
Relational Database Anonymization
A Model-driven Guiding Approach
Feten Ben Fredj
1
, Nadira Lammari
1
and Isabelle Comyn-Wattiau
2
1
CEDRIC-CNAM, 2 Rue Conté, 75003 Paris, France
2
ESSEC Business School, 1 Av. Bernard Hirsch, 95021 Cergy, France
Keywords: Model-driven Approach, Meta-model, Guidance, Anonymization, Ontology.
Abstract: Personal data anonymization requires complex algorithms aiming at avoiding disclosure risk without
compromising data utility. In this paper, we describe a model-driven approach guiding the data owner during
the anonymization process. Depending on the step, the guidance is informative or suggestive. It helps in
choosing the most relevant algorithm given the data characteristics and the future usage of anonymized data.
It also helps in defining the best input values for the chosen algorithm. The contribution is twofold: a meta-
model describing the anonymization process and components and an approach based on this meta-model. In
this paper, we focus on microdata generalization algorithms. Both theoretical and experimental knowledge
regarding anonymization is stored in an ontology. An experiment, conducted with sixteen participants
allowing us to check the usability of the approach, is described.
1 INTRODUCTION
The advent of the Internet, combined with the
constant growth of the technology has made data
shareable out of the boundaries of organizations. The
countries’ commitment to openness and sharing of
public data, better known as “open data”, has
accentuated this phenomenon. This raises the issue of
disclosure risk of sensitive data, namely personal data
for which the anonymization is identified as a
solution. The ISO/TS 25237:2008 defines the latter as
the process that removes the association between the
identifying data set and the data subject. It is a
complex process, especially since it attempts to
satisfy two contradictory objectives: the usefulness of
the data (i.e. their quality) and their security (i.e. their
confidentiality). Therefore, data publishers are
always looking for a solution that best meets the
confidentiality and the usefulness of their data.
Performing an anonymization process requires
making decisions at different stages. In particular,
they have to select an appropriate anonymization
algorithm, to choose an adequate parameterization of
this algorithm and to judge the quality of the
rendering after execution of the process. Therefore,
they are engaged in a decision-making process based
on their domain knowledge. On the other hand, the
existing tools, due to their opacity and their lack of
guidance in the choice and parameterization of
algorithms, do not sufficiently assist professionals
with a low expertise in the field. Finally, the scientific
literature on anonymization is abundant. However, it
concentrates on proposing and/or improving
algorithms. Thus, we have noticed the lack of guiding
approaches assisting in conducting the anonymiza-
tion process. These observations motivated us to
design a domain ontology (BenFredj and al., 2015),
named OPAM, for the anonymization of microdata
(i.e. atomic data describing individual objects) as well
as a guiding approach, called MAGGO (a French
acronym for “Méthodologie pour une Anonymisation
par Généralisation Guidée par une Ontologie”) based
on this ontology. The latter capitalizes the
anonymization domain knowledge. In its current
state, it has been instantiated only by the knowledge
gathered for the generalization technique. Thus,
MAGGO serves as a guide for a professional in its
decision-making during anonymization of microdata
by generalization. Nevertheless, MAGGO is a
generic approach since it can be instantiated for
another technique. We developed a prototype to
support the approach.
After a brief state of the art (Section 2), we
describe the general approach (Section 3) and its
detailed steps (Sections 4 and 5). In Section 6, we
illustrate the approach through an example. Section 7
Fredj, F., Lammari, N. and Comyn-Wattiau, I.
Relational Database Anonymization - A Model-driven Guiding Approach.
DOI: 10.5220/0006659201610170
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy (ICISSP 2018), pages 161-170
ISBN: 978-989-758-282-0
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
161

briefly reports on the evaluation conducted with the
MAGGO tool. Finally, we conclude in Section 8 and
present some research avenues.
2 STATE OF THE ART
Several anonymization techniques exist. They differ
from each other in respect of their reliability degree
and applicability context. The reliability degree is
directly related to the re-identification risk of
anonymous data. Facing the information technology
evolution that makes possible linking data from
different sources, it is almost impossible to carry out
anonymization whilst guaranteeing a zero-re-
identification risk. The applicability context is
characterized, among other things, by the intended
use (e.g. software test or data publishing for analysis
purposes) and by the type of the original data (micro
or macro data, images, texts, etc.).
Microdata anonymization includes a wide variety
of techniques that could be classified into two
categories: non-perturbative and perturbative
techniques (Patel and Gupta, 2013). The first category
represents procedures in which the resulting data are
not denatured, that is, the data is true but may lack
details. Although they are inaccurate, they could be,
for instance, used for testing or statistical purposes.
This is not the case for the second category of
techniques. As examples of perturbative techniques,
we can mention (1) data swapping which switches the
values of one at-tribute between pairs of records
(Fienberg and McIntyre, 2004), (2) adding noise
(Brand, 2002) that consists in adding a random value
to a data to hide the exact value, (3) micro-
aggregation (Defays and Nanopoulos, 1993) which
divides the original data into homogeneous groups
and replaces some original values by a central
measure (e.g. the mean or the median) of the group to
which they belong. The suppression is a non-
perturbative technique consisting in re-moving data
from the table to avoid disclosure. The generalization
(Samarati, 2001) on which we focus on this paper is
also non-perturbative. It replaces effective values
with more general ones (a date is truncated into a
month, a city is generalized into its related region,
etc.) leading, hence, to true data but less precise one.
Several algorithms combine generalization and
suppression.
Let a quasi-identifier (QI) be an attribute set
which, when linked to external information, may
enable re-identifying individuals whose explicit
identifiers (EI) (e.g. social security number) were
removed. The set {sex, zip code, and birthdate} is a
well-known quasi-identifier in many microdata sets.
Microdata generalization technique applies to a
quasi-identifier (QI), of a microdata set where explicit
identifiers (EI) have been removed. Its goal is to
reinforce k-anonymity on anonymized microdata. K-
anonymity is one of privacy models that techniques
implement to avoid re-identification. A microdata set
satisfies k-anonymity if each data release is such that
every combination of values of quasi-identifiers can
be indistinctly matched to at least k individuals
(Sweeney, 2002). Thus, each individual is identical
with k-1 other individuals sharing the values of the
quasi-identifiers after generalization. To perform the
transformation of QI values, the generalization
technique relies on predefined generalization
hierarchies (one hierarchy per attribute of the QI).
Each hierarchy contains at least two levels. The root
is the most general value. It represents the highest
level. The leaves correspond to the original microdata
values and constitute the lowest level. Generalizing a
value of QI at-tribute will consist in replacing this
value by one of its ancestors in the generalization
hierarchy. For instance, a value of age can be
generalized to increasingly wide value interval until
the hierarchy root.
Each anonymization technique may be
implemented through different algorithms. For
example, dozens of algorithms have been proposed
for the generalization technique. Thus, there is a wide
variety of anonymization techniques and even more
algorithms that implement them. Comparisons of
techniques are proposed in the literature (e.g.
(Ilavarasi, Sathiyabhama and Poorani, 2013), (Fung
and al., 2010)). Some are certainly usage-oriented but
remain not accessible to data publishers with low
skills in the field. Moreover, algorithms associated
with techniques are only accessible through research
publications. Their specification is close to the
programming code. They are, most often, partially
illustrated with examples. Their basic principles are
textually described. Therefore, only computer
scientists or professionals with programming skills
can understand them.
Anonymization software are available (e.g.
(Poulis and al., 2015), (Dai and al., 2009) and (Xiao
and al., 2009)). However, they are rather opaque.
Even if they propose several techniques, they
generally implement a single algorithm per technique
without mentioning its details. Most of these tools do
not provide guidance in the choice of a technique and
algorithm. They do not offer any help in the
parameterization of the proposed algorithms.
Guidance is limited to the application of metrics on
anonymized data which al-low the data publisher to
ICISSP 2018 - 4th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy
162

assess, in particular, the residual risk and the
degradation due to anonymization.
Furthermore, the state of the art also includes
numerous metrics to assess the quality of anonymized
data, in terms of loss of information and/or precision,
and preservation of a given usage (Ilavarasi,
Sathiyabhama and Poorani, 2013). Finally, to the best
of our knowledge, with the exception of our OPAM
ontology (BenFredj and al., 2015), there is no
knowledge base where a data publisher can seek the
knowledge guiding him/her to useful anonymization
while at best preserving privacy. There is also no
approach that can carry out the process of
anonymizing data while offering decision-making
aids. Thus, in this paper, we propose an ontology-
based decision support method allowing to guide the
data publisher in the choice of an algorithm and in its
parameterization. One main characteristic of
MAGGO is its underlying meta-model. The next
sections present our approach, detailing its main
steps.
3 A GENERAL OVERVIEW OF
MAGGO
Data anonymization is one of the security solutions
that can be advocated in the context of privacy
protection. Once this measure decided, the person in
charge of anonymization (PIA) must design and
execute a masking process. For this purpose, he (or
she) must firstly detect identifying (EI), quasi-
identifying (QI) and sensitive data (i.e. data that
individuals generally do not want to disclose, such as
medical data or salaries). Then he (or she) selects
appropriate techniques with adequate orchestration.
For each technique, he (or she) must also choose the
most relevant algorithm, define a parameterization
that reflects its usage needs, and evaluate the quality
of the anonymized data in terms of both utility and
safety with respect to the anonymization
requirements. This process includes several key
decisions points with potentially high impact on the
anonymization quality. Without cognitive help, the
PIA must have a great mastery of the domain.
Providing assistance over the entire process requires
considerable effort given the variety of data
susceptible to be masked (microdata, linked data,
geographic data, etc.) and the diversity of existing
techniques and algorithms. In our research, we
contribute in the anonymization process of relational
databases (microdata) using the generalization
technique. More precisely, we propose a guiding
approach that allows the PIA, given an
anonymization context (defined in a specification), to
choose and to execute the microdata generalization
algorithm that best meets the anonymization
specification. The chosen algorithm is one that offers
the best trade-off be-tween the two contradictory
requirements: security and utility. More precisely, the
best trade-off will be achieved after evaluating
several algorithms with several possible
combinations of parameters. As described at Figure
1, MAGGO encompasses five steps. The first step al-
lows specifying the anonymization to be carried out.
The context is then de-scribed. This task is performed
in conjunction with the user who provides his/her
microdata set and describes his/her expectations. The
second step provides the user with some assistance in
the choice and the parameterization of generalization
algorithms. It suggests, given a specification, a
signature set for candidate algorithms (i.e. candidate
algorithms with, for each one, a set of input parameter
values).
Figure 1: MAGGO steps.
During the third step, among all these signatures,
the user selects a sub-set. MAGGO executes them on
the microdata set in the fourth step. The latter also
includes an evaluation of the different anonymized
microdata sets. The assessment is made from both
User requirements
Micro-data set
Loading and qualifying the anonymization context
Set of candidate signatures
Anonymization context loaded and qualified
Deducing and suggesting signatures for candidate algorithms
Selecting signatures to be executed
Set of signatures to be executed
Deducing and suggesting set of relevant anonymization
relevant anonymizations set
Selecting of an anonymization
Anonymizedmicro-data set
OPAM
ontology
Activity result stored into the
anonymization meta-model
Automatic activity
Activity requiring
user interaction
Possible solicitation of OPAM
Legend
Relational Database Anonymization - A Model-driven Guiding Approach
163
safety and quality points of view, by means of metrics
extracted from OPAM. MAGGO provides the user
with necessary knowledge, making him/her capable
of deciding while specifying the context and selecting
anonymization solutions. This knowledge is made
available through OPAM. Thereby, at each of its
steps, MAGGO involves expert knowledge enabling
suggestive or informative guidance (Silver, 2006).
The first one guides the user in his/her choices while
the second one provides him/her with information
that can enlighten his choice. In our context, the
suggestive guidance helps the PIA in the selection of
the appropriate algorithm while the informative
guidance provides him information to facilitate his
choice regarding an algorithm or a technique. Thus,
MAGGO offers suggestive guidance in its Step 2 and
4 and informative one in its other steps.
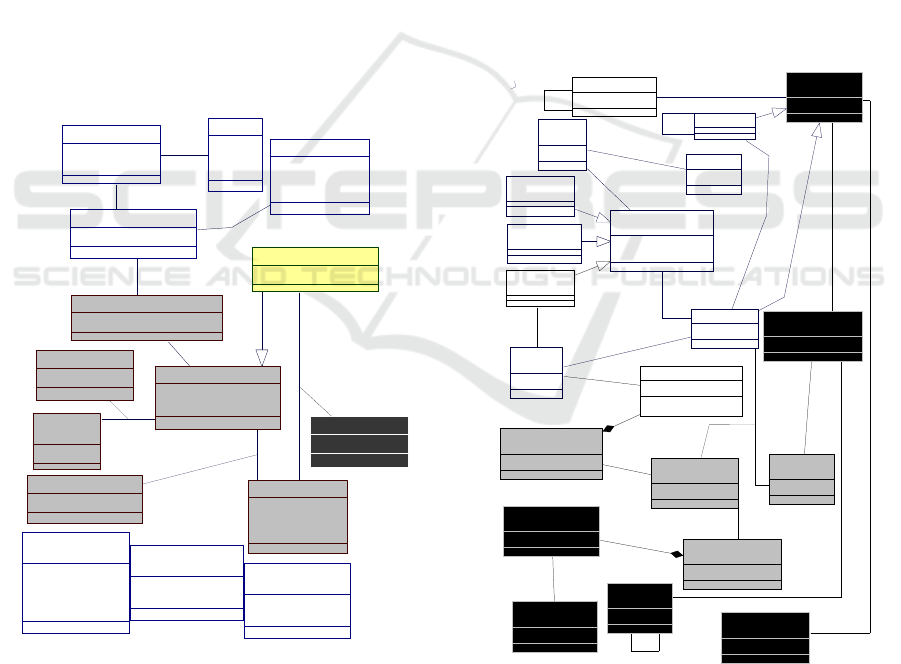
The underlying meta-model plays a significant
role in our approach. Indeed, while OPAM provides
the required knowledge for anonymization, the meta-
model gathers the conceptual abstractions of
MAGGO sources and target artefacts. Figure 2
describes this meta-model.
Figure 2: The meta-model of MAGGO.
In this figure, the concepts involved in a same step
of MAGGO are represented by the same colour. An
attribute comes from an original relational database.
It can be sensitive, not sensitive, part of a QI or of an
EI (Type 1). It can also be continuous or categorical
(Type 2). The definition of the anonymization context
associated to an original database involves
parameters provided by the PIA as well as others
generated by MAGGO. The deduced signatures (step
2 of MAGGO) and, among them, those selected by
the PIA are, respectively, stored in the classes
“Proposed Signature” and “Selected Signature”. The
result of theoretical (i.e. deduced from similar cases)
and real evaluations conducted by MAGGO are
stored respectively in the association classes “Local
Assessment” and “Real Assessment”.
Thus, the execution of the first step of MAGGO
instantiates our meta-model with data describing the
anonymization context as well as its qualification.
The following steps carry out an incremental
enrichment of the model with complementary data.
MAGGO is based on the OPAM ontology (Ben
Fredj and al. 2015). To facilitate the understanding of
its different steps, presented above, we recall in
Figure 3 the main concepts of the meta-model of
OPAM.
Figure 3: An extract of the conceptual schema of OPAM.
Classes with a white background are those that
represent the "theoretical" knowledge related to
anonymization techniques and algorithms. The grey
background classes describe the concepts that
Parameter Type
Supplied
Generated
<<Enumeration>>Type1
EI
QI
Sensitive
Non sensitive
<<Enumeration>>
Type2
Continuous
Categorical
<<Enumeration>>
Value Assignment
Value
Local Assessment
Theoretical Estimation
Real Assessment
Real Estimation
Selected Signature
Anonymized DB Address
Algorithm
Parameter
Name
Evaluation Criterion
Criterion Label
Epsilon List
Metric
1..*
1..*
1..*
1..*
Attribute
Name
Type 1
Type2
Proposed Signature
Signature Label
Overall Theoretical Score
1..*
1..*
1..*
1..*
1..*
1..*
1..*
1..*
Original DataBase
Original DB Name
Address DB
1
1..*
1
1..*
Context Parameter
Parameter Name
Parameter Value
Parameter Type
Algorithm to be Parameterized
Label
1
1..*
1
1..*
Anonymization Context
Context Identifier
1..*
1
1..*
1
1..*
1
1..*
1
1
1..*
1
1..*
Output
Characteristic
Process
Characteristic
Database
descriptor
Descriptor Name
Database descriptor
Value
Value
1..*
1
1..*
1
Is concerned with
Set of database
Descriptor Values
Set Identifier
1..*1..*
Experimental
Assessment
Data Value
1..*
0..1
1..*
0..1
Is valid for
Valuation
Value
Set of input parameter
values
Set Identifier
0..1
1..*
0..1
1..*
Is valid for
Domain
Value
Label
1..*
1..*
1..*
1..*
Has
Input
Characteristic
Input Parameter Value
Value
1..*1..*
Technique
0..*
0..1
0..*
Is kind of
0..1
Algorithm
Characteristic
Characteristic Label
name
1
1..*
1
1..*
Has
Algorithm
Input
Name
1
1..*
1
1..*
Characterizes
1..*
1
1..*
1
Is concerned with
Algorithm
Specification
1..*
1
1..*
1
Implements
1..*
1..*
1..*
1..*
Owns
1..*
1..*
1..*
1..*
Requires
Anomymizatio
n Goal
Goal Name
0..1
0..*
0..1
Refines
0..*
Assessment
Metric
Metric Name
1..*
1..*
1..*
1..*
Abstraction
Abstraction Name
0..1
0..*
0..1
Instantiates
0..*
Anonymization
Constraint
Label
Anonymization
Requirement
Label
1
0..*
1
0..*
Generates
1..*
1
1..*
1
Evaluates
Anonymization
Process
Process Name
1
1
1
1
Describes
1..*
1..*
1..*
1..*
is imposed to
1..*
1..*
1..*
1..*
Is associated to
ICISSP 2018 - 4th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy
164
contribute to the description of the context. Finally,
the classes with dark background represent the
empirical knowledge collected from the experiments
published in the literature.
The following sections describe each step of
MAGGO.
4 LOADING AND QUALIFYING
THE ANONYMIZATION
CONTEXT (STEP 1)
Anonymization aims at preventing potential privacy
attacks. Consequently, the anonymization requires
first the selection of one technique (or several) that
implements the privacy model intended to counter
these attacks. Then, given a privacy model and one
anonymization technique, we must find out the
algorithms that meet the expectations of the PIA.
These expectations constitute a requirement set that
anonymization must satisfy. Two categories of
requirements must be considered. In the first one, the
requirements are independent of the technique,
namely the usage of the anonymous data, the re-
identification risk threshold, the acceptable
suppression rate and the required quality for
anonymized data. This quality is difficult to measure.
It can be expressed as the relative importance of the
quality criteria to be checked by anonymous data. In
the second category, the requirements depend on the
anonymization technique and impact the choice of
algorithm. In the case of the generalization technique,
the desired type of generalization can constitute a
specific requirement. For instance, anonymization by
generalization is compatible with data classification.
It requires a risk of re-identification below 10% and a
suppression rate of more than 5%. The PIA can also
indicate that he/she prefers the preservation of
privacy rather than the completeness of anonymous
data. Finally, he/she could opt for a multidimensional
generalization (i.e. two identical data in the original
table can be generalized differently while respecting
the generalization hierarchy). Even if this in-
formation is available, it is not sufficient to select
suitable algorithms. Indeed, as we have mentioned in
our state of the art on anonymization by
generalization (Benfredj and al., 2014), the choice of
algorithms is also based on metadata (descriptive data
of the database). The latter can be computed
automatically or provided by the PIA. An example of
metadata is the nature of the attributes (EI / QI /
sensitive / non-sensitive, categorical / continuous)
and the dataset distribution type. Moreover, some of
these descriptors are required regardless of the
technique. Others are specific to a technique. For
instance, the list of attributes constituting the QI is
necessary for all anonymization techniques.
However, the information regarding the dataset
distribution type can help selecting the algorithms
related to certain techniques, including the
generalization.
To summarize, for the sake of genericity, the
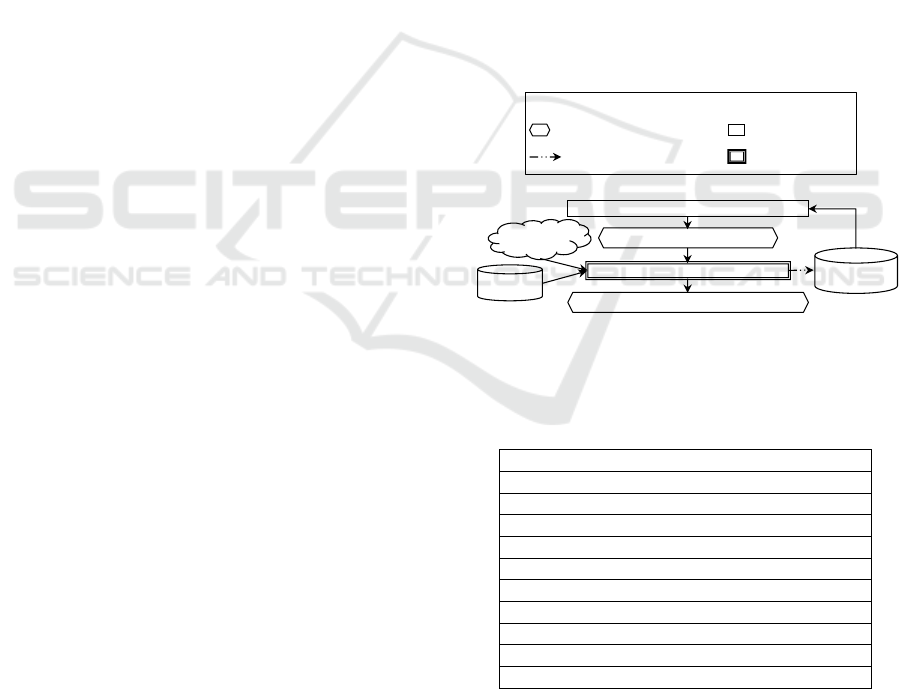
anonymization context requested by a user for his/her
microdata is built in two stages (Figure 4). First,
MAGGO constructs the context to be qualified, by
retrieving in the ontology, its parameters, i.e. the
kinds of user requirements to be met as well as the
metadata, associated to the solicited anonymization
type. The sub-schema of OPAM (Figure 3) queried
by MAGGO is the one with dark background. As an
example, in the case of anonymization by generaliza-
tion, our MAGGO approach, after querying the
OPAM ontology, will construct the context of
anonymization by generalization. This context
consists of the parameters described in Table 1.
Figure 4: Step 1: Loading and qualifying the anonymization
context.
Table 1: Context parameters for microdata generalization
technique.
QI and EI
Sensitive attributes
Micro-data set size
Expected generalization type
Type of the QI: categorical or continuous
Tolerated re-identification risk threshold
Allowable deletion rate
Usage requirement
Original micro-data set
k
MaxSup
The two last ones are deduced by MAGGO. The rest
of the parameters are supplied by the user. Although
currently provided, the first five ones are deductibles.
The user assigns a value to some of these context
parameters, stored in the anonymization meta-model,
Loading the context elements to be qualified
qualifying the anonymization context
Anonymization context loaded and qualified
Anonymization context loaded
OPAM
ontology
User
requirements
Micro-data
set
Activity result stored into the
anonymization meta-model
Automatic activity
Activity requiring
user interaction
Possible solicitation of OPAM
Legend
Relational Database Anonymization - A Model-driven Guiding Approach
165

since they correspond to his/her requirements. This
assignment is performed in the second phase of this
first step. Except k and MaxSup, all parameters are
deduced from the analysis of the datasets. In the
current version, MAGGO does not offer this
functionality. In the future, we intend to integrate
components to automatically perform this type of
extraction. Thus, in MAGGO, MaxSup is calculated
from the size of the dataset and the user-authorized
suppression rate by applying Formula (1). To
compute k which refers to k-anonymity, MAGGO
uses Formula (2). This formula is the same as that
used by PARAT tool. It expresses the fact that the re-
identification risk rate is inversely proportional to k.
In other words, the smaller k is, the greater the re-
identification risk.
MaxSup=Microdata size*Allowable deletion rate (1)
k = 100 / re-identification risk rate (2)
Once the context of anonymization filled, MAGGO
suggests to the user, in the second step, in the form of
signatures, a potential set of parameterized algorithms
capable of satisfying his/her requirements.
5 DEDUCING AND SUGGESTING
SIGNATURES FOR
CANDIDATE ALGORITHMS
(STEP 2 AND FOLLOWING
STEPS)
The second step of MAGGO aims at building,
evaluating, and submitting signatures meeting as far
as possible quality requirements of the PIA (Figure
5). Its first phase consists in building relevant
signatures. First, MAGGO extracts the algorithms in
accordance with the anonymization context and
provides them with parameter values within the
constraints specified in the context. Then, among the
Figure 5: Step 2: Deducing and suggesting signatures for
candidate algorithms.
relevant signatures, MAGGO proposes those offering
the best score in terms of accordance with the quality
requirements. The following paragraphs give details
regarding each of these phases.
5.1 Building Relevant Signatures
There are several forms of generalizations. As an
example, multidimensional generalization is such
that, in the resulting dataset, the data are not
necessarily at the same level of generality. Thus, one
can imagine that an age range may be more or less
wide according to individuals. The advantage is that
we can refine the generalization level depending on
data and thus avoid too much generalization, which
would restrict their utility. Thus, in our approach, the
type of generalization is a context parameter
impacting the choice of algorithms. MAGGO takes
them into account before eliciting parameter values
for these algorithms. For instance, regarding
anonymization by generalization, if the user has not
specified a requirement defining the type of
generalization to be obtained, at this step, all
generalization algorithms are eligible. On the other
hand, if his/her requirement is to obtain
multidimensional generalizations, then this set is
limited to the algorithms providing this type of
generalization such as Median Mondrian. This
filtering of algorithms according to an anonymization
context relies on the OPAM ontology which contains
the knowledge used to confront the characteristics of
the algorithms with the requirements of the
anonymization. This knowledge is represented thanks
to the part of OPAM subschema with white
background at Figure 3.
The selection of algorithms results in the
instantiation of the anonymization meta-model (some
classes with grey background of the meta-model at
Figure 2. This instantiation also contains, for each
algorithm, the set of possible combinations of
parameter values that can be assigned to it. Each
algorithm coupled with each combination of possible
parameter values constitutes a relevant signature. The
parameters may be considered as anonymization
constraints. Thus, we grant to the parameter of the
algorithm the value of the context parameter in accor-
dance with the anonymization constraints imposed by
the user. For instance, in the case of anonymization by
generalization, the user expresses these two
constraints: the tolerated re-identification risk
threshold, and the allowable suppression rate. These
two constraints generate, in the anonymization context,
a value for k and MaxSup. These two values combined
with each algorithm constitute a relevant signature.
Building relevant signatures
Set of relevant signatures
Theoretical assessment of relevant signatures
Set of signatures to be executed
OPAM
ontology
Anonymization context loaded and qualified
ICISSP 2018 - 4th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy
166

5.2 Theoretical Assessment of Relevant
Signatures
This phase aims to provide the user with the
signatures that are closest to his/her quality and
security requirements. It is a multi-criteria decision
making (MCDM) process for which we apply the
AHP (Analytical Hierarchy Process) technique
(Saaty and Sodenkamp, 2008). The latter, on the basis
of pairwise comparisons of evaluation criteria,
determines the overall score of each of the signatures
in order to retain the best ranked ones. It is thus
possible to provide the user with the three relevant
signatures having the highest score. To compute the
score of each signature, MAGGO provides AHP with
a hierarchy. The first level of this hierarchy represents
the objective of this step. The intermediate levels
correspond to the hierarchy of requirements stored in
OPAM (the class “Anonymization Requirement” and
the class “Anonymization Goal”). Its last level (the
leaves of the tree) gathers the relevant signatures to
be evaluated. For example, the anonymization of data
that we want to use for classification may be
represented by the hierarchy of Figure 6.
Figure 6: Example of AHP hierarchy for anonymization.
Once the hierarchy has been built, the process defines
the judgments about the relative importance of the
elements of this hierarchy. The judgments between
the elements of the intermediate level of the hierarchy
(i.e. criteria and sub-criteria) are expressed by the
user and stored in the anonymization context. Then,
MAGGO automatically computes the judgments on
the relative importance of signatures (overall
theoretical score) after an evaluation of each signature
according to a given criterion. This approximate
evaluation, called "local assessment", results from the
experiments performed by the anonymization experts
and stored in OPAM (white background classes at
Figure 3). The relative importance of each signature
is also computed automatically, based on their local
assessments and on a comparison scale available in
MAGGO. The following paragraphs describe these
local and global assessment processes.
5.2.1 Local Assessment of Relevant
Signatures
Several assessments of microdata anonymization
algorithms are available in the literature. Each of
them measures the quality of an anonymous dataset
with respect to a criterion (security, precision,
completeness, etc.) given an algorithm signature and
the specific characteristics of the original dataset.
Metrics are used to compute these qualities. OPAM
stores evaluations found in the literature (white
background classes at Figure 3). In the case where
there is no theoretical assessment for a signature (i.e.
no measures found in the literature that we can adapt)
and for the characteristics of the dataset at hand,
MAGGO executes a supervised learning technique to
predict the quality of this dataset when anonymized.
To this end, we use the regression tree technique since
it lends itself to the type of the predictor and target
variables. We also opted for this technique given the
small size of the training sample (Loh, 2011). The
target variable is the criterion to be measured. The
predictor variables are the different context elements
influencing the target variable. The training dataset is
extracted from the OPAM ontology (i.e. the
association class “Experimental assessment”). Thus,
for example, for anonymization by generalization
serving classification purposes, we need four training
datasets: one per sub-criterion i.e. per leaf of the
intermediate level of the AHP hierarchy described at
Figure 6. All datasets contain the same information: a
value for "k", a value for "number of attributes of the
QI", and a value for "the original microdata set
distribution". The output is the measurement of the
target criterion for each training example. Once each
signature is evaluated, the meta-model is enriched by
these new estimations (instantiating the association
class “Local assessment”).
5.2.2 Global Assessment of Signatures
Once the local evaluations of the various signatures
have been carried out, it is necessary to make pairwise
comparisons to deduce the relative importance of the
signatures with respect to each criterion. This
comparison leads to the construction of a matrix of
comparisons that AHP exploits for deriving scores.
Provide signatures closest to the user's quality
and safety requirements
Privacy preservation Quality
Completeness
precision
Classification preservation
Goal
Criteria
Sub-criteria
Alternatives
Relational Database Anonymization - A Model-driven Guiding Approach
167
The automatic deduction of the matrix is based on the
semantic scale defined at Table 2.
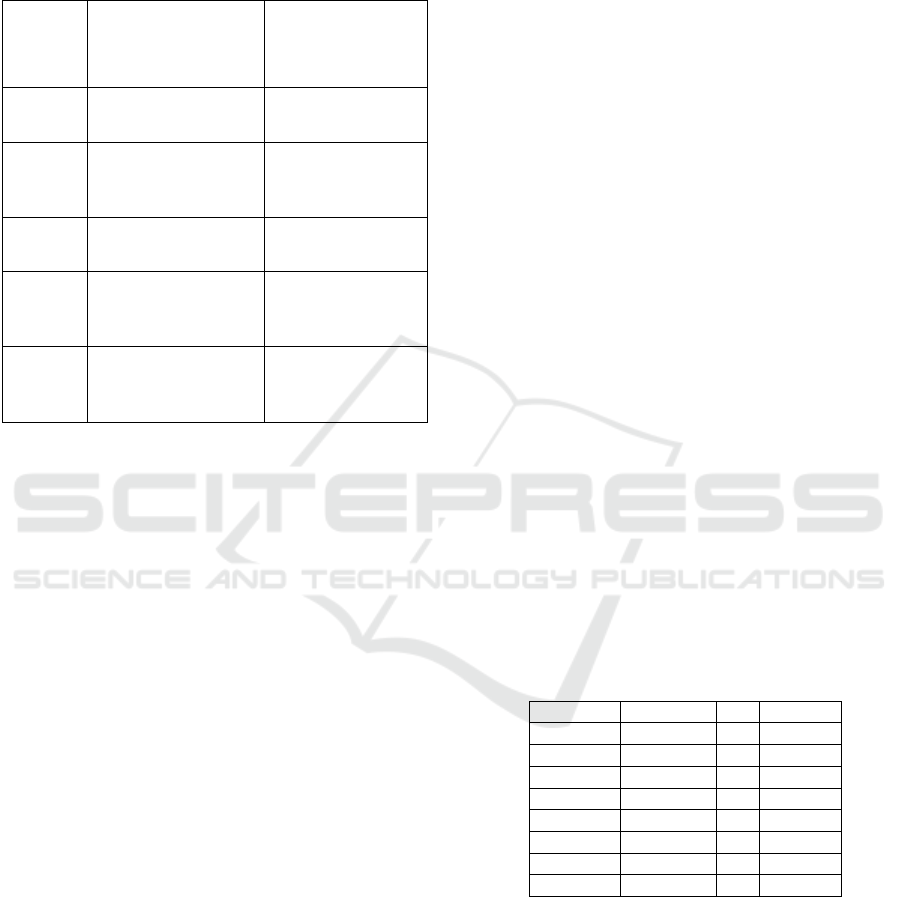
Table 2: Semantic scales of relative importance for
signatures.
Intensity
Meaning with
respect to criterion
Ci
Formal
interpretation
1
Sj and Sj’ are of
equal quality
1
'
_
E
Ci
Sj
E
Ci
Sj
2
Sj has a quality
slightly better than
Sj'
2
'
_1
E
Ci
Sj
E
Ci
Sj
3
Sj has a better
quality than Sj’
3
'
_2
E
Ci
Sj
E
Ci
Sj
4
Quality of Sj is much
better than quality of
Sj '
4
'
_3
E
Ci
Sj
E
Ci
Sj
5
Quality of Sj is
extremely better than
that of Sj '
4
'
_4
E
Ci
Sj
E
Ci
Sj
This scale is inspired by the semantic scale of (Saaty
and Sodenkamp, 2008). The first column of this table
is a number that indicates how many times is Sj is
over Sj’ with respect to the criterion Ci.
E
Ci
Sj
(respectively
E
Ci
Sj'
) represents the local assessment of
the signature Sj (respectively Sj’) for the criterion Ci.
We also have: ε1< ε2< ε3 <ε4 < ε5. These values are
predefined by MAGGO for each quality criterion (see
the class “Evaluation Criterion” of the meta-model).
5.3 Steps 3, 4 and 5 of MAGGO
Once the pairwise comparisons have been performed,
AHP provides the global score of each relevant
signature, which allows to prioritize these signatures
and to propose those having the best score to the user,
during the third step of MAGGO. The user has the
possibility to choose one or more signatures that will
be executed on the data set. The execution of these
signatures is the aim of step 4. During this step, an
anonymous dataset is delivered for all relevant,
highest-score, user-selected signatures. To guide the
user in the choice of anonymous datasets, different
real evaluations are carried out according to the
anonymization context. These evaluations are also
carried out using AHP. Each of them consists in
evaluating each anonymous dataset according to each
expected quality requirement.
6 ILLUSTRATIVE EXAMPLE
To illustrate our approach, let us suppose that we have
an anonymization context characterized as follows.
The table to be anonymized has a large size (e.g. 1000
records) with a uniform distribution of microdata. We
assume that the threshold tolerated for the re-
identification risk is 10%. Similarly, no more than
20% of the tuple can be deleted. The QI includes three
attributes. The future usage of the anonymized data is
classification. The PIA attaches as much importance
to the data usefulness as to their protection from
disclosure. The data precision of the produced data is
slightly more important for him/her than the usage
requirement (which is in this case the classification)
but very strongly more important than the data
completeness. However, the classification is of
greater importance to him/her than the data
completeness. In the first step of MAGGO, the user
must enter its context. Some context elements (table
size, data distribution, QI size) are calculated
automatically after loading the table. MAGGO also
computes k and MaxSup. For this context, the
parameters k and MaxSup are respectively 10 and
200. Algorithm signatures can also be defined for k =
12 and MaxSup = 150. In its second step, MAGGO
deduces a set of candidate signatures. MAGGO
exploits OPAM to find algorithms that fulfill the
constraints enunciated in the anonymization context.
Let us assume that only Datafly, Median Mondrian
and TDS algorithms fulfill these constraints.
Therefore, the generated signatures are summarized
in the first four columns of Table 3.
Table 3: The generated signatures.
Signature
Algorithm
k
MaxSup
Sig 1
Datafly
10
150
Sig 2
Datafly
10
150
Sig 3
Datafly
12
200
Sig 4
Datafly
12
200
Sig 5
Mondrian
10
0
Sig 6
Mondrian
12
0
Sig 7
TDS
10
0
Sig 8
TDS
12
0
They are evaluated per each AHP hierarchy sub-
criterion of Figure 6. The local evaluations
corresponding to the criteria “privacy preservation”
and “completeness” have been deduced according to
k and MaxSup. Those related to the criteria
“classification preservation” and “precision” have
been learned, using the regression tree technique
applied on the experimental evaluation stored in
OPAM. The “Discernability Metric” (DM) (Fung,
ICISSP 2018 - 4th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy
168

and al., 2010) has been used for the precision
criterion. The overall evaluation, computed by
MAGGO, for each signature, using AHP, appears in
the last column of Table 4. This global score is based
on the relative importance of each criterion that the
user has expressed before. This score allows the user
to choose to execute, on the original data set, the
signatures (for example the last four) that offer the
best trade-off between the four criteria.
Table 4: Local and global assessment of signatures.
Signature
Local Evaluations
Global
Score
PP
C
P
CP
Sig 1
0.9
0.85
50000
0.54
0.1
Sig 2
0.9
0.85
50000
0.54
0.05
Sig 3
0.92
0.8
60000
0.61
0.04
Sig 4
0.92
0.8
60000
0.61
0.05
Sig 5
0.9
1
15000
0.65
0.27
Sig 6
0.92
1
20000
0.63
0.18
Sig 7
0.9
1
35000
0.79
0.19
Sig 8
0.92
1
40000
0.71
0.12
PP: Privacy Preservation C: Completeness
CP: Classification Preservation P: Precision
7 MAGGO VALIDATION
After prototyping MAGGO, we carried out an
experiment to evaluate the effect of its decision-
making aid on the user. For this purpose, we have first
defined a usability model, inspired by those found in
the literature (Madan and Dubey, 2012), to assess
each type of guidance (informative and suggestive).
Our model comprises the effectiveness, efficiency,
learnability, and satisfaction attributes. According to
ISO 9241-11 (1998), effectiveness is the performance
measure of a system to complete task or goal
successfully within time. Efficiency is the successful
completion of the task by a system. The satisfaction
is acceptability of a system by the users. The
learnability attribute is defined, in ISO9126 (2001),
as the capability of the software product to enable the
user to learn its application. We also have considered
four kinds of guidance and thus built four tool
versions. The first kind of guidance is a predefined
informative one. It is similar to the one found in the
current tools. It consists of a tutorial and aids
throughout research papers. The second kind of
guidance is an on-demand informative guidance
appearing over the course of the anonymization steps.
The third kind is the suggestive guidance proposed in
MAGGO. The last one combines both the second and
third types of guidance. Sixteen participants have
been recruited to perform the same decision task in a
controlled environment. They were all either doctoral
students or researchers, in computer science, with
neither experience nor knowledge in anonymization.
Therefore, we have considered that they have the
same profiles in both the computer science and
anonymization fields. To avoid any biased
interpretation of the results, the same anonymization
context was given to each participant. Each tool
version was run by four participants randomly
assigned to it.
Before running the tool, each participant has
received a brief oral presentation of the microdata
anonymization with an emphasis on the
generalization technique. He (or she) has been invited
to use the tool for anonymizing the provided original
data (given the predefined context) and to choose the
“best” one among the resulting sets of anonymized
data. Once the anonymization process has been
finalized, the participant was invited to fill a multiple-
choice questionnaire (MCQ) consisting of fifteen
questions. This MCQ has been designed to evaluate
the participant’s learnability. The participant had also
to evaluate his/her satisfaction level, for the provided
guidance, on a scale of 1 to 10. To avoid erroneous
results, we presented him the other three versions
before he/she evaluated his/her satisfaction. The
efficiency of a version has been measured by
considering the quality of the decisions made by the
participants. The effectiveness of the version has been
defined from a user’s view point. Therefore, it
corresponds to the efficiency of participants in
carrying out the anonymization divided by the time it
took them to complete this task. For lack of space, we
resume our analysis of all the obtained measures. The
latter have confirmed the non-negligible contribution
of simultaneously suggestive and informative
guidance in the proper accomplishment of
anonymization. It also confirmed the requirement of
suggestive guidance for users having little or no skills
in anonymization.
8 CONCLUSION
Data publishers face two major challenges during an
anonymization process. The first one is the choice of
the appropriate algorithm. The second one is related
to the parameterization of the algorithm so that it
delivers secure and useful data. Our MAGGO
approach guides the PIA through these two tasks
using an ontology named OPAM. Its guidance can be
qualified as both incremental and interactive. It is
incremental in the sense that it is introduced at various
points of key decisions throughout the process. It is
Relational Database Anonymization - A Model-driven Guiding Approach
169

interactive since it involves the user in the decision-
making process. The latter can also query the
ontology to obtain the necessary knowledge. Securing
data by anonymization and preserving an intended
quality are usually contradictory objectives.
Therefore, the anonymization process, implemented
in MAGGO, aims at a trade-off between these
objectives, depending on the usage requirement of the
anonymized data. Our approach is currently limited
to anonymization of microdata sets by generalization.
However, we have endeavored to make it as generic
as possible so that it can be applied to other microdata
anonymization techniques. Finally, to promote its
evolution and its incremental implementation, we
opted for a model driven approach. OPAM was
published in a previous paper. The contribution of this
paper is twofold: i) a meta-model to describe the
different components of the approach, ii) the
methodology MAGGO which performs the whole
anonymization process. Moreover, we illustrate the
contributions with an example and describe a
controlled experiment conducted to validate the
added value of the approach. There are two main
avenues for future work. First, we want to conduct an
experiment on a larger scale including users that have
low skills in computer science in order to obtain a
stronger evaluation of MAGGO. This will allow us to
confirm the usability of our approach and tool.
Second, we want to perform the same effort to extend
MAGGO to other micro-data anonymization
techniques.
REFERENCES
BenFredj, F., Lammari, N., Comyn-Wattiau, I., 2015.
Building an Ontology to Capitalize and Share
Knowledge on Anonymization Techniques. In ECKM
2015, 16th European Conference on Knowledge
Management, pp 122-131. Edited by Massaro, M. &
Garlatti, A., ISBN: 978-1-910810-46-0.
BenFredj, F., Lammari, N., Comyn-Wattiau, I., 2014.
Characterizing Generalization Algorithms-First
Guidelines for Data Publishers, In KMIS 2014,
International Conference on Knowledge Management
and Information Sharing, pp 360-366. SciTePress
Science and Technology Publications. ISBN: 978-989-
758-050-5.
Brand, R., 2002. Microdata Protection through Noise
Addition, In Inference Control in Statistical Databases-
From Theory to Practice. Domingo-Ferrer (Ed.), pp
97-116. Springer.
Dai, C., Ghinita, G., Bertino, E., Byun, J., Li, N.2009.
TIAMAT: a Tool for Interactive Analysis of Microdata
Anonymization Techniques, In VLDB’09, Vol 2(2),
1618-1621.
Defays, D., Nanopoulos, P., 1993. Panels of Enterprises and
Confidentiality: the Small Aggregates Method, In 92nd
Symposium on Design and Analysis of Longitudinal
Surveys, pp 195-204, Ontorio, Canada.
Fienberg, S.E., McIntyre, J., 2004. Data swapping:
Variations on a theme by dalenius and reiss, In PSD
2004, Privacy in statistical databases, LNCS 3050, pp.
14-29. Domingo-Ferrer & Torra (Eds.), Springer.
Fung, B. C. M., Wang, K., Chen, R., Yu, P. S., 2010.
Privacy Preserving Data Publishing-a survey of recent
developments, In ACM Comput. Survey, Vol. 42(4), pp
14:1-14:53.
Ilavarasi, B., Sathiyabhama, A. K., Poorani, S., 2013. A
survey on privacy preserving data mining techniques,
In IJCSBI journal, 7(1), ISSN: 1694, pp 209-221.
Loh, W-Y., 2011. Classification and regression trees, In
Wiley Interdisc. Rew.: Data Mining and Knowledge
Discovery, Vol 1(1), pp 14-23.
Madan, A., Dubey, S. K., 2012. Usability Evaluation
Methods: a Literature Review. In IJEST journal, ISSN
0975-5462, Vol 4(2).
Patel, L., Gupta, R., 2013. A Survey of Perturbation
Technique for Privacy-Preserving of Data, In IJTAE
journal, Vol 3(6), pp 162-166, ISSN 2250-2459.
Poulis, G., Gkoulalas-Divanis, A., Loukides, G.,
Skiadopoulos, S., Tryfonopoulos, C., 2015. SECRETA:
A System for Evaluating and Comparing Relational and
Transaction Anonymization algorithms, In Medical
Data Privacy Handbook, Chapter 4, Springer Int.
Publishing, pp.83-109.
Saaty, T.L, Sodenkamp, M.A., 2008. Making decisions in
hierarchic and network systems, In IJADS journal,
ISSN 1755-8077, Vol 1(1), pp 24-79.
Samarati, P., 2001. Protecting respondents’ identities in
microdata release, In IEEE Trans. on Knowl. and Data
Eng., Vol 13(6), pp 1010-1027.
Silver, M. S., 2006. Broadening the Scope. Human-
Computer Interaction and Management Information
Systems: Foundations, 90.
Sweeney, L., 2002. k-Anonymity: A model for Protecting
Privacy, Int. Journal of Uncertainty, Fuzziness and
Knowledge-Based Systems, Vol 10(5), pp 557-570.
Xiao, X., Wang, G., Gehrke, G., 2009. Interactive
Anonymization of Sensitive Data, In SIGMOD’09,
Binnig C. & Dageville B.(Eds.), pp 1051–1054, New
York, USA.
ICISSP 2018 - 4th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy
170
