
Temporal Evolution of Vehicular Network Simulators: Challenges and
Perspectives
Mauricio J. Silva
1
, Genilson I. Silva
2
, Fernando A. Teixeira
3
and Ricardo A. Oliveira
1
1
Universidade Federal de Ouro Preto, Ouro Preto, MG, Brazil
2
Instituto Federal Sudeste Minas Gerais, Barbacena, MG, Brazil
3
Universidade Federal de Sao Joao Del Rei, Sao Joao Del Rei, MG, Brazil
Keywords:
Vehicular Network Simulators, Traffic Simulators, Mobility Models.
Abstract:
New proposals of applications and protocols for vehicular networks appear every day. Its crucial to evaluate,
test and validate these proposals on a large scale before deploying them in the real world. Simulation is by
far the preferred method by the community when conducting the evaluation. In this paper we survey the
main simulators for vehicular networks and show how they evolved over time. Thus, we provide information
that leads to an understanding of how, and how long does it take for the scientific community to absorb a new
simulator proposal. Additionally, valuable insights are presented to help researchers make better choices when
selecting the appropriate simulator to evaluate new proposals.
1 INTRODUCTION
Communication-capable vehicles allowed the emer-
gence of collaborative Intelligent Transport Systems
(ITS). The ITS comprises services developed with the
aim to improve the road safety (e.g., warning about
road conditions), reduce traffic jams (e. g., intelligent
intersections) and make the travel more enjoyable
for drivers (e.g., informing about gas stations nearby,
roadside restaurants, among other things) (Fischer,
2015).
The design and evaluation of algorithms and pro-
tocols for ITS have been a constant topic of re-
search (Tornell et al., 2015). Given the unique char-
acteristics of vehicular networks, recent works have
pointed towards the emergence of new traffic models
and the impact analysis of these models on the behav-
ior of proposed protocols and algorithms (Arellano
and Mahgoub, 2013; Zemouri et al., 2012). These
models must be fed by data collected in current net-
works so that it is possible to make a reasonably accu-
rate estimate of the performance of new applications.
Such an assessment is a challenge, and can usually be
done using three different methods, which are Math-
ematical Analysis, Field Operational Tests and Sim-
ulations (Guan et al., 2014; Nimje and Dorle, 2013).
Each of these methods has its advantages and disad-
vantages (summarized on Table 1), and the method to
be used should be chosen cautiously as it directly in-
fluences the results (Harri et al., 2009; Eckhoff and
Sommer, 2015).
Mathematical analysis allows an analytical study
of the problem, and can provide valuable information,
allowing a better understanding of the designed sys-
tem. Statistical distributions are used to generate the
models that are necessary for the simulation. How-
ever, this method tends to simplify certain simulation
parameters such as the mobility models. Such simpli-
fications can lead to inaccurate results.
Field Operational Tests allow a better evaluation
of applications and protocols for vehicular networks.
In this type of analysis, the devices are exposed to
real environments, which can lead to unpredicted sit-
uations. The disadvantages related to this type of test
usually involve high costs in terms of time and money
as well as the difficulty to perform large-scale tests.
Simulations make it possible to assess the new
proposals on a large scale and at low cost. However,
similarly to what happens in the mathematical analy-
sis, complex models need to be simplified so that they
can be simulated. Again, this simplification must be
done cautiously, as they may make the results inaccu-
rate.
Researchers prefer to evaluate their proposals
through the simulation method, which demands sim-
ulators that produce results increasingly closer to re-
ality (Harri et al., 2009). Researchers used to believe
Silva, M., Silva, G., Teixeira, F. and Oliveira, R.
Temporal Evolution of Vehicular Network Simulators: Challenges and Perspectives.
DOI: 10.5220/0006696900510060
In Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS 2018), pages 51-60
ISBN: 978-989-758-298-1
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
51
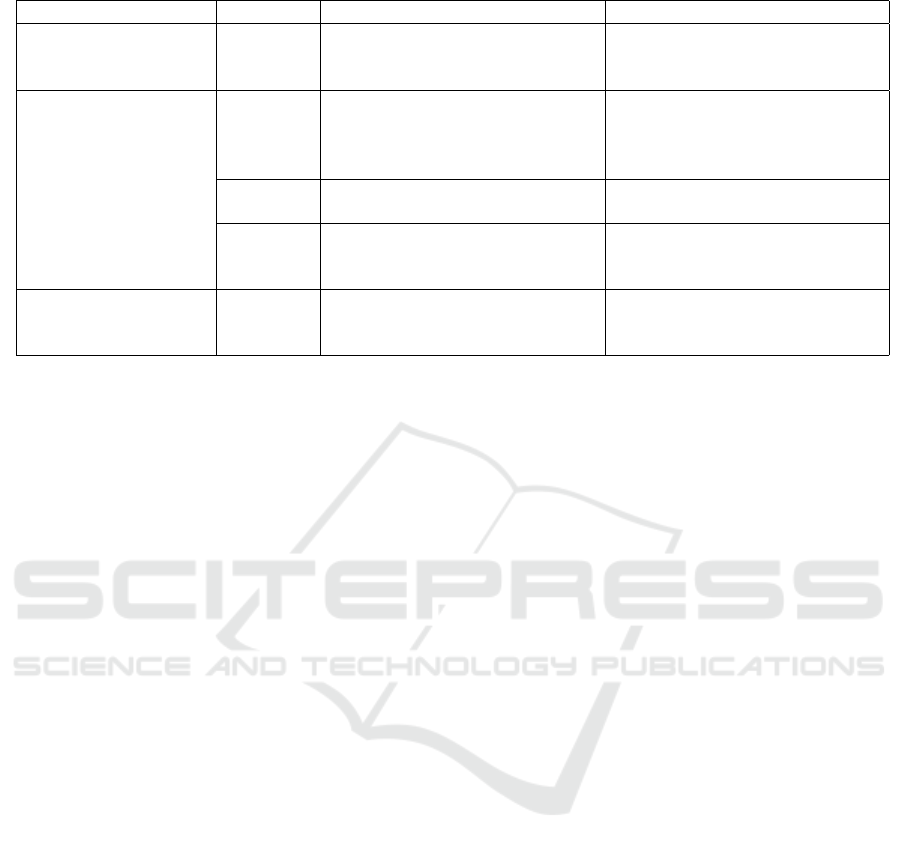
Table 1: A comparison of assessment methods for ITS applications.
Assessment method Category Advantages Drawbacks
Mathematical Analysis Valuable insights on overall be-
havior; Lower and upper bounds
of problem.
Undergo simplifications that com-
promise the results
Simulation
Offline Reproducible; Faster; Acceptable
degree of realism
Changes in one domain simula-
tor do not affect the other; nodes
mobility are immutable; scalabil-
ity by cloning
Embedded Reproducible; Reliable degree of
realism
Communication does not change
mobility and vice-versa.
Online Communication changes might
affect mobility and vice-versa;
Results more realistic; Scalable
Unreproducible; Hard to set and
parameterize;
FOTs Real scenario, generating real
data;
Not scalable; Few prototypes or
vehicles; High costs (time and
money)
that Vehicular Networks were a specific application of
Mobile Networks, and for that reason, random mod-
els have been applied to simulate the vehicles’ mobil-
ity. It was not long ago that they realized that vehic-
ular networks had their own characteristics, so spe-
cific mobility models should be proposed to represent
them. The vehicular mobility models evolved from
random models, where the mobility of all nodes was
generated in a single file that was used as input to
a network simulator (called offline), to the behavior-
based models, where network and traffic simulators
interact to represent the behavior of the driver (called
online).
Unfortunately, the more realistic a simulator is,
the harder it is to use it. Because of this, one of the
biggest difficulties in simulating a vehicular network
is to ensure that the mobility patterns of a real en-
vironment are reproduced. According to (Sommer
and Dressler, 2008) and (Marfia et al., 2007), existing
simulators that use models that are able to generate
scenarios closer to the real ones, are often complex
to use. As a result, many of the new proposed pro-
tocols and algorithms are evaluated using customized
simulators, which introduce bias and compromise the
reproducibility of these algorithms by other members
of the scientific community (Mota et al., 2014).
This article provides an overview of the vehicu-
lar network simulators evolution, answering the fol-
lowing questions: how did the evolution of vehicu-
lar network simulators happened from the beginning
until now? How long does the scientific community
need to absorb a new approach for a vehicular net-
work simulator? Do we have a pragmatic solution for
vehicular network simulators? In addition to answer-
ing these questions, we will provide valuable insights
to help researchers make better choices when select-
ing the appropriate simulator to evaluate new propos-
als.
The rest of this article is organized as follows:
Section 2 presents the necessary requirements to ob-
tain better results in specific-domain simulators. In
Section 3 we survey the most used simulators to as-
sess algorithms and protocols for vehicular networks,
describing their features and drawbacks. Section 4
discusses the temporal evolution and the future chal-
lenges related to vehicular simulations. Finally, we
conclude the paper in Section 5.
2 OVERVIEW OF
DOMAIN-SPECIFIC
SIMULATORS
Vehicular networks have drawn attention from the
academia, industry and government. The goal is not
only to develop applications that contribute to a safer
transport system, but also to propose new applications
based on high quality of service. Such applications
must be tested, evaluated and validated in a controlled
environment before being deployed in the real world.
Simulation is the preferred method by the aca-
demic community to evaluate new proposals for vehi-
cle networks, because it enables scalable evaluations,
with low cost and an acceptable degree of realism.
Scalability and low cost are well defined requirements
in a simulation. However, vehicular networks have
their own mobility requirements, and for a simulation
to have an acceptable degree of realism it is necessary
that the mobility models comply with such require-
ments. To resolve this issue, three approaches can be
used, which (Zemouri et al., 2012) called offline, em-
bedded and online (see Figure 1). We will use the
ICEIS 2018 - 20th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
52

same classification because we believe that in addi-
tion to being simple, it encompasses unambiguously
all existing proposals.
In the offline approach 1(a), trace files are ex-
tracted from the real movements of vehicles, which
are either obtained from navigation systems, or gen-
erated by a vehicular mobility simulator that has real
mobility capable models. This approach allows the
nodes in the network simulator to move in accordance
with the data read from the trace files. It is called of-
fline because the trace file is not modified after it has
been generated. This implies that there is no inter-
action between the mobility and network simulators.
Some simulators that are in this category are Bonn-
Motion (Aschenbruck et al., 2010), MOVE (Karnadi
et al., 2007) and VanetMobiSim (H
¨
arri et al., 2006).
In the embedded approach 1(b) the traffic and net-
work simulators are natively coupled to form a sin-
gle simulator. In fact, most of the platforms of this
category were either designed for traffic simulations
or for network simulations, not both. Some modules
that would allow such platforms to be used in vehic-
ular networks were later implemented, for instance,
VISSIM that has MOVE (Karnadi et al., 2007), the
NCTUns (Wang and Chou, 2009) and VCOM (Killat
et al., 2007) as embedded modules.
The online approach 1(c) was introduced to ad-
dress the limitations of the previous two approaches.
It provides a bidirectional communication between
network simulators (developed by computer scien-
tists) and traffic simulators (developed by traffic en-
gineers). Thus, vehicular mobility is handled by ex-
perts in traffic, and communication is handled by ex-
perts in computing. In the online approach the net-
work simulator controls the traffic simulator by send-
ing commands that modify the behavior of the nodes.
The traffic simulator responds to the network simula-
tor with the position of the affected node. This ap-
proach is considered, thus far, the best solution for
simulations in vehicular networks, for it allows a high
degree of realism.
Vehicular networks simulators face many chal-
lenges. Some of them are related to the communi-
cation, more specifically, physical layer, link layer,
and, in some cases, transport layer. The other chal-
lenges are related to the mobility, which is one of
the main factors that affect the assessment of proto-
cols and applications for vehicular networks. Com-
munication challenges are dealt with by the network
simulator, which must implement all models needed
to represent a real vehicle-to-vehicle communication.
Mobility challenges are dealt with by the mobility
simulator, which is responsible for all models needed
to represent a real vehicle mobility, including change
lane models, driver behavior models, traffic sign mod-
els, etc. In the following sections, we present the
main simulators used by the scientific community
in each specific-domain (network and mobility), and
also show how these simulators were combined to
achieve better results.
2.1 Network Simulators
Simulations based on discrete events have become the
main method used by simulators. In this type of sim-
ulator, simulation behavior is not based on continuous
equations, but rather in discrete events distributed in
time. The most used simulators for vehicle networks
are OMNeT ++, ns-2/ns-3, Jist/Swans, GloMoSim
and GTNetS. All of them are based on discrete events
and will be discussed in greater detail below.
OMNeT++ (Varga, 2010) is a discrete event
simulator that allows communication modeling in
networks, parallel systems and distributed systems.
Available since 1997 under the GPL, it has become
one of the most used simulators by the scientific com-
munity. The OMNeT++ was designed from the be-
ginning to support large-scale simulations. For this
reason, it was built completely modular, enabling bet-
ter reuse of code and facilitating the implementa-
tion of new libraries that extend its functionality. As
an example, we can mention the INET, which is an
open-source framework that has the models to simu-
late mobile, wired and wireless networks. The OM-
NeT++ modular feature, allows each model to be im-
plemented separately and then combined to form a
protocol stack similar to the real one. INET has mod-
els of the physical layer (PPP, Ethernet and 802.11),
various communication protocols (IPV4, IPV6, TCP,
SCTP, UDP) and various application models.
The ns-2 (ns2, 2017) simulator is one of the most
popular and it is widely used by the academic com-
munity. Its first version was launched in 1996, and
derived from its ns-1 predecessor. It includes detailed
models of a great number of TCP variations and many
applications (such as HTTP traffic). It also supports
wired and wireless networks modeling. In the wire-
less networks field, there are models for routing algo-
rithms such as AODV and DSR, as well as models for
the MAC protocol of the 802.11b protocol specifica-
tion.
Scalable Wireless Ad hoc Network Simulator
(SWANS) (Barr et al., 2005) is a wireless network
simulator that can be used for sensor networks. It
was built on top of the Java in Simulation Time (JIST)
simulation platform. The JIST is general purpose en-
gine simulation based on discrete events, which was
developed in the JAVA language. This simulator is fo-
Temporal Evolution of Vehicular Network Simulators: Challenges and Perspectives
53
(a) Offline category (b) Embedded category (c) Online category
Figure 1: Categories of Vehicular network simulators.
cused on high performance and efficiency, and it sim-
ulates networks with four times higher performances
than the ns-2 networks, with the same system require-
ments and level of detail (Kargl and Schoch, 2007).
Jist/Swans was developed to meet the needs related
to simulations of wireless networks and sensor net-
works. One of the main advantages of Jist/Swans
is that it allows simulation of networks that require
large-scale tests.
GloMoSim is a modular library for parallel simu-
lation of wireless networks. This library was devel-
oped to be extended and combined and it has an API
defined to each layer of the communication protocol
stack. The GloMoSim has implemented: MAC layer
of 802.11b protocol in detail; routing algorithms to
wireless networks (AODV, DSR, and some others);
transport layer protocol TCP; some application in the
application layer level. Moreover, new protocols can
be developed to extend GloMoSim capabilities. Ex-
ecuting a parallel model in GloMoSim is often trans-
parent to the user. An interface can be used to set
up the simulation parameters and also to designate a
mapping strategy for running a parallel simulation.
GTNetS is a network simulator that had its devel-
opment focused on parallelism. For this reason, it has
shown a good performance as well as good scalabil-
ity, even considering networks with millions of ele-
ments. The GTNetS was implemented in C++ using
the object-oriented paradigm, which allows an easy
extension of existing protocols. The GTNetS imple-
ments the following models: on the physical layer, it
has implemented the 802.11, for wireless simulations,
and the 802.3, for wired simulations. On the network
layer, it has implemented the routing protocols AODV
and DSR for wireless and the BGP and IEGRP for
wired simulations. On the transport layer, it has im-
plemented the TCP and UDP protocols. Finally, the
application layer includes implementations for FTP,
P2P, and client-server applications. The community
has not provided support for GTNetS since 2008.
Although all networks simulators mentioned
above have mobility models for mobile network sim-
ulations, they should not be used to simulate a vehic-
ular network. That is because the network simulators
implement random models, and as we have seen be-
fore, these models do not represent real mobility. A
good alternative is to delegate the vehicular mobility
to a traffic simulator.
2.2 Traffic Simulators
When vehicular networks emerged, researchers be-
lieved that it was a specific application of mobile net-
works. It means that at the beginning, vehicular net-
work protocols were evaluated using random models.
Such models worked perfectly for mobile networks,
because generally it was about networks that simu-
lated human behavior in an open field, such as a uni-
versity campus or a conference. But it soon became
clear that the random models did not represent the ve-
hicular mobility, which produced undesirable results
when evaluating new protocols.
Since then the study of vehicular mobility has be-
come an open topic of constant research. This re-
searches resulted in an evolution from random mod-
els, where the direction, speed and origin and desti-
nation points were chosen completely randomly, to
models that extract information from actual maps and
aim to generate vehicular mobility that are closer and
closer to reality.
Thus far, several proposals of models and tools
that simulate vehicular mobility have emerged. Some
of them are based on mathematical models that simu-
late the streets as well as the driver’s behavior. Others
use maps to extract all kinds of information possible,
for instance, the limits of the streets, the number of
lanes, the direction of the tracks, the speed limits of
each vehicle category,etc. Some of the main mobility
simulators will be mentioned below.
VISSIM, proposed by (Fellendorf, 1994) in 1994,
ICEIS 2018 - 20th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
54

is a stochastic simulator of microscopic vehicular mo-
bility, meaning that it simulates the behavior of each
car individually. The quality of a traffic simulator
is highly dependent on the quality of the traffic flow
model. For this reason, the cars in queue and the lane
change models are both part of VISSIM kernel. The
model of cars in queue describes the behavior of a
vehicle with respect to the vehicle that is in front of
it, and may include overtaking models when there is
a lane change model. Instead of using a determinis-
tic cars in queue model, VISSIM uses a model based
on a psychological study created in 1974 (Fritzsche
and Ag, 1994). This approach uses random models to
calculate the parameters that determine the potential
acceleration of each driver.
VISSIM has standardized and well-defined inter-
faces that allow C-based programs to be implemented
and integrated to it. This allowed the first Bidirec-
tionally coupled simulators to emerge (Lochert et al.,
2005) (Gorgorin et al., 2006). Bidirectionally coupled
simulators are formed by the combination of a traffic
simulator with a network simulator.
Another traffic simulator widely used by the aca-
demic community is the SUMO (Krajzewicz et al.,
2012). SUMO is the acronym for Simulation of Ur-
ban Mobility, and it is a platform for microscopic traf-
fic simulation, intermodal and multimodal, of contin-
uous space and discrete events. The development of
SUMO started in 2001, but it was only in 2002 that it
was released under the GPL (Krajzewicz et al., 2002).
SUMO is not only a traffic simulator, but rather
a set of applications that help perform and prepare
traffic simulations. To allow greater flexibility, var-
ious configuration file formats are supported. These
files can be imported from other tools or generated by
SUMO itself. As previously mentioned, simulations
representing the real world need high quality mobility
models. For this reason, the SUMO has tools to gen-
erate the network topology, the vehicles and the traffic
demand.
In SUMO, the real-world networks are repre-
sented as graphs, where nodes are the intersections
and streets are represented by edges. The intersec-
tions consist of their own position, plus informa-
tion about their shape and right-of-way rules. The
edges are one-way connections between two nodes,
and they have geometry information, the permitted
classes of vehicles and the maximum speed allowed.
Two tools can be used to generate the network topol-
ogy, which are the “netconverter” and “netgener-
ate”. The “netconverter” allows the topology to be
imported from other tools, such as VISSIM, Open-
StreetMaps, etc. The “netgenerate” allows the gen-
eration of three different types of networks, which are
manhatam grid, circular spider network and random
network, as shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2: Examples of networks generated by “netgen-
erate”, from left to right, manhatam grid, circular spider
network and random network (figure extracted from (Kra-
jzewicz et al., 2012)).
SUMO is a purely microscopic traffic simulator.
Because it is multimodal, it allows not only car traffic
modeling, but also the modeling of public transport
systems, rail systems and any other system that may
influence or participate in the simulation.
The VanetMobiSim (H
¨
arri et al., 2006) is an ex-
tension of CanuMobiSim (Tian et al., 2002), a gen-
eral purpose user mobility simulator. Coded in Java,
both are platform independent and produce traces that
can be used by different network simulators such
as ns-2 (ns2, 2017), QualNet (qua, 2017) and Glo-
MoSim (Zeng et al., 1998). CanuMobiSim provides
an easily extensible architecture for mobility. How-
ever, the fact that it is designed for multiple purposes
causes the level of detail in specific scenarios to be
reduced. The VanetMobiSim therefore is a dedicated
extension for vehicle networks.
As we have seen, a critical aspect for vehicle net-
works is the need for a simulation to reflect, as closely
as possible, the actual behavior of vehicular traffic.
When dealing with vehicular mobility models, we can
separate the scenarios in a macro and a micro views.
In the macro view, both the network topology and
its structure (number of lanes and direction) must be
taken into account. Other factors that are relevant are
the characteristics of the traffic (speed limits and ve-
hicle restrictions by class), the presence of traffic re-
strictions (traffic signs and traffic lights) and finally
the effects caused by points of interest (path between
home and job).
Micro mobility refers to the behavior of each
driver individually when interacting with other drivers
or the road infrastructure. Examples of parameters
that need to be informed to the models of micro mo-
bility are: Travel speed in different traffic conditions,
deceleration and overtaking criteria, driver behavior
in the presence of intersections and traffic lights and
general attitudes of the driver (which are usually re-
lated to age, sex, maturity, etc.). To model micro
mobility parameters the VanetMobSim implemented
two models that are familiar to researchers in the
field, which are the FTM (Seskar et al., 1992) and the
Temporal Evolution of Vehicular Network Simulators: Challenges and Perspectives
55

IDM (Treiber et al., 2000).
STRAW (Choffnes and Bustamante, 2005)
(acronym of STreet RAndom Waypoint) was devel-
oped in 2005 and is publicly available
1
for download.
It was implemented as an extension of SWANS (Scal-
able Wireless Ad Hoc Network Simulator) (Barr,
2004), a Java-based, publicly available, and scalable
wireless network simulator. The STRAW extract
topology information, like road names, location, and
shapes of roads, from a TIGER data set to create
the topology of the network. According to (Rothery,
1992), the the car-following model is used to control
the nodes movement and intersection management.
As a drawback, the STRAW does not support lane
changing and not consider a vehicle’s current lane
when it attempts to make a turn.
MOVE (Karnadi et al., 2007) is implemented in
Java and runs atop of SUMO. MOVE consists of two
main components: the Map Editor and the Vehicle
Movement Editor. To build the road topology, the
Map Editor allows three possibilities, which are: (i)
the user can create the map manually, (ii) The map
can be generate automatically and; (iii) the map can
be imported from existing real maps, such as TIGER
database. The Vehicle Movement Editor allows the
user to specify the trip and the route that vehicles
should take. Then, the data is fed into SUMO to gen-
erate a mobility trace, which can be used by network
simulators such as ns-2 and QualNet to simulate a re-
alistic vehicle movement. One of the main strengths
of MOVE is the fact that it was implemented to allow
users to rapidly generate realistic mobility models for
vehicular networks.
In the previous sections, we presented the main
simulators for a specific-domains which are relevant
to vehicular networks. In the next section we will
help the reader understand how the vehicular network
researchers combined traffic simulators with network
simulators to get a reliable analysis of protocols and
applications on vehicular environments.
3 VEHICULAR NETWORK
SIMULATORS
It is clear to vehicular networks researchers that nei-
ther traffic simulators nor network simulators meet all
the requirements for a simulation. An alternative to
solve this problem would be to record the mobility
generated by a traffic simulator in a trace file and then
use this file on the network simulator to update the
1
http://http://aqualab.cs.northwestern.edu/projects/111-
c3-car-to-car-cooperation-for-vehicular-ad-hoc-networks
position of the nodes. However, this approach does
not allow mobility to be influenced by the network
simulator, and therefore, does not reflect the topol-
ogy changes. The current state of the art is the bidi-
rectional coupling between traffic and network sim-
ulators. To make it possible, both simulators run the
same simulation and exchange information on the sta-
tus of each node. Although this approach enables high
degree of realism, it requires the exchanging of a lot
of messages between the simulators, which results in
high computational cost when it is used in large sce-
narios. Characteristics and restrictions of bidirection-
ally coupled simulators are discussed below.
The MSIECV, also called VISSIM/NS-2, (Lochert
et al., 2005) is the first simulator to propose the bidi-
rectionally coupling between traffic and network sim-
ulators. The MSIECV architecture combines the ns-
2 network simulator, VISSIM traffic simulator, and
the Matlab/Simulink applications simulator. A simu-
lation controller was implemented to manage the in-
teraction between all simulators. A sync class was
implemented to ensure that traffic and network simu-
lators are synchronized in time during their execution.
GrooveNet (Mangharam et al., 2006), for Linux,
was developed in 2006, and it was implemented in
C++ and Qt. All types of vehicles communications
are supported, that is, vehicle-to-vehicle, and vehicle-
to-infrastructure through DSRC and 802.11. For ve-
hicular mobility, the GooveNet includes the models
for car-following, traffic light, lane changing and sim-
ulated GPS. Despite the authors say that the models
were validated, they did not provide any information
about its implementation. The main characteristic
highlighted by the authors, is the ability of GrooveNet
to make hybrid simulations, including real and simu-
lated vehicles.
VanetSim (Tomandl et al., 2014) had its first ver-
sion developed in 2008, but it was only in 2014 that
its stable version was made available. Developed in
Java, it is open source (GNU GPLv3) and can be
downloaded in http://www.vanet-simulator.org/. The
VanetSim was specifically designed to analyze at-
tacks on privacy and security. To ensure a ap-
proximated real-world simulation providing realistic
results, the VanetSim implements the state-of-the-
art micro-mobility model (Krauß, 1998) and allows
the importing of the network topology from Open-
StreetMap
2
.
(Wu et al., 2005) proposed a simulator that
combines CORSIM to control the mobility of ve-
hicles and the QualNet to model the communica-
tion between them. These two simulators were com-
bined using a distributed simulation software pack-
2
http://www.openstreetmap.org
ICEIS 2018 - 20th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
56

age called the Federal Simulations Development Kit
(FDK) (McLean et al., 2001). The FDK imple-
ments services defined in the Interface Specification
of High-level Architecture (Russo et al., 1995). Also,
a Communication Layer was developed to define in-
teractions between CORSIM and QualNet.
VCOM (Killat et al., 2007) is a hybrid library
which combines the micro traffic simulator VIS-
SIM with a discrete event based inter-vehicle com-
munication simulator. The VCOM takes advantage
from mathematical modeling to reduce the number of
events generated by the communication. According
to the authors, this approach can overcome ns-2 by
a considerable speed-up. Also, an application mod-
ule that contains all application logic provides a well-
defined interface to simplify the implementation and
evaluation of new applications.
NCTUns (Wang et al., 2007) and MoVES (Bononi
et al., 2008) are embedded simulators developed re-
spectively in 2007 and 2008, which implement their
own network and traffic models. The difference be-
tween them is that MoVES was developed to be a par-
allel and distributed simulator. Another simulator that
was proposed in the same year as NCTUns is the Au-
toMesh (Vuyyuru and Oguchi, 2007). The AutoMesh
implements a custom mobility simulator, but uses ns-
2 as network simulator.
The ExNS3 (Arbabi and Weigle, 2010) is extended
from the ns-3 and implements custom traffic models
to be applied in vehicular network simulations. Un-
like ExNS3, the TraNS (Pi
´
orkowski et al., 2008) uses
ns-2 for network simulation and SUMO for traffic
simulation. A TraCI interface is used to allow data
exchange between the network and traffic simulators.
Veins is a simulation framework that provides
coupling of the OMNET++ network simulator with
the SUMO traffic simulator. It was initially proposed
in 2008 by (Sommer and Dressler, 2008), after the
authors discuss the development of simulators for ve-
hicular networks. But it was only in (Sommer et al.,
2011), in 2011, that it gained greater visibility in the
academic community. The coupling between the OM-
NeT++ and SUMO happens through dedicated com-
munication modules that have been implemented for
both. During the simulation, these communication
modules exchange information over TCP.
The iTETRIS (Rondinone et al., 2013) is a sim-
ulation platform developed in 2013, which is freely
available to members of the iTETRIS community. It
integrates and extends the SUMO and ns-3, which are
two open source platforms widely used for traffic and
network simulations. The iTETRIS is an open source
platform, and its architecture is completely modular,
which facilitates for the community to expand it in
the future. It was designed to be aligned with inter-
national standards, more specifically, to be compat-
ible with the ETSI architecture for intelligent trans-
port systems, and it allows simulations to use either
the 802.11p (Teixeira et al., 2014) or the ETSI ITS
G5 standards.
Unlike the other bidirectionally coupled simula-
tors, the VSimRTI (Schnemann, 2011) is a runtime
simulation infrastructure that enables integration be-
tween any pair of simulators. Its goal is to make it as
easy as possible for the user to prepare and implement
a simulation. To achieve this, it uses a high-level ar-
chitecture (HLA) simulation and modeling standard
defined by the IEEE (893, 2000). For immediate use,
a set of simulators is already coupled to VSimRTI,
such as the traffic simulators VISSIM and SUMO,
the network simulators JIST/SWANS and OMNeT ++
and the application simulator VSimRTI APP as well
as various data analysis tools.
The OVNIS (Pign et al., 2010), proposed in 2010,
is one of the bidirectionally coupled simulator that
uses SUMO as traffic simulator and ns-3 as network
simulator. Another simulator that uses SUMO and
ns-3 is the HINTS (Zemouri et al., 2012), proposed
in 2012. HINTS differs from previously mentioned
simulators by using a hybrid approach to generate ve-
hicular mobility. It manages to bring together the best
of both worlds, that is, the flexibility of the online ap-
proach and low computational cost of the offline ap-
proach. The authors mention that the new approach
advances the state of the art in terms of performance
by using resources more efficiently, thereby reducing
the simulation time and the computational cost.
Although the bidirectionally coupled simulators
allow simulations to be performed with a high degree
of realism, some issues that are not treated by them
need to be considered. As an example, we can men-
tion the traffic demand, in which unrealistic traffic can
be generated if random origin and destination points
are chosen. Or, the poor quality of the maps, where
the absence or incompleteness of information can in-
fluence network topology. Another factor that should
be taken into consideration is the presence of differ-
ent elements in the network. In the case of vehicu-
lar networks, future efforts should be applied to the
insertion of elements in the simulation such as Un-
manned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs), people walking and
autonomous cars.
4 DISCUSSIONS
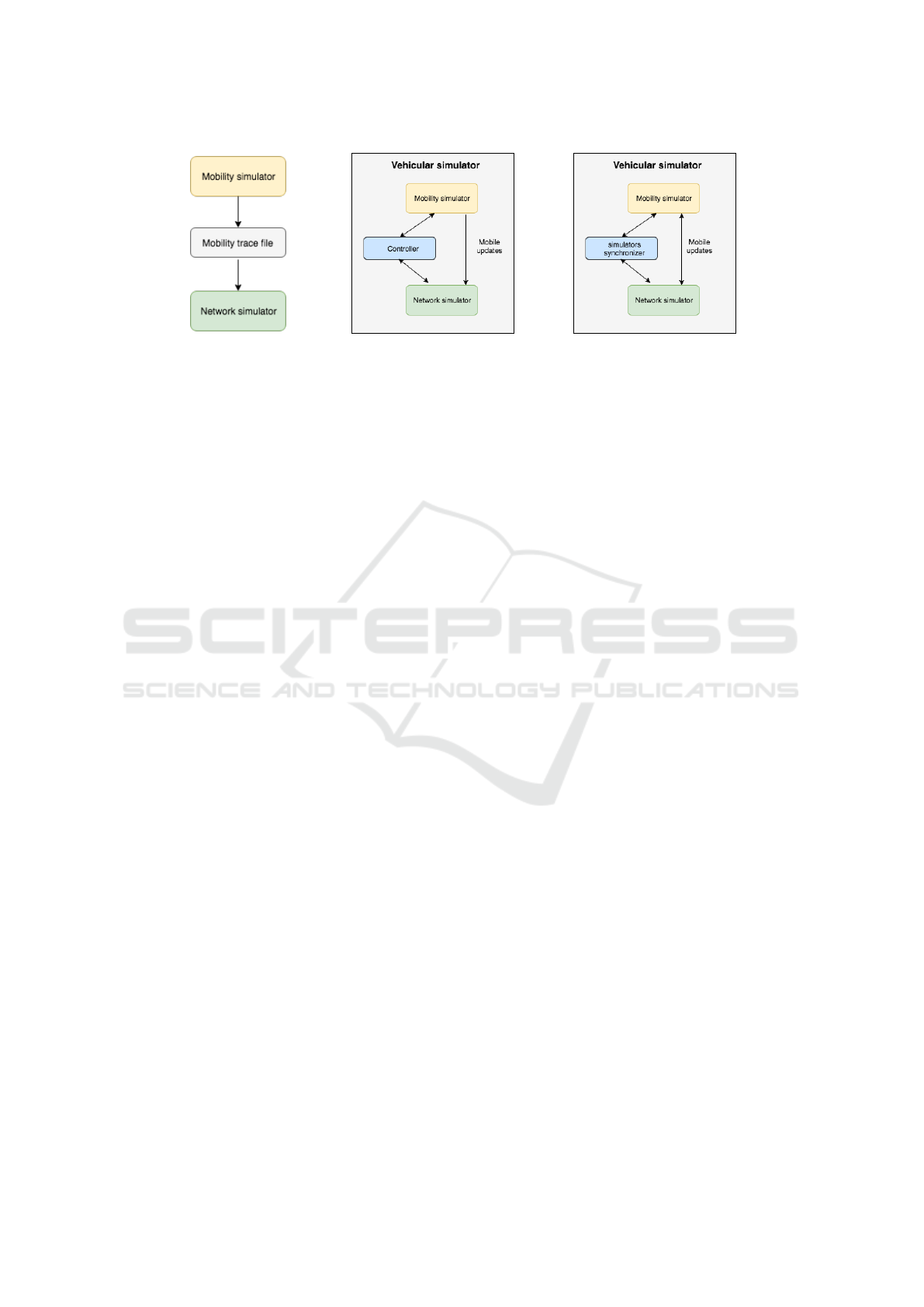
To understand the current state and future challenges
in vehicular network simulators it is necessary to
Temporal Evolution of Vehicular Network Simulators: Challenges and Perspectives
57
Figure 3: Evolution timeline of vehicular network simulators.
know how the evolution happened from the begin-
ning. As we can see on Figure 3, until 2005 the appli-
cations and protocols proposed for vehicular networks
were evaluated using random models. That is because
all existing simulators until then had others purposes,
more specifically, the traffic simulators were devel-
oped and used exclusively by traffic engineers, and
network simulators were proposed to be applied in
other types of networks, typically, sensor networks.
This scenario changes when, in 2005, (Lochert
et al., 2005) proposed the MSIECV, which combines
VISSIM (a micro-traffic simulator) with ns-2 (a net-
work simulator) to generate scenarios that are closer
to real ones. It is important to highlight that the tech-
nique proposed by (Lochert et al., 2005) comprises
the current state-of-the-art. Although MSIECV was
the first vehicular network simulator to combine traf-
fic and network simulators (online simulators), it was
only with Veins that this approach gained prominence
in the scientific community. The Veins simulator was
published three years latter by (Sommer and Dressler,
2008) and was consolidated in (Sommer et al., 2011).
We believe that one of the reasons for the lack
of attention of the scientific community with the
MSIECV, is the fact that VISSIM is a commercial
tool that is not freely available. On the other hand,
the Veins uses two freely and well-established tools
that have a bigger support of the community, which
are OMNeT++ and SUMO.
The Figure 3 also shows that most of the exist-
ing vehicular network simulators were proposed over
a period of 3 years after the first one was proposed,
in 2005. During this period, the computer scien-
tists used to believe that implementing mathematical
models to represent vehicular mobility was the bet-
ter solution (embedded simulators). In 2008, (Som-
mer et al., 2011) turned the bidirectionally coupling
between traffic and network simulators more popular,
thus gaining attention of the researchers. It is impor-
tant to notice, that the scientific community took five
year to absorb the concept of online simulators, and
three year more to start to use them.
As far as we know, after 2013 to date, there has
been no significant effort to propose new vehicular
network simulators. We believe that this is due to the
fact that the scientific community changed focus and
concentrated their efforts on implementing new mod-
els and improving the existing ones. Some examples
of these models are: 802.11p (Eckhoff et al., 2012),
DSRC/WAVE (Eckhoff and Sommer, 2012), Obsta-
cle Shadowing (Sommer et al., 2014) and Antenna
Patterns (Eckhoff et al., 2016)
5 CONCLUSION
New proposals of applications and protocols for ve-
hicular networks appear every day. Simulation is the
preferred method by the community when conducting
the evaluation. In this context, this paper presented a
temporal evolution of vehicular applications assess-
ment from random models until the emergence and
subsequent development of vehicular network sim-
ulators. We discussed the problems related to ran-
dom models used to assess vehicular applications and
how the bidirectionally coupling of network and traf-
fic simulators can solve these problems. Additionally,
we showed that the scientific community took more
than five years to consolidate and use a new simulator
paradigm.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
We acknowledge support from the Brazilian research
agency (CNPq), the Research Foundation of the State
of Minas Gerais (FAPEMIG), the CAPES Foundation
ICEIS 2018 - 20th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
58

and the Federal University of Ouro Preto (UFOP).
REFERENCES
(2000). IEEE Standard for Modeling and Simulation
(M&S) High Level Architecture (HLA) - Framework
and Rules. IEEE Std. 1516-2000, pages i–22.
(2017). Ns-2. http://www.isi.edu/nsnam/ns/. Accessed:
2017-09-29.
(2017). Qualnet. http://web.scalable-networks.com/
content/qualnet. Accessed: 2017-09-30.
Arbabi, H. and Weigle, M. C. (2010). Highway mobility
and vehicular ad-hoc networks in ns-3. In Proceedings
of the Winter Simulation Conference.
Arellano, W. and Mahgoub, I. (2013). Trafficmodeler exten-
sions: A case for rapid vanet simulation using, omne,
sumo, and veins. In 10th High Capacity Optical Net-
works and Emerging/Enabling Technologies.
Aschenbruck, N., Ernst, R., Gerhards-Padilla, E., and
Schwamborn, M. (2010). Bonnmotion: A mobility
scenario generation and analysis tool. In Proceedings
of the 3rd International ICST Conference on Simula-
tion Tools and Techniques.
Barr, R. (2004). An Efficient, Unifying Approach to Simula-
tion Using Virtual Machines. PhD thesis.
Barr, R., Haas, Z. J., and Van Renesse, R. (2005). Scal-
able wireless ad hoc network simulation. Handbook
on Theoretical and Algorithmic Aspects of Sensor, Ad
hoc Wireless, and Peer-to-Peer Networks, pages 297–
311.
Bononi, L., Felice, M. D., DAngelo, G., Bracuto, M., and
Donatiello, L. (2008). Moves: A framework for paral-
lel and distributed simulation of wireless vehicular ad
hoc networks. Computer Networks, 52:155–179.
Choffnes, D. R. and Bustamante, F. E. (2005). An integrated
mobility and traffic model for vehicular wireless net-
works. In Proceedings of the 2Nd ACM International
Workshop on Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks.
Eckhoff, D., Brummer, A., and Sommer, C. (2016). On the
Impact of Antenna Patterns on VANET Simulation. In
8th IEEE Vehicular Networking Conference.
Eckhoff, D. and Sommer, C. (2012). A Multi-Channel
IEEE 1609.4 and 802.11p EDCA Model for the Veins
Framework. In 5th ACM/ICST International Confer-
ence on Simulation Tools and Techniques for Commu-
nications, Networks and Systems.
Eckhoff, D. and Sommer, C. (2015). Simulative perfor-
mance evaluation of vehicular networks. Vehicular
Communications and Networks: Architectures, Pro-
tocols, Operation and Deployment, pages 255–274.
Eckhoff, D., Sommer, C., and Dressler, F. (2012). On the
Necessity of Accurate IEEE 802.11p Models for IVC
Protocol Simulation. In 75th IEEE Vehicular Technol-
ogy Conference, pages 1–5.
Fellendorf, M. (1994). Vissim: A microscopic simulation
tool to evaluate actuated signal control including bus
priority. In 64th Institute of Transportation Engineers
Annual Meeting.
Fischer, H.-J. (2015). Standardization and Harmoniza-
tion Activities Towards a Global C-ITS, pages 23–36.
Springer International Publishing.
Fritzsche, H.-T. and Ag, D.-b. (1994). Amodel for traffic
simulation. Traffic Engineering and Control, 35:317–
321.
Gorgorin, C., Gradinescu, V., Diaconescu, R., Cristea, V.,
and Ifode, L. (2006). An integrated vehicular and net-
work simulator for vehicular ad-hoc networks. In Pro-
ceedings of the European Simulation and Modelling
Conference.
Guan, S., Grande, R. E. D., and Boukerche, A. (2014).
Real-time 3d visualization for distributed simulations
of vanets. In Proceedings of the IEEE/ACM 18th In-
ternational Symposium on Distributed Simulation and
Real Time Applications.
Harri, J., Filali, F., and Bonnet, C. (2009). Mobility mod-
els for vehicular ad hoc networks: a survey and tax-
onomy. IEEE Communications Surveys Tutorials,
11(4):19–41.
H
¨
arri, J., Filali, F., Bonnet, C., and Fiore, M. (2006). Vanet-
mobisim: Generating realistic mobility patterns for
vanets. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Work-
shop on Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks.
Kargl, F. and Schoch, E. (2007). Simulation of manets: A
qualitative comparison between jist/swans and ns-2.
In Proceedings of the 1st International Workshop on
System Evaluation for Mobile Platforms.
Karnadi, F. K., Mo, Z. H., and c. Lan, K. (2007). Rapid
generation of realistic mobility models for vanet. In
2007 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking
Conference.
Killat, M., Schmidt-Eisenlohr, F., Hartenstein, H., R
¨
ossel,
C., Vortisch, P., Assenmacher, S., and Busch, F.
(2007). Enabling efficient and accurate large-scale
simulations of vanets for vehicular traffic manage-
ment. In Proceedings of the 4th ACM International
Workshop on Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks.
Krajzewicz, D., Erdmann, J., Behrisch, M., and Bieker,
L. (2012). Recent development and applications of
SUMO - Simulation of Urban MObility. International
Journal On Advances in Systems and Measurements,
5:128–138.
Krajzewicz, D., Hertkorn, G., R
¨
ossel, C., and Wagner,
P. (2002). Sumo (simulation of urban mobility)-an
open-source traffic simulation. In Proceedings of the
4th Middle East Symposium on Simulation and Mod-
elling.
Krauß, S. (1998). Microscopic modeling of traffic flow: In-
vestigation of collision free vehicle dynamics. PhD
thesis.
Lochert, C., Barthels, A., Cervantes, A., Mauve, M., and
Caliskan, M. (2005). Multiple simulator interlink-
ing environment for ivc. In Proceedings of the 2Nd
ACM International Workshop on Vehicular Ad Hoc
Networks.
Mangharam, R., Weller, D., Rajkumar, R., Mudalige, P.,
and Bai, F. (2006). Groovenet: A hybrid simulator for
vehicle-to-vehicle networks. In 3rd Annual Interna-
Temporal Evolution of Vehicular Network Simulators: Challenges and Perspectives
59

tional Conference on Mobile and Ubiquitous Systems
- Workshops.
Marfia, G., Pau, G., De Sena, E., Giordano, E., and Gerla,
M. (2007). Evaluating vehicle network strategies for
downtown portland: Opportunistic infrastructure and
the importance of realistic mobility models. In Pro-
ceedings of the 1st International MobiSys Workshop
on Mobile Opportunistic Networking.
McLean, T., Fujimoto, R., and Fitzgibbons, B. (2001). Next
generation real-time rti software. In 5th IEEE Interna-
tional Workshop on Distributed Simulation and Real-
Time Applications.
Mota, V. F., Cunha, F. D., Macedo, D. F., Nogueira, J. M.,
and Loureiro, A. A. (2014). Protocols, mobility mod-
els and tools in opportunistic networks: A survey.
Computer Communications, 48:5–19.
Nimje, T. G. and Dorle, S. (2013). A survey on various mo-
bility models to improve realistic simulation and accu-
racy of ivc protocols. In International Conference on
Emerging Trends in Computing, Communication and
Nanotechnology (ICE-CCN).
Pign, Y., Danoy, G., and Bouvry, P. (2010). A platform
for realistic online vehicular network management. In
IEEE Globecom Workshops.
Pi
´
orkowski, M., Raya, M., Lugo, A. L., Papadimitratos, P.,
Grossglauser, M., and Hubaux, J.-P. (2008). Trans:
Realistic joint traffic and network simulator for vanets.
SIGMOBILE Mobile Computer Communication Re-
view, 12:31–33.
Rondinone, M., Maneros, J., Krajzewicz, D., Bauza, R.,
Cataldi, P., Hrizi, F., Gozalvez, J., Kumar, V., Rckl,
M., Lin, L., Lazaro, O., Leguay, J., Hrri, J., Vaz, S.,
Lopez, Y., Sepulcre, M., Wetterwald, M., Blokpoel,
R., and Cartolano, F. (2013). itetris: A modular sim-
ulation platform for the large scale evaluation of co-
operative {ITS} applications. Simulation Modelling
Practice and Theory, 34:99–125.
Rothery, R. W. (1992). Car following models. Traffic flow
theory.
Russo, K. L., Shuette, L. C., Smith, J. E., and McGuire,
M. E. (1995). Effectiveness of various new bandwidth
reduction techniques in modsaf. In Proceedings of the
13th Workshop on Standards for the Interoperability
of Distributed Simulations.
Schnemann, B. (2011). {V2X} simulation runtime infras-
tructure vsimrti: An assessment tool to design smart
traffic management systems. Computer Networks,
55:3189–3198.
Seskar, I., Maric, S. V., Holtzman, J., and Wasserman, J.
(1992). Rate of location area updates in cellular sys-
tems. In IEEE 42nd Vehicular Technology Confer-
ence.
Sommer, C. and Dressler, F. (2008). Progressing toward
realistic mobility models in vanet simulations. IEEE
Communications Magazine, 46(11):132–137.
Sommer, C., Eckhoff, D., and Dressler, F. (2014). IVC
in Cities: Signal Attenuation by Buildings and How
Parked Cars Can Improve the Situation. IEEE Trans-
actions on Mobile Computing, 13(8):1733–1745.
Sommer, C., German, R., and Dressler, F. (2011). Bidirec-
tionally coupled network and road traffic simulation
for improved ivc analysis. IEEE Transactions on Mo-
bile Computing, 10:3–15.
Teixeira, F. A., e Silva, V. F., Leoni, J. L., Macedo, D. F.,
and Nogueira, J. M. S. (2014). Vehicular networks
using the IEEE 802.11p standard: An experimental
analysis. Vehicular Communications, 1:91–96.
Tian, J., Hahner, J., Becker, C., Stepanov, I., and Rothermel,
K. (2002). Graph-based mobility model for mobile ad
hoc network simulation. In Simulation Symposium,
2002. Proceedings. 35th Annual.
Tomandl, A., Herrmann, D., Fuchs, K. P., Federrath, H., and
Scheuer, F. (2014). Vanetsim: An open source simu-
lator for security and privacy concepts in vanets. In
12th International Conference on High Performance
Computing Simulation (HPCS).
Tornell, S. M., Calafate, C. T., Cano, J. C., and Manzoni,
P. (2015). Dtn protocols for vehicular networks: An
application oriented overview. IEEE Communications
Surveys Tutorials, 17:868–887.
Treiber, M., Hennecke, A., and Helbing, D. (2000). Con-
gested traffic states in empirical observations and mi-
croscopic simulations. Physical Review E, 62:1805–
1824.
Varga, A. (2010). OMNeT++, pages 35–59. Springer Berlin
Heidelberg.
Vuyyuru, R. and Oguchi, K. (2007). Vehicle-to- vehicle
ad hoc communication protocol evaluation using re-
alistic simulation framework. In 2007 Fourth Annual
Conference on Wireless on Demand Network Systems
and Services.
Wang, S. and Chou, C. (2009). {NCTUns} tool for wireless
vehicular communication network researches. Sim-
ulation Modelling Practice and Theory, 17(7):1211–
1226.
Wang, S. Y., Chou, C. L., Chiu, Y. H., Tzeng, Y. S., Hsu,
M. S., Cheng, Y. W., Liu, W. L., and Ho, T. W.
(2007). Nctuns 4.0: An integrated simulation platform
for vehicular traffic, communication, and network re-
searches. In IEEE 66th Vehicular Technology Confer-
ence.
Wu, H., Lee, J., Hunter, M., Fujimoto, R., Guensler, R.,
and Ko, J. (2005). Efficiency of simulated vehicle-to-
vehicle message propagation in atlanta, georgia, i-75
corridor. Transportation Research Record: Journal of
the Transportation Research Board, (1910):82–89.
Zemouri, S., Mehar, S., and Senouci, S. M. (2012). Hints:
A novel approach for realistic simulations of vehicular
communications. In Proceedings of the 4th Global In-
formation Infrastructure and Networking Symposium.
Zeng, X., Bagrodia, R., and Gerla, M. (1998). Glomosim:
a library for parallel simulation of large-scale wireless
networks. In Proceedings 12th Workshop on Parallel
and Distributed Simulation.
ICEIS 2018 - 20th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
60
