
An Evaluation Framework for Fastest Oblivious RAM
Seira Hidano, Yuto Nakano and Shinsaku Kiyomoto
KDDI Research, Inc., Saitama, Japan
Keywords:
Memory Access Pattern, Oblivious RAM, Average Min-Entropy, Collision Entropy.
Abstract:
Oblivious RAM (ORAM) is security provable approach for memory access pattern hiding. However, since
ORAM incurs high computational overheads due to repeated shuffles of data blocks in a memory, numerous
constructions have been proposed to reduce it. While the computational cost has been improved by these
constructions as compared to early ones, it is still expensive from the practical point of view. Specifically, in
its application to IoT devices, less computational cost is expected for avoiding high energy consumption. We
thus focus on an ORAM construction proposed by Nakano et al. in 2012, which we call the fastest ORAM.
The computational cost of this construction is much less than any other conventional ORAM constructions.
However, the security has not been analyzed sufficiently, due to the lack of practical security definitions.
Therefore, we formulate a new security definition for the fastest ORAM on the basis of the average min-
entropy, and propose a framework for evaluating the security.
1 INTRODUCTION
IoT devices usually adopt Low Power Wide Area net-
works (LPWAN) for sending data and receiving con-
trol command from an administrator. In many LP-
WAN technologies including LoRa and Sigfox, end
devices and servers share secret keys for authentica-
tion, confidentiality, and integrity. Therefore, it is crit-
ical to protect these keys from adversaries for security
of services. One of the challenges is that an adver-
sary can easily gain access to IoT devices as they are
widely deployed in wide area. Once the adversary
obtains the device, one can try to extract the key by
using reverse engineering. In the case of LoRaWAN,
the master secret key called AppKey is used to derive
two session keys called AppSKey and NwkSKey just
after the device joins the network. If the adversary
can detect which data is accessed during generating
the session keys, one can also obtain the master key.
Oblivious RAM (ORAM) can be used to mitigate the
risk of leaking the secret key. By using ORAM, we
can hide which data is actually used during the session
key generation even if the adversary has full access to
RAM. The drawback of using ORAM is its relatively
high demanding in computation, hence high energy
consumption. Since many IoT devices are designed
for long-term use with batteries, ORAM for IoT de-
vices should be lightweight.
The first constructions of ORAM was introduced
by Goldreichis et al. in (Goldreich, 1987; Goldreich
and Ostrovsky, 2007). These ORAM constructions
hide memory access patterns by shuffling locations
where data are stored on a memory at a certain in-
terval. However, the shuffling process imposes con-
siderable computational overheads. Although there is
a rich literature on ORAM constructions devoted to
improving the overheads (Pinkas and Reinman, 2010;
Goodrich and Mitzenmacher, 2011; Goodrich et al.,
2011; Shi et al., 2011; Stefanov et al., 2011; Kushile-
vitz et al., 2012; Williams and Sion, 2012; Stefanov
and Shi, 2013; Stefanov et al., 2013), their compu-
tational overheads are still expensive, which means
these constructions are not suitable for practical use.
Meanwhile, there is a construction to dramatically im-
prove the overheads, instead of involving information
leakage (Nakano et al., 2012). This construction has
been proposed by Nakano et al., and has the com-
putation overhead of only two times. We call it the
fastest ORAM in this paper. The fastest ORAM is
expected to be applied to IoT devices, yet there re-
main concerns on its security. Nakano et al. also pro-
vided a new security definition called δ-security for
the fastest ORAM. However, this concept was differ-
ent from that of generic security definitions, such as
unpredictability and indisguishability. Analysis with
a metric incomparable with well-known ones may en-
gender the degradation of security. We thus revisit the
security of the fastest ORAM.
114
Hidano, S., Nakano, Y. and Kiyomoto, S.
An Evaluation Framework for Fastest Oblivious RAM.
DOI: 10.5220/0006690701140122
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Internet of Things, Big Data and Security (IoTBDS 2018), pages 114-122
ISBN: 978-989-758-296-7
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

1.1 Our Contribution
In this paper, we propose a framework for evaluating
the fastest ORAM. The contributions of this work are
the following:
• We formulate a new security definition based on
the average min-entropy for ORAM constructions
involving information leakage, which is called l-
leakage access pattern hiding. This definition is
one of the metrics to capture security in the worst
case scenario, and comparable with the traditional
security definition for ORAM, namely, perfect ac-
cess pattern hiding. This definition allows us to
configure the security level by properly evaluat-
ing the amount of the leakage, which means that
we can optimize some system specific-parameters
used in the fastest ORAM according to security
requirements.
• We introduce a practical way to evaluate the
amount of information leakage in the fastest
ORAM. In order to calculate the amount of the
leakage, it is usually required to estimate the
probability distribution of memory access pat-
terns. However, the means to the estimation is
not known in both cases: theoretical and experi-
mental settings. We thus provide an upper bound
of amount of the leakage on the basis of the col-
lision entropy, and give an experimental way to
estimate the amount of the leakage from the prob-
ability distribution of distance between two access
patterns.
• We applied the fastest ORAM to a program of
AES, and evaluated the average min-entropy and
the amount of information leakage. From the re-
sults, we confirm that given a security requirement
l, the fastest ORAM can achieve l-leakage access
pattern hiding by optimizing its specific parame-
ters.
1.2 Paper Organization
The rest of the paper is organized as follows: Sec-
tion 2 overviews early studies on Oblivious RAM
(ORAM). Section 3 gives some definitions on ORAM
and its security, as well as the definitions of some
entropic metrics. Section 4 formulates a new secu-
rity definition based on the average min-entropy and
gives an upper bound related to the new definition.
Section 5 proposes a framework for evaluating the se-
curity of the fastest ORAM. Section 7 concludes this
paper.
2 RELATED WORK
Oblivious RAM (ORAM) is a security probable ap-
proach for memory access pattern hiding. The main
ORAM construction consists of two algorithms: an
initialization algorithm and an execution algorithm.
The initialization algorithm takes data blocks as in-
put and initializes the oblivious structure in a mem-
ory containing the data blocks. The execution algo-
rithm compiles each logical access into the virtual ac-
cess(es). In some ORAM constructions, the initializa-
tion algorithm is executed repeatedly at certain inter-
val to ensure the security.
The first construction of ORMA has been pro-
posed by Godreich (Goldreich, 1987), and then ex-
tended by Goldreich and Ostrovsky (Goldreich and
Ostrovsky, 2007). They introduced the following
two ORAM constructions: Square-Root ORAM, and
Hierarchical ORAM. The Square-Root ORAM pro-
vides the computational overhead of a square root
every access, and the Hierarchical ORAM has poly-
logarithmic computational complexity. Recently, nu-
merous constructions have been proposed to reduce
the overheads (Pinkas and Reinman, 2010; Goodrich
and Mitzenmacher, 2011; Goodrich et al., 2011; Shi
et al., 2011; Stefanov et al., 2011; Kushilevitz et al.,
2012; Williams and Sion, 2012; Stefanov and Shi,
2013; Stefanov et al., 2013). In particular, a series
of ORAM constructions, beginning with the construc-
tion of Shi et al. (Shi et al., 2011), adopted binary
trees as the underlying structure of a memory. Such
Tree-based ORAMs are more efficient than the hier-
archical approach, they still have logarithmic compu-
tational complexity (Stefanov et al., 2013). The high
computational overhead is caused by repeated shuf-
fling processes.
Meanwhile, Nakano et al. have proposed an
ORAM construction where the shuffling process is
not executed repeatedly. Instead, a client is required
to access a memory on a server twice every access.
The construction of Nakano et al. has the computa-
tional overhead of only two times. While the over-
heads are dramatically improved, the security has not
been analyzed sufficiently. Nakano et al. focused
on the repeated accesses to the same data block and
provided a security definition for their construction,
which is called δ-security. However, they did not
mention the relation between δ-security and the def-
inition for security probable ORAM constructions,
which means that we cannot compare the security
level between different constructions. We thus revisit
the security of the construction proposed by Nakano
et al., and propose a framework for evaluating the se-
curity.
An Evaluation Framework for Fastest Oblivious RAM
115

3 PRELIMINARIES
In this section, we give some definitions on oblivious
RAM (ORAM) and its security as well as the defini-
tions of some entropic metrics.
Memory Access Pattern. We consider a client-
server model as a target one (e.g. in terms of com-
puter architecture, a CPU is a client, and a data mem-
ory is a server storage). A server has a memory
M = {m
1
,... ,m
N
} consisting of N data blocks for
managing a data array of a client. Given a program
R , a client accesses the memory M on the server
according to R . Each access is denoted by 3-tuple
(op,m
i
,v). op is one of the following two operations:
read or write. When op = read, v is denoted by ⊥,
and the client accesses the data block m
i
∈ M to get
the value stored in it. Otherwise, the client accesses
the data block m
i
to store the value v in it. Let c
m
i
be the address of a data block m
i
∈ M on the server.
When a client has an access (op,m
i
,v), a server ob-
serves a = (op,c
m
i
,v). If a client accesses a memory
M on a server n times, the access pattern is defined by
a sequences of n accesses, a = (a
1
,. .. ,a
n
) ∈ A
n
. For
the sake of simplicity, we below consider an access as
a = c
m
i
.
Oblivious RAM. An oblivious RAM (ORAM) con-
struction ORAM is a tuple of the following two algo-
rithms:
Init: Given a memory M , this algorithm initializes
the structure of the memory while shuffling data
blocks in M . After the initialization process is
completed, the memory M is used by the algo-
rithm Exec. In some ORAM constructions, the
algorithm Init is executed every T executions of
the algorithm Exec for ensuring security.
Exec: Let a = (a
1
,. .. ,a
n
) ∈ A
n
be an access pat-
tern that a program R outputs. In order to hide
the access pattern a from a server, this algo-
rithm compiles a into another access patten b =
(b
1
,. .. ,b
q
) ∈ B
q
, where B is the same set as A
and q ≥ n. We below refer to a and b as a private
access pattern and an observable access pattern,
respectively.
ORAM Security. The security of ORAM construc-
tions is generally defined as follows:
Definition 3.1 (Perfect access pattern hiding
(Goodrich et al., 2012)). Let a = (a
1
,. .. ,a
n
) ∈ A
n
and a
0
= (a
0
1
,. .. ,a
0
n
) ∈ A
n
be private access patterns.
Let b = (b
1
,. .. ,b
q
) ∈ B
q
and b
0
= (b
0
1
,. .. ,b
0
q
) ∈ B
q
be observable access patterns of the private access
patterns a and a
0
, respectively. An ORAM construc-
tion ORAM = (Init,Exec) is perfect access pattern
hiding if the observable access patterns b and b
0
are
computationally indistinguishable for anyone but the
client.
While most of existing ORAM constructions were
built with the objective of achieving perfect access
pattern hiding, the fastest ORAM construction pro-
posed by Nakano et al. (Nakano et al., 2012) was
aimed at dramatically improving the computational
overheads instead of allowing information leakage. In
the case of constructions involving information leak-
age, the amount of the leakage is required to be prop-
erly evaluated for achieving security requirements.
Nakano et al. thus gave a different security definition
for such ORAM constructions as follows:
Definition 3.2 (δ-length security). Assume that a data
block m
i
∈ M is accessed twice at i-th access and
(i + δ)-th access by a program R , which is called
a δ-distance access of m
i
. An ORAM construction
ORAM is δ-length ε-secure if the probability that an
adversary identifies any d-distance access in a private
access pattern a = (a
1
,. .. ,a
n
) is at most ε for every
d ≤ δ.
The above security definition was introduced in
terms that one of the main challenges of ORAM was
to hide repeated accesses to the same data block.
Renyi Entropy. Let X be a random variable on a
set X of possible values. The Renyi entropy (Renyi,
1960) of X for a real number α ≥ 0 is defined as fol-
lows:
H
α
(X) =
1
1 − α
log
∑
x∈X
Pr[X = x]
α
. (1)
In particular, we refer to the Renyie entropy for α = 2
and the one for α = ∞ as collision entropy and min-
entropy, respectively. Note that the base of the loga-
rithm is 2 throughout this paper.
Conditional Renyi Entropy. While there are dif-
ferent types of formalization of conditional Renyi en-
tropy, we follow the definition introduced by Fehr et
al. (Fehr and Berens, 2014). Let X and Y be random
variables on different sets X and Y of possible val-
ues, respectively. The conditional Renyi entropy of X
given Y for a real number α ≥ 0 is defined as follows:
˜
H
α
(X|Y ) = −log
E
y∈Y
R
α
(X|Y = y)
α−1
α
α
α−1
, (2)
where
R
α
(X|Y = y) =
∑
x∈X
Pr[X = x|Y = y]
α
!
1
α−1
. (3)
IoTBDS 2018 - 3rd International Conference on Internet of Things, Big Data and Security
116

In the case of this formalization, the following
chain rule holds for all α ≥ 0:
˜
H
α
(X|Y ) = H
∞
(X,Y ) − H
0
(Y ). (4)
The average min-entropy (Dodis et al., 2008) of X
given Y is the conditional Renyi entropy for α = ∞,
which can be written as follows:
˜
H
∞
(X|Y ) = −log E
y∈Y
max
x∈X
Pr[X = x|Y = y]. (5)
4 NEW SECURITY DEFINITION
We here revisit the security of ORAM constructions
involving information leakage. The security level
of such ORAM constructions is adjustable by some
system-specific parameters. However, if these pa-
rameters are configured on the basis of δ-security,
the ORAM construction may not fully satisfy with
the other security requirements. This is because δ-
security captures the resistance to a particular attack
(which is not the worst case scenario), and the relation
between δ-security and the other security definitions
is also not obvious. Thus we formulate a new security
definition which can capture the worst-case security.
The average min-entropy, formulated by Dodis et
al. (Dodis et al., 2008), is one of practical measures
corresponding to the difficulty of guessing or predict-
ing a secret in the worst case scenario. We define l-
leakage security based on the average min-entropy for
ORAM constructions involving information leakage
as follows:
Definition 4.1 (l-leakage access pattern hiding). Sup-
pose that a memory M consists of N data blocks. Let
A
n
and B
q
be sets of possible values of a private ac-
cess pattern a and an observable access pattern b,
respectively. Given random variables A and B, on
the sets A
n
and B
q
, respectively, an ORAM construc-
tion ORAM is l-leakage access pattern hiding if the
average min-entropy
˜
H
∞
(A|B) ≥ −log
1
N
n
− l.
When an ORAM construction is perfect access
pattern hiding, the average min-entropy is
˜
H
∞
(A|B) =
−log
1
N
n
. Namely, we can configure the security level
in the worst case by properly evaluating the amount
of the leakage l.
We also introduce the following lemma regarding
the average min-entropy, which allow us to easily cal-
culate the amount of information leakage (see Sec-
tion 5 for details):
Lemma 4.1. Given random variables A and B, on
sets A
n
and B
q
of private access patterns and observ-
able access patterns, respectively, we have the follow-
ing lower bound of the average min entropy
˜
H
∞
(A|B):
˜
H
∞
(A|B) ≥
1
2
log
1
N
q
+ H
2
(A,B)
. (6)
Proof. Since max
a∈A
n
Pr[A = a|B = b] ≤
p
∑
a∈A
n
Pr[A = a|B = b]
2
is obvious for any
b ∈ B
q
, 2
˜
H
∞
(A|B) ≥
˜
H
2
(A|B) holds. From
this inequality and the cain rule of Equation (4),
we have
˜
H
∞
(A|B) ≥
1
2
(H
2
(A,B) − H
0
(B)).
H
0
(B) = −log
1
|B
q
|
= − log
1
N
q
, and hence we
obtain Equation (6).
From Definition 4.1 and Lemma 4.1, we obtain the
following theorem:
Theorem 4.1. Given a real number l ≥ 0 as a security
parameter, when the following inequality holds, an
ORAM construction ORAM is l-leakage access pat-
tern hiding:
l ≤ −log
1
N
n
−
1
2
log
1
N
q
−
1
2
H
2
(A,B). (7)
5 EVALUATION FRAMEWORK
We propose a framework to evaluate security of the
fastest ORAM (Nakano et al., 2012). In this sec-
tion, we describe the concrete algorithm of the fastest
ORAM, and then introduce a practical way to esti-
mate the amount of information leakage in it from
the probability distribution of distance between two
memory access patterns.
5.1 Algorithms of Fastest ORAM
In the fastest ORAM, the Init algorithm is executed
once before the Exec algorithm. These algorithms are
given as follows:
Init: On loading data blocks to a memory M ,
the corresponding addresses are permuted. Then
dummy data blocks are added. A total of N data
blocks are loaded to the memory. This process
partitions the memory M into the following two
regions: a secure buffer S and an unsecured mem-
ory U, consisting of N
S
data blocks and N
u
data
blocks, respectively, which means N = N
S
+ N
U
.
The secure buffer S is implemented within client’s
trusted boundary, and the unsecured memory U is
kept in a server. In addition, a history table H
of size N
H
is required to store addresses of data
blocks that has been moved from the secure buffer
S to the unsecured memory U. The history table
is implemented as part of the secure buffer S.
Exec: The access to a data block m ∈ M is proceeded
as follows:
1. If m is in S, two random elements (not m) from
S are replaced with a random element from U
An Evaluation Framework for Fastest Oblivious RAM
117

and a random element from U which had al-
ready been accessed before (as recorded in the
history table H ).
2. If m is not in S and its address c
m
is in H , two
random elements from S are replaced with a
random element from U and m.
3. If m is not in S, and its address c
m
is not in
H , two random elements from S are replaces
with m and a random element from U which
had already been accessed before (as recorded
in the history table H ).
If the history table H gets full, N
H
elements are
selected at random among N
H
+2 elements to up-
date H . After the above processes, m is accessed.
Algorithm 1 is the concrete algorithm of Exec.
Algorithm 1: The Exec algorithm of the fastest ORAM.
Scan S for m.
if m ∈ S then
Replace two random elements (not m) in S with
two random elements in U, one of them is
chosen from H and the other is chosen from U.
else
Scan H for c
m
.
if c
m
∈ H then
Replace two random elements in S with a
random element in U and m.
else
Replace two random elements in S with m
and a random element whose address is
registered in H .
end if
end if
Choose N
H
elements from N
H
+ 2 to update H .
Access m.
Security. Suppose that a client accesses m ∈ M at t-
th access. After δ accesses, we have P
S
= Pr[m ∈ S] ≥
(
N
S
−2
N
S
)
δ
and P
H
= Pr[c
m
∈ H ] ≥ (
N
H
N
H
+2
)
δ
. Nakano et
al. introduced the following theorem:
Theorem 5.1. The fastest ORAM construction is δ-
length ε-secure, where
ε ≤
P
S
(N
S
− 2)
2
+
(1 − P
S
)P
H
(N
S
− 2)
2
+
(1 − P
S
)(1 − P
H
)
2(N
S
− 2)
. (8)
Although Theorem 5.1 shows the probability of
the adversary detecting the repeated accesses to the
same block, the amount of infomation leakage is not
clear. In the following, we propose a method to eval-
uate the leakage.
5.2 How to Evaluate l-Leakage
We here provide a practical way to estimate the aver-
age min-entropy
˜
H
∞
(A|B) for the fastest ORAM by
using Equation (6) in Lemma 4.1. The number of
possible values of observable access patterns, N
q
, can
be calculated as N
2n
because the Exec algorithm of
the fastest ORAM accesses the unsecured memory U
twice every private access. To calculate the collision
entropy H
2
(A,B), the marginal probability distribu-
tion of A and B, p
A,B
, is required, yet it is not known
to estimate p
A,B
theoretically or experimentally for
the fastest ORAM. For the theoretical estimation, ex-
tremely complex calculation of probabilities would be
involved. The experimental estimation is not also an
easy means because a vast number of samples of ac-
cess patterns must be collected. We thus consider esti-
mating H
2
(A,B) without the marginal probability dis-
tribution p
A,B
.
Hidano et al. have proposed a way to estimate the
collision entropy H
2
(X) of a random variable X on
a set X experimentally by using the probability dis-
tribution p
D
of distance d between two elements in
the set X (Hidano et al., 2010; Hidano et al., 2012).
Specifically, the H
2
(X) is given as −log p
D
(0). In ad-
dition, the distance distribution p
D
can be estimated
experimentally with fewer samples of the distance d
as compared to the probability distribution of X, de-
noted as p
X
, because the number of possible values of
the distance is typically far fewer than that of X.
Suppose that the fastest ORAM is applied to a pro-
gram R . By using the property introduced by Hidano
et al., H
2
(A,B) can be estimated by the following pro-
cedure:
1. Execute the program R k times (k N
2n
),
and obtain the set of observable access pat-
terns DB
B
= {
ˆ
b
1
,. .. ,
ˆ
b
k
}, in which each pattern
corresponds with any of private access patterns
{
ˆ
a
1
,. .. ,
ˆ
a
k
} that the program R outputs.
2. Calculate their distance
ˆ
d = (
ˆ
b,
ˆ
b
0
) for any two
samples of observable access patterns
ˆ
b,
ˆ
b
0
∈
DB
B
, and have a set DB
D
= {
ˆ
d
1
,. .. ,
ˆ
d
k(k−1)
2
} of
samples of the distance.
3. Estimate the probability distribution p
D
of the dis-
tance d from the samples DB
D
(See Section 5.3
for the details).
4. Calculate the probability p
D
(0), and have
H
2
(A,B) = −log
∑
a∈A
n
,b∈B
q
Pr[B = b|A =
a]
2
Pr[A = a]
2
= −log
1
N
2n
− log p
D
(0) (assuming
that Pr[A = a] =
1
N
n
for all a ∈ A
n
).
From the above results, an lower bound of the av-
IoTBDS 2018 - 3rd International Conference on Internet of Things, Big Data and Security
118

erage min-entropy
˜
H
∞
(A|B) is given as:
˜
H
low
∞
(A|B) = −
1
2
log p
D
(0). (9)
Then, an upper bound of amount of information
leakage in the fastest ORAM is given as:
l
up
= −log
1
N
n
+
1
2
log p
D
(0). (10)
Given a real number l ≥ 0 as a security parameter,
if l ≤ l
up
, we say from Theorem 4.1 that the fastest
ORAM is l-leakage access pattern hiding.
5.3 Estimating Distance Distribution
Let us consider the definition of distance between two
memory access patterns and a way to estimate its
probability distribution. Edit metrics can be consid-
ered to be suitable for the distance. The distance d
between two observable access patterns b and b
0
is
defined as the smallest number of character insertions
and deletions needed for the transformation of b into
b
0
. Specifically, we utilize the hamming distance as
an edit distance, because the length of any access pat-
tern is the same. Given two observable access patterns
b = (b
1
,. .. ,b
i
,. .. ,b
2n
) and b
0
= (b
0
1
,. .. ,b
0
i
,. .. ,b
0
2n
)
of length 2n, the Hamming distance between b and b
0
can be written as follows:
d(b, b
0
) =
∑
i
I(b
i
,b
0
i
)
2n
, (11)
where I is an indicator function that takes value 1
when b
i
6= b
0
i
and value 0 otherwise. We give the fol-
lowing two ways to estimate the distance distribution
of the Hamming distance experimentally: parametric
approach and non-parametric approach.
Parametric Approach. Assuming that the proba-
bility that b
i
and b
0
i
are identical can be represented
by θ for any index i, the probability distribution of the
Hamming distance d can be written as the following
binomial distribution Bi(θ, ˆq):
p
D
(d) =
ˆq!
( ˆqd)!( ˆq!(1 − d))!
θ
ˆq(1−d)
(1 − θ)
ˆqd
, (12)
where ˆq is the number of meaningful accesses. If
there is some correlation between accesses, ˆq may be
reduced from 2n. θ and ˆq can be calculated by esti-
mating the values of expectation and variance of the
Hamming distance d from its samples DB
D
. The ex-
pectation and the variance of the binomial distribution
Bi(θ, ˆq) can be represented by 1 − θ and
θ(1−θ)
ˆq
, re-
spectively. Once the values of θ and ˆq are given, the
collision entropy can be easily calculated parametri-
cally as H
2
(B|A) = −log θ
ˆq
. However, in some cases,
the probability that b
i
and b
0
i
are identical is different
for some index i. In this case, the distance distribu-
tion p
D
cannot be modeled as the Binomial distribu-
tion of Equation (12), and there does not exist other
suitable parametric approach. Thus, if the probabil-
ity that b
i
and b
0
i
are identical, the probability cannot
be represented by the same parameter θ, the follow-
ing non-parametric approach should be applied to the
estimation.
Non-parametric Approach. Since the probability
distribution of the Hamming distance is discrete, it is
required to utilize a non-parametric estimator with a
discrete kernel function. We thus adopt an estimator
with a discrete triangular kernel proposed by Koko-
nendji et al. (Kokonendji et al., 2007). Given a data
set DB
D
= {
ˆ
d
1
,. .. ,
ˆ
d
i
,. .. ,
ˆ
d
k(k−1)
2
} of samples of the
Hamming distance of Equation (11), the probability
distribution can be estimated as:
p
D
(d) =
1
q
k(k−1)/2
∑
i=1
K
α,β,d
(
ˆ
d
i
), (13)
where q = 2n is the length of an observable access
pattern. K
α,β,d
is a discrete triangular kernel of the
order α with the arm β, which is defined as follows:
K
α,β,d
(
ˆ
d
i
) =
(
(β+1)
α
−|q(
ˆ
d
i
−d)|
α
P(α,β)
(d ∈ D
β,d
i
)
0 (otherwise)
, (14)
where P(α,β) = (2β + 1)(β + 1)
α
− 2
∑
β
j=0
j
α
, and
D
β,d
i
= [
ˆ
d
i
−
β
q
,
ˆ
d
i
+
β
q
]. Hence, p
D
(0) can be esti-
mated as:
p
D
(0) =
1
q
β
∑
i=0
w
i
[(β + 1)
α
− i
α
]
P(α,β)
, (15)
where w
i
is the number of samples of the distance
whose value is
i
q
. See (Kokonendji et al., 2007) for
optimizing the parameters α and β. However, non-
parametric approach requires more samples as com-
pared parametric one. Thus the parametric estimation
based on the Binomial distribution should be utilized
in preference to this non-parametric approach if ap-
plicable.
6 EXPERIMENTAL EVALUATION
We applied the fastest ORAM to a program of
AES, and evaluated the average min-entropy and the
amount of information leakage by using the experi-
mental evaluation method provided in Section 5.2.
An Evaluation Framework for Fastest Oblivious RAM
119
6.1 Setup
In the experiments, we used an unsecured mem-
ory with N
U
= 1424 data blocks. We also used
seven kinds of secure buffers of different sizes N
S
=
8,16, 32,64, 128,256, 512. The half of data blocks
in each secure buffer were used for a history ta-
ble, i.e. the sizes of the history tables were N
H
=
4,8, 16,32, 64,128, 256. Under the above conditions,
we applied the fastest ORAMs to a program of AES
with a 128-bit key, which accesses the memory 3,344
times. Namely, the lengths of the private access pat-
tern and the observable access patterns were n = 3344
and q = 6688, respectively. The following experi-
ments were conducted for each secure buffer, which
means we obtained seven kinds of results.
We, first of all, executed the AES program 1,500
times to have samples of observable access patterns.
Then, we calculated the Hamming distance of Equa-
tion (11) for any pair of samples of observable access
patterns, and obtained 1,124,250 samples of the Ham-
ming distance. For estimation of the probability dis-
tribution of the Hamming distance, we adopted both
of our parametric approach and non-parametric ap-
proach provided as Section 5.3. However, we adopted
only the parametric approach for the calculation of the
collision entropy (See Section 6.2 for the reason). Fi-
nally, we evaluated the average min-entropy and the
amount of information leakage by using Equations (9)
and (10), respectively.
6.2 Evaluation Results
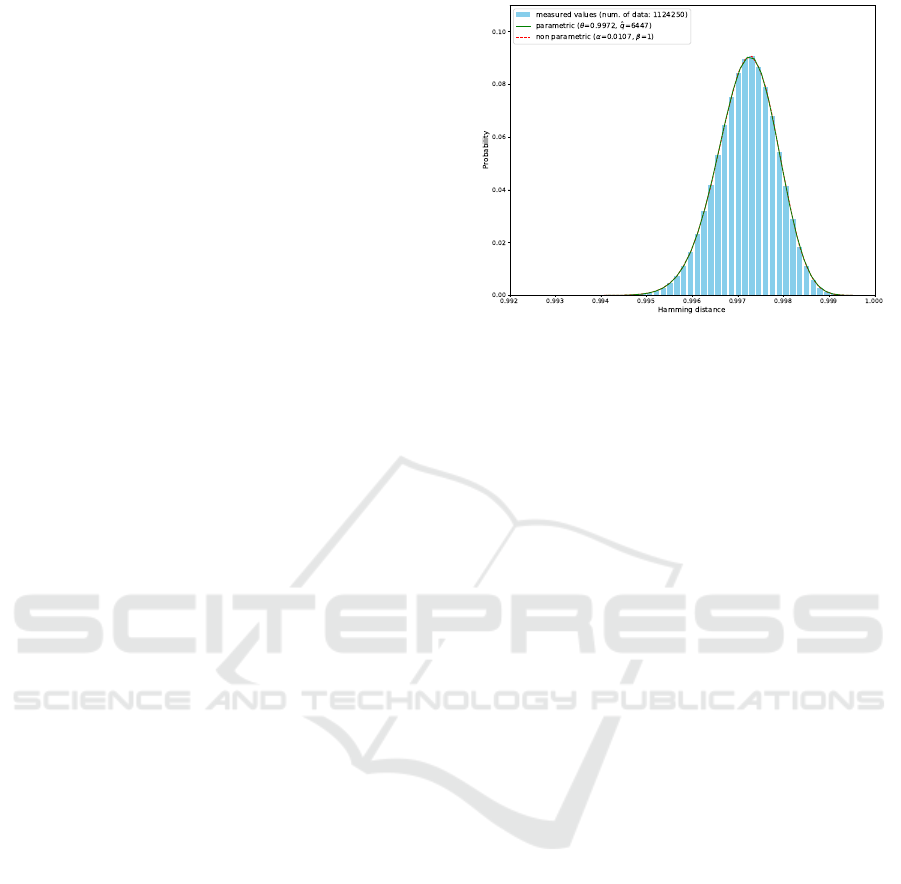
Distance Distribution. Figure 1 shows an example
of measured and estimated distributions of the Ham-
ming distance between observable access patterns.
These distributions are for the fastest ORAM with a
secure buffer of the size N
S
= 32. Both of paramet-
rically and non-parametrically estimated distributions
well-fitted the measured values. However, we adopted
only the parametric approach for evaluating the aver-
age min-entropy and the amount of information leak-
age, as mentioned in Section 6.1. This is because the
sample taking value zero or 1/6688 was not observed.
Since the optimized value of the parameter arm for
our non-parametric approach was β = 1, such samples
were needed for calculating the collision entropy by
using Equation (15). For the fastest ORAMs with se-
cure buffers of different sizes, the same property was
observed. Therefore, in addition to the collision en-
tropy, all the results shown in Section 6.2 were calcu-
lated from parametrically estimated distributions.
Figure 1: The distribution of the Hamming distance be-
tween observable access patterns, for the fastest ORAM
with a secure buffer of the size N
S
= 32. The horizon-
tal axis represents a value of the Hamming distance while
the vertical axis indicates the probability that the value is
taken. The histogram was made from samples of the Ham-
ming distance. The solid line is the distribution estimated
by our parametric approach. Parameters of the binomial dis-
tribution Bi(θ, ˆq) were given as p = 0.9972 and ˆq = 6447.
The dashed line is the distribution estimated by our non-
parametric approach. The optimized values of the order and
the arm of the discrete triangular kernel were α = 0.0107
and β = 1.
Average Min-entropy and Amount of Information
Leakage. Table 1 shows evaluation results on the
average min-entropy and the amount of information
leakage for the fastest ORAMs with secured buffers
of different sizes. We see from the results that there
is the possibility the fastest ORAM involves large
amount of information leakage, depending on the
sizes of the secure buffer and the history table. On the
other hand, the information leakage was improved by
increasing these sizes. We thus say that by optimizing
these sizes on the basis of a required security level,
i.e. the leakage l to be allowed, the fastest ORAM
can achieve l-leakage access pattern hiding.
In the case where the fastest ORAM is introduced
to IoT devices, as mentioned in Section 1, since such
devises do not usually have CPUs with large amount
of storage, if a secure buffer of larger size is needed
for ensuring security, the size is required to be de-
termined at the design stage of the device. Thus,
for such IoT devices that the long-term operation is
expected, the CPU storage with an enough margin
should be equipped in preparation of coming secu-
rity risks, which allows us to re-configure the security
level of the fastest ORAM.
IoTBDS 2018 - 3rd International Conference on Internet of Things, Big Data and Security
120

Table 1: The evaluation results on the average min-entropy and the amount of information leakage for the fastest ORAMs
with secure buffers of different sizes N
S
= 8, 16,32,64,128,256, 512.
Size of secure buffer 8 16 32 64 128 256 512
Average min-entropy 24564 25032 26391 27319 27981 28224 28246
Amount of information leakage 10467 9998.5 8639.5 7712.1 7049.6 6806.6 6784.6
7 CONCLUSION
We proposed an evaluation framework for the fastest
Oblivious RAM (ORAM) . While the computational
overhead is dramatically improved by avoiding re-
peated shuffles of data blocks in a memory, the secu-
rity of the fastest ORAM has not been analyzed suffi-
ciently. We thus formulated a new security definition
for ORAM constructions involving information leak-
age on the basis of the average min-entropy, namely,
l-leakage access pattern hiding. We also provided a
lower bound using the collision entropy for the av-
erage min-entropy. Then, for the fastest ORAM we
introduced a practical way to evaluate the amount of
information leakage from the probability distribution
of distance between memory access patterns. Finally,
we applied the fastest ORAM to a program of AES,
and evaluated the actual amount of information leak-
age in the fastest ORAM. As a result, we confirmed
that by optimizing the size of a secure buffer used for
the fastest ORAM, it can achieve l-leakage access pat-
tern hiding for a required security level l. In the fu-
ture, we will evaluate the amount of the leakage when
the fastest ORAM is applied to other types of pro-
grams for validating the usefulness of our proposed
framework.
REFERENCES
Dodis, Y., Ostrovsky, R., Reyzin, L., and Smith, A. (2008).
Fuzzy extractors: How to generate strong keys from
biometrics and other noisy data. SIAM Journal of
Computing, 38(1):97–139.
Fehr, S. and Berens, S. (2014). On the conditional r
´
enyi
entropy. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory,
60(11):6801–6810.
Goldreich, O. (1987). Towards a theory of software protec-
tion and simulation by oblivious rams. In Proceedings
of the 19th annual ACM symposium on Theory of com-
puting (STOC 1987), pages 182–194.
Goldreich, O. and Ostrovsky, R. (2007). Software protec-
tion and simulation on oblivious rams. Journal of the
ACM (JACM), 19(6–8):241–254.
Goodrich, M. T. and Mitzenmacher, M. (2011). Privacy-
preserving access of outsourced data via oblivious ram
simulation. In Proceedings of the 38th International
Colloquium on Automata, Languages and Program-
ming (ICALP 2011), pages 576–587.
Goodrich, M. T., Mitzenmacher, M., Ohrimenko, O., and
Tamassia, R. (2011). Oblivious ram simulation with
efficient worstcase access overhead. In Proceedings
of the 3rd ACM Cloud Computing Security Workshop
(CCSW 2011), pages 95–100.
Goodrich, M. T., Mitzenmacher, M., Ohrimenko, O., and
Tamassia, R. (2012). Practical oblivious storage. In
Proceedings of the second ACM conference on Data
and Application Security and Privacy (CODASPY
2012), pages 13–24.
Hidano, S., Ohki, T., Komatsu, N., and i, K. T. (2010).
A metric of identification performance of biomet-
rics based on information content. In Proceedings
of the 11th International Conference on Control, Au-
tomation, Robotics and Vision (ICARCV 2010), pages
1274–1279.
Hidano, S., Ohki, T., and Takahashi, K. (2012). Evaluation
of security for biometric guessing attacks in biomet-
ric cryptosystem using fuzzy commitment scheme.
In Proceedings of 2012 International Conference of
the Biometrics Special Interest Group (BIOSIG 2012),
pages 1–6.
Kokonendji, C. C., Kiesse, T. S., and Zocchi, S. S. (2007).
Discrete triangular distributions and non-parametric
estimation for probability mass function. Journal of
Nonparametric Statistics, 43(3):431–473.
Kushilevitz, E., Lu, S., and Ostrovsky, R. (2012). On the
(in)security of hash-based oblivious ram and a new
balancing scheme. In Proceedings of the 23rd ACM-
SIAM Symposium on Discrete Algorithms (SODA
2012), pages 143–156.
Nakano, Y., Cid, C., Kiyomoto, S., and Miyake, Y.
(2012). Memory access pattern protection for
resource-constrained devices. In Proceedings of the
11th international conference on Smart Card Re-
search and Advanced Applications (CARDIS 2012),
pages 188–202.
Pinkas, B. and Reinman, T. (2010). Oblivious ram revis-
ited. In Proceedings of the 30th Annual Cryptology
Conference (CRYPTO 2010), pages 512–519.
Renyi, A. (1960). On measures of entropy and informa-
tion. In Proceedings of the 4th Berkeley Symposium on
Mathematical Statistics and Probability, pages 547–
561.
Shi, E., Chan, T. H., Stefanov, E., and Li, M. (2011). Obliv-
ious ram with o((logn)
3
) worst-case cost. In Proceed-
ings the 17th International Conference on the Theory
and Application of Cryptology and Information Secu-
rity (ASIACRYPT 2011), pages 197–214.
An Evaluation Framework for Fastest Oblivious RAM
121

Stefanov, E., Dijk, M. V., Shi, E., Fletcher, C., Ren, L., Yu,
X., and Devadas, S. (2013). Path oram: an extremely
simple oblivious ram protocol. In Proceedings of the
20th ACM Conference on Computer and Communica-
tions Security (CCS 2013), pages 299–310.
Stefanov, E. and Shi, E. (2013). Oblivistore: high per-
formance oblivious cloud storage. In Proceedings of
2013 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP
2013), pages 253–267.
Stefanov, E., Shi, E., and Song, D. (2011). Towards
practical oblivious ram. In Proceedings of the 19th
Network & Distributed System Security Symposium
(NDSS 2012), pages 1–40.
Williams, P. and Sion, R. (2012). Single round access pri-
vacy on outsourced storage. In Proceedings of the
19th ACM Conference on Computer and Communi-
cations Security (CCS 2012), pages 293–304.
IoTBDS 2018 - 3rd International Conference on Internet of Things, Big Data and Security
122
