
Shared Admittance Control for Human-Robot Co-manipulation based
on Operator Intention Estimation
Jonathan Cacace, Alberto Finzi and Vincenzo Lippiello
PRISMA Lab, Dipartimento di Ingegneria Elettrica e Tecnologie dell’Informazione,
Universit
`
a degli Studi di Napoli, Federico II, via Claudio 21, 80125, Naples, Italy
Keywords:
Variable Admittance Control, Human-Robot Co-manipulation, Shared Control.
Abstract:
Collaborative robots are increasingly employed in industrial workplaces, assisting human operators in decreas-
ing the weight and the repetitiveness of their activities. In this paper, we assume the presence of an operator
cooperating with a lightweight robotic arm, able to autonomously navigate its workspace, while the human
co-worker physically interacts with it leading and influencing the execution of the shared task. In this scenario,
we propose a human-robot co-manipulation method in which the autonomy of the robot is regulated according
to the operator intentions. Specifically, the operator contact forces are assessed with respect to the autonomous
motion of the robot inferring how the human motion commands diverges from the autonomous ones. This in-
formation is exploited by the system to adjust its role in the shared task, leading or following the operator
and to proactively assist him during the co-manipulation. The proposed approach has been demonstrated in
an industrial use case consisting of a human operator that interacts with a Kuka LBR iiwa arm to perform a
cooperative manipulation task. The collected results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach.
1 INTRODUCTION
The widespread of lightweight robots enables to the
development of novel service robotic applications,
where humans and robots collaborate for the execu-
tion of shared tasks (Corrales et al., 2012). Such sys-
tems, also known as cobots, can share their workspace
with human workers ensuring safe physical human-
robot cooperation and allowing humans and robots to
work side-by-side to merge their complementary abil-
ities. In this perspective, advanced human-robot col-
laborative methods can facilitate the human work in
all the operations difficult to automatize both in in-
dustrial tasks, such as assembly of heavy or complex
parts (Giordano et al., 2008), and service tasks like
cyclic object manipulation in dynamic environments.
This paper presents a framework that supports
physical human-robot interaction during the execu-
tion of cooperative tasks. In the proposed approach,
the robotic system on-line adapts its behaviour ac-
cording to the operator intention, which is continu-
ously estimated from his/her contact forces. In par-
ticular, we assume a shared control system, where the
robot can autonomously execute a requested manip-
ulation action, while the human operator can physi-
cally interact with the robot end effector, adjusting or
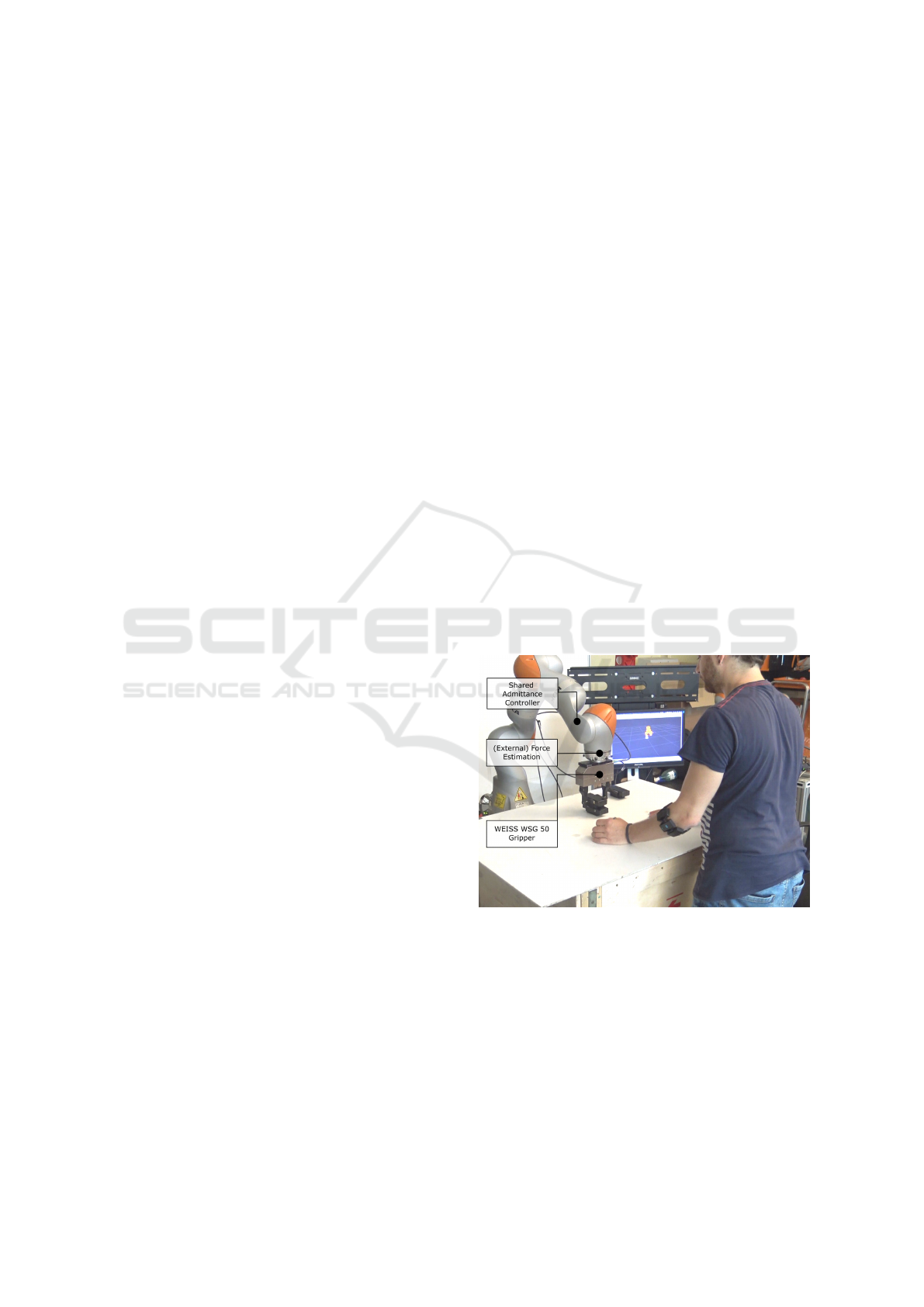
Figure 1: The human operator physically interacts with a
lightweight manipulator during a cooperative manipulation
task.
modifying the motion of the robot or its target. In this
scenario, human interventions can be associated with
different intentions: lead the robot, slightly adjust its
motion, change the target of the action, speed up its
execution or use the manipulator as a passive tool. In
order to exploit these interaction modes in an intuitive
manner, human interventions are to be interpreted and
the robotic behaviour must be consequently adapted.
Cacace, J., Finzi, A. and Lippiello, V.
Shared Admittance Control for Human-Robot Co-manipulation based on Operator Intention Estimation.
DOI: 10.5220/0006831800610070
In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics (ICINCO 2018) - Volume 2, pages 61-70
ISBN: 978-989-758-321-6
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
61

For this purpose, we propose a shared control
system supporting different autonomous and semi-
autonomous operative modes, regulated according to
the operator intentions, which are interpreted consid-
ering contact forces provided by the human operator.
In this context, the contact forces are continuously as-
sessed to inform the robot about the next target point
to reach or to interpret the motion deviation intended
by the human during cooperative manipulation. The
intention recognition process relies on a 3-Layer Neu-
ral Networks that, upon receiving as input the robot
motion direction and the operator contact forces, in-
fers the intention of the operator to follow/contrast
the manipulator motion towards a target point, devi-
ate from the latter, or use the robot manipulator in
direct manual control in order to perform other ac-
tions. In this scenario, the robot can operate in ei-
ther a passive or an active mode. When the estimated
intention of the human is not aligned with the target
of the robot, the latter passively follows the human
guidance and the robot behaviour is fully compliant
to the operator contact. On the other hand, when
human interventions are coherent with respect to the
current robot target, the robotic system can keep ex-
ecuting the current task, while suitably adjusting its
motion trajectory following the corrections provided
by the operator. In summary, this work proposes a
novel mixed-initiative co-manipulation framework in
which physical interaction, interpretation of the hu-
man interventions, task/target switching, and admit-
tance adjustment are seamlessly integrated. The aim
is to conciliate, in a flexible and adaptive manner, the
precision and the strength of the robotic system with
the dexterity and the decisional capability of the hu-
man operators.
In order to demonstrate the proposed framework,
we designed a human-robot interaction setup (see
Fig. 1), where the human operator cooperates with a
Kuka LBR iiwa robot during the execution of a ma-
nipulation task. In this scenario, the effectiveness of
the system is assessed by comparing the fatigue and
the effort needed by the operator to accomplish the
task with and without the assistance of the proposed
framework.
The remainder of this paper is organized as fol-
lows. In Section 2 a brief overview of related works
is presented, in Section 3 the system architecture is
described, while in Sections 4 and 6 the human in-
tention estimation process is discussed. Section 5 de-
scribes how the operator intention estimation is ex-
ploited in the shared controller. Finally, in Section 7
an experimental case study to test the effectiveness of
our approach is presented.
2 RELATED WORKS
Estimating the operator intentions in order to regulate
the robot behavior during the execution of a shared
task is crucial in any kind of Human-Robot collabo-
ration activity (Hoffman and Breazeal, 2004; Hoff-
man and Breazeal, 2007). Flexible and natural in-
teraction with humans is often needed to enable co-
operation with robots in social and industrial or ser-
vice robotic applications. This problem has been ad-
dressed by different works in the robotic literature.
For instance, a method to adapt the role of the robot
considering operator fatigue during a co-manipulation
task is presented in (Peternel et al., 2016), in which
the robot learns by imitation how to assist the oper-
ator taking contact forces into account, but without
inferring his/her intentions. More related to our work,
in (Jlassi et al., 2014) a shared trajectory generator
based on operator force contact is proposed to trans-
late human intentions into ideal trajectories the robot
should follow. In this case an on-line trajectory gen-
erator is combined with a classical impedance con-
trol system, instead we rely on an integrated inten-
tion estimation system. Other approaches exploit hu-
man intention estimation to increase the efficiency of
task planning algorithms ((Hoang and Low, 2013) and
(Caccavale et al., 2016)). Intention recognition meth-
ods typically consider external forces excreted by the
human operator on the robot side to regulate the low
level behaviour of the robot (Park et al., 2016)(Pe-
ternel and Babic, 2013)(Gribovskaya et al., 2011)(Li
et al., 2015). Differently, our approach is aimed to
adapt robot task execution, without influencing the
low level control of the robot.
In (Li and Ge, 2014) motion intention of the hu-
man partner is detected using the human limb model
to estimate the desired trajectory, while in (Kouris
et al., 2017) external force information is exploited to
discern between a human contact and an unexpected
collision. Human motion estimation is also deployed
in (Ge et al., 2011), where the authors exploit Neu-
ral Networks to extract human motion parameter and
predict whether the human interventions are active or
passive. In contrast, we exploit Neural Networks to
directly classify the human force contacts with respect
to the robot motion during the execution of a coopera-
tive task, as already proposed in (Cacace et al., 2018).
Several other works exploit visual sensors to pre-
dict human intentions, as in (Bascetta et al., 2011),
where human motion trajectories are monitored to
predict the human presence in robotic cells, or like
in (Cacace et al., 2016), where the authors address
the problem of implicitly selecting a robot of a team
given the sequence of commands issued by the op-
ICINCO 2018 - 15th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
62
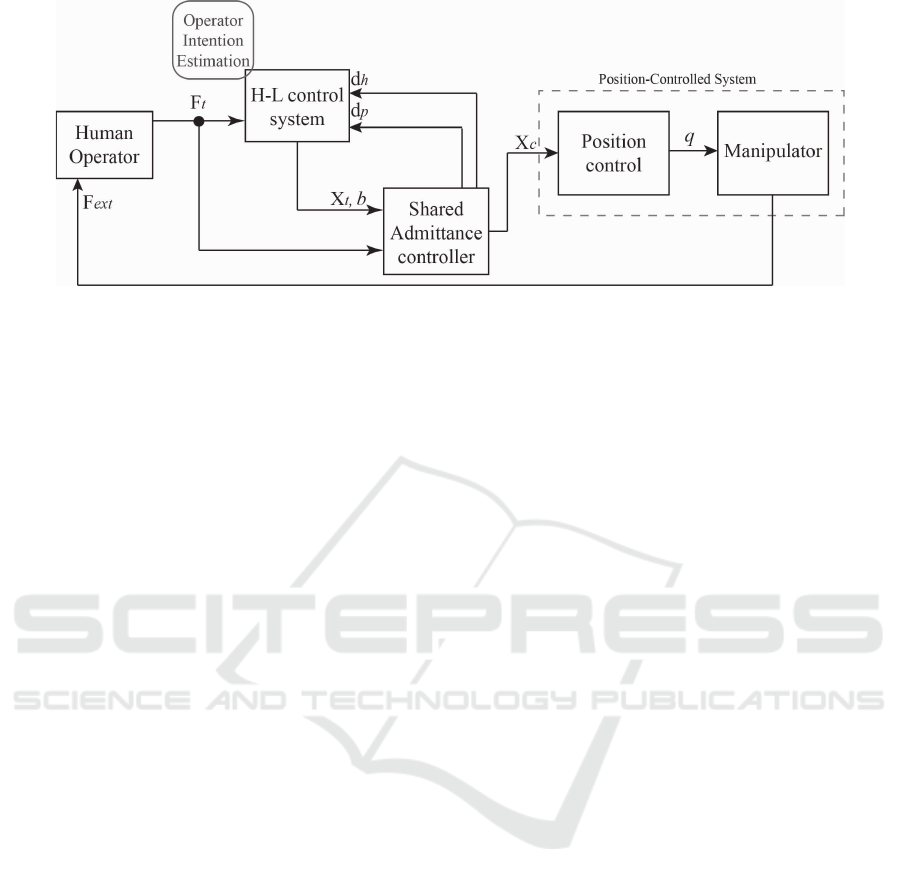
Figure 2: Shared control architecture.
erator. Other approaches propose probabilistic meth-
ods to infer human intentions. For instance, in (Kel-
ley et al., 2008) a Hidden Markov Model (HMM) has
been used to estimate the most likely human activ-
ity perceived by a mobile robot, or in (Awais and
Henrich, 2010) and (Best and Fitch, 2015), where
Bayesian inference and weighted probabilistic state
machines, respectively, have been used to perform in-
tention recognition.
Notice that, in contrast with other approaches to
physical human-robot interaction framework based
on human intention estimation that asses operator in-
tentions to enable a compliant physical human-robot
interaction, we use this information to switch from
an active to passive participation of the robot to the
shared task and replan when a novel intended target is
estimated from the human physical interventions. In
this perspective, the approach proposed in this work
can be related to the one proposed by (Cacace et al.,
2014) for shared teleoperation of an aerial vehicles;
however this approach is less explored in physical col-
laborative manipulation.
3 CONTROL ARCHITECTURE
In this section, we describe the proposed control ar-
chitecture, which is depicted in Figure 2. The mo-
tion of the robot is managed by the Shared Admit-
tance Controller module, whose goal is to command
the robot to reach desired targets. As for the robotic
manipulator, we assume to control the position and
orientation of its end effector, relying on the robot
inner control loop to solve inverse kinematic prob-
lem; we also assume that the (external) forces act-
ing on the gripper are directly estimated by the robot
itself. During physical human-robot interaction, the
operator contact forces exerted on the end effector
are continuously monitored by the H-L control sys-
tem that exploits the Operator Intention Estimation
sub-module to assess human intentions. This infor-
mation is exploited by the Shared Admittance Con-
troller module in order to suitably adapt the robot be-
haviour during the execution of the cooperative task.
In the following, all modules of the architecture are
further detailed.
As already stated, the Human Operator can physi-
cally interact with the manipulator moving its end ef-
fector within a defined workspace. In particular, we
assume that he/she applies a force F
t
on the robot end
effector and perceives a force feedback F
ext
. On the
other hand, the H-L control system is responsible to
select the target point to be reached in order to ac-
complish a given task. The target point X
t
is sent
to the Shared Admittance Controller along with the
classified user behaviour b to start the motion of the
robot. This module is to generate the motion data X
d
needed to reach the target X
t
. In addition, exploiting
an admittance controller, this module is responsible to
combine the autonomous motion data with the con-
trol inputs F
t
provided by the operator. In physical
Human-Robot Interaction, the admittance control is
used to establish a dynamic relationship between the
forces applied to the robot and the displacement from
its desired position (Hogan, 1984). The admittance
controller is described by the typical second-order re-
lationship:
m ¨x + d ˙x + kx = F (1)
that can be represented as (see (Siciliano and Villani,
2000)):
M
d
(
¨
X
c
−
¨
X
d
) + D
d
(
˙
X
c
−
˙
X
d
) + K
d
(X
c
− X
d
) = F
t
(2)
Where M
d
, D
d
and K
d
are the desired virtual iner-
tia, the virtual damping and the virtual stiffness, re-
spectively, modelling the behaviour of the system as
a mass-spring-damper system. Typically, during co-
manipulation tasks the operator aims at moving the
robotic arm in free motion. For this reason, the stiff-
ness K
d
is set to zero in order to nullify the elastic
Shared Admittance Control for Human-Robot Co-manipulation based on Operator Intention Estimation
63
behaviour of the system. The output of this module
is the compliant position X
c
, representing the control
command for the Position-Controlled System. Finally,
the commanded position is converted into joint values
q, which are then applied to the manipulator. When no
target is selected by the H-L control system, the posi-
tion X
t
is set to the current position of the end effector.
The Operator Intention Estimation sub-module is
used to asses the operator intentions. Its goal is to
estimate human intentions of following or diverging
from the autonomous motion, while classifying dif-
ferent possible behaviours of the user. The operator
intentions are inferred exploiting a Neural Network
(see Section 4) using the following information: the
contact forces F
t
the operator exerts on the robotic
gripper, the motion direction d
h
inducted by the op-
erator, and the motion direction d
p
generated by the
shared controller. The classified behaviour is then
sent to the Shared Controller module that uses this
information to modify its level of autonomy during
the execution of the task as described in Section 5.
In order to lead the robot towards a new position, the
H-L control system must select the target the operator
is trying to reach. For this reason, we assume that,
for each task, the system is provided with the set of
possible positions to be reached during the execution
of that task. This module exploits this knowledge to
infer the operator intention to move the manipulator
toward one of these points.
4 OPERATOR INTENTION
ESTIMATION
In this section, we detail the operator intention estima-
tion process. As already stated, this process relies on
a Neural Network classifier (Bishop, 1995) properly
adapted to our domain. An Artificial Neural Network
(ANN) is composed by a list of nodes, called artificial
neurons distributed on multiple layers. Typically, data
to classify travel from the first (input) to the last (out-
put) layer, possibly after traversing different internal
(hidden) layers. In this structure, the number of nodes
of the first and last layer, represents the number of ex-
pected input parameters and the number of possible
output classes, respectively. In order to classify hu-
man intentions, we designed a neural network of three
layers. The input and output layers contain, respec-
tively, 3 and 4 nodes, while we considered 25 nodes
in the middle hidden layer. Our aim is to use this neu-
ral network to compare the motion direction intended
by the operator with respect to the one planned and
executed by the autonomous system in order to un-
derstand whether the human and the robot activities
Table 1: Operator behaviour interpretation.
Class ID Class Name Description
#0 Accompany The operator is
touching the end
effector without
providing any con-
tribution to the
task.
#1 Opposite The operator moves
the manipulator in
the opposite direc-
tion of the planned
path.
#2 Coinciding The operator moves
the manipulator fol-
lowing the planned
path.
#3 Coinciding deviation The operator devi-
ates from the planned
path, trying to reach a
target.
and goals are aligned or not. The input of this net-
work is calculated starting from the information about
the contact forces F
t
, the motion direction induced by
the operator d
c
, the motion generated by the controller
d
d
to follow the path toward the target point. We as-
sume that only linear segments are used to navigate
the workspace. In addition, the closest point C
p
of
the end effector with respect to the path segment un-
der execution is continuously calculated in order to
inform the system on how far is the robot with respect
to the planned trajectory. Therefore, the input of the
Neural Network is represented by:
• ||F
t
||: The magnitude of forces exerted by the op-
erator.
• ||X
c
−C
p
||: The distance between the current end
effector position and the closest point on the path
segment under execution.
• ∠(
−→
d
c
,
−→
d
d
): The deviation between the planned and
human motions, calculated as the angle between
the two movement vectors.
Table 1 reports the classes recognized by the Neu-
ral Network along with a brief description of the as-
sociated interpretation of the operator behaviours. We
distinguish the following four behaviours (three of
them are shown in Figure 3). In the first place, we
consider the case in which the operator is in physical
contact with the gripper, but only accompanying the
manipulator (i.e. waiting that the autonomous system
accomplishes its goal), without providing any addi-
tional contribution to the task execution (Accompany).
The second case is illustrated in Figures 3(c) and 3(d),
where the operator is driving the robot in the oppo-
site direction with respect to the trajectory and target
planned by the autonomous system (Opposite). In-
stead, in Figure 3(a), the operator is moving the robot
end effector in the same direction of the planned path
ICINCO 2018 - 15th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
64
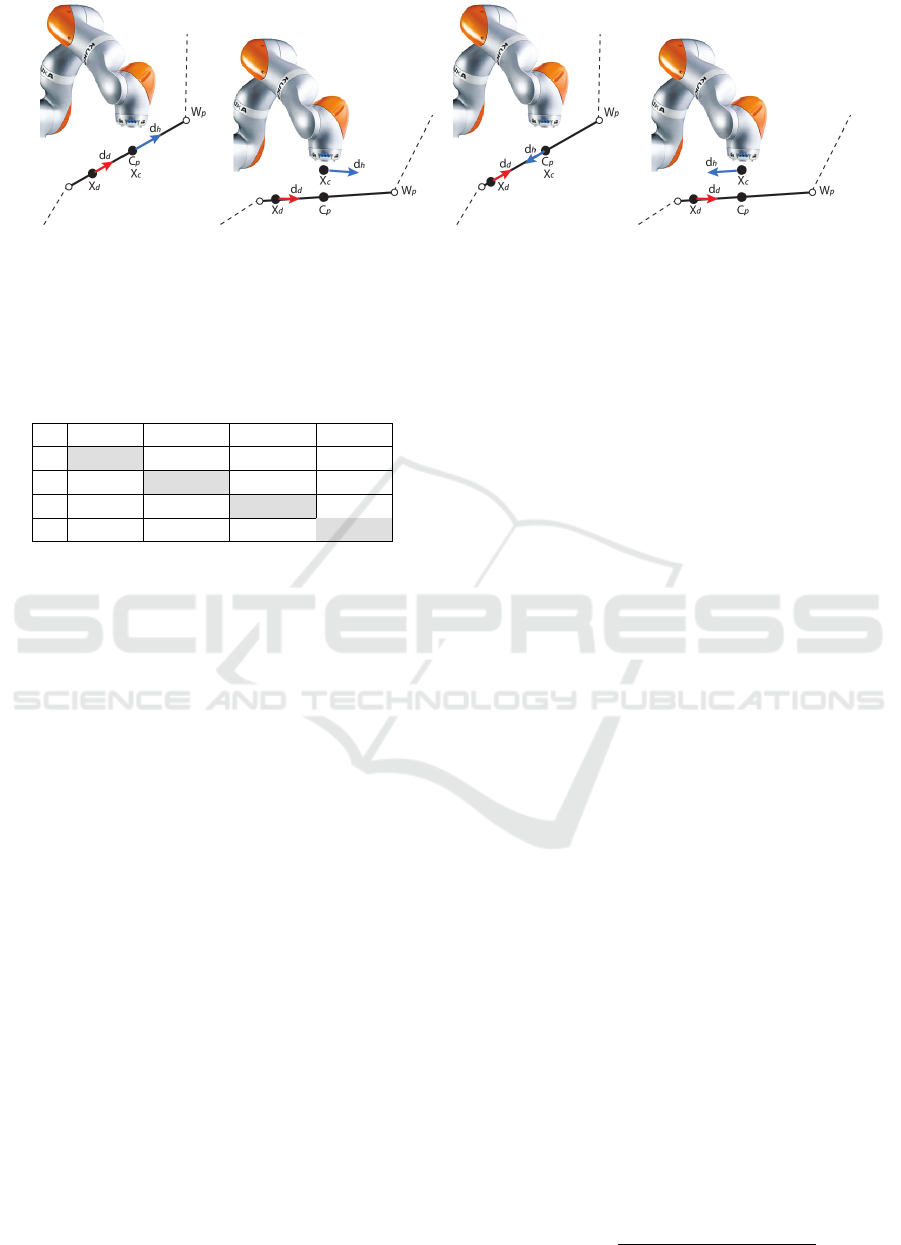
(a) Coinciding be-
haviour
(b) Coinciding deviation be-
haviour
(c) Opposite behaviour (d) Opposite behaviour
Figure 3: Different operator behaviours. The red arrow represents the autonomous motion direction D
d
, the blue arrow is the
operator motion direction d
h
. The robot is moving toward the waypoint W
p
, while C
p
is the closest point between the end
effector and the planned path.
Table 2: Confusion Matrix.
0 1 2 3
0 89.2% 0.23% 10.57% 0%
1 3.2% 95.02% 0.0% 1.78%
2 6.3% 0.6% 84.1% 9.0%
3 0.0% 5.58% 5.12% 89.3%
(Coinciding). Finally, Figure 3(b) illustrates the case
in which the operator moves the end effector away
from the planned path, but he/she is still trying to
reach the planned target (Coinciding deviation).
As for the training of the Neural Network, we in-
volved a group of 10 users (students and researchers)
asking them to physically interact with the robotic
arm (10 minutes each) in different interactive super-
vised situations covering the intentions classes intro-
duced above. During the training phase, the manipu-
lator is programmed to move towards predefined way-
points. This way, we collected several examples of
the operator interactive behaviour for each class. The
final training set used for the system evaluation is
composed of about 10000 samples and the network
has been trained using the back propagation function.
Once trained, we tested the recognition system with a
different group of users similarly composed, interact-
ing with the manipulator whose task is to follow a pre-
planned squared path with its end effector. Table 2
reports the confusion matrix of the intention classifier
showing that the recognition system has been able to
correctly classify 89.4% of the samples.
5 SHARED ADMITTANCE
CONTROL BASED ON
OPERATOR INTENTION
ESTIMATION
In this section, we discuss how the robot uses the esti-
mation of the operator intentions to adapt its role and
interaction mode during the execution of the shared
task. As already stated, the robot can switch from a
passive to an active operative mode. In the first case,
the manipulator is fully compliant to operator contact
without providing any contribution to the task, while
in the second case the manipulator is actuated to bet-
ter assist the operator in reaching the target position
X
wp
= (x
wp
,y
wp
,z
wp
). Referring to schema depicted
in Figure 2, in order to reach the target state, a velocity
reference
˙
X
d
command at a certain time i is generated
as follow:
¨
X
d
i
= ω
2
e
p
− 2ζ
˙
X
d
i−1
(3)
˙
X
d
i
=
˙
X
d
i−1
+
¨
X
d
i
τ (4)
Where ω and ζ are gains representing frequency and
damping of the system respectively, while τ is the
sampling time of the controller. The position error
e
p
= (X
t
− X
c
) is calculated as the distance of the ma-
nipulator (X
c
) from the designed target position (X
t
).
The velocity obtained with the Formula 4 is succes-
sively integrated to get the desired position of the
robot:
X
d
i
= X
d
i−1
+
˙
X
d
i
τ (5)
The compliant behaviour of the manipulator is en-
abled with the following formula, in which the com-
pliant position of the end effector is calculated con-
sidering both the operator forces and the autonomous
control data:
¨
X
c
i+1
=
M
¨
X
d
i
+ D(
˙
X
d
i
−
˙
X
c
i
) + F
t
M
(6)
Shared Admittance Control for Human-Robot Co-manipulation based on Operator Intention Estimation
65

We allow the switching from the passive to the ac-
tive mode by nullifying the autonomous contribution
of the robot from the previous equation, i.e. by set-
ting to zero the desired acceleration and velocity, as
described in Algorithm 1. In particular, we want to in-
hibit the contribution of the autonomous motion when
the user behaviour is recognized as Opposite, for this
purpose we set
¨
X
d
i
=
˙
X
d
i
= 0 in Equation 6. This way,
the robot is fully compliant to human contact forces,
without trying to came back to the initial position X
d
i
.
Differently, when the operator behaviour is classified
as Coinciding or Coinciding deviation we have two
different situations associated with two different tar-
get points selected by the H-L control system. In the
Coinciding case, the point to reach is represented by
the one assessed as the current operator target X
wp
. In-
stead, in the second case, a new target point is selected
in order to help the operator in order to move back the
end effector towards to the planned path. Specifically,
in order to provide the human with a smooth guid-
ance towards the planned path, during Coinciding de-
viation, the robotic system is provided with a target
point X
cp
, which is a midpoint between the final tar-
get position X
t
and the closest point to the planned
path C
p
. This target point is then continuously up-
dated during the Coinciding deviation until a differ-
ent human intention is recognized. Notice that, the
described approach to Coinciding deviation not only
provides the operator with a smooth guidance toward
the planned path and the target point, but also pro-
duces a force feedback on the human side, which is
associated with a feeling of the displacement between
the current robot position and the planned path. This
haptic feedback is conceptually similar to the one al-
ready proposed by (Cacace et al., 2014) for mixed-
initiative teleoperation of aerial vehicles.
Finally, in order to avoid discontinuity of the con-
trol input that could induce instability in the system,
a smooth transition between the different levels of au-
tonomy (e.g from passive to active and viceversa or
from coinciding to deviating and viceversa) has to
be considered. For this reason we adopted a time-
vanishing smoothing term as proposed by (Lippiello
et al., 2016). Specifically, given a switch from the ac-
tive to the passive control mode which starts at time
t = 0, the velocity command introduced in Equation 7
is computed as follow:
v(t) = v
a
(t) + e
1/γ
(v
p
(0) − v
a
(0)) (7)
where γ is a time constant representing the dura-
tion of the transition phase, while v
a
and v
p
are the
velocity commands related to the system acting in the
active and passive mode, respectively.
Algorithm 1: Shared admittance control based on operator
intention.
Require: Target point: X
wp
, Behaviour: b
1: procedure X
c
= shared controller(X
wp
,b)
2: while X
wp
is not reached do
3: if b == Opposite then
4:
¨
X
d
= 0.0
5:
˙
X
d
= 0.0
6: else
7: e
p
= (X
t
− X
c
)
8:
¨
X
d
i
= ω
2
e
p
− 2ζ
˙
X
d
i−1
9:
˙
X
d
i
=
˙
X
d
i−1
+
¨
X
d
i
τ
10: if b == Coinciding deviation then
11: X
t
= X
cp
12: else
13: X
t
= X
wp
14: end if
15: end if
16: end while
17: end procedure
6 PREDICTION OF THE
OPERATOR TARGET
In the proposed system, the operator intention esti-
mation is also exploited to recognize his/her inten-
tion to bring the robot towards specific target posi-
tions within the workspace. In particular, we assume
that each task is associated with a set of possible states
characterized by target positions to be reached in or-
der to accomplish a given task. We also assume that
this set is available to the system and can analysed
by the H-L control system module in order to assess
the most probable target point the operator is trying to
reach. For this purpose, the system generates a set of
virtual trajectories, each connecting the current posi-
tion of the end effector with an available target point.
The operator intention is estimated with respect to all
the virtual trajectories, until the estimated intention
becomes Coinciding for only one trajectory; this tra-
jectory is then assumed as the one aimed by the oper-
ator. This decision process is exemplified in Figure 4,
where the system is initialized with four states. At the
start, the operator is not providing any contribution to
the task, hence the system cannot infer the target (in
Figure 4(a) all the virtual trajectories are colored in
black). Successively, the operator starts moving the
end effector toward one of the target points, while the
system identifies two of them as target candidates (in
Figure 4(b) the two red paths represent the target can-
didates). Finally, the operator intention becomes Co-
inciding for only one trajectory, hence the associated
ICINCO 2018 - 15th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
66
(a) No target candidates
(b) Two target candidates
(c) Target predicted
Figure 4: Prediction of the operator target.
state is selected as the one intended by operator and
a cartesian trajectory is generated and executed (Fig-
ure 4(c)). On the other hand, if the operator intention
is classified as Opposite during the execution of the
selected trajectory, we assume that the operator target
may be changed/refined hence a novel target decision
process starts in order to generate the new target along
with the new trajectory.
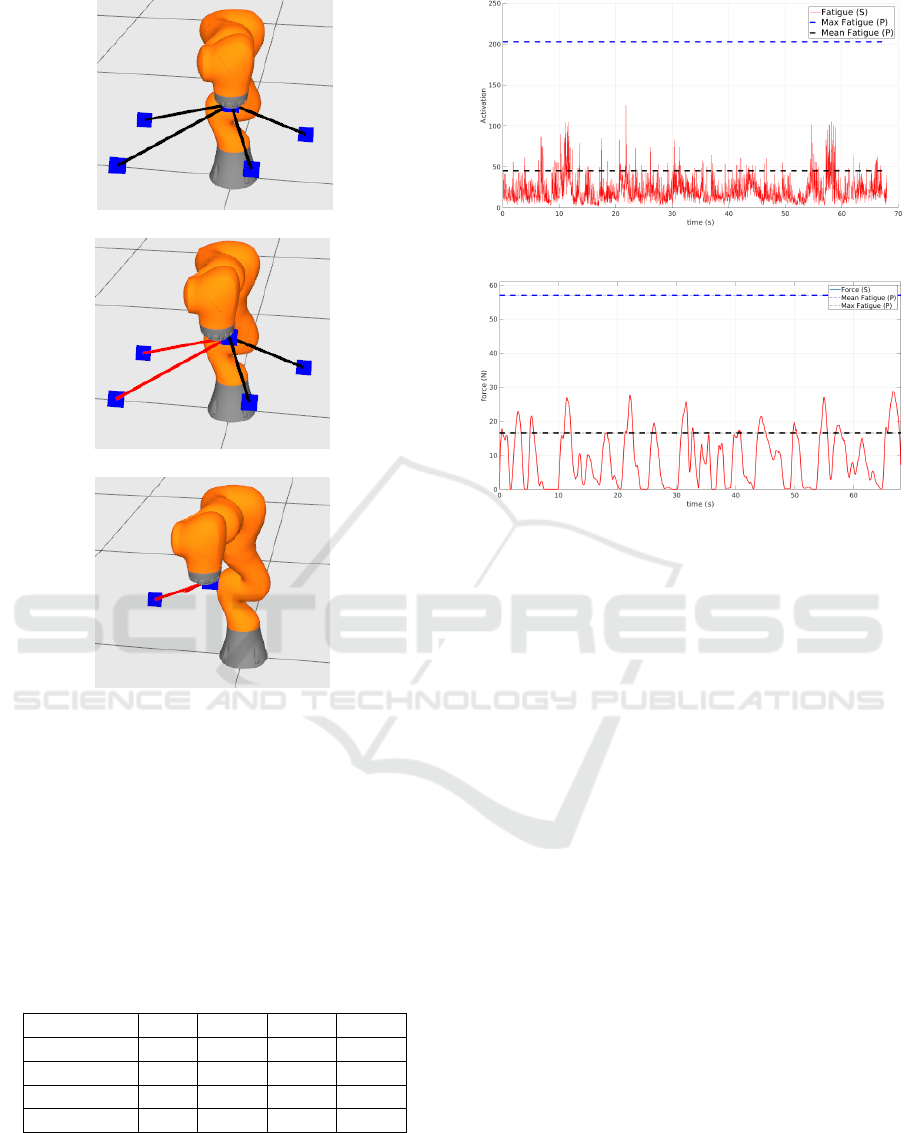
Table 3: Experimental Results.
min. max. mean std.
Fatigue (S) 1.9 143.3 24.5 17.26
Fatigue (P) 1.8 202.7 45.3 30.4
Force (S) 0 32.04 9.14 8.31
Force (P) 0 57 16.59 13.9
(a) Operator fatigue in shared operative mode, compared
with the maximum and mean fatigue values in passive mode.
(b) Operator contact force in shared operative mode, com-
pared with the maximum and mean contact force values in
passive mode.
Figure 5: Operator fatigue (a) and contact force (a).
7 CASE STUDY
The effectiveness of the proposed system has been
assessed by defining a collaborative manipulation
case study where a human worker cooperates with a
lightweight robotic arm in order to grasp different ob-
jects and plug them in predefined locations. In order
to show the advantage of the presented approach, a
user already trained on the system performed repeti-
tive tries of the designed task. We compared the sys-
tem performance with respect to a baseline version of
the framework in which the H-L control system is dis-
abled and the manipulator operates as a completely
passive robotic assistant. We refer to this operative
mode as Passive (P). During test execution, we evalu-
ated both task performance, considering the distance
covered by the manipulator, and the human physi-
cal effort, measuring operator muscle fatigue and the
norm of the force that he/she exerts on the manipula-
tor. In this context, we measured muscle fatigue ex-
ploiting a set of electromyographic sensors, that pro-
vide us the activation level of the arm muscles. The
experimental setup is depicted in Figure 6. Tests have
been performed using the Kuka LWR iiwa robot, con-
trolled via ROS middleware running on GNU/Linux
OS, as in (Hennersperger et al., 2016). Regarding the
Shared Admittance Control for Human-Robot Co-manipulation based on Operator Intention Estimation
67
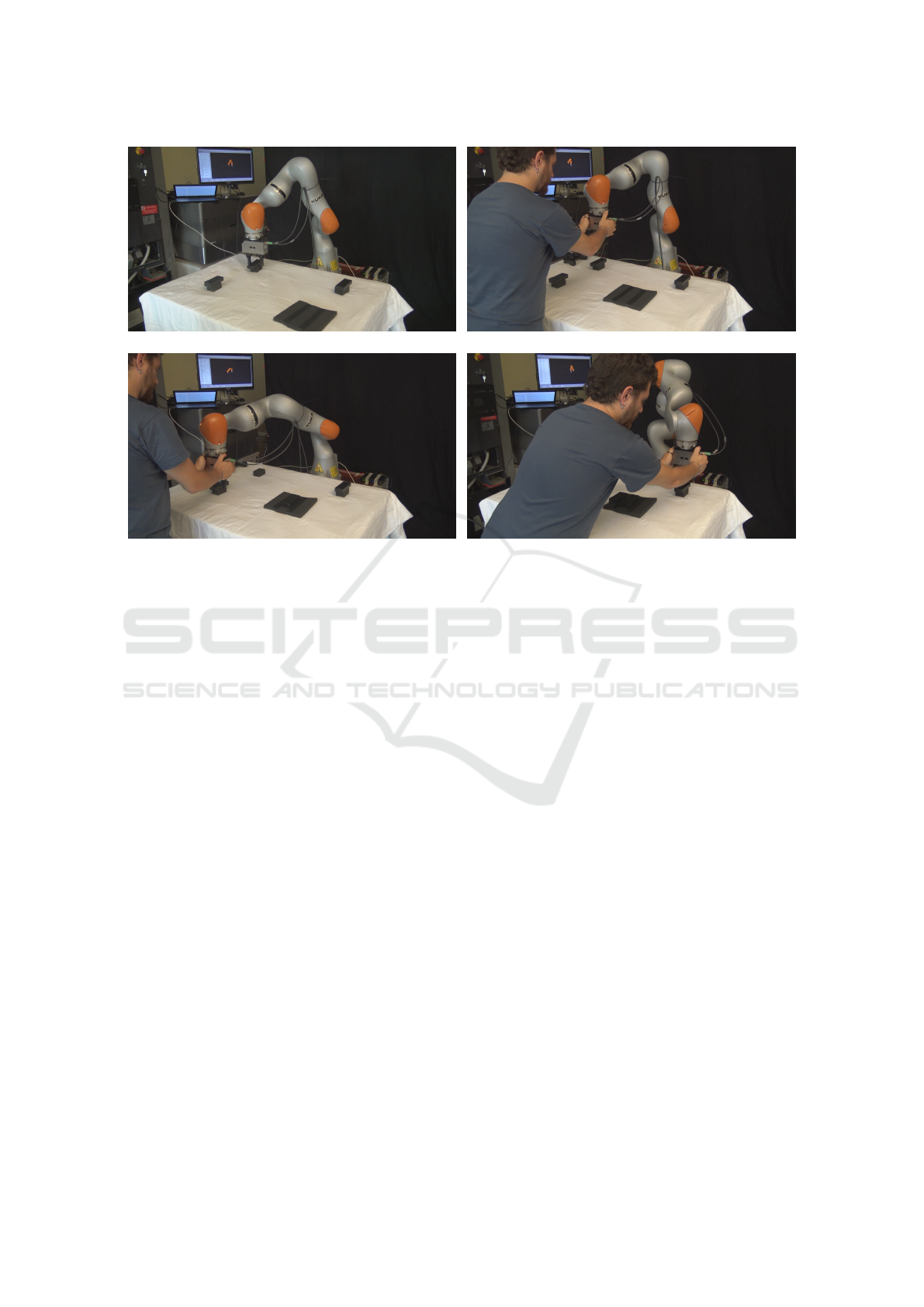

(a) Experimental setup (b) Grasping the first object
(c) Grasping the second object (d) Grasping the last object
Figure 6: Human operator interacting with the Kuka iiwa equipped with WEISS Wsg50 during system testing.
gripper, we used the WEISS Wsg50 controlled via a
standard joypad to close and open its fingers. The
overall manipulation task consists in grasping three
objects, one at a time, bringing them to specific po-
sitions of the workspace, as shown in Figures 6(b) -
6(d). Therefore, task accomplishment requires six ac-
tions: three picks and three places. During the experi-
ment, the operator is free to decide when to interact
with the manipulator by selecting any of the avail-
able objects and positions as targets. A demonstra-
tive video is available at this link: goo.gl/7xLA4r. Ta-
ble 3 reports the mean of norm of human force and
fatigue data over all the the experiments. In this table,
the minimum, the maximum, the mean, and the stan-
dard deviation of the operator fatigue and the norm of
the force related to shared (S) and passive (P) settings
are reported. As for task performance, the mean dis-
tance covered by the manipulator end effector during
the tests is 3.6 meters in the shared setting against the
4.51 meters in the passive mode, therefore the shared
system not only enables a more comfortable interac-
tion, but also a more efficient task execution.
The benefits of the proposed system are also illus-
trated in Figure 5, where we compare the human force
and fatigue measured in the two settings during one of
the experiments. For this purpose, illustrate the EMG
signal (red plot in Figure 5(a)) and the force contact
one (red plot in Figure 5(b)) detected in the shared
mode (adaptive shared controller), with respect to the
maximum and mean values (upper and lower dotted
lines in Figure 5) of the same signals obtained in the
passive mode. The clear reduction of both fatigue and
force highlight the advantage of the approach.
8 CONCLUSION
We presented a framework that supports physical
human-robot interaction in collaborative manipula-
tion tasks. In the proposed approach, the human
physical interaction with the robotic system is con-
tinuously assessed in order to infer the operator in-
tentions with respect to the current robotic behavior.
The recognized intentions are then exploited by the
shared control system to on-line adjust the robotic be-
havior with respect to the human interventions. We
described the overall architecture detailing the oper-
ator intention estimation method and the associated
shared control system. The proposed system has been
demonstrated presenting the case study of a collabora-
tive manipulation tasks, where the performance of the
proposed method have been compared with respect to
a baseline system relying on an admittance controller
with disabled intention estimation and the associated
adaptive mechanisms. The collected results shows the
effectiveness of the approach in terms of both task
performance and human fatigue.
ICINCO 2018 - 15th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
68

ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The research leading to these results has been sup-
ported by the ERC AdG-320992 RoDyMan, H2020-
ICT-731590 REFILLs and MADWALK projects re-
spectively. The authors are solely responsible for its
content. It does not represent the opinion of the Euro-
pean Community and the Community is not responsi-
ble for any use that might be made of the information
contained therein.
REFERENCES
Awais, M. and Henrich, D. (2010). Human-robot collab-
oration by intention recognition using probabilistic
state machines. In 19th International Workshop on
Robotics in Alpe-Adria-Danube Region (RAAD 2010),
pages 75–80.
Bascetta, L., Ferretti, G., Rocco, P., Ard
¨
o, H., Bruyninckx,
H., Demeester, E., and Lello, E. D. (2011). Towards
safe human-robot interaction in robotic cells: An ap-
proach based on visual tracking and intention estima-
tion. In 2011 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on
Intelligent Robots and Systems, pages 2971–2978.
Best, G. and Fitch, R. (2015). Bayesian intention infer-
ence for trajectory prediction with an unknown goal
destination. In 2015 IEEE/RSJ International Confer-
ence on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), pages
5817–5823.
Bishop, C. M. (1995). Neural Networks for Pattern Recog-
nition. Oxford University Press, Inc., New York, NY,
USA.
Cacace, J., Finzi, A., and Lippiello, V. (2014). A mixed-
initiative control system for an Aerial Service Vehicle
supported by force feedback. In IEEE International
Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems.
Cacace, J., Finzi, A., and Lippiello, V. (2016). Implicit
robot selection for human multi-robot interaction in
Search and Rescue missions. In 25th IEEE Interna-
tional Symposium on Robot and Human Interactive
Communication, RO-MAN 2016.
Cacace, J., Finzi, A., and Lippiello, V. (2018). Enhancing
human-robot collaborative task execution via contact
force classification. Human Friendly Robotics.
Caccavale, R., Cacace, J., Fiore, M., Alami, R., and Finzi,
A. (2016). Attentional supervision of human-robot
collaborative plans. In 25th IEEE International Sym-
posium on Robot and Human Interactive Communica-
tion, RO-MAN 2016.
Corrales, J. A., Garcia Gomez, G. J., Torres, F., and
Perdereau, V. (2012). Cooperative tasks between hu-
mans and robots in industrial environments. Interna-
tional Journal of Advanced Robotic Systems, 9.
Ge, S. S., Li, Y., and He, H. (2011). Neural-network-based
human intention estimation for physical human-robot
interaction. In 2011 8th International Conference on
Ubiquitous Robots and Ambient Intelligence (URAI),
pages 390–395.
Giordano, P. R., Stemmer, A., and Arbter, K. (2008).
Robotic Assembly of Complex Planar Parts : An Ex-
perimental Evaluation. pages 22–26.
Gribovskaya, E., Kheddar, A., and Billard, A. (2011). Mo-
tion learning and adaptive impedance for robot con-
trol during physical interaction with humans. In 2011
IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Au-
tomation, pages 4326–4332.
Hennersperger, C., Fuerst, B., Virga, S., Zettinig, O., Frisch,
B., Neff, T., and Navab, N. (2016). Towards mri-based
autonomous robotic us acquisitions: A first feasibility
study. IEEE transactions on medical imaging.
Hoang, T. N. and Low, K. H. (2013). Interactive POMDP
lite: Towards practical planning to predict and exploit
intentions for interacting with self-interested agents.
CoRR, abs/1304.5159.
Hoffman, G. and Breazeal, C. (2004). Collaboration in
human-robot teams. Proceeding of the AIAA 1st In-
telligent Systems Technical Conference, page 1.
Hoffman, G. and Breazeal, C. (2007). Effects of antic-
ipatory action on human-robot teamwork efficiency,
fluency, and perception of team. Proceeding of the
ACM/IEEE international conference on Human-robot
interaction - HRI ’07, page 1.
Hogan, N. (1984). Impedance Control: An Approach to
Manipulation. IEEE American Control Conference,
pages 304–313.
Jlassi, S., Tliba, S., and Chitour, Y. (2014). An Online
Trajectory generator-Based Impedance control for co-
manipulation tasks. IEEE Haptics Symposium, HAP-
TICS, pages 391–396.
Kelley, R., Nicolescu, M., Tavakkoli, A., Nicolescu, M.,
King, C., and Bebis, G. (2008). Understanding human
intentions via hidden markov models in autonomous
mobile robots. In 2008 3rd ACM/IEEE International
Conference on Human-Robot Interaction (HRI), pages
367–374.
Kouris, A., Dimeas, F., and Aspragathos, N. (2017). Con-
tact distinction in human-robot cooperation with ad-
mittance control. 2016 IEEE International Confer-
ence on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, SMC 2016 -
Conference Proceedings, pages 1951–1956.
Li, Y. and Ge, S. S. (2014). Human–Robot
Collaboration Based on Motion Intention Estima-
tion. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics,
19(3):1007–1014.
Li, Y., Tee, K. P., Chan, W. L., Yan, R., Chua, Y., and
Limbu, D. K. (2015). Continuous Role Adaptation
for Human Robot Shared Control. IEEE Transactions
on Robotics, 31(3):672–681.
Lippiello, V., Cacace, J., Santamaria-Navarro, A., Andrade-
Cetto, J., Trujillo, M.
¨
o., Esteves, Y. R., and Vig-
uria, A. (2016). Hybrid visual servoing with hierar-
chical task composition for aerial manipulation. IEEE
Robotics and Automation Letters, 1(1):259–266.
Park, J. S., Park, C., and Manocha, D. (2016). Intention-
aware motion planning using learning based human
motion prediction. CoRR, abs/1608.04837.
Peternel, L. and Babic, J. (2013). Learning of compliant
Shared Admittance Control for Human-Robot Co-manipulation based on Operator Intention Estimation
69

human-robot interaction using full-body haptic inter-
face. Advanced Robotics, 27:1003–1012.
Peternel, L., Tsagarakis, N., Caldwell, D., and Ajoudani, A.
(2016). Adaptation of robot physical behaviour to hu-
man fatigue in human-robot co-manipulation. IEEE-
RAS International Conference on Humanoid Robots,
pages 489–494.
Siciliano, B. and Villani, L. (2000). Robot Force Control.
Kluwer Academic Publishers, Norwell, MA, USA, 1st
edition.
ICINCO 2018 - 15th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
70
