
Strategies for Resolving Normative Conflict That Depends on
Execution Order of Runtime Events in Multi-Agent Systems
Mairon Belchior
1
, Jéssica Soares dos Santos
1
and Viviane Torres da Silva
2
1
Computer Science Department, Fluminense Federal University, Niterói, Brazil
2
IBM Research (on leave from Fluminense Federal University), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
Keywords: Norms, Runtime Normative Conflict, Conflict Detection, Conflict Resolution, Multi-Agent Systems.
Abstract: Norms are being used in multi-agent systems to control the behavior of software agents and maintain social
order. They define which actions each agent can or not perform in different circumstances. Systems regulated
by multiple norms must be able to detect and resolve normative conflicts to guarantee the expected behavior
of the system. A normative conflict arises when a given agent is prohibited and obliged to perform the same
action at the same time. Our work aims to resolve normative conflict that occurs at runtime and where its
detection depends on the execution order of runtime events in multi-agent systems. This paper presents two
independent approaches to resolve the conflicts. The first approach resolves the conflict at design time by
eliminating the overlaps between two norms in conflict. The second approach resolves the normative conflict
at runtime by extending an existing automated planning algorithm in order to get plans that do not produce
sequence of conflicting actions.
1 INTRODUCTION
Open multi-agent systems (MAS) require a
mechanism to regulate the behavior of autonomous
and heterogeneous agents of the system. Norms can
be used as a powerful mechanism to maintain social
order, by establishing system-level constraints to be
followed by the agents. Those constraints define
obligations, permissions and prohibitions and do not
depend from the particular implementation of the
agents (Aphale et al., 2013).
It is important taking into account the possible
existence of normative conflicts in MAS regulated by
multiple norms. A normative conflict is a situation in
which the fulfillment of one norm causes a violation
of another one. Two norms are said to be in conflict
if (i) they are active at the same time, (ii) have
contradictory deontic concepts (i.e., prohibition
versus permission or prohibition versus obligation),
(iii) are associated with the same entity, (iv) regulate
the same behavior, and (v) are defined in the same
context. The detection of conflicts among norms is
not a trivial task to the system designer since a MAS
can be regulated by a big set of norms.
There are many approaches in the literature that
deal with normative conflicts in MAS. Some of them
deals with the detection of direct conflict, which are
simple conflicts between a prohibition and an
obligation or permission regulating the same agent,
the same behavior and defined in the same context.
Other approaches can also detect indirect conflicts.
Indirect conflict involves two norms whose norm
elements (i.e., entity, behavior, context of the norm)
are not the same but are related. The detection of
indirect conflicts can be done only when the
relationships among elements of the norms are
known.
In addition, there are conflicts that occur at
runtime. The detection of this conflict depends on
execution order of runtime events in the Multi-agent
Systems. In Belchior and da Silva (2017a, 2017b), the
authors investigated two approaches, in the design
phase, based on execution scenarios to deal with the
detection of normative conflicts that depends on
information about the runtime execution of the
system. In the first approach, the system designer is
able to provide examples of execution scenarios and
evaluate the conflicts that may arise if those scenarios
would be executed in the system. The second
approach, reported in Belchior and da Silva (2017b),
detects potential normative conflicts and generates
the execution scenarios to the system designer. The
conflict checker identifies potential normative
216
Belchior, M., Santos, J. and Silva, V.
Strategies for Resolving Normative Conflict That Depends on Execution Order of Runtime Events in Multi-Agent Systems.
DOI: 10.5220/0006593202160223
In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2018) - Volume 1, pages 216-223
ISBN: 978-989-758-275-2
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
conflicts by switching the position order of runtime
events referred in the norm conditions. It is called
potential conflict because it can be arisen or not
depending on the execution order of those events. The
output is an ordered list of events that caused the
normative conflict.
In this paper, we proposed two independent
approaches to resolve this normative conflict given
the output provided by the second conflict detection
approach. The first approach resolves the conflict at
design time by eliminating the overlaps between two
norms in conflict. The central idea of the first
approach is to eliminate the overlaps between two
norms by changing the after and before conditions of
one of the norms in conflict. Our mechanism chooses
to change the norm where the result does not
eliminate the entire norm. The result is a set of norms
free of conflict. The second resolution approach
resolves the normative conflict at runtime by
extending an existing automated planning algorithm
(Ghallab et al., 2004) in order to get plans that do not
produce sequence of conflicting actions.
This paper is organized as follows. Section 2
summarizes the norm representation and the potential
conflict detection approach. Section 3 describes the
two approaches to solve the normative conflict.
Section 4 presents related work and Section 5
concludes the paper and presents further research.
2 NORM REPRESENTATION
AND CONFLICT DETECTION
In Belchior and da Silva (2017a, 2017b), we have
proposed to use OWL DL and Semantic Web Rule
Language (SWRL) and reasoning tools to represent
the main concepts of a norm in MAS and to detect
norm violations and norm conflict. The main
concepts related to a nom are deontic concept, entity,
action, and context. The deontic concept describes
behavior restrictions for agents in the form of
obligations, permissions and prohibitions. Norms are
applied to a given entity whose behavior is being
controlled. The entities represented here are single
agents. Actions represent the behavior being
controlled by the norm and are executed by an entity.
Contexts determine the area of application of a norm.
Norms can be defined usually in two different
contexts, which are environment or organization. A
norm defined in a context should be fulfilled only by
agents executing in that context.
A norm is also related with a condition, which
determines the period during which a norm is active.
The conditions in Belchior and da Silva (2017a,
2017b) are runtime events, such as, execution of an
action by an agent, a fact that become true for an
agent, the fulfillment or violation of a norm and the
activation or deactivation of a norm. We have
considered two kinds of conditions: after condition,
and before condition. A norm can have one before
condition, one after condition, both of them or no
condition. Therefore, a norm can have one of the five
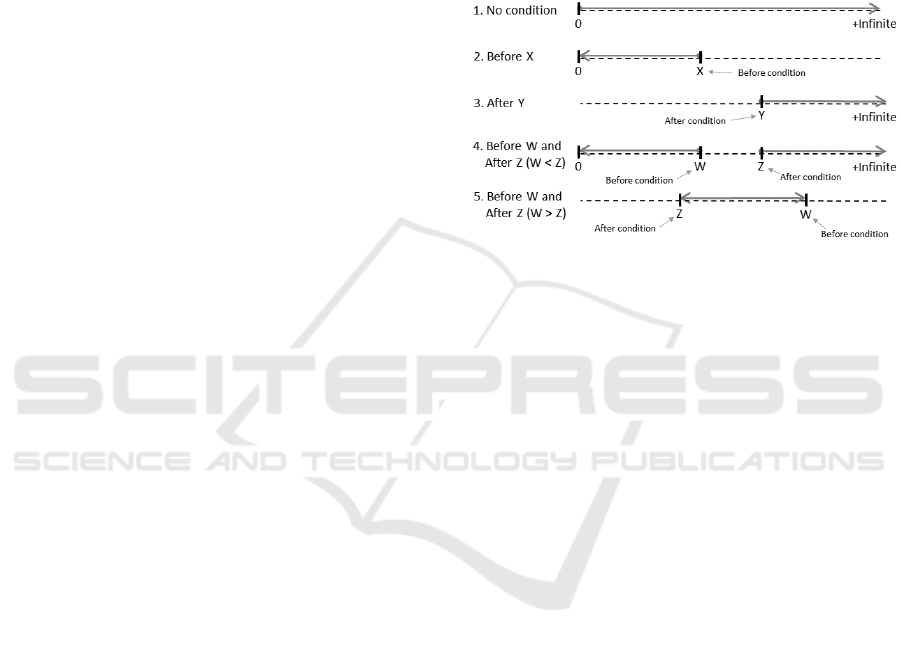
types of activation intervals illustrated in Figure 1.
Figure 1: Five types of activation intervals.
The first type is when a norm has no condition and
is always active. Its activation interval starts at time
zero and lasts until +infinite, i.e., the norm is always
active until the ending of the system execution. The
second type refers to a norm associated with only one
before condition. This interval starts from zero and
lasts until whenever that condition happens in the
system. The third type represents a norm with only
one after condition and the interval starts whenever
that condition happens and lasts until +infinite. The
fourth and fifth types refer to a norm associated with
both before and after conditions. They differ each
other by the moment the conditions happen in the
system. If the before condition happens first, then the
norm activation period is characterized by the fourth
interval type. Otherwise, the norm activation period
is represented by the fifth interval type.
The detection mechanism proposed in Belchior
and da Silva (2017b) identifies potential conflicts that
can be arisen depending on the execution order of
runtime events referred in the norm conditions. The
detection mechanism calculates all possible
combinations of those events by permuting the
positions of each event referred in the norms. The
output is potential normative conflicts along with
execution scenarios where the conflict may exist if
those scenarios would be executed in the system.
These execution scenarios are composed by an
ordered list of events, referred in the norm conditions,
which caused the conflict.
Strategies for Resolving Normative Conflict That Depends on Execution Order of Runtime Events in Multi-Agent Systems
217
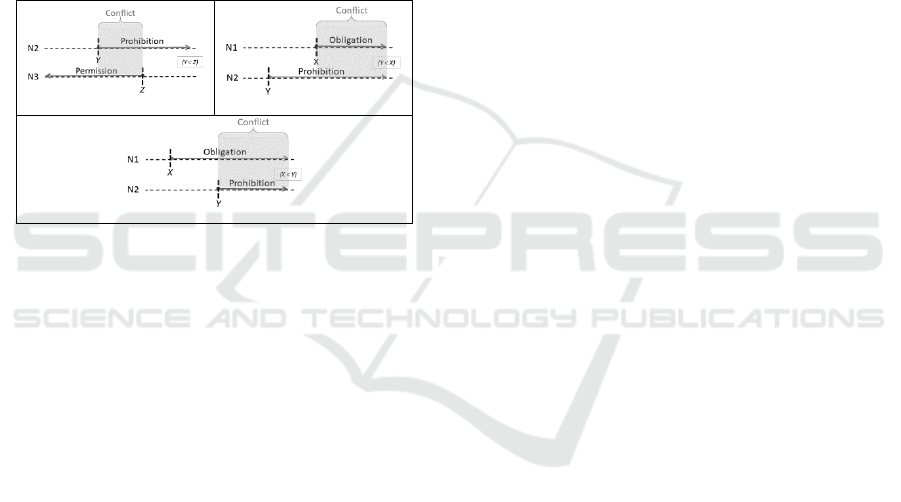
For example, let us consider that there are three
norms n1, n2 and n3, defined as follows. Norm n1
obligates agent ag to perform action ac after an event
X, norm n2 prohibits the same agent from performing
the same action after an event Y and norm n3 is a
permission that authorizes the same agent to perform
the same action, but before an event Z. The detection
mechanism produces the following potential conflicts
followed by their execution scenarios, which are
graphically illustrated in Figure 2.
• Conflict between n2 and n3 if execution
order is: Y happens before Z, as shown in (a);
• Conflict between n1 and n2 if execution
order is: X happens after Y, as shown in (b);
• Conflict between n1 and n2 if execution
order is: X happens before Y, as shown in (c);
(a)
(b)
(c)
Figure 2: Scenarios of potential conflicts.
As can be seen, independently of the execution
order of X and Y, there is going to be a conflict
between norms n1 and n2. In addition, the conflict
detection identified a normative conflict between
norms n2 and n3 when the execution order in the
system is event Y happening before Z.
3 CONFLICT RESOLUTION
We proposed two approaches to resolve the
normative conflicts described in section 2. The first
approach resolves the conflict in design time by
eliminating the overlaps between two norms in
conflict. The second approach extends an existing
automated planning algorithm (Ghallab et al., 2004)
in order to get plans that do not produce sequences of
conflicting actions. The second approach resolves the
conflict at runtime and it can be used when the events
related in the norms are only actions. These
approaches are detailed in the following sections.
3.1 Eliminating Conflicting Activation
Intervals
The first approach resolves the normative conflicts at
design time. The resolution mechanism resolves all
normative conflicts by eliminating the overlap of
pairs of norms in conflict based on four strategies,
described later in this section. The resolution
mechanism receives, as input, a set of norms and one
pair of norms in conflict along with an ordered list of
events that caused the conflict, returned by detection
approach. The resolution mechanism chooses one
norm of the pair and applies one or more strategies,
depending on the types of activation intervals of the
pair of norms in conflict. Unless the activation
interval of the conflicting norms are identical, our
mechanism chooses to change the norm where the
result does not eliminate the entire norm. After
applying the strategies, the result are new norms that
are created to replace one of the original conflicting
norms in order to eliminate the conflict. The new
norms are added to the set of norms and the old one
is removed. The detection mechanism is called again
and the resolution mechanism receives the new set of
norms and another pair of norms in conflict along
with an ordered list of events that caused the conflict.
These steps are repeated until the detection
mechanism does not return any conflict.
Figures 3-11 illustrate different kinds of conflict
and resolution strategies. The parts with “X” in the
figures represent conflicting activation intervals,
which are removed during the resolution process. The
circled parts in the figures indicate the new norms that
are added after the resolution process.
We defined four strategies to eliminate the
conflict, which are used by the resolution algorithm.
Let n1 and n2 be a pair of norms in conflict. Each
strategy, except the first one, changes somehow the
after and before conditions of the norms. The four
strategies are defined as follow.
• Strategy 0: One of the norms in conflict are
removed by taking into account its modality
and the modality of the other norm. There
are several lines of research that also choose
to curtail/remove a conflicting norm
according to its modality, such as Kagal and
Finin (2007), Gaertner et al. (2007) and Oren
et al. (2008). We assume that when a conflict
involves a prohibition and a permission, the
permission is removed; and when a conflict
involves a prohibition and an obligation, the
prohibition is removed. However, the
decision to remove a norm according to its
modality is dependent on the requirements
ICAART 2018 - 10th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
218

of the system addressed and the order of
relevance of the modalities of the norms
could be easily changed by the system
designer (Gaertner et al., 2007).
• Strategy 1: Norm n1 is removed and a new
norm n1' is included in the set of norms. The
norm n1’ is a copy of n1, but whose after
condition is the before condition of n2 and
before condition is the after condition of n2.
• Strategy 2: Norm n1 is removed and a new
norm n1' is added in the set of norms, which
is a copy of n1, but its before condition is
changed to be the after condition of n2.
• Strategy 3: Norm n1 is removed and a new
norm n1’ is included in the set of norms,
which is a copy of n1, but its after condition
is changed to be the before condition of n2.
The resolution mechanism applies one or more
strategies, depending on the types of activation
intervals of the pair of norms in conflict, detailed as
follow. We consider a combination of all possible
types of activation intervals to decide how to change
the after and before conditions of the norms. When
both conflicting norms are active exactly in the same
intervals, the resolution mechanism apply Strategy 0
in order to remove the overlap. This specific case
occurs when the conflict involves norms whose
activation intervals are type 1 (norms without before
and after conditions) or when after/before conditions
of the conflicting norms are the same, i.e., norms
whose activation intervals are exactly the same.
When a conflict involves a norm n1 whose
activation interval is type 1 and a norm n2 whose
activation interval is types 2, 3, 4 or 5, the strategy 1
can be used to solve the conflict. It is also the case
when n1 has activation interval type 2 and n2 has
activation interval type 3. Figure 3 illustrates those
cases. As mentioned above, the resolution mechanism
chooses to change the norm where the result does not
eliminate the entire norm. Thus, norm n1 is selected
in Figures 3.a, 3.b, 3.c and 3.d. In Figure 3.e, the
resolution mechanism could choose either norm,
since it does not eliminate neither one. In this case,
the first norm was selected.
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
(e)
Figure 3: Conflict resolution involving activation interval
type 1 and type 2 (a), type 1 and type 3 (b), type 1 and type
4 (c), type 1 and type 5 (d), and type 2 and type 3 (e), all
using Strategy 1.
When both conflicting norms n1 and n2 have
activation intervals type 2, assuming that the after
condition of n1 occurs before the after condition of
n2, a new norm n1' is created by using Strategy 2. The
norm n1' is a copy of n1, but its before condition (an
empty condition) is changed to be the after condition
of n2 (see Figure 4.a). After that, the new norm n1' is
included in the set of norms and n1 is removed. When
both conflicting norms have activation intervals type
3, assuming that before condition of n1 occurs after
the before condition of n2, the resolution mechanism
uses Strategy 3 for solving the conflict (Figure 4.b).
(a)
(b)
Figure 4: Conflict resolution involving activation intervals
type 2 (a) by using Strategy 2 and (b) activation intervals
type 3 by using Strategy 3.
When the conflict involves a norm n1 whose
activation interval is type 2 and a norm n2 whose
activation interval is type 4, the resolution mechanism
uses Strategy 2 and Strategy 3 for solving the conflict.
By using Strategy 3, a copy of n1, called n1', is
created but its after condition is changed to be the
before condition of n2 (see Figure 5.a). If the after
condition of n1 occurs before the after condition of
n2, in addition of creating n1', a new norm n1'' is also
created by using Strategy 2. The norm n1'' is a copy
of n1, but its before condition (an empty condition) is
changed to be the after condition of n2 (see Figure
5.b). After that, the new norms n1' and n1'' are
included in the set of norms and n1 is removed.
(a)
(b)
Figure 5: Conflict resolution involving activation interval
type 2 and type 4 (a) by using Strategy 3 and (b) by using
Strategy 2 and 3.
When the conflict involves a norm n1 whose
activation interval is type 2 and a norm n2 whose
activation interval is type 5, the resolution mechanism
uses Strategy 1, Strategy 2 or Strategy 3 for resolving
the conflict. If n1 has an after condition that occurs
after the after condition of n2, Strategy 3 is adopted.
In the Strategy 3, a copy of n2, called n2', is created
and its after condition is changed to be the before
condition of n1 (an empty condition). In addition of
creating n2', a new norm n2'' is created by using
Strategy 2. The norm n2'' is a copy of n2, but its
before condition is changed to be the after condition
of n1 (see Figure 6.a). Note that, the activation
Strategies for Resolving Normative Conflict That Depends on Execution Order of Runtime Events in Multi-Agent Systems
219

interval of the norm n1 is contained within the
activation interval of the norm n2 and, for this reason,
we chose to modify the activation interval of n2,
avoiding n1 to be completely removed.
If the after condition of n1 is the same of n2, only
n2' is created. The new norms n2' and n2'' are
included in the set of norms and n2 is removed. On
the other hand, if the after condition of n1 occurs
before the before condition of n2, only a new norm
n1' is created by using Strategy 1 (see Figure 6.b). The
norm n1' is included in the set of norms and n1 is
removed. However, if the after condition of n1 occurs
after the before condition of n2 and before the after
condition of n2, a new norm n1' is created by using
Strategy 2 (see Figure 6.c).
(a)
(b)
(c)
Figure 6: Conflict resolution involving activation interval
type 2 and type 5 by using (a) Strategy 2 and Strategy 3, (b)
Strategy (1), and (c) Strategy 2.
When the conflict involves a norm n1 whose
activation interval is type 3 and a norm n2 whose
activation interval is type 4, the resolution mechanism
uses Strategy 2 and Strategy 3 for resolving the
conflict. A new norm n1' is created by using Strategy
2, i.e., n1' is a copy of n1, but its before condition is
changed to be the after condition of n2 (see Figure
7.a). If the before condition of n1 occurs after the
before condition of n2, in addition of creating n1', a
new norm n1'' is created by using Strategy 3. Norm
n1'' is a copy of n1, but its after condition (an empty
condition) is changed to be the before condition of n2
(see Figure 7.b).
(a)
(b)
Figure 7: Conflict resolution involving activation intervals
type 3 and type 4 by using Strategy 2 (a), and by using
Strategy 2 and Strategy 3 (b).
When the conflict involves a norm n1 whose
activation interval is type 3 and a norm n2 whose
activation interval is type 5, the resolution mechanism
uses Strategy 1, Strategy 2 and Strategy 3. If the
before condition of n1 occurs before the before
condition of n2, two new norms n2' and n2'' are
created, where both norms are copies of n2, but the
after condition of n2'' is changed to be the before
condition of n1 (Strategy 3) and the before condition
of n2' is changed to be the after condition of n1 (an
empty condition) (Strategy 2) (see Figure 8.a). On the
other hand, if the before condition of n1 occurs after
the before condition of n2 and before the after
condition of n2, a new norm n1' is created by using
Strategy 3 (see Figure 8.b). Otherwise, if the before
condition of n1 occurs after the after condition of n2
or if the before condition of n1 is the after condition
of n2, a new norm n1' is created by using Strategy 1
(see Figure 8.c). Otherwise, if the before condition of
n1 is the before condition of n2, a new norm n2' is
created by using Strategy 2 (see Figure 8.d).
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
Figure 8: Conflict resolution involving activation interval
type 3 and type 5 by using Strategy 2 and Strategy 3 (a), by
using Strategy 3 (b), by using Strategy 1 (c), and by using
Strategy 2 (d).
When both norms involved in the conflict have
activation intervals type 4, the resolution mechanism
uses Strategy 2 and Strategy 3 for resolving the
conflict. If the before condition of n1 occurs after the
before condition of n2 and the after condition of n1
occurs after the after condition of n2 or n1 and n2
have the same after condition, a new norm n1' is
created by using Strategy 3 (see Figure 9.a).
Otherwise, if the after condition of n2 occurs after the
after condition of n1 and the before condition of n2
occurs before the before condition of n1, in addition
of creating n1', a new norm n1'' is created by using
Strategy 2 (see Figure 9.b). On the other hand, if the
after condition of n2 occurs after the after condition
of n1 and the before condition of n2 occurs after the
before condition of n1 or n1 and n2 have the same
before condition, only n1' is created (see Figure 9.c).
(a)
(b)
(c)
Figure 9: Conflict resolution involving activation intervals
type 4 by using Strategy 3 (a), by using Strategy 3 and 2 (b),
and by using Strategy 2 (c).
When the conflict involves a norm n1 whose
activation interval is type 4 and a norm n2 whose
activation interval is type 5, the resolution mechanism
uses Strategy 1, Strategy 2 and Strategy 3 for
resolving the conflict. If the after condition of n1
occurs before the before condition of n2 and the
before condition of n1 occurs after the after condition
of n2, the Strategy 1 is adopted for creating a new
norm n1' (see Figure 10.a). Otherwise, if the after
ICAART 2018 - 10th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
220

condition of n1 occurs before the before condition of
n2, and the before condition of n1 occurs before the
before condition of n2 or the before condition of both
norms are the same, a new norm n2' is created by
using Strategy 2. If the before conditions of n1 and n2
are not the same, in addition of creating n2', a new
norm n2'' is created by using Strategy 3 (see Figure
10.b). On the other hand, if the after condition of n1
occurs after the after condition of n2 or n1 and n2
have the same after condition, a new norm n2' is
created by using Strategy 3. If the after condition of
n1 and n2 are not the same, in addition of creating n2',
a new norm n2'' is created by using Strategy 2 (see
Figure 10.c).
(a)
(b)
(c)
Figure 10: Conflict resolution involving activation interval
type 4 and type 5 by using Strategy 1 (a), and by using
Strategy 2 and Strategy 3 (b) (c).
When both norms involved in the conflict have
activation intervals type 5, Strategies 1, 2 and 3 are
adopted for solving the conflict. If the before
condition of n1 occurs after the after condition of n2,
a new norm n1' is created by using Strategy 1 (see
Figure 11.a). However, if the before condition of n2
occurs after the after condition of n1, a new norm n1'
is created by using Strategy 1 (see Figure 11.b).
Otherwise, if the before condition of n2 occurs after
the before condition of n1 and the after condition of
n2 occurs before the after condition of n1, two new
norms n2' and n2'' are created, where both norms are
copies of n2, but the after condition of n2' is changed
to be the before condition of n1 (Strategy 3) and the
before condition of n2'' is changed to be the after
condition of n1 (Strategy 2) (see Figure 11.c).
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
(e)
Figure 11: Conflict resolution involving activation intervals
type 5 by using Strategy 1 (a) (b), by using Strategy 2 and
Strategy 3 (c), by using Strategy 2 (d), and by using Strategy
3 (e).
On the other hand, if the before conditions of n1
and n2 are the same, assuming that the after condition
of n1 occurs before the after condition of n2, a new
norm n1' is created by using Strategy 2 (see Figure
11.d). Otherwise, if the after conditions of n1 and n2
are the same, assuming that the before condition of n1
occurs before the before condition of n2, a new norm
n2' is created by using Strategy 3 (see Figure 11.e).
The main structure of the resolution algorithm is
described in Algorithm 1. It invokes the function
assignArbitraryTime (line 2) that assigns arbitrary
values to the events received as input according to a
conflicting order returned by the detection
mechanism and creates a copy of the original set of
norms (line 3). After that, it invokes the function
removeOverlapping that decides which resolution
strategy to choose. Note that, removeOverlapping is
invoked two times, when the first time does not
modify the set of norms. In the second time, n1 and
n2 are passed to the function removeOverlapping in
different orders (lines 4 to 6) to guarantee that all
possible combinations of kinds of conflict are
considered. Finally, Algorithm 1 returns the copy of
the original set of norms (setOfNorms') after
removing the normative conflict between n1 and n2.
Algorithm 1: Algorithm that solves conflicts between
two norms and returns the set of norms without the
given conflict.
Input: n1, n2: Norms in conflict, setOfNorms: Set of
norms, listOfConditions: Ordered list of conditions
Output: setOfNorms': Set of norms without the given
conflict
1. function solveConflicts(n1, n2, setOfNorms,
listOfConditions)
2. assignArbitraryTime(listOfConditions);
3. setOfNorms' ← setOfNorms;
4. removeOverlapping(n1, n2, setOfNorms');
5. if (setOfNorms'==setOfNorms) then
6. removeOverlapping(n2, n1, setOfNorms');
7. return setOfNorms';
3.2 Resolution based on Artificial
Intelligence Planning
The second approach resolves the normative conflict
described in Section 2 by avoiding them at runtime.
We propose to extend an existing automated planning
algorithm (Ghallab et al., 2004) in order to get plans
that do not produce sequence of conflicting actions.
The detection conflict approach outputs sequences of
actions that would cause a normative conflict.
Therefore, the planner must find a plan that does not
contain any of the sequence of actions returned by the
normative detection approach. That way, at runtime,
the agents would never perform actions that would
cause normative conflict. This second approach can
be used when the events related in the norms are
actions or can be represented as actions.
Artificial Intelligence Planning is the task of
coming up with a sequence of actions that will
Strategies for Resolving Normative Conflict That Depends on Execution Order of Runtime Events in Multi-Agent Systems
221

achieve a goal (Russel and Norvig, 2003). A planning
problem is represented by states, actions and goals.
Planners decompose the world into logical conditions
and represent a state as a conjunction of positive
literals. A goal is a partially specified state,
represented as a conjunction of positive ground
literals. A propositional state s satisfies a goal g if s
contains all the atoms in g (and possibly others). An
action is specified in terms of the preconditions that
must hold before it can be executed and the effects
that ensue when it is executed.
In order to demonstrate this second resolution
approach, we choose to extend the forward-search
planning algorithm (Ghallab et al., 2004), because it
is one of the simplest planning algorithms. The
forward-search planning algorithm searches forward
from the initial state of the world to try to find a state
that satisfies the goal formula. Algorithm 2 extends
the forward-search planning algorithm in lines 7 to
12. After choosing an action from applicable action
set (line 9), the algorithm checks if that action added
to the current plan p would cause any normative
conflict by calling isConflictingPlan function. If so,
that action is removed from applicable action set (line
11) and a new action are chosen. This repeats until it
finds a no conflicting plan or the applicable set of
actions is empty. Algorithm 3 checks if a plan p
would generate any normative conflict by verifying if
any sequence of conflicting actions returned by
detection conflict approach is in plan p (line 4). If that
is the case, the algorithm returns true. Otherwise, it
returns false.
Algorithm 2: Free conflict planning algorithm
Input: O: Actions, S
0
: Start State, G: Goal State
Output: p: No conflicting plan
1. function freeConflictPlan(O, S
0
, G)
2. S ← S
0
3. p ← the empty plan
4. loop
5. if S satisfies G then return p
6. applicable ← {a | a is a ground instance of an
operator in O, and precond(a) is true
in s}
7. do
8. if applicable = ∅ then return failure
9. nondeterministically choose an action a ∈
applicable
10. conflicting ← isConflictingPlan(p . a)
11. if conflicting then remove a from applicable
12. while conflicting
13. S ← 𝛾(S, a)
14. p ← p . a
15. return p
Algorithm 3: Checks if a plan contains conflicting
actions.
Input: p: Plan
Output: An boolean value stating if plan p would
generate any normative conflict or not
1. function isConflictingPlan(p)
2. SCA ← all sequences of conflicting actions
3. foreach sequence s ∈ SCA do
4. if s in p then return true
5. return false
4 RELATED WORK
In the literature, there are several strategies applied to
resolve conflicts among norms of a multi-agent
system, as described in (Santos et al., 2017).
In the work described in Vasconcelos et al.
(2009), norms can have variable terms in their
definition that relate actions to constraints. The
authors assume that a normative conflict occurs when
the variables of a prohibition overlap with the
variables of an obligation or permission. They present
an algorithm for conflict resolution that manipulates
the constraints of norms to avoid overlapping values
of variables, i.e., it adds constraints to restrict the
scope of influence of one of the conflicting norms,
eliminating the normative conflict.
Similarly, the resolution method described in
Gaertner et al. (2007) and Vasconcelos et al. (2012)
also curtails the scope of influence of the norms after
verifying which values the norms cannot assume to
avoid the conflict. The authors curtail prohibitions but
state that the same mechanism can be applied to
curtail obligations. Our strategy differs from those
approaches because we reduce the scope of influence
by modifying the before/after conditions of the norms
while them change variables associated with the
actions being regulated.
The work detailed in Aphale et al. (2013) presents
strategies to solve conflicts based on standard
techniques and norm refinement. The standard
techniques consist of determining an order of norm
overruling after determining norm precedence, based
on three classical principles to resolve deontic
conflicts: lex posterior (the most recent norm is
prioritized); lex specialis (the most specific norm is
prioritized); and lex superior (the norm imposed by
the most important authority is prioritized)
(Vasconcelos et al., 2009). The strategy of norm
refinement uses planning, as in Sensoy et al. (2012),
to expire the activation interval of one of the
conflicting norms. In this case, an automated planner
searches for a plan that implies a state of the world in
which the expiration condition of one of the
ICAART 2018 - 10th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
222

conflicting norms holds. Our approach differs from
the one described in Aphale et al. (2013) because we
use a planner to avoid certain actions to be performed.
In the research described in Günay and Yolum
(2013), obligations and prohibitions are represented
through commitments and the conflicts are solved by
changing the activation condition of the
commitments.
Although the related approaches also reduce the
scope of influence of the norms or use a method based
on planning to solve the conflicts, none of them
focuses on conflicts that depends on execution order
of runtime events in multi-agent systems.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Norms are being used in multi-agent systems to
control the behavior of software agents, without
restricting their autonomy. It is important taking into
account the possible existence of normative conflicts
in MAS regulated by multiple norms. A normative
conflict arises when the fulfilment of one norm causes
the violation of another. This paper presented two
approaches to resolve normative conflicts that
depends on execution order of runtime events in
multi-agent systems. The first approach eliminates, at
design time, the overlaps between two norms in
conflict by changing the activation intervals of the
conflicting pair. The result is a set of norms free of
conflict. The second approach resolves the normative
conflict by extending an existing automated planning
algorithm in order to get plans that do not produce
sequence of conflicting actions. Therefore, the
planner would generate sequence of actions that are
free of normative conflict. As future work, we intend
to extend the proposed approach to support several
before and after conditions in the norm definition. In
this version, the norm definition only supports one
after and one before conditions. Moreover, we would
like to exploit our mechanisms in real world
scenarios.
REFERENCES
Aphale, M., Norman, T. J., & Sensoy, M., 2013. Goal-
directed policy conflict detection and prioritisation. In
Aldewereld, H., Sichman, J.S., (Eds), Coordination,
organisations, institutions and norms in agent systems
VIII, volume 7756 of Lecture notes in computer science
(pp. 87-104), Springer.
Belchior, M., & da Silva, V. T. (2017a). Detection of
Runtime Normative Conflict based on Execution
Scenarios. ICAS 2017, 21.
Belchior, M., & da Silva, V. T. (2017b). Detection of
Normative Conflict that Depends on Execution Order
of Runtime Events in Multi-Agent Systems. In WI’17,
IEEE/WIC/ACM International Conference on Web
Intelligence. August 23-26, 2017, Leipzig, Germany.
Gaertner, D., Garcia-Camino, A., Noriega, P., Rodriguez-
Aguilar, J. A., & Vasconcelos, W. W., 2007.
Distributed norm management in regulated multiagent
systems. In Proceedings of the 6th international joint
conference on Autonomous agents and multiagent
systems. ACM, p. 90.
Ghallab, M., Nau, D., & Traverso, P., 2004. Automated
Planning: theory and practice. Elsevier.
Günay, A., & Yolum, P., 2013. Engineering conflict-free
multiagent systems. In First international workshop on
engineering multiagent systems (EMAS).
Kagal, L., & Finin, T. 2007. Modeling conversation policies
using permissions and obligations. Autonomous Agents
and Multi-Agent Systems, 14(2), 187–206.
Kollingbaum, M. J., & Norman, T. J., 2004. Strategies for
resolving norm conflict in practical reasoning. In ECAI
workshop coordination in emergent agent societies
(Vol. 2004).
Oren, N., Luck, M., Miles, S., & Norman, T. J. 2008. An
argumentation inspired heuristic for resolving
normative conflict. In 5th international workshop on
coordination, organisations, institutions and norms in
agent systems (COIN@AAMAS 2008).
Russel, S., & Norvig, P. Artificial Intelligence: A Modern
Approach, 2003. EUA: Prentice Hall.
Santos, J. S., Zahn, J. O., Silvestre, E. A., Silva, V. T., &
Vasconcelos, W. W., 2017. Detection and resolution of
normative conflicts in multi-agent systems: a literature
survey. Autonomous Agents and Multi-Agent Systems,
1-47.
Sensoy, M., Norman, T. J., Vasconcelos, W. W., & Sycara,
K., 2012. OWL-POLAR: A framework for semantic
policy representation and reasoning. Web Semantics:
Science, Services and Agents on the World Wide Web,
12, 148-160.
Vasconcelos, W. W., García-Camino, A., Gaertner, D.,
Rodríguez-Aguilar, J. A., & Noriega, P., 2012.
Distributed norm management for multi-agent systems.
Expert Systems with Applications, 39(5), 5990–5999.
Vasconcelos, W. W., Kollingbaum, M. J., & Norman, T. J.,
2009. Normative conflict resolution in multi-agent
systems. Autonomous agents and multi-agent systems,
19(2), 124-152.
Vasconcelos, W. W., & Norman, T. J., 2009. Contract
formation through preemptive normative conflict
resolution. In Proceedings of the 2009 conference on
artificial intelligence research and development:
Proceedings of the 12th international conference of the
catalan association for artificial intelligence (pp. 179–
188). Amsterdam: IOS Press.
Strategies for Resolving Normative Conflict That Depends on Execution Order of Runtime Events in Multi-Agent Systems
223
