Mueller Optical Coherence Tomophraphy Technique for
Non-Invasive Glucose Monitoring
Tseng-Lin Chen
1
, Quoc-Hung Phan
1
and Yu-Lung Lo
2,*
1
Department of Mechanical Engineering, National Cheng Kung University, Taiwan 70101, Taiwan
2
Advance Optoelectronics Technology Centre, National Cheng Kung University, Taiwan 70101, Taiwan
Keywords: Optical Coherence Tomography, Non-Invasive Glucose Sensing.
Abstract: A new and novel technique for non-invasive (NI) glucose sensing based on Mueller optical coherence
tomography (OCT) technique is proposed. The feasibility of the proposed technique is demonstrated by
detecting the optical rotation angle and depolarization index of phantom solution containing de-ionized
water (DI), glucose solutions with concentrations ranging from 0~4000 mg/dL and 0.02% lipofundin. The
practical applicability of the proposed technique is demonstrated by measuring the optical rotation angle and
depolarization index properties of the human fingertip of normal healthy volunteers.
1 INTRODUCTION
With rising obesity levels around the world, diabetes
has emerged as a major concern with serious health
and economic implications. Consequently, reliable
methods for its testing and diagnosis are urgently
required. Of the various methods available, NI
techniques based on measuring the glucose
concentration in human blood are particularly
attractive due to their accuracy and painless aspects.
However, NI devices are presently not widely used
in clinical diabetes applications due to their poor
precision, robustness, stability and analytical
performance compared to that of conventional blood
glucose meters. Consequently, much work remains
to be done in improving the performance of NI
glucose monitoring systems such that they provide a
more viable approach for clinical diagnosis.
OCT is a powerful technique for performing the
in-depth cross-sectional imaging of scattering-type
media. Moreover, recent enhancements to the
traditional OCT structure now make possible the
incorporation of polarization control into the system
such that the anisotropic properties of certain optical
materials can be observed. In this study, an
analytical model based on a hybrid Mueller matrix
formalism for extracting the optical rotation angle
and depolarization index of anisotropic optical
samples. The validity of the proposed technique is
demonstrated by detecting optical rotation angle of
phantom solution samples and on human fingertip of
volunteers.
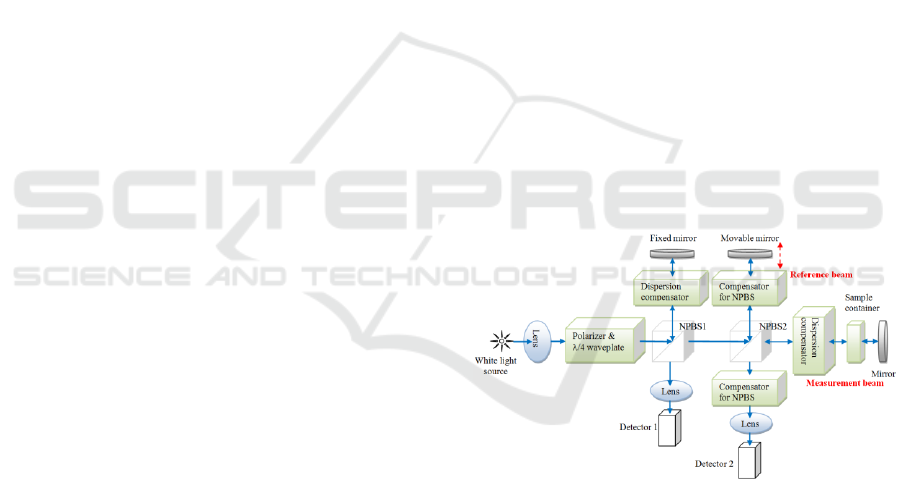
2 MUELLER OCT SYSTEM
Figure 1: The schematic illustration of Mueller OCT
system.
The schematic of the proposed Mueller OCT system
is illustrated as Fig. 1. As shown in Fig 1, the OCT
system additionally includes two compensators for
non-polarized beam splitter (NPBS), each
comprising two quarter-waveplates and one half-
waveplate, designed to compensate the polarization
distortion induced by the non-perfect beam splitters.
In performing experiments, signals obtained by
detector 2 are employed to measure anisotropic
properties of the sample by calculating the amplitude
of the interferometric signal. To calculate the
Mueller matrix of the sample, the quarter-wave plate
174
Chen, T-L., Phan, Q-H. and Lo, Y-L.
Mueller Optical Coherence Tomophraphy Technique for Non-Invasive Glucose Monitoring.
DOI: 10.5220/0006601201740177
In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Photonics, Optics and Laser Technology (PHOTOPTICS 2018), pages 174-177
ISBN: 978-989-758-286-8
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All r ights reserved

and polarizer shown in Fig. 1 are rotated to obtain
four different polarization states of the light incident
on the sample, namely H (horizontal linear
polarization), V (vertical linear polarization), P (45°
linear polarization), and R (right-circular
polarization). In addition, the variable wave plate in
the reference arm is adjusted to change the
polarization state of the reference beam sequentially
to H, V, P, and R, respectively, for each of the four
incident lights. Thus, a total of 16 interferometric
signals are produced with which to investigate the
sample and detected by detector 2. The 16 elements
in the 44 Mueller matrix are then computed as
(Liao, 2015)
11 12 13 14
21 22 23 24
31 32 33 34
41 42 43 44
11 11
21 21
11 12 31
2 2 2 2
2 2 2 2
2 2 2 2 4 2 2 4 2
M M M M
M M M M
M M M M
M M M M
HH HV VH VV HH HV VH VV PH PV M RH RV M
HH HV VH VV HH HV VH VV PH PV M RH RV M
HP VP M HP VP M PP PH PV M RP RH
M
31
11 12 41 41
2
2 2 2 2 4 2 2 4 2 2
RV M
HR VR M HR VR M PR PH PV M RR RH RV M
(1)
3 DIFFERENTIAL MUELLER
MATRIX FORMALISM
An optical sample can be described by the matrix
formulation S=MS
where S is the Stokes vector of
the output light, M is the 44 Mueller matrix of the
sample, and S
is the Stokes vector of the input light.
Given the use of five different input lights, is
providing the sufficient equation to determine the
complete Mueller matrix M of the sample. The
differential Mueller matrix can be obtained from an
Eigen value analysis of M as follow (Phan, 2017)
11 12 13 14
21 22 23 24
1
31 32 33 34
41 42 34 44
ln( )
D
MM
m m m m
m m m m
V
m V V
z
m m m m
m m m m
(2)
where V
M
and V
D
are the Eigenvectors and
Eigenvalues of Mueller matrix M, respectively. The
differential Mueller matrix of samples with circular
birefringence properties under consideration of
depolarization effect can be obtained as
'
'
1 0 0 0
0 0 2 0
0 2 0 0
0 0 0 1
v
CB
v
m
(3)
where and
v
are the optical rotation angle and
differential parameters described the the anomalous
depolarization. Thus, the optical rotation angle can
be determined as
23 32
,0 180
4
mm
(4)
And the depolarization index can be determined as
2 2 2
1 2 3
1 ,0 1
3
e e e
(5)
where e
1
, e
2
, e
3
are the diagonal elements of the
Mueller matrix describing the depolarization effects.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Glucose Concentration Detection
for Aqueous Phantom Samples
Figure 2: Experimental results for extracted values of for
the aqueous phantom samples with glucose concentration
ranging from 0-4000 mg/dL.
Glucose samples in phantom solution were prepared
using 100 ml glucose solution samples (100 mg/ml-
Merck Ltd) with concentration over the range of 0-
4000 mg/dL in 1000 mg/ml increments mixed with
0.02% lipofundin (lipofundin MCT/LC1 20%
BBraun). Figure 2 shows the experimental results
obtained for the optical rotation angle. As shown,
the optical rotation angle values increase linearly
with an increasing glucose concentration. The
standard deviation of the experimental values
obtained over four repeated tests for each glucose
sample was found to be 0.26. Furthermore, the
sensitivity of the measured values was determined
as 7.510
-5
(degree)/(mg/dl).
Mueller Optical Coherence Tomophraphy Technique for Non-Invasive Glucose Monitoring
175

Figure 3: Experimental results for extracted values of for
the aqueous phantom samples with glucose concentration
ranging from 0-4000 mg/Dl.
Figure 3 shows the experimental results obtained
for the depolarization index of the samples. As
shown, the depolarization index values decrease
linearly with an increasing glucose concentration.
The standard deviation of the experimental values
obtained over four repeated tests for each glucose
sample was found to be 0.04. Furthermore, the
sensitivity of the measured values was determined
as 1.510
-5
/(mg/dl).
4.1.1 NI Measurement of Glucose
Concentration on Human Fingertip
The practical feasibility of the proposed technique
was evaluated by measuring the optical rotation
angle and depolarization index of human fingertip of
four selected normal healthy volunteers. The
volunteers were asked to swallow sugar rich water
contained 75 gram sugar. The test was performed
before and 1 hours after volunteers consumed sugar
water. Figure 4 and 5 show the experimental results
for extracted and values of volunteer’s fingertip
over four repeated tests, respectively. As shown the
average extracted values increases after the
ingestion of sugared water for all volunteers other
than volunteer 3. Furthermore, the average extracted
values decreases after the ingestion of sugared
water for all volunteers. Therefore, the results are in
good qualitative agreement with the extracted values
for the aqueous phantom samples from section 4.1.
The high deviation might be contributed by the
imperfection of the optical elements, the calibration
procedure, the moisture of the skin and the change in
glucose concentration within the volunteer’s body
over the time. In overall, the feasibility of the
proposed technique for NI glucose monitoring is
confirmed.
Figure 4: experimental results for extracted values of of
fingertip of selected normal healthy volunteers
Figure 5: Experimental results for extracted values of of
fingertip of selected normal healthy volunteers.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The novel technique for NI glucose monitoring
based on Mueller OCT system has been proposed.
The proposed technique has measured the optical
rotation angle and depolarization index of samples
for detecting glucose concentration. The feasibility
of the proposed technique has been demonstrated by
detecting glucose concentration of aqueous phantom
solution over the range of 0-4000 mg/dl with 0.02%
lipofundin. The results have shown that the proposed
techniques enable to detect and with a sensitivity
of 7.510
-5
(degree)/(mg/dl) and 1.510
-5
/(mg/dl),
respectively. Furthermore, the practical application
of the proposed technique has been demonstrated by
measuring the optical rotation angle and
depolarization index of human fingertip of four
normal healthy selected volunteers. In general, the
proposed technique provides a potential tool for NI
PHOTOPTICS 2018 - 6th International Conference on Photonics, Optics and Laser Technology
176

glucose monitoring and diabetes diagnosis
applications.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial
support provided to this study by the Ministry of
Science and Technology of Taiwan (MOST) under
Grant Nos.104-2221-E-006-125-MY2, 104-2221-E-
006-114-MY2. The research was also supported in
part by the Ministry of Education, Taiwan, under the
“Aim for Top University Project” of National Cheng
Kung University (NCKU), Taiwan.
REFERENCES
Liao, C. C.., Lo, Y. L., 2015. Extraction of linear
anisotropic parameters using optical coherence
tomography and hybrid Mueller matrix formalism.
Optics Express.
Phan, Q. H.., Lo, Y. L., 2017. Differential Mueller matrix
polarimetry technique for non-invasive measurement
of glucose concentration on human fingertip. Optics
Express.
Mueller Optical Coherence Tomophraphy Technique for Non-Invasive Glucose Monitoring
177
