
Mapping of Periodic Tasks in Reconfigurable Heterogeneous Multi-core
Platforms
Aymen Gammoudi
1,2,3
, Daniel Chillet
1
, Mohamed Khalgui
2,4
and Adel Benzina
2,3
1
IRISA Lab, University of Rennes1, Rennes, France
2
LISI Lab, University of Carthage, Tunis, Tunisia
3
Tunisia Polytechnic School, University of Carthage, Tunis, Tunisia
4
School of Electrical and Information Engineering, Jinan University (Zhuhai Campus), Zhuhai 519070, China
Keywords:
Heterogeneous Multi-core Platform, Reconfiguration, Task Mapping and Scheduling.
Abstract:
Multi-core Real-time Systems (MRS) powered by a battery have been adopted for a wide range of high per-
formance applications, such as mobile communication and automotive systems. A system is composed of
N dependent and periodic Operating System (OS) tasks to be assigned to p heterogeneous cores linked by a
network-on-chip (NoC). This paper deals with the problem of task allocation in MRS in such a way that the
cost of communication between cores is minimized by trying to place the dependent tasks as close as possible
to each other. The main objective is to develop a new strategy for allocating N tasks to p cores of a given
distributed system using task clustering by considering both the cost of inter task communication and that of
communication between cores. The proposed strategy guarantees that, when a task is mapped into the system
and accepted, then it is correctly executed prior to the task deadline. A novel periodic task model based on
elastic coefficients is proposed to compute useful temporal parameters allowing to assign all tasks to p cores,
by minimizing the traffic between cores. Experimental results reveal the effectiveness of the proposed strategy
by comparing the derived solutions with the optimal ones, obtained by solving an Integer Linear Program
(ILP).
1 INTRODUCTION
Multi-core real-time platforms typically are com-
posed of multiple processors (processing units),
memories, and a communication infrastructure. Het-
erogeneous multi-core platforms contain different
types of processing units. Therefore, the system de-
signers can take advantage of their properties when
mapping tasks to specific processor types and opti-
mize criteria such as computational performance, cost
and energy consumption (Schranzhofer et al., 2010).
Several academic and industrial studies reported in
(Wang et al., 2016), (Cecilio and Furtado, 2014),
(Li et al., 2014) have addressed the dynamic recon-
figuration of real-time systems. These approaches
can be divided into two categories: manual applied
by users (Rooker et al., 2007); and automatic ap-
plied by intelligent control agents (Vrba and Marik,
2010). The most promising approach is the elastic
scheduling reported in (Wang et al., 2016), (Wang
et al., 2015), (Marinoni and Buttazzo, 2007), (But-
tazzo et al., 1998).
A multi-core real-time system, denoted MRS, can
be implemented by N reconfigurable real-time depen-
dent and periodic tasks to be assigned to p heteroge-
neous cores linked by a network-on-chip (NoC) (Hu
and Marculescu, 2005) in order to ensure the commu-
nication between dependent tasks. Since we consider
a heterogeneous platform, each task cannot be exe-
cuted by all cores, it can be supported only by one
or more specific cores according to system specifi-
cation. Similarly to the research works reported in
(Wang et al., 2016), (Marinoni and Buttazzo, 2007),
we consider a more flexible task model, in which
the tasks can operate within a given range of peri-
ods with different performances. A reconfiguration
scenario is defined in this paper as any internal or
external event that leads to the addition and/or re-
moval of periodic tasks as well as their exchanged
messages to adapt the system’s behavior to its envi-
ronment (Quadri et al., 2012). In this paper, we are
interested basically in reconfiguration scenarios that
add new software tasks. New tasks must be assigned
to their appropriate cores by trying to place the depen-
Gammoudi, A., Chillet, D., Khalgui, M. and Benzina, A.
Mapping of Periodic Tasks in Reconfigurable Heterogeneous Multi-core Platforms.
DOI: 10.5220/0006698500990110
In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to Software Engineering (ENASE 2018), pages 99-110
ISBN: 978-989-758-300-1
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
99

dent tasks as close as possible to each other in order
to reduce the traffic on the NoC. Therefore the en-
ergy consumption, proportional to the data commu-
nication volume, will be decreased. As partitioned
scheduling converts the problem of scheduling real-
time tasks into a set of uniprocessor scheduling prob-
lems (Baruah and Goossens, 2004), we decided to se-
lect earliest deadline first (EDF) scheduler to schedule
the local tasks for each core.
For two new added dependent tasks assigned to
different cores, a new periodic message is added au-
tomatically to the NoC. Consequently, the real-time
constraints can be not satisfied when a task misses
the related deadline and a message can take a long
time to arrive to its destination. Therefore, the system
MRS will be unfeasible. An MRS is feasible if and
only if it satisfies two constraints: (i) the deadlines
of the tasks, and (ii) the messages’ deadlines on the
communication medium. Moreover, the provided so-
lutions must be optimal real-time ones that minimize
the power consumption of system.
The general goal of this paper is to propose a new
mapping strategy based on grouping heavily commu-
nicating tasks into the same cluster. The tasks that are
grouped into the same cluster are assigned to the same
core while keeping its processor utilization coefficient
less than or equal to 1 and the communication bus is
feasible. Whenever these constraints are not satisfied,
the proposed strategy offers two solutions (A and B)
based on the modification of temporal parameters of
the processed tasks to meet the real-time and commu-
nication constraints. If after assigning the new task
to core C
j
, the real-time constraint is violated, then
the proposed strategy starts by modifying the periods
of tasks and the exchanged messages until reaching
their specific maximal periods (Solution A) in order
to decrease the processor utilization of C
j
. If the sec-
ond constraint is also violated after assigning one or
more new tasks, then the proposed strategy applies the
second solution (Solution B) that modifies the mes-
sage’s period and the associated tasks to slow down
the communicating tasks to satisfy the communica-
tion constraint. To evaluate this strategy, we formalize
the problem as an optimization problem by using in-
teger linear programming (ILP) and compare the pro-
posed solutions with the optimal results provided by
the CPLEX solver (CPLEX, 2013). The originality of
this paper is to propose a new strategy of mapping and
scheduling tasks in reconfigurable architectures. The
proposed strategy looks for the near optimal place-
ment of tasks on cores after any reconfiguration sce-
nario in order to minimize the traffic on the NoC. The
proposed strategy is deterministic since it is able to
find the suitable solutions for each situation.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows: Sec-
tion 2 reviews some related works. Section 3 presents
the system model and the used terminologies. We
formalize the considered problem in Section 4. The
proposed strategy is presented in Section 5 that deals
with the modification of temporal parameters of the
processed tasks to guarantee the related real-time and
communication constraints after any reconfiguration
scenario. The strategy is implemented, simulated and
analyzed in Section 6. Finally, Section 7 concludes
this work.
2 RELATED WORK
Reducing the cost of communication between cores
becomes a major concern for the high-performance
and reliability of such systems. Several academic
studies reported in (Carle et al., 2015), (Bhardwaj
and Kumar, 2013), (Tosun et al., 2009) have ad-
dressed the mapping algorithms using task clustering
by taking both inter task communication and execu-
tion costs. The basic idea of clustering based algo-
rithm in (Bhardwaj and Kumar, 2013), (Tosun et al.,
2009) is to group heavily communicating tasks into
the same cluster. The tasks that are grouped into the
same cluster are assigned to the same processor in
an effort to avoid communication costs. These algo-
rithms are interesting since the communication cost is
reduced, but the authors are not interested in the veri-
fication of the processor utilization after assigning the
tasks. In certain cases, the processor utilization ex-
ceeds 100%. In addition, they are not interested to
check the overflow on the communication medium.
To resolve these two problems, effective solutions
based on the modification of WCETs, deadlines, and
periods of tasks in order to verify the processor uti-
lization after any assignment of tasks are reported in
(Gammoudi et al., 2015), (Wang et al., 2016), (Wang
et al., 2015), (Gharsellaoui et al., 2013), (Marinoni
and Buttazzo, 2007).
The work presented in (Wang et al., 2015) pro-
poses a feasible low-power dynamic reconfiguration
of real-time systems where addition and removal of
tasks are applied at run-time. Three solutions are
presented to cut-down the energy consumption af-
ter any reconfiguration scenario. The authors pro-
pose to prolong the periods (or reduce the WCETs)
of tasks by assigning a single value to all the tasks
in order to re-obtain the system feasibility. Recently,
the work reported in (Gammoudi et al., 2015) im-
proves these solutions by proposing a new approach
based on the modification of task parameters with
classification in packs by assigning a unique period
ENASE 2018 - 13th International Conference on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to Software Engineering
100

(or WCET) to all the tasks related to the same pack.
Each pack is a group of tasks having “similar” peri-
ods (or WCETs). For each reconfiguration scenario,
specific modifications are performed on the parame-
ters of the packs and their related tasks in order to
meet the real-time and energy constraints. In the re-
search work reported in (Gammoudi et al., 2016c),
the authors develop the Recon f − Pack simulator to
evaluate and compare these two approaches by gen-
erating a large number of random systems and recon-
figuration scenarios for each one. The authors show
that the total cost introduced by applying the solu-
tion presented in (Wang et al., 2015) in 88% of ran-
dom cases is largely higher than that introduced by
the method reported in (Gammoudi et al., 2015). To
show that the pack solution, proposed in (Gammoudi
et al., 2015), can be implemented in a real applica-
tion, the work reported in (Gammoudi et al., 2016a)
proposes a new reconfigurable middleware, named
Recon f − Middleware, that presents a plugin imple-
mented in RTLinux and describes the transition from
the pack theory to the implementation. An exten-
sion of the technique reported in (Gammoudi et al.,
2015) to homogeneous multi-core platforms is de-
scribed in (Gammoudi et al., 2016b). The authors
propose four solutions to schedule a real-time appli-
cation composed of independent periodic tasks under
energy constraints. Nevertheless, they do not consider
the scheduling of dependent tasks onto heterogeneous
platforms and they do not treat the influence of the
task mapping on the communication and therefore on
the energy consumption.
3 SYSTEM MODEL AND
ASSUMPTIONS
In this section, we present the task model and the
platform architecture that consists of a reconfigurable
MRS composed of N periodic OS tasks executed by
p heterogeneous cores. We also present the models
of the processor architecture and the communication
between cores.
3.1 Task Model
We suppose that MRS processes a task set Π contain-
ing N periodic tasks, i.e., Π = {τ
1
, τ
2
, ..., τ
N
}. Some
tasks are considered as flexible, whose utilization can
be modified by changing their periods within a spec-
ified range. According to (Wang et al., 2016), (Mari-
noni and Buttazzo, 2007), (Buttazzo et al., 1998), a
periodic task τ
i
is characterized by: (i) a release time
A
i
, (ii) a worst-case execution time (WCET) W
i
, (iii)
a relative deadline D
i
, (iv) a period T
i
, and (v) a max-
imum tolerable period T
i
max
. The relative deadline
of a periodic task is considered as a hard deadline
if its missing is unacceptable (Baruah and Goossens,
2004). According to (Liu and Layland, 1973), assum-
ing that the period is equal to the deadline for each
task, the tasks are schedulable if and only if the pro-
cessor utilization coefficient is less than 1. Hence, we
apply in this paper the EDF policy to schedule the lo-
cal tasks for each core.
3.2 Platform Model
Let the considered MRS consists of a set of p het-
erogeneous cores Γ={C
1
,C
2
, ...,C
p
}, interconnected
by communication links. Since we consider hetero-
geneous platforms, we suppose that each task τ
i
can
be executed by one or more specific cores according
to system specification. Hence, we define the matrix
γ that represents the different possibilities to execute
tasks on cores.
γ
i, j
=
1 τ
i
can be executed by C
j
.
0 otherwise.
In order to ensure that all the tasks are mapped on the
cores, we define the mapping matrix H where
H
i, j
=
1 if task τ
i
is running on core C
j
.
0 otherwise.
3.3 Communication Model
Each core runs periodic OS tasks which can exchange
messages on the NoC (Khemaissia et al., 2016), (Hu
and Marculescu, 2005). We denote in the following
by M
i, j
, the message to be exchanged between a pair
of tasks τ
i
and τ
j
. According to (Bui et al., 2012) the
communication model is based on: (i) a regular inter-
arrival time T M
i, j
, (ii) a spent time to transmit a mes-
sage W M
i, j
, (iii) an absolute deadline DM
i, j
, and (iv)
an amount of exchanged data SM
i, j
(in bits). We con-
sider that the period T M
i, j
of message M
i, j
is equal to
the period T
i
of the related sending task τ
i
(T M
i, j
=T
i
).
If the task’s period is changed, then the periods of the
related messages will be changed implicitly.
The NoC architecture implies a communication cost
between each pair of cores depending on the distance
between them. We model each NoC architecture by a
specific cost matrix called Cost such as
Cost
C
k
,C
l
=
X
C
k
,C
l
if k 6= l, ∀ k, l ∈ [1..p].
0 otherwise.
where X
C
k
,C
l
is the cost (e.g. energy) of sending one
bit from core C
k
to core C
l
.
To calculate the cost of communication between each
Mapping of Periodic Tasks in Reconfigurable Heterogeneous Multi-core Platforms
101

pair of cores C
k
and C
l
, it is necessary to multiply
the volume of exchanged data by Cost
C
k
,C
l
. Then, the
total cost of communications (in units of cost) is given
by
TotalCost =
p
∑
k=1
p
∑
l=1
N
∑
i=1
N
∑
j=1
SM
i, j
∗Cost
C
k
,C
l
∗H
i,k
∗H
j,l
(1)
We suppose, in this paper, that the energy consumed
by the communication is proportional to the distance
between cores.
3.4 Processor Utilization Model
According to (Liu and Layland, 1973) the processor
utilization U
C
j
of core C
j
is given by
U
C
j
=
N
∑
i=1
W
i
T
i
∗ H
i, j
;∀ j ∈ [1..p] (2)
The core C
j
is feasible, if and only if
U
C
j
≤ 1;∀ j ∈ [1.. p] (3)
Eq. 3 is the real-time constraint.
According to the works reported in (Bui et al., 2012),
(Khemaissia et al., 2014), (Khemaissia et al., 2016),
to evaluate the communication feasibility between
two cores, the related medium is considered as a vir-
tual processor. Based on this hypothesis, the uti-
lization of the communication medium between two
cores C
k
and C
l
, denoted U
Com
(C
k
,C
l
), is given by
U
Com
(C
k
,C
l
) =
N
∑
i=1
N
∑
j=1
W M
i, j
T M
i, j
∗H
i,k
∗H
j,l
;∀k, l ∈ [1..p]
(4)
According to the work reported in (Khemaissia et al.,
2016), to ensure that the communication between
cores that are physically close is feasible, it is nec-
essary to check
U
Com
(C
k
,C
l
) ≤ 1; ∀k, l ∈ [1.. p] | Cost
C
k
,C
l
= 1 (5)
Eq. 5 is the communication constraint.
4 PROBLEM FORMULATION
The problem, being addressed in this paper, is con-
cerned with an optimal allocation of the tasks to the
cores after any reconfiguration scenario. An optimal
allocation is considered as one that minimizes the cost
of communication between cores such that the real-
time and communication constraints are satisfied. We
present, in this section, the formulation of the map-
ping problem and formalize each constraint as an op-
timization problem by using ILP.
4.1 Mapping Problem
We suppose that at time t
i
MRS is composed of Γ(t
i
) =
{C
1
,C
2
, ...,C
p
} and Π(t
i
) = {τ
1
, τ
2
, ..., τ
n
1
}. An MRS
is feasible if and only if it satisfies the two constraints
(real-time and communication constraints). We as-
sume in the following that MRS is dynamically re-
configured at time t
k
(t
k
> t
i
) by adding n
2
tasks.
Therefore, the new implementation of tasks is Π(t
k
) =
{τ
1
, τ
2
, ..., τ
n
1
, τ
n
1
+1
, ..., τ
N
}, with N = n
1
+ n
2
. The
new tasks provided by this reconfiguration must be
mapped to their appropriate cores.
We consider, in this paper, that the initial mapping
at time t
1
is also a reconfiguration scenario such that
Π(t
0
) = {∅} and Π(t
1
)6={∅}.
To guarantee that each task is executed at most by one
of its appropriate cores, it is necessary to satisfy
p
∑
j=1
H
i, j
∗ γ
i, j
= 1;∀i ∈ [1..N] (6)
We need to assign all the old/new tasks to their appro-
priate cores by minimizing the cost of communication
between them. This idea is formalized by
RE
Minimize TotalCost
s.t.
U
C
j
≤ 1, ∀ j ∈ [1.. p] (Eq.3)
U
Com
(C
k
,C
l
) ≤ 1 | Cost
C
k
,C
l
= 1 (Eq.5)
∀ k, l ∈ [1..p]
∑
p
j=1
H
i, j
∗ γ
i, j
= 1, ∀ i ∈ [1..N] (Eq.6)
where, TotalCost is calculated by Eq.1. Eq.3 satis-
fies the real-time scheduling under the EDF policy
for each core, Eq.5 ensures that the communication
between the cores C
k
and C
l
is feasible and Eq.6 en-
sures that each task is executed at most by one of its
appropriate cores. The RE problem can be solved by
integer linear programming solvers such as CPLEX
(CPLEX, 2013), which is hard to be implemented in
an embedded platform since it is too complex to be
executed on-line. We note that this solver does not
produce any solution if one or more constraints are
not satisfied. To solve the problem RE, it is necessary
that all the constraints are satisfied. We suppose that
ILP is only used to compute the optimal solution to
have a comparison reference for the heuristic we will
propose later. After different reconfiguration scenar-
ios, one or more of these constraints can be violated
and ILP cannot provide a solution for that situation.
ENASE 2018 - 13th International Conference on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to Software Engineering
102

4.2 Real-time Problem
After assigning one or more tasks on C
j
, the processor
utilization of C
j
will increase and it can be unfeasible
(U
C
j
> 1). Since U
C
j
=
∑
N
i=1
W
i
T
i
∗ H
i, j
;∀ j ∈ [1..p], we
propose first of all to modify the periods of the local
OS tasks in order to decrease the processor utilization.
The idea is to extend the periods of tasks until they
reach T
i
max
. Using the ILP model, we formalize this
problem by ∀ j ∈ [1..p] | U
C
j
> 1
Pb1 =
Minimize
∑
N
i=1
∆T
i
∗ H
i, j
s.t.
∑
N
i=1
W
i
T
i
+ ∆T
i
∗ H
i, j
≤ 1
T
i
+ ∆T
i
≤ T
i
max
, ∀ i ∈ [1..N]
where ∆T
i
is an integer that extends the period of the
real-time tasks. This formalization exploits the pos-
sible flexibility of the periods in order to reduce the
processor utilization.
4.3 Communication Problem
After the addition of a pair of dependent tasks on two
cores, a periodic message will be added to the NoC
and should respect a corresponding deadline related
to these tasks. Then, it is necessary to verify the fea-
sibility of the communication between each pair of
cores C
k
and C
l
(k, l ∈ [1..p]). According to Eq. 5,
if U
Com
(C
k
,C
l
) is greater than 1, then the communi-
cation between these two cores is not feasible. In or-
der to solve this problem, we propose to modify the
period of messages exchanged between the tasks run-
ning on cores C
k
and C
l
. The idea here is to slow
down the communicating tasks to satisfy the commu-
nication constraint. We can formalize this problem by
∀ k, l ∈ [1..p] | U
Com
(C
k
,C
l
) > 1
Pb2 =
Minimize
∑
N
i=1
∑
N
j=1
∆T M
i, j
∗ H
i,k
∗ H
i,l
s.t.
∑
N
i=1
∑
N
j=1
W M
i, j
T M
i, j
+ ∆T M
i, j
∗ H
i,k
∗ H
i,l
≤ 1
T M
i, j
+ ∆T M
i, j
≤ T
i
max
, ∀ i, j ∈ [1..N]
where ∆T M
i, j
is an integer value that extends the pe-
riod of message M
i, j
(with M
i, j
=T
i
).
Pb1 and Pb2 can be solved by CPLEX (CPLEX,
2013) that provides an optimal solution since it seeks
Figure 1: Example of application.
for each task and message the suitable and exact mod-
ification with a minimal cost. Nevertheless, it is not
reasonable to implement an ILP solver in an embed-
ded system. Therefore, we present in the next Section
some efficient and implementable heuristics and we
compare them to the optimal solutions provided by
the CPLEX solver to solve these problems.
5 CONTRIBUTION
When the configuration (or reconfiguration) scenario
is applied, each new task must be assigned to its ap-
propriate core by minimizing the cost of communica-
tion. We present in the next subsection a mapping
strategy based on grouping heavily communicating
tasks into the same cluster. The tasks that are grouped
into the same cluster are assigned to the same core
such that its processor utilization coefficient is less
than or equal to 1 and the communication bus is fea-
sible.
5.1 Proposed Task Allocation Algorithm
Before presenting the allocation algorithm, we intro-
duce some definitions:
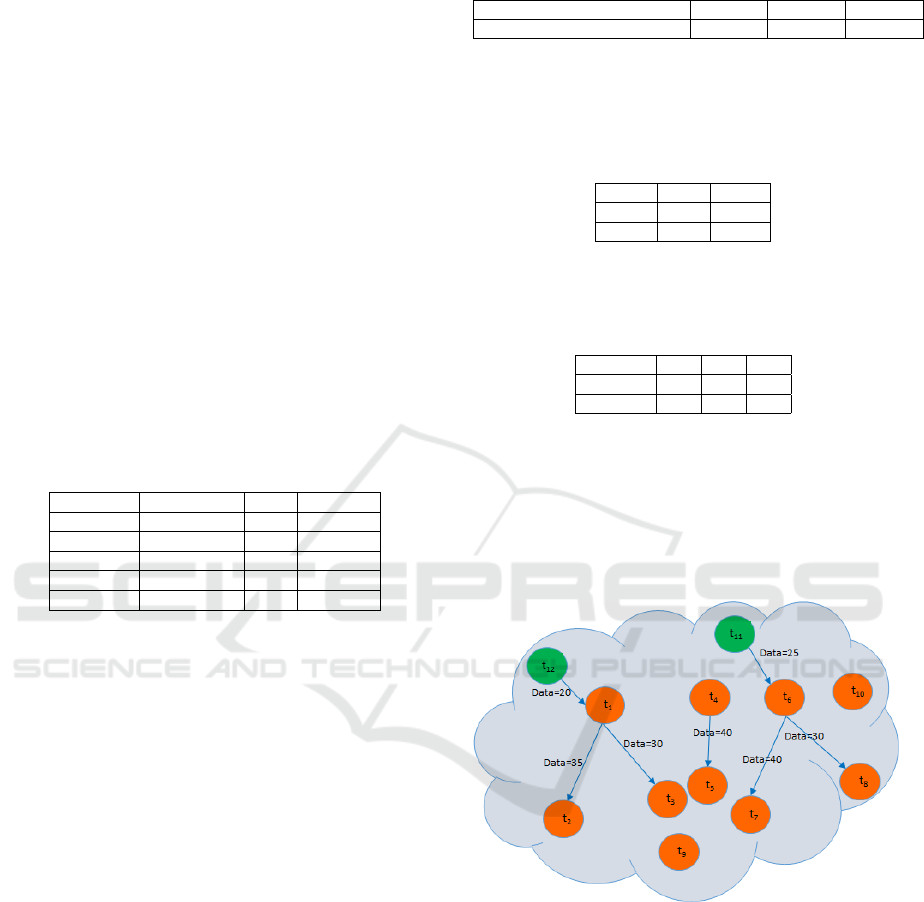
SingleCore Task: any task that can be executed only
by one specific core. Example : τ
2
in Fig. 1.
Cluster (CL): a group of communicating tasks.
Example : τ
1
, τ
2
and τ
3
are grouped in CL
1
(Fig. 1).
Common Processor (CP): a processor that can exe-
cute all tasks of a cluster CL such that its processor
utilization is less than or equal to 1. Example : C
1
can
be the CP of CL
1
. C
2
and/or C
4
can be the CP of CL
2
(Fig. 1).
CPCL: we denote by CPCL each cluster CL that has
a common processor CP.
Data Traffic (TD): is the total volume of data ex-
changed between tasks in CL. Example : T D(CL
1
) =
Mapping of Periodic Tasks in Reconfigurable Heterogeneous Multi-core Platforms
103
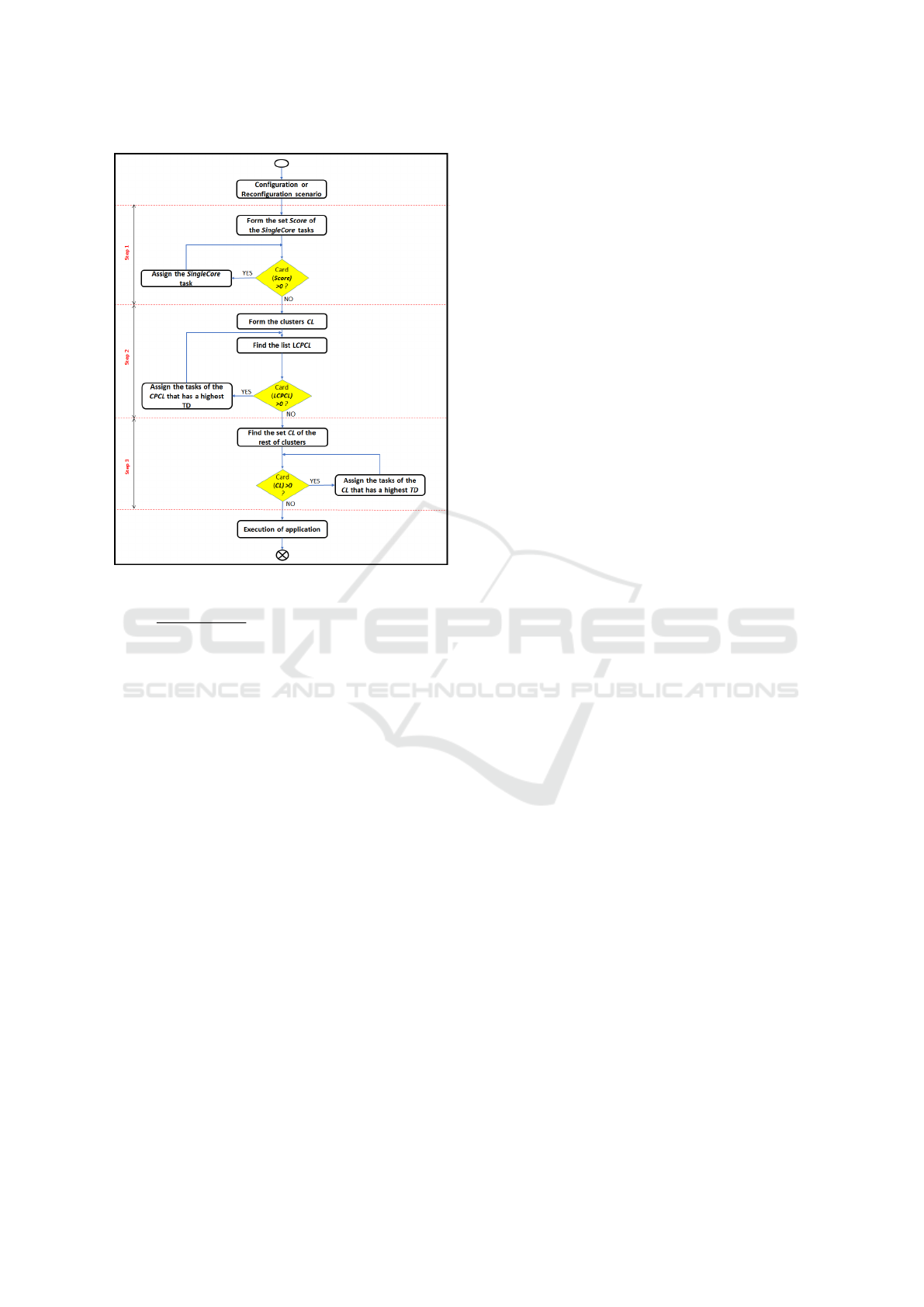
Figure 2: Global MappingTasks algorithm.
TU ∗ (
data1 + data2
T
1
) and T D(CL
2
) = 0 (Fig. 1).
The global structure of the proposed strategy is pre-
sented in Fig. 2 and is based on three main steps:
Step 1: Assign all the SingleCore tasks.
Step 2: Assigning the communicating tasks that have
a common processor CP:
Step 2.1: Each group of communicating tasks are
grouped in a cluster CL.
Step 2.2: Calculate the data traffic (TD) for each
CL.
Step 2.3: Sort all the CL in a descending order
according to their TD.
Step 2.4: A CL that has a CP will be denoted by
CPCL. The list of all CPCLs called LCPCL.
Step 2.5: Assign the tasks of each CPCL.
Step 3: Assigning the tasks of CL as close as
possible.
Step 3.1: Take the CL that has a highest TD.
Step 3.2: Place each task on the best position (in
term of communication cost).
The detailed structure of the proposed strategy is
presented in Fig. 3. Its objective is to find the near
optimal mapping of the tasks on cores in order to op-
timize the energy consumption while meeting tem-
poral and communication constraints. Communicat-
ing tasks are placed as close as possible. The pro-
posed strategy solves the problem formalized by RE
in sub-section 4.1. As shown in this figure, the pro-
posed strategy takes the task’s characteristics, the ma-
trix γ, the matrix of architecture Cost and the size of
exchanged messages as inputs and outputs the map-
ping of the tasks on the architecture.
After assigning the new tasks, the processor uti-
lization of certain cores will certainly increase. If
the new utilization is greater than 1, then the real-
time constraint is violated as reported in (Wang et al.,
2015), (Liu and Layland, 1973). Besides, the commu-
nication constraint can be violated after the addition
of tasks and consequently MRS will be unfeasible. To
solve these two problems that have been formalized
in 4.2 and 4.3, we present two solutions in the next
subsection.
5.2 Task Scheduling for Feasible
Reonfigurable Platforms
We propose two heuristics based on grouping the
tasks that have “similar” periods in several packs, de-
noted Pack, to re-obtain the system feasibility. After
a reconfiguration, we do not calculate a new period
for each task, but assign a new one period to all tasks
of the first pack Pack
1, j
( j ∈ [1..p]). Moreover, all
the new periods affected to the tasks of pack Pack
x, j
are multiple of the one affected to the tasks of Pk
1, j
.
Hence, we have only to compute the suitable value
Pk
1, j
. We show in the following solutions how the
tasks are grouped in packs.
5.2.1 Solution A: Modification of Periods under
Real-Time Constraint
If C
j
( j ∈ [1..p]) is not feasible after assigning some
new tasks to it, then we propose to extend the periods
of tasks that run on C
j
. In order to satisfy the real-time
constraints, we assign each task to pack Pack
T
x, j
ac-
cording to its period. To construct the packs, we need
to find the suitable new period Pk
T
1, j
that minimizes
the cost of the new solution for the whole system. We
formalize this problem by
Min
∑
N
i=1
(Pk
T
1, j
− (T
i
mod Pk
T
1, j
)) mod Pk
T
1, j
∗ H
i, j
s.t.
Pk
T
1, j
≥ Min(T
i
), ∀ i ∈ [1..N] | H
i, j
= 1
Once Pk
T
1, j
is calculated, we construct the packs of
the system tasks as follows: Pack
T
x, j
, x ≥ 1, includes
the tasks that have a period in the range [(x − 1) ∗
Pk
T
1, j
+ 1 ; x ∗ Pk
T
1, j
], x ∈ N
+
. The first value of
x is 1 and when all tasks are affected, x is no more
ENASE 2018 - 13th International Conference on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to Software Engineering
104
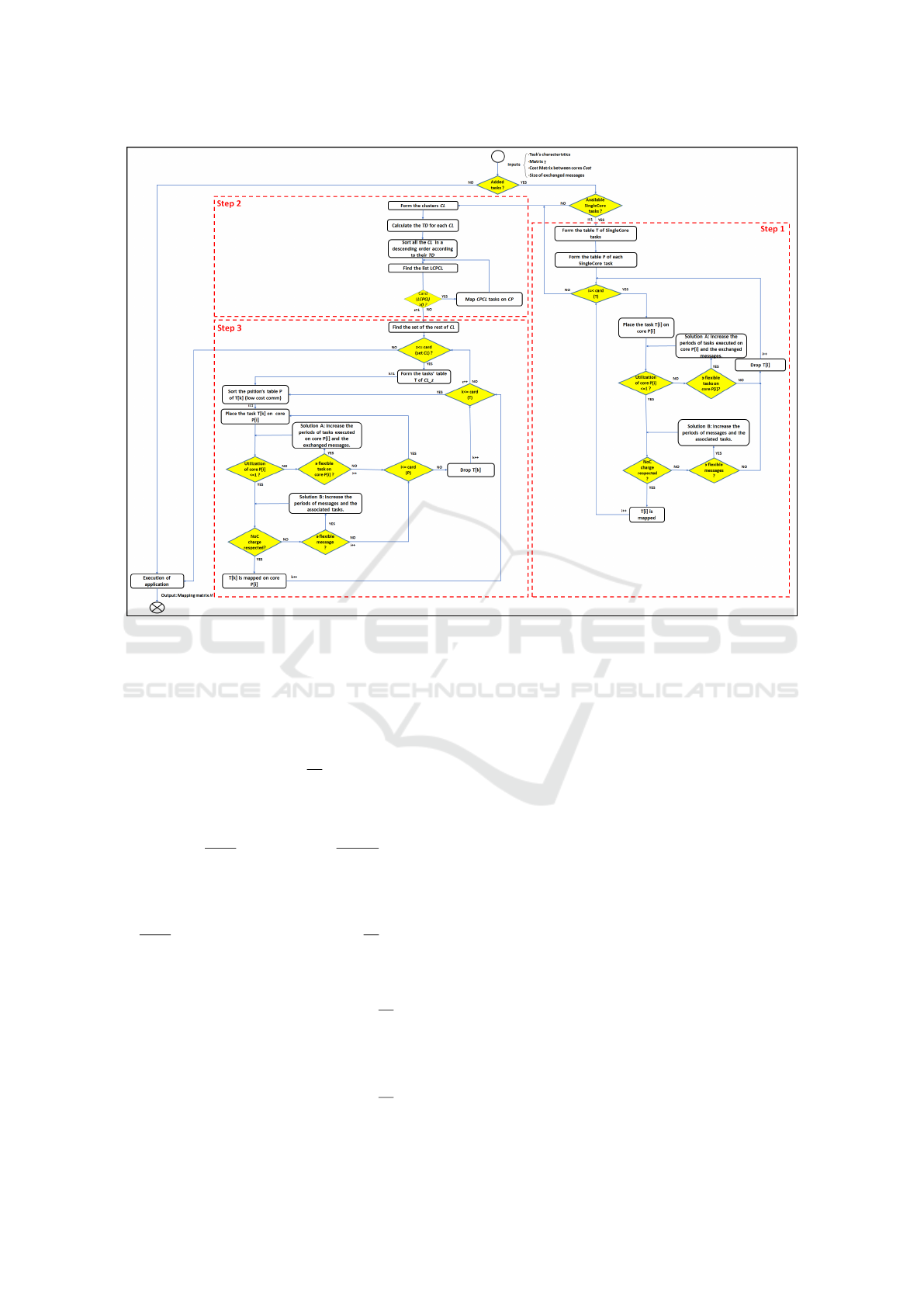
Figure 3: MappingTasks algorithm.
incremented. Hence, Pack
T
1, j
includes the tasks that
have a period in the range [1 ; Pk
T
1, j
], Pack
T
2, j
includes the tasks that have a period in the range
[Pk
T
1, j
+ 1 ; 2 ∗ Pk
T
1, j
], etc.
To satisfy the real-time constraints under the EDF pol-
icy, it is necessary that
∑
N
i=1
W
i
T
i
∗ H
i, j
≤ 1. Since
the periods are now multiple of the same value Pk
T
1, j
,
we get
∑
τ
i
∈Pack
T
1, j
W
i
Pk
T
1, j
+ ... +
∑
τ
i
∈Pack
T
x, j
W
i
x.Pk
T
1, j
≤ 1
thus,
1
Pk
T
1, j
∗
∑
τ
i
∈Pack
T
1, j
W
i
+ ... +
∑
τ
i
∈Pack
T
x, j
W
i
x
≤ 1
then,
Pk
T
1, j
≥
∑
τ
i
∈Pack
T
1, j
W
i
+ ... +
∑
τ
i
∈Pack
T
x, j
W
i
x
Since the periods are integer values, then,
Pk
T
1, j
=
∑
τ
i
∈Pack
T
1, j
W
i
+ ... +
∑
τ
i
∈Pack
T
x, j
W
i
x
(7)
where Pk
T
1, j
is the new period affected to tasks of the
first pack Pack
T
1, j
, x ∗ Pk
T
1, j
to the tasks of x
th
pack
Pack
T
x, j
. After adapting the tasks’ parameters running
on C
j
, all the tasks are executed without missing their
deadlines. Therefore, the real-time constraint can be
satisfied. As described in subsection 3.3, if the task’s
period is changed implicitly, then the message’s pe-
riod will be changed since T M
i, j
=T
i
. For that, the pe-
riods of messages that are associated to the adapted
tasks will be changed.
5.2.2 Solution B: Modification of Message’s
Period under Communication Constraint
For two added dependent tasks assigned to different
processors, a message is added automatically on the
NoC, we are interested in this part in the communi-
cation feasibility. If U
Com
(C
k
,C
l
) (∀ k, l ∈ [1..p]) is
greater than 1, then the communication between the
cores is not feasible. We propose to extend the peri-
ods of exchanged messages between the tasks running
on cores C
k
and C
l
. In order to satisfy the communi-
cation constraint, we assign each message to Pack
T M
x,k,l
according to its period. We formalize this problem by
Mapping of Periodic Tasks in Reconfigurable Heterogeneous Multi-core Platforms
105

∀ k, l ∈ [1..p] | U
Com
(C
k
,C
l
) > 1
Min
∑
N
i=1
∑
N
j=1
(Pk
T M
1,k,l
− (T M
i, j
mod Pk
T M
1,k,l
)) mod
Pk
T M
1,k,l
∗ H
i,k
∗ H
i,l
s.t.
Pk
T M
1,k,l
≥ Min(T M
i, j
), ∀ i, j ∈ [1..N]
Once Pk
T M
1,k,l
is calculated, the packs of messages are
processed such that Pack
T M
x,k,l
includes the messages
that have a period in the range [(x − 1) ∗ Pk
T M
x,k,l
+
1 ; x ∗ Pk
T M
1,k,l
], x ∈ N
+
.
To satisfy the communication constraint, it is neces-
sary that
∑
N
i=1
∑
N
j=1
W M
i, j
T M
i, j
∗ H
i,k
∗ H
j,l
≤ 1. Since
the periods T M
i, j
are now multiple of the same value
Pk
T M
1,k,l
, we get
∑
M
i, j
∈Pack
T M
1,k,l
W M
i, j
Pk
T M
1,k,l
+ ... +
∑
M
i, j
∈Pack
T M
x,k,l
W M
i, j
x.Pk
T M
1,k,l
≤ 1
Since the periods are integer, then,
Pk
T M
1,k,l
=
∑
M
i, j
∈Pack
T M
1,k,l
W M
i, j
+ ... +
∑
M
i, j
∈Pack
T M
x,k,l
W M
i, j
x
(8)
where Pk
T M
1,k,l
is the new period affected to the mes-
sages of the first pack Pack
T M
1,k,l
, x ∗ Pk
T M
x,k,l
to the mes-
sages of x
th
pack Pack
T M
x,k,l
. After adapting the param-
eters of messages running on the communication bus
between cores C
k
and C
l
, U
Com
(C
k
,C
l
) will be smaller
than 1. Therefore, the communication constraint can
be satisfied. Since the periods of messages are modi-
fied, it is necessary to adapt the periods of their send-
ing tasks.
6 EXPERIMENTAL STUDY
We present in the first subsection a case study in
which we calculate the communication cost through
the use of the proposed strategy. In the second, we
evaluate the performance of the strategy by generat-
ing a large number of random tasks.
6.1 Implementation of the Proposed
Strategy
Example - 1 In this example, we have considered
a typical program made up of 10 executable tasks
Figure 4: Inter task communication graph of example 1 (in
kilo bits).
{τ
1
, τ
2
, ..., τ
10
} to be executed on a MRS having three
cores {C
1
,C
2
,C
3
}. The tasks’ characteristics are de-
scribed in Tab. 1 and the inter task communication
graph is illustrated in Fig. 4. The cores connections
matrix Cost is shown as follow:
Cost =
C
1
C
2
C
3
↓ ↓ ↓
0 1 1
1 0 1
1 1 0
← C
1
← C
2
← C
3
Table 1: Tasks’ characteristics.
Task T
i
T
i
max
τ
1
5 6
τ
2
6 8
τ
3
10 10
τ
4
4 6
τ
5
12 22
τ
6
5 16
τ
7
8 21
τ
8
8 32
τ
9
6 14
τ
10
7 12
The WCET W
i
of each task is presented in Tab. 2
Table 2: WCET W
i
of tasks.
WCET C
1
C
2
C
3
W
1
1 3 0
W
2
1 0 2
W
3
2 0 0
W
4
1 2 0
W
5
2 0 0
W
6
0 2 0
W
7
0 0 3
W
8
0 2 1
W
9
0 0 2
W
10
0 2 1
The matrix γ
i, j
that represents the different possi-
ENASE 2018 - 13th International Conference on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to Software Engineering
106
bilities to execute tasks on cores is
γ =
C
1
C
2
C
3
↓ ↓ ↓
1 1 0
1 0 1
1 0 0
1 1 0
1 0 0
0 1 0
0 0 1
0 1 1
0 0 1
0 1 1
← τ
1
← τ
2
← τ
3
← τ
4
← τ
5
← τ
6
← τ
7
← τ
8
← τ
9
← τ
10
Step 1 Assign the SingleCore tasks:
τ
3
, τ
5
, τ
6
, τ
7
and τ
9
are SingleCore tasks and they
must be assigned.
Step 2 Assign the tasks of CPCL to their related com-
mon processor CP:
Tab. 3 shows the clusters CPCL that have common
processors CP and their data traffic T D.
Table 3: CPCL and CL clusters.
Clusters Tasks TD CP
CPCL
1
τ
1
, τ
2
, τ
3
13 C
1
CPCL
2
τ
4
, τ
5
10 C
1
CL
1
τ
6
, τ
7
, τ
8
14 -
CL
2
τ
9
0 C
3
CL
3
τ
10
0 C
2
, C
3
The proposed strategy assigns CPCL
1
and CPCL
2
on C
1
.
Step 3 Assign the tasks of the CL:
We start to assign the tasks of CL
1
because it has the
highest T D. Since τ
6
and τ
7
are already mapped in
step 1 to C
3
, the proposed strategy assigns τ
8
to C
2
(same core of the related task τ
6
).
The output of the proposed strategy is the mapping
matix H
H =
C
1
C
2
C
3
↓ ↓ ↓
1 0 0
1 0 0
1 0 0
1 0 0
1 0 0
0 1 0
0 0 1
0 1 0
0 0 1
0 1 0
← τ
1
← τ
2
← τ
3
← τ
4
← τ
5
← τ
6
← τ
7
← τ
8
← τ
9
← τ
10
The total cost of communication TotalCost is 40 units
of cost.
The processor utilization of the cores after assigning
tasks is presented in Tab. 4.
Table 4: Processor utilization for each core.
Core
1
Core
2
Core
3
Processor utilization U 0.983 0.935 0.708
At a particular time, the system undergoes the first
reconfiguration by adding two tasks that are presented
in Tab. 5.
Table 5: Added tasks.
Task T
i
T
i
max
τ
11
12 20
τ
12
4 15
The WCET W
i
of each new task is presented in
Tab. 6
Table 6: WCET W
i
of each new task.
WCET C
1
C
2
C
3
W
11
0 2 0
W
12
1 0 1
γ =
C
1
C
2
C
3
↓ ↓ ↓
0 1 0
1 0 1
← τ
11
← τ
12
The new inter task communication graph is illustrated
in Fig. 5.
Figure 5: Inter task communication graph application’s ex-
ample after adding tasks (in kilo bits).
After assigning τ
11
on C
2
, since it is a SingleCore
task, the processor utilization U
C
2
= 1.102 > 1. The
proposed strategy decreases U
C
2
by applying Solution
A, i.e., U
C
2
equals to 0.933, and the new periods of
tasks running on C
2
are presented in Tab. 7.
Since the task τ
12
communicates with τ
1
, then the
best position to place it, is C
1
(same core to τ
1
). Thus,
the processor utilization of C
1
after assigning τ
12
will
be equal to 1.233. The proposed strategy begins by
applying Solution A to decrease the processor utiliza-
tion. After calculating the new periods, it appears that
Mapping of Periodic Tasks in Reconfigurable Heterogeneous Multi-core Platforms
107
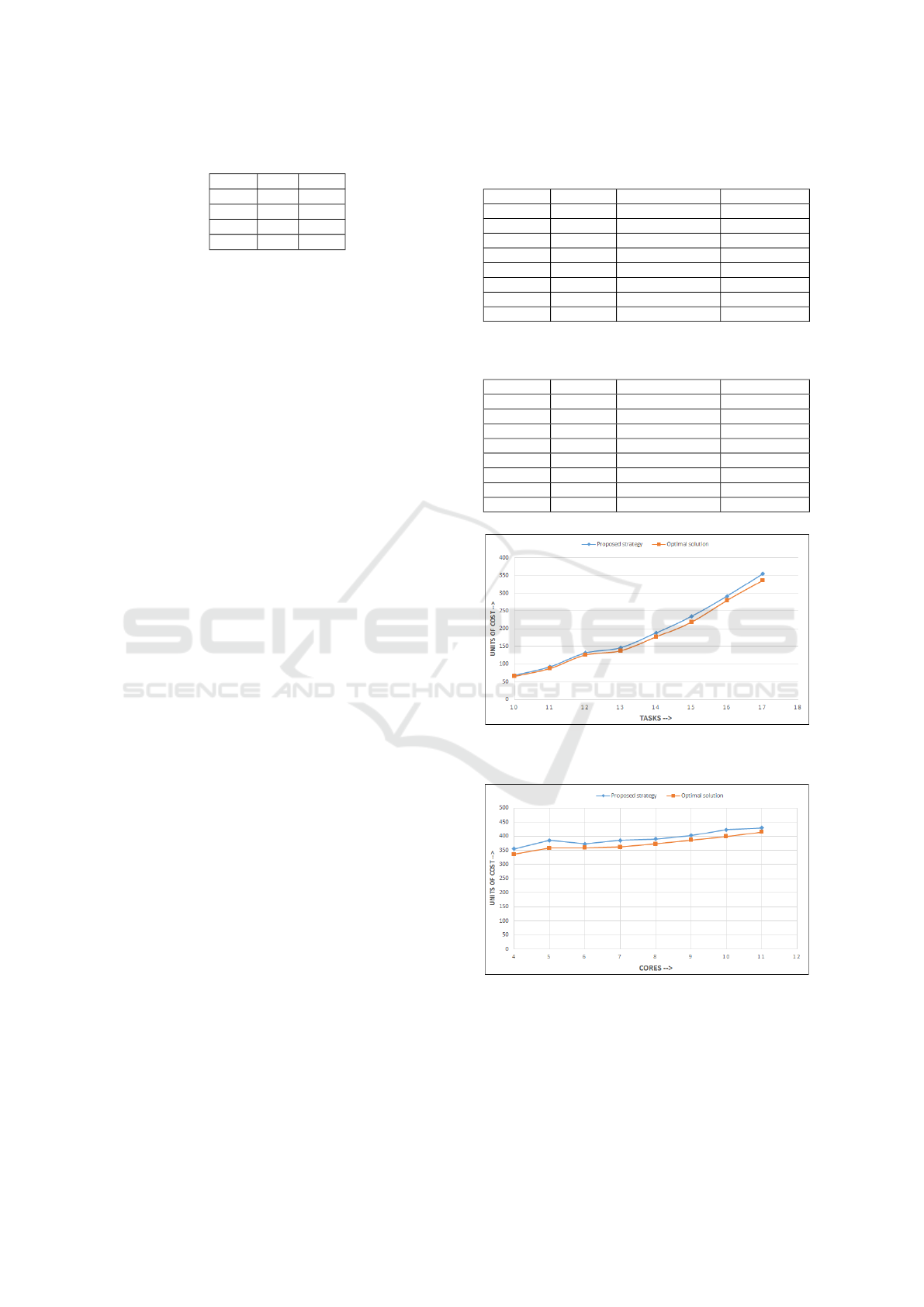
Table 7: Modification of period’s tasks running on C
2
.
Task T
i
T
i
max
τ
6
5 16
τ
8
10 32
τ
10
10 12
τ
11
15 20
Solution A can not increase the periods of tasks run-
ning on C
1
because their T
i
max
are not enough. Conse-
quently, the proposed strategy proposes to assign τ
12
to the next core C
3
and U
C
3
= 0.958.
Thus, the new mapping matrix H is given by
H =
C
1
C
2
C
3
↓ ↓ ↓
1 0 0
1 0 0
1 0 0
1 0 0
1 0 0
0 1 0
0 0 1
0 1 0
0 0 1
0 1 0
0 1 0
0 0 1
← τ
1
← τ
2
← τ
3
← τ
4
← τ
5
← τ
6
← τ
7
← τ
8
← τ
9
← τ
10
← τ
11
← τ
12
The new total cost of communication TotalCost is
equal to 40+20=60 units of cost.
6.2 Evaluation of Performance
In order to generalize the performance evaluation of
the proposed strategy, we generate randomly tasks by
using the developed tool Task −Generator presented
in (Gammoudi et al., 2016c). The proposed strategy
tries to form clusters of tasks and then allocate these
clusters to the cores. The effectiveness of the pro-
posed algorithm is compared with the optimal solu-
tion provided by the CPLEX solver (CPLEX, 2013).
For several sets of input data (N, p), the comparison
is shown in a tabular form as well as in a graphical
form. Tabs. 8 and 9 illustrated in the form of Figs. 6
and 7 respectively.
It can be observed from Fig. 6 that the values of
total cost obtained by the proposed strategy are near
to those obtained by the optimal solution, in the case,
when the number of cores is kept fixed and number
of tasks are taken in increasing order. The similar ob-
servation can also be made from Fig. 7 in the case
when the number of tasks is fixed and that of cores is
taken in an increased order. Thus, it is concluded that
the proposed strategy results in a near optimal cost in
both cases.
Table 8: Communication cost when number of tasks in-
creases.
Tasks N Cores p Proposed algo Optimal sol
10 4 68 66
11 4 92 88
12 4 131 126
13 4 146 138
14 4 188 177
15 4 235 219
16 4 292 280
17 4 355 336
Table 9: Communication cost when number of cores in-
creases.
Tasks N Cores p Proposed algo Optimal sol
17 4 355 336
17 5 385 358
17 6 372 359
17 7 385 361
17 8 390 372
17 9 402 386
17 10 423 399
17 11 430 415
Figure 6: Communication cost of our strategy when tasks
are in increasing order and number of cores is 4.
Figure 7: Communication cost of our strategy when cores
are in increasing order and number of tasks is 17.
7 CONCLUSIONS
Task allocation problem for reconfigurable multi-
core systems, using task clustering, is discussed.
ENASE 2018 - 13th International Conference on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to Software Engineering
108

A novel task model based on elastic coefficients is
proposed. This is to adapt task parameters allowing
task allocation and reconfiguration while minimizing
communication costs. The task allocation problem
is known to be NP-hard. When considering com-
munication costs, the proposed technique gives a
near optimal solution while respecting real-time
and communication constraints. Optimal solution
is obtained by formulating the problem as an ILP
problem and we compare the results of the proposed
technique with the optimal solution. After some
evaluations, we conclude that the proposed technique
results in a near optimal ones provided by the CPLEX
solver.
In a future work, we will focus on the implemen-
tation of the paper’s contribution in a real-time oper-
ating system that will be evaluated by assuming real
case studies.
REFERENCES
Baruah, S. and Goossens, J. (2004). Scheduling real-
time tasks: Algorithms and complexity. Handbook
of scheduling: Algorithms, models, and performance
analysis, 3.
Bhardwaj, P. and Kumar, V. (2013). An effective load bal-
ancing task allocation algorithm using task cluster-
ing. International Journal of Computer Applications,
77(7).
Bui, B. D., Pellizzoni, R., and Caccamo, M. (2012). Real-
time scheduling of concurrent transactions in multido-
main ring buses. IEEE Transactions on Computers,
61(9):1311–1324.
Buttazzo, G. C., Lipari, G., and Abeni, L. (1998). Elastic
task model for adaptive rate control. In Real-Time Sys-
tems Symposium, 1998. Proceedings. The 19th IEEE,
pages 286–295. IEEE.
Carle, T., Potop-Butucaru, D., Sorel, Y., and Lesens, D.
(2015). From dataflow specification to multiprocessor
partitioned time-triggered real-time implementation.
Leibniz Transactions on Embedded Systems, 2(2):01–
1.
Cecilio, J. and Furtado, P. (2014). Architecture for uniform
(re) configuration and processing over embedded sen-
sor and actuator networks. IEEE transactions on in-
dustrial informatics, 10(1):53–60.
CPLEX (2013). Ibm ilog cplex optimize. In http://www-
03.ibm.com/software/products/en/ibmilogcpleoptistud/.
Gammoudi, A., Benzina, A., Chillet, D., and Khalgui, M.
(2016a). New reconfigurable middleware for adaptive
rtos in ubiquitous devices. In 10th International Con-
ference on Mobile Ubiquitous Computing, Systems,
Services and Technologies.
Gammoudi, A., Benzina, A., Khalgui, M., and Chillet,
D. (2015). New pack oriented solutions for energy-
aware feasible adaptive real-time systems. In Interna-
tional Conference on Intelligent Software Methodolo-
gies, Tools, and Techniques, pages 73–86. Springer.
Gammoudi, A., Benzina, A., Khalgui, M., and Chillet,
D. (2016b). Real-time scheduling of reconfigurable
battery-powered multi-core platforms. In Tools with
Artificial Intelligence (ICTAI), 2016 IEEE 28th Inter-
national Conference on, pages 121–129. IEEE.
Gammoudi, A., Benzina, A., Khalgui, M., Chillet, D., and
Goubaa, A. (2016c). Reconf-pack: A simulator for
reconfigurable battery-powered real-time systems. In
30th European Simulation and Modelling Conference.
Gharsellaoui, H., Khalgui, M., and Ahmed, S. B. (2013).
Reconfiguration of synchronous real-time operating
system. International Journal of System Dynamics
Applications (IJSDA), 2(1):114–132.
Hu, J. and Marculescu, R. (2005). Energy-and
performance-aware mapping for regular noc architec-
tures. IEEE Transactions on computer-aided design
of integrated circuits and systems, 24(4):551–562.
Khemaissia, I., Mosbahi, Olfa, K., Mohamed, L., and Zhiwi
(2016). New methodology for feasible reconfigurable
real-time network-on-chip noc. In Proc. 11th Int.
Conf. Softw. Eng. App on.
Khemaissia, I., Mosbahi, O., and Khalgui, M. (2014). Re-
configurable can in real-time embedded platforms.
In Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
(ICINCO), 2014 11th International Conference on,
volume 1, pages 355–362. IEEE.
Li, L., Li, S., and Zhao, S. (2014). Qos-aware scheduling
of services-oriented internet of things. IEEE Transac-
tions on Industrial Informatics, 10(2):1497–1505.
Liu, C. L. and Layland, J. W. (1973). Scheduling algo-
rithms for multiprogramming in a hard-real-time en-
vironment. Journal of the ACM (JACM), 20(1):46–61.
Marinoni, M. and Buttazzo, G. (2007). Elastic dvs man-
agement in processors with discrete voltage/frequency
modes. IEEE Transactions on industrial informatics,
3(1):51–62.
Quadri, I. R., Gamati
´
e, A., Boulet, P., Meftali, S., and
Dekeyser, J.-L. (2012). Expressing embedded sys-
tems configurations at high abstraction levels with uml
marte profile: Advantages, limitations and alterna-
tives. Journal of systems architecture, 58(5):178–194.
Rooker, M. N., S
¨
under, C., Strasser, T., Zoitl, A., Hum-
mer, O., and Ebenhofer, G. (2007). Zero downtime re-
configuration of distributed automation systems: The
εcedac approach. In Holonic and Multi-Agent Systems
for Manufacturing, pages 326–337. Springer.
Schranzhofer, A., Chen, J.-J., and Thiele, L. (2010). Dy-
namic power-aware mapping of applications onto het-
erogeneous mpsoc platforms. IEEE Transactions on
Industrial Informatics, 6(4):692–707.
Tosun, S., Ozturk, O., and Ozen, M. (2009). An ilp for-
mulation for application mapping onto network-on-
chips. In Application of Information and Communi-
cation Technologies, 2009. AICT 2009. International
Conference on, pages 1–5. IEEE.
Vrba, P. and Marik, V. (2010). Capabilities of dynamic
reconfiguration of multiagent-based industrial control
Mapping of Periodic Tasks in Reconfigurable Heterogeneous Multi-core Platforms
109

systems. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and
Cybernetics-Part A: Systems and Humans, 40(2):213–
223.
Wang, X., Khemaissia, I., Khalgui, M., Li, Z., Mosbahi,
O., and Zhou, M. (2015). Dynamic low-power re-
configuration of real-time systems with periodic and
probabilistic tasks. IEEE Transactions on Automation
Science and Engineering, 12(1):258–271.
Wang, X., Li, Z., and Wonham, W. (2016). Dynamic
multiple-period reconfiguration of real-time schedul-
ing based on timed des supervisory control. IEEE
Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 12(1):101–
111.
ENASE 2018 - 13th International Conference on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to Software Engineering
110
