
Control of the Chaotic Phenomenon in Robot Path using Differential
Flatness
Salah Nasr
1
, Amine Abadi
1
, Kais Bouallegue
2
and Hassen Mekki
1
1
Laboratory of Networked Objects Control and Communication Systems, National Engineering School of Sousse,
University of Sousse, Tunisia
2
Department of Electrical Engineering, Higher Institute of Applied Sciences and Technology of Sousse, Tunisia
Keywords:
Chaotic Phenomenon, Mobile Robot, Flatness Control, Chaos Theory.
Abstract:
This paper deals with the complex chaotic behavior that can appear in the dynamic trajectory of a mobile
robot, when the robot is broken or partly damaged. However, a flatness-based controller is designed to ensure
the trajectory planning and tracking. Different mathematical tools have been used such as the flatness control
technique and non linear chaotic systems. The simulation results for the kinematic controller are presented to
demonstrate the effectiveness of this approach.
1 INTRODUCTION
The control of mobile robots has been the subject
of much research in recent years, due to the increa-
singly frequent use in dangerous or inaccessible envi-
ronments where human beings can hardly intervene.
For autonomous mobile robotics, path generation and
execution are very important tasks. Path planning is
the process of generating a sequence of trajectory de-
riving from the assigned task to the mobile robot to be
able to perform it.
The general problem is reduced in most cases to
move the robot in a known or unknown environment
(Belaidi et al., 2017), while avoiding any fixed or mo-
bile obstacles, to carry out a prescribed task. It should
define a strategy of movement (path planning)(Hargas
et al., 2015), and then execute the prescribed displa-
cement.
The robot controller, which is a major compo-
nent, has received a lot of attention from researchers.
This is why it has a direct impact on its robust-
ness and could prevent its deployment and applica-
bility in several domains (Kumar et al., 2014; Lai,
2014). Many control techniques have been propo-
sed for modern robots including the classical PID,
feedback linearization (Korayem et al., 2016; Tinh
et al., 2016), inverse dynamics, model predictive con-
trol (Klan
ˇ
car and
ˇ
Skrjanc, 2007), adaptive fuzzy-logic
control (Bakdi et al., 2017) etc.
Up to now, there has been no experimental work
that has treated the chaotic phenomenon in the ro-
bot trajectory. On the other hand, the interaction be-
tween the theory of chaos and mobile robotics has
been only recently studied, as it can be seen in (Nehm-
zow, 2003), for the generation of the unpredictable
trajectory for the robot. For example, the integration
between a chaotic system and the robot motion sy-
stem, dynamic systems, is used to impart the chaotic
behavior to a robot like the Arnold system in (Na-
kamura and Sekiguchi, 2001). An extension of this
strategy, applying various chaotic systems on the in-
tegration with the kinematics model of the robot, can
be found in (Jansri et al., 2004). In (Martins-Filho
et al., 2004), the author proposed an open loop cont-
rol approach to produce unpredictable trajectories so
as to control the velocities of the robot wheels, and the
state variables of the Lorenz chaotic system are used.
Neverthless, there has been no research work to solve
the chaotic phenomenon problem that can appear in
the robot trajectory.
In this context we propose to use a controller to
solve this problem and to facilitate the implementa-
tion of our work in a real mobile robot. One stra-
tegy of nonlinear control gaining popularity among
researchers is the differential-flatness-based control
(Veslin Diaz et al., 2011; Levine, 2009). It has been
investigated to control flexible robots (Markus et al.,
2012; Markus et al., 2017), mobile robots (Coulaud
and Campion, 2007), under-actuated planar robots
(Vivek et al., 2010), and so on. Differential flatness is
known to be well suited for the problem of trajectory
generation and tracking (Markus et al., 2013). With
Nasr, S., Abadi, A., Bouallegue, K. and Mekki, H.
Control of the Chaotic Phenomenon in Robot Path using Differential Flatness.
DOI: 10.5220/0006828302370243
In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics (ICINCO 2018) - Volume 2, pages 237-243
ISBN: 978-989-758-321-6
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
237
this strategy, the trajectories (position, velocity and
acceleration ) of a nonlinear system can be easily in-
terpolated by defining a smooth curve with initial and
final conditions. The control variables and state can
be reconstructed without having to integrate the sy-
stem equations(Levine, 2009). Thus, we utilize the
flatness control method to solve the problem of path
planning and chaotic phenomena , which can appear
in the robot trajectory; and we ensure that the mobile
robot tracks this trajectory.
This paper is organized as follows. In section 2,
we explain the basic description model of the robot.
The basic definition and control strategy of the diffe-
rential flatness theory is presented in section 3. We
describe the kinematic system and its flatness pro-
perty and we propose the control law to solve the tra-
jectory tracking problem. In section 4, we present the
chaotic phenomenon and the control law to solve the
trajectory problem. We give the concluding remarks
in section 5.
2 MODEL DESCRIPTION
The mobile robot considered in this work is a differen-
tial motion robot with two degrees of freedom, com-
posed by two independent active wheels, and a third
passive wheel (a kind of standard free-wheel). This
type of robots represents an important compromise
between the simplicity of control and the degrees of
freedom that allow the robot to accomplish the mobi-
lity requirements (Siegwart et al., 2011).
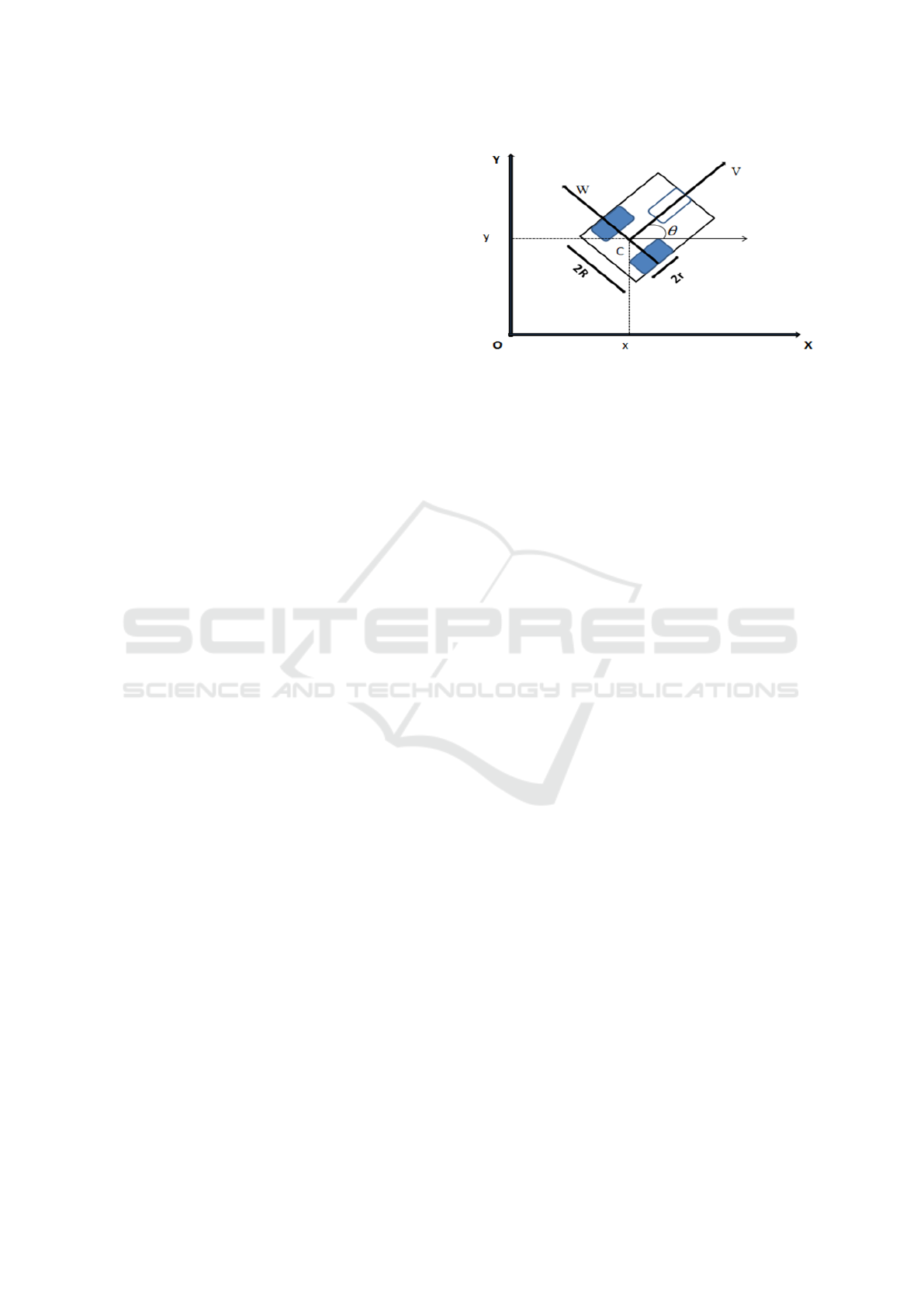
The robot structure is considered as a rigid body
operating on the horizontal plane (figure 1).Its kine-
matic model can be described as a differential system
composed of two control parameters, v and ω, which
respectively represent the values of linear and angu-
lar speeds. The state equation of the wheeled mobile
robot is written as follows:
˙x(t)
˙y(t)
˙
θ(t)
=
cosθ(t) 0
sinθ(t) 0
0 1
v(t)
ω(t)
(1)
where x and y are the position of the robot and θ
is the orientation angle of the robot. The robot displa-
cement control can be performed by supplying the li-
near and angular velocities of the body, v(t) and ω(t),
called control variables or inputs.
Figure 1: Geometry of mobile robot on Cartesian plane.
3 FLATNESS CONTROL
METHOD
Flatness is a characteristic or property of a particular
system in which all solutions of the system can be pa-
rameterized by a finite number of functions and their
derivatives (Nicolau and Respondek, 2013). For the
analysis and design of controllers for nonlinear sys-
tems with this characteristic, this mathematical pro-
perty is extensively used.
3.1 Flatness Theory
Differential flatness is a property of control systems
Dynamics, as presented by Fliess et al. (Fliess et al.,
1995). Differential flatness, provides a unified ana-
lysis framework for trajectory planning and control
of nonlinear systems. This is particularly useful for
non-linear sub-actuated systems where it is difficult
to plan and to analytically design possible trajecto-
ries. The necessary condition for a control system to
be differentially flat is that it must be controlled.
From a control perspective, a good explanation of
differential flatness for any nonlinear systems of the
form,
˙x = f (x, u);x ∈ R
n
, u ∈ R
m
(2)
The system can be stated to be differentially flat if and
only if there exists a finite set of independent varia-
bles, equal to the number of inputs, called flat outputs
y = [y
1
, ..., y
m
]
T
in such a way that :
y = y
x, u, ˙u, ...,
u
(p)
.
(3)
x = x(y, ˙y, ¨y, ...,
y
(r)
) (4)
u = u(y, ˙y, ¨y, ...,
y
(q)
) (5)
ICINCO 2018 - 15th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
238

Moreover, for a flat system, there is an inverti-
ble input and state transformations that can transform
non-linear systems into linear canonical forms (con-
trollable linear chain of integrators). An arbitrary
trajectory for flat outputs corresponds to the original
state of the system of reference trajectories.This ma-
kes planning possible in the flat output domain. In
addition, the linear feedback of the control can be de-
signed in the field of linear flat outputs by closing the
loop on errors in the flat outputs and their derivatives.
3.2 Flatness Control Strategy
The Control design and trajectory planning for flat sy-
stems are relatively easy because the trajectory can be
defined in terms of flat outputs while the required con-
trol input can be obtained using the flatness property.
In order to prove how the kinematic model of the
mobile robot is differentially flat, we choose the Car-
tesian position of the robot center (x, y) as flat out-
puts. To design a diffeomorphism between flat out-
puts and their derivatives and original states, the in-
put prolongation is utilized. Prolongation is a crucial
method used where the vector representing the state
is extended by some system parameters which is used
to describe a particular system as a differentially flat
system. A very common prolongation way means is
the input prolongation where the input also becomes
a state. This property is utilized in optimal trajectory
generation and tracking control laws.
Now, on performing one prolongation of v as an
additional state, we describe the prolonged systems
by:
˙x = v cos θ
˙y = v sin θ
˙v =
¯
U
1
˙
θ =
¯
U
2
(6)
Here,
¯
U
1
,
¯
U
2
are the new inputs for the prolonged
system that satisfy:
¯
U
1
= ˙v
¯
U
2
= ω
(7)
By choosing the flat outputs
Fo = [Fo
1
, Fo
2
]
T
= [x, y]
T
(8)
All the inputs and the state variables can be ex-
pressed in terms of flat outputs and their derivatives.
With (x, y) = (Fo
1
, Fo
2
)
v =
q
˙
Fo
1
2
+
˙
Fo
2
2
, θ = arctan
˙
Fo
2
˙
Fo
1
, (9)
The inputs
¯
U
1
,
¯
U
2
can be defined as follows:
¯
U
1
= ˙v =
˙
Fo
1
¨
Fo
1
+
˙
Fo
2
¨
Fo
2
q
˙
Fo
1
2
+
˙
Fo
2
2
(10)
¯
U
2
=
˙
θ =
˙
Fo
1
¨
Fo
2
+
¨
Fo
1
˙
Fo
2
˙
Fo
1
2
+
˙
Fo
2
2
(11)
By differentiating the flat outputs up to an input
appears, an invertible relation between inputs and hig-
her derivatives of the flat outputs can be equivalently
build from equation 10 and equation 11 as described
follows:
¨
Fo
1
¨
Fo
2
= D
¯
U
1
¯
U
2
(12)
With
D =
cosθ −vsinθ
sinθ vcosθ
(13)
the inputs are choosing as
¯
U
1
¯
U
2
= D
−1
V =
1
v
vcosθ vsinθ
− sinθ cosθ
V (14)
Then equation 12 can be written as
¨
Fo = V. (15)
The reference trajectory must allow the robot
to move, from an initial position with coordinates
(x, y) at time t=0 to a final position with coordinates
(x f , y f ) at time t = 10 s, with minimum of energy and
also avoid some static circular obstacles. These ob-
stacles are defined by the following equation:
Ob
i
= (x − x
r
)
2
+ (y − y
r
)
2
− R (16)
Where x
r
andy
r
are the coordinates of the center of
the circle and r denotes the radius, i is the number of
obstacles.
The constraint which means that the mobile robot
avoids the obstacle is defined as follows:
Ob
1
(x, y) = (x − 2)
2
+ (y − 2)
2
− 1 ≥
0 (27)
Ob
2
(x, y) = (x − 6)
2
+ (y − 3)
2
− 1 ≥
0 (28)
Ob
3
(x, y) = (x − 8)
2
+ (y − 5)
2
− 1 ≥
0 (29)
Ob
4
(x, y) = (x − 6)
2
+ (y − 6)
2
− 1 ≥
0 (29)
Ob
5
(x, y) = (x − 2)
2
+ (y − 6)
2
− 1 ≥
0 (29)
To meet these objectives, the problem of reference
trajectory generation is formulated as an optimization
problem in the following way:
Control of the Chaotic Phenomenon in Robot Path using Differential Flatness
239

min
p
˙x
2
+ ˙y
2
(17)
Ob
i
≥ 0 (18)
This problem of optimization is solved by the
most efficient method based on the flatness and the
B-spline function (Bahrami et al., 2009).
x(0) = 0 x(10) = 9
y(0) = 0 x(10) = 9
θ(0) = 0 θ(10) = 0
v(0) = 0 v(10) = 0
(19)
Figure 2: Simulation results of reference and real trajecto-
ries of x position.
Figure 3: Simulation results of reference and the real trajec-
tories of y position.
In Figure 2and 3, we show that the flatness con-
trol input defined by equation 10 and equation 11
permits a good tracking of the desired trajectory for
the mobile Robot. Therefore, the flatness property is
considered as a powerful tool for path planning and
tracking trajectory. As depicted in Figure6, the mo-
bile robot can easily avoid the defined static obstacle.
Figure 4: Simulation results of the control input U1.
Figure 5: Simulation results of the control input U2.
Figure 6: Simulation results of optimal trajectory with ob-
stacle avoidance.
4 CHAOTIC PHENOMENA
Deterministic chaos has been employed for develo-
ping consumer electronic products and intelligent in-
dustrial systems.
ICINCO 2018 - 15th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
240

4.1 Chaos Theory
During the 20th century, three great revolutions
occurred: quantum mechanics, relativity and chaos.
The theory of chaos, also called the dynamical system
theory, is the study of unstable aperiodic behavior in
deterministic dynamical systems, which show a sen-
sitive dependence on initial conditions (Vaidyanathan,
2013).
The chaos theory has drawn a great deal of at-
tention in the scientific community for almost two
decades. Chaos is a very interesting phenomenon
in nonlinear dynamical systems, which has been in-
tensively studied during the last decades and used
in several possible commercial applications (Trejo-
Guerra, 2008).
The Lorenz system has become one of paradigms
in the research of chaotic systems. The Lorenz chao-
tic system is utilized for investigation. The dynamical
equations of the Lorenz system is given as follows:
˙
X
1
= −10X
1
+ 10.X
2
˙
X
2
= 28X
1
− X
2
− X
1
.X
3
˙
X
3
= −
8
3
X
3
+ X
1
.X
2
(20)
The implementation of this dynamic system is
presented in figure 7.
Figure 7: Lorenz chaotic system.
4.2 Chaos Analysis in Mobile Robot
The most applications of chaos in robotics are clas-
sified into two types: chaos synthesis and chaos ana-
lysis ; chaos synthesis in robotics is defined as the
application of chaotic systems for motion planning of
autonomous robots and entails the generation of artifi-
cial chaos to make different mobile robots accomplish
specific tasks (Aihara and Katayama, 1995). Whe-
reas, chaos analysis implies the observation of chaotic
behavior in autonomous robots. Therefore, control-
ling the chaotic behavior of the mobile robot becomes
a worthwhile endeavor.
In this subsection, based on the Lorenz chaotic sy-
stem, we give a chaotic behavior to the mobile robot.
Subsequently, we use the control technique based on
differential flatness to control this chaotic behavior
in order to allow the robot to complete its trajectory,
despite its behavior, and to achieve its objective.
By using the dynamic equation of the Lorenz sy-
stem, introduced in equation 20, we will find the robot
equation of motion as follows:
˙
X
1
= −10X
1
+ 10.X
2
˙
X
2
= 28X
1
− X
2
− X
1
.X
3
˙
X
3
= −
8
3
X
3
+ X
1
.X
2
˙x = v cos(X
1
)
˙y = v sin(X
1
)
(21)
The proposed system described in equation 21
generates an unpredictable path by giving a chaotic
behavior of the mobile robot with two independent
active wheels.
Figure 8: Chaotic phenomena in mobile robot.
As depicted in figure 8, the sensitivity to initial
conditions makes the robot trajectory extremely un-
predictable. Then with this behavior, the robot can
not reach its objective. Thus, moving from an initial
position to a final one is almost impossible with this
behavior.
In this context, control over flatness may be a good
solution to solve this problem. We adopt the techni-
que used in section 3 to restore the control of the new
kinematic system combined with the Lorenz chaotic
system. In this case, we choose θ = X
1
.
5 DISCUSSION
Figures 2, 3, 4 and 5 illustrate the effectiveness of the
closed-loop flatness control which allows the mobile
robot to follow the desired reference trajectory pro-
perly. By ensuring a good tracking of the trajectory,
Control of the Chaotic Phenomenon in Robot Path using Differential Flatness
241

Figure 9: Flatness control of x chaotic trajectory of mobile
robot.
Figure 10: Flatness control of y chaotic trajectory of mobile
robot.
Figure 11: Flatness control of x-y chaotic trajectory of mo-
bile robot with obstacle avoidance.
the mobile robot can move by avoiding the static ob-
stacles with the minimal energy and by choosing the
optimal trajectory.
Time [s]
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
x
-4
-2
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
Figure 12: Flatness control of second chaotic trajectory of
mobile robot.
Figure 7 shows the behavior of the Lorenz chaotic
system in the Cartesian plan.
In figures 9, 10 and 12 we present the good ef-
fectiveness of chaotic trajectory tracking , and we en-
sure that the robot better reaches its desired trajectory.
Even more, as depicted in figure 11, we can show the
robustness of the control strategy with chaotic pheno-
menon and in the presence of obstacles.
Next, some endeavors for uncovering the chaotic
behavior of robots are presented. Chaos can be em-
ployed for analyzing robotic arms, and chaos quan-
tifiers can be used for analyzing chaotic dynamics in
robot-environment interaction.
6 CONCLUSIONS
This article has described the path planning and the
flatness based tracking control of a wheeled mobile
robot. The flatness-based approach to trajectory con-
trol and optimal trajectory tracking offers a fast al-
ternative to the classical control for such robots. Ha-
ving determined the flat output of the mobile robot,
the trajectory control has been determined with rea-
sonable accuracy. Secondly, we have presented a cha-
otic phenomenon tuned to the behavior of the auto-
nomous mobile robot, so we have solved the problem
related to this phenomenon using the differential flat-
ness method.
In recent years, the discovery of chaos has attrac-
ted much interest among investigators. Deterministic
chaos leads to a quantitative analysis, which is the es-
sence of science. In spite of several efforts to find evi-
dence of chaotic dynamics in robotics, useful appli-
cations of deterministic chaos in robotics have rarely
been studied.
ICINCO 2018 - 15th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
242

REFERENCES
Aihara, K. and Katayama, R. (1995). Chaos engineering in
japan. Communications of the ACM, 38(11):103–107.
Bahrami, M., Jamilnia, R., and Naghash, A. (2009). Trajec-
tory optimization of space manipulators with flexible
links using a new approach. International Journal of
Robotics, 1(1):48–55.
Bakdi, A., Hentout, A., Boutami, H., Maoudj, A., Hachour,
O., and Bouzouia, B. (2017). Optimal path planning
and execution for mobile robots using genetic algo-
rithm and adaptive fuzzy-logic control. Robotics and
Autonomous Systems, 89:95–109.
Belaidi, H., Bentarzi, H., and Belaidi, M. (2017). Imple-
mentation of a mobile robot platform navigating in dy-
namic environment. In MATEC Web of Conferences,
volume 95, page 08004. EDP Sciences.
Coulaud, J. and Campion, G. (2007). Optimal trajectory
tracking for differentially flat systems with singulari-
ties. In Control and Automation, 2007. ICCA 2007.
IEEE International Conference on, pages 1960–1965.
IEEE.
Fliess, M., L
´
evine, J., Martin, P., and Rouchon, P. (1995).
Flatness and defect of non-linear systems: introduc-
tory theory and examples. International journal of
control, 61(6):1327–1361.
Hargas, Y., Mokrane, A., Hentout, A., Hachour, O., and
Bouzouia, B. (2015). Mobile manipulator path plan-
ning based on artificial potential field: Application on
robuter/ulm. In Electrical Engineering (ICEE), 2015
4th International Conference on, pages 1–6. IEEE.
Jansri, A., Klomkarn, K., and Sooraksa, P. (2004). On com-
parison of attractors for chaotic mobile robots. In In-
dustrial Electronics Society, 2004. IECON 2004. 30th
Annual Conference of IEEE, volume 3, pages 2536–
2541. IEEE.
Klan
ˇ
car, G. and
ˇ
Skrjanc, I. (2007). Tracking-error model-
based predictive control for mobile robots in real time.
Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 55(6):460–469.
Korayem, M., Yousefzadeh, M., and Manteghi, S. (2016).
Dynamics and input–output feedback linearization
control of a wheeled mobile cable-driven parallel ro-
bot. Multibody System Dynamics, pages 1–19.
Kumar, N., Panwar, V., Borm, J.-H., and Chai, J.
(2014). Enhancing precision performance of trajec-
tory tracking controller for robot manipulators using
rbfnn and adaptive bound. Applied Mathematics and
Computation, 231:320–328.
Lai, C. Y. (2014). Improving the transient performance
in robotics force control using nonlinear damping.
In Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics (AIM), 2014
IEEE/ASME International Conference on, pages 892–
897. IEEE.
Levine, J. (2009). Analysis and control of nonlinear sys-
tems: A flatness-based approach. Springer Science &
Business Media.
Markus, E., Agee, J., Jimoh, A., Tlale, N., and Zafer, B.
(2012). Flatness based control of a 2 dof single link
flexible joint manipulator. In SIMULTECH, pages
437–442.
Markus, E. D., Agee, J. T., and Jimoh, A. A. (2013). Tra-
jectory control of a two-link robot manipulator in the
presence of gravity and friction. In AFRICON, 2013,
pages 1–5. IEEE.
Markus, E. D., Agee, J. T., and Jimoh, A. A. (2017). Flat
control of industrial robotic manipulators. Robotics
and Autonomous Systems, 87:226–236.
Martins-Filho, L. S., Machado, R. F., Rocha, R., and Vale,
V. (2004). Commanding mobile robots with chaos. In
ABCM Symposium Series in Mechatronics, volume 1,
pages 40–46.
Nakamura, Y. and Sekiguchi, A. (2001). The chaotic mo-
bile robot. IEEE Transactions on Robotics and Auto-
mation, 17(6):898–904.
Nehmzow, U. (2003). Quantitative analysis of robot–
environment interactiontowards scientific mobile ro-
botics. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 44(1):55–
68.
Nicolau, F. and Respondek, W. (2013). Multi-input control-
affine systems linearizable via one-fold prolongation
and their flatness. In Decision and Control (CDC),
2013 IEEE 52nd Annual Conference on, pages 3249–
3254. IEEE.
Siegwart, R., Nourbakhsh, I. R., and Scaramuzza, D.
(2011). Introduction to autonomous mobile robots.
MIT press.
Tinh, N. V., Linh, N. T., Cat, P. T., Tuan, P. M., Anh, M. N.,
and Anh, N. P. (2016). Modeling and feedback line-
arization control of a nonholonomic wheeled mobile
robot with longitudinal, lateral slips. In Automation
Science and Engineering (CASE), 2016 IEEE Inter-
national Conference on, pages 996–1001. IEEE.
Trejo-Guerra, R., T.-C. E. C.-H. C. S.-L. C. F. M. (2008).
Current conveyor realization of synchronized chuas
circuits for binary communications. IEEE . DTIS, pa-
ges 1–4.
Vaidyanathan, S. (2013). Analysis and adaptive synchro-
nization of two novel chaotic systems with hyperbolic
sinusoidal and cosinusoidal nonlinearity and unknown
parameters. Journal of Engineering Science and
Technology Review, 6(4):53–65.
Veslin Diaz, E., Slama, J., Dutra, M., Lengerke, O., and Mo-
rales Tavera, M. (2011). Trajectory tracking for robot
manipulators using differential flatness. Ingenier
´
ıa e
Investigaci
´
on, 31(2):84–90.
Vivek, S., Sunil, K., Jaume, F., et al. (2010). Differential
flatness of a class of n-dof planar manipulators driven
by 1 or 2 actuators.
Control of the Chaotic Phenomenon in Robot Path using Differential Flatness
243
