
Implementation of Smart Parking Solution by Image Analysis
Aleksejs Zacepins, Vitalijs Komasilovs and Armands Kviesis
Department of Computer Systems, Faculty of Information Technologies, Latvia University of Agriculture, Jelgava, Latvia
Keywords:
Smart City, Smart Parking, Video Processing, Image Analysis.
Abstract:
Modern smart city concept implies various smart aspects including smart parking management. Searching
for a free parking lot can be a challenging task, especially during major events, therefore automatic system,
which will help drivers to find a free parking is very valuable. There are many intrusive and non-intrusive
technologies available for smart parking development, but authors of this paper developed a system based on
video processing and analysis. Authors developed Python application for real-time parking lot monitoring
based on video analysis of public video stream. Five classifier models (Logistic Regression, Linear Support
Vector Machine, Radial Basis Function Support Vector Machine, Decision Tree and Random Forest) were
compared for parking lot occupancy detection. Logistic regression classifier showed better results and was
chosen for real-time parking monitoring application. System shows good performance and correctly predicted
parking lot occupancy almost in all test cases.
1 INTRODUCTION
Smart City concept is highly dependent on the use of
Information and Communication Technologies (ICT)
for a more efficient use of existing resources, with
main aim to improve citizens quality of life (Albino
et al., 2015). As far as the livability of cities is con-
cerned, traffic is one of the most frequent and complex
factors directly affecting citizens (Sevillano et al.,
2014).
In Latvia more than 3 000 new vehicles are
registered each month, but road infrastructure is
not developing so quickly. There are 664 177
of passenger cars on the Latvian roads (based
on Road Traffic Safety Directorate statistics:
https://www.csdd.lv/en/vehicles/statistics-of-
registered-vehicle) and there are insufficient car
parking facilities especially during the major concerts
or sport events. Development of Smart parking
can minimize the parking problem in modern cities
(Pham et al., 2015).
Smart parking systems are implemented world-
wide, mainly in Europe, United States and Japan
(Shaheen, 2005; Kuran et al., 2015; Lan and Shih,
2014). Implementation of smart parking systems has
many advantages for municipality, parking owners
and drivers. Drivers can easily find vacant park-
ing lots and avoid driving to fully occupied parkings
(Shoup, 2006; Idris et al., 2009; Polycarpou et al.,
2013), this also minimizes the air pollution (Arnott
and Inci, 2006).
Smart parking systems usually are divided into
several categories: parking guidance and informa-
tion system (PGIS), transit based information sys-
tem, smart payment system, E-parking and automated
parking (Shaheen, 2005). Each system has its advan-
tages and disadvantages. This paper deals with park-
ing guidance and information system sub-component,
named parking lot occupancy detection.
Critical point in smart parking operation is park-
ing lot occupancy detection. There are many tech-
nologies available for this, which are mainly divided
into two categories: intrusive (inductive loops, piezo-
electric cables, active infrared sensors, etc) and non-
intrusive (passive infrared sensors, ultrasonic, video
image processing, etc).
This paper describes software solution for parking
lot occupancy monitoring using video processing and
image interpretation methods. Many authors tried to
develop smart parking system based on video analysis
(Sevillano et al., 2014; Al-Kharusi and Al-Bahadly,
2014), but still there are no one universal system,
which can be used in all parking cases. This solu-
tion can extend the existing Smart parking solutions
in Jelgava city
1
, which are based on inductive sensors
1
Jelgava is the fourth largest city in Latvia, is historical cen-
ter of Zemgales region, distance from Latvia capital Riga
is 42 km.
666
Zacepins, A., Komasilovs, V. and Kviesis, A.
Implementation of Smart Parking Solution by Image Analysis.
DOI: 10.5220/0006629706660669
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Vehicle Technology and Intelligent Transport Systems (VEHITS 2018), pages 666-669
ISBN: 978-989-758-293-6
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
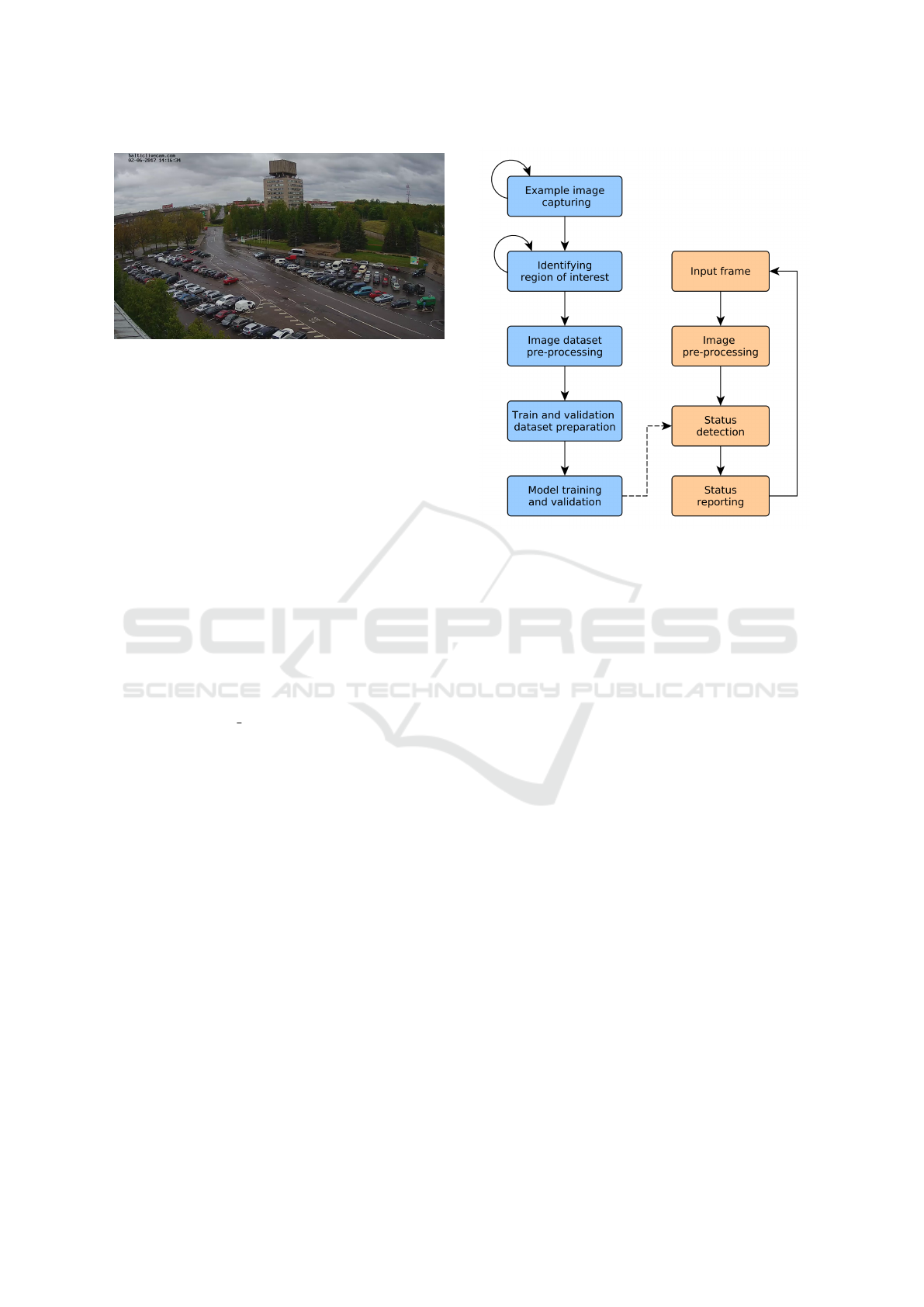
Figure 1: Frame example from live video stream.
for each parking lot monitoring and video monitoring
of entering and exiting cars (Zacepins et al., 2017).
For demonstration purposes the live
video is obtained from public video stream
(https://balticlivecam.com/cameras/estonia/narva/)
from fix camera positioned above the parking in
Narva, Estonia (see Figure 1).
2 MATERIAL AND METHODS
Figure 2 shows basic workflow of solution for parking
lot monitoring on live stream video. Input images are
extracted directly from FullHD stream (1920 ×1080),
cropped to area of interest and used for further pro-
cessing and analysis, described in subsections below.
Solution is implemented and tested in Python
3.5.2 environment using different provided libraries
(cv2, sklearn.linear model, numpy, matplotlib, etc).
OpenCV 3.2.0 library (Bradski, 2000) is used for
low level image manipulations and processing (im-
age scaling, resizing, changing image color schema,
image saving and opening, etc).
2.1 Model Development
This paper describes parking lot status (free or occu-
pied) detection approach based on machine learning
techniques. Extensive phase of sample image prepa-
ration is crucial for precise model development.
First of all variety of example images where cap-
tured from live stream video camera. Authors used
custom made automated utility which connected to
the video stream and downloaded FullHD frames
(1920 × 1080 px) on defined interval (every 10 min-
utes). More than 2 100 images where captured during
two weeks, which gave good variety in weather and
parking conditions (different time of the day, day of
the week).
Next, manual region of interest identification took
place. The captured frames contain overhead view of
Figure 2: Parking status monitoring process workflow.
parking with about 130 lots. Vehicles are oriented in
different angles and occlusions are common. During
daytime a lot of buses are using the parking. More-
over car drivers often disobey parking lot markup
(two cars in one lot, parking outside and across lots).
For demonstration purposes few parking lots were se-
lected and analyzed as described below. All other
parking lots can be processed following the same pro-
cedure.
Defined areas of interest (selected parking lots)
are cropped from example images and pre-processed.
First, parking lot images are scaled down to uniform
size of 50 × 30 px which allows generic processing
of different lots. In order to decrease number of in-
put parameters for further modeling images are also
converted to gray-scale color schema.
Training and validation datasets are created from
normalized gray-scale images (pixel color values c ∈
[−1 : 1]) of specific parking lots. Due to lack of night
mode in selected live camera images captured from
20:00 till 8:00 where excluded from datasets. Images
are manually separated into two classes: positive (car
exists, parking lot is occupied) and negative (park-
ing lot is free without car) (see Figure 3). There are
2 000 samples in positive and 1 000 samples in neg-
ative datasets. 25% of randomly selected samples are
used for validation purposes, while others are used for
model training. For better handling training and vali-
dation image sets were converted to numeric arrays.
Five classification models from sklear n package
were trained for image classification by two classes:
Implementation of Smart Parking Solution by Image Analysis
667
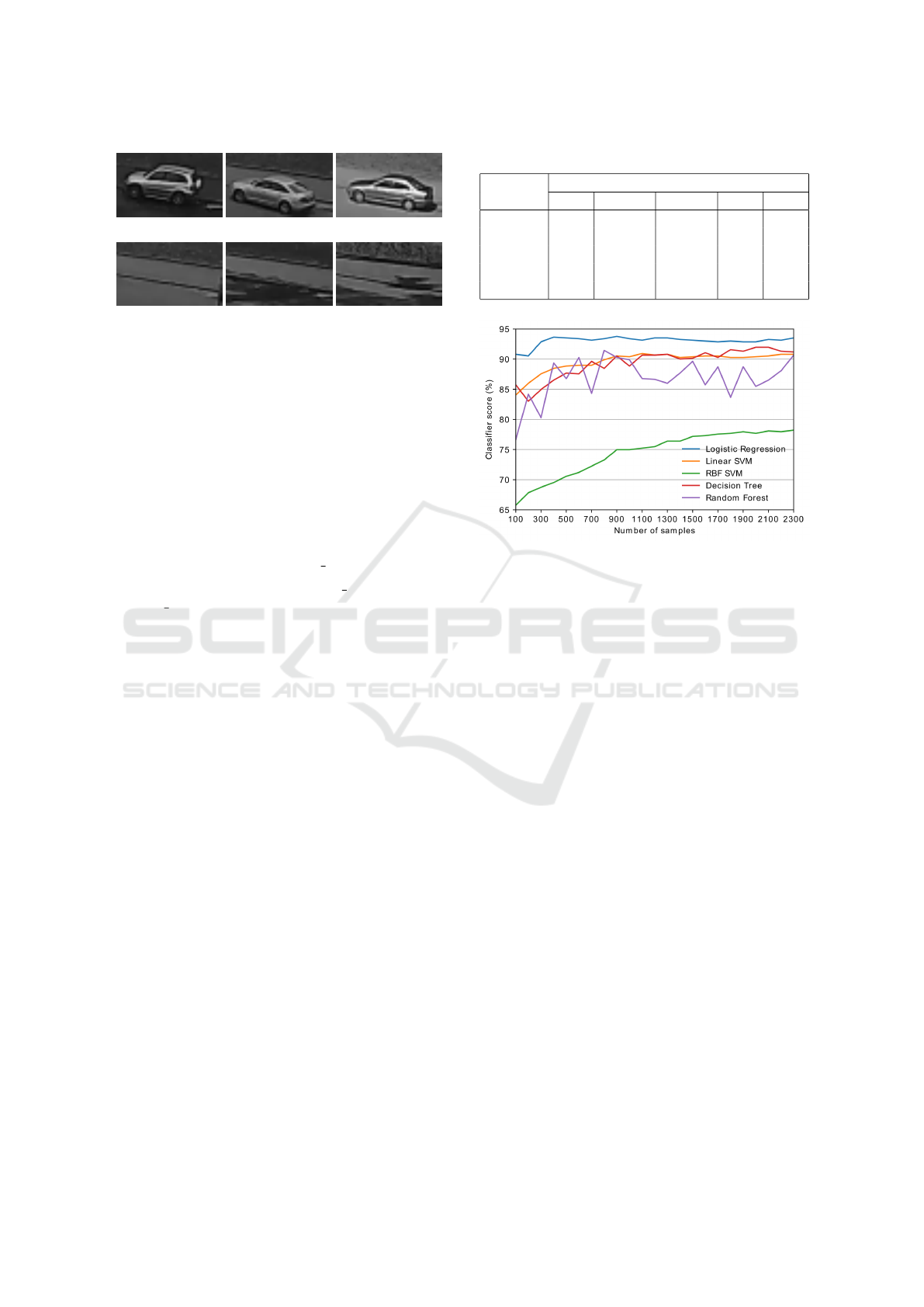
(a) (b) (c)
(d) (e) (f)
Figure 3: Positive (a, b, c) and negative (d, e, f) image sam-
ples.
either parking lot is free or occupied. Authors com-
pared classifiers modes without any tuning or im-
provement. Selected models with parameters are:
• Logistic Regression (LR) with default parameters;
• Linear Support Vector Machine (l-SVM) with
kernel = linear and C = 0.025;
• Radial Basis Function Support Vector Machine (r-
SVM) with gamma = 2 and C = 1.0;
• Decision Tree (DT) with max depth = 5;
• Random Forest (RF) with max depth = 5 and
max f eatures = 1.
Due to model implementation specifics input im-
ages (matrices) are converted to vectors. Model com-
parison and precision analysis are described in details
in results section. Finally based on comparison results
one model with highest precision was chosen for real-
time parking monitoring.
2.2 Parking Lot Monitoring
The model selected in previous phase is used for on-
line parking status monitoring. Current input frame
is captured from live video stream. Then it is pre-
processed in a way similar to model building phase:
regions of interest (parking lots) are cropped out of
the frame, scaled to uniform size and converted to
gray-scale color schema.
Next each captured region is processed through
the model, which returns its prediction: probabilities
of each class indicating either certain parking lot is
free or occupied. Regions with ”occupied” probabil-
ity P(car) ≥ 0.6 are considered as occupied (this pa-
rameter can be manually adjusted depending on user
requirements).
Results of classification are reported as status of
parking lot. All analysis and processing take less than
1 sec (connection establishment to the live stream
takes most of the time) and therefore such system is
applicable for real-time parking lot monitoring.
Table 1: Comparison of classification models by scores (%).
Num of
samples
Classification model
LR l-SVM r-SVM DT RF
100 90.8 84.0 65.8 85.7 76.7
500 93.5 88.8 70.6 87.7 86.8
1 000 93.4 90.4 75.0 88.8 89.9
1 500 93.1 90.4 77.2 90.1 89.6
2 000 92.9 90.4 77.7 92.0 85.5
Figure 4: Classifier score depending on number of training
samples.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Model development and classifier selection is impor-
tant task. To select appropriate model for given task
five classifiers were trained on the same dataset and
evaluated. Training and testing datasets are distinct
and image samples do not overlap over datasets. Ta-
ble 1 summarizes scores (mean accuracy of predic-
tion) of all selected classifiers trained with different
numbers of sample images.
Logistic regression (LR) classifier has highest av-
erage score and is not significantly affected by num-
ber of sample images. Linear SVM (l-SVM) and De-
cision Tree (DT) classifiers has comparable scores
and slightly improve average score depending on
number of samples. RBF SVM (r-SVM) has signifi-
cantly lower score compared to others, while it shows
noticeable increase of score for whole range of tested
sample numbers. Random forest (RF) classifier has
fluctuations of scoring values and is comparable with
l-SVM and DT. Detailed plot of classifier score de-
pending on number of training samples is shown on
Figure 4.
Based on classifier comparison Logistic regres-
sion were selected for live parking status monitoring
application. According to obtained results there is no
significant increase of classifier precision after 300
training samples, therefore smaller training set can
RESIST 2018 - Special Session on Resilient Smart city Transportation
668

Figure 5: Parking lot status report.
be used for parking status detection with precision of
90% and more.
Results can be considered as good taking into ac-
count camera position, parking lot configuration and
drivers’ parking habits. Figure 5 shows an example
of parking status report. Frame colors indicate either
parking lot is free (green) or occupied (red). Percent-
ages show probability of lot occupancy P(car) calcu-
lated by model.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Results show that classification precision is not signif-
icantly dependent on number of image samples used
for model training (about 300 samples is enough for
desired precision).
Disadvantage of video based parking monitoring
approach is that if car is not parked directly at consid-
ered lot, than system will not detect car correctly. In
case parking lots are differently oriented to camera,
than several models have to be trained for each park-
ing lot orientation. In future it is planned to extend
this solution for whole parking monitoring.
Significant advantage of video based parking
monitoring is that existing infrastructure can be used:
already installed surveillance, security or other cam-
eras can be used for image acquisition.
For better results pixel spatial location aware mod-
els should be used (e.g. convolutional neural net-
works, histogram of oriented gradients, etc).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
Scientific research, publication and presentation are
supported by the ERANet-LAC Project Enabling re-
silient urban transportation systems in smart cities
(RETRACT, ELAC2015/T10-0761).
REFERENCES
Al-Kharusi, H. and Al-Bahadly, I. (2014). Intelligent
parking management system based on image process-
ing. World Journal of Engineering and Technology,
2(02):55.
Albino, V., Berardi, U., and Dangelico, R. M. (2015). Smart
cities: Definitions, dimensions, performance, and ini-
tiatives. Journal of Urban Technology, 22(1):3–21.
Arnott, R. and Inci, E. (2006). An integrated model of
downtown parking and traffic congestion. Journal of
Urban Economics, 60(3):418–442.
Bradski, G. (2000). The OpenCV Library. Dr. Dobb’s Jour-
nal of Software Tools.
Idris, M., Leng, Y., Tamil, E., Noor, N., and Razak, Z.
(2009). park system: a review of smart parking sys-
tem and its technology. Information Technology Jour-
nal, 8(2):101–113.
Kuran, M. S¸., Viana, A. C., Iannone, L., Kofman, D., Mer-
moud, G., and Vasseur, J. P. (2015). A smart parking
lot management system for scheduling the recharg-
ing of electric vehicles. IEEE Transactions on Smart
Grid, 6(6):2942–2953.
Lan, K.-C. and Shih, W.-Y. (2014). An intelligent driver lo-
cation system for smart parking. Expert Systems with
Applications, 41(5):2443–2456.
Pham, T. N., Tsai, M.-F., Nguyen, D. B., Dow, C.-R., and
Deng, D.-J. (2015). A cloud-based smart-parking sys-
tem based on internet-of-things technologies. IEEE
Access, 3:1581–1591.
Polycarpou, E., Lambrinos, L., and Protopapadakis, E.
(2013). Smart parking solutions for urban areas. In
World of Wireless, Mobile and Multimedia Networks
(WoWMoM), 2013 IEEE 14th International Sympo-
sium and Workshops on a, pages 1–6. IEEE.
Sevillano, X., M
`
armol, E., and Fernandez-Arguedas, V.
(2014). Towards smart traffic management systems:
Vacant on-street parking spot detection based on video
analytics. In Information Fusion (FUSION), 2014
17th International Conference on, pages 1–8. IEEE.
Shaheen, S. (2005). Smart parking management field test:
A bay area rapid transit (bart) district parking demon-
stration. Institute of Transportation Studies.
Shoup, D. C. (2006). Cruising for parking. Transport Pol-
icy, 13(6):479–486.
Zacepins, A., Komasilovs, V., Kviesis, A., Gatins, A., Sku-
dra, M., and Pierhurovics, A. (2017). Implementation
of smart parking system in jelgava city in latvia. In
Application of Information and Communication Tech-
nologies (AICT), 2016 IEEE 10th International Con-
ference on, pages (in–print). IEEE.
Implementation of Smart Parking Solution by Image Analysis
669
