
Improving Urban Simulation Accuracy through Analysis of Control
Factors: A Case Study in the City Belt along the Yellow River in
Ningxia, China
Rongfang Lyu, Jianming Zhang, Mengqun Xu and Jijun Li
College of Earth Environmental Sciences, Lanzhou University, Tianshui South Road 222, Lanzhou, China
Keywords: Urban Simulation, Spatial Heterogeneity, Macro-control Influence, SLEUTH-3r Model, City Belt along
Yellow River in Ningxia.
Abstract: Spatial heterogeneity of urban expansion and macro-scale influence of socioeconomic development are the
two main problems in urban-expansion modelling. In this study, we used the SLEUTH-3r model to simulate
urban expansion at a fine scale (30 m) for a large urban agglomeration (22000 km
2
) in north-western China.
Multiple spatial constraint factors were integrated into the model through Ordinary Least Regression and
Binary Logistic Regression to simulate the spatial heterogeneity in urban expansion. A critical
parameter—the diffusion multiplier (D
M
)—was used to simulate the macro-scale influence of socioeconomic
development in the urban model. These two methods have greatly enhanced the ability of the SLEUTH-3r
model to simulate urban expansion with high heterogeneity, and adapt to urban growth driven by
socioeconomic development and government policy.
1 INTRODUCTION
Urbanization, an unprecedented global phenomenon,
has significantly altered natural landscapes and
human lives (Zhang et al., 2012). Urban expansion,
a significant performance of urbanization, has
brought numerous threats to ecosystem, such as loss
of natural resources (Delphin et al., 2016), climate
change (Singh et al., 2017), and biodiversity
decrease (Haase et al., 2012). Therefore, it is critical
to predict urban expansion patterns for sustainable
development, especially in metropolitan areas,
which form the basic unit in future socioeconomic
development (Poyil and Misra, 2015).
Urbanization is a dynamic process influenced by
geophysical, environmental, demographic, and
social factors at multiple scales (Akın et al., 2014).
Complicated interactions between these factors, and
associated temporal changes lead to spatial and
temporal heterogeneity in urban expansion (Li et al.,
2017). A number of techniques have been developed
to simulate urban expansion, ranging from static
models based on gravity theory and optimization
mathematics to dynamic models (Berling-Wolff and
Wu, 2004). In particular, the cellular automata (CA)
model is widely used in urban simulation for its
simplicity, flexibility, intuitiveness, and transparency
in modeling complex systems (Santé et al., 2010).
However, the CA model often fails to capture the
change magnitude of urban expansion driven by
political and economic strategies (Qi et al., 2004).
Despite its successful application in many cities, the
SLEUTH model is also a CA model that fails to
consider the macro-scale driving influence of
socioeconomic development (Berberoğlu et al., 2016,
Chaudhuri and Clarke, 2013). Since urbanization in
China is highly driven by government policies, it is
essential to integrate these macro-scale control
factors into urban model.
The SLEUTH model has been always used to
simulate urban land distribution in a single city at
coarse resolution (Chaudhuri and Clarke, 2013), but
not for large urban agglomerations consisting of
several cities with high spatial heterogeneity (Jat et
al., 2017). Several approaches have been developed
to evaluate the effects of driving forces on urban
expansion, such as binary (Haregeweyn et al., 2012),
multiple linear (Gao and Li, 2011), and
geographically-weighted regressions (Su et al.,
2012), analytic hierarchy process (Thapa and
Murayama, 2012), and logistic regression (Long et
al., 2012). Among them, multiple linear and binary
Lyu, R., Zhang, J., Xu, M. and Li, J.
Improving Urban Simulation Accuracy through Analysis of Control Factors: A Case Study in the City Belt along the Yellow River in Ningxia, China.
DOI: 10.5220/0006627201590166
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Geographical Information Systems Theory, Applications and Management (GISTAM 2018), pages 159-166
ISBN: 978-989-758-294-3
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
159
regression, both reliable and easy to manipulate,
were selected to integrate multiple factors into the
SLEUTH model to simulate urban spatial expansion
with high heterogeneity (Liu et al., 2014).
To date, most of urban studies in China focused
on fast-growing coastal and major interior cities;
however, urban growth in inner northwestern China,
especially in large urban agglomerations, has not
been well described. Our study will help to bridge
the gap, as the study area is a large city belt in
northwestern China. The main objectives of our
study were to: (1) identify factors that control urban
expansion, and quantify their impacts, (2) simulate
urban expansion with high spatial heterogeneity, and
(3) integrate the macro-scale driving influence of
socioeconomic development into model to simulate
urban expansion with proper magnitude.
2 STUDY AREA AND METHODS
2.1 Study Area
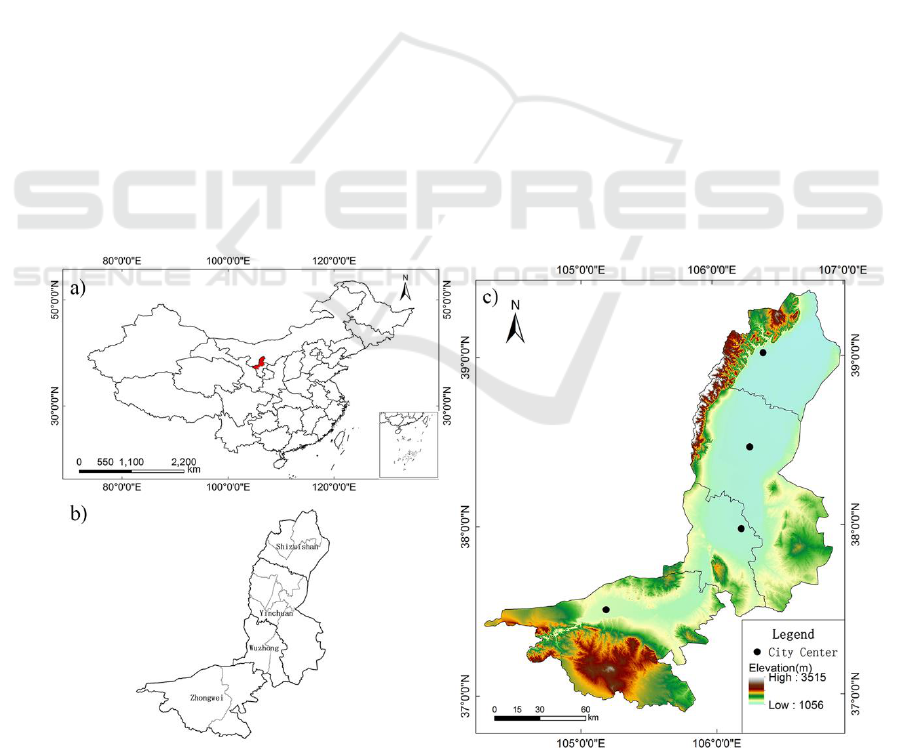
The City Belt along the Yellow River in Ningxia
(CBYN), located in northwestern China, is a large
urban agglomeration consisting of four cities:
Shizuishan, Yinchuan, Wuzhong and Zhongwei
(Fig. 1). The study area, with Tengger desert in the
west, the Maowusu desert in the east, and the Ulan
Buh desert in the north, is one of the core areas of
the west Longhair-Lanxin xian economic belt. Since
2000, socioeconomic development in this area has
been deliberately enhanced by the government
through West Development Project. Gross Domestic
Product (GDP) increased from 5045.93 million Yuan
in 1990 to 223,550.29 million Yuan in 2013, with an
annual growth rate of 188.27%, while population
increased at an annual rate of 2.75 %. (Ningxia
Statistical Yearbook, 1990-2014). Growing industry
and commerce in the urbanized areas provide more
work opportunities, and attract population from the
rural areas, further promoting urbanization.
2.2 Data Collection and Processing
Twelve scenes of Landsat MSS/TM/ETM+/OLI
images, covering the study area in 1989, 1999, 2006
and 2016, were used as the primary resource data
(involving path/row of 129/33, 129/34 and 130/34).
Images were preprocessed in ENVI 5.3, including
geographical registration, radiometric calibration
and atmospheric correction, and then were
exportedinto eCognition 8.7 for an object-based
classification. Reference samples were identified
in Google Earth and field survey to examine
classification accuracy. The Kappa coefficients
Figure 1: Location and administrative division of the study area—Shizuishan, Yinchuan, Wuzhong and Zhongwei:a) the
study area in China; b) the study area in Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region; c) topography and the city center of Shizuishan,
Yinchuan, Wuzhong and Zhongwei.
GISTAM 2018 - 4th International Conference on Geographical Information Systems Theory, Applications and Management
160

(consistency test between classification results and
reference samples) reached 0.93, 0.89, 0.91 and 0.87
in 1989, 1999, 2006 and 2016, respectively, thus the
results were reliable.
The ASTER DEM data (version 4.1)
(https://search.earthdata.nasa.gov/) was resampled to
30 m in ArcGIS 10.3, and used to generate slope and
hillshade layers. Transportation layers were
extracted from satellite images and by visual
interpretation using Google Earth. All the input
layers were resampled for 30 m in ArcGIS 10.3, and
then imported into Photoshop CS6 to be exported in
GIF format. Socioeconomic data, such as population
and GDP, was obtained from Ningxia Statistical
Yearbook (1990-2014), compiled by the statistical
bureau of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region and
Ningxia Survey Office of National Statistical Bureau,
and published by China Statistics Press.
2.3 Overview of the SLEUTH Model
The SLEUTH model (Clarke et al., 1997) is
designed to simulate urban growth and land use
change. The name includes the first letters of the
input layers: slope, land cover, excluded, urban,
transportation, and hillshade. The model simulates
urban expansion with four rules: spontaneous
growth that simulates the random urbanization, new
spreading center growth that establishes new urban
centers, edge growth and road influenced growth.
The model behavior are controlled by five growth
coefficients (diffusion, breed, spread, road gravity,
and slope) that range from 0 to 100, indicating the
relative contribution of each growth types for whole
urban growth. Moreover, self-modification is applied
to better predict rapid or depressed urban growth.
Model calibration allows users to obtain parameters
describing past urban expansion, while prediction
helps forecast urban growth and land use change
under different scenarios.
Due to the large amounts of input data, we
selected the 3r-version of the SLEUTH model
(SLEUTH-3r) for our study; it has more efficient
utility of computer memory and higher simulation
accuracy of dispersed settlements (Jantz et al., 2010).
Two new accuracy parameters—area fractional
difference (AFD) and clusters fractional difference
(CFD)—were designed in SLEUTH-3r model to
compare urban pixels and clusters between
simulated and real maps. Besides that, Lee-Sallee
metric, the shape index of spatial fit between actual
urban map and predicted one, has also been used in
our study to examine the simulation accuracy.
2.4 Simulating Spatial Heterogeneity
To address spatial heterogeneity in urban expansion,
we first established a suitability system of factors
driving urban growth from past studies (details in
2.4.1 below). Second, we detected the spatial
relationships between factors and urban expansion
through the Ordinary Least Square (OLS) regression
model in ArcGIS 10.3 (details in 2.4.2 below).
Finally, suitability for urban expansion was
calculated and mapped through Binary Logistic
Regression with weighted factors derived from the
former step (details in 2.4.3 below). Then the
suitability map was transformed into the excluded
layer for the SLEUTH-3r model.
2.4.1 Suitability-Factor System
Different types of explanatory variables have been
identified (Gao and Li, 2011, Su et al., 2012), and
categorized based on physical conditions, ecological
protection, and socio-economic development (Table
1). Ecological factors are protected from urban
expansion and are assigned value of 100 in the
excluded layer. Slope factor is not included in the
system, as it is already in SLEUTH-3r model. All
variables were first normalized into the range of 0-1
to eliminate the effect of magnitude. Based on
correlation analysis, multicollinearity did not exist
among the explanatory variables in the subsequent
regression analysis.
Table 1: Factors influencing urban development.
Type
Factor
Code
Physical
Elevation
X
E
Geomorphic type
X
M
Ecological
Water areas
X
W
National natural reserves
X
N
Socio-economic
Growth rate of GDP
X
G
Growth rate of population
X
P
Distance to city centers
X
D1
Distance to county centers
X
D2
2.4.2 Weights Estimation
OLS, which could minimize the sum of squared
vertical distance between observed variables and
simulation values (Gao and Li, 2011), was used to
explore the relationships between urban expansion
and its driving factors, as follows:
Z=C+
w
i
X
in
+er
(1)
Where Z was the dependent variable, C was the
constant parameter; w
i
was the parameter of
independent variable X
i
; er was the error term.
Improving Urban Simulation Accuracy through Analysis of Control Factors: A Case Study in the City Belt along the Yellow River in
Ningxia, China
161

Because non-urbanized area greatly surpassed
urbanized area in CBYN, we randomly selected
5,000 points in each area, with a distance between
each point > 300 m to minimize the impacts of
spatial autocorrelation. The “extract multi values to
points” tool in ArcGIS 10.3 was used to obtain the
values of driving parameters and urban expansion (0
for non-urbanized area and 1 for urbanized area) at
each point. They were then used to establish the
OLS model in ArcGIS 10.3.
2.4.3 Generating Suitability Maps
If the probability of a cell suitable for urbanization
followed the logistic curve described in Eq. (2), the
possibility of a cell being urbanized was estimated
with Eq. (3):
ln
p
i
1-p
i
=C+
w
i
X
i
n
i=1
(2)
p
i
=
1
1+exp(-C-
w
i
X
i
n
)
(3)
Where p
i
was the probability of a cell becoming
urbanized, X
i
was the driving factor for urban
expansion, w
i
was the coefficient of each factor
derived from OLS, and C was a constant.
2.5 Socioeconomic Factors in the Model
In SLEUTH-3r model, spontaneous urban growth
was the foundation of other growth types, and
mainly determined by a diffusion multiplier (D
M
),
diffusion coefficient (D
C
), and the size of input
images (Jantz et al., 2010). Thus D
M
could generally
determine the simulation magnitude of urban growth
in model, and allowed the integration of
socioeconomic development into the model.
The D
M
value was 0.005 in the original version,
and 0.015 in the 3r version of the SLEUTH model,
and neither could generate enough urban growth
(AFD ranging from -0.847 to -0.06). Thus, the first
problem was obtaining an appropriate D
M
. As
discussed above, D
M
was related to simulation
magnitude, so we explored the relationship between
D
M
and simulation magnitude of urban area and
cluster (AFD and CFD) to find appropriate D
M
.
We selected the annual growth rates of GDP and
population as the representatives for socioeconomic
development, and generated an indicator (SE) using
factor analysis in SPSS 22.0. Then we explored the
relationship between SE and D
M
through regression
analysis in SPSS 22.0, to use D
M
representing
different socioeconomic development conditions.
3 RESULTS
3.1 Urban Expansion Suitability Map
Multiple linear regression analysis processed in
SPSS 22.0 had the same results as OLS in ArcGIS
10.2 (Eq. (4)). The six factors had different effects
on urban expansion, indicated by the coefficients of
each factor. And the influence of geophysical factors
was greater than that of socioeconomic factors. The
regression model was as follows (Eq. (4)):
ln
p
i
1-p
i
=1.53-1.32×X
E
-0.4×X
M
-0.51×
X
D1
-0.53×X
D2
+0.05×X
G
+0.02×X
P
(4)
Where p
i
was the urbanization probability of each
cell.
Based on binary logistic regression, a probability
map for urban suitability was generated (Fig. 2a).
Then, we converted it to an excluded layer that
contained areas ranging from unsuitable for
urbanized (value=100) to suitable (value=0) in
SLEUTH-3r model using the “map algebra” tool in
ArcGIS 10.3 (Fig. 2b). The transformation equation
was as follows (Eq. (8)):
R
E
=(
MAX
R
suit
-R
suit
MAX
R
suit
-MIN
R
suit
)×100]
(5)
Where R
E
and R
suit
were the raster maps of excluded
layer and suitability map, respectively.
Figure 2: Suitability map for urbanization probability (a)
and excluded map for SLEUTH-3r model (b).
3.2 Determination of D
M
We explored the relationships between AFD/CFD
and D
M
in the calibration mode of the model with
the five growth coefficients ranging from 0 to 100
GISTAM 2018 - 4th International Conference on Geographical Information Systems Theory, Applications and Management
162

and an increment of 50. We found that the minimum
values of AFD and CFD were almost the same
(-0.847 and -0.73) under different D
M
, while the
maximum value increased with an increase in D
M
.
The relationships between the maximum values of
AFD/CFD and D
M
were established through
regression analysis in SPSS 22.0. The equations and
simulated curves were as follows (Eq (6) with R
2
of
0.975, Eq (7) with R
2
of 0.997, and Fig. 3)):
AFD
max
=3.323+0.79×ln(D
M
)
(6)
CFD
max
=2.69+202.67×D
M
-188.45×D
M
2
+71.49×D
M
3
(7)
Figure 3: Maximum and minimum values of AFD and
CFD over increasing D
M
.
From the testing data shown in figure 3, three
values of D
M
—0.03/0.04/0.05—were considered to
have the largest opportunity to simulate sufficient
amount of urban area with fewer clusters. We
calibrated the model with the three D
M
values (Table
2), and 0.04 was the most suitable value for D
M
in
our study. Under D
M
of 0.04, the maximum value of
AFD was 0.783. As discussed in Section 2.5, 0.783
of the maximum value of AFD was appropriate for
D
M
determination.
Table 2: Coarse calibration performance of the model under
different D
M
.
D
M
AFD
CFD
Lee-Sallee
0.03
0.002
6.9
0.301
0.04
0.001
5.162
0.351
0.05
0.001
6.283
0.309
3.3 The Socioeconomic Factor
The socioeconomic development indicator (SE) was
generated with the following equation (Eq. (8),
Section 2.5):
SE=8.23×10
-7
×GDP
S
+2.74×10
-5
×P
S
-0.94
(8)
We obtained 30 values of D
M
through the method
discussed in Section 3.2 for the five different areas
(4 cities and the whole region) in the six periods
(1989-1999, 1999-2006, 2006-2016, 1989-2006,
1999-2016, and 1989-2016). The relationship
between D
M
and SE was estimated with regression
analysis in SPSS 22.0 (Eq. 9) with a R
2
of 0.981).
Therefore, SLEUTH-3r model could predict urban
expansion driven by different socioeconomic
development conditions by setting the D
M
value.
D
M
=0.083×SE+0.043×SE
2
-0.011×SE
3
+0.056
(9)
3.4 Simulation Accuracy of the Model
The SLEUTH-3r model was calibrated to find a
combination of coefficients that best simulated
historical urban expansion through the “brute-force”
method (Silva and Clarke, 2002). The selection
criterion used the minimum absolute value of CFD
and AFD of < 0.05. Then the model was initialized
in 1989 and ran in predict mode to 2016, with the
coefficients derived from calibration. In the
prediction mode, we utilized two scenarios, in which
one (S
1
) came from the suitability map, and the other
(S
2
) coded water with 100 and other land with 50 as
comparison.
To evaluate the simulation accuracy, we
calculated the Kappa metric and spatial topology for
the predicted maps (Table 3). The Kappa metric
(consistency between predicted and real maps) in
2016 under S
1
reached 0.77, while the one under S
2
was 0.56, indicating that S
1
could significantly
improve model accuracy. Urban spatial topology can
further describe the simulation accuracy
(Kantakumar et al., 2016), and was classified based
on proportion of built-up area (using 30% and 50%
as a boundary) within the neighborhood of 3×3 cells
through “block statistics” tool in ArcGIS 10.3.
Prediction under S
1
accurately simulated the area of
the urban core, 74.82% of the real urban fringe, but
172.86% of the scattered settlement; this indicated
that most of the simulation error occurred in
scattered settlements. Under S
2
, the main error
occurred in simulating the urban core (at 78.29%)
and urban fringe (at 62.38%). Overall, integrating the
effects of multiple drivers into the model can greatly
enhance the ability to simulate urban expansion with
high spatial heterogeneity.
Table 3: Urban spatial pattern predicted in 2016 under
different scenarios.
Urban
area
(km
2
)
Kappa
Urban topology type
Urban
core
(km
2
)
Urban
fringe
(km
2
)
Scatter
settlement
(km
2
)
S
1
1205.81
0.77
1165.67
146.25
349.05
S
2
931.51
0.56
911.66
121.94
212.81
Real
1182.123
—
1164.51
195.48
201.93
Improving Urban Simulation Accuracy through Analysis of Control Factors: A Case Study in the City Belt along the Yellow River in
Ningxia, China
163

4 DISCUSSION
Documentation and source code of the SLEUTH
model have been publicly available, thus interested
researchers were able to modify and improve it.
Several successful efforts reduced computation time
and increased model efficiency, including OSM
(Charles Dietzel, 2007), pSLEUTH (Guan and
Clarke, 2010), SLEUTH-3r (Jantz et al., 2010), and
SLEUTH-GA (Shan et al., 2008), among others.
These modifications helped to overcome some of the
limitations, enhance model applicability, and provide
suggestions for more accurate simulation (Chaudhuri
and Clarke, 2013). Using the SLEUTH-3r model, we
simulated urban expansion in CBYN during
1989-2016. We confronted three main problems.
First, the determination methods for D
M
were not
appropriate for our study as they could not generate
sufficient urban growth area. Second, urban growth
in China, largely driven by socioeconomic
development at macro-scale, could not be effectively
expressed in this model. Third, spatial heterogeneity
in urban growth, such as city and villages in a large
urban agglomeration, was an important source of
simulation error that needed to be addressed.
4.1 Parameters Driving Urban Growth
Similar to most studies that analysed urban
expansion, the factor system we built in this study
was incomplete, due to lack of data and the presence
of unknown urban-growth driving factors (Hietel et
al., 2007). For example, urban planning has been
shown to greatly affect urban expansion (Long et al.,
2012), however, it has not been included in this
study due to lack of data. The incomplete picture of
the factors driving urbanization was one source of
simulation error.
In 1989-2016, physical factors impacted urban
expansion more than socioeconomic conditions did
at spatial scale. Elevation and morphology exhibited
significantly negative effects on urban expansion in
CBYN, while low elevation and flat areas were more
suitable for urban growth. Previous studies
suggested that the effects of elevation on urban
expansion depended on the topography (Li et al.,
2013). Positive effects of elevation on urban
expansion have been shown in Lagos and Nigeria,
where low elevation areas necessitated drainage,
possibly increasing the cost of building construction
(Dewan and Yamaguchi, 2009). In CBYN, areas of
high elevation were more likely to be situated in the
mountains, where costs of development were higher
than at low elevations.
The significant relationships between urban
expansion and social factors of proximity to urban
centers (negatively correlated), and growth rate of
GDP and population (positively correlated) were
consistent with previous findings (Luo and Wei,
2009, Poelmans and Rompacy, 2009). Moreover, the
effects of proximity exceeded those of economic
development and population growth. This was
mainly due to the coarser resolution of census data
compared with other factors. The spatial
heterogeneity of urban and suburban areas could not
be expressed by GDP or population data, indicating
that data at finer-scales were needed.
Previous studies on megacities in China and
USA have shown that positive relationships existed
between socioeconomic development and urban
expansion, especially in developing countries
(Kuang et al., 2014), and that the socioeconomic
factors would play an increasingly important role in
urbanization. For example, studies in Beijing (Liu et
al., 2014) suggested that the importance of
urbanization drivers varied over time, and the effects
of physical and neighborhood factors decreased with
increasing socioeconomic factors. Compared with
Beijing, CBYN developed at a slower pace in the
past thirty years, as indicated by urban population
rate of 67.56% in CBYN in 2015, and 86% in
Beijing in 2010 (Liu et al., 2014). As a result, the
impacts of socioeconomic development were less
important than those of geophysical conditions, but
would increase in the future.
4.2 Implications of Model Simulation
Chinese megacities are in a stage of development at
which population growth, economic development,
and policy significantly influence urban expansion
patterns and rates. This is unlike megacities in
developed countries where population and economic
conditions are not important forces of urban growth
(Kuang et al., 2014). The effects of socioeconomic
development on urban expansion were classified in
this study into two categories: spatial heterogeneity
and temporal dynamics; the former was expressed in
the excluded layer from the suitability map, and the
latter was reflected in the changing value of D
M
.
Spatial differences in physical conditions,
cultural background, socioeconomic development,
and human preferences were responsible for the high
heterogeneity in urban distribution and expansion
(Lin et al., 2014); this was also reflected in D
M
with
value ranging from 0.008 to 0.38 among different
cities. This heterogeneity improved the difficulty in
precise urban simulation, and can be an important
GISTAM 2018 - 4th International Conference on Geographical Information Systems Theory, Applications and Management
164

source of simulation error. Linear or logistic
regression-based models cannot calculate
heterogeneous urban expansion due to their
dependability on weights (Hu and Lo, 2007).
Artificial neural network models also have limited
capacity for accurate modeling of spatial
heterogeneity (Almeida et al., 2008).
The SLEUTH model can simulate urban growth
at coarse resolution well, and has been successfully
applied to cities all over the world (Akın et al., 2014,
Al-shalabi et al., 2012, Bihamta et al., 2014).
However, the SLEUTH model is still inadequate for
simulating urban growth with high heterogeneity, or
at high resolution at large-scales (Jat et al., 2017). In
our study, integrating various spatial factors into the
model greatly enhanced the simulation accuracy in
an urban agglomeration. The influence of
socioeconomic growth on urban expansion, and the
fundamental function of D
M
in controlling the
magnitude of urbanization (suggested by Eq. (9)),
allowed D
M
to exert temporal influence in the model.
The high correlation between D
M
and SE further
supports this conclusion. Future research needs to
focus on predicting urban expansion under different
socioeconomic growth scenarios, and on
comparing the effects of government policies on
urbanization.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Urban expansion is unavoidable and has significant
impacts on ecosystem services and functions. The
successful application of the SLEUTH-3r model in
the City Belt along the Yellow River in Ningxia at a
resolution of 30 m has shown its utility in simulating
urban expansion in a large area with high precision.
In the past 27 years, the effects of elevation and
geomorphology on urban expansion exceeded those
of socioeconomic development. We quantitatively
integrated these factors into the model to simulate
urban expansion with high heterogeneity across a
large area with high accuracy.
The influence of socioeconomic development
was introduced into model with D
M
, which can be
set interactively. Both of these actions improve
model accuracy in simulating urban expansion in
urban agglomerations. However, the excessive
amounts of scatter settlements in the simulation
indicated the need for further research.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research was supported by the National Natural
Science Foundation of China under grant No.
41371176 and the Fundamental Research Funds for
the Central Universities under grant No.
lzujbky_2017_it91.
REFERENCES
Akın, A., Clarke, K. C. & Berberoglu, S. (2014). The
impact of historical exclusion on the calibration of the
SLEUTH urban growth model. International Int J
Geographical Inf. Sci, 27: 156-168.
Al-shalabi, M., Billa, L., Pradhan, B., Mansor, S. &
Al-Sharif, A. A. A. (2012). Modelling urban growth
evolution and land-use changes using GIS based
cellular automata and SLEUTH models: the case of
Sana’a metropolitan city, Yemen. Environmental Earth
Sciences, 70(1): 425-437.
Almeida, C. M., Gleriani, J. M., Castejon, E. F. & Soares
Filho, B. S. (2008). Using neural networks and cellular
automata for modelling intra-urban land-use dynamics.
Int J Geographical Inf. Sci, 22(9): 943-963.
Berberoğlu, S., Akın, A. & Clarke, K. C. (2016). Cellular
automata modeling approaches to forecast urban
growth for adana, Turkey: A comparative approach.
Landscape Urban Plan., 153: 11-27.
Berling-Wolff, S. & Wu, J. (2004). Modeling urban
landscape dynamics: a review. Ecol. Res., 19(1):
119-129.
Bihamta, N., Soffianian, A., Fakheran, S. & Gholamalifard,
M. (2014). Using the SLEUTH Urban Growth Model to
Simulate Future Urban Expansion of the Isfahan
Metropolitan Area, Iran. Journal of the Indian Society
of Remote Sensing, 43(2): 407-414.
Charles Dietzel, K. C. C. (2007). Toward optimal
calibration of the SLEUTH land use change model.
Transactions in GIS, 11(1): 29-45.
Chaudhuri, G. & Clarke, K. C. (2013). The SLEUTH land
use change model: A review. The International Journal
of Environmental Resources Research, 1(1): 88-104.
Clarke, K. C., Hoppen, S. & Gaydos, L. J. (1997). A
self-modifying cellular automaton model of historical
urbanization in the San Francisco Bay Area. Environ.
Plann. B, 24: 247-261.
Delphin, S., Escobedo, F. J., Abd-Elrahman, A. & Cropper,
W. P. (2016). Urbanization as a land use change driver
of forest ecosystem services. Land Use Policy, 54:
188-199.
Dewan, A. M. & Yamaguchi, Y. (2009). Land use and land
cover change in Greater Dhaka, Bangladesh: using
remote sensing to promote sustainable urbanization.
Appl. Geogr., 29(3): 390-401.
Gao, J. & Li, S. (2011). Detecting spatially non-stationary
and scale-dependent relationships between urban
landscape fragmentation and related factors using
Improving Urban Simulation Accuracy through Analysis of Control Factors: A Case Study in the City Belt along the Yellow River in
Ningxia, China
165

Geographically Weighted Regression. Appl. Geogr.,
31(1): 292-302.
Guan, Q. & Clarke, K. C. (2010). A general-purpose
parallel raster processing programming library test
application using a geographic cellular automata model.
Int J Geographical Inf. Sci, 24(5): 695-722.
Haase, D., Schwarz, N., Strohbach, M., Kroll, F. & Seppelt,
R. (2012). Synergies, Trade-offs, and Losses of
Ecosystem Services in Urban Regions: an Integrated
Multiscale Framework Applied to the Leipzig-Halle
Region, Germany. Ecology and Society, 17(3): 22.
Haregeweyn, N., Fikadu, G., Tsunekawa, A., Tsubo, M. &
Meshesha, D. T. (2012). The dynamics of urban
expansion and its impacts on land use/land cover
change and small-scale farmers living near the urban
fringe: A case study of Bahir Dar, Ethiopia. Landscape
Urban Plan., 106(2): 149-157.
Hietel, E., Waldhardt, R. & Otte, A. (2007). Statistical
modelling of land-cover changes based on key
socio-economic indicators. Ecol. Econ., 62: 496-507.
Hu, Z. & Lo, C. P. (2007). Modeling urban growth in
Atlanta using logistic regression. Comput. Environ.
Urban., 31(6): 667-688.
Jantz, C. A., Goetz, S. J., Donato, D. & Claggett, P. (2010).
Designing and implementing a regional urban
modeling system using the SLEUTH cellular urban
model. Comput. Environ. Urban., 34(1): 1-16.
Jat, M. K., Choudhary, M. & Saxena, A. (2017). Urban
growth assessment and prediction using RS, GIS and
SLEUTH model for a heterogeneous urban fringe. The
Egyptian Journal of Remote Sensing and Space Science.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrs.2017.02.002.
Kantakumar, L. N., Kumar, S. & Schneider, K. (2016).
Spatiotemporal urban expansion in Pune metropolis,
India using remote sensing. Habitat Inter., 51: 11-22.
Kuang, W., Chi, W., Lu, D. & Dou, Y. (2014). A
comparative analysis of megacity expansions in China
and the U.S.: Patterns, rates and driving forces.
Landscape Urban Plan., 132: 121-135.
Li, C., Zhao, J. & Xu, Y. (2017). Examining
spatiotemporally varying effects of urban expansion
and the underlying driving factors. Sustainable Cities
and Society, 28: 307-320.
Li, X., Zhou, W. & Ouyang, Z. (2013). Forty years of urban
expansion in Beijing: What is the relative importance
of physical, socioeconomic, and neighborhood factors?
Appl. Geogr., 38: 1-10.
Lin, J., Huang, B., Chen, M. & Huang, Z. (2014). Modeling
urban vertical growth using cellular automata:
Guangzhou as a case study. Appl. Geogr., 53: 172-186.
Liu, R., Zhang, K., Zhang, Z. & Borthwick, A. G. (2014).
Land-use suitability analysis for urban development in
Beijing. J Environ Manage, 145: 170-179.
Long, Y., Gu, Y. & Han, H. (2012). Spatiotemporal
heterogeneity of urban planning implementation
effectiveness: Evidence from five urban master plans of
Beijing. Landscape Urban Plan., 108: 103-111.
Luo, J. & Wei, Y. H. D. (2009). Modeling spatial variations
of urban growth patterns in Chinese cities: The case of
Nanjing. Landscape Urban Plan., 91(2): 51-64.
Poelmans, L. & Rompacy, A. V. (2009). Detecting and
modellling spatial patterns of urban sprawl in highly
fragmented areas: a case study in the Flanders-Brussels
region. Landscape Urban Plan., 93(1): 10-19.
Poyil, R. P. & Misra, A. K. (2015). Urban agglomeration
impact analysis using remote sensing and GIS
techniques in Malegaon city, India. International
Journal of Sustainable Built Environment, 4(1):
136-144.
Qi, Y., Henderson, M., Xu, M., Chen, J., Shi, P., He, C. &
Skinner, W. (2004). Evolcing core-periphery
interactions in a rapidly expanding urban landscape: the
case of Beijing. Landscape Ecology, 19: 491-497.
Santé, I., García, A. M., Miranda, D. & Crecente, R. (2010).
Cellular automata models for the simulation of
real-world urban processes: A review and analysis.
Landscape Urban Plan., 96(2): 108-122.
Shan, J., Alkheder, S. & Wang, J. (2008). Genetic
algorithms for the calibration of cellular automata
urban growth modeling. Photogrammetric Engineering
and Remote Sensing, 74: 1267-1277.
Silva, E. A. & Clarke, K. C. (2002). Calibration of the
SLEUTH urban growth model for Lisbon and Porto,
Portugal. Comput. Environ. Urban., 26: 525-552.
Singh, P., Kikon, N. & Verma, P. (2017). Impact of land use
change and urbanization on urban heat island in
Lucknow city, Central India. A remote sensing based
estimate. Sustainable Cities and Society, 32: 100-114.
Su, S., Xiao, R. & Zhang, Y. (2012). Multi-scale analysis of
spatially varying relationships between agricultural
landscape patterns and urbanization using
geographically weighted regression. Appl. Geogr, 32(2):
360-375.
Thapa, R. B. & Murayama, Y. (2012). Scenario based urban
growth allocation in Kathmandu Valley, Nepal.
Landscape and Urban Planning, 105: 140-148.
Zhang, C., Tian, H., Chen, G., Chappelka, A., Xu, X., Ren,
W., Hui, D., Liu, M., Lu, C., Pan, S. & Lockaby, G.
(2012). Impacts of urbanization on carbon balance in
terrestrial ecosystems of the Southern United States.
Environ Pollut, 164: 89-101.
GISTAM 2018 - 4th International Conference on Geographical Information Systems Theory, Applications and Management
166
