
Internet Interventions for Family Caregivers of People with
Neurocognitive Disorder
A Literature Review
Audrey Duceppe, Caroline Camateros and Jean Vézina
Department of Psychology, Laval University, 2325 allée des bilbiothèques, Quebec, Canada
Keywords: Family Caregiver, Dementia, Neurocognitive Disorder, Internet, Technology, Web, Literature Review.
Abstract: Taking care of a loved one can be a new, yet challenging role for caregivers. However, these caregivers are
usually overbooked and do not have the time needed to reach for help. Internet interventions are a great way
to offer psychoeducation, support and tools for caregivers, in the comfort of their home. This literature review
explores the impact of internet intervention programs. Twenty-two studies were found in PsychNet, Medline
and Google scholar using "family caregiver, dementia, neurocognitive disorder, internet, technology, web" as
keywords. A review of these studies showed that internet intervention for caregivers have an impact on the
caregiver’s psychological health (e.g. feeling of burden, stress, depression, anxiety, etc.), on their relation to
the care receiver (reaction to disruptive behaviors, self efficacy, positive aspects of caregiving, better
understanding of the illness, etc.) and even of the care receiver himself (disruptive behaviors occurrence and
severity). However, internet intervention programs for caregivers show a great versatility in their effectivity
results, but they still appear to be a good way to provide psychoeducation on neurocognitive disorder, to
reduce negative emotion associated with caregiving and improve the caregiving relationship itself.
1 INTRODUCTION
It is well-known that caring for a loved one affected
by a neurocognitive disorder can lead to negative
consequences for the caregiver, such as a feeling of
burden (Glueckauf, Ketterson, Loomis and Dages,
2004; Griffiths, Whitney, Kovaleva and Hepburn,
2016; Lorig et al., 2016), depression (Blom, Zarit,
Groot Zwaaftink, Cuijpers and Pot, 2015; Griffiths et
al., 2016) and anxiety (Beauchamp, Irvine, Seeley,
and Johnson, 2005; Griffiths et al., 2016). Caregivers
often feel lost and overwhelmed with this new role
(Collins and Swartz, 2011). In addition to memory
and functional loss associated with neurocognitive
disorder, caregivers also have to deal with disruptive
behavior like aggression, agitation, wandering, etc.
(Kamiya, Sakurai, Ogama, Maki and Toba, 2014).
These behaviors appear to be the most distressing for
caregivers, contributing to the feeling of burden and
depression symptoms (e.g. Brodaty Woodward,
Boundy, Ames, Balshaw and PRIME Study Group,
2014; Kamiya et al., 2014).
Many interventions type exist to reduce the
burden of care, like respite, support groups or
psychoeducation or internet intervention programs.
Interventions designed for caregivers have multiple
benefits. In addition to improving the caregiver’s
well-being, this kind of intervention can help them
offer a better care for their loved one and delay their
institutionalization, which is very costly in terms of
quality of life and healthcare costs (Keefe and
Manning, 2005). In this sense, these positive
outcomes are not limited to the caregivers and their
loved one, but also offer an economic and
personalized solution for society (Åkerborg et al.,
2016; Keefe and Manning, 2005).
Among all intervention aimed to reduce negative
consequences of caregiving, internet intervention
programs appear to be the ones most suited for the
caregiver’s reality. In fact, with all the tasks and
responsibilities associated with care, caregivers often
do not have the time needed to seek for help. The lack
of accessibility of interventions is an obstacle to the
participation of caregivers. One study reported that up
to 60% of caregivers contacted for an intervention
refused to participate because of the time required
(Wiprzycka, Mackenzie, Khatri, and Cheng, 2011).
With internet intervention, they have the
opportunity to choose the service and use it at their
96
Duceppe, A., Camateros, C. and Vézina, J.
Internet Interventions for Family Caregivers of People with Neurocognitive Disorder.
DOI: 10.5220/0006671700960102
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies for Ageing Well and e-Health (ICT4AWE 2018), pages 96-102
ISBN: 978-989-758-299-8
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
suitability. Internet interventions reduce time travel,
they are adapted to the caregiver schedule and allow
caregivers to select the types of services they need
(Blom, Bosmans, Cuijpers, Zarit, and Pot, 2013).
Studies show that the majority of participants are
comfortable with computers and appreciate their
virtual participation in the group. The majority of
participants say the web sessions are comparable to
traditional face-to-face meetings and would recom-
mend the intervention to their friends (Chiu et al.,
2009; Finkel et al., 2007).
Despite the ease of access to internet
interventions, recent studies show conflicting results
on the efficacy of these programs. This article
proposes a review of the literature of the
characteristics of internet intervention programs and
their impacts on caregivers. This article may help
researchers in creating effective internet interventions
for caregivers. Clinicians seeking evidence on which
to build treatment may also draw on the findings of
this article.
2 METHOD
The search for this review was made mainly though
PsychNet Medline and Google Scholar. We used
"family caregiver, dementia, neurocognitive disorder,
the internet, technology, web" as keywords. These are
the combinations used: Family caregivers, dementia,
and technology; family caregivers, dementia and
internet, family caregivers, dementia and web-
conference; family caregivers, intervention, dementia
and internet. The snowball method was used to
identify articles from the reference list of articles
already included in the review.
2.1 Inclusion Criteria
The selected studies needed to be aimed at family
caregivers of individuals affected by a major
neurocognitive disorder and use computers to offer an
intervention program. They also had to be written in
French or English.
There was no limit on the age of articles, however,
articles were closely analyzed to ensure their
technological methods were still relevant, for
example a study using videophones or VHS was
excluded (studies using smartphones were
included).
2.2 Exclusion Criteria
Studies with no use of computers (traditional face-to-
face meetings or telephone calls), studies that
included caregivers of all older adults with no
specification concerning the presence of major
neurocognitive disorder were excluded. We also
excluded studies with attrition superior to 45% were
excluded.
2.3 Selection of the Studies
When we searched through the databases,
1725 articles were found. There were 1096 articles
left after removing duplicates. Then, 574 articles were
excluded after reading the title and abstract.
Among the 55 articles fully red, 36 papers were
excluded because they did not meet the inclusion
criteria or covered additional facets of studies already
included in the review. In the end, 19 articles were
selected from a database and three more were added
from the articles reference list, for a total of 22
articles.
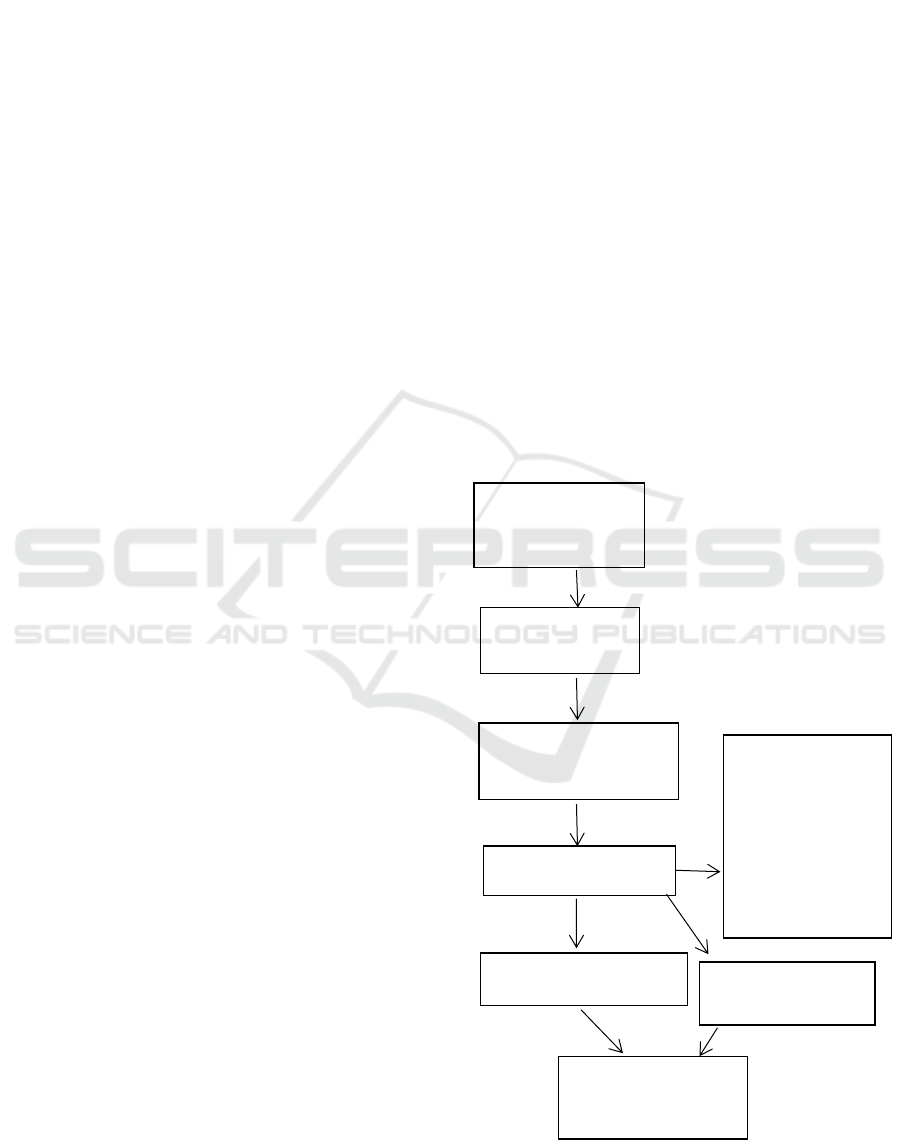
Figure 1: Flow diagram of article selection process.
1725 papers found
in initial searches
1096 duplicates
removed
574 excluded after title
and abstract were read
.
55 papers read in full
19 papers were eligible
3 papers added from
reference lists
22 papers were
included in the review
36 papers were
excluded because
they did not meet
inclusion criteria
or covered
additional facets of
studies already
included in review.
Internet Interventions for Family Caregivers of People with Neurocognitive Disorder
97

2.4 Studies’ Description
We identified 22 studies of internet intervention for
caregivers of a person affected by a neurocognitive
disorder. These studies were published between 1995
and 2017. These studies are specific to internet
intervention programs designed to reduce the
negative impact of caring, improve the caregiving
relationship or reduce the disruptive behaviors. The
passive intervention includes a website, video capsule
or for psychoeducation. Interventions could also be
active like group meetings by web conference
forums, emails or even web support groups to
encourage communication between caregivers or
caregivers and resources. Certain studies may include
multiple intervention types (Bass, Mcclendon,
Brennan, and Mccarthy, 1998; Blom et al., 2015;
Boots, de Vugt, Withagen, Kempen and Verhey,
2016; Chiu et al., 2009; Glueckauf et al., 2004 ;
Kelly, 2003; Lai, Wong, Liu, Lui, Chan and Yap.,
2013; Lorig et al., 2010; Marziali, Damianakis and
Donahue, 2006)
In this sample, twelve studies used a randomized
protocol, eight had a pre-experimental protocol (of
which three are pilot studies), one used a qualitative
methodology (O'Connell et al., 2014) and an other
used a mixted method (Kelly 2003). Control groups
included routine care (Cristancho-Lacroix, Wrobel,
Cantegreil-Kallen, Dub, Rouquette and Rigaud,
2015; van der Roest, Meiland, Jonker and Dröes,
2010), waiting lists (Beauchamp et al., 2005) leaflets
with various information (Blom et al., 2015; Finkel et
al., 2007, Hicken, Daniel, Luptak, Grant, Kilian and
Rupper, 2016; Lai et al., 2013; Marziali and Garcia,
2011) and a placebo website (Brennan, Moore, and
Smyth, 1995). Sample sizes of intervention groups
varied widely from 3 (Lai et al., 2013) to 700 (Kelly,
2003) with an average of 71,36 caregivers. The
control groups, meanwhile, had an average of 57,15
caregivers (8 to 149). Attrition also varied from 0%
(Torkamani et al., 2014) to 41% (Boots et al., 2016),
with a mean of 19.4%. Attrition was not mentioned in
four of the 22 studies.
Where possible, studies were compared using the
effect sizes (Cohen's d). Among the randomized
studies, this was done with the following formula
(mean of post-test control group - mean of the
experimental group at post-test) / common standard
deviation. For single-group protocols, the following
formula was used; (mean pre-test - mean post-test) /
common standard deviation.)
3 RESULTS
3.1 Intervention’s Modality
Most aid programs used several modalities to reach
caregivers. The most popular method was the
interactive website, used in 18 studies. In general,
websites were used to facilitate psychoeducation and
participants visit the site individually, where
appropriate. The material was accessible for 6 weeks
(Lorig et al., 2010) and one year (Bass et al., 1998;
Brennan et al., 1995), depending on the study. Web
sites generally offered information on neurocognitive
disorder and on various care skills. In addition, some
offered more specialized tools, for example, to
facilitate decision-making (Brennan et al., 1995), to
help the caregiver better identify their needs (van der
Roest et al., 2010) or to teach emotional management
strategies (Beauchamp et al., 2005).
Seven authors pointed out that some of the
material was presented via video capsules
(Beauchamp et al., 2005; Glueckauf et al., 2004;
Griffiths, Whitney, Kovaleva and Hepburn, 2016;
Hicken et al., 2016; Jajor et al., 2016; Kajiyama et al.,
2013; Lorig et al., 2010; Torkamani et al., 2014).
Sometimes, asynchronous communication modalities
were also added to the website to encourage sharing
between caregivers. A forum or the option to
communicate with other participants via emails was
present on 12 websites (Bass et al., 1998; Brennan et
al., 1995, Blom et al., 2015; Boots et al., 2016;
Glueckauf et al., 2004; Jajor et al., 2016; Kelly, 2003;
Lai et al., 2013; Lorig et al., 2010; Marziali et al.,
2006; O'Connor, Arizmendi et Kaszniak, 2014;
Torkamani et al., 2014). With the use of email
between the participant and a health professional, the
studies of Chiu et al. (2009) and Kwok et al. (2014)
also provided individual psychotherapy sessions at a
distance. Finally, the assistance program of Marziali
et al. (2006) included 12 group meetings with web
conference to encourage social support. The 4 studies
that do not use a website offered psychoeducation via
audio conferences (Finkel et al., 2007) and web
conferencing (Griffiths et al., 2016) or social support
groups via audio conferencing (O'Connell et al.,
2014) or with a virtual reality tool (O'Connor et al.,
2014). These authors emphasized that these modes of
communication are synchronous, which facilitates
exchanges between the participants.
Overall, the majority of studies offered complex
assistance programs that address a variety of needs
and use several modalities. Their results were mixed.
As noted in Boots, Vugt, van Knippenberg, Kempen,
and Verhey (2014), it is difficult to interpret the
ICT4AWE 2018 - 4th International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies for Ageing Well and e-Health
98

specific effects of each study since the characteristics
of the programs are not always well detailed. In
addition, data on usage rates and adhesion are rare.
Some of the findings from the meta-analyzes of
traditional caregiver programs can still inform
programs remotely. For example, it appeared that the
studies which target specific difficulties also have
encouraging results when offered at a distance. In
fact, the aid program of Glueckauf et al. (2004), by
web site and audio conference, led to significant
changes in perceived personal effectiveness for
different caring activities.
3.2 Intervention’s Utilization
Among the studies included in this review, 10 offered
information on participation rate or rates of use. In
synchronized interventions, the numbers of sessions
attended are one way to convey participation rate. For
example, in Finkel and colleagues’ study, 94% of
participants attended 7 or more out of a possibility of
8 sessions (2007). An other study also mentions high
participation rates but fail to provide them (O'Connell
et al., 2014) . Web site based programs reported using
in different ways. Some authors report the number of
visits; websites were consulted on average between
5.14 and 6.98 times per month (Bass et al., 1998;
Kajiyama et al., 2013; van der Roest et al., 2010).
Others report the average amount of time spent
consulting the web-site, they ranged from 14:36 min
to 106.41 minutes (Bass et al., 1998; Beauchamp et
al., 2005; van der Roest et al., 2010). The number of
modules or sessions completed are also reported, they
ranged from 70 to 83% of participants completing
sections (Cristancho-Lacroix et al., 2015). Finally,
studies with forums did report the number of posts by
participants, with a mean of 36.9 (Lorig et al., 2010).
3.3 Intervention’s Content
The intervention’s structure was missing in most of
the studies and protocol’s description was missing in
all of the studies. Therefore, some studies shared the
themes discussed in their intervention.
Most studies included an educational theme on
neurocognitive illness and/or caregiving role (e.g.
Bass et al., 1998; Beauchamp et al., 2005; Blom et al.,
2013; Brennan et al., 1995; Chiu et al., 2009;
Cristancho-Lacroix et al., 2015; Glueckauf et al.,
2016; Griffith et al., 2016; Hockem et al., 2016;
Kajiyama et al., 2013; Kwok et al., 2014; Lorig et al.,
2010; O’Connell et al., 2014; O’Connor et al., 2014).
Many studies also added problem solving skills or
decision-making, especially oriented towards
behavioral problems (Blom et al., 2013; Cristancho-
Lacroix et al., 2015; Kajiyama et al., 2013; Kwok et
al., 2014; Lorig et al., 2010), daily difficulties
(Beauchamp et al., 2005; Brennan et al., 1995; Chiu
et al., 2009; Cristancho-Lacroix et al., 2015) or to
enhance communication with the care receiver (Blom
et al., 2013; Hicken et al., 2016). Dealing with
emotions or even their care receiver’s emotions were
frequent themes too (Beauchamp et al., 2005; Chiu et
al., 2009; Hicken et al., 2016; Kajiyama et al., 2013;
Lorig et al., 2010). Some studies added a self-care
theme (Griffith et al., 2016; Hicken et al., 2016;
Kajiyama et al., 2013), which could contain sleeping
habits, alimentation habits (Lorig et al., 2010),
pleasant activities (Kajiyama et al., 2013) and
physical exercise (Lorig et al., 2010). Three studies
included information and exercises about relaxation
(Blom et al., 2013; Hicken et al., 2016; Kajiyama et
al., 2013). Planning the future also seemed to be a
recurrent theme (Kajiyama et al., 2013; Lorig et al.,
2010). In addition to these more frequent themes,
some studies included education or discussion on
seeking help (Blom et al., 2013; Cristancho-Lacroix
et al., 2015; Lorig et al., 2010), respite (Cristancho-
Lacroix et al., 20015), social and\or financial support
(Cristancho-Lacroix et al., 2015), pharmacotherapy,
non-pharmacotherapy and avoiding falls (Cristancho-
Lacroix et al., 2015).
Finally, most studies included emotional support,
by other caregivers or by health professionals, which
emerges to be central for caregivers, (Hicken et al.,
2016; Kajiyama et al., 2013) even when the study’s
results were inconclusive. This support could be
offered by email (Chiu et al., 2009) or telephone
(Hicken et al., 2016). One study also mentioned that
participants needed more dynamic interactions
(Cristancho-Lacroix et al., 2015).
Even though most studies showed great
acceptability of the internet format, one study showed
that man might have more positive feedback for
online intervention than women (Cristancho-Lacroix
et al., 2015). Furthermore, Bass and colleagues found
that online intervention is more effective if the
caregiver has a larger informal support network is
caring for a spouse or did not live alone with the care
receiver (1998), supposing that isolation might an
important issue for caregivers. In Kajiyama and
collegues’ study, caregivers mentioned they would
need more contacts with other caregivers and the
health professionals (2014).
Internet Interventions for Family Caregivers of People with Neurocognitive Disorder
99

3.4 Effect of Internet Interventions
Variables used to measure the effectiveness of aid
programs are also varied. These studies measured one
or many of those variables: feeling of burden,
depression, anxiety, stress, self-efficacy, fatigue,
distress, ability to reach objectives, confidence in
decision, ability to ask for help, positive aspects of
caregiving, perception of caregiving, occurrence and
severity of disruptive behaviors, reaction to disruptive
behaviors and distress related to disruptive behaviors.
Significant results were obtained in 12 of the 21
quantitative studies.
Three out of 12 studies (25%) identified a
significant reduction in the emotional burden, 60% (3
out of 5) decreased stress, 25% (3 out of 12)
decreased depressive symptoms, 100% anxiety (3 out
of 3), 67% (4 out of 6) showed an increase in self-
efficacy, 50% (3 out of 6) showed a decrease of the
disruptive behaviors and 33% showed a decrease of
the caregiver’s reaction to disruptive behaviors (1 out
of 3). Beauchamp et al. (2005) also reported a
significant increase in the intention to seek help and
positive aspects of caregiving, while (Brennan et al.,
1995) obtain an increase in confidence in decision-
making. (Boots et al., 2016) reported that caregivers
increased their achievement of goals. (Van der Roest
et al., 2010) have also reported an increase in
perceived competence in their sample.
When the intervention had a significant effect on
caregivers, Cohen’s d were calculated to ease the
comparison of studies. Caregiver’s feeling of burden
is a recurrent variable. In three studies found Cohen’s
d between 0.43 (Griffiths et al., 2016) and 0.57
(Torkamani et al., 2014) with a mean of 0.49. Self-
efficacy is also frequently measured and in two
studies the Cohen’s d found are between 0.28
(Beauchamp et al., 2005) and 0.77 (Lorig et al., 2010)
with a mean of 0.52. Cohen’s d for stress in present
in three studies and is between 0.13 (Beauchamp et
al., 2005) and 0.5 (Lorig et al., 2010), with a mean of
0.24. For anxiety, Cohen’s d is between 0.15
(Beauchamp et al., 2005) and 0.51 (Griffiths et al.,
2016) with a mean of 0.38 in three studies. Cohen’s d
for depression is measured by two studies and the
result found was 0.26 (Blom et al., 2015) and 0.52
(Griffiths et al., 2016), with a mean of 0.39. The
Cohen’s d was also available for four studies on
disruptive behavior studies. The Cohen’s d was
between 0.11 (Kajiyama et al., 2013) and 0.71 (Kwok
et al., 2014), with a mean of 0.49. Single studies also
provides Cohen’s d for many variables. Internet
intervention seems to have a small effect on fatigue
(0.08; Beauchamp et al., 2005), depressive symptoms
(0.10; Beauchamp et al., 2005), trust in decision
(0.31; Brennan et al., 1995), asking for help (0.25:
(Beauchamp et al., 2005), positive aspects of
caregiving (0.25; Beauchamp et al., 2005), reaction
(0.43; Griffiths et al., 2016) and distress (0.47; Kwok
et al., 2014) associated with disruptive behaviors.
Moderate Cohen’s d was found in the perception of
caregiving demands (0.49), obtaining respite (0.59)
and cognition with caregiving role (0.52; Glueckauf
et al., 2004).
4 DISCUSSION
4.1 Conclusions of This Review
In conclusion, this review presented an overlook of
22 studies measuring the effectivity of internet
interventions for caregivers. It showed that internet
interventions include a large diversity of intentions,
from synchronous psychoeducation to web therapy.
The variables used to measure the effectiveness of
these programs also differ from one to another. Some
studies focused on caregiver variable (ex. feeling of
burden, stress, depression, anxiety, etc.), on their
relation to the care receiver (ex. reaction to disruptive
behaviors, self-efficacy, positive aspects of
caregiving, better understanding of the illness, etc.)
and even of the care receiver himself (disruptive
behaviors occurrence and severity).
Theses internet intervention programs showed
their versatility with their improvement of the
caregiver’s psychological well-being (Blom et al.,
2015; Glueckauf et al., 2004; Griffiths et al., 2016;
Lorig and al., 2010), with promoting tools to improve
the caregiving relationship (Beauchamp et al., 2005;
Boots et al., 2016; Glueckauf et al., 2004; Griffiths et
al., 2016; Lorig et al., 2010) and even with improving
the care receiver’s behavior (Griffiths et al., 2016;
Kajiyama et al., 2013; Kwok et al., 2014). However,
we found a great variability in the effectivity
measured. In fact, 57% of the studies showed a
significant impact of the program on the caregivers.
Even if a majority of studies showed significant
impact on stress, anxiety and self-efficacy, more
studies are needed to measure the impact of these
programs on the burden, depressive symptoms and
reaction to disruptive behaviors. As internet
intervention programs will probably increase in the
next years, further studies will need to document the
effect of these kinds of interventions with a larger
number of studies to compare and less variability in
the programs assessed and variables measured.
ICT4AWE 2018 - 4th International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies for Ageing Well and e-Health
100

4.2 Reflexion on Internet Intervention
In a larger view, literature shows issues with the
description and classification of interventions. In fact,
the authors differ in their way of describing their
interventions, so what ones consider psychoeducation
can be considered therapy by one another. This
therefore brings an important limitation in the
comparison of studies.
A standardization proposing clear descriptions for
each type of intervention would be preferred in order
to unify the literature. It would also be appropriate to
encourage authors to provide a more detailed
description of the intervention delivered. This
description is unfortunately missing in most of the
articles (Gaugler, Jutkowitz, Shippee and Brasure,
2017). Moreover, the complexity of the interventions
offered complicates the interpretation of the results.
In fact, the majority of studies combine several
modalities of intervention (e.g. a website and a
forum). It is therefore difficult to identify which
modality has beneficial results for caregivers. New
studies aiming at isolating the active agent from the
treatments offered would therefore be necessary in
order to clarify the conclusions on the interventions
by the Internet.
Finally, the increasing popularity of Internet
interventions brings some challenges with updating
the knowledge of caregivers. In this sense, studies are
rapidly outdated due to technological advances.
Therefore, new updates will always be required.
REFERENCES
Åkerborg, Ö., Lang, A., Wimo, A., Sköldunger, A.,
Fratiglioni, L., Gaudig, M., and Rosenlund, M., 2016.
Cost of Dementia and Its Correlation with Dependence.
Journal of Aging and Health, 1–17.
Bass, D. M., McClendon, M. J., Brennan, P. F., and
McCarthy, C., 1998. The buffering effect of a computer
support network on caregiver strain. J Aging Health,
10(1), 20-43. doi:10.1177/089826439801000102.
Beauchamp, N., Irvine, A. B., Seeley, J., and Johnson, B.,
2005. Worksite-Based Internet Multimedia Program for
Family Caregivers of Persons with Dementia.
Gerontologist, 45(6), 793-801. doi:10.1093/geront/45.
6.793.
Blom, M. M., Bosmans, J. E., Cuijpers, P., Zarit, S. H., and
Pot, A. M., 2013. Effectiveness and cost-effectiveness
of an internet intervention for family caregivers of
people with dementia: design of a randomized
controlled trial. BMC psychiatry, 13(1), 17.
Blom, M. M., Zarit, S. H., Groot Zwaaftink, R. B., Cuijpers,
P., and Pot, A. M., 2015. Effectiveness of an Internet
intervention for family caregivers of people with
dementia: results of a randomized controlled trial.
PLoS One, 10(2), e0116622. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.
0116622.
Boots, L. M. M., Vugt, M. E., Knippenberg, R. J. M.,
Kempen, G. I. J. M., & Verhey, F. R. J., 2014. A
systematic review of Internet‐ based supportive
interventions for caregivers of patients with dementia.
International journal of geriatric psychiatry, 29(4),
331-344.
Boots, L. M., de Vugt, M. E., Withagen, H. E., Kempen, G.
I., and Verhey, F. R., 2016. Development and initial
evaluation of the web-based self-management program
“partner in balance” for family caregivers of people
with early stage dementia: an exploratory mixed-
methods study. JMIR Res Protoc, 5(1).
Brennan, P. F., Moore, S. M., and Smyth, K. A., 1995. The
effects of a special computer network on caregivers of
persons with Alzheimer's disease. Nursing research,
44(3), 166-172.
Brodaty, H., Woodward, M., Boundy, K., Ames, D.,
Balshaw, R., and PRIME Study Group., 2014.
Prevalence and predictors of burden in caregivers of
people with dementia. The American Journal of
Geriatric Psychiatry, 22(8), 756-765.
Camateros, C., and Vézina, J., 2016. Évaluation d’une
intervention par conférence web à l’intention d’aidantes
d’un proche atteint d’un trouble neurocognitif sévère.
NPG Neurologie-Psychiatrie-Gériatrie, 16(96), 320-
325.
Chiu, T., Marziali, E., Colantonio, A., Carswell, A.,
Gruneir, M., Tang, M., and Eysenbach, G., 2009.
Internet-based caregiver support for Chinese Canadians
taking care of a family member with Alzheimer's
disease and related dementia. Can J Aging, 28(4), 323-
336. doi:10.1017/S0714980809990158.
Collins, L. G., & Swartz, K., 2011. Caregiver care.
American family physician, 83(11), 1309.
Cristancho-Lacroix, V., Wrobel, J., Cantegreil-Kallen, I.,
Dub, T., Rouquette, A., and Rigaud, A. S., 2015. A
web-based psychoeducational program for informal
caregivers of patients with Alzheimer's disease: a pilot
randomized controlled trial. J Med Internet Res, 17(5),
e117. doi:10.2196/jmir.3717.
Finkel, S., Czaja, S. J., Schulz, R., Martinovich, Z., Harris,
C., and Pezzuto, D., 2007. E-care: a telecommunica-
tions technology intervention for family caregivers of
dementia patients. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry, 15(5), 443-
448. doi:10.1097/JGP.0b013e3180437d87.
Gaugler, J. E., Kane, R. L., Kane, R. A., and Newcomer, R.,
2005. The longitudinal effects of early behaviour
problems in the dementia caregiving career. Psychol
Aging, 20(1), 100-116. doi:10.1037/0882-7974.20.1.
100.
Glueckauf, R. L., Ketterson, T. U., Loomis, J. S., and
Dages, P., 2004. Online support and education for
dementia caregivers: overview, utilization, and initial
program evaluation. Telemed J E Health, 10(2), 223-
232. doi:10.1089/tmj.2004.10.223.
Griffiths, P. C., Whitney, M. K., Kovaleva, M., and
Hepburn, K., 2016. Development and Implementation
Internet Interventions for Family Caregivers of People with Neurocognitive Disorder
101

of Tele-Savvy for Dementia Caregivers: A Department
of Veterans Affairs Clinical Demonstration Project.
Gerontologist, 56(1), 145-154. doi:10.1093/geront/
gnv123.
Hicken, B. L., Daniel, C., Luptak, M., Grant, M., Kilian, S.,
and Rupper, R. W., 2016. Supporting Caregivers of
Rural Veterans Electronically (SCORE). The Journal of
Rural Health.
Jajor, J., Rosołek, M., Skorupska, E., Krawczyk-
Wasielewska, A., Lisiński, P., Mojs, E., and Samborski,
W., 2016. ''UnderstAID–a platform that helps informal
caregivers to understand and aid their demented
relatives”–assessment of informal caregivers–a pilot
study. Journal of Medical Science, 84(4), 229-234.
Kajiyama, B., Thompson, L. W., Eto-Iwase, T., Yamashita,
M., Di Mario, J., Marian Tzuang, Y., and Gallagher-
Thompson, D., 2013. Exploring the effectiveness of an
internet-based program for reducing caregiver distress
using the iCare Stress Management e-Training
Program. Aging Ment Health, 17(5), 544-554.
doi:10.1080/13607863.2013.775641.
Kamiya, M., Sakurai, T., Ogama, N., Maki, Y., and Toba,
K., 2014. Factors associated with increased caregiver’s
burden in several cognitive stages of Alzheimer ’ s
disease. Geriatric Gerontology, 14(Suppl. 2), 45–55.
http://doi.org/10.1111/ggi.12260.
Keefe, J., and Manning, M. (2005). The Cost Effectiveness
of Respite: A Literature Review.
Kelly, K., 2003. Link2Care: Internet-based information and
support for caregivers. Generations, 27(4), 87-88.
Kwok, T., Au, A., Wong, B., Ip, I., Mak, V., and Ho, F.,
2014. Effectiveness of online cognitive behavioural
therapy on family caregivers of people with dementia.
Clin Interv Aging, 9, 631-636. doi:10.2147/CIA.
S56337.
Lai, C. K., Wong, L., Liu, K. H., Lui, W., Chan, M., and
Yap, L. S., 2013. Online and onsite training for family
caregivers of people with dementia: results from a pilot
study. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry, 28(1), 107-108.
Lorig, K., Thompson-Gallagher, D., Traylor, L., Ritter, P.
L., Laurent, D. D., Plant, K., . . . Hahn, T. J., 2010.
Building Better Caregivers: A Pilot Online Support
Workshop for Family Caregivers of Cognitively
Impaired Adults. Journal of Applied Gerontology,
31(3), 423-437. doi:10.1177/0733464810389806.
Marziali, E., Damianakis, T., and Donahue, P., 2006.
Internet-Based Clinical Services: Virtual Support
Groups for Family Caregivers. Journal of Technology
in Human Services, 24(2-3), 39-54. doi:10.1300/
J017v24n02_03.
Marziali, E., and Garcia, L. J., 2011. Dementia caregivers'
responses to 2 Internet-based intervention programs.
Am J Alzheimers Dis Other Demen, 26(1), 36-43.
doi:10.1177/1533317510387586.
O'Connell, M. E., Crossley, M., Cammer, A., Morgan, D.,
Allingham, W., Cheavins, B., Morgan, E., 2014.
Development and evaluation of a telehealth
videoconferenced support group for rural spouses of
individuals diagnosed with atypical early-onset
dementias. Dementia (London), 13(3), 382-395.
doi:10.1177/1471301212474143.
O'Connor, M. F., Arizmendi, B. J., and Kaszniak, A. W.,
2014. Virtually supportive: a feasibility pilot study of
an online support group for dementia caregivers in a 3D
virtual environment. J Aging Stud, 30, 87-93.
doi:10.1016/j.jaging.2014.03.001.
Torkamani, M., McDonald, L., Aguayo, I. S., Kanios, C.,
Katsanou, M.-N., Madeley, L., Jahanshahi, M., 2014. A
randomized controlled pilot study to evaluate a
technology platform for the assisted living of people
with dementia and their carers. Journal of Alzheimer's
Disease, 41(2), 515-523.
van der Roest, Meiland, F. J., Jonker, C., and Droes, R. M.,
2010. User evaluation of the DEMentia-specific Digital
Interactive Social Chart (DEM-DISC). A pilot study
among informal carers on its impact, user friendliness
and, usefulness. Aging Ment Health, 14(4), 461-470.
doi:10.1080/13607860903311741.
Wiprzycka, U. J., Mackenzie, C. S., Khatri, N., and Cheng,
J. W., 2011. Feasibility of recruiting spouses with
DSM-IV diagnoses for caregiver interventions.
Journals of Gerontology Series B: Psychological
Sciences and Social Sciences, 66(3), 302-306.
ICT4AWE 2018 - 4th International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies for Ageing Well and e-Health
102
