
Target Recognition Approach for Efficient Sensing in Wireless
Multimedia Sensor Networks
Manal Alsabhan and Adel Soudani
1
1
College of computer and information systems, Department of Computer Sciences, King Saud University, Riyadh, KSA
Keywords WMSN, Multimedia Sensing, Object Recognition, Low-power, Fourier Descriptors, Zernike Moments
Abstract In Wireless Multimedia Sensor Networks (WMSN), image-based sensing applications face the issue of
energy efficiency and the availability of resources. This issue leads to image sensing and transmission
severely exhausting the sensor energy, potentially flooding the network with unnecessary data at the
application level. Compression of the image fails to solve this issue efficiently, due to the complexities of
the algorithm. Thus, the approach of employing image sensing to detect an event of interest locally prior to
transmission of the Region of Interest (ROI) would avoid useless data transmission, and consequently save
energy. This approach promises to extend the life of the entire network while reducing the sensing time. The
main contribution of this work is to establish a low-complexity scheme for image sensing in WMSN. This
scheme based on 2D General Fourier shape descriptors for target recognition and notification to the end
user. This current paper outlines the specification of the proposed scheme and its implementation on
wireless multimedia sensors. It addresses the performances evaluation regarding time and energy
consumption. The results reveal the high levels of accuracy of the proposed approach in efficiently
recognizing the target and notifying the end user. It shows a significant performance that overcomes the
efficiency of alternative similar sensing approaches that have been proposed in the literature.
1 INTRODUCTION
Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) have a
number of limitations related to processing, storage,
and communication capabilities, which severely
restrict their adequacy for multimedia sensing and
communication. In the majority of the new
applications of IoT and advanced communication
systems, the low cost of WSNs leads to them being
viewed as an attractive technology. The deployment
of WMSN is very attractive in the context of remote
image-based target recognition and tracking
applications. However, issues of power consumption
are of fundamental concern in these systems, leading
to questions concerning their efficiency and raising
the need to design new low-power approaches to
deliver multimedia content with a certain level of
quality of service to the end user.
The literature has confirmed that, due to the
complexities of these algorithms, image
compression techniques employed in WMSN form
inefficient approaches for low-power sensing (Chefi
A, 2014). One attractive method of minimizing
power consumption and extending the lifetime of a
network is to apply a local event-based sensing and
detection scheme. One way to accomplish this
method is the use of an ROI descriptors, firstly, to
detect, locally, whether the image captures
phenomena of interest and secondly, to send the
minimum required data to the end user. This
approach reduces the transmitted data to the sink
node. Consequently, it preserves the energy of the
source sensor, along with that of the complete
network. This method is based on notifying the end
user solely when an interesting phenomenon has
been detected in the observation scenes. It requires
the detection of the presence of a new object,
recognizing the target and notifying the end user
with the minimum number of bytes to increase the
network lifetime. This requires the design of a low-
complexity approach for image-based target
recognition, in order to implement it in an efficient
manner in the context of WMSN. A potential
candidate, for this objective, is the application of
shape descriptors (i.e., General Fourier descriptors)
for their low levels of complexity and accuracy in
the recognition process (Yang et al., 2008)
Alsabhan, M. and Soudani, A.
Target Recognition Approach for Efficient Sensing in Wireless Multimedia Sensor Networks.
DOI: 10.5220/0006603900910098
In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Sensor Networks (SENSORNETS 2018), pages 91-98
ISBN: 978-989-758-284-4
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
91
The main contribution of this paper is to present a
promising new multimedia sensing-scheme, based
on the concept of event detection, employing 2D
General Fourier Descriptors as the feature’s
extraction method. The novelty of this scheme is its
ability to reduce communication overheads and per-
node power consumption, while also ensuring
efficient notification to the end user. Furthermore, it
addresses the performance of this scheme in relation
to efficient detection and low-energy processing.
This paper presents comparisons with related
solutions and demonstrates the power of the
proposed concept.
2 RELATED WORK
There are a number of contributions to the literature
addressing the design of efficient image-based
techniques for object recognition. However, these
primarily addressed computer-based applications,
and, as a result of design limitations, cannot be
adapted directly in sensors. Yang et al. (2008)
classified a number of approaches to the extraction
and representation of shape-based features according
to their processing methods. They presented a
number of different functions, i.e., a one-
dimensional function for shape representation;
polygonal approximation; a spatial interrelation
feature; moments; scale-space approaches; and
shape transform domains. This survey concluded
GFD techniques to be highly efficient and accurate
for object recognition.
Further research has attested to the efficiency of
employing GFD for feature extraction and
enhancing accuracy (Teague, 1980; AlSabhan,
2016). Zhang (2002) considered GFD an effective
detection method. However, he did not focus on
object detection and recognition in the context of
WMSN. Belongie et al. (2002), however, presented
a simple and accurate scheme for object matching in
the context of WMSN, based on the distance
between shapes, while Vasuhi et al. (2012)
employed the Haar wavelet for object feature
extraction. However, both works failed to address
the issue of power consumption. Zuo et al. (2012)
outlined a distributed two-hop clustered image
transmitting scheme, consisting of a trade-off
between computation and processing load, reflected
in enhancing the lifetime of the network. Irgan
(2014) employed hardware platforms for power
conservation (which have a high level of estimated
implementation costs) and made no consideration of
a scalable solution. Nikolakopoulos et al. (2013)
outlined a new scheme based on quadtree
decomposition for image compression, suggesting it
as an efficient solution for a low-power solution in
WMSN. Wang et al. (2008) outlined an artificial
immune system-based image pattern recognition.
This, however, contains very high levels of
associated energy consumption, rendering it
unsuitable for low-power processing.
3 IMAGE-BASED SENSING
SCHEME FOR TARGET
RECOGNITION
In the proposed approach, the sensor should be
capable of locally detecting the appearance of a new
object within the camera scene. It needs to decide
locally if the detected object is with interest to the
end user, followed by notifying the end user with a
few-bytes. The proposed concept is intended to
avoid transmitting multiple-images with the
potential to exhaust the local battery and load the
network with an unnecessarily high volume of data
as a result of the characteristics of multimedia
applications.
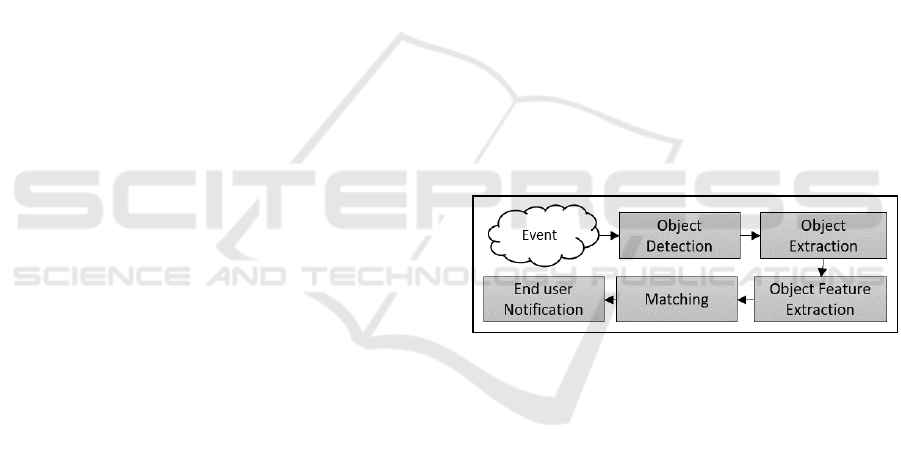
Figure 1: Structure of the image-based sensing scheme
based on GFD.
In order to achieve an efficient sensing scheme, the
design of the new approach focuses on addressing
the limitations of low-cost sensors, by ensuring: (1)
low computational complexity; (2) a low level of
required memory storage; and (3) an avoidance of
congesting the network bandwidth by limiting the
per-node communication overhead. These goals are
accomplished by allowing the end-user to remotely
configure the smart multimedia sensors by means of
target shape descriptors. Each sensor, subsequently,
begins to sense the surrounding environment in a
periodic manner. Once an event is detected, the
sensor commences the object detection and
extraction process internally from the captured scene
and applies feature extraction methods to obtain a
set of features vectors to match with a previously
memory loaded set. A notification is submitted to
the end user when the matching indicates significant
similarities. Otherwise, the sensed event is
SENSORNETS 2018 - 7th International Conference on Sensor Networks
92

discarded, and the sensor recommences the search
for an event. The structure of the proposed scheme
for object detection and recognition is described by
the sequential steps described in Figure1.
The proposed approach is a new scalable multimedia
sensing scheme capable of satisfying the constraints
of the limited energy and resources in WMSN. In
this approach, each multimedia sensor node
performs the sensing scheme for target detection and
recognition in an autonomous manner. It decides
whether the object appearing in the camera scene is
of interest to the end user, based on local
recognition-processing tasks. The basic assumption
of this approach is the reduction of node
communication activities through the radio link
while increasing local processing activities. Thus,
the capacity of this scheme to extend the per-node
lifetime depends on the complexity of the different
tasks involved during the processing cycle of the
detected object. The structure of proposed scheme
consists of the sequential steps as outlined below.
3.1 Detection of New Object
The detection of a new object is based on the
approach of background subtraction. It divides the
image into a set of blocks of eight by eight pixels.
The difference between the new image and the
background image is calculated at the pixel level
intensity changes, in order to detect a new object. If
the foreground block is noted by β
n
(j) and
background β
n-1
(j) respectively, then when the whole
difference through all the image blocks is greater
than a certain threshold (T
ther
), a new object should
be detected, as expressed in (1) (Lu, 2012).
(1)
3.2 Extraction of the Region of Interest
The set of blocks representing the ROI of useful
information in the image will be isolated to reduce
the processing load. Once the object is detected, the
scheme will extract set of blocks that form the useful
area and isolate it from unnecessary blocks. These
blocks will subsequently be transformed to binary
level for further processing to identify the shape (see
Figure 2). This step reduces both the memory
occupancy and energy consumption related to pixel
processing.
Figure 2: Binarizing useful extracted blocks.
3.3 Extraction of Feature’s Vectors
Our presented approach for extracting a set of
signature features vector is based on General Fourier
Descriptor (GFD). It is one of shape classification
and description approach, employed in a large
number of application fields based on image
processing, due to: (1) ease of computation; (2) low
complexity; (3) robustness to noise; and (4)
compactness. From a mathematical perspective, a
comparison with Zernike Moments (ZM) (i.e., a
well-known technique for describing shapes (Zhang
et al., 2002)) reveals that GFD has no redundant
features because there is no repetition and it permits
examination of features in both radial and angular
directions. These are also compared in the
implementation section below from the perspective
of in-node power consumption
.
GFD is primarily deployed to transform the shape
signature using Fourier transformation based on
signature region. Firstly, GFD transforms the input
image f(xi,yi) of size N*M where f defined by
{f(xi,yi): 1≤ i ≤ M, 1 ≤ j ≤ N} into a polar image
f(r,ө) using the following equations:
(2)
(3)
where and are the mass center of the shape.
They are calculated by the following equations:
(4)
(5)
Secondly, the Fourier transformation takes place in
order to extract the signature feature vector set,
Target Recognition Approach for Efficient Sensing in Wireless Multimedia Sensor Networks
93
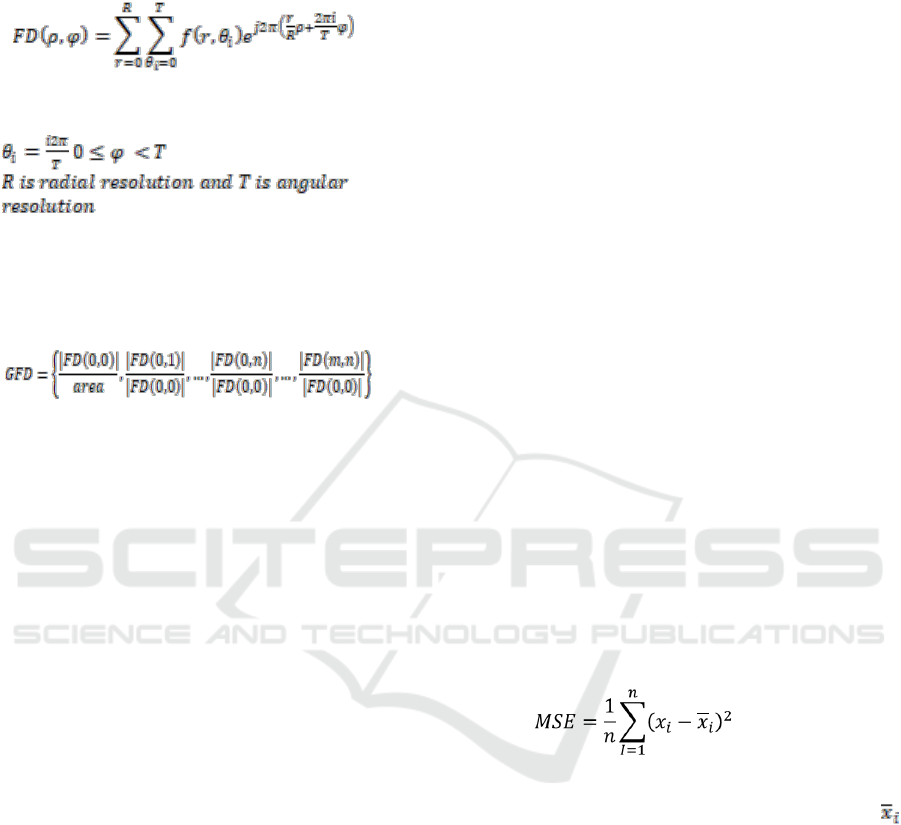
referred to as Fourier Descriptors (FD), using the
following equation:
(6)
Where ρ and φ reflect the image size,
, and
The FD is translation invariant. However, in order
to achieve the rotation and scaling invariant, a
normalization step should be applied to the extracted
feature vector set, as in the following equation:
(7)
where m is the maximum number of radius
frequencies, and n is the maximum number of
angular frequencies. To establish an efficient
signature description, Zhang et al. (2002)
recommended thirty-six GFD features, reflecting
four radial frequencies and nine angular frequencies.
The most important step is that of the extracted
shape vectors, which play a significant role in the
overall performance of the identification scheme. An
examination of the image based object identification
approach reveals a need to focus on how they
address the important challenges of WMSN, the
most significant of which are as follows.
3.3.1 Low Sensing Power Consumption
The processor consumes a considerable proportion
of power from the overall sensor resident battery. In
computational theory, there is a proportional
relationship between the total number of processor
clock cycles and the arithmetic and logic operations
undertaken in a microprocessor. This is also true of
the amount of power consumed.
3.3.2 Preserve Memory Capacity
Sensor nodes are equipped with a low memory
capacity, to ensure the memory size is not exhausted
by the extraction of the signature information. The
memory in the current scheme is preserved through
the set extracted signatures features being expressed
in a limited size (i.e., one feature vector requires
eight bytes, ensuring that thirty-six feature vectors
are required for 288 bytes).
3.3.3 Communication Overhead
The limited size of the extracted feature vector set
promises few communication overheads, while also
minimizing traffic over the bandwidth in comparison
to sending whole image bytes or employing the
compression method. An efficient sensing scheme
for object identification in WMSN is essential for
the consideration of limitations and challenges.
There are a large number of effective shape
descriptor approaches employed in the image
processing field for object identification and
classification, a minor set is also present (due to the
constraints of the sensor node’s design) capable of
being adapted in WMSN. These constraints are
divided into two factors: (1) low process capability
and (2) limited memory capacity. Further
approaches can be adapted for use in the context of
WMSN, but these require definite modifications in
node design, which raise the cost of implementation,
resulting in imperfect scalability.
3.4 Target identification
The Mean Square Errors (MSE) was employed to
identify whether the isolated signature forms a
promising target, in order to estimate the similarity
between the remotely loaded reference descriptors
within the local memory.
(8)
Where n represents the total vector set, x
i
denotes
the i
th
feature vector of the extracted signature and
denotes the i
th
feature vector of the reference. The
features vector set obtained from the previous step
was employed to establish the similarity with the
remotely loaded reference features vector set. If the
difference is less than certain threshold T
Difference
, the
detected object is declared as the target, and the
sensor notifies the user. Otherwise, the detected
object does not represent useful information to the
end user, and the image is therefore ignored.
3.5 End User Notification
Finally, when the sensor identifies the target, it
notifies the end user. Notification is undertaken
according to the requirements of remote user
SENSORNETS 2018 - 7th International Conference on Sensor Networks
94

applications. Thus, this step represents the potential
for achieving a considerable saving in time and
power-consumption by sending a single byte
message, a set of feature vectors or useful extracted
blocks from the image. On-demand notification
requests by the end user relieve the bandwidth from
congestion by minimizing both the volume of
transmitted data and the need for retransmitting in
case of error. The approach leads to unheavy traffic
load, thus prolonging the life of the entire network.
4 IMPLEMENTATION AND
PERFORMANCES ANALYSIS
4.1 Target Recognition Capabilities
The scheme based on the GFD algorithm using
Matlab was implemented to establish the efficiency
of the selected shape descriptor and demonstrate that
it satisfies the requirements of accurate recognition.
A set of images (AlSabhan, 2016) was employed to
evaluate the capability of the scheme in target
recognition to recognize an object under different
invariance conditions, i.e., rotation, scale, and
translation. The images employed were those in the
experiment of 64*64 and 128*128 grayscale eight
bpp. Figure 3 demonstrates the test image set, which
was composed of twelve images.
Figure 3: Testing images set: (1) original reference; (2)
Translated object to up; (3) to corner; (4) to down; (5)
Rotated object by 30°; (6) by 55°; (7) by 65°; (8) by 90°;
(9) maximize object by 55%; (10) maximize by 65%; (11)
minimize by 25%; and (12) minimize by 35%.
Based on the recommendations of Zhang et al.
(2002), the GFD radiance frequencies were set in
equation (6) to three, and angular frequencies to
eight, thus giving a total set of twenty-four different
features vectors. The features of these objects were
employed to calculate the similarity with the
reference target-image features vectors, using MSE
to identify the target. Figures 4 and 5 illustrate the
extracted features for all images in Figure 3 using
GFD and ZM (AlSabhan, 2016) techniques,
respectively.
Figure 4: Extracted vector set using GFD.
Figure 5: Extracted vector set using ZM.
In figures 4 and 5, curves represent by how much the
tested images are close to the reference, by
measuring the deviation of the signature features’
vectors from the reference features vector set using
MSE. These curves can be seen as being almost
identical using GFD or ZM, but GFD reveals more
accurate results with a neglected difference in
comparison to ZM for scaled objects, with a very
low difference, i.e., less than 1. This resulted from
the nature of the ZM computational algorithm,
which is insensitive to rotation only and needs to
normalize the object to a predefined scale ratio.
However, the use of a pre-processor step to establish
the object in normalization form overrides this
difference but increases the complexity of the
algorithm. ZM needs to consider the re-center of the
Target Recognition Approach for Efficient Sensing in Wireless Multimedia Sensor Networks
95
object and to return it to a predetermined scale size.
This pre-processing step is not mandatory in GFD,
due to the normalization equation (7) that drives the
GFD ability to be invariant to all object translation,
scaling and rotation, thus resulting in lower
processing complexity and energy consumption than
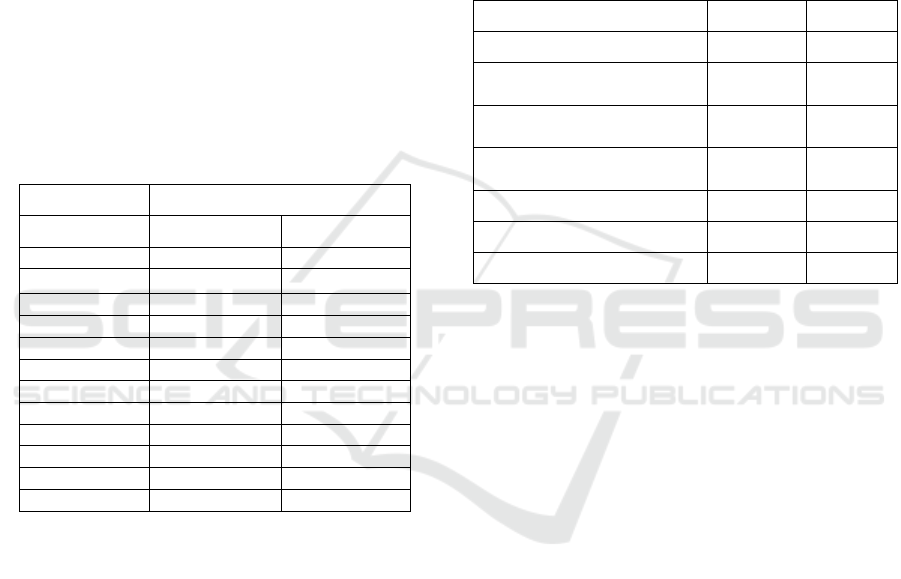
in ZM. Table 1 provides a summary of the capacity
of the proposed scheme to recognize the target
employing GFD and ZM methods. This reveals a
high accuracy in acknowledging that the target with
MSE almost equals zero under different positions,
including translation, rotation, and scaling. In ZM,
the scaled image loses some of its details and ZM is
highly sensitive to such differences. A comparison
between GFD and ZM results revealed that GFD
feature vectors contain less deviation from the
reference vector set in comparison to the ZM results,
and in particular for scaled images.
Table 1: MSE between features of the target and the new
object extracted by GFD and ZM techniques.
Mean Square Error (MSE)
Image Number
ZM
GFD
2
0.0001
5.410-06
3
0.0001
3.00E-06
3
0.0002
9.10E-07
4
0.0001
2.50E-07
5
0.00001
6.00E-07
6
0.0002
1.10E-05
7
0.0001
1.80E-06
8
0.0004
1.00E-05
9
0.0007
1.00E-06
10
0.0045
1.40E-07
11
0.0004
1.00E-05
12
0.0048
5.10E-07
These results establish that the proposed scheme
provides a robust and accurate method of shape
descriptors to recognize a specific target. It also
establishes a high capacity for capturing significant
features of the sensed object while minimizing the
complexity of the algorithm by its invariant
characteristics, leading to the potential for lower
power consumption.
4.2 Energy Consumption Evaluation
The efficiency of the proposed image-based
sensing scheme for low-power target recognition
should be evaluated in relation to its capability to
save energy in the camera node, consequently
extending the lifetime of the network, as well as
evaluating the memory occupancy in the node. The
proposed scheme generates a set of twenty-four
different features vectors, extracted from the image
of the detected object. Each of these vectors requires
four bytes to be represented in the memory, leading
to a total of ninety-six bytes from the memory
storage capacity. In comparison to the features
extracted with ZM (AlSabhan, 2016), a hundred
bytes are required in the memory to store the set of
twenty-five features of four bytes. Table 2
summarizes the storage required for both detection
and recognition schemes.
Table 2: Memory storage for sensing scheme based on
GFD and ZM
Size of
ZM
GFD
Stored program text
10 KB
3 KB
Stored background image
(64*64 of 8bpp)
4 KB
4 KB
Captured image (64*64 of
8bpp)
4 KB
4 KB
Stored 24 reference
descriptors (float-number)
100 bytes
96 bytes
Region of interest in binary
512 bytes
512 bytes
Extracted ROI descriptors
100 bytes
96 bytes
Total Approx.
19 KB
12 KB
This scheme can save up to 7KB of memory storage,
while (due to the equation complexity of ZM)
additional processing space is required in
comparison to GFD. Recent memory designs have
ensured that this algorithm can accomplish a
reasonable low level of storage. The performance of
the proposed scheme was estimated for
implementation in wireless sensors (MICA2 sensors)
in terms of energy and time. The focus was
primarily placed on the evaluation of the processing
related performances of the scheme using GFD. The
AVRORA simulator for the ATmega128L
microcontroller (MICA2) was employed to
implement the algorithm. This tool determined the
number of clock cycles for the Atmel series for the
different tasks (J. Palsberg et al., n.d. ). The power
consumption and processing time were subsequently
estimated using the characteristics of
microcontrollers for MICA2. Grey-scale images of
(128*128 pixels- 8bpp) and (64*64 pixels- 8bpp)
were employed to extract the feature’s vector of the
detected object with a size of ninety-six bytes as a
total for twenty-four different image feature
descriptors.
Tables 3 and 4 illustrate the time and energy
consumption of internal processing when
implemented in the Camera-equipped MICA2
sensor, using ATmega128L for both sensing
SENSORNETS 2018 - 7th International Conference on Sensor Networks
96
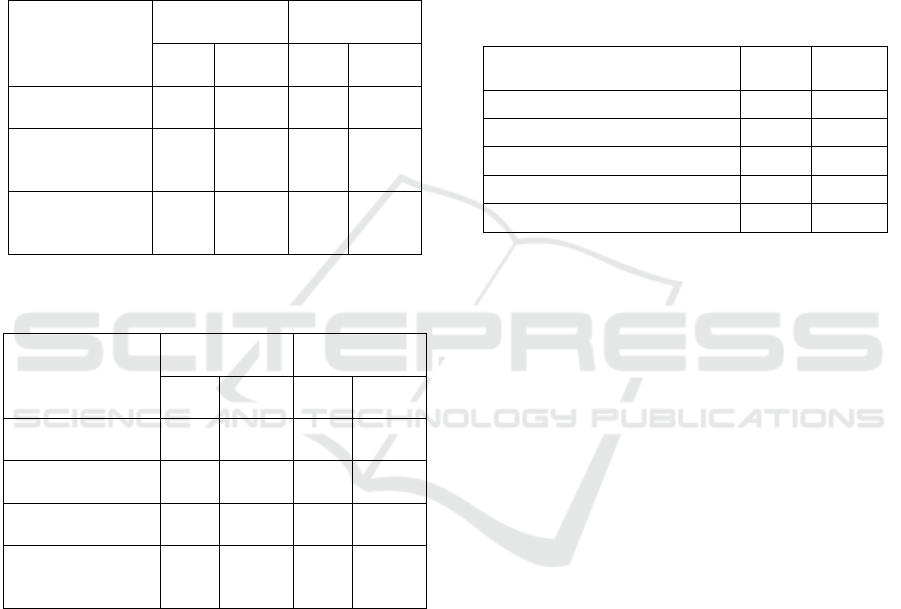
schemes. Table 4 demonstrates identical
measurements for a similar sensing scheme using
ZM in the features extraction (AlSabhan, 2016). This
reveals the consumed energy for 64*64 pixels of 8
bpp image is 2.59 mJ, and for 128*128 pixels of 8
bpp is 10.34 mJ, while in the sensing scheme using
ZM, the internal processing was 33.5 mJ and 121
mJ, respectively to 64*64 pixels of 8 bpp and
128*128 pixels of 8 bpp image sizes.
Table 3: Evaluation of sensing scheme based on GFD
features on MICA2.
64 ∗ 64 pixels
8 bpp
128∗128 pixels
8 bpp
Time
(s)
Energy
(mJ)
Time
(s)
Energy
(mJ)
Object Detection
and Extraction
0.1
2.25
0.39
9.06
Feature
Extraction using
GFD
0.015
0.34
0.06
1.37
Total scheme for
GFD without
Notification
0.12
2.59
0.45
10.43
Table 4: Evaluation of the sensing scheme based on ZM
features on MICA2 sensors.
64 ∗ 64 pixels
8 bpp
128∗128 pixels
8 bpp
Time
(s)
Energy
(mJ)
Time
(s)
Energy
(mJ)
Object Detection
and Extraction
0.47
10
1.9
43
Target
Normalization
0.06
1.5
0.26
6
Feature Extraction
using ZM
0.98
22
3.18
72
Total scheme for
ZM without
Notification
1.51
33.5
5.34
121
Thus, the sensing scheme employing GFD
features outperforms the scheme based on ZM, i.e.,
saving approximately 91% additional energy than
the scheme using ZM features. This difference in
power consumption is explained by the low-
complexity of the extraction method of GFD
features, which requires less pre-processing of the
image.
Table 5 establishes different notification scenarios
and their associated energy costs, assuming the use
of IEEE 802.15.4 and ZigBee communication
standards. The simulation program is developed
using NesC language and evaluated on AVRORA,
using the TinyOS platform. This table illustrates that
the cheapest manner of notification is to send a 1-
byte message, with costs increasing if the extracted
feature set is sent to the end user (which is helpful in
some applications for further classification), but
remaining less than sending the whole image or RoI.
The notification with the GFD features vector
requires the same energy of the transmission of the
ZM features. However, the accuracy of the features
extracted by the GFD method should be noted, in
addition to low energy consumption in the internal
processing.
Table 5: End user’s notification types using MICA2
sensors.
Notification Type
Time
(s)
Energy
(mJ)
Notification with 1 byte
0.01
0.3
25 ZM features vectors
1.0
30
24 GFD features vectors
0.96
28.8
ROI transmission
4.40
132
captured image
40.96
1228.8
4.2.1 Comparison with Related Works
In comparison to similar approaches for multimedia
sensing, this current scheme presents a number of
attractive characteristics in relation to both
complexity and power consumption. A summary
takes place below of the most relevant reported
solutions in the literature and their characteristics in
comparison to the current proposal efficient
solutions for low-power sensing.
A comparison of the current scheme with
compression techniques discussed in the literature
establishes that this scheme achieves very low
processing complexity and efficient power
consumption. Irgan (2014) based the compression
algorithm on the priorities of the segment blocks for
compression, but consumed around (130 mJ), where
that of Nikolakopoulos (2013) consumed
approximately (45 mJ) for sending (64*64 of 8 bpp)
of image size. The scheme of Zuo (2012) consumed
approximately (1.4 J) for sending (512*512 of 8
bpp) of image size. However, the presented
distributed processing fits within the context of the
current scheme, in order to prolong the network life
and it will be addressed as future work. Wang
(2008) presented an image recognition pattern
algorithm but failed to evaluate the performance
analysis of power consumption from local
processing. Pham (2013) presented a scheme for
extracting ROI based on a hardware solution, which
demonstrated high-performance levels in low-
Target Recognition Approach for Efficient Sensing in Wireless Multimedia Sensor Networks
97

complexity, but proved inflexible and was not
considered as scalable.
Alhilal (2015) employed recognition methods based
on centroid distance curvature features. However,
these failed to prove highly accurate and contained a
wide sensitivity to the characteristics of the detected
object in the image. Alsabhan (2016) investigated
ZM where it outperforms in term of the accuracy of
detection and algorithm complexity.
As outlined in Section 4.2, this current design
presents a low-complexity scheme and high
detection and recognition capability using GFD. It is
therefore concluded that the current work
outperforms other solutions presented in the
literature for image detection and recognition in
WMSN, in term of accuracy, efficiency, and
scalability.
5 CONCLUSIONS
This paper has presented a new sensing approach
based on GFD, as a shape descriptor for target
recognition in a monitored environment using
WMSN. The presented scheme is intended to
prolong the life of a network by minimizing the
power consumed by both the internal processor and
the transmitter antenna. The paper introduced the
simulation results attesting to the robustness,
accuracy, and low levels of complexity for target
recognition in WMSN. It was concluded that, in
comparison to a scheme based on ZM, the current
scheme requires less memory space for processing.
However, the internal sensor processing saves 91%
of energy in comparison to the application of ZM. It
is suggested that future work could include an
investigation of the communication overheads in the
network, which would result in a clearer concept of
the efficiency of this solution for deployment in
WMSN. Prior to such research, this current scheme
will be upgraded to handle multiple target detection
for simultaneous monitoring. It is concluded that the
concept of distributed processing as an approach to
energy saving appears promising. However, the
design and the implementation of a generic
clustering and processing architecture is still a
subject of open research.
REFERENCES
N. Lu; J. Wang; Q. Wu; L. Yang. An improved Motion
Detection method for real-time Surveillance, IAENG
International Journal of Computer Science, 35:1,
IJCS_35_1_16, February 2012.
J. Palsberg et al., "Avrora: Scalable Sensor Network
Simulation with Precise Timing," Information
Processing in Sensor Networks conference, 2005, pp.
477-482.
A Chefi, A Soudani, Sicard G "Hardware compression
scheme based on low complexity arithmetic encoding
for low power image transmission over WSNs." AEU-
International Journal of Electronics and
Communications, 2014, 68 (3) pp :193-200.
M. Teague, “Image analysis via the general theory of
moments,” J, Opt. Soc. Amer., vol. 70, no. 8, pp. 920-
930, Aug. 1980.
M. Yang et al., “A survey of shape feature extraction
techniques” in Pattern Recognition Techniques,
Technology and Applications, chapter 3, pp. 43–90,
InTech, 2008.
S. Belongie et al., “Shape matching and object recognition
using shape contexts,” IEEE Transactions on Pattern
Analysis and Machine Intelligence, vol. 24, no. 4,
pages 509–522, 2002.
S. Vasuhi et al., “Object detection and tracking in a
secured area with the wireless and multimedia sensor
network,” in Networked Digital Technologies, vol.
294 of Communications in Computer and Information
Science, pp. 356–367, Springer, Berlin, Germany,
2012.
Z. Zuo et al., “A two-hop clustered image transmission
scheme for maximizing network lifetime in wireless
multimedia sensor networks,” Computer
Communications, vol.35, no. 1, pp. 100–108, 2012.
D. Pham and S. M. Aziz, “Object extraction scheme and
protocol for energy efficient image communication
over wireless sensor networks,” Computer Networks,
vol. 57, no. 15, pp. 2949–2960, 2013.
K. Irgan et al., “Low-cost prioritization of image blocks in
wireless sensor networks for border surveillance,”
Journal of Network and Computer Applications, vol.
38, no. 1, pp. 54–64, 2014.
G. Nikolakopoulos et al., “A dual scheme for compression
and restoration of sequentially transmitted images over
Wireless Sensor Networks,” Ad Hoc Networks, vol.
11, no. 1, pp. 410–426, 2013.
H. Wang et al., “Artificial immune system based image
pattern recognition in energy efficient wireless
multimedia sensor networks,” in Proceedings of the
IEEE Military Communications, 2008.
M. Alhilal et al., “Image-based object identification for
efficient event-driven sensing in a wireless multimedia
sensor network,” Hindawi publishing corporation,
Article ID 850869, volume 2015.
M. Al-Sabhan, A. Soudani, Efficient Event Driven
Sensing in WMSN Using Zernike Moment, In
Procedia Computer Science, Volume 83, 2016, Pages
520-528.
Zhang et al. “Generic-Fourier Descriptor for Shape-based
Image Retrieval.” IEEE (2002): 425-42
SENSORNETS 2018 - 7th International Conference on Sensor Networks
98
