
Evaluation of Two Solar Radiation Algorithms on 3D City Models for
Calculating Photovoltaic Potential
Syed Monjur Murshed
1
, Alexander Simons
1
, Amy Lindsay
2
, Solène Picard
3
and Céline De Pin
4
1
European Institute for Energy Research, Emmy-Noether Str. 11, 76131 Karlsruhe, Germany
2
EDF Inc. Innovation Lab, 4300 El Camino Real, Los Altos, CA 94022, U.S.A.
3
École Supérieure d'Électricité, Plateau du Moulon, 3 Rue Joliot Curie, 91190 Gif-sur-Yvette, France
4
ESILV - Paris La Défense, 12 Avenue Léonard de Vinci, 92400 Courbevoie, France
Keywords: Solar Irradiance, Algorithms, 3D City Models, Python.
Abstract: Different algorithms are used to calculate solar irradiance on horizontal and vertical surfaces of the 3D city
models. The goal of this paper is to evaluate the hourly solar irradiance calculated by two widely used
algorithms in order to assess photovoltaic (PV) potential of the 3D city models. Both algorithms are
implemented in an open source software infrastructure consisting of PostgreSQL database connected with
PostGIS, Python, etc. The results show a significant variation of solar irradiances on horizontal, vertical and
tilted surfaces. Finally, the justification of a particular algorithm to assess citywide PV potentials is made.
1 INTRODUCTION
Calculation of solar irradiance on horizontal, vertical
and tilted building surfaces helps to correctly estimate
techno-economic photovoltaic (PV) potential, assess
building heating and cooling energy needs (Murshed
et al., 2017; Bahu et al., 2014), identify the Urban
Heat Island (UHI) effects (Vitucci et al., 2014).
Solar energy is one of the environmentally
sustainable resources for producing electricity using
photovoltaic systems (Šúri and Hofierka, 2004).
Different building surfaces are exposed to the sun,
which can be utilized to generate energy by efficient
installation and design of the PV panels. In this
regard, it is important to know the exact irradiance
received by the horizontal, vertical and tilted surfaces.
Moreover, based on the different tilt angles and
orientation of the panels, the same surface may
receive more or less radiation. Several other factors
such as shading, sky condition also influence the
amount of solar irradiance received by a surface.
Numerous algorithms (methods) and tools have
been developed across different climatic conditions to
analyze solar irradiance (Šúri and Hofierka, 2004). A
comprehensive and comparative overview has been
given by Freitas et al. (2015), Catita et al. (2014),
Redweik et al. (2013), Gueymard (2012) The GIS-
based analysis of solar irradiance was also performed
in different spatial-temporal scales and resolution:
from building surfaces to districts, hourly or monthly
basis, using vector or raster data (Huld, 2017; Li and
Liu, 2017; Hachem et al., 2013; Nguyen and Pearce,
2010; Lee and Zlatanova, 2009). However, the use of
3D city models is rather recent and innovative
(Freitas et al., 2015; Wieland et al., 2015). With the
availability of comprehensive 3D building data across
many cities, it is possible to carry out sophisticated
analysis of solar irradiance at a greater detail. It
allows assessing the shadow effect from the
neighbouring buildings, terrain or other urban
objects, calculating slope and orientation of the
surface, etc. Several commercial tools such as
Archiwizard, Rhinosolar, Autodesk Ecotect, ArcGIS
are also available but they are not able to perform
analyses on vertical surfaces or are not suitable to be
used in large 3D city models.
The aim of this paper is to perform a comparative
evaluation of two widely used solar irradiance
algorithms i.e., Šúri and Hofierka (2004) and Duffie
and Beckman (2006) to identify the more suitable
algorithm for assessing PV potential at an urban scale.
The hourly solar irradiance on horizontal, vertical and
tilted surfaces is calculated using an open source
software infrastructure. In this regard, the input
weather data, 3D city models and other assumptions
are considered identical in the implementation of both
algorithms.
296
Murshed, S., Simons, A., Lindsay, A., Picard, S. and Pin, C.
Evaluation of Two Solar Radiation Algorithms on 3D City Models for Calculating Photovoltaic Potential.
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Geographical Information Systems Theory, Applications and Management (GISTAM 2018), pages 296-303
ISBN: 978-989-758-294-3
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
2 METHODOLOGY
2.1 Main Approach
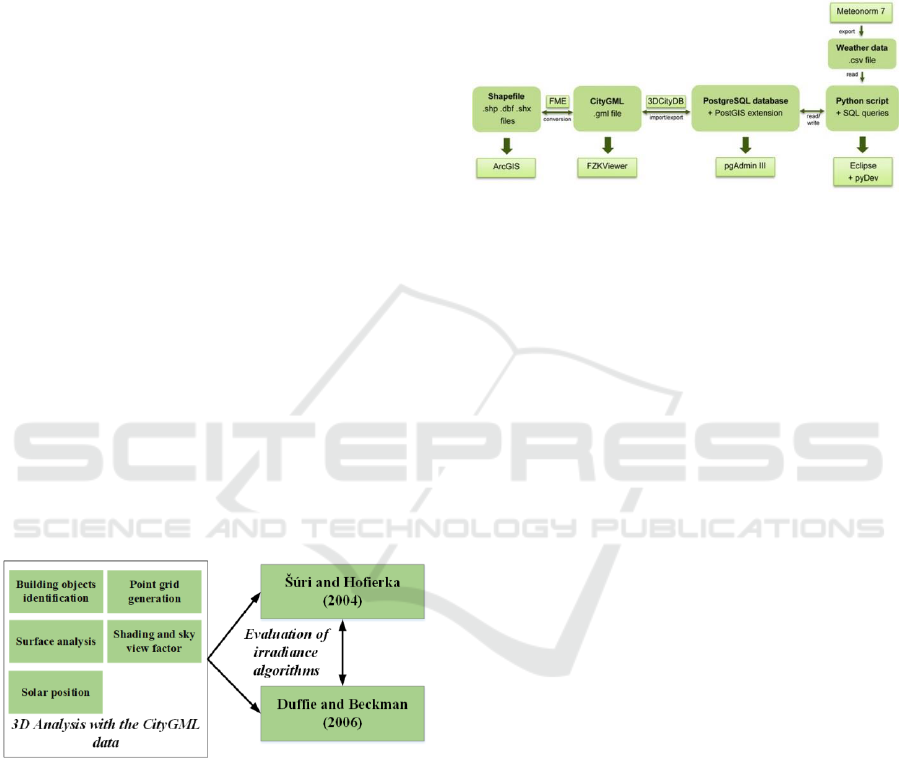
The broad methodological steps of this study can be
divided into 3 main parts (Figure 1). First, the
analyses of the 3D city models (e.g., CityGML
format) include preparation of the data, configuration
of the software and tools, generation of the point grids
on the building surface, calculation of the shading and
sky view factor of the points, solar position, etc.
(Section 3.1). Then the outcomes of these analyses
are considered as inputs to both solar irradiance
algorithms. The algorithm proposed by Šúri and
Hofierka (2004) was adapted earlier to calculate
monthly irradiation on CityGML data (Wieland et al.,
2015). This study improves the previous modelling
approach to incorporate the calculation of hourly
irradiance and advance the 3D analyses part. In this
regard, hourly measured weather data of a ground
station is considered (Section 3.2). Afterwards, the
algorithm proposed by Duffie and Beckman (2006) is
implemented, which also requires the same weather
data (Section 3.3). Both algorithms estimate solar
irradiance (direct and diffuse) on horizontal, vertical
and tilted surfaces on an hourly basis. In order to
perform a comparative evaluation of both algorithms,
the spatial and temporal irradiation results are
aggregated to buildings and annual level,
respectively. Finally, the results are visualized and
evaluated (Section 4).
Figure 1: Broad methodological approach.
2.2 Data
The hourly weather data on wind speed, temperature
and horizontal radiation are collected from the
Meteonorm software in TMY3 format (Wilcox and
Marion, 2008). The 3D city model of the CityGML
format having Level of Detail 2 (LoD2 includes
appropriate roof structure) of the city of Karlsruhe is
also gathered. A detailed description of the CityGML
data format and different LoDs is given in (OGC,
2012).
2.3 Software Architecture
Several software such as FME, 3DCityDB,
pgAdminIII and Eclipse are deployed to perform the
3D and solar irradiance analysis (Murshed et al.,
2017). The algorithms are written in Python scripts,
considering the object oriented approach (Figure 2).
Figure 2: Software architecture and data flow (Murshed et
al., 2017).
The LoD2 data of the CityGML format are
imported in a PostgreSQL database provided with
PostGIS extension, which allows treating spatial
objects by creating a special structure in the database.
The original CityGML file is adapted to the relational
schema by transforming through 3DCityDB, which
reorganizes files into specific tables. Finally, the data
can be retrieved using the Python code for further
calculations, analysis, and saving of results.
3 IMPLEMENTATION
3.1 3D Analysis Part
The 3D analysis part involves treating of CityGML
data and performing necessary geometric
calculations. The main steps are:
a. Surface analysis,
b. Definition of the objects: building, surface
and surface points,
c. Creation of the grid of surface points,
d. Shading characterization and sky view
factor calculation,
e. Solar position and characterization.
Figure 3 explains the different processing steps,
inputs and calculated results.
a. Surface analysis is the main module from which
all other 3D analysis parts are called. It determines
which points are “shared” i.e., in-between two
surfaces. This is done by spatial analysis and by
checking for an intersection of a buffer (0.1 m)
around the point, if any other wall surface is nearby.
Such an assumption helps to avoid unnecessary
Evaluation of Two Solar Radiation Algorithms on 3D City Models for Calculating Photovoltaic Potential
297
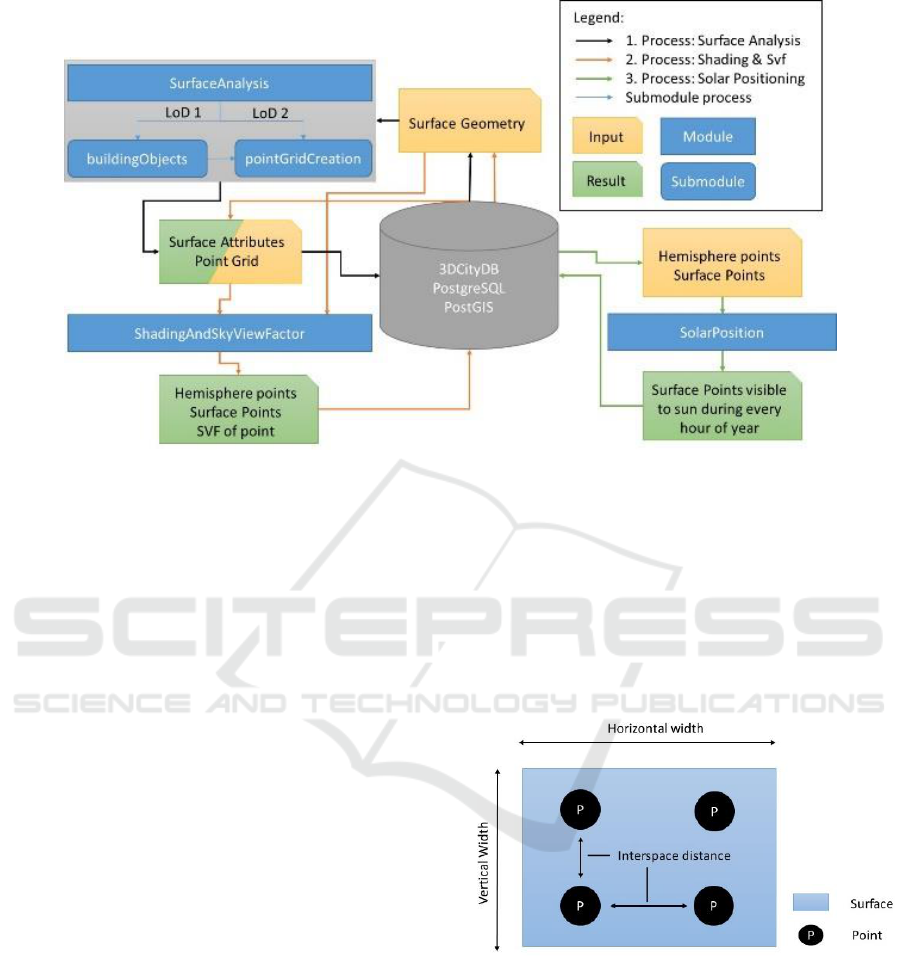
Figure 3: Detailed description of the inputs, different steps and associated results of the 3D analysis part. The outcome of the
analyses are saved in the PostgreSQL database.
spatial calculations, in case surface objects of
neighboring buildings may have geometric problems
(due to the bad quality of 3D city model).
b. The building object module identifies the wall,
roof or ground surfaces of the LoD2 (or LoD1) city
models. Then it performs different geometric
calculations such as normal vector, slope and aspect
of surface, using linear algebra.
c. The point grid module creates an homogenous
point grid on geometrical objects in 3D space (Figure
4). At first, considering the envelope of the geometry
(i.e., building surface), a starting point (3D point with
X,Y,Z) is defined. From this point, a distance is added
to the right (horizontal) as long as the sum of
interspaces (distance among points) is below the
expansion value X. Afterwards, the same procedure
is performed for all points as a step up (vertical) as
long as the interspace distance is below the expansion
value Y. Then the newly created points are checked,
if they are inside the polygon. This check is done once
per surface after the point distribution. Points outside
of the polygon are deleted. This approach is applied
for the horizontal polygons/surfaces. For non-
horizontal surfaces, points are rotated around the
axes, according to the orientation of the
corresponding polygon.
Therefore, technically speaking, the point grid
distribution is performed in 4 ways, depending on the
LoDs of the surface and the type of surface (e.g.,
ground, wall or roof surface). For LoD1, two
methods, one for horizontally orientated surfaces and
the other for vertically orientated surfaces are
observed. For LoD2, the points for horizontal
surfaces are distributed with the same method as
LoD1. For vertical surfaces, each point is rotated with
a matrix calculation into the plane of the surface
orientation. For tilted surfaces, different height values
of the geometry are taken into account to perform
point distribution.
Figure 4: Point grid creation on the surface.
d. Shading is performed through spatial analysis.
From each surface point, a line is created towards a
point of the hemisphere (a hemisphere of points is
created according to the horizontal and vertical
intervals chosen earlier, see Figure 5). If the line
intersects with another object (e.g., surface of the
same building, or another building) the surface point
is considered as shaded. If the line is not intersected
with another object, the corresponding surface point
is considered as not shaded. This process is done for
GISTAM 2018 - 4th International Conference on Geographical Information Systems Theory, Applications and Management
298
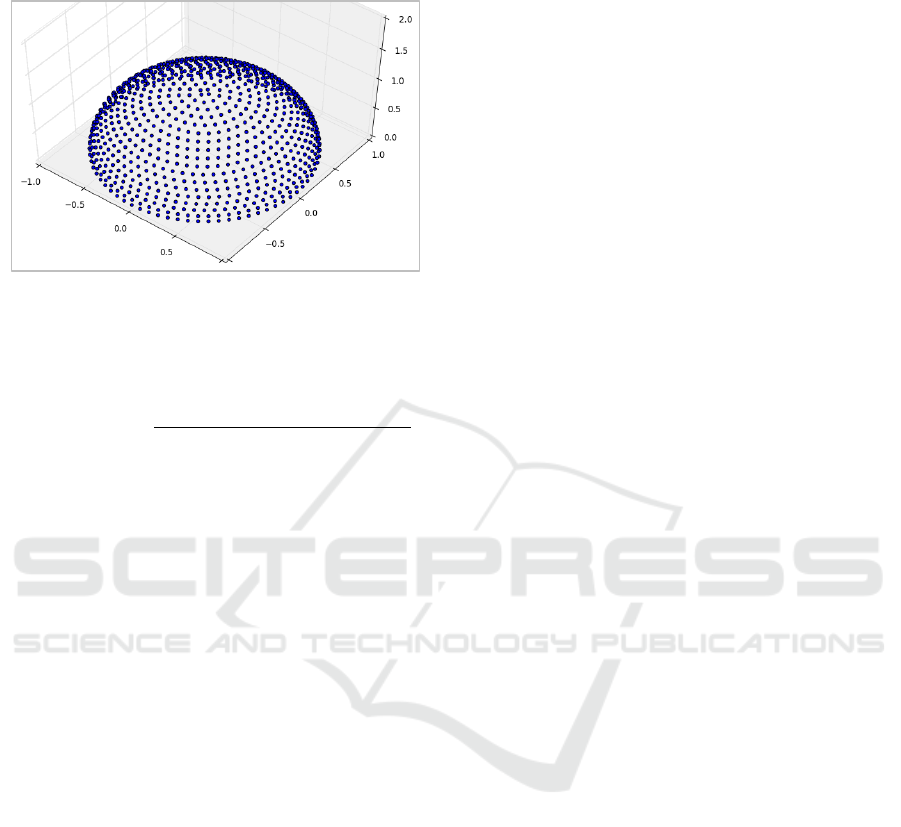
each surface point for every hemisphere direction
separately.
Figure 5: Hemisphere represented by sample points.
The sky view factor for each point is calculated as
the ratio between the number of visible hemisphere
points and the total number of hemisphere points.
𝑠𝑘𝑦 𝑣𝑖𝑒𝑤 𝑓𝑎𝑐𝑡𝑜𝑟 =
𝑛𝑢𝑚𝑏𝑒𝑟 𝑜𝑓 𝑣𝑖𝑠𝑖𝑏𝑙𝑒 ℎ𝑒𝑚𝑖𝑠ℎ𝑒𝑟𝑒 𝑝𝑜𝑖𝑛𝑡𝑠
𝑡𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑛𝑢𝑚𝑏𝑒𝑟 𝑜𝑓 ℎ𝑒𝑚𝑖𝑠ℎ𝑒𝑟𝑒 𝑝𝑜𝑖𝑛𝑡𝑠
e. Finally, solar position is calculated. For each
surface point, the IDs of the hemisphere directions,
which are visible, are stored in an array. To detect
whether a surface point is shaded at a certain time, the
position of the sun is computed for a specific time of
the day and the closest hemisphere direction is
determined. If the ID of this hemisphere direction is
contained in the array of the surface point, the point
is considered not to be shaded at that time of the day.
For each surface point this is performed 8760 times,
which corresponds to the number of hours per year.
The information of whether a surface point is shaded
at a certain hour is stored as a Boolean value, either
“True = is shaded” or “False = is not shaded”.
3.2 Solar Irradiance Algorithm by Šúri
and Hofierka (2004)
This algorithm is applied in many studies and an open
source GIS environment is employed. Computation is
quick and local meteorological data can be adapted to
the model. It is robust, and requires few input
parameters (Gueymard, 2012).
The process of computing solar irradiance (clear
sky) begins with the determination of the
extraterrestrial irradiance, which varies during the
year. After the position of the sun is calculated with
respect to time, the day and the latitude of the location
of interest, the beam and diffuse component of solar
irradiance on a horizontal surface can be determined
for the time of interest with respect to the Linke
turbidity. By incorporating the slope and the surface,
the incidence angle of solar rays on this surface can
be computed. With this angle, the horizontal radiation
components are adjusted according to the orientation
of the surface (Šúri and Hofierka, 2004). In this
model, only shadowing of the beam component is
taken into account, and not of the diffuse irradiance.
3.3 Solar Irradiance Algorithm by
Duffie and Beckman (2006)
It is calculated in four main steps. At first, the sun
position is calculated depending on the location
coordinates and time. Then the direct normal
irradiance is calculated considering the sinus of the
solar elevation angle, global horizontal and diffuse
horizontal irradiances that can be found in the
weather data. Then, based on the sun position vector
and the normal vector to the surface, the incidence
angle of the beam irradiance is computed and the
shadowing of the beam irradiance is included as
calculated previously. The sky view factor is applied
to diffuse irradiance.
Afterwards, an anisotropic sky model, known as
the Hay-Davies-Klucher-Reindl model is used to take
into account circumsolar diffuse irradiance and
horizon-brightening (Duffie and Beckman, 2006).
Finally, hourly direct and diffuse radiation are
calculated.
3.4 Assumptions
Both algorithms calculate only direct and diffuse
solar radiation. In order to have a comparative
evaluation, all relevant parameters are considered
identical. About 96 hemisphere points were created to
determine the sky view factor and to identify if each
surface is visible to particular hemisphere points (and
to solar position) throughout each hour of a year. A
point grid of 5m resolution is created on the building
surfaces. The measured weather data of a weather
station are used as inputs to both algorithms.
4 VISUALIZATION AND
DISCUSSION OF RESULTS
In order to perform a quick comparative evaluation of
the irradiance results, both algorithms were run on 95
buildings (having 650 surfaces) in a neighborhood in
the City of Karlsruhe in Germany. Then in order to
test the applicability of the implemented model, we
ran it for about 12000 LoD2 buildings in another
district of the same city.
Evaluation of Two Solar Radiation Algorithms on 3D City Models for Calculating Photovoltaic Potential
299
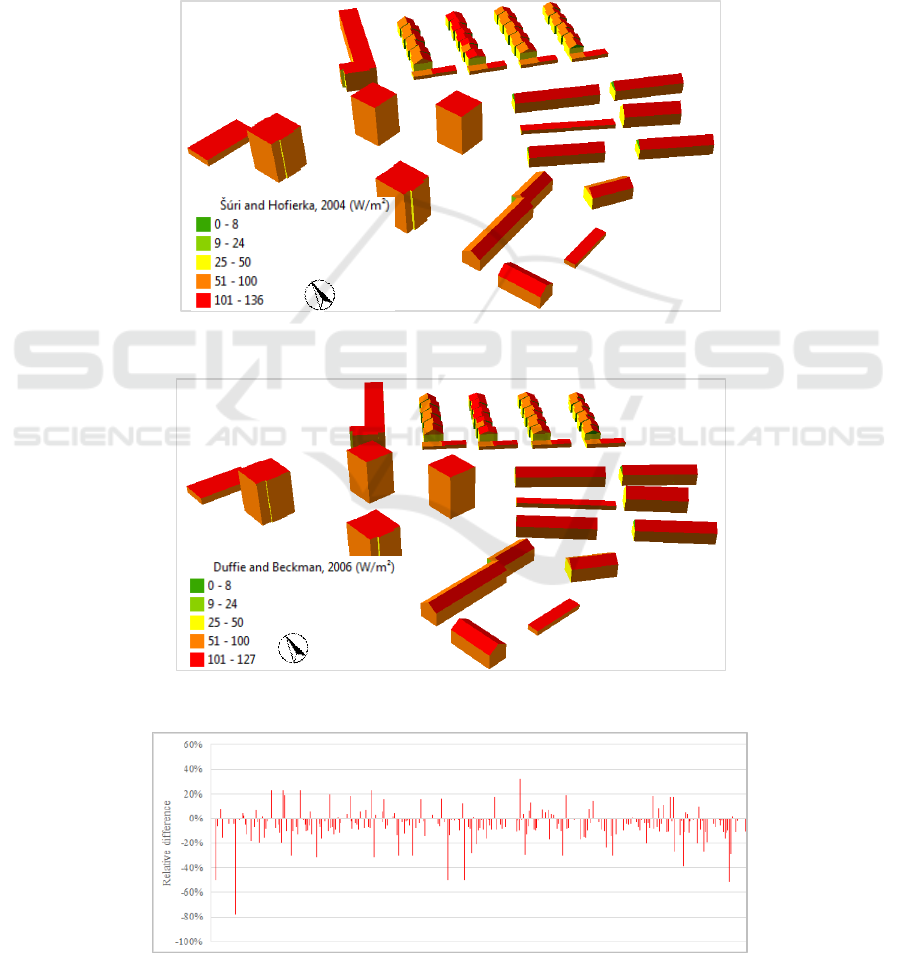
The direct and diffuse radiation were first
calculated for each point on the building surface,
which were then aggregated for each surface to
display the hourly averaged irradiance throughout the
year (W/m²). In analyzing the results of the first
method, we found the minimum and maximum values
to be 25 and 136 W/m² (Figure 6), whereas in the
second method, the values were 8 and 127 W/m²
(Figure 7), respectively.
Some surfaces displayed exactly the same results
for both algorithms. We observe that the initial
method estimates higher solar irradiances (up to 78%)
on the surfaces that are partially shaded by
neighboring surfaces (Figure 8).
We also observe that both algorithms calculate
almost the same solar irradiance on the roof surfaces.
It is found out that the second algorithm calculates
slightly higher solar irradiances (up to 36%) on the
north oriented surfaces (Figure 9).
It is evident that tilted surfaces (directing towards
the sun) will receive more irradiance than flat
surfaces. In case of flat roofs (e.g., where slope is
Figure 6: Hourly average solar irradiation on horizontal and vertical surfaces after Šúri and Hofierka (2004).
Figure 7: Hourly average solar irradiation on horizontal and vertical surfaces after Duffie and Beckman (2006).
Figure 8: Relative difference of irradiance results on some surfaces detected by the two algorithms.
GISTAM 2018 - 4th International Conference on Geographical Information Systems Theory, Applications and Management
300
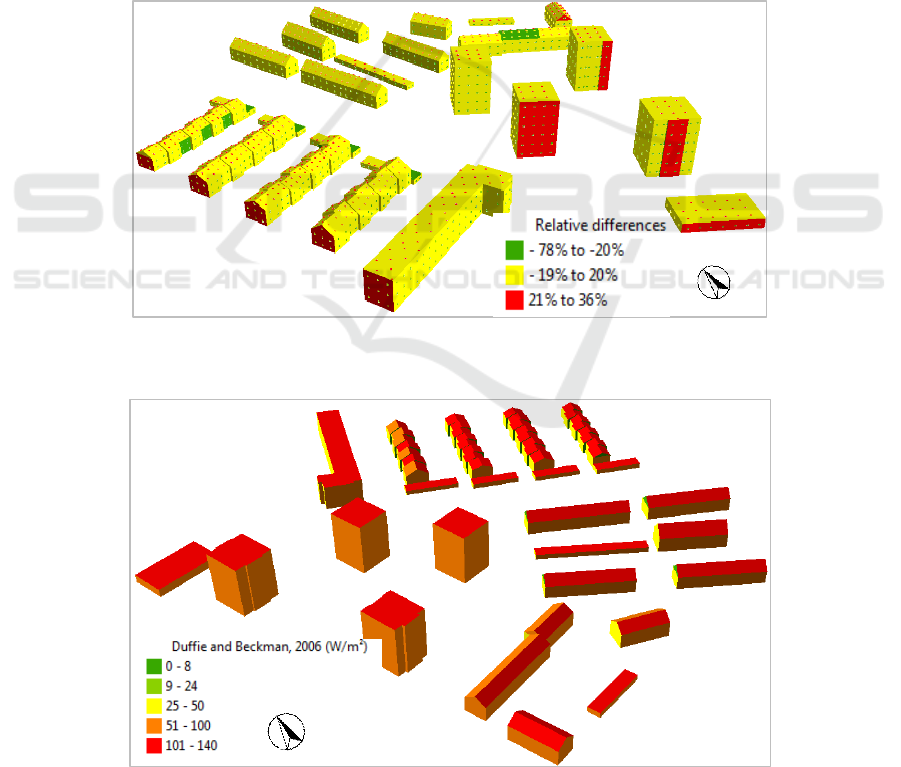
<20°), the PV installations are normally optimized by
tilting the panels so that they can receive maximum
solar radiation and thus can optimize energy
production for the PV panels. Therefore, the
calculation of irradiance on such tilted surfaces
(analogous to the PV installation surfaces) is very
important. The second method can be adapted to
calculate radiation on such surfaces. For example, we
found that the irradiance on a tilted surface is 140
W/m², which is higher than the radiation calculated
earlier on the actual roof surface (127 W/m²), which
has a slope less than <20° (Figure 10).
Both models were run on the same virtual
machine with standard configurations. The run time
of both models with 95 buildings was almost the same
(approximately 4 minutes). The multi-processing
functions of python helped to improve the model run
time.
Based on the results, it is difficult to justify which
method is more accurate and suitable for PV potential
analyses, although both of them considered similar
input datasets and assumptions. Nevertheless,
observing the evidence that the method by Duffie and
Beckman (2006) performs more realistic calculations
for the surfaces which are next to shaded surfaces
(confirmed after site inspection) and the flexibility of
assessing the irradiance on tilted surfaces, this
method is more suitable for photovoltaic assessment
in urban areas. Therefore, the algorithm proposed by
Duffie and Beckman (2006) was applied to around
12000 LoD2 buildings (consisting of approximately
96000 surfaces and 442000 points) in the city of
Karlsruhe in Germany to calculate hourly irradiance
on the tilted and vertical surfaces. It took
approximately 7 hours to complete the analysis.
Figure 9: Relative difference in solar irradiance on the wall and roof surfaces observed by the two methods. The grid points
are displayed on the surface on which solar radiation is calculated first.
Figure 10: Hourly average solar irradiation over a year on tilted surfaces (where slope was <20°) after Duffie and Beckman
(2006).
Evaluation of Two Solar Radiation Algorithms on 3D City Models for Calculating Photovoltaic Potential
301
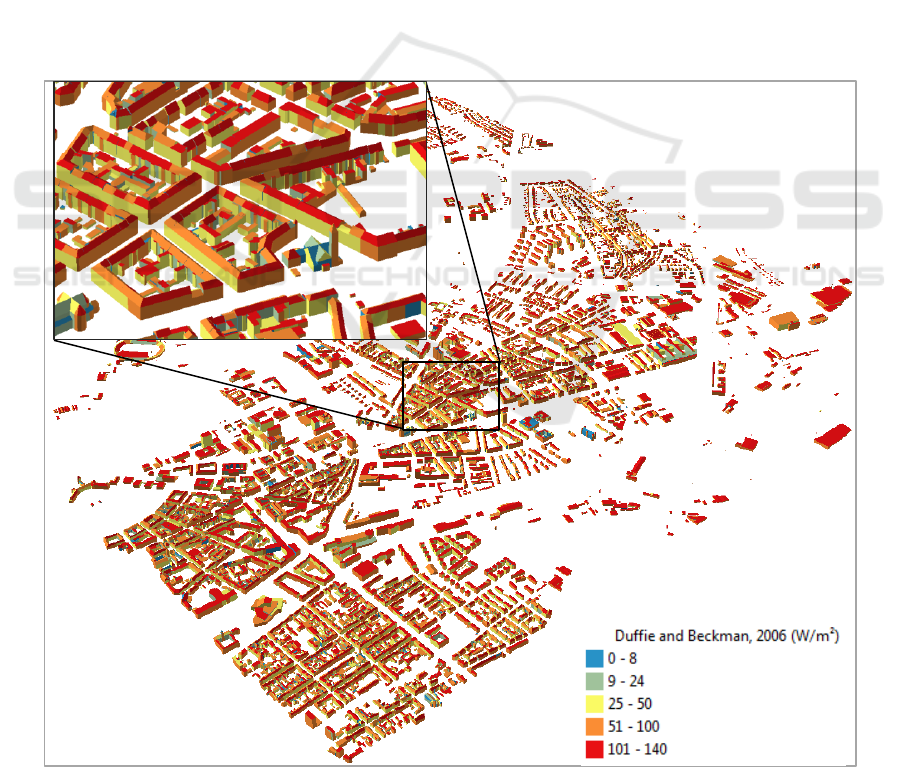
Figure 11 illustrates the hourly average solar
irradiance over a year on the vertical and tilted
surfaces of the buildings. The surfaces that strike out
in red are those that have few neighbouring buildings
obstructing sunlight. Generally, these are tilted
rooftops and this visualization quickly identifies the
best sun exposure.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Two solar irradiation algorithms were tested in this
study to perform a comparative evaluation of
irradiation results with a view to assess PV potential
in a city or district. For this reason, CityGML data and
an open source software infrastructure was used to
perform a quick but robust calculation of direct and
diffuse radiation of different building surfaces.
Moreover, with the semantic relationship among the
points, surfaces and buildings within the CityGML
data, it was possible to aggregate the results on
different spatial and/or temporal (hourly, monthly,
yearly, etc.) resolutions. The testing of the model with
about 12000 LoD2 buildings in the city of Karlsruhe
showed the applicability of these algorithms at a city
scale.
Several limitations are also evident in this study.
For instance, reflected radiation was not calculated. It
can be added by calculating the ground view factor.
Increasing the number of hemisphere points will
improve the model accuracy but will also increase the
run time. Therefore, in the future, the results can be
tested with a varying number of hemisphere points
and grid points. Consideration of shading due to
vegetation or chimneys will also improve the
calculation of solar irradiance.
As a continuation of this study, considering the
amount of solar radiation received by the sun, the PV
potential in terms of electrical energy (kWh),
investment costs (Euro) and levelized cost of energy
(LCOE) on the horizontal, vertical and tilted surfaces
will be calculated. The results can be integrated into
Figure 11: Hourly average solar irradiation (W/m²) over a year on tilted (where slope was <20°) and vertical surfaces after
Duffie and Beckman (2006) on 12000 LoD2 buildings in Karlsruhe, Germany.
GISTAM 2018 - 4th International Conference on Geographical Information Systems Theory, Applications and Management
302

a web platform, in order to visualize in 3D and to
allow the decision makers and citizens to ascertain the
solar irradiance and techno-economic PV potentials
in a flexible manner.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We would like to thank City of Karlsruhe for the
permission of using CityGML data and the project
“Smart and Low Carbon Cities” of EDF R&D for
funding the research. We are also grateful to Manfred
Wieland for his initial contribution in coding and the
three anonymous reviewers for their constructive
comments on our manuscript.
REFERENCES
Bahu, J.-M., Koch, A., Kremers, E. & Murshed, S. M. 2014.
Towards a 3D spatial urban energy modelling
approach. International Journal of 3-D Information
Modeling (IJ3DIM), 3, 1-16.
Catita, C., Redweik, P., Pereira, J. & Brito, M. C. 2014.
Extending solar potential analysis in buildings to
vertical facades. Computers & Geosciences, 66, 1-12.
Duffie, J. A. & Beckman, W. A. 2006. Solar engineering of
thermal processes, Wiley New York.
Freitas, S., Catita, C., Redweik, P. & Brito, M. 2015.
Modelling solar potential in the urban environment:
State-of-the-art review. Renewable and Sustainable
Energy Reviews, 41, 915-931.
Gueymard, C. A. 2012. Clear-sky irradiance predictions for
solar resource mapping and large-scale applications:
Improved validation methodology and detailed
performance analysis of 18 broadband radiative
models. Solar Energy, 86, 2145-2169.
Hachem, C., Fazio, P. & Athienitis, A. 2013. Solar
optimized residential neighborhoods: Evaluation and
design methodology. Solar Energy, 95, 42-64.
Huld, T. 2017. PVMAPS: Software tools and data for the
estimation of solar radiation and photovoltaic module
performance over large geographical areas. Solar
Energy, 142, 171-181.
Lee, J. & Zlatanova, S. 2009. Solar radiation over the urban
texture: LIDAR data and image processing techniques
for environmental analysis at city scale. In: LEE, J. &
ZLATANOVA, S. (eds.) 3D Geo-Information
Sciences, Lecture Notes in Geoinformation and
Cartography. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer.
Li, Y. & Liu, C. 2017. Estimating solar energy potentials
on pitched roofs. Energy and Buildings, 139, 101-107.
Murshed, S. M., Picard, S. & Koch, A. 2017. CityBEM: An
Open Source Implementation and Validation of
Monthly Heating and Cooling Energy Needs for 3D
Buildings in Cities. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote
Sens. Spatial Inf. Sci., IV-4/W5, 83-90.
Nguyen, H. & Pearce, J. M. 2010. Estimating potential
photovoltaic yield with r. sun and the open source
geographical resources analysis support system. Solar
energy, 84, 831-843.
Ogc 2012. OGC City Geography Markup Language
(CityGML) Encoding Standard 2.0.0. Open Geospatial
Consortium.
Redweik, P., Catita, C. & Brito, M. 2013. Solar energy
potential on roofs and facades in an urban landscape.
Solar Energy, 97, 332-341.
Šúri, M. & Hofierka, J. 2004. A new GIS‐based solar
radiation model and its application to photovoltaic
assessments. Transactions in GIS, 8, 175-190.
Vitucci, E. M., Falaschi, F. & Degli-Esposti, V. 2014. Ray
tracing algorithm for accurate solar irradiance
prediction in urban areas. Applied optics, 53, 5465-
5476.
Wieland, M., Nichersu, A., Murshed, S. M. & Wendel, J.
2015. Computing Solar Radiation on CityGML
Building Data. 18th AGILE International Conference
on Geographic Information Science. June 9 - 12, 2015,
Lisbon.
Wilcox, S. & Marion, W. 2008. Users manual for TMY3
data sets. Colorado: National Renewable Energy
Laboratory (NREL).
Evaluation of Two Solar Radiation Algorithms on 3D City Models for Calculating Photovoltaic Potential
303
