
A Concept for Comprehensive IT Support for Environmental and
Energy Management in SMEs
Anna O’Faol
´
ain de Bhr
´
oithe
1
, Frank Fuchs-Kittowski
1
, J
¨
orn Freiheit
1
, Detlef H
¨
uttemann
2
,
Stefan Voigt
3
and Thomas Dinkel
3
1
HTW Berlin, Wilhelminenhofstr. 75 A, 12459 Berlin, Germany
2
CosmoCode GmbH, Prenzlauer Allee 36g, 10405 Berlin, Germany
3
Fraunhofer IFF, Sandtorstr. 22, 39106 Magdeburg, Germany
{stefan.voigt, thomas.dinkel}@iff.fraunhofer.de
Keywords:
Energy Management, Environmental Management, IT, QuiXel, SMEs.
Abstract:
Environmental and energy management (EnvM and EM, respectively) are important aspects in the everyday
running of companies. However, there is no single software tool that completely supports companies throug-
hout the entire management process. The aim of the QuiXel project is to develop an integrated data and
information platform for evolving and collaborative EnvM and EM in small and medium-sized enterprises
(SMEs). The platform will provide comprehensive software support for the complete management process
and will simplify tasks such as planning goals and targets, data structuring, data acquisition, data analysis,
report generation, and documentation. In addition, the platform will provide an integrated manual providing
instructions and guidelines for the best practice of EnvM/EM in accordance with the ISO 14001 and ISO
50001 norms. The requirements for such a platform are presented in this paper, along with an overview of the
system concept.
1 INTRODUCTION
Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) can gain
significant benefits from implementing energy ma-
nagement; they can reduce their costs, protect the
environment, increase the sustainability of the eco-
nomy, and improve their public image (Bundesminis-
terium f
¨
ur Umwelt, Naturschutz und Reaktorsicher-
heit (BMU), 2012). However, many tasks covering a
broad range of areas including documentation, con-
trol, planning, monitoring, evaluation and decision-
making must be fulfilled as part of a complete energy
management process. It is not possible to success-
fully implement energy management without the sup-
port of appropriate tools as the tasks are too nume-
rous and too complex (Wohlgemuth, 2015). It is no-
teworthy, then, that no single software tool capable of
supporting all these tasks currently exists (EnergieA-
gentur.NRW, 2013). At present, only certain aspects
of the management process are addressed by speciali-
zed software solutions, e.g., energy data management
or energy control (R
¨
oßler et al., 2013). A single tool
capable of guiding users through the complete process
as well as managing all necessary data (including do-
cumentation, raw data, analysis results, and reports)
would be helpful for experienced environmental and
energy managers as well as for beginners.
The QuiXel project, funded by the BMBF “KMU-
innovativ” program, is pursuing a comprehensive ap-
proach to providing complete IT support throughout
the management process with a single platform. Ba-
sed on the European norms for environmental ma-
nagement (EnvM) and energy management (EM) as
well as discussions with industry partners, the requi-
rements for such a system have been determined and
consequently integrated into an all-inclusive concept.
The platform must aid in a multitude of tasks such as
planning efficiency measures, setting goals and tar-
gets, data structuring, data acquisition (both manual
and automatic), data analysis, reporting, and docu-
mentation. The system should also provide informa-
tion and instructions to its users on EnvM/EM best
practices so that non-experts can quickly start making
progress. These instructions should be compliant with
ISO norms for EnvM and EM so that users who fol-
low the guidelines are eligible for certification. The
project is currently in the implementation phase, with
the testing and evaluation phase to be completed by
O’Faoláin de Bhróithe, A., Fuchs-Kittowski, F., Freiheit, J., Hüttemann, D., Voigt, S. and Dinkel, T.
A Concept for Comprehensive IT Support for Environmental and Energy Management in SMEs.
DOI: 10.5220/0006660501870194
In Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS 2018), pages 187-194
ISBN: 978-989-758-298-1
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
187

the end of 2018.
This paper is structured as follows: Section 2 pre-
sents the current status of technology in the area of
tool-assisted energy management in SMEs. Section 3
discusses the procedure used to perform the require-
ments analysis for software support of the complete
EnvM/EM process. The concept derived from this
analysis is presented in Section 4. The paper con-
cludes with a summary and outlook on the continuing
work in the project.
2 TECHNOLOGICAL STATUS
AND RELATED WORK
The main tasks of industrial environmental infor-
mation systems (IEISs) are to provide information
and documentation, support evaluation and decision-
making, and enable control, planning, and monitoring
throughout the management process (Wohlgemuth,
2015). Software solutions are available for each of
these tasks, however, usually as separate, isolated ap-
plications or stand-alone systems (Heldt and Wohlge-
muth, 2009). Established definitions of IEISs, for ex-
ample (Wohlgemuth, 2015, S. 224), only require par-
tial support for environmental and sustainability ma-
nagement tasks, as no comprehensive solution exists.
The European norms for energy management
(ISO 50001) and environmental management (ISO
14001, 14004, 14006, 14031, 14044, and 14063) do
not provide explicit instructions for implementing and
executing EM/EnvM in specific cases, but rather per-
tain to the general process that is followed. Corre-
sponding handbooks such as (Bundesministerium f
¨
ur
Umwelt, Naturschutz und Reaktorsicherheit (BMU),
2012; S
¨
achsische Energieagentur SAENA GmbH,
2015; Umweltgutachterausschuss (UGA), 2011) pro-
vide organisational guidance and recommendations,
but do not offer any tool support. Additionally, SMEs
generally lack financial and human resources, as well
as knowledge and experience in the area of imple-
menting such systems (Eichhammer et al., 2011).
Software support — i.e., the use of IEISs — is the-
refore necessary for processing environmental and
energy data for administration, analysis, visualisation
and simulations (Hilty and Rautenstrauch, 1995).
Model-based approaches, such as that presented
in (R
¨
oßler et al., 2013), provide helpful support in
the form of a manual or reference process for imple-
menting energy management. Similar to the system
proposed in this paper, model-based approaches are
based on a detailed analysis of the requirements pre-
sented in the norms and therefore ensure a formally
valid implementation of energy management. Howe-
ver, they lack any tool-based support for analysis, vi-
sualisation, or simulations.
Currently, IEISs are mainly used to ensure legal
compliance, provide support for EnvM, and collect
and display data (Wohlgemuth, 2015). However, the
present trend is to take material aspects (raw materi-
als and energy consumption) into account alongside
the classical control parameters of the production si-
mulation in tactical and strategic problems (Wohlge-
muth, 2015). Accordingly, attempts are being made
to utilise and further develop pre-existing information
resources and applications in companies in order to
achieve this (Boß and Wohlgemuth, 2015). The open-
source tool “OpenResKit-Framework” has similar go-
als, but mainly concentrates on the integration of ex-
isting data and information (Boß and Wohlgemuth,
2015) and is therefore focused on providing informa-
tion and documentation (Wohlgemuth, 2015). In the
area of analysis and decision-making support, the tool
“e!Sankey” is used in conjunction with a Microsoft
Excel
R
table to visualise energy, material, or cost
flows (Boß and Wohlgemuth, 2015). Even the ap-
plication of the OpenResKit-Framework to learning
energy-efficiency networks (Schneider et al., 2014)
does not pursue a comprehensive approach to sup-
porting all aspects of the management process, but
instead focuses on the areas of information and do-
cumentation.
The QuiXel project, presented in this paper, at-
tempts to provide an all-inclusive approach to suppor-
ting EnvM and EM by addressing the areas of plan-
ning, data structuring, data acquisition, analysis, vi-
sualisation, and documentation. Guidelines that are
compliant with the European norms will also be pro-
vided within the system in the form of a platform-
integrated manual so that the necessary expertise is
always readily available without the need to consult
external resources.
3 PROCEDURE FOR
REQUIREMENTS ANALYSIS
In order to assess the requirements for comprehensive
IT support of the entire EnvM/EM process in SMEs,
a model of the work packages necessary for obtaining
certification was first drafted based on the ISO 50001
(DIN, 2011) and ISO 14001 (DIN, 2015) norms. This
model is shown in Figure 1. The numbers of the work
packages correspond to the section numbers of the re-
spective norm.
In the next step, a refined model was created by
further detailing all work packages according to the
norms. This ensured that all necessary functions for
ICEIS 2018 - 20th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
188

Figure 1: Implementation and operation of EM and EnvM systems.
all work packages were taken into account and resul-
ted in a detailed list of requirements for the software
system. Figure 2 shows the details of the “Planning”
work package as an example. The numbers of the sub-
packages also reflect the numbering of the relevant
subsections in the norms.
Workshops were then held with pilot users of the
platform based on the refined model. The workshops
addressed, in particular, the question of what type of
software support could be expected for which tasks.
Functional “focus areas” were identified during the
workshops by considering all the tasks in the context
of different use cases.
4 REQUIREMENTS AND
CONCEPT
Based on the refined model, a requirements catalo-
gue for the entire system was collated. These requi-
rements were categorised according to the individual
work packages as shown in Figure 1. One further ca-
tegory “General/other” was defined to cover the re-
maining requirements, such as user management. The
full list of requirements is briefly presented below.
Management
• A1.1 Team definition: It shall be possible to define
and document the EnvM/EM team and differenti-
ate between different roles (e.g., manager, mem-
ber).
• A1.3 Configurability: The system should provide
a customised experience to the user in terms of
information provided and task emphasis based on
the target level of EnvM/EM (e.g., if certification
is sought or not).
Planning
• A0.3 Action plan creation: The platform shall in-
clude a function to designate and describe effi-
ciency measures, i.e., an action plan.
• A0.4 Action plan maintenance: It shall be possible
to edit the action plan. It should be possible to
document the status of the edits.
• A1.2a Goal definition: It shall be possible to de-
fine and document individual goals.
• A1.2b Goal specification: It shall be possible to
differentiate between strategic and operative go-
als.
• A1.2c Goal designation: It shall be possible to
link operative goals with any number of associ-
ated strategic goals.
• A2.2.1a Acquisition of variables: The energy ma-
nager and the energy team shall be able to colla-
boratively define a variable (e.g., a meter such as
a gas, water, or electricity meter) with the aid of
real-time hints from the system (tooltips).
• A2.2.1b Description of variables: The energy ma-
nager and the energy team shall be able to add a
text description to variables.
• A2.2.1c Authentication of variables: The energy
manager and the energy team shall be able to au-
thenticate variables in order to make them availa-
ble for further use in the system.
• A2.2.1d Templates for variables: It should be pos-
sible for the energy team to reuse already-defined
variables as well as save variables as templates in
order to use these as the starting point for subse-
quent definitions.
• A2.2.2 Structuring of variables: Single variables
shall be available for evaluation in different com-
binations/structures.
A Concept for Comprehensive IT Support for Environmental and Energy Management in SMEs
189
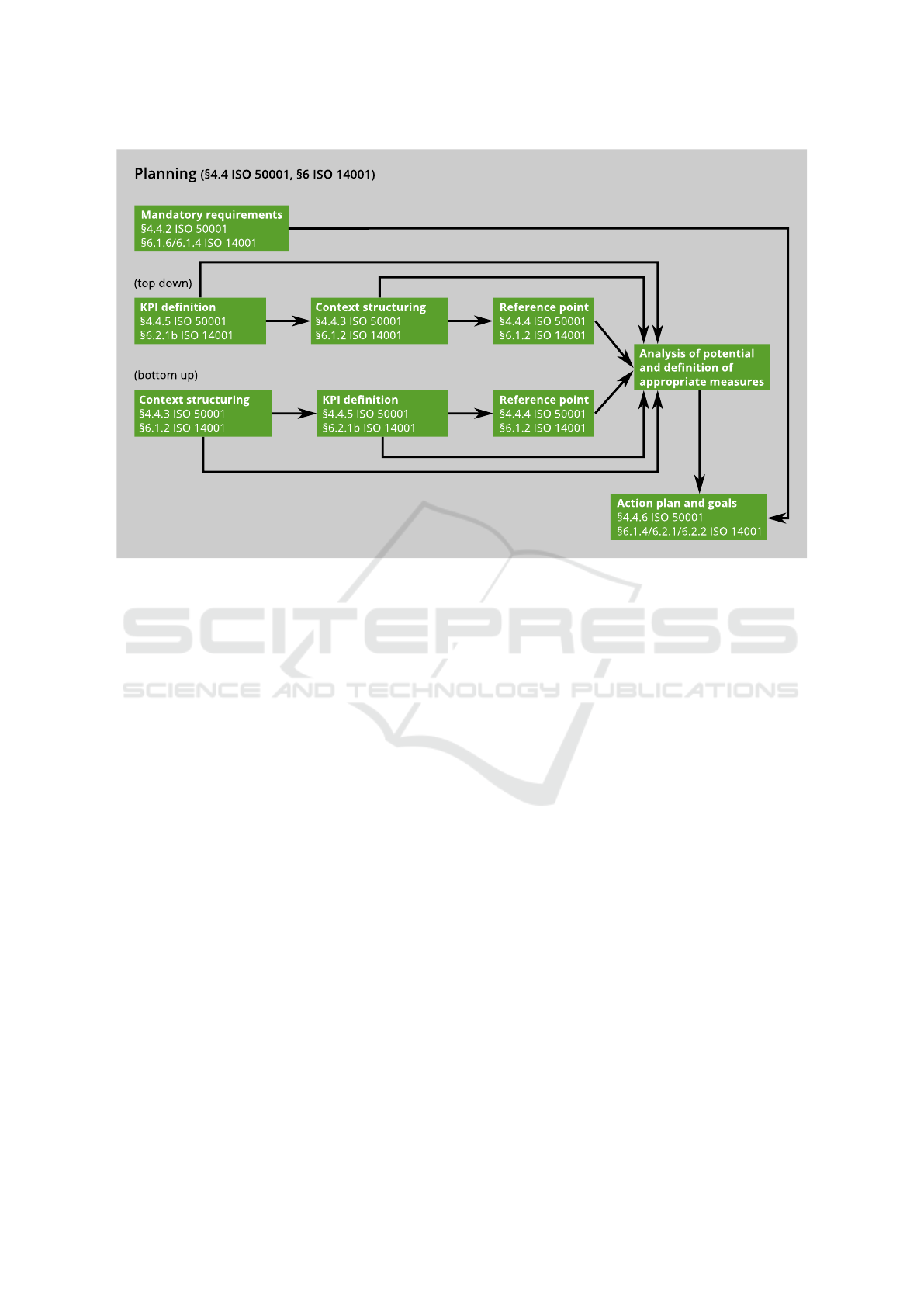
Figure 2: Detailed view of the “Planning” work package.
• A2.2.3 Evolving collaborative process: It shall
be possible to continuously develop energy and
environmental key performance indicators (KPIs)
via an iterative process of collaborative discussion
and negotiation, as changes to company goals as
well as in company structure lead to changes in
the structure of the data and the variables.
• A2.2.4 Release procedure of final model: It shall
be possible for the team to organise the collabo-
rative work process over multiple hierarchical le-
vels. Only the highest level of the hierarchy shall
have the right to validate and release the model
consisting of the structured variables and KPIs
produced throughout this process.
• A2.3.1a Selection of reference data: It shall be
possible to define a reference data set to be used
as a comparison for the current review period.
• A2.3.1b Comparison with reference data: It shall
be possible to calculate KPIs for the reference pe-
riod as well as the current review period.
• A2.4.1 Assigning KPIs to defined goals: It shall
be possible to link individual KPIs to one or more
goals set forth in the action plan.
• A2.4.2 Bottom-up KPI definition: It shall be pos-
sible to define KPIs by selecting and aggregating
a set of suitable variables from those already defi-
ned in the system.
• A2.4.3 Top-down KPI definition: It shall be possi-
ble to define KPIs and then check if all necessary
variables are available in the system.
• A2.4.4 Definition of KPIs as a function of the vari-
able structure: It shall be possible to define KPI as
a function of variables. For this purpose, it shall
be possible to define the mathematical equation
for calculating the KPIs in a formula editor using
mathematical operations and multiple variables.
Execution
• A0.1 Dashboard: It should be possible to see an
overview of the current status of individual mana-
gement tasks.
• A3.3.1 Documentation of the EnvM/EM process:
It shall be possible for the team to document the
EnvM/EM process in a collaborative manner.
• A3.4.1 Reading of data from external systems: In
order to maintain existing business processes, it
shall be possible to read data from external sys-
tems (e.g., Tekla, SteelOffice).
• A3.4.2 Raw data import: It shall be possible to
import meter readings from existing spreadsheets
or tables.
• A3.4.3 Manual data entry: The system shall faci-
litate manually saving a reading from a meter de-
fined in the system. An appropriate, standardised
ICEIS 2018 - 20th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
190

input form containing information about the me-
ter as well as an input field for the meter reading
shall be provided for this purpose.
• A3.4.4a Data quality control: The platform shall
continuously check if the data in the system are
complete, i.e., measurements for all defined me-
ters arrive at the expected times.
• A3.4.4b Data quality alerts: The system should
notify the responsible person if data are missing
for a particular meter or for a given time period.
Validation
• A5.1.1 Creation of reports: The system should au-
tomatically create reports allowing an evaluation
of the data from the defined KPIs and/or data on-
hand in the system. The report shall be available
both in a format that is easily viewed on-screen as
well as in a print-ready format (e.g., pdf).
• A5.1.2a Comparison of results with reference
data: The system shall be able to compare the
data and KPIs from the current review period with
those from the reference period.
• A5.1.2b Comparison of results with reference data
failure alert: If the current KPIs cannot be calcu-
lated for the reference period, the system should
report that the chosen reference period is no lon-
ger valid.
• A5.1.3 Analysis of review period: It shall be pos-
sible to assess the data with respect to the goals
defined in the action plan.
Management Review
• A5.4.1a Measures for improvement: The system
shall allow a review of the current review period
with respect to the goals set out in the action plan.
• A5.4.1b Documentation of measures: It shall be
possible to document progress towards the diffe-
rent goals.
• A5.4.1c Continuous improvement: It shall be pos-
sible to define new efficiency measures, and to ex-
tend or amend those that already exist based on
the most recent results.
General/Other
• A0.2 Administrative functions: An administrator
shall be able to add, change, and delete users from
the system, as well as control user rights. In the
case that the system comprises multiple compo-
nents requiring user authentication, a Single Sign
On is desirable.
• A0.5 Model export: It shall be possible to export
the validated data model (structured variables and
KPIs).
• A0.6 Model transformation: It shall be possible to
generate a formal description of the data model.
• A0.7 Model storage: It shall be possible to save
the data model in a formal manner (e.g., in a rela-
tional database).
• A0.8 Integrated manual: The system shall provide
instructions and guidelines for the best practice
of EnvM/EM in the form of a platform-integrated
manual.
4.1 Overall Concept
The overall concept developed from the requirements
is depicted in Figure 3. The figure is split into two
distinct layers: the top layer of pictograms shows the
necessary tasks and the bottom layer represents the
actions that must be performed by one or more of the
system users in order to complete the steps shown in
the top layer. The corresponding requirement ID is
written in grey beside each task or action. Except
for documentation, all tasks are grouped according to
their work packages (and therefore according to the
specific areas described in the ISO norms). Docu-
mentation — shown in Box A — is instead visualised
as a continuous task that is supported throughout the
entire management process with input coming from
other tasks that are performed in parallel.
Box B “Management” represents the task of choo-
sing the target level of EnvM/EM to be implemented.
The system should be automatically adapted accor-
ding to the chosen target level (e.g., a company that
wishes to be certified will require much more rigorous
procedures and documentation than a company that
only wishes to reduce its electricity costs). In parti-
cular, this includes configuring the guidelines that are
presented to the user as well as selecting which docu-
mentation the user is obliged to produce.
Box C shows the individual steps that must be
completed in the “Planning” work package. The steps
correspond to those from Figure 2, and are embedded
here in a use case that describes the entire process of
energy and environmental management.
The actual data is collected in “Execution — data
acquisition” (Box D). Data can be acquired by the
system from manual user input (collaborative data
entry), by automatically collecting data provided by
electronic meters, or by importing raw data from other
sources (e.g., enterprise resource planning systems).
In the “Validation” work package (Box E), reports
are generated that can then be made available to the
A Concept for Comprehensive IT Support for Environmental and Energy Management in SMEs
191

Figure 3: Illustration of the overall concept of the system.
ICEIS 2018 - 20th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
192

decision-makers. The reports include the calculated
values of the KPIs that were defined earlier in the
“KPI definition” step (see “Planning”, Box C). These
values are calculated using the data collected in Box
D.
An automatically generated (and adapted) data
model is a necessary interface between the “Planning”
and “Execution — data acquisition” work packages in
order to ensure data consistency and to facilitate the
collection of the data necessary for the analysis. This
data formalisation process does not require any input
from the user and therefore takes place in the back-
ground.
Overall, the system offers a comprehensive appro-
ach to EnvM/EM in which the level of management
can be iteratively improved by adapting the action
plan and efficiency measures in the company based
on the information contained in the reports and the
documentation (see “Management review”, Box F).
4.2 Technical Concept
In a technical sense, the system must provide two ba-
sic functions: it must support collaborative content
modification (e.g., documentation and KPI definition)
as well as facilitating data acquisition and analysis. A
structured wiki could provide a technical basis for col-
laborative KPI definition. On the other hand, a spre-
adsheet is the best solution for the data acquisition,
as this provides a familiar environment for data entry.
One option is to create a system using existing wiki
and spreadsheet software as front ends to a common
database. However, this is an inelegant solution, as
the workflow is split across multiple front ends/user
interfaces and it is difficult to define exactly what in-
formation should be entered from which interface wit-
hout making a somewhat arbitrary divide in the work
process.
Although more implementation-intensive, a cus-
tom front end containing both wiki-like elements and
spreadsheet-like elements as needed provides a much
better interface to the system. With this solution,
users can complete all aspects of the entire EnvM/EM
process from a single, unified front end. It is there-
fore planned to realise the user interface as a custom-
built web front end. To ensure multi-user capabi-
lity (collaboration) and data consistency, this front
end will be connected to a central database back end.
An export/import function to/from popular spreads-
heet formats (e.g., csv, LibreOffice Calc or Microsoft
Excel
R
) is a feasible addition that would allow users
to acquire data with well-known and widely used soft-
ware (Junker, 2010; Leyh et al., 2011).
Another focus area is the configurability of the
process depending on the objectives of the company.
The scope and level of detail of the management pro-
cess should be adapted to the goals and needs of the
specific company. It is planned that the company ini-
tially identifies its EnvM/EM goals and on this basis,
the system offers a tailored process for the company
to follow, i.e., the guidelines and documentation tem-
plates are adapted based on the company’s manage-
ment targets. In addition, the KPI definition compo-
nent is configured in such a way that the complexity of
the KPIs corresponds to the user’s goals. Customer-
oriented step-by-step instructions and tailored docu-
mentation templates are provided. Since the model
beneath this system configuration contains all the es-
sential aspects of the European EnvM and EM norms,
it is ensured that the management process is carried
out in accordance with regulations.
5 SUMMARY AND OUTLOOK
This paper presents the central concept of the QuiXel
project: an integrated data and information plat-
form for collaborative and evolving environmental
and energy management in SMEs. The need for com-
prehensive IT support for all aspects of EnvM/EM is
discussed.
The requirements for such a platform are deri-
ved from a detailed analysis of the European envi-
ronmental and energy management norms as well as
from workshops held with potential industry partners.
A catalogue of essential functional requirements for
a comprehensive EnvM/EM system is presented. A
sketch of the technical concept, based on this catalo-
gue, is outlined.
The project is currently in the implementation
phase. A prototype platform will be delivered to the
industry partners by mid-2018 for testing and evalu-
ation. The software will be improved based on input
and feedback from the pilot users and the final evalu-
ation phase will be concluded by the end of 2018.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work is kindly supported by the German Federal
Ministry of Education and Research.
REFERENCES
Boß, J. and Wohlgemuth, V. (2015). Integration und
Weiterentwicklung bestehender Energiemanagement-
Applikationen mit dem OpenResKit-Framework. In
A Concept for Comprehensive IT Support for Environmental and Energy Management in SMEs
193

Cunningham, D., Hofstedt, P., Meer, K., and Schmitt,
I., editors, INFORMATIK 2015, Lecture Notes in In-
formatics (LNI), Bonn. Gesellschaft f
¨
ur Informatik
(GI) e.V.
Bundesministerium f
¨
ur Umwelt, Naturschutz und Reaktor-
sicherheit (BMU) (2012). Energiemanagementsys-
teme in der Praxis. ISO 50001: Leitfaden f
¨
ur Unter-
nehmen und Organisationen.
DIN (2011). DIN EN ISO 50001:2011-12. Energiemanage-
mentsysteme - Anforderungen mit Anleitung zur An-
wendung.
DIN (2015). DIN EN ISO 14001:2015-11. Umweltmanage-
mentsysteme - Anforderungen mit Anleitung zur An-
wendung.
Eichhammer, W., Kohlhaas, M., Neuhoff, K., Rohde, C.,
Rosenberg, A., and Schlomann, B. (2011). Untersu-
chung des Energieeinsparpotentials f
¨
ur ein Nachfolge-
modell ab dem Jahr 2013ff zu Steuerbeg
¨
unstigungen
f
¨
ur Unternehmen des Produzierenden Gewerbes sowie
der Land- und Forstwirtschaft bei der Energie- und
Stromsteuer — Endbericht. Technical report, Bundes-
ministerium der Finanzen (BMF), Berlin.
EnergieAgentur.NRW (2013). EMS.marktspiegel. http://
www.energieagentur.nrw/energieeffizienz/ems.
marktspiegel.
Heldt, K. and Wohlgemuth, V. (2009). Typische
Entwicklungs- und Entscheidungsprozesse zu betrie-
blichen Umweltinformationssystemen am Beispiel
der Daimler AG. In Fischer-Stabel, P., Kremers, H.,
Susini, A., and Wohlgemuth, V., editors, Environ-
mental Informatics and Industrial Environmental Pro-
tection Concepts, Methods and Tools, volume 3, pa-
ges 83–90, Aachen. Shaker Verlag.
Hilty, L. and Rautenstrauch, C. (1995). Umweltinformatik
- Informatikmethoden f
¨
ur den Umweltschutz und Um-
weltforschung, pages 295–312. Oldenbourg Wissen-
schaftsverlag, 2 edition.
Junker, H. (2010). Die Beliebigkeit betrieblicher Umweltin-
formationssysteme. In Greve, K. and Cremers, A. B.,
editors, EnviroInfo 2010 — Integration of Environ-
mental Information in Europe, pages 232–247. Shaker
Verlag.
Leyh, C., Krischke, A., and Strahinger, S. (2011). Die Her-
ausforderungen der IT-Unterst
¨
utzung des Nachhaltig-
keitsmanagements in KMU: eine vergleichende Be-
trachtung ausgew
¨
ahlter KMU und Großunternehmen.
In Nachhaltigkeit in kleinen und mittleren Unter-
nehmen, pages 269–288. Euler Verlag.
R
¨
oßler, R., Schlieter, H., and Esswein, W. (2013). Modell-
gest
¨
utzte Dokumentation und Steuerung von Energie-
managementsystemen. HMD — Praxis Wirtschaftsin-
formatik, 291:26–39.
S
¨
achsische Energieagentur SAENA GmbH (2015). An-
leitung zur Einf
¨
uhrung eines Energiemanagementsys-
tems in KMU.
Schneider, M., Weissenbach, K., and Wohlgemuth, V.
(2014). EnergieNetz - Eine webbasierte, erweiterbare
Open-Source-Software f
¨
ur das Energiemangement in
lernenden Energieeffizienznetzwerken. In INFORMA-
TIK 2014, Lecture Notes in Informatics - Proceedings,
pages 1889–1900, Bonn. Gesellschaft f
¨
ur Informatik
(GI) e.V.
Umweltgutachterausschuss (UGA) (2011). EMAS-
Leitfaden In f
¨
unf Etappen sicher zum Ziel.
Wohlgemuth, V. (2015). Ein
¨
Uberblick
¨
uber Einsatzberei-
che von betrieblichen Umweltinformationssystemen
(BUIS) in der Praxis. In INFORMATIK 2015, Lecture
Notes in Informatics - Proceedings, pages 223–237,
Bonn. Gesellschaft f
¨
ur Informatik (GI) e.V.
ICEIS 2018 - 20th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
194
