). A multi-context BDI recommender
system: From theory to simulation. In 2016
IEEE/WIC/ACM International Conference on Web In-
telligence, WI 2016, pages 602–605.
Othmane, A. B., Tettamanzi, A., Villata, S., Thanh, N. L.,
and Buffa, M. (2016b). An agent-based architecture
for personalized recommendations. In Agents and Ar-
tificial Intelligence - 8th Int. Conf., volume 10162 of
LNCS, pages 96–113.
Parsons, S., Jennings, N. R., Sabater, J., and Sierra, C.
(2002). Agent specification using multi-context sys-
tems. In Foundations and Applications of Multi-Agent
Systems, pages 205–226. Springer.
Randell, D. A., Cui, Z., and Cohn, A. G. (1992). A spatial
logic based on regions and connection. KR, 92:165–
176.
Schockaert, S., Cornelis, C., De Cock, M., and Kerre, E. E.
(2006). Fuzzy spatial relations between vague regions.
In 3rd Int. IEEE Conf. Intell. Systems, pages 221–226.
Schockaert, S., De Cock, M., and Kerre, E. E. (2009). Spa-
tial reasoning in a fuzzy region connection calculus.
Artificial Intelligence, 173(2):258–298.
Schuele, M. and Karaenke, P. (2010). Qualitative spatial
reasoning with topological information in BDI agents.
In 2nd Work. on Artif. Intell. and Logistics, pages 7–
12.
Schweizer, B. and Sklar, A. (1960). Statistical metric
spaces. Pacific J. Math., 10(1):313–334.
Schweizer, B. and Sklar, A. (1983). Probabilistic metric
spaces. North Holland series in probability and ap-
plied mathematics. North Holland.
Sierra, C. and Sonenberg, L. (2005). A real-time negotiation
model and a multi-agent sensor network implementa-
tion. JAAMAS, 11(1):5–6.
Vahidnia, M., Alesheikh, A., and Alavipanah, S. K. (2015).
A multi-agent architecture for geosimulation of mov-
ing agents. J. of Geographical Systems, 17(4):353–
390.
Zadeh, L. A. (1965). Fuzzy sets. Information and control,
8(3):338–353.
Zadeh, L. A. (1975). The concept of a linguistic variable
and its application to approximate reasoning. Infor-
mation sciences, 8(3):199–249.
CARS - A Spatio-temporal BDI Recommender System: Time, Space and Uncertainty
57
