
Focus
ST
Solution for Analysis of Cryptographic Properties
Maria Spichkova and Radhika Bhat
School of Science, RMIT University, Melbourne, Australia
Keywords:
Software Engineering, Formal Methods, Specification, Verification, Tool-support.
Abstract:
To analyse cryptographic properties of distributed systems in a systematic way, a formal theory is required. In
this paper, we present a theory that allows (1) to specify distributed systems formally, (2) to verify their crypto-
graphic wrt. composition properties, and (3) to demonstrate the correctness of syntactic interfaces for specified
system components automatically. To demonstrate the feasibility of the approach we use a typical example
from the domain of crypto-based systems: a variant of the Internet security protocol TLS. A security flaw in
the initial version of TLS specification was revealed using a semi-automatic theorem prover, Isabelle/HOL.
1 INTRODUCTION
Systems are often specified and implemented follow-
ing the modularity principle: a number of separate
components are combined together to build the de-
sired system. This usually leads to the question on
how to derive the system properties from the proper-
ties of its components. In the case of crypto-based
systems, the most important and the most difficult
question is to derive which of the cryptographic (se-
curity/secrecy) properties the composed system will
have. Thus, a formal theory is required to not only
specify systems and their cryptographic formally,
but also to analyse them. As the paper-and-pencil
proofs are not enough for this case, applying theo-
rem provers or model checkers is necessary to have
semi-automated solutions.
In this paper, we discuss a formal theory for spec-
ification and verification of security-critical systems
and their cryptographic properties. The focal point
of this approach is readability of formal specifica-
tions as well as the composition of components and
their properties. The modelling language we use in
our approach, FOCUS
ST
, allows us to create concise
but easily understandable specifications and is appro-
priate for application of the specification and proof
methodology presented in our previous works.
FOCUS
ST
(Spichkova et al., 2014; Spichkova,
2016) is based on human factor analysis within formal
methods to offer more readable specifications. The
FOCUS
ST
language was inspired by FOCUS (Broy and
Stølen, 2001), a framework for formal specification
and development of interactive systems.
In both languages, specifications are based on
the notion of streams that represent a communica-
tion history of a directed channel between compo-
nents. However, in the original FOCUS input and
output streams of a component are mappings of
natural numbers N to the single messages, where
a FOCUS
ST
stream is a mapping from N to lists
of messages within the corresponding time inter-
vals. The FOCUS
ST
specification layout also differs
from the original one: it is based on human factor
analysis within formal methods (Spichkova, 2012b;
Spichkova, 2013a).
This theory is a result of optimization and ex-
tension (on the verification as well as on the speci-
fication level) of the draft ideas presented in techni-
cal reports (Spichkova and J
¨
urjens, 2008; Spichkova,
2012a). Similar to our previous work on formal speci-
fication of security-critical systems, we apply the pro-
posed theory on a typical example from the domain of
crypto-based systems: a variant of the Internet secu-
rity protocol TLS (Apostolopoulos et al., 1999). We
also discuss the differences to the corresponding FO-
CUS specifications, especially focusing on the read-
ability aspects. Using the extended approach with
FOCUS
ST
, we can demonstrate a security flaw in the
protocol and show how to prove security properties
of a corrected version. We also can apply to the
FOCUS
ST
solution the verification methodology Fo-
cus on Isabelle (Spichkova, 2007), which allows ver-
ification using an interactive semi-automatic Higher-
Order Logic theorem prover Isabelle/HOL. The corre-
sponding proofs are presented in the Archive of For-
mal Proofs (Spichkova, 2014).
320
Spichkova, M. and Bhat, R.
FocusST Solution for Analysis of Cryptographic Properties.
DOI: 10.5220/0006772103200327
In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to Software Engineering (ENASE 2018), pages 320-327
ISBN: 978-989-758-300-1
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

2 RELATED WORK
Security is critical to the development of software
systems in many application areas. Thus, there also
are many approaches on developing of such systems.
A brief survey of software engineering techniques
for computer security can be found in (Devanbu and
Stubblebine, 2000). The closest to our work in this
field is the approach for secure software engineering
using the CASE tool AutoFocus presented in (Wim-
mel, 2005): it uses a modelling tool based on the re-
stricted part of the FOCUS specification language, but
do not cover the aspects of verification and properties
composition, which we concentrate on.
There are also many papers on verifying crypto-
graphic protocols (Paulson, 1998; Meadows, 2000;
Ryan and Schneider, 2000). In comparison to them,
we do not focus in our work on the protocol verifica-
tion itself, but use the TLS protocol as a case study to
show the advantages of our theory.
A large number of the approaches focus on model-
based development of security-critical systems, cf.
e.g., (Alam et al., 2007; Whittle et al., 2008), how-
ever, a correct composition of system specifications or
system models and, in particular, deriving the prop-
erties of a composed system is treated as one of the
most difficult objective (Broy, 1997; B
´
ezivin et al.,
2006; Brunet et al., 2006) independently which kinds
of system properties are discussed. Moreover, dealing
with the composition of security-critical components
and their security properties we get even more com-
plex and costly task, to solve it we need to develop
an appropriate theory of composition which allows a
formal verification/derivation of system properties in
addition to a readable specification of system compo-
nents.
An approach on the verification of equivalence
properties was introduced in (Chadha et al., 2012).
For security analysis of padding-based encryption
schemes was presented in (Barthe et al., 2013). There
were also a number of approaches applied symbolic
analysis of security protocols. For example, approach
based on multi-set rewriting systems and first-order
logic was presented in (Schmidt et al., 2012). An ap-
proach presented in (Meier et al., 2013), focuses on
efficient deduction and equational reasoning, and in-
troduces the corresponding TAMARIN prover. Model
Checking solutions are also very popular, cf. e.g.,
(Permpoontanalarp, 2010). Comparative Analysis of
15 Model Checking tools for security protocol verifi-
cation was presented in (Patel et al., 2010), proposing
the Scyther and AVISPA tools as mostly suitable for
the purpose. In our case, the approach is supported by
Isabelle/Isar theorem prover for higher-order logic.
3 BACKGROUND: FOCUS
ST
A system in FOCUS and FOCUS
ST
is represented by
its components that are connected by communication
lines called channels, and are described in terms of its
input/output behaviour. The components can interact
and also work independently of each other. A speci-
fication can be elementary or composite, where com-
posite specifications are built hierarchically from the
elementary ones. In both languages, any specification
characterizes the relation between the communication
histories for the external input and output channels,
and the formal meaning of a specification is exactly
this external input/output relation.
For any set of messages M, M
ω
denotes the set of
all streams, M
∞
and M
∗
denote the sets of all infinite
and all finite streams respectively, M
ω
denotes the set
of all timed streams, M
∞
and M
∗
denote the sets of all
infinite and all finite timed streams respectively.
The FOCUS and FOCUS
ST
specifications can be
structured into a number of formulas each charac-
terizing a different kind of properties. These lan-
guages support a variety of specification styles which
describe system components by logical formulas or
by diagrams and tables representing logical formulas.
The most general style in FOCUS and FOCUS
ST
is an
Assumption/Guarantee style, where a component is
specified in terms of an assumption and a guarantee:
whenever input from the environment behaves in ac-
cordance with the assumption asm, the specified com-
ponent is required to fulfill the guarantee gar.
We specify the semantics of a composite compo-
nent S = S
1
⊗ ··· ⊗ S
n
as defined in (Broy and Stølen,
2001):
[[ S ]]
def
= ∃l
S
∈ L
S
:
n
^
j=1
[[ S
j
]] (1)
where l
S
denotes a set of local streams and L
S
denotes
their corresponding types, [[ S
j
]] denotes semantics of
the specification S
j
, 1 ≤ j ≤ n, which is a specification
of subcomponent of S.
The collection of FOCUS
ST
operators over timing
aspects and their properties specified and verified us-
ing the theorem prover Isabelle is presented in the
Archive of Formal Proofs (Spichkova, 2013b). In this
work we focus on modelling of security aspects and
the corresponding properties of composition. Before
introducing the new concepts, we would like to men-
tion very shortly a small number of operators we used
in the paper:
An empty stream is represented by hi.
hxi denotes the one element stream consisting of the
element x.
#s denotes the length of the stream s.
ith time interval of the stream s is represented by s
i
.
FocusST Solution for Analysis of Cryptographic Properties
321

msg
n
(s) denotes a stream s that can have at most n
messages at each time interval.
4 SECRECY
In this section we introduce a FOCUS
ST
formalization
of security properties of data secrecy, corresponding
definitions, and a number of abstract data types used
in this formalization. This formalization yields a basis
for verification in the theorem prover Isabelle/HOL,
technical details of verification and the corresponding
proofs are presented in (Spichkova, 2012a)).
We assume here disjoint sets Data of data val-
ues, Secret of unguessable values, and Keys of crypto-
graphic keys. Based on these sets, we specify the sets
EncType of encryptors that may be used for encryp-
tion or decryption, CExp of closed expressions, and
Expression of expression items:
KS
def
= Keys ∪ Secret
EncType
def
= Keys ∪ Var
CExp
def
= Data ∪ Keys ∪ Secret
Expression
def
= Data ∪ Keys ∪ Secret ∪ Var
Below, we will treat an expression (that can for ex-
ample be sent as an argument of a message within the
distributed system) as a finite sequence of expression
items. hi then denotes an empty expression.
The decryption key corresponding to an encryp-
tion key K is written as K
−1
. In the case of asymmet-
ric encryption, the encryption key K is public, and
the decryption key K
−1
secret. For symmetric en-
cryption, K and K
−1
coincide. For the encryption,
decryption, signature creation and signature verifica-
tion functions we define only their signatures and gen-
eral axioms, because in order to reason effectively,
we view them as abstract functions and abstract from
their bit-level implementation details, following the
usual Dolev-Yao approach to crypto-protocol verifi-
cation (Dolev and Yao, 1983):
Enc, Decr, Sign, Ext ::
EncType × Expression
∗
→ Expression
∗
∀e ∈ Expression : Ext(K,Sign(K
−1
,e)) = e
Decr(CKey
−1
,Enc(CKey,e)) = e
We denote by K
P
⊆ Keys and S
P
⊆ Secret the set of
private keys of a component P and the set of unguess-
able values used by a component P, respectively.
We assume in our specification that the compo-
sition of components has a number of general prop-
erties which sometimes seem to be obvious, but for
a formal representation is essential to mention these
properties explicitly either we can’t (edit:cannot)
make the proofs in a correct way.
The sets of private keys and unguessable values
used by a composed component C = C
1
⊗ · ·· ⊗ C
n
must be defined by union of corresponding sets.
(1) If xb is a private key of the composed compo-
nent C, then this key must belong to the set of private
keys of one subcomponents of C:
C = C
1
⊗ ··· ⊗ C
n
∧ xb ∈ K
C
→ ∃i ∈ [1..n]. xb ∈ K
C
i
(2) If xb is an unguessable value used by the com-
posed component C, then this value must belong to
the set of unguessable values used by one subcompo-
nents of C:
C = C
1
⊗ ··· ⊗ C
n
∧ xb ∈ S
C
→ ∃i ∈ [1..n]. xb ∈ S
C
i
(3) If xb is a private key of one subcomponents of
the composed component C, then this key must be-
long to the set of private keys of C:
C = C
1
⊗ ··· ⊗ C
n
∧ 1 ≤ i ≤ n ∧ xb ∈ K
C
i
→ xb ∈ K
C
(4) If xb is an unguessable value used by one sub-
components of the composed component C, then this
value must belong to the set of unguessable values
used by C:
C = C
1
⊗ ··· ⊗ C
n
∧ 1 ≤ i ≤ n ∧ xb ∈ S
C
i
→ xb ∈ S
C
(5) If xb does not belong to the set of private
keys and unguessable values of any subcomponent of
PQ = P ⊗ Q, then xp does not belong to the set of pri-
vate keys and unguessable values of PQ:
PQ = P ⊗ Q ∧ xb 6∈ KS
P
∧ xb 6∈ KS
Q
→ xb 6∈ KS
PQ
(6) If a channel x belongs to the set of input (out-
put) channels of the composition PQ = P ⊗ Q for any
two components P and Q, then this channel must be-
long to the set of input (output) channels of P or Q:
x ∈ i
P⊗Q
→ x ∈ i
P
∨ x ∈ i
Q
x ∈ o
P⊗Q
→ x ∈ o
P
∨ x ∈ o
Q
For the collection of the theorems and prepo-
sitions on the input/output properties proven in Is-
abelle/HOL (more than 50 Isabelle/HOL lemmas) we
would like to refer to (Spichkova, 2014).
4.1 Knowledges of an Adversary
An (adversary) component A knows a secret m ∈
KS, m 6∈ KS
A
(or some secret expression m, m ∈
(Expression \ KS
A
)
∗
), if
• A may eventually get the secret m,
• m belongs to the set LS
A
of its local secrets,
• A knows a one secret hmi,
• A knows some list of expressions m
2
which is an
concatenations of m and some list of expressions
m
1
,
• m is a concatenation of some secrets m
1
and m
2
(m = m
1
_
m
2
), and A knows both these secrets,
ENASE 2018 - 13th International Conference on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to Software Engineering
322

• A knows some secret key k
−1
and the result of the
encryption of the m with the corresponding public
key,
• A knows some public key k and the result of the
signature creation of the m with the corresponding
private key,
• m is an encryption of some secret m
1
with a public
key k, and A knows both m
1
and k,
• m is the result of the signature creation of the m
1
with the key k, and A knows both m
1
and k.
Formally, we define this term by mutually recursive
predicates know
A
(k) (for the case of a single secret
m) and knows
A
(k) (for the case when expression (or
list) k, containing a secret) respectively.
know
A
∈ KS \ KS
A
→ Bool
know
A
(m)
def
= A
ine
(m) ∨ m ∈ LS
A
knows
A
∈ (Expression \ KS
A
)
∗
→ Bool
knows
A
(m)
def
=
(∃m
1
: m = hm
1
i ∧ know
A
(m
1
))
∨
(∃m
1
,m
2
: (m
2
= m
_
m
1
∨ m
2
= m
1
_
m)∧
knows
A
(m
2
))
∨
(∃m
1
,m
2
: m = m
1
_
m
2
∧ knows
A
(m
1
)∧
knows
A
(m
2
))
∨
(∃k, k
−1
: know
A
(k
−1
) ∧ knows
A
(Enc(k, m)))
∨
(∃k, k
−1
: know
A
(k) ∧ knows
A
(Sign(k
−1
,m)))
∨
(∃k, m
1
: m = Enc(k,m
1
) ∧ knows
A
(m
1
) ∧
know
A
(k))
∨
(∃k, m
1
: m = Sign(k,m
1
) ∧ knows
A
(m
1
)∧
know
A
(k))
Subsequently, we add axioms that describe relations
between the predicates know/knows and the predicate
describing that a component may eventually output an
expression.
Axiom 1. For any component C and for any secret
m ∈ KS (or expression e ∈ Expression
∗
), the following
equations hold:
∀m ∈ KS : C
eout
(m) ≡ (m ∈ KS
C
) ∨ know
C
(m)
∀e ∈ Expression
∗
:
C
eout
(e) ≡ (e ∈ KS
C
∗
) ∨ knows
C
(e)
2
Axiom 2. For any component C and for an empty ex-
pression hi ∈ Expression
∗
, holds:
∀C : knows
C
(hi) = true. 2
For the collection (more than 50 Isabelle lem-
mas) of propositions and theorems on the properties
of the predicates know/knows, we would like to refer
to (Spichkova, 2014).
5 TLS PROTOCOL
To demonstrate the feasibility and usability of our ap-
proach, we specified a variant of the TLS protocol
1
in
FOCUS
ST
and discuss the features of the specification
templates that were introduces to increase the read-
ability of the language. After that we present the for-
mal analysis of the protocol.
The goal of TLS is to let a client send a secret over
an untrusted communication link to a server in a way
that provides secrecy and server authentication, by us-
ing symmetric session keys. Let us recall the general
idea of the handshake protocol of TLS, cf. Figure 1.
The protocol has two participants, Client and Server,
that are connected by an Internet connection. We used
the following auxiliary data types:
• Obj = {C,S} to represent participants names (C
for the Client and S for the Server),
• StateC = {st0,st1,st2} to represents the states of
the Client,
• StateS = {initS,waitS, sendS1,sendS2} to repre-
sent the states of the Server,
• Event = {event} to represent events of message
sending (e.g., an abort message or an acknowl-
edgement), and
• InitMessage = im(ungValue ∈ Secret,key ∈
Keys, msg ∈ Expression) to represent the event of
protocol initiation by the Client.
Client initiates the protocol by sending the mes-
sage that contains an unguessable value N ∈ Secret,
its the public key K
C
, and a sequence hC, CKeyi of
its name and its public key signed by its secret key
CKey
−1
. Server checks whether the received public
key matches to the second element of the signed se-
quence. If that is the case, it returns to the Client
the received unguessable value N, an encryption of
a sequence hgenKey,Ni (signed by its secret key
SKey
−1
) using the received public key, and a sequence
hS,SKeyi of its name and its public key, signed using
the secret key CAKey
−1
of the certification authority.
1
TLS (Transport Layer Security) is the successor of the
Internet security protocol SSL (Secure Sockets Layer).
FocusST Solution for Analysis of Cryptographic Properties
323

Client Server
init: InitMessage
xchd: Expresion
abortC: Event
abortS: Event
resp: Expression
Figure 1: Protocol of TLS.
After that, Client checks whether the certificate is ac-
tually for S and the correct N is returned. If that is
the case, it sends the secret value secretD encrypted
with the received session key genKey to the Server. If
any of the checks fail, the respective protocol partic-
ipant stops the execution of the protocol by sending
an abort signal. Figures 2 and 3 present the FOCUS
ST
specification of Client and Server components respec-
tively.
For the corresponding representation in Is-
abelle/HOL we would like to refer to the technical
report. We continue with the discussion how our ap-
proach can be used to demonstrate a security flaw in
the TLS variant introduced above, as well as how to
correct it.
We specify every component using assumption-
guarantee-structured templates. This helps avoiding
the omission of unnecessary assumptions about the
system’s environment since a specified component is
required to fulfil the guarantee only if its environ-
ment behaves in accordance with the assumption. We
also use in FOCUS
ST
so-called implicit else-case con-
structs: if a variable is not listed in the guarantee part
of a transition, it implicitly keeps its current value.
An output stream not mentioned in a transition will
be empty.
Without these extensions, the specification of the
components would become less readable, as the core
properties would be lost in a huge set of properties
that might be specified implicitly. For example, the
specification of the Client would require 4 additional
properties, such as
• xchd
0
= hi,
• abortC
0
= hi,
• init
t+1
= hi,
• abortS
t
= hi ∧ resp
t
= hi ∧ check = st0 →
abortC
t+1
= hi ∧ xchd
t
= hi ∧ check
0
= st0
Thus, the corresponding FOCUS specifications of
Client and Server would have 10 and 9 properties re-
spectively, in contrast to 6 and 5 properties we have in
Client timed
in abortS : Event; resp : Expression
out init : InitMessage,xchd : Expression; abortC : Event
local check : StateC; enc : Keys
init check = st0;
asm true
gar
1 init
0
= him(N,CKey,Sign(CKey
−1
,hC, CKeyi))i
∀t ∈ N :
2 abortS
t
6= hi → ∧check
0
= st0
3 abortS
t
= hi ∧ resp
t
6= hi ∧ check
0
= st0 → check
0
= st1
4 abortS
t
= hi ∧ resp
t
6= hi ∧ check = st1 ∧ ft.secr = S
→ check
0
= st2 ∧ enc
0
= snd.secr
5 abortS
t
= hi ∧ resp
t
6= hi ∧ check = st2
∧ ft.extRes = S ∧ snd.res = N
→ xchd
t+1
= Enc(ft.res,secretD) ∧ check
0
= st0
6 abortS
t
= hi ∧
((check = st1 ∧ (resp
t
= hi ∨ (resp
t
6= hi ∧ ft.secr 6= S))) ∨
(check = st2 ∧ (resp
t
= hi ∨ (resp
t
6= hi ∧ snd.res 6= N))))
→ abortC
t+1
= heventi ∧ check
0
= st0
where
secr = Ext(CAKey,resp
t
)
res = Ext(enc, Decr(CKey
−1
,resp
t
))
Figure 2: FOCUS
ST
specification of the Client component.
the FOCUS
ST
version. Even when for a small example
like TLS the difference might not look huge, it scales
dramatically for large systems.
Moreover, the specifications of the properties
would be more complicated without these optimisa-
tions. For example, the 4th property of Server in the
FOCUS version would be
abortC
t
= hi ∧ stateS = sendS1
→ resp
t+1
= Sign(CAKey
−1
,hS, SKeyi) ∧
stateS
0
= sendS2 ∧ uValue
0
= uValue ∧
kValue
0
= kValue ∧ abortS
t+1
= hi
In FOCUS
ST
also do not require to introduce auxiliary
variables explicitly: The data type of an unintroduced
variable is universally quantified in the specification
such that it can be used with any data value.
ENASE 2018 - 13th International Conference on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to Software Engineering
324
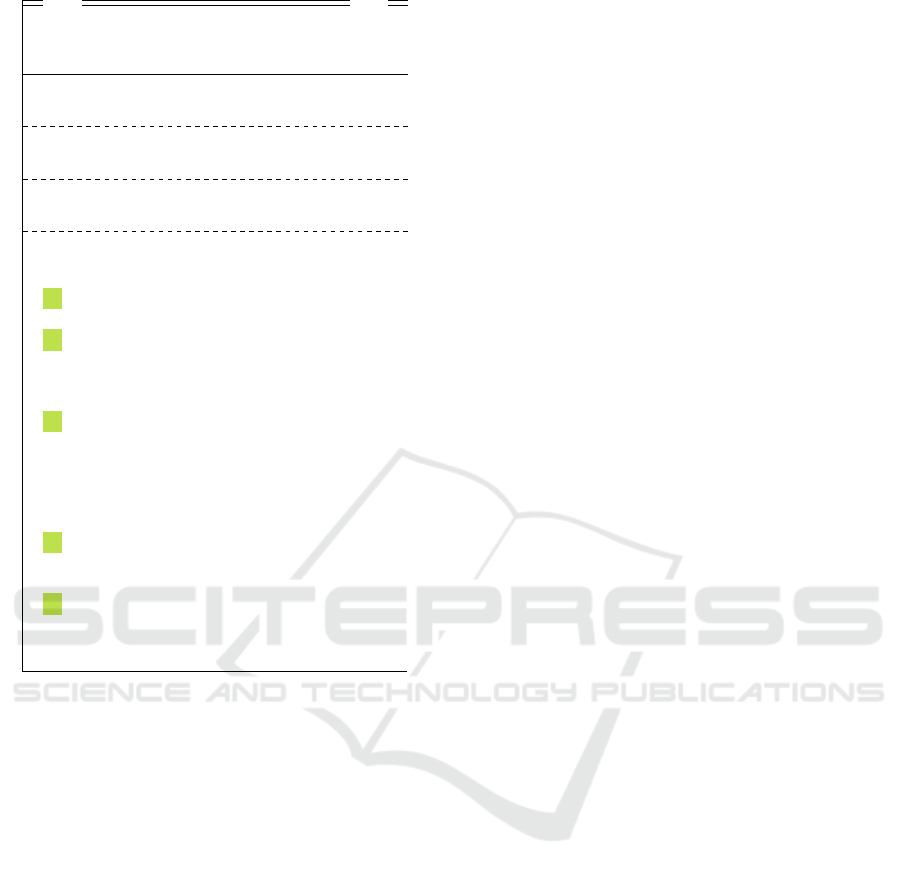
Server timed
in init : InitMessage; abortC : Event; xchd : Expression
out resp : Expression; abortS : Event
local stateS ∈ StateS; kValue ∈ Keys; uValue ∈ Secret
init stateS = initS
asm msg
1
(init) ∧ msg
1
(xchd)
gar
∀t ∈ N :
1 abortC
t
6= hi → stateS
0
= initS
2 abortC
t
= hi ∧ stateS = initS ∧ init
t
6= hi ∧
snd.Ext(hkey(init
t
ft
),msg(init
t
ft
)i) 6= key(init
t
ft
)
→ abortS
t+1
= heventi
3 abortC
t
= hi ∧ stateS = initS ∧ init
t
6= hi ∧
snd.Ext(hkey(init
t
ft
),msg(init
t
ft
)i) = key(init
t
ft
)
→ resp
t+1
= hungValue(init
t
ft
)i
∧ stateS
0
= sendS1 ∧ uValue
0
= ungValue(init
t
ft
)
∧ kValue
0
= key(init
t
ft
)
4 abortC
t
= hi ∧ stateS = sendS1
→ resp
t+1
= Sign(CAKey
−1
,hS,SKeyi) ∧ stateS
0
= sendS2
5 abortC
t
= hi ∧ stateS = sendS2
→ resp
t+1
= Enc(kValue, Sign(SKey
−1
,hgenKey,uValuei))
∧ stateS
0
= waitS
Figure 3: FOCUS
ST
specification of the Server component.
5.1 Security Analysis
In this section, we use our approach to demonstrate
a security flaw in the TLS variant introduced above,
and how to correct it. Let us assume a composite
component P = Client ⊗ Server. To show that P does
not preserve the secrecy of secretD, secretD ∈ KS, we
need to find an adversary component Adversary with
I
Adversary
⊆ O
P
such that
• knows
Adversary
(m) holds with regards to the com-
position, and
• m does not belong to the set of private keys of
Adversary or to the set of unguessable values of
Adversary,
This can be formalised as the below statement:
∃Adversary :
I
Adversary
⊆ O
P
∧ m 6∈ KS
Adversary
∧ knows
Adversary
(m)
(2)
This means, we have to analyse a possible composi-
tion Client ⊗ Adversary ⊗ Server, cf. Figure 4.
The protocol assumes that there is a secure (wrt.
integrity) way for the client to obtain the public key
CAKey of the certification authority, and for the server
to obtain a certificate
Sign(CAKey
−1
,hS, SKeyi)
signed by the certification authority that contains its
name and public key. For an arbitrary process Z, an
adversary may also have access to
• CAKey,
• Sign(CAKey
−1
,hS, SKeyi), and
• Sign(CAKey
−1
,hZ,ZKeyi).
Consider the FOCUS
ST
specification of the
component Adversary presented in Figure 5. This
component is weakly causal: we assume that the
adversary does not delay any message. We used in
this specification an auxiliary data type
AdvStates = {initA, sendA1,sendA2}.
The value genKey ∈ Keys is a symmetric session
key generated by the server: genKey
−1
= genKey.
This implies that
knows
Adversary
(genKey)
holds if and only if
knows
Adversary
(genKey
−1
)
holds. Thus, if the adversary knows the value of
genKey it also knows the value of genKey
−1
. If we
trace its knowledge base as its evolves in interaction
with the protocol components, we get that Adversary
will know the secret secretD at the time unit 4.
Translating the FOCUS
ST
specifications to Is-
abelle/HOL, we can prove formally that the security
flaw exists. These proof (together with protocol com-
ponent specifications and auxiliary lemmas) takes 1,5
klop (thousands lines of proofs). This also allows us
to demonstrate the correctness of syntactic interfaces
for specified system components automatically.
In this paper we present only the main lemma
which says that the during the 4th time unit the se-
cret data secretD will be send to the adversary by
the Client component and no abort-signal will be pro-
duced: For further details we would like to refer to the
Isabelle/HOL-theories we uploaded to the Archive of
Formal Proofs (Spichkova, 2014).
5.2 Fixing the Security Weakness
To fix the security weakness, we need to change the
protocol: the client must find out the situation, where
an adversary try to get the secret data. Thus, we need
to correct the specification of the server in such a way
FocusST Solution for Analysis of Cryptographic Properties
325
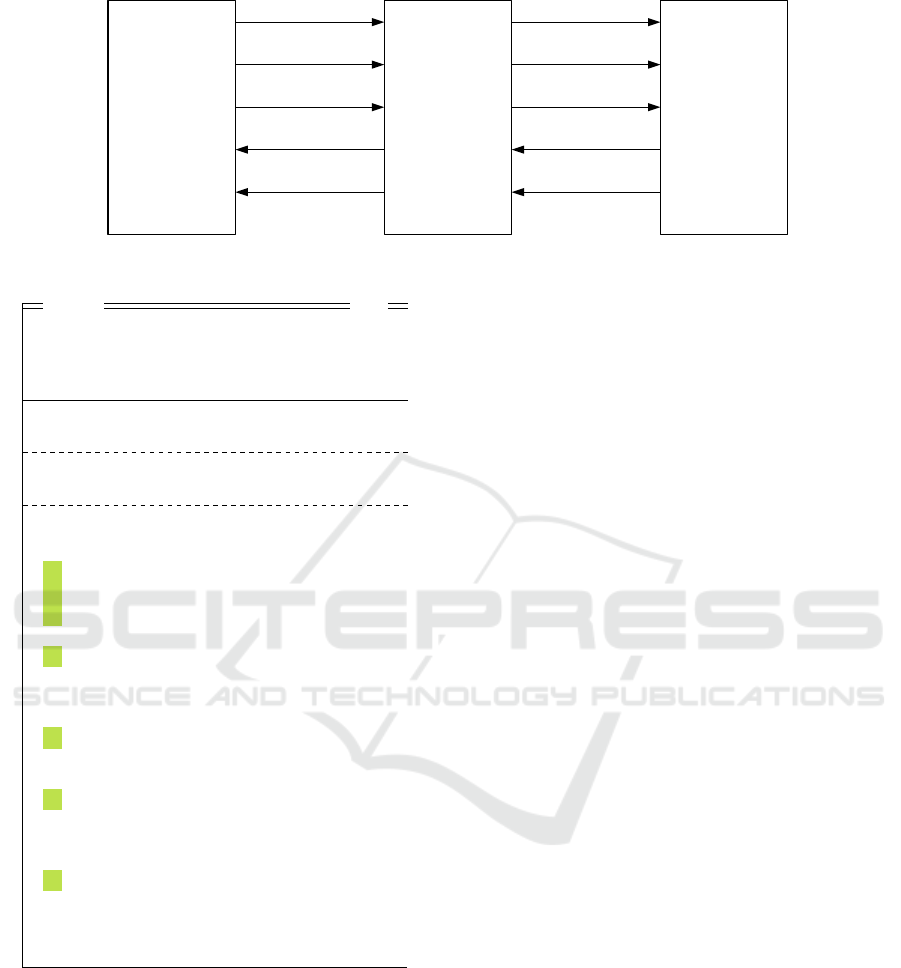
Client Server
init
1
: InitMessage
xchd
1
: Expresion
abortC
1
: Event
abortS
2
: Event
resp
2
: Expression
Adversary
init
2
: InitMessage
xchd
2
: Expression
abortC
2
: Event
abortS
1
: Event
resp
1
: Expression
Figure 4: Protocol of TLS: Situation with an Adversary component involved.
Adversary timed
in
abortC
1
,abortS
1
: Event; xchd
1
,resp
1
: Expression;
init
1
: InitMessage
out
abortC
2
,abortS
2
: Event; xchd
2
,resp
2
: Expression;
init
2
: InitMessage
local aCKey,aSKey,aKey ∈ Keys; stateA ∈ AdvStates
asm msg
2
(resp
1
) ∧ msg
1
(xchd
1
)
gar
∀t ∈ N :
1 abortC
t
2
= abortC
t
1
2 abortS
t
2
= abortS
t
1
3 xchd
t
2
= xchd
t
1
4 init
t
1
6= hi
→ aCKey
0
= key((init
1
)
t
ft
) ∧
init
t
2
= him(ungValue((init
1
)
t
ft
),AKey,Sign(AKey
−1
,hC, AKeyi))i
5 resp
t
1
6= hi ∧ stateA = initA
→ stateA
0
= sendA1 ∧ resp
t
2
= resp
t
1
6 resp
t
1
6= hi ∧ stateA = sendA1
→ stateA
0
= sendA2 ∧ aSKey
0
= snd.Ext(CAKey,resp
t
1
) ∧
resp
t
2
= resp
t
1
7 resp
t
1
6= hi ∧ stateA = sendA2
→ stateA
0
= initA ∧
aKey = ft.Ext(aSKey,Decr(AKey
−1
,resp
t
1
))
resp
t
2
= Enc(aCKey,Decr(AKey
−1
,resp
t
1
))
Figure 5: FOCUS
ST
specification of the Adversary compo-
nent that fulfils statement (2).
that the client will know with which public key the
data was encrypted at the server, and this information
must be received by the client without any possible
changes by the adversary. The only part of the mes-
sages from the server which cannot be changed by the
adversary is the result of the signature creation – the
adversary does not know the secret key SKey
−1
and
cannot modify the signature or create a new one with
modified content. Therefore, we add the public key
received by the server to the content hgenKey, Ni of
the signature. If there is not attack, this will be CKey,
in the attack scenario explained above, it would be
AKey. Accordingly, in the specification of the Server,
we change the value of resp
t+1
in the 5th formula to
the following one:
Enc(key(init
t
ft
),
Sign(SKey
−1
,
hgenKey,ungValue(init
t
ft
),key(init
t
ft
)i))
Also, correspondingly we add a new conjunct to the
condition for the correct data receipt in the specifica-
tion of the client:
trd.Ext(snd.Ext(CAKey,resp
t
trd
),
Decr(CKey
−1
,resp
t
snd
))
= CKey
If we trace the knowledge base of the adversary
Adversary considered above, the secret is not leaked,
the transmission will be aborted by the client on the
4th time unit.
We omit here the complete presentation of the FO-
CUS and Isabelle/HOL specification of the corrected
components Client and Server, because they have
only the minor changes vs. the specification presented
in the previous section. The Isabelle/HOL proof takes
also about 1,5 klop, but the most number of lemmas
can be reused from the uncorrected version.
6 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, we present a theory that allows (1) to
specify distributed systems formally, (2) to verify
their cryptographic wrt. composition properties, and
(3) to demonstrate the correctness of syntactic inter-
faces for specified system components automatically.
The theory is based on the FOCUS
ST
formal language,
and the verification is conducted using the theorem
prover Isabelle/HOL.
ENASE 2018 - 13th International Conference on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to Software Engineering
326

The feasibility of this approach was demonstrated
by specifying and formally analysing a variant of
the Internet security protocol TLS, which is a typ-
ical example from the domain of crypto-based sys-
tems. We analysed the protocol using both paper-and-
pencil proofs and the automated verification with Is-
abelle/HOL. The analysis revealed a security flaw in
the initial version of TLS specification. The proto-
col specification was harden according the proposed
approach.
REFERENCES
Alam, M., Hafner, M., and Breu, R. (2007). Model-
driven security engineering for trust management in
SECTET. Journal of Software, 2(1).
Apostolopoulos, V., Peris, V., and Saha, D. (1999). Trans-
port layer security: How much does it really cost? In
Infocom, pages 717–725. IEEE.
Barthe, G., Crespo, J. M., Gr
´
egoire, B., Kunz, C.,
Lakhnech, Y., Schmidt, B., and Zanella-B
´
eguelin, S.
(2013). Fully automated analysis of padding-based
encryption in the computational model. In Computer
& communications security, pages 1247–1260. ACM.
B
´
ezivin, J., Bouzitouna, S., Fabro, M. D. D., Gervais, M.-P.,
Jouault, F., Kolovos, D. S., Kurtev, I., and Paige, R. F.
(2006). A canonical scheme for model composition.
In ECMDA-FA, pages 346–360.
Broy, M. (1997). Compositional refinement of interactive
systems. J. ACM, 44(6):850–891.
Broy, M. and Stølen, K. (2001). Specification and Develop-
ment of Interactive Systems: Focus on Streams, Inter-
faces, and Refinement. Springer.
Brunet, G., Chechik, M., and Uchitel, S. (2006). Properties
of behavioural model merging. In FM, pages 98–114.
Chadha, R., Ciob
ˆ
aca, S., and Kremer, S. (2012). Automated
verification of equivalence properties of cryptographic
protocols. In ESOP, volume 7211, pages 108–127.
Springer.
Devanbu, P. and Stubblebine, S. (2000). Software engineer-
ing for security: A roadmap. In ICSE, pages 227–239.
ACM.
Dolev, D. and Yao, A. C. (1983). On the security of pub-
lic key protocols. IEEE Transactions on Information
Theory, 29(12):198–208.
Meadows, C. (2000). Open issues in formal methods for
cryptographic protocol analysis. In DARPA ISCE, vol-
ume 1, pages 237–250. IEEE.
Meier, S., Schmidt, B., Cremers, C., and Basin, D. (2013).
The tamarin prover for the symbolic analysis of secu-
rity protocols. In CAV, pages 696–701. Springer.
Patel, R., Borisaniya, B., Patel, A., Patel, D. R., Rajarajan,
M., and Zisman, A. (2010). Comparative analysis of
formal model checking tools for security protocol ver-
ification. In CNSA, pages 152–163. Springer.
Paulson, L. C. (1998). The inductive approach to verify-
ing cryptographic protocols. J. Comput. Secur., 6(1-
2):85–128.
Permpoontanalarp, Y. (2010). On-the-fly trace generation
and textual trace analysis and their applications to the
analysis of cryptographic protocols. Formal Tech-
niques for Distributed Systems, pages 201–215.
Ryan, P. and Schneider, S. (2000). The modelling and
analysis of security protocols: the CSP approach.
Addison-Wesley Professional.
Schmidt, B., Meier, S., Cremers, C., and Basin, D. (2012).
Automated analysis of diffie-hellman protocols and
advanced security properties. In CSFS, pages 78–94.
IEEE.
Spichkova, M. (2007). Specification and Seamless Verifi-
cation of Embedded Real-Time Systems: FOCUS on
Isabelle. PhD thesis, TU M
¨
unchen.
Spichkova, M. (2012a). Formal Specification and Verifi-
cation of Cryptographic Properties. Technical report,
TU M
¨
unchen.
Spichkova, M. (2012b). Human Factors of Formal Meth-
ods. In Interfaces and Human Computer Interaction.
IADIS.
Spichkova, M. (2013a). Design of formal languages and
interfaces: formal does not mean unreadable. In
Emerging Research and Trends in Interactivity and the
Human-Computer Interface. IGI Global.
Spichkova, M. (2013b). Stream processing components: Is-
abelle/HOL formalisation and case studies. Archive of
Formal Proofs.
Spichkova, M. (2014). Compositional properties of crypto-
based components. Archive of Formal Proofs.
Spichkova, M. (2016). Spatio-temporal features of Focus
ST
.
arXiv preprint arXiv:1610.07884.
Spichkova, M., Blech, J., Herrmann, P., and Schmidt, H.
(2014). Modeling spatial aspects of safety-critical
systems with Focus
ST
. In MoDeVVa, pages 49–58.
CEUR.
Spichkova, M. and J
¨
urjens, J. (2008). Formal Specifica-
tion of Cryptographic Protocols and Their Composi-
tion Properties: FOCUS-oriented approach. Technical
report, TU M
¨
unchen.
Whittle, J., Wijesekera, D., and Hartong, M. (2008). Exe-
cutable misuse cases for modeling security concerns.
In ICSE, pages 121–130. ACM.
Wimmel, G. (2005). Model-based Development of Security-
Critical Systems. PhD thesis, TU M
¨
unchen.
FocusST Solution for Analysis of Cryptographic Properties
327
