
Tool-assisted Game Scenario Representation Through Flow Charts
Maria-Eleni Paschali
1
, Nikolaos Bafatakis
1
, Apostolos Ampatzoglou
1
,
Alexander Chatzigeorgiou
2
and Ioannis Stamelos
1
1
Department of Informatics, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Thessaloniki, Greece
2
Department of Applied Informatics, University of Macedonia, Thessaloniki, Greece
Keywords: Game Development, Game Scenarios, Flow Charts, Case Study.
Abstract: Game development is one of the fastest-growing industries in IT. In order for a game to be successful, the
game should engage the player through a solid and interesting scenario, which does not only describe the
state of the game, but also outlines the main characters and their interactions. By considering the increasing
complexity of game scenarios, we seek for existing methods for scenario representation approaches, and
based on the most popular one, we provide tool support for assisting the game design process. To evaluate
the usefulness of the developed tool, we have performed a case study with the aim to assess the usability of
the tool. The results of the case study suggested that after some interaction with end-users the tool has
reached a highly usable state that to some extent guarantees its applicability in practice.
1 INTRODUCTION
During the last decades, games have become an
integral part of young people lives. This observation
establishes them not only as a very strong and prof-
itable industry, but also as a significant field of re-
search (Ampatzoglou A. and Stamelos I., 2010). As
the interest of researchers around game development
grows, it becomes clearer that game development is
nowadays far away from being treated as a soft-skill
topic (or a more artistic one), but holds a strong
software engineering part. However, we note that
game engineering poses different challenges com-
pared to traditional software engineering, especially
with respect to requirements elicitation and specifi-
cation. In particular, games’ success cannot be guar-
anteed by just deploying a functional version, but it
should also be safeguarded that the game is enter-
taining as well, since user satisfaction / enjoyment
are major success factors (Callele D. et al., 2006).
Therefore, an interesting research direction aims at
finding the factors that lead to user satisfaction.
To this end, Ham and Lee (Ham H and Lee Y.,
2006), and Paschali et al. (Paschali M. et al, 2014),
explored the importance of seven high-level charac-
teristics (namely Scenario, Graphics, Speed, Sound,
Control, Characters, and Community) as parameters
of users’ satisfaction. Based on the results of the
most recent study Scenario, Character Solidness and
Sound have proven to be the most important factors
that influence user satisfaction (Paschali M. et al,
2014). Nevertheless, since characters are usually
described as part of scenarios, we assume that an
interesting scenario is a prominent factor in game
design.
Additionally, by considering that game scenarios
contain quite complex and dynamic structures (i.e.,
different possible endings based on gamers’ input),
there is a need to find an appropriate way to handle
the required complexity of scenarios and easily de-
pict game dynamics in game design documents.
Most of the traditional requirements specification
methods that provide textual descriptions of re-
quirements (e.g., use cases, user stories, etc.) do not
seem to suffice, since the end-results might be too
lengthy and inconsistent. Thus, the goal of this paper
is two-fold: (a) to review the literature for identify-
ing methods for scenario representation, and (b)
based on the most popular method, we intent to
provide tool support for assisting the game design
process and evaluate the usability of the tool.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows: in
Section 2, we present scenario representation ap-
proaches, and in Section 3, the tool that we have
developed for supporting the selected approach. We
note that since Section 2 provides a solid literature
review, we do not include a separate related work
section, due to space limitations. Next, in Section 4,
Paschali, M., Bafatakis, N., Ampatzoglou, A., Chatzigeorgiou, A. and Stamelos, I.
Tool-assisted Game Scenario Representation Through Flow Charts.
DOI: 10.5220/0006681402230232
In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to Software Engineering (ENASE 2018), pages 223-232
ISBN: 978-989-758-300-1
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
223
we describe the case study design that has been used
for its validation, whereas in Section 5 we provide
an overview of results, which are discussed in Sec-
tion 6. Finally, in Sections 7 and 8 we present threats
to validity and conclude the paper, respectively.
2 SCENARIO REPRESENTATION
APPROACHES
In literature, one can identify several techniques for
effectively representing stories (e.g., books, movies,
etc.) for over a hundred years. However, regarding
games, representation approaches have only recently
attracted the attention of researchers. Specifically,
based on the findings of a non-systematic literature
review, we have identified seven approaches for
scenarios representation (see Table 1).
Table 1: Scenario Representation Approaches.
Name Count Advantages Disadvantages
Character
Model
2
Description of
characters
Poor description
of scenes
Narrative
Structure
5
Description of
the background
and the outline
of overall story
Poor description
of the transitional
scenes. Informal
model
Flow Chart 10
Suitable for the
flow of the
story, event
causality, condi-
tion
Poor description
of characters
Use Case
UML
diagram
4
Story Beats
and Boards
6
Show how the
game will
appear to the
p
layer per scene
in a similar way
with the one
used in films
and television
Loss of the interac
-
tion between the
scenario and
p
layers. Concentra
-
tion on artistic
interpretations of
scenes and loss of
story’s continuity
and event causality
Petri Net 7
Rich description
of quest / event,
interactive
scenario
Complex repre-
sentation
Poor description
of characters
We note that since the results presented in Table 1,
have not been obtained through a systematic litera-
ture review, our goal is not to claim which are the
most frequent scenario representation approaches,
but only to provide a coarse-grain estimation. Next,
a brief description of these approaches and their
known uses for research purposes is provided.
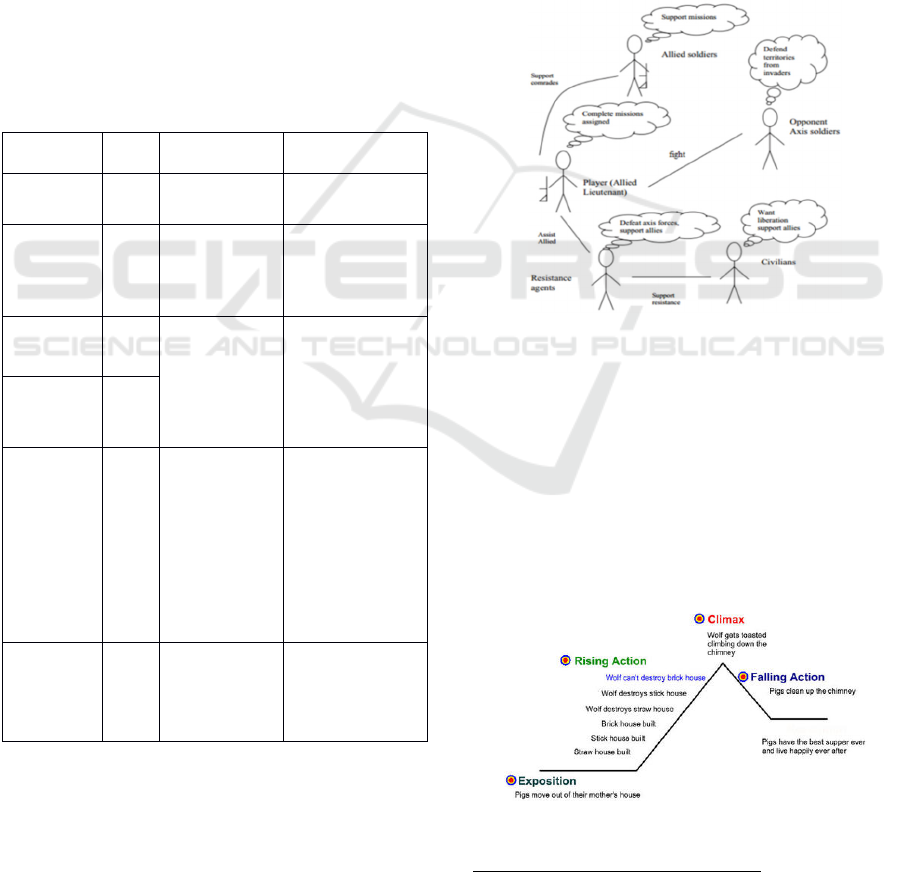
A Character Model (referenced in
(
Fairclough
C., 2005
), (
Rolfe B. et al, 2010
)
) is a diagrammatic
representation of the characters that are involved in a
story / scene, along with their interactions, as de-
scribed by Rolfe et al. (Rolfe B. et al, 2010). For
example, in
(
Rolfe B. et al, 2010) the authors de-
scribe a scene from the Medal of Honor game, with
the following character model (see Figure 1). The
notations of the diagram are the characters of the
game (stickmen – e.g., Allied Soldier), their interac-
tions (continuous lines – e.g., the Player is fighting
with Opponent Axis Soldiers), and their high-level
goals (though bubbles – e.g., the goal of the Civil-
ians is to be liberated and receive support by allies).
Figure 1: Character Model - Medal of Honor (33).
When describing a scenario by using a Narra-
tive Structure (referenced in (Csikszentmihalyi M.,
1998), (Fairclough C., 2005), (Freytag G., 1863),
(Gobel S. et al, 2005), and (Rolfe B. et al, 2010)),
the story is divided into five parts: Exposition, Ris-
ing Action, Climax, Falling Action, and Conclusion.
When using narrative structure game designers re-
port their scenarios on plot diagrams, as for example
the one presented in Figure 2 for the well-known tale
of the Three Little Pigs.
Figure 2: Narrative Structure - Three Little Pigs
1
.
1
The narrative structure has been retrieved online.
ENASE 2018 - 13th International Conference on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to Software Engineering
224

Flow Charts (referenced in (Hill R. et al, 2001),
(Kistler F. et al., 2011), (Koenitz H. and Chen K.,
2012), (Lewinski J.S, 1999), (Marne B. et al., 2013),
(Medler B. and Magerko B., 2006), (Robertson M.,
2007), (Rouse R., 2000), (Ruda I. et al., 2009),
(Ryan M., 2001), and (Verbrugge C., 2003)) may
often be included as part of the game design docu-
ment, similarly to those of traditional software engi-
neering. Flow charts are diagrams that represent an
algorithm, workflow or process, showing the steps
as boxes, and their sequence of execution by con-
necting them with arrows. In game development,
flowcharts are used to track (Rouse R., 2000): (a)
players’ navigation of out-of-game menu options
(e.g., starts a new game or loads a saved one), and
(b) areas the players progress to and from in the
game, particularly in level-based games. Beyond
these most obvious applications, flowcharts can be
quite useful for visually representing the results of
any decision players may take during a game (Rouse
R., 2000). In some games genres (e.g., MMOG -
Massively Multiplayer On-Line Games) interactivity
is a distinguishing feature and an attraction for gam-
ers, since participants can change the state of affairs
with their actions. In such games, due to the dynam-
ic flow of events, gameplay can be resembled to the
execution of an algorithm, where elementary actions
are defined by game rules, rendering the flowchart a
fitting means for their representation (Rouse R.,
2000). Additionally, narrative flow graphs, i.e., a
simple description format, can lead to story specifi-
cation, without representation gaps (Verbrugge C.,
2003).
Use Cases (UCs) and Use Case Diagrams (ref-
erenced in (Kendra C. et al., 2014), (Longstreet C.S.,
2012), and (Taylor M. et al., 2007)) are part of the
Unified Modeling Language (UML) (Booch G. et
al., 1999) and aim at specifying software require-
ments. In game engineering, use case specifications
and use case diagrams are used to demonstrate the
connection between scenes / actions. Taylor et al.
(Taylor M. et al., 2007) suggest that detailed use-
case diagrams, enriched with some aspects of deci-
sion trees, could be useful for professionals involved
in computer game development (e.g., story, level,
and character designers, 3-D modelers, artists, ani-
mators, and musicians). Specifically, they describe a
game-flow design approach that can be used in order
to model the individual levels of a computer game.
In a similar line of thought, Longstreet et al. (Long-
street C.S., 2012) present how tailored UML models
(i.e., UML diagrams and UC specifications) with
additional features from story boarding techniques
(see below) could model serious educational games.
Finally, Kendra et al. (Kendra C. et al., 2014)
demonstrated how game requirements engineering
(RE) processes can be enhanced by standard nota-
tions, tools, and techniques. Specifically, they pro-
pose a three step model-based approach: (a) creation
of an informal model of the game requirements
(narrative captured like a storyboard – see below),
(b) transformation of the narrative into a semi-
formal model, and (c) transformation of the semi-
formal model into a tailored UML use case model.
As an example we present a UC diagram from Pro
Evolution Soccer, in Figure 3.
Figure 3: UC Model - Pro Evolution Soccer
2
.
Story Boards (or Beats) (referenced in (Bethke
E., 2003), (Henno J., 2009), (Rouse R., 2000), (Ruda
I., et al., 2009), (Skorupski J., 2009), and (Truong K.
et al., 2006) represent how each game scene will
appear to the player, in a way similar with the one
used in films and television. Usually, they describe
the location and the objects through an action/event
table. Regarding story beats, Henno (Henno J.,
2009), presents an event-driven, object-oriented-like
high level specification for computer games. This
level of abstraction that such specifications use,
allows the description of games, without details on
programming languages or used game engines. An
example of a story board is presented in Figure 4.
Concerning story boards, Rousse (Rouse R., 2000)
suggests that this approach is the easiest way of
depicting cut-scenes (i.e., non-interactive kinematics
so as to offer information to the gamer), sketches or
mock-ups (e.g., informing the players that the game
is about to start—probably while loading).
2
The use case model has been retrieved online
Tool-assisted Game Scenario Representation Through Flow Charts
225

Figure 4: Storyboard - Aladdin for Disney
3
.
Using Petri Nets (referenced in (Araujo M. and
Roque L., 2009), (Brom C. and Abonyi A., 2006),
(Brom C. et al., 2007), (Brom C. et al., 2010), (De
Oliveira G.W. et al., 2011), (El-Sattar H., 2012), and
(Peterson J., 1977)), the game designers can describe
how each quest or event is organized, by using the
following notations: place/states (circles), transitions
(rectangles), tokens and transition functions (ar-
rows). One of the most distinctive characteristic of
Petri Nets, as a formal way to specify requirements,
is that they enable the specification of asynchronous
systems, where actions can take place in parallel,
something which is obviously of major importance
for game requirements engineering. For example,
Araújo et al. (Araujo M. AND Roque L., 2009)
suggest that Petri Nets outbalance other modeling
languages, because of the simplicity of their graph-
ical notation, which however is not a barrier for
modeling complex game systems. The strengths and
weaknesses of Petri Nets in virtual storytelling have
already been discussed by Brom et al. (Brom C. et
al., 2007). An example is presented in Figure 5.
Figure 5: Petri Net - Europe 2045 (7).
3
The storyboard has been retrieved online
3 SCENARIO REPRESENTATION
Based on the above, we selected to provide a method
(accompanied by a tool) for scenarios design, based
on flow charts, narrative structure, and character
models.
Proposed Representation Approach. To tailor flow
charts for designing game scenarios, we propose the
use of some additional notations that are useful for
the desired representation. Under this tailored repre-
sentation, the story will be divided into three parts
(Exposition, Rising Action, Climax, and Endings),
as dictated by the narrative structure. The notations
used for the tailored flow charts are:
• Rectangles/Actions represent sequences of ac-
tions or events during which the player is pas-
sive. These sequences are used to set up the next
situation or show the consequences of successful
(or unsuccessful) completion of previous tasks.
• Choice/Fork represent a “ free play area ”
inside the story, i.e., choice. The players can take
control and make choices which will impact on
the unfolding of the story or on the players. In
addition to that, as a choice we classify any ac-
tion of the player that can alter the flow of
events. For example, solving a puzzle or winning
a battle, can lead to unlocking a completely new
path in the game flow, which would not be re-
vealed to the player, if he/she would not be able
to solve the puzzle or if he/she had lost the battle.
• Filled rectangles/Goals are used to show the
goals in the story.
• Ovals/Ends denote the endings and starts of the
story. The possible different endings of the story
are denoted with white for “happy ending”,
and black for “bad ending”, whereas the start
of the story is denoted with a grey oval. In the
special case of games with only one type of end-
ing (e.g., the game finishes and the player is pro-
vided with a score, so as to compare it with other
players), this end is denoted as a “happy end”.
For games that do not have an obvious ending,
e.g., SIMS, there is no denoted ending.
• Arrows are used to show the direction of the
flow in the story.
• Swimlanes denote the different parts of the story
(Exposition, Rising Action, and Climax).
A sample legend for the above notations is provided
in Figure 6.
ENASE 2018 - 13th International Conference on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to Software Engineering
226

Figure 6: Sample Notations for Flow Charts.
Tool Support. To assist the popularization of the
proposed approach, we have built an online
4
Open
Source Software (OSS) tool that provides an inte-
grated environment for "Game Scenario" design. In
particular through the tool, the designer can create a
project that includes one or more flow charts related
to the story of the game and one or more character
models that correspond to the interactions of actors
in the scenes. The developed tool reuses components
of two other existing OSS projects, namely: Vis.js
and Chart.js. The source code of the tool is available
in GitHub
5
. The main functional requirements of the
tool have can be summarized as follows (accompa-
nied by screenshots).
Generic Functionalities: Create Game Scenario
(Project), Create Flow Chart, Create Character Mod-
el, Save / Load Project.
Figure 7: Generic Functionalities.
Design Functionalities on Flow Charts: Add Nar-
rative Nodes, Edit Nodes, Add Edge Between
Nodes, Edit Edges, Overview of Node Details (Ex-
pand / Collapse).
4
http://nikompaf.webpages.auth.gr/main.php
5
https://github.com/nickbaf/Umbra-GameScenario-Designer
Figure 8: Designing Flow Charts.
Design Functionalities of Character Models: Add
New Character, Edit Character, Add Character In-
teraction Edge, Overview of Node Details (Expand /
Collapse).
Figure 9: Designing Flow Charts.
4 CASE STUDY DESIGN
In this section we present the case study design. The
study has been designed and reported according to
the template suggested by Runeson et al. (Runeson
P. and Host M., 2009). The high-level goal of this
case study is to improve and evaluate the usability of
the developed tool. To achieve this goal we have
performed two rounds of empirical evaluation, be-
tween which we performed maintenance activities.
We organized the two rounds as follows: the case
study was conducted once for 10 participants and
Tool-assisted Game Scenario Representation Through Flow Charts
227

then based on the feedback taken from the think
aloud results we implemented changes to the tool.
Next, we repeated the case study with 10 different
participants. However, the reporting will be made
only for the last version of the tool.
4.1 Research Objectives & Questions
The main objective of the empirical evaluation in
terms of the Goal-Question-Metric (GQM) approach
(Basili V. et al, 1994) is formulated as follows: ana-
lyze the developed tool for the purpose of evalua-
tion, with respect to its usability from the point of
view of game designers. According to ISO 9241-11,
usability can be decomposed to three sub-
characteristics: effectiveness, efficiency, and satis-
faction (Frokjaer E. et al, 2000). Based on the above,
we derived three research questions (RQ):
RQ
1
: What is the effectiveness of the tool?
Effectiveness is a measure of how accurately the
users can perform a set of tasks. In order to answer
this research question, we will provide the subjects a
set of tasks to be accomplished, and we will assess
their success with qualitative and quantitative analy-
sis (see Section 4.3).
RQ
2
: What is the efficiency of the tool?
The efficiency quality attribute measures the timely
behavior of users when performing several tasks.
The same research setting as RQ
1
will be used, in
which a well-known approach for assessing the task
duration will be used (see Section 4.3).
RQ
3
: What is the level of satisfaction that the users
get from using the tool?
User satisfaction is related to the evaluation of the
overall experience of the user. A questionnaire based
approach will be used for this assessment using estab-
lished data collection methods (see Section 4.3).
4.2 Case and Task Selection
This study is a holistic case study, in which for every
case (subject / usability tester) we record one unit of
analysis. Each subject has been asked to complete a
list of tasks, for which the evaluation and data col-
lection has taken place.
Case Selection: According to Charters (Charters E.,
2003), a usability test with five users that test the
system (by using the think-aloud method (Charters
E., 2003)) can identify up to 2/3 of existing usability
issues. Therefore, in order to identify an ever larger
portion of usability issues, we performed the two
rounds of usability testing with 10 different subjects
as evaluators (in each round), so as to avoid bias,
and familiarity with the system. Through such a set
of evaluators, we expect to find a minimum of 95%
of system errors with a probability of 98% (Turner
C.W., 2006). The sample we chose mainly come
from higher education, i.e. undergraduate, postgrad-
uate students and PhD candidates with a level of
knowledge in using software applications, and inter-
est in game design.
Task Selection: The tasks that the users have been
asked to complete are divided into two main catego-
ries: (a) observation tasks in which the user is invit-
ed to recognize a situation or answer questions about
the program (e.g., see T3, T4 from the list below),
and (b) action tasks, which the user is called to de-
sign-edit on the program. (e.g., see T1-T2). First, the
usability testers will be provided with some pre-
defined stories
6
. The tasks that have been used in the
usability testing are based on these stories are:
T1. Load the file with the name "archive"
T2. Open the history flow chart named "Stage 1"
T3. Add a new "bad ending" node.
T4. What are the features of the node labeled "30"?
T5. Connect with an edge the node that you built
before to the node with the number 30.
T6. Edit the node labeled "12" to be part of the
"Rising Action".
T7. Edit the figure so that the node labeled "5" is
connected only to the node labeled "9".
T8. Delete the node that has been out of use by the
preceding action.
T9. How many choices does the story have?
T10. Delete the Story Flow Diagram "Stage 3"
T11. Create a new character named "Red".
T12. Add an edge between "Vincent" and Barret"
T13. Delete the "Teddie" character and then the tab.
T14. Delete the Character Model
4.3 Data Collection
To measure effectiveness we observed users, while
dealing with the assigned tasks, without first having
been instructed on how to use the program. During
the observation sessions, users should think aloud to
implement the think-aloud protocol that is wide-
spread in software testing (Charters E., 2003). In
order to measure efficiency we ask users to perform
the tasks presented in Section 4.2. Efficiency has
been measured with the use of Keystroke Level
Model (KLM) (11). Additionally, to assess efficien-
cy we also used the data from the think-aloud data
collection process, so as to record their actions and
6
https://www.dropbox.com/s/7vdq5hwgep6b6fn/Stories.zip?dl=0
ENASE 2018 - 13th International Conference on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to Software Engineering
228

the causes of their wrong choices. Finally, to assess
user satisfaction a standard usability questionnaire
has been distributed to the participants. The ques-
tionnaire, namely System Usability Scale — SUS
(Brooke J., 1996) that gives a comprehensive picture
of subjective usability assessment.
4.4 Data Analysis
During the execution of tasks the observer notes,
which have been executed correctly and which not.
Based on this, the overall effectiveness is calculated
as the percentage of correctly executed tasks. An
average is used to aggregate from the single subject
to the sample. Apart from quantifying each quality
criterion, a major aspect of this evaluation is the
provision of feedback to the development tool.
Therefore, by analyzing the transcripts of each ses-
sion the identified problems have been divided into
the following categories:
• Layout problems, the user fails to locate a partic-
ular item on the program’s screen,
• Operating problems, the user is unable to under-
stand the function of an element in the program,
• Understanding problem, the user fails to under-
stand the data presented by the program.
To quantify efficiency, the observer has recorded
the movements of the tester according to KLM and
calculated the expected completion time for each
task according to the model. Following the case
study, the times will be compared to the ones that
are actually achieved by the testers. Thus, regarding
efficiency, both the completion time of the work
according to the KLM model, the errors made and
the success or not of work will be used. Similarly to
before, aggregation will be performed by using the
average function.
With respect to user satisfaction, based on the
System Usability Scale questionnaire, we sum up the
adjusted result of each response. We note that in
SUS, some questions have a negative phrasing and
others a positive one. Thus, we follow the prescribed
way of handling and grading the answers. Since the
SUS results range from 0 to 100 and the optimum
satisfaction is achieved with scores higher than 90
(9), we set a goal of average satisfaction > 90%.
5 RESULTS
Effectiveness (RQ
1
). In Table 2 we present the com-
pletion rates for each Task (T1-T14), regarding RQ
1
.
First, we note that tasks T1, T2, T3, T6, T8, and T9
were completed by all participants. We note that
between the 1
st
and the 2
nd
round of usability testing,
the task completion rate improved by approximately
5%, suggesting that the improvement performed
between rounds were successful. By comparing the
task completion rates that aimed at flow charts and
character modelling, we can observe that the design
of a character model was less effective, compared to
designing the flow of the story (i.e., tasks T10-T14
had a lower completion rate, compared to tasks T1-
T9). Nevertheless, the most difficult task proved to
be T4 (i.e., reading the properties of nodes in flow
charts), that still needs to be improved by the devel-
opers of the proposed tool.
Table 2: Task Completion Rates per Task.
Task
Completion
Rate
Task
Completion
Rate
T1 100% T8 100%
T2 100% T9 100%
T3 100% T10 70%
T4 30% T11 80%
T5 90% T12 80%
T6 100% T13 90%
T7 100% T14 100%
When focusing on specific participants, and differ-
ences between their efficiency, we observed a mean
completion rate of approximately 89% (min value:
78.6%, max value: 92.9%—achieved by 5 partici-
pants, and std. dev.: 5.01%). Thus, we can observe a
satisfactory uniformity of task completion rates
among different practitioners.
Efficiency (RQ
2
). To access the efficiency of the
tool, we selected a subset of the 14 tasks presented
in Section 4.2 (i.e., T5, T7, T8, and T10 – T14).
Table 3 refers to RQ
2
and shows the average time
Table 3: Task Completion Time per Task.
Task
Required Time
Usability
Testers Expert KLM
T5 4.47 1.60 5.30
T7 2.31 0.50 1.30
T8 1.51 0.90 2.40
T10 1.37 0.70 2.40
T11 4.03 0.50 1.40
T12 3.01 0.90 3.85
T13 1.91 0.40 2.65
T14 1.30 0.80 2.40
Tool-assisted Game Scenario Representation Through Flow Charts
229

that users need to complete each of the aforemen-
tioned tasks, the time that an expert (the core devel-
oper of the tool) needed to complete the task, and the
average required time according to KLM.
The usability testers needed 316% more time
compared to the expert user to complete the tasks,
reaching a total time of 19.9 seconds compared to
the 6.3 seconds required by the skilled user. By
comparing the usability testers to the average time
required based on KLM, we can observe that the
usability testers performed better than expected
(approximately 10%), suggesting that the tool can be
efficiently used by non-trained users. Thus, the
learning curve of the tool is quite steep, since even
inexperienced users can perform as average ones —
see Figure 10. Similarly to RQ
1
, the usability testers
have found more time consuming to complete the
task related to character modelling, compared to
flow modelling. In particular, on the one hand re-
garding flow modelling, the usability testers were
faster than the average KLM user by 15% and slow-
er than the expert user by 260%. On the other hand,
regarding character modelling, usability testers were
2% faster than the KLM estimation, and 390% slow-
er than the expert. Nevertheless, we note that the
expert user was 30% faster in character modelling
activities compared to flow modelling. This observa-
tion suggests that when familiarizing with the tool,
character modelling activities are more efficient, but
have a smoother learning curve (since novices find
them more difficult).
Figure 10: Task Efficiency among Groups.
User Satisfaction (RQ
3
). On the completion of the
tasks presented in Section 4.2, the usability testers
were asked to fill in a user satisfaction questionnaire
(namely System Usability Scale—SUS). The results
on the SUS questionnaire are presented in Table 4.
We note that for RQ
3
, the specifics of the tool (e.g.,
character vs. flow modeling) cannot be discussed
since the SUS instrument treats the system as a
whole, without discriminating between different use
cases.
Based on the results presented in Table 4, we ob-
served a mean user satisfaction of approximately
89.75% (min value: 77.5%, max value: 97.5%, and
std. dev.: 8.55%). Additionally, we can observe that
the participants can be easily separated into two
groups: (a) those with very high satisfaction (i.e.,
SUS >90%)—7 participants, and (b) those which
were less satisfied—3 participants. As a way to
explore the reason for those that are dissatisfied, we
explored the existence of a relationship between
SUS and task completion rate. The results suggest
that the completion rate for each user and the rate of
satisfaction from the system according to SUS ques-
tionnaire. Thus, a direct link between the tasks'
completion rate and the users' satisfaction can be
observed. The user who successfully completes the
tasks feels more comfortable with the behavior of
the system, since he/she does not doubt on the
knowledge that he/she possesses on the system and
how to use it. Therefore, we believe that if in future
versions of the system we manage to further increase
its effectiveness, the user satisfaction will be in-
creased as well.
Table 4: User Satisfaction per Usability Tester.
Participant
SUS Participant SUS
P1 77,50 P6 97,50
P2 92,50 P7 97,50
P3 92,50 P8 97,50
P4 72,50 P9 95,00
P5 92,50 P10 82,50
6 DISCUSSION
The results of our case study (i.e., a usability testing
procedure with game enthusiasts) suggest that the
tool that we have developed for representing scenar-
ios is usable and therefore is ready for evaluation by
experts (i.e., professional game designers). Howev-
er, the results pointed out some weak aspects of the
tool that need to be considered for refactoring before
we proceed to the next stage. A uniform conclusion
that we got by comparing the modelling of charac-
ters to modelling the flow of the games, is that char-
acter modelling needs further improvement, both in
terms of effectiveness of tasks and completion time.
These results can be considered quite intuitive in the
sense that a flow chart is an established representa-
tion in traditional software engineering, and there-
fore designers feel more comfortable against it,
compared to the completely new notations offered
ENASE 2018 - 13th International Conference on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to Software Engineering
230

by the character model. An additional interesting
observation is that all three usability sub-
characteristics that we have examined (i.e., effec-
tiveness, efficiency, and user satisfaction) appear to
be interconnected, in the sense that users that fail a
task are dissatisfied with the tools and that also,
users that are not time effective are dissatisfied as
well. Based on this observation, we can assume that
user satisfaction will improve if we manage to de-
crease task completion time and failure rates.
Based on the aforementioned discussion, we plan to
prompt professional game engineers to use our tool
and evaluate, not only its usability, but also its fit-
ness in the current processes of game development
firms. Also, as part of future work, we plan to inves-
tigate the benefits that game development companies
get by integrating into their process tool-support for
scenario representation. Although we acknowledge
that these research questions are very important, we
consider the evaluation of usability as a prerequisite
for their unbiased answer in an industrial context.
Nevertheless, even at this stage we can claim that
the tool is fitted for representing scenarios, since the
task completion rates are adequate and game devel-
opment enthusiasts that participated in the case study
are satisfied with the level of assist that it provides.
7 THREATS TO VALIDITY
The results of the usability testing are subject to
external validity threats since the study has been
performed with 10 participants and a particular sub-
set of tasks. However, these threats are mitigated
because according to the literature even five users
can reveal the majority of usability issues. Concern-
ing the coverage of the tool’s functionality, the se-
lected tasks exercise representative use cases of a
scenario representation tool and thus we believe that
effectiveness, efficiency and user satisfaction have
been adequately assessed. Another typical threat to
construct validity for this kind of studies is the ten-
dency of participants to be positive about an approach
that offers automation to tasks. However, the think
aloud protocol for the study of the first research ques-
tion revealed that the usability testers have been neu-
tral and identified weaknesses of the tool.
8 CONCLUSIONS
The success of any computer game depends largely
on its scenario since these fictional narratives or
diagrammatic representations can be effectively used
to discuss and picture the interaction between users
and the system. After reviewing existing scenario
representation approaches we propose a scenario
representation approach accompanied by an online
tool, based on flow charts, narrative structure, and
character models. The effectiveness, efficiency and
user satisfaction have been evaluated by a case study
involving 10 participants. The results of the study
suggested that the tool enables users to achieve their
intended goal with high completion rates, is relative-
ly easy to master and is perceived as highly usable
by most users. However, it has also identified weak-
nesses regarding the support for character modelling
which needs to be further improved both in terms of
effectiveness of tasks and completion time.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
This work was financially supported by the action
"Strengthening Human Resources Research Poten-
tial via Doctorate Research" of the Operational Pro-
gram "Human Resources Development Program,
Education and Lifelong Learning, 2014-2020", im-
plemented from State Scholarship Foundation (IKY)
and co-financed by the European Social Fund and
the Greek public (National Strategic Reference
Framework (NSRF) 2014 – 2020).
REFERENCES
A. Ampatzoglou and I. Stamelos, “Software Engineering
Research for Computer Games: A systematic Re-
view”, Information and Software Technology, Else-
vier, 52 (9), pp. 888-901, September 2010.
M. Araújo and L. Roque, “Modeling Games with Petri
Nets”, Digital Games Research Association Confer-
ence, London, UK, September 2009.
V.Basili, G. Caldiera and D. Rombach, “The Goal Ques-
tion Metric Approach”, Encyclopedia of Software En-
gineering. Wiley & Sons, 528-532, 1994.
E. Bethke, “Game Development and Production”, Word-
ware Game Developer's Library, 2003.
G. Booch, J. Rumbaugh, and I. Jacobson, “The Unified
Modelling Language User Guide”, 1999.
C. Brom, A. Abonyi, “Petri-Nets for Game Plot”, AISB
Artificial Intelligence and Simulation Behaviour Con-
vention”, Bristol, vol. 3, pp. 6–13, 2006.
C. Brom, V. Sisler and T. Holan,. “Story Manager in
'Europe 2045' Uses Petri Nets”. International Confer-
ence on Virtual Storytelling, pages 38-50, 2007.
C. Brom, T. Holan, D. Balas, A.Abonyi, V. Sisler, G. Leo,
“Petri nets for representing story plots in serious
game”. AISB Journal 2, vol. 1, 2010.
Tool-assisted Game Scenario Representation Through Flow Charts
231

J. Brooke, “SUS - A quick and dirty usability scale,”
Usability Eval. Ind., vol. 189, pp. 4–7, 1996.
D. Callele, E. Neufeld, K. Schneider, Emotional require-
ments in video games, in: Proceedings of the Interna-
tional Conference on Requirements Engineering
(RE’06), IEEE Computer Society, Minneapolis, MN,
USA, 11–15 September 2006.
Card, S. K, Moran, T. P., Allen, N., "The keystroke-level mo-
del for user performance time with interactive systems",
Communications of the ACM, 23 (7): 396–410, 1980.
Charters, E., “The Use of Think-aloud Methods in Quali-
tative Research An Introduction to Think-aloud Meth-
ods”, Brock, 12 (2), pp.68-82, 2003
M. Csikszentmihalyi, “Finding flow: The psychology of
engagement with everyday life”, asicBooks, ISBN 0-
465-02411-4, 1998.
G.W De Oliveira, S. Julia, S. Passos, "Game modeling
using WorkFlow nets," 2011 IEEE International Con-
ference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics
(SMC), pp.838-843, 2011
H. El-Sattar, “A Novel Narrative Intelligence Structure for
Interactive Drama in Computer Games Workflow”, In-
telligent Computer Graphics, 2012
C. Fairclough, “Story Games and the OPIATE System”,
thesis Trinity College, 2005.
G. Freytag, “Freytag’s technique of the drama: An exposi-
tion of dramatic composition and art”, Scott, For-
esman and Company, Chicago, USA, 1863.
E. Frokjaer, M. Hertzum and K.Hornbaek “Measuring
Usability: Are Effectiveness, Efficiency, and Satisfac-
tion Really Correlated?”, Chi, vol 2, 2000
S. Göbel, F. Becker and A. Felix, “INSCAPE: Story
models for Interactive Storytelling and Edutainment
Applications”, 3
rd
International Conference, France,
November 30 - December 2. 2005
H. Ham and Y. Lee, “An Empirical Study for Quantitative
Evaluation of Game Satisfaction”, 2006 International
Conference on Hybrid Information Technology, ACM,
pp. 724-729, November 2006.
J. Henno, “Towards Intelligent Engineering and Infor-
mation Technology”, Springer Berlin Heidelberg,
243, pp 307-322, 2009
R. Hill, J. Gratch, W. L. Johnson, C. Kyriakakis, C. La-
Bore, R. Lindheim, S. Marsella, D. Miraglia, B.
Moore, J. Morie, J. Rickel, M. Thiébaux, L. Tuch, R.
Whitney, J. Douglas, and W. Swartout.” Toward the
holodeck: integrating graphics, sound, character and
story”, 5
th
Int. Conference on Autonomous
Agents (AGENTS '01), ACM, pp. 409-416, 2001.
C. Kendra, Nasr E. and C.S Longstreet, “Towards Model-
Driven Requirements Engineering for Serious Educa-
tional Games: Informal, Semi-formal, and Formal
Models”, 20
th
Int. Working Conference, Essen, Ger-
man. Proceedings pp 17-22, 2014
F. Kistler, D. Sollfrank, N. Bee and E. André. “Full Body
Gestures Enhancing a Game Book for Interactive Sto-
ry Telling”, Fourth International Conference on Inter-
active Digital Storytelling, ICIDS 2011, Vancouver,
Canada, November 28 – 1 December, 2011, Proceed-
ings pp 207-218, 2011.
H. Koenitz and K. Chen, “Genres, Structures and Strate-
gies in Interactive Digital Narratives – Analyzing a
Body of Works Created in ASAPS”, 5
th
International
Conference, ICIDS, San Sebastián, Spain, November
12-15, pp 84-95, 2012.
J.S Lewinski, “Developer's Guide to Computer Game
Design”, Wordware Publishing Inc., Plano, TX, USA,
1999. 32.
C. S Longstreet, “Towards model-driven game engineer-
ing for serious educational games: Tailored use cases
for game requirements”, 17
th
Int. Conference on Com-
puter Games, IEEE, pp 208-212, 2012.
B. Marne, T. Carron, J.M Labat,, and M. Schottman,
"MoPPLiq: A Model for Pedagogical Adaptation of
Serious Game Scenarios", 13
th
International Confer-
ence Advanced Learning Technologies (ICALT),
IEEE, pp. 291-293, 2013
B. Medler and B. Magerko, “A Tool for Authoring Event Dri-
ven Interactive Drama”, In Third International Confer-
ence, TIDSE 2006, pp 139-150, December 4-6, 2006 39.
M. E. Paschali, A. Ampatzoglou, A. Chatzigeorgiou, and
I. Stamelos, “Non-functional requirements that influ-
ence gaming experience: A survey on gamers satisfac-
tion factors”, 18
th
Academic MindTREK Conference,
ACM, 4 – 6 November 2014, Finland.
J. Peterson, “Petri Nets”. ACM, Comput. Surv. 9, vol. 3,
pp.223-252, September 1977.
M. Robertson, “Visual Scenario Representation in the
Context of a Tool for Interactive Storytelling”, Inter-
national Conference on Virtual Storytelling, pp. 3-12,
Saint-Malo, France, Springer, 2007.
B. Rolfe, C. Jones and H. Wallace, “Designing dramatic
play: story and game structure. 24th BCS Interaction
Specialist Group Conference (BCS '10).” British
Computer Society, Swinton, UK, 2010.
R. Rouse, “Game Design Theory and Practice (2
nd
ed.)”,
Wordware Publishing Inc., 44, 2000.
I. Ruda, J.Fodor, J. Kacprzyk, “High-Level Specification
of Games”, Springer, pp 307-322, 2009,
P. Runeson and M. Host, “Guidelines for conducting and
reporting case study research in software engineering,”
Empir. Softw. Eng., pp. 131–164, 2009.
M. Ryan, “Narrative as Virtual Reality: Immersion and
Interactivity in Literature and Electronic Media”, In
John Hopkins University Press, 2001
J. Skorupski, “Storyboard authoring of plan-based interac-
tive dramas”. 4
th
International Conference on Founda-
tions of Digital Games (FDG '09). ACM, New York,
NY, USA, 349-351, 2009.
M. Taylor, M. Baskett, G. Hughes and S. Wade, “Using
soft systems methodology for computer games de-
sign”, Systems Research and Behavioral Science, 24,
3, pp. 359—368, 2007.
C. W. Turner, J. R. Lewis, and J. Nielsen, “Determining
usability test sample size,” Int. Encycl. Ergon. Hum.
Factors, 2
nd
Ed. pp. 3084–3088, 2006
K. Truong, G. Hayes, and G. Abowd. “Storyboarding: an
empirical determination of best practices and effective
guidelines”. In Proceedings of the 6th Conference on
Designing Interactive systems (DIS '06). ACM, New
York, NY, USA, pp 12-21, 2006.
C. Verbrugge, “A Structure for Modern Computer Narra-
tives”, Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2003
ENASE 2018 - 13th International Conference on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to Software Engineering
232
