
APT RPG: Design of a Gamified Attacker/Defender Meta Model
Robert Luh
1,2,3
, Marlies Temper
1
, Simon Tjoa
1,2
and Sebastian Schrittwieser
1,2
1
St. P
¨
olten University of Applied Sciences, St. P
¨
olten, Austria
2
Josef Ressel Center TARGET, St. P
¨
olten, Austria
3
De Montfort University, Leicester, U.K.
Keywords:
Security Model, Gamification, Attack Patterns, Controls, Malware, Intrusion Detection.
Abstract:
We present a meta model for comprehensive, time-enabled attacker/defender behavior ready for incorpora-
tion in a dynamic, imperfect information multi-player game that derives significant parts of its ruleset from
established information security sources such as STIX, CAPEC, CVE/CWE and NIST SP800-53. Concrete
attack patterns, vulnerabilities, and mitigating controls are mapped to their counterpart strategies and actions
through practical, data-centric mechanisms. The gamified model furthermore considers and defines a wide
range of actors, assets, and actions, thereby enabling a detailed assessment of cyber risks while giving analysts
the opportunity to explore specific attack scenarios in the context of their own infrastructure.
1 INTRODUCTION
IT systems are threatened by a growing number of
cyber-attacks. With the emergence of Advanced Per-
sistent Threats (APTs), the focus shifted from off-the-
shelf malware to multipartite attacks that are tailo-
red to one specific entity. These targeted threats are
driven by varying motivations, such as espionage or
high-profile sabotage, and often cause significantly
more damage.
APTs are typically conducted by dedicated groups
within organized crime, industry, or nation state intel-
ligence and increasingly affect less prominent targets
as well. While APTs utilize malware like most other,
more conventional attacks, their level of complexity
and sophistication is usually significantly higher. It is
becoming increasingly difficult to plan and implement
an organization’s defense in response to the targeted
threat. At the same time, attack patterns, vulnerabili-
ties, and mitigation control catalogs provide a infor-
mation that can rarely be interleaved due to varying
levels of granularity or abstraction. Most importantly,
few models provide a means to map concrete system
events as seen on affected assets to a semantic inter-
pretation, known system flaw or definitive counterme-
asure. Time and system interdependencies are rarely
considered. The multi-stage nature of emerging APTs
makes it even harder for analysts or business actors to
address current threats from the cyber domain. This
increasing complexity makes it vital to explore no-
vel approaches to attack/defense modeling, threat in-
telligence, knowledge extraction, and malicious acti-
vity detection on multiple layers, while preserving the
flexibility needed to model new scenarios.
The gamified model introduced in this paper helps
to assess the risk of targeted attacks on arbitrary infra-
structures by providing an extensible framework for
simulating attacker and defender behavior in an ad-
versarial setting. APT campaigns of various scope
and impact can be modeled on different levels of ab-
straction, while incorporating the temporal factor in
addition to systemic provider/consumer relationships.
Even though the model has been created with maxi-
mum flexibility in mind, the introduced rule set also
provides a concrete solution for depicting and as-
sessing real-life cyber-attacks on private, corporate,
and national IT infrastructures. All the required in-
teracting components are based on established lan-
guages and standards for observables, actors, attack
patterns, and defense measures. Means to mapping
on-system events such as sequences of system opera-
tions, function calls or kernel operations to the game
model are an integral part of the RPG and can be lin-
ked to novel and existing pattern or anomaly detection
systems.
Furthermore, the game based on the introduced
model helps to generate new knowledge and to un-
derstand how specific threats impact a system. Shor-
tcomings in current defense implementations are in-
advertently highlighted. Managers are encouraged to
Luh R., Temper M., Tjoa S. and Schrittwieser S.
APT RPG: Design of a Gamified Attacker/Defender Meta Model.
DOI: 10.5220/0006717805260537
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy (ICISSP 2018), pages 526-537
ISBN: 978-989-758-282-0
Copyright
c
2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

explore new threats and are presented with possible
organizational and system-level mitigations as sugge-
sted by accepted security standards. Analysts and IT/-
security experts are provided the means to model con-
crete hacks and link them to the output of intrusion
detection systems currently in place at their organiza-
tion. Altogether, the gamified approach is designed
to raise awareness and improve risk assessment while
closing the gap between high-level kill chains, in-
dependently published countermeasures and policies,
and concrete attacks depicted by real-word events and
carried out through the exploitation of systemic vul-
nerabilities and weaknesses.
Specifically, we contribute by:
• presenting an easily expandable, time-enabled at-
tacker/defender meta model for depicting and as-
sessing advanced persistent threats;
• providing a link to various standards and formats,
such as STIX-defined data observables, CAPEC
attack patterns, as well as operational risk asses-
sment and mitigation planning within a gamified
setting;
• introducing a mapping mechanism for linking at-
tacker behavior to opposing security and privacy
controls listed in the NIST SP800-53 standard.
Please bear in mind that the game implementation
itself is not part of this model-centric paper. It will be
discussed and evaluated in an upcoming publication.
The remainder of this paper is structured as fol-
lows: After exploring related work in both the in-
trusion modeling and game theory domains (Section
2), we discuss the theoretical aspects of our model
and present a high-level view on the multi-layered ap-
proach employed (Section 3). We furthermore define
actions and all their component classes in the context
of the APT RPG, while paving the way for an acces-
sible game rule system that has been concurrently de-
veloped. Section 4 specifies our practical approach
to combining STIX vocabularies, CAPEC patterns,
CWE, CVE entries, and NIST SP800-53 controls into
one model, which takes all its components from ex-
isting sources across the threat information domain.
Section 5 concludes the paper and provides a research
outlook.
2 RELATED WORK
Since the APT RPG borrows concepts from attack
modeling as well as game theoretic approaches, we
take a closer look at similar works in both areas.
Several researchers introduced attacker/defender mo-
dels that consider numerous factors and properties:
Like the APT RPG, the Diamond Model of Intru-
sion Analysis (Caltagirone et al., 2013) establishes the
basic elements of generic intrusion activity, called an
event, which is composed of four core features: ad-
versary, infrastructure, capability, and victim. It ex-
tends events with a confidence score that can be used
to track the reliability of the data source or a speci-
fic event. While some of its premises are similar to
our own work, the Diamond Model does not consi-
der Enablers or Disablers (see Section 3.3) or any au-
tomation for determining specific actions on the at-
tacker’s and defender’s side. While it is a powerful
template in its own regard, the APT RPG provides
these mechanisms – and more. Its gamified core pro-
vides the ready-to-use framework for simulation and
automated knowledge discovery. In summary, the Di-
amond Model and the APT RPG share commonalities
and could potentially benefit from each other in terms
of feature modeling, terminology, and approach to ga-
mification.
In the work by Syed et al. (2016), the authors pre-
sent a unified cyber security ontology (UCO) exten-
ding the Intrusion Detection System ontology by Un-
dercoffer et al. (2004). UCO is a semantic version of
STIX with a link to cyber security standards similar
to the ones used in the APT RPG. Real-world kno-
wledge appended using the Google knowledge graph
and various other knowledge bases. Syed et al. pro-
vide little information about data retrieval mecha-
nisms and general automation. The main use ca-
ses emphasized are the identification of similar soft-
ware, and the association of vulnerabilities with cer-
tain (classes of) products. Unlike the APT RPG, UCO
does not consider temporal information or measures
of uncertainty.
On the side of game theory, introduced models
are usually separated into several classes, depending
on a multitude of factors. Roy et al. (2010) survey a
number of approaches for the network security dom-
ain and categorize non-cooperative games into static
and dynamic scenarios of varying levels of informa-
tion quality and completeness. A good starting point
for literature review, we classified the APT RPG in
accordance to Roy et al.’s schema (see Section 3.2).
Cook et al. (2016) presents an overview of risk
assessment strategies for industrial control systems
(ICS) that includes, among others, the game theo-
retic approach. The authors conclude that there ex-
ists no unified risk model for hitherto unconsidered
ICS scenarios that incorporates events, threats, vulne-
rabilities, and general consequences with a measure
of uncertainty. Suggested future work includes the
development of an environment to allow an intelli-
gent adversary to test an ICS’s defenses in a nonde-

structive (e.g. game theoretic) manner. This is spe-
cifically addressed by the APT RPG. Similarly, Le-
wis (2014) offers an introduction to risk assessment
strategies for critical infrastructure protection, inclu-
ding an in-depth look at Bayesian belief networks and
game theory applications.
Applied to a power grid scenario, Holmgren et al.
(2007) introduce a model for studying defense strate-
gies against hostile actions leading to a power shut-
down. Outages are split into stages ranging from pre-
vention to recovery. Unlike the more flexible APT
RPG, Holmgren et al.’s model is a perfect and com-
plete information game that does not allow adding
new components to the existing network of assets. In
addition, only qualified attackers of static skill, deter-
mination, and existing access to the system are con-
sidered. The overall motivation of implementing the
power grid game is still comparable to our approach:
It aims to help with resource planning, risk screening,
and with studying generic mechanisms that enhance
the overall understanding of attacks against a system.
Contrary to the above, Nguyen et al. (2009) for-
mally describe an abstract zero-sum, incomplete in-
formation game for network security scenarios. Their
network model is based on the concept of linear in-
fluence networks (Miura-Ko et al., 2008), which is
represented by two weighted directed graphs that sig-
nify the relationship of security assets as well as deno-
ting vulnerability correlation among the nodes. The
resulting influence matrix describes the contribution
of an asset to overall security. If an asset is taken
down by the attacker, its node is removed from the
network, lowering the security rating for all connected
assets. For common assets, compromising one node
changes the probability that another linked asset will
come under attack. Unlike the APT RPG, Nguyen
et al. do not consider specific actors, assets, scenarios,
or data sources. Since compromised nodes are remo-
ved entirely from the network, the model does not di-
rectly support stepped attacks or semi-successful at-
tacker actions. As a pure zero-sum game, the model
does not offer the same level of flexible payoff as the
system introduced in this paper.
3 ATTACKER/DEFENDER
MODEL
3.1 Overview
Our gamified approach is based on a novel attacker/-
defender model tailored to depict interconnected ser-
vices that maintain – and operate with – various ty-
pes of information. Consuming and providing servi-
ces are represented by parent and child entities that
enable the modeling of arbitrary, interdependent sys-
tems and infrastructures. At the same time, the APT
RPG considers on-system events that define nominal
and anomalous behavior, thereby establishing a link
to actual attacker behavior in the form of individual
actions.
Another main advantage of the model is its flexi-
bility: Services, information and behavioral data can
range from individual system processes on a single
computer system to networked components in an en-
tire branch of infrastructure. Figure 1 provides an
overview of the interplay of the three main layers –
service, information, and data – and sketches the link
to the APT RPG core model. Below axioms describe
the cornerstones of our model. More in-depth defini-
tions of terms can be found in Section 3.3.
• Axiom 1 – Each service maintains and is main-
tained by information. Specifically, a service
(hVictimi class, see Section 3.3) is controlled
by configuration (technical or organizational set-
tings and policies controlling the service’s functi-
ons and parameters) while it maintains knowledge
that either represents potentially sensitive infor-
mation relevant to the service owner, or the confi-
guration itself. Information is protected by con-
trols (technical or organizational measures, see
hEnableri class) that focus on safeguarding con-
fidentiality and integrity.
• Axiom 2 – Services are both consumers and pro-
viders for other services. A service (hVictimi)
is an interdependent entity that consumes and/or
provides functionality for other entities. The sta-
tus (ability to provide functionality to a consumer)
of a service and its place in a hierarchical tree of
services is protected by controls mitigating avai-
lability attacks. Erroneous behavior of a provider
negatively impacts its consumers.
• Axiom 3 – Service behavior is described by
events. Both nominal (baseline) and anoma-
lous (attacker) behavior is synonymous to one
or several events (hEventi class) captured and
pre-evaluated by a dedicated detection measure.
Events are the link between the attacker/defender
model, the APT RPG core system, and actual mo-
nitoring data. In the context of the game, a se-
quence of these behavioral snippets are referred
to as actions X.
Based on these premises, we can tell straightfor-
ward attack stories with significant depth and level of
detail, which we later build upon.
For example, an operating system process might

Figure 1: High-level view on the APT-RPG meta model. The top half represents the layers of the base attacker/defender
model while the lower portion depicts the APT RPG gamified rule system.

trigger the event Evt(operation, layer, argument) =
create-data-dropped.exe, followed by the event
start-operation-dropped.exe, which results in
an anomaly with a specific value denoting its devia-
tion from a set baseline. Here, this occurrence would
affect the confidentiality of user-specific knowledge
that is handled by the modeled service chrome.exe,
thereby changing integrity of the service and its child-
ren to ‘compromised’, while its status (‘running’) re-
mains unaffected.
On a less granular IT service level, a generic event
destroy-config-webserver caused by the purpo-
seful alteration of a web server’s settings would affect
the configuration on an availability level, which in
turn affects the electronic campus service of an edu-
cation organization, changing its status and the status
of its children to ‘stopped’/‘compromised’.
Since we want to not only sketch attack scenarios
but also bridge the gap between actors, assets, vulne-
rabilities, concrete attack patterns, events and coun-
termeasures, we extended the model with formally
defined actions, which in turn shape the foundation
for the APT RPG game model. In the following, we
detail some of the game theoretic principles of our
model before defining classes and mappings of model
components.
3.2 Game Principles
Instead of relying solely on decision models, adver-
sarial behavior can be studied using game situati-
ons (Lewis, 2014). Techniques associated with game
theory, which is defined as “the study of models of
conflict and cooperation between intelligent, rational
decision-makers” (Roger, 1991), can be used to mo-
del multi-player scenarios that allow participants to
pursue goals and rewards by acting in the most fa-
vorable, risk-adverse, or cost-effective way possible.
The outcome of a game presents the actors with a stra-
tegy for resource allocation, risk minimization, or a
general strategy to meet a certain attack or defense
objective.
Even though it is a model/game hybrid, our RPG
can be categorized according to several principles of
game theory, as summarized by Roy et al. (2010).
Specifically, the APT RPG has the following proper-
ties:
• Non-cooperative Nonzero-sum Game: Opposi-
tion between players is an integral part of the cur-
rent design: Player 1 (attacker) is always combats
player 2 (defender) and tries to achieve adverse
goals by stealing information, manipulating the
integrity of data or systems, or by shutting them
down entirely. Even though actions are not typi-
cally assigned points that are symmetrically gai-
ned/lost (making it nonzero-sum), it can be argued
that the mechanism of asset compromise is in fact
a zero-sum game, where the defender loses inte-
grity while the attacker gains an advantage. In ot-
her situations, win/loss is represented by an incre-
ase or decrease of attributes or action success and
detection chance. These bonuses are one-sided,
yet always shift the balance between the players
away from equilibrium.
• Asymmetric Strategy: The strategy sets of the
two players are not identical – the attacker draws
from a different pool of actions than the defen-
der. This stems from the difference in goal and
purpose: Attackers will attempt to penetrate a sy-
stem using malware and by exploiting vulnerabi-
lities, while a defender tries to counter these acti-
ons by implementing technical and organizational
controls.
• Dynamic/Extensive game with Static Elements
(Roy et al., 2010): While the game uses sequen-
tial moves characteristic for dynamic games, the
second player typically remains unaware of the
first player’s actions, making the model bear some
resemblance to a strategic setting where players
act simultaneously and in secret. At its core, the
APT RPG remains dynamic – emphasized by its
multi-stage nature.
• Imperfect Incomplete Information: As stated
above, player 1 does not necessarily know the mo-
ves previously made by the attacker. It is in fact
vital to his or the success of player 2 that acti-
ons performed remain secret, thereby potentially
causing the defender to make imperfect decisions.
At the same time, the general set of strategies is
known to both sides, however the exact payoff in
a certain situation is not, due to the lack of in-
formation about past activity and their impact on
success and detection chances (incomplete infor-
mation).
• Bayesian Formulation of Static Elements: In
the RPG, players have incomplete information on
the other players, especially when it comes to acti-
ons and strategies, which are derived from the at-
tacker’s type and ultimate objective. There is, ho-
wever, a fixed probability that players, being one
of 8 available classes, need to conduct/ defend
against one of three kinds of attacks on a finite
set of assets in order to win the game.
• Finite & Discrete: While some action com-
binations are continuous in nature, the general
action/reaction game follows a discontinuous se-
quence. The number of game turns is limited by

Figure 2: Information set of the defending player for victim
system compromise through attacker action a
v1
, shown in
extensive form (Kuhn, 2009). In the above case, player 2
successfully unveils a
v1
, giving him the chance to specifi-
cally counteract the gain L(a
v
) of player 1 by increasing his
own score L(d
v
) through defense action d
v1
. Below tree re-
presents the limited information set for player 2, when a
v1
remains undetected.
an exhaustible resource – Initiative (i.e. time effi-
ciency).
Following Roy et al.’s taxonomy, our game can be
classified as non-cooperative, dynamic game with im-
perfect and incomplete information that draws from
static elements of Bayesian formulation. Akin to You
and Shiyong (2003), our two-party hybrid zero-sum
game G is defined by the triplet:
G = (A, D, F), where:
• A is a set of strategies of player 1 (attacker),
• D is a set of player 2 (defender) strategies, and
• L is, for select game concepts (see below), a real-
valued function A× D. Therefore, L(a, d) is a real
number for every a ∈ A and d ∈ D.
During the game, player 1 chooses action a ∈ A
targeted at victim v ∈ V , which is kept secret un-
less player 2 meets detection requirements (see Figure
2). If action a
v
is conducted successfully, player 1
gains a number of points L(a
v
) representing the le-
vel of victim compromise, which are directly or in-
directly deducted from the respective defender’s tally
(payoff). Independently from the outcome of the de-
tection attempt, player 2 chooses d ∈ D for victim
v ∈ V , attempting to counter the (assumed) action a
v
.
Points L(d
v
) are computed, fully negating L(a
v
) in
the best of cases. Specifically, this principle applies
to victim system integrity and status (see Figure 2 as
well as the hVictimi definition in Section 3.3), success
chance of hostile attacks and defensive actions (see
hPropertiesi and hEnablersi/hDisablersi below), and
some other attribute or resource bonuses or penalties.
It is important to bear in mind that the RPG’s vic-
tory conditions are only indirectly affected by these
shifts and that an increased numeric distance from
the equilibrium of factors other than victim system
integrity and status does not always guarantee one
player’s domination over the other. In fact, victory is
determined by the exhaustion of available (temporal)
resources or the successful compromise of the victim
asset within an allotted time window.
In the following, we introduce the class specifics
of our model and define the concept of an action.
3.3 Definitions
Actions are at the core of the joint model and link
real-world service and actor behavior to concrete data
points such as observable attack patterns or event se-
quences. Formally, an action X is defined as n-tuple of
typical length n = 11, whereas the model’s flexibility
allows for the omission of unneeded elements. Sim-
ply put, an action is performed by an actor and furt-
her enabled or disabled by equipment, policies, and
tools. It is assigned a category within the model, in-
cluding usage requirements, properties pertaining to
its success, and a detection chance. Attack patterns
and associated events tie it to measurable real-world
data points.
X = h
hAttackActorhClass, Motivation, Attributes,
Resourcesii,
hDe f enseActorhClass, Attributes, Resourcesii,
hEnablerhType, E f f ect, Attributes, Nameii,
hDisablerhType, E f f ect, Attributes, Nameii,
hVictimhType, Name, Exposure, Parent,
Con f iguration, Knowledge,Status, Integrityii
hAttackClasshStage,PatternClass, Modeii,
hDe f enseClasshCategory,ControlClass,
ActionClassii,
hRequirementsh∗ActorhAttributes,
Resourcesi,VictimhExposure, Integrityii,
hPropertieshSophistication, SuccessChance,
DetectionChanceii,
hAttackPatternhImpact, IDii,
hEventshType, Time, Sequence, Parent,
Operation, Argumentii
i

AttackActor and DefenseActor correspond to the
actor types introduced in the ThreatActorType vo-
cabulary schema of the STIX threat information lan-
guage (Barnum, 2012). Each attacker is described
as a unique class with their own motivation, primary
attributes in the form of Sophistication (measure of
an actor’s skill, SO), Determination (measure of ac-
tor motivation and the strength of their cause, DE)
and Wealth (financial resources of an actor, W E), as
well as operational resources such as Initiative (INI)
and Insight (INS): Initiative (i.e. time efficiency) is
an attribute derived from SO and DE that determines
the number of overall actions each actor can perform.
Each action in the strategy set has a time requirement,
making this attribute the main resource for all attack
and defense activities. Insight, on the other hand, me-
asures the knowledge gained about their opponent and
thereby increases the overall chance of success when
attacking/defending.
The currently modeled hAttackActori classes in
the RPG include: Cyber Espionage Operations (T H),
Hacker (white (EX ), gray (RO), black hat (RA)),
Hacktivist (CR), State Actor/Agency (OP), Insider
(IN), and Disgruntled Customer (PR).
Each attacker class has a range of possible moti-
vations. These goals represent the overall objective of
the attack and provide additional context for determi-
ning attacker attributes and skills. They correspond to
the STIX Threat Actor Motivation vocabulary and
encompass various ideological goals (id.∗), as well as
ego-centered (eg), financial ( f i), military (mi), oppor-
tunistic (op), and political (po) motivations. The actor
creation routine of the RPG supports automation of
the entire process and provides percentages defining
likely actor/goal combinations.
AttackActor = h
hClass{T H, EX, RO, RA,CR,OP, IN, PR}i,
hMotivation{id.∗, eg, f i, mi, op, po}i,
hAttributeshSO{1..n}, DE{1..n},W E{1..n}ii,
hResourceshINI{1..n}, INS{1..n},
hEnableriii
i
Following the same approach, hDe f enseActori
classes include the three primary sectors (CP, CM,
CS), infrastructure (IF), military (MI), state actors/a-
gencies (SA), the education sector (ED), and private
individuals (PI).
De f enseActor = h
hClass{CP,CM,CS, IF, MI, SA, ED, PI}i,
hAttributeshSO{1..n}, DE{1..n},W E{1..n}i,
hResourceshINI{1..n}, INS{1..n},
hDisableriii
i
So-called Enablers represent attack tools and vul-
nerabilities employed by the aggressor. They have spe-
cific effects on the target system and come with a wide
range of properties (e.g. level of impact or maturity of
a vulnerability-type Enabler (see CVE/CVSS mapping
in Section 4)) and prerequisites (e.g. privileges and le-
vel of user interaction required) that need to be con-
sidered. Attacker equipment (AT T.∗) subsumes mos-
tly attack tools (MPT , Pwd), OS, application and (wi-
reless) network scanners (Sca), various types of mal-
ware (Mal), and vulnerabilities (VU L) that modify the
chance of success against specific target assets or ac-
tors.
Some enablers and disablers only target or ap-
ply to specific equipment categories. The general
hE f f ecti of using equipment (or attack actions for that
matter) is described by the respective subclass. Ty-
pically, various resources, attributes, and detection/-
success (∗DC/∗SC) probabilities are either increased
(inc∗) or decreased (dec∗) upon use, which further
impacts future events and the overall course of the
game. For the hE f f ectTargeti, we generally diffe-
rentiate host-based (H), network-based (N), industrial
(I), mobile (M), and third-party (T ) equipment. Ena-
blers have an adverse hImpacti on the CIA status of
the victim (more details below).
Enabler = h,
hType{AT T.∗,VUL.∗}i,
hE f f ecthType{incSC, decDC}, E f f ectValue{1..n},
E f f ectTarget{H, N, I, M, T }ii,
hAttributeshSophistication{1..n}, Level{1,2}i,
hPropertieshPrivileges{high, low},
UserInteraction{none, required},
hImpacthC{low, med, high},
I{low, med,high}, A{low, med, high}i,
Maturity{unproven, PoC, f unctional, high}iii,
hName{ ToolName }i
i
Defenders use Disablers to thwart their adversary.
Such defender equipment encompasses assets to be
protected (AST ), security policies (POL), fixes (FIX )
that counter vulnerabilities, as well as tools that incre-
ase security (SEC.∗, e.g. through prevention (Pre)), de-
tect (Det), delay (Del), or generally hinder the attacker
(Cnt). The respective effects aim to reverse or mitigate
the damage caused by attacker equipment and actions.

Disabler = h,
hType{AST.∗, SEC.∗, POL.∗, FIX.∗}i,
hE f f ecthType{decSC, decSC}, E f f ectValue{1..n},
E f f ectTarget{H, N, I, M, T }ii,
hAttributeshSophistication{1..n}, Level{1,2}ii,
hPropertieshMaturity{o f f icial, temporary,
workaround}ii,
hName{ SystemName }i
i
The Victim class describes the system that might
be targeted by the attacker, may that be a specific
asset or a disabler. Furthermore, victim information
differentiates between internal and exposed systems,
which can be accessed directly from within the DMZ,
and identifies service status, integrity, and systemic
parents that represent consumers and providers.
In each gamified scenario, the attacker attempts to
achieve his or her goal by compromising a victim in
a specific fashion, i.e. one tries to compromise one of
the defender’s assets (change its hVictimhIntegrityii
to ‘compromised’ or its hVictimhStatusii) to ‘stop-
ped’). There are three kinds of possible attacks on
any asset, in accordance to the CIA triangle (Whitman
and Mattord, 2011): Confidentiality attacks (theft of
information), integrity attacks (altering of informa-
tion), and availability attacks (system status changes),
which are part of the hAttackClassi component below.
Victim = h
hType{Asset, SecuritySolution}i,
hName{ SystemName }i,
hExposure{internal, exposed}i,
hParent{hVictimi, hDisableri}i,
hCon f iguration{tech, org}i,
hKnowledge{In f ormation, hCon f igurationi}i,
hStatushOperationStatus{running, stopped}i,
hIntegrity{nominal, a f f ected, compromised}ii
i
AttackClass contains categorization into the APT
kill chain (sub-)stage (hStagei), as well as the class
of attack patterns as defined by the CAPEC link ca-
tegorization introduced below. hModei identifies the
optional CIA goal and impact rating of the action. Re-
spectively, the DefenseClass refers to the NIST link
categories which allows the assignment of a mitiga-
ting control to the modeled attack. See Section 4 for
more information about categorization.
AttackClass = h
hStage{R.∗,W.∗, D.∗, E.∗, I.∗,C.∗, A.∗}i,
hPatternClass{IG, IN, SE, SA, FA, BF, IA, DM,
PR,CO}i,
hModehGoal{C, I, A}, Rating{low, med, high}ii
i
De f enseClass = h
hCategory{organization, in f ormation
system}i
hControlClass{IL,CP, AW,SP, FI, AP, AC, DI,
SI,CS}i
hActionClass{ACM,ACE, IFE, LEP, REA,
AMO, RST,COM,CCC,COS,COP,COP, AUM
INH, NOM, MES,PAC, SEP, SCP, BOP,CRP,
FLR, MCP, ISM}i
i
Requirements identify the minimum actor attribu-
tes and resources needed to conduct the attack, as
well as other prerequisites in the form of system ex-
posure. Requirements are optional and depend on the
complexity of the respective attack, which is defined
through its Properties, namely minimum skill (So-
phistication SO) and the chance of success (SC) and
detection (DC). This information is largely gleaned
from CAPEC and CVE.
Requirements = h
h∗ActorhAttr.hSO{1..n}, DE{0..n},W E{0..n}iii,
h∗ActorhResourceshINI{1..n}, INS{1..n}iii,
hVictimhExposure{internal, exposed}ii,
hVictimhIntegrity{nominal, compromised}ii
i
Properties = h
hSO{1..n}i, hSC{1..100}i, hDC{1..100}i
i
Each action corresponds to an AttackPattern,
which is identified by its ID and its impact on the CIA
triangle. Attack patterns link the modeled action to
specific hostile activity as described in the CAPEC
schema. Ultimately, each attack pattern is mapped
to a set of monitored Events with specific underlying
operations and arguments, triggers (parents), times-
tamps, and sequence numbers. The ‘pattern’ type
describes event sequences that directly represent the
action, while anomalies describe the behavioral devi-
ation from a baseline. The modeling of unique events

closes the gap to the data layer and allows us to lower
the level of abstraction to the actual systemic repre-
sentation. Refer to Section 4 for a mapping example.
AttackPattern = h
hImpacthC{low, med, high},
I{low, med, high}, A{low, med, high}ii,
hID{n}i
i
Event = h
hType{Pattern,Anomaly}i
hTimehStart{ timestmp }, End{ timestmp }ii,
hSequence{n}i,
hParent{ ParentName }i,
hOperation{ OperationName }i,
hArgument{ OperationArgument }i
i
4 DATA MAPPING
In this section, we specify the mapping of external
data to the various classes and categories that are part
of our model. This includes the formal link between
actions and events, the mapping of APT kill chain to
CAPEC attack patterns, the CAPEC to CVSS map-
ping, and the association of controls to defense acti-
ons. Using below information, it is possible to easily
extend or adapt the game system to new or updated
scenarios in cyber-security and beyond.
4.1 Actions to Events
Each action available in our APT RPG rule system
can be modeled using the structure introduced in
Section 3. The possible link between in-game acti-
ons and real-world events is an integral part of the
model. In the following, we exemplify this mapping
using the star graph based anomaly detection appro-
ach by Luh et al. (2017). In that paper, the authors
describe a system for detecting and interpreting ab-
normal Windows OS behavior expressed through se-
quences of kernel events defined as G = (U,V, E),
where U and V are nodes (parametrized event type)
and E is the respective edge (type of operation). Spe-
cific attacks (here, the example is limited to APT kill
chain phases) can be learned by monitoring malware
activity and comparing it to a pre-established baseline
of known process behavior. If we apply this principle
to CAPEC attack patterns, the accuracy of the inter-
pretation mechanism could be further improved.
In Luh et al.’s system, such a sequence of kernel
events could look like this:
Table 1: Example event sequence describing the process
of making a dropped executable persist through a system
restart (CAPEC-564: “Run Software at Logon”). Time
stamps and full paths omitted for legibility.
Start node (U) End node (V) Edge (E)
process-shell.exe process-drop.exe start (3)
process-drop.exe image-library.dll load (1.5)
process-drop.exe registry-HKLM/
Software/.../Run
open (0.25)
process-drop.exe registry-REG SZ
evil.exe
add (0.75)
This real-world data could be collected using any
kernel monitor or API monitoring tool. More impor-
tantly, our APT RPG can seamlessly integrate this
information into a gamified scenario. Specifically,
our system would model the above event sequence as
action, where the hEventi class looks like this:
Event = h
hType = Patterni
hTimehStart = 16.53.661, End = 16.53.729ii,
hSequence = 1i,
hParent = shell.exei,
hOperation = process starti,
hArgument = drop.exei
hSequence = 2i,
hParent = drop.exei,
hOperation = image loadi,
hArgument = library.dlli
...
i
This simple interface makes it easy for analysis to
add their own data to the game model. Thanks to its
flexibility, the level of abstraction can be freely spe-
cified – ranging from the discussed kernel events to
high-level behavior such as ‘set fire to house’.
4.2 Kill Chain to Attack Patterns
We use Hutchins et al.’s cyber kill chain 2011 as foun-
dation for the high-level view on our model. For furt-
her granularity, we expanded the 7 stages to a total of
19 subcategories that largely adhere to the APT onto-
logy design by Luh et al. (2016). To link kill chain
elements to CAPEC attack patterns, we introduced
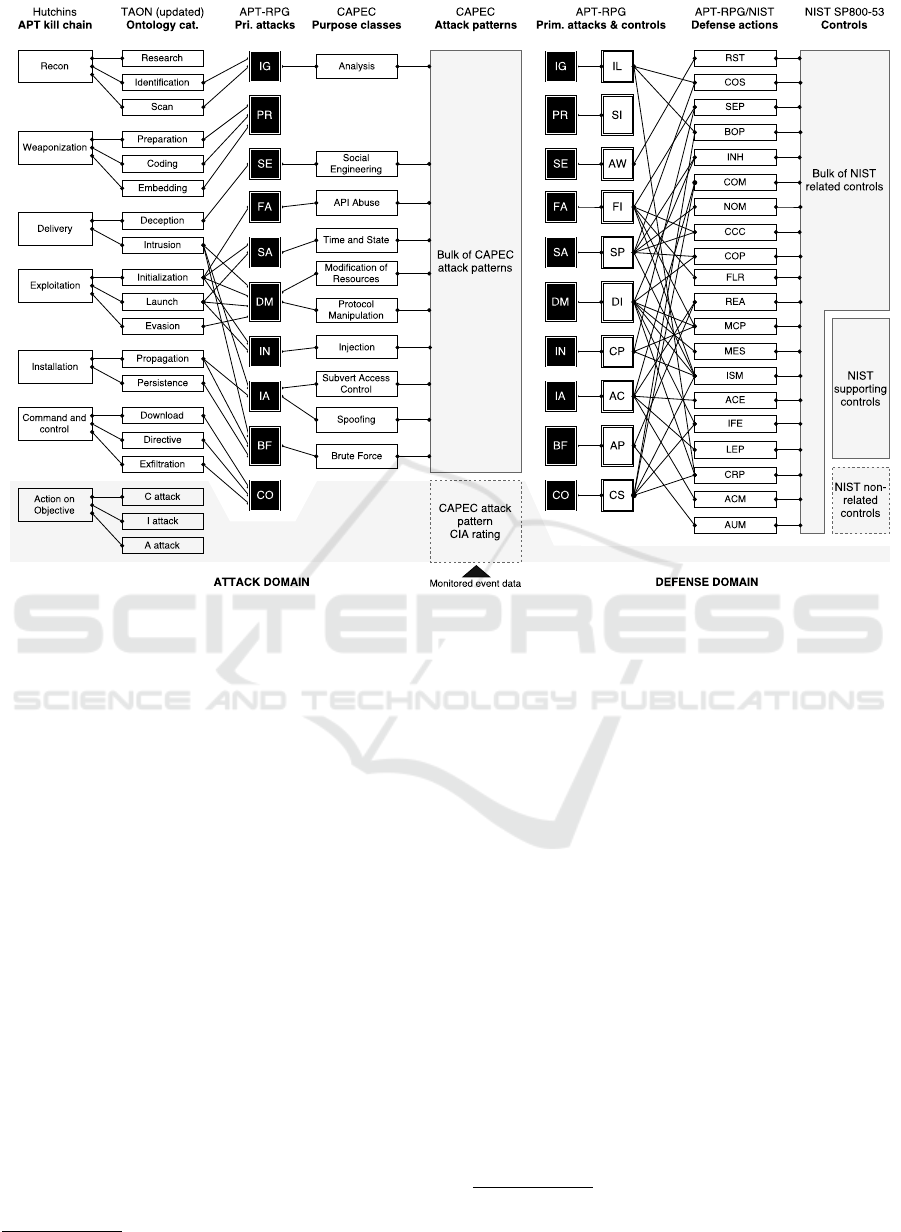
Figure 3: Mapping of NIST controls to CAPEC attack patterns via extended APT kill chain. The introduced link categories
based on CAPEC are highlighted in black. A full key and table for all abbreviations/mappings is available on request.
the concept of primary attacks, which were abstrac-
ted from CAPEC’s ‘purpose classes’ and assigned to
kill chain categories. Figure 3 depicts the mapping.
Since the list of attack patterns in CAPEC is par-
tially incomplete or offers too little information in
terms of abstraction required for a meta-model, we
only considered patterns of ‘standard’ and ‘meta’ ab-
straction level – the ‘detailed’ class was omitted in
this initial iteration of the game. In addition, we op-
ted to remove deprecated attacks and focus only on
stable and draft patterns found in version 2.11 of CA-
PEC
1
. Incomplete patterns with no purpose classes
were disregarded as well. Overall, this selection re-
tained a total of 65 representative patterns out of 516.
The remainder can easily be added at a later point.
4.3 Attack Patterns to Vulnerabilities
Vulnerabilities are a key component of any intrusion
scenario. In order to automatically map CAPEC at-
tack patterns to CVSS vulnerabilities, we took a clo-
ser look at these and other related MITRE information
exchange standards. Ultimately, we use the ‘related
weaknesses’ information provided by CAPEC to map
1
https://capec.mitre.org
each pattern to specific weaknesses represented by the
Common Weakness Enumeration (CWE) list. CWE
“provides a common language for describing security
weaknesses in architecture, design, or code”
2
. For ex-
ample, CAPEC ID 1 (“Accessing Functionality Not
Properly Constrained by ACLs”) is related to CWE
ID 276, 285, 434, etc.).
To close the gap between weaknesses and the
more concrete vulnerabilities, we use open source
information to map CWE entries to their Common
Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE) counterpart.
For example, CWE-276 (“Incorrect Default Permis-
sions”) contains the vulnerabilities CVE-2005-1941,
CVE-2002-1713, CVE-2001-1550, CVE-2002-1711,
CVE-2002-1844, CVE-2001-0497, and CVE-1999-
0426. Armed with this ID, the specific vulnerability
can be looked up in the National Vulnerability Data-
base (NVD
3
), where a specific CVSS score is assig-
ned. This multipartite score is the basis for the re-
quirements and impact calculations used in our mo-
del (see hEnableri in Section 3). In our example, the
score for CVE-2005-1941 can be easily retrieved
4
.
2
https://cwe.mitre.org/about/index.html
3
https://nvd.nist.gov
4
https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2005-1941
CP-1
AT-1
PS-5
PS-6
IR-1
PE-2
MP-1
PE-5
SC-1
RA-1
AU-3
PM-6
SI-11
CA-8
AU-12
CA-9
PM-5
SI-6
AU-7
SI-5
AU-4
SI-12
AU-5
AU-8
SI-15
AU-14
SA-13
AU-1
PS-3
SA-1
SC-36
MA-1
SA-21
CA-1
IA-1
PE-1
PS-4
PS-1
CM-1
PL-1
SI-1
CM-8
PE-18
IA-10
CM-7
CM-11
MP-3
RA-3
CM-5
RA-5
AC-1
PM-8
SA-11
SA-15
MA-6
SA-3
SA-2
PM-7
SC-21
SC-3
SC-22
SC-24
CP-12
SA-16
PM-3
PM-11
SC-39
SA-5
SC-37
SI-14
SC-34
AC-8
SC-28
SI-7
CP-13
AC-12
SC-32
SC-23
SC-10
SC-11
SC-2
SI-17
PE-10
SI-13
PL-7
PM-1
SA-18
SC-26
SC-25
SC-27
SA-20
SC-35
SC-44
SA-19
SA-17
SA-14
AC-25
PE-15
SC-30
SI-16
PE-14
SC-29
PL-8
PS-2
MA-5
PE-4
AU-11
PE-9
MA-3
SC-4
AC-5
SC-43
MP-6
CA-3
AC-20
IA-3
SA-9
IA-4
IA-2
PS-7
AC-14
IA-8
SC-20
SC-8
AC-11
AU-16
AC-9
SC-15
IA-7
AC-7
IA-11
AC-21
SC-19
AU-2
SC-12
MP-2
AC-16
AU-9
PE-6
IR-6
SC-17
PE-11
MP-5
IR-2
IR-8
PE-17
CP-9
IR-7
AT-2
PE-12
CP-10
CP-8
CP-7
CP-6
PM-4
CA-6
PM-10
AU-10
AC-10
SC-16
IR-5
CM-2
MP-7
MA-2
PE-16
SI-8
SC-6
CP-3
CM-4
CP-4
CA-5
SC-5
SC-40
CA-2
IR-3
SA-4
RA-2
SC-18
CM-9
SC-38
SA-10
AT-4
AC-22
AU-13
PM-14
PM-2
PM-15
SC-42
PE-8
MP-8
PS-8
PM-13 PL-9
PM-12
CP-11
PE-13
AC-24SC-41
IR-9
PM-16
RA-6
IA-6
SC-31
PE-19
PE-20
CM-10
SI-10
AC-23
SA-22
IR-10
IA-9
AU-15
AC-19
AC-18
AC-3
AC-2
AC-17
AC-4
CA-7
AU-6
SA-8
AC-6
SI-3
CM-3
CM-6
SI-2
AT-3
SC-13
IA-5
MA-4
PM-9
PL-4
SA-12
SI-4
IR-4
PE-3
CP-2
PL-2
SC-7
MP-4
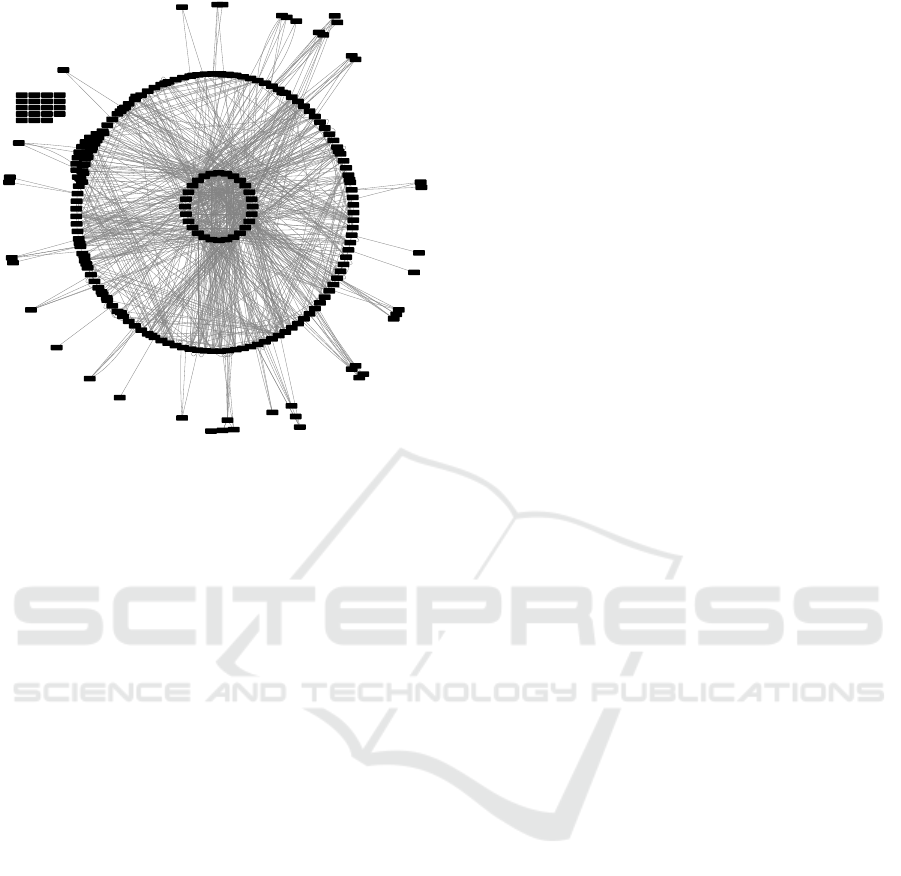
Figure 4: Relations between NIST controls rendered in Cy-
toscape (Shannon et al., 2003). The inner circle represents
controls with a degree of ≥ 20. Elements beyond the outer
circle have a degree of 1, while the isolated nodes to the left
are not linked to any other controls (orphan controls).
4.4 Primary Controls to Defense
Actions
The mapping of controls to defense actions and pri-
mary controls was automatically computed from the
NIST SP800-53r4 standard. To achieve this, we ex-
tracted all links of relationship between the individual
controls and modeled them as a graph. We subse-
quently separated each control into one of three cate-
gories by their level of degree. Controls with a degree
d >= 20 were defined as parent defense actions (see
Figure 3). Controls with degree d < 20 and d >= 1
form the bulk of related controls which operate on in-
formation system and/or organization level and trans-
late to the remainder of the defense strategy set for
the respective parent action. The model can be furt-
her extended by adding control enhancements that, in
turn, are associated with numerous parent and related
controls. Figure 4 depicts the relationship between all
224 NIST controls. General measures (NIST suffix *-
1) were converted into policies, which are part of the
hDisablersi class.
4.5 Limitations
There are a number of limitations that need to be con-
sidered before employing the described version of the
APT RPG for attack analysis, risk assessment, or sim-
ply as an awareness game. Most of these factors also
offer opportunities for future research.
Firstly, one needs to keep in mind that using exter-
nal data sources or threat intelligence can be limiting:
Attack patterns may outdate due to a lack of database
maintenance or novel threats might not be conside-
red immediately after disclosure. For CAPEC speci-
fically, there are patterns that lack CIA impact or pur-
pose information, e.g. CAPEC-2: “Inducing account
lockout”. This might make it necessary for the player
to expand the repository of attack strategies/actions
with their own information.
Secondly, the assignment of primary controls to
defense actions (see Figure 3) is currently done semi-
manually by a group if IT security experts. Auto-
mated mechanisms have proven to be too inaccurate
during initial experiments that utilized a natural lan-
guage approach using several IT security glossaries.
Because of this limitation, the attack–defense map-
ping of data sources that are significantly larger than
the NIST standard might not be feasible.
Another minor drawback of the NIST control ap-
proach is the small number (19) of orphan controls,
which are not related to any other countermeasures.
Currently, these controls are not considered in the
game, since they would have to be manually added
and assigned a specific category, levering out most
mechanisms of automation currently in place.
On the CAPEC side, we do not currently restrict
attacks to a specific target type like we do for equip-
ment, since CAPEC does not offer a clean way to as-
sign systems (hosts, network, industrial components,
etc.) to a particular pattern. That means that e.g. the
BF primary attack such as CAPEC-49: “Password
Brute Forcing” can, in the game, be used on an ar-
bitrary victim without further distinction into target
categories. This limitation might in some cases sim-
plify a hostile action at the expense of realism. Coun-
tering this drawback is possible, but currently requires
manual intervention: Depending on the description of
the respective attack pattern, the information provi-
ded in CAPEC’s database (namely the ‘summary’ and
‘example instances’ columns) can be parsed and as-
signed one of the equipment type categories used for
assets (hE f f ectTargeti).
5 CONCLUSION
We have presented the design of a gamified meta mo-
del that can be used to train personnel, assess risk mi-
tigation strategies, and compute new attacker/defen-
der scenarios in arbitrary IT infrastructures. While
the model itself is extremely flexible and supports
varying levels of granularity, the initial game pro-

totype design based upon this model utilizes accepted
taxonomies and security standards to support out-of-
the-box organization-level gameplay for simulating
cyber-attacks on various types of local or networked
assets. Our data mapping mechanisms enable domain
experts to easily extend the system with new actors,
actions, and (mitigating) equipment. We also exem-
plified how real-world data such as OS kernel events
can be linked to the model.
The development of the first educational game
prototype based on the introduced model has been
completed. Ultimately, it is planned to evaluate both
the physical release candidate as well as a simula-
tion app that will allow us to automatically compute
new attack stories and identify systemic weaknesses
in only slightly abstracted infrastructures.
Next to simulation, the APT RPG offers a solid
foundation for the development of an ontology
for targeted attacks, which can be populated by
both threat information sources as well as host and
network monitoring data. The synergies between
the data-centric and model-based game system will
significantly aid in understanding and closing the
semantic gap.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The financial support by the Austrian Federal Mini-
stry of Science, Research and Economy and the Nati-
onal Foundation for Research, Technology and Deve-
lopment is gratefully acknowledged.
REFERENCES
Barnum, S. (2012). Standardizing cyber threat intelligence
information with the Structured Threat Information
eXpression (STIX
TM
). MITRE Corporation, 11:1–22.
Caltagirone, S., Pendergast, A., and Betz, C. (2013). The di-
amond model of intrusion analysis. Technical report,
Center for Cyber Intelligence Analysis and Threat Re-
search, Hanover.
Cook, A., Smith, R., Maglaras, L., and Janicke, H. (2016).
Measuring the risk of cyber attack in industrial control
systems. BCS eWiC.
Holmgren, A. J., Jenelius, E., and Westin, J. (2007). Evalu-
ating strategies for defending electric power networks
against antagonistic attacks. IEEE Transactions on
Power Systems, 22(1):76–84.
Hutchins, E. M., Cloppert, M. J., and Amin, R. M. (2011).
Intelligence-driven computer network defense infor-
med by analysis of adversary campaigns and intrusion
kill chains. Leading Issues in Information Warfare &
Security Research, 1:80.
Kuhn, H. W. (2009). Lectures on the Theory of Games.
Princeton University Press.
Lewis, T. G. (2014). Critical infrastructure protection in ho-
meland security: Defending a networked nation. John
Wiley & Sons.
Luh, R., Schrittwieser, S., and Marschalek, S. (2016).
TAON: An ontology-based approach to mitigating tar-
geted attacks. In Proc. of the 18th Int. Conference on
Information Integration and Web-based Applications
& Services. ACM.
Luh, R., Schrittwieser, S., Marschalek, S., and Janicke, H.
(2017). Design of an anomaly-based threat detection
& explication system. In Proc. of the 3rd Int. Con-
ference on Information Systems Security & Privacy.
SCITEPRESS.
Miura-Ko, R. A., Yolken, B., Bambos, N., and Mitchell, J.
(2008). Security investment games of interdependent
organizations. In Communication, Control, and Com-
puting, 2008 46th Annual Allerton Conference on, pa-
ges 252–260. IEEE.
Nguyen, K. C., Alpcan, T., and Basar, T. (2009). Security
games with incomplete information. In Communica-
tions, 2009. ICC’09. IEEE International Conference
on, pages 1–6. IEEE.
Roger, B. M. (1991). Game theory: Analysis of conflict.
Roy, S., Ellis, C., Shiva, S., Dasgupta, D., Shandilya, V.,
and Wu, Q. (2010). A survey of game theory as app-
lied to network security. In System Sciences (HICSS),
2010 43rd Hawaii International Conference on, pages
1–10. IEEE.
Shannon, P., Markiel, A., Ozier, O., Baliga, N. S., Wang,
J. T., Ramage, D., Amin, N., Schwikowski, B., and
Ideker, T. (2003). Cytoscape: A software environment
for integrated models of biomolecular interaction net-
works. Genome research, 13(11):2498–2504.
Syed, Z., Padia, A., Finin, T., Mathews, M. L., and Joshi,
A. (2016). UCO: A Unified Cybersecurity Ontology.
Undercoffer, J., Pinkston, J., Joshi, A., and Finin, T. (2004).
A target-centric ontology for intrusion detection. In
18th International Joint Conference on Artificial In-
telligence, pages 9–15.
Whitman, M. E. and Mattord, H. J. (2011). Principles of
information security. Cengage Learning.
You, X. Z. and Shiyong, Z. (2003). A kind of network secu-
rity behavior model based on game theory. In Parallel
and Distributed Computing, Applications and Techno-
logies, 2003. PDCAT’2003. Proceedings of the Fourth
International Conference on, pages 950–954. IEEE.
