
Evaluating the Robustness of Global Appearance Descriptors in a Visual
Localization Task, under Changing Lighting Conditions
Vicente Rom
´
an, Luis Pay
´
a and
´
Oscar Reinoso
Engineering Systems and Automation Department, Miguel Hernandez University, Elche (Alicante), Spain
Keywords:
Mobile Robots, Global Appearance Descriptors, Omnidirectional Images, Mapping, Localization.
Abstract:
Map building and localization are two important abilities that autonomous mobile robots must develop. This
way, much research has been carried out on these topics, and researchers have proposed many approaches to
address these problems. This work presents some possibilities to solve these problems robustly using global
appearance descriptors. In this way, robots capture visual information from the environment and obtain,
usually by means of a transformation, a global appearance description for each whole image. Using these
descriptors, the robot is able to estimate its position in a previously built map, which is also composed of
a set of global appearance descriptors. In this work, the global appearance descriptors performance at the
localization task inside a known environment has been studied. In the assignment a map is already built
and the goal is to evaluate the descriptors’ robustness to perform localization tasks when the environment
visual appearance changes substantially. To achieve this objective, a comparative evaluation of several global
appearance descriptors is carried out.
1 INTRODUCTION
Over the last few years, the presence of mobile robots
in industrial and domestic environments has increased
substantially. This increase has been facilitated by the
development of their abilities in perception and com-
putation, which allow them to improve the operation
in large and heterogeneous areas without the neces-
sity of introducing changes into the robot or environ-
ment structure. However, the mobile robot boom will
not be definitive until the level of autonomy and the
adaptability to different conditions enhance substan-
tially. An autonomous robot has to find a good solu-
tion to two critical problems: building a model of the
environment (mapping) and estimating the position of
the robot within this model (localization). Both have
to be solved with an acceptable accuracy and compu-
tational cost.
Nowadays, one of the most extended systems to
obtain information from the environment are vision
sensors, which permit extracting local information
from the scenes. The use of local appearance descrip-
tors has been the classical approach for obtaining rel-
evant information from the images. This is a mature
and very developed alternative and many researchers
make use of it in mapping and localization. For ex-
ample Valgren and Lilienthal (Valgren and Lilienthal,
2010) have proposed using these descriptors to per-
form topological localization. Murillo et al. (Murillo
et al., 2007) present a comparative study for the local-
ization task in indoor environments. A comparative
evaluation of this kind of local appearance methods
was made by Gil et al. (Gil et al., 2010). In this paper
they evaluated, the repeatability of these detectors, as
well as the invariance and distinctiveness of the de-
scriptors under different perceptual conditions. More
recently, an alternative has emerged, which consists
in representing each image as a whole, without ex-
tracting local features. This method could offer com-
parative results and it also simplifies the structure of
the map. Additionally, localization can be carried out
with a simple process, based on the pairwise compar-
ison of global descriptors. As a disadvantage, it has
to work a large amount of data, so is necessary to use
a compression technique that minimize the computa-
tional cost.
Some researchers have proposed different meth-
ods to describe the global appearance of the scenes,
which maintain the necessary information to do the
localization and mapping tasks. The discrete Fourier
Transform is one alternative. (Menegatti et al., 2004)
submit the Fourier Signature (FS) concept and define
a method to carry out mapping and localization. Other
studies support a method based on the Histogram of
258
Román, V., Payá, L. and Reinoso, Ó.
Evaluating the Robustness of Global Appearance Descriptors in a Visual Localization Task, under Changing Lighting Conditions.
DOI: 10.5220/0006837802580265
In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics (ICINCO 2018) - Volume 2, pages 258-265
ISBN: 978-989-758-321-6
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

Oriented Gradients (HOG). For example (Dalal and
Triggs, 2005) use this method to detect pedestrians
with a good performance and (Pay
´
a et al., 2016) prove
the robustness of the descriptor in mapping and lo-
calization tasks.Furthermore, a method know as gist,
which tries to imitate the human vision system, can be
used. Oliva and Torralba were precursors of this idea
(Oliva and Torralba, 2001). Other authors, like Sia-
gian and Itti, have used this method in their work (Sia-
gian and Itti, 2009) where they have described this bi-
ological inspired vision localization system and have
tested it in different outdoor environments. Finally,
the Radon Transform could be used to compress the
information too, as (Berenguer et al., 2016) show in
their studies .
In our experiments we use omnidirectional im-
ages, which give a 360 range vision so they offer more
information than other visual systems. With this sys-
tem, features are more time in the camera range vision
so it allows to obtain stabler ones. Moreover, omnidi-
rectional systems contains information enough to cre-
ate a model if a person or an object occlude the image
during the route.
In this area, previously works like (Pay
´
a et al.,
2016) present a comparative evaluation of these
global-appearance techniques in topological mapping
tasks. (Pay
´
a et al., 2017) present an evaluation of
these descriptors in compacting visual maps using FS,
HOG and gist descriptors. The goal of this paper is to
extend these previous works. On the one hand, we in-
clude a new scene descriptor called Radon transform
and; on the other hand, we compare the methods on a
real and changing environment.
We have studied the global-appearance descrip-
tors strength, verifying their performance when the
environment visual appearance changes substantially.
In real-operating conditions the robot has to cope with
different events: not the same lighting conditions be-
tween the model and the new localization; scenes oc-
cluded by people or other mobile robots and changes
in the scene like the furniture position.
2 REVIEW OF GLOBAL
APPEARANCE DESCRIPTORS
In this section we summarize some alternatives to ex-
tract global information from panoramic images try-
ing to keep relevant data with the minimum memory.
As the images used in this work are given in an om-
nidirectional form, the first step is to transform them
into a panoramic ones. This process is fairly slow and
it will affect to the computational cost. The starting
point is a panoramic image i(x,y) ∈ R
N
x
×N
y
and after
using the global appearance method the result is a de-
scriptor
~
d ∈ R
l×1
.
The robot has a planar movement and to cap-
ture the images a catadioptric vision system is used
(Pronobis and Caputo, 2009). This system is mounted
vertically on a robot, a camera and a convex mir-
ror were aligned and mounted together on a portable
bracket to build the vision system. The movement of
this robot is restricted to the floor plane.
2.1 Fourier Signature
(Menegatti et al., 2004) show that when we calcu-
late the Discrete Fourier Transform of each row of
a panoramic image f(x,y), we obtain a new complex
matrix F(u,v) that can be split in two matrices: one
with the modules A(u,v) and other with the arguments
Φ(u,v).
Two images that have been taken from the same
position but with different orientation would have the
same modules’ matrix but a change in the arguments’
matrix is produced, according to the shift property of
the Fourier Transform. The relative rotation between
images could be calculated (Pay
´
a et al., 2009). So we
can use A(u,v) as a localization descriptor and Φ(u,v)
as an orientation estimator.
Furthermore, in the Fourier domain, the most rele-
vant information is concentrated in the low frequency
components so we can discard a number of high fre-
quency components that are usually affected by noise.
It allows us to minimize the computational cost in the
subsequent comparisons. In this work we use the pa-
rameter k
1
which indicates the number of frequencies
we retain. N
x
is the panoramic image number of rows.
The image is reduced into a global appearance de-
scriptor
~
d ∈ R
N
x
·k
1
×1
.
2.2 Histogram of Oriented Gradient
As (Dalal and Triggs, 2005) describes, the HOG tech-
nique works with the orientation of the gradient in
specific areas. Hofmeister et al. use a weighted his-
togram of oriented gradients in small and controlled
environments (Hofmeister et al., 2009).
Essentially it consists in calculating the gradient
of the panoramic image obtaining module and orien-
tation of each pixel to localize mobile robots. Af-
terwards, the image is divided in a set of cells and
the orientation histogram of each cell is calculated,
weighting the each bin with the module of the gra-
dient of each pixel. Although the image is rotated,
two panoramic images contain the same information
in each row, but a shift of the pixels. As a result, if
we divide the image into horizontal cells, a descriptor
Evaluating the Robustness of Global Appearance Descriptors in a Visual Localization Task, under Changing Lighting Conditions
259

will be obtained which is invariant to rotations of the
robot in the floor plane and can be used as a localiza-
tion descriptor.
Moreover, the whole image can be reduced to a
vector whose size will depend on the number of cells
and bins. In this work we use b
1
, which is the number
of bins per histogram and k
2
, which is the number of
horizontal cells in which the image has been divided.
This method transform the panoramic image into a
descriptor
~
d ∈ R
b
1
·k
2
×1
.
2.3 Gist
This descriptor was initially described in (Oliva and
Torralba, 2006), and further developed in other stud-
ies like (Siagian and Itti, 2009) where gist descriptor
had been tested in three outdoor environments.
The method offers rotational invariance when it is
applied to panoramic images. The descriptor is built
from orientation information, obtained after exposing
some Gabor filters with different orientations to the
image in several resolution levels. Finally, the volume
of data is reduced for an average; like when we use
HOG, we divide the image with horizontal cells and
we calculate the mean intensity of each cell.
On this way, we use m
1
which indicates the num-
ber of orientations of Gabor filters and k
3
that desig-
nates the number of horizontal cells in which the im-
age has been split. With these parameters the image
can be reduced to a descriptor whose size depends on
m
1
, k
3
and the number of different resolution models
used, but in the experiments we maintain this parame-
ter constant in 2 levels. So finally the result is a global
appearance descriptor
~
d ∈ R
2·m
1
·k
3
×1
.
2.4 Radon Transform
The Radon Transform can also be used to describe
globally an omnidirectional image. This transforma-
tion was described in (Radon, 2005). It was used in
some computer vision activities, such as (Hoang and
Tabbone, 2010) where the Radon transform (RT) was
used as a geometric shape descriptor. In the robotic
field we can find the study (Berenguer et al., 2016)
where RT was employed to find the nearest neighbor
in a position estimation.
Radon method can be used directly with omnidi-
rectional images so they have not to be transformed
into panoramic. It will presume a reduction in the
computational cost. The method consists in apply-
ing the Radon Transform along several sets of straight
lines, with a variety of orientations between consecu-
tive sets. The difference of orientation is considered
a variable parameter named p
1
(deg.). This way, an
omnidirecctional image data can be transformed to
a vector that fulfills some interesting properties. (a)
It reduces the information; figure 1 shows an image
N
x
× N
x
which could be reduced into a
360
p
1
× 0.5 · N
x
matrix; (b) invariability of the information if against
changes of the robot orientation and (c) possibility of
calculate the orientation with a column shift.
(a) (b) (c)
Figure 1: Radon transform. (a) omnidireccional image
(N
x
× N
x
), (b) Radon transform of a the image (
360
p
1
× N
x
)
and (c) final Radon transform (
360
p
1
× 0.5 · N
x
).
When the Radon transform has been calculated,
the localization process could be addressed with some
methods. In this paper we use a method based on FS.
We apply the Fourier Signature to transform the data
we obtain after we have calculated the Radon Trans-
form. We get two matrices (magnitudes and argu-
ments) and the descriptors are built as described in
section 2.1.
In this case, the descriptor size will depend on p
1
and the number of columns we retain once we apply
the FS. This parameter is called k
4
. The descriptor
obtained is
~
d ∈ R
360
p
1
·0.5·N
x
×1
.
3 SETS OF IMAGES
In this work, the COLD database (Pronobis and Ca-
puto, 2009) is used. This database provides omnidi-
reccional image sequences taken under three different
lighting conditions: a sunny day, a cloudy one and at
night. The images were acquired across several days
under illumination variations as well as changes intro-
duced by human activity in the environment (people
appearing in the rooms, objects and furniture being
relocated or moved and so on). These different con-
ditions can be seen in figure 2
Therefore, the COLD database is an ideal test
bench to evaluate the localization and mapping al-
gorithms’ robustness because it offers variations that
might occur in real-world environments. COLD
database offers diverse routes captured in indoor envi-
ronments in several universities. Among those possi-
bilities we use Freiburg dataset and the longest route,
called Part A, Path 2, size 3 (Pronobis and Caputo,
2009). Freiburg route supposes an especial challeng-
ing one because many walls between rooms are made
of glass and there are lots of windows so the extern
ICINCO 2018 - 15th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
260

(a) Image from the sunny dataset
(b) Image from the night dataset
Figure 2: Panoramic images from COLD database.
light conditions affect substantially the localization
task.
The sequences of this set of images were recorded
using a mobile robot and both perspective and om-
nidirectional cameras. The catadioptric vision sys-
tem was made using a hyperbolic mirror was mounted
with the cameras on a portable bracket. The robot was
also equipped with a laser range scan and wheels en-
coders to detect the odometry.
4 EXPERIMENTS
In this section we test the global-appearance descrip-
tors effectiveness. First we outline the distances and
measurement error models used, then we present the
localization results considering different illumination
(Cloudy weather, sunny weather and at night) and the
computational cost of these experiments.
4.1 Method to Create a Model of the
Environment
As explained in the previous section, COLD offers
different databases captured in diverse buildings and
conditions. We use Freiburg cloudy dataset to build
the model. COLD database took an image every
0.06m approximately. To build our model we make a
reduction taking one every five images, so our model
follow the same route but the distance between im-
ages is around 0.30m. This method allows us to have
a model with 556 images instead of 2778 images that
cloudy dataset (Part A, Path 2, size 3) have.
Once we have built the model with known images,
the method to solve the localization task consists in
comparing each image from a test group with the im-
ages in the model. The program calculates the near-
est neighbor. To obtain the nearest neighbor differ-
ent distances can be used. In our study we compare
Table 1: Distances.
Measure Distance Mathematical expression
d1 Cityblock d
1
(~a,
~
b) =
∑
l
i=1
|
a
i
− b
i
|
d2 Euclidean d
2
(~a,
~
b) =
q
∑
l
i=1
(a
i
· b
i
)
2
d3 Correlation d
3
(~a,
~
b) = 1 −
~
a
T
d
·
~
b
d
|
a
d
|
·
|
b
d
|
d4 Cosine d
4
(~a,
~
b) = 1 −
~
a
T
·
~
b
|
a
|
·
|
b
|
Where:
~a
d
= [a
1
− a, ...,a
l
− a]; a =
1
l
·
∑
j
·a
j
~
b
d
= [b
1
− b, ..., b
l
− b]; b =
1
l
·
∑
j
·b
j
these ones: cityblock, Euclidean, correlation and co-
sine. Table 1 shows the definition of each distance.
At the mathematical expression,~a ∈ R
lx1
and
~
b ∈ R
lx1
are two vectors where: a
i
,b
i
,i = 1, ...,l.
Once the nearest neighbor is obtained we calculate
the geometric distance between the test image and his
neighbor, and the result will be the error. This real
distance can be calculated because COLD database
offers the coordinates where each image had been
captured but the coordinates have been only used as
ground truth to check the error. The localization task
is carried out with pure visual information.
The experiments have been done using different
descriptors and varying the parameters that could be
modified in order to evaluate the influence of each pa-
rameter in the task. These parameters can be seen in
table 2. As shown in section 2, therse parameters de-
fine the descriptor size. The larger the descriptor is,
the slower the process will be.
Table 2: Parameters that impact on the location process.
Descriptor Parameters
FS k
1
⇒ number of retained columns.
HOG b
1
⇒ number of bins per histogram.
k
2
⇒ number of horizontal cells.
gist m
1
⇒ number of Gabor filters.
k
3
⇒ number of horizontal blocks.
Radon p
1
⇒ degrees between sets of lines.
k
4
⇒ number of retained columns.
4.2 Position Estimation
Initially, the cloudy images are used to create the ref-
erence model. Afterwards, to study the robustness
of the global-appearance descriptors, the test images
used to solve the localization problem will be chosen
from the sunny and night datasets, which are com-
posed of 2231 and 2896 images, respectively. The
localization process evaluates which image in the ref-
erence model is the most similar to each test image.
The error is calculated as the geometric distance be-
tween the capture points of both images. After re-
Evaluating the Robustness of Global Appearance Descriptors in a Visual Localization Task, under Changing Lighting Conditions
261
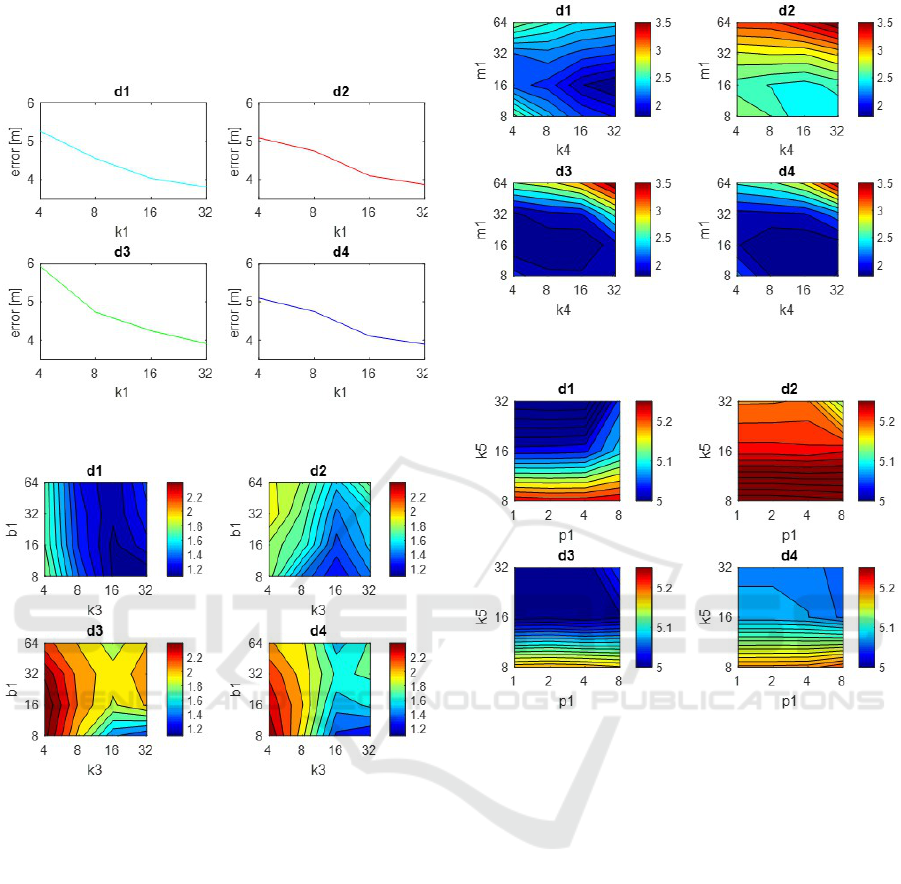
peating this process considering all the sunny images
as test image, figures 3, 4, 5 and 6 show the average
error (m) with each descriptor method.
Figure 3: FS. Localization error (m) using test images from
the sunny dataset versus k
1
.
Figure 4: HOG. Localization error (m) using test images
from the sunny dataset versus k
2
and b
1
.
The behaviour of the FS changes depending on the
distance measure used, although d2 and d4 offer sim-
ilar results. The error varies between 3 and 7 meters.
The higher k
1
is, the better results we obtain but the
process will be slower. We obtain the best accuracy
with d3 and k
1
=128 where the location error is 3,56m;
when k
1
=32 the error is 3,91m.
About HOG, a medium-high value of k
2
and an
intermediate value of b
1
offer the best results. The
lowest error is obtained using distance d1 and b
1
=32
and k
2
=8 and it is 1,09m.
In general, using the gist descriptor, the error is
about 2m. The error decreases with medium values of
k
3
and medium-low values of m
1
. The best solution
is detected with d3 and k
3
=m
1
=16 where the error is
1,69m.
At last, in the case of RT, the results are in general
worse. The error is higher than 5m in most cases. The
Figure 5: gist. Localization error (m) using test images from
the sunny dataset versus k
3
and m
1
.
Figure 6: Radon. Localization error (m) using test images
from the sunny dataset versus p
1
and k
4
.
error depends more on the k
4
parameter and the higher
it is, the lower the error is. The lowest error is detected
when k
4
=32 and p
1
=1. With these parameters and d1
the error is 4,93m.
Analysing globally these figures, HOG and gist
are the description algorithms with a lower error that
varies between 1 an 2 m when they use d1 and d3.
There are remarkably good results taking into account
that not only the illumination changes, but also furni-
ture movements and occlusions appear in the scenes.
After this experiment, the localization process is
repeated considering all the images in the night set as
test images. Like in the previous case, the reference
model is preciously created with cloudy images. Fig-
ures 7, 8, 9 and 10 present the results showing the
error in meters.
The results using FS are between 0,6 and 2,5m.
Low values of k
1
offer lower errors, obtaining the
best one with k
1
=4 and distance d1 where the error
is 0,597m.
The behaviour with HOG presents an error be-
ICINCO 2018 - 15th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
262
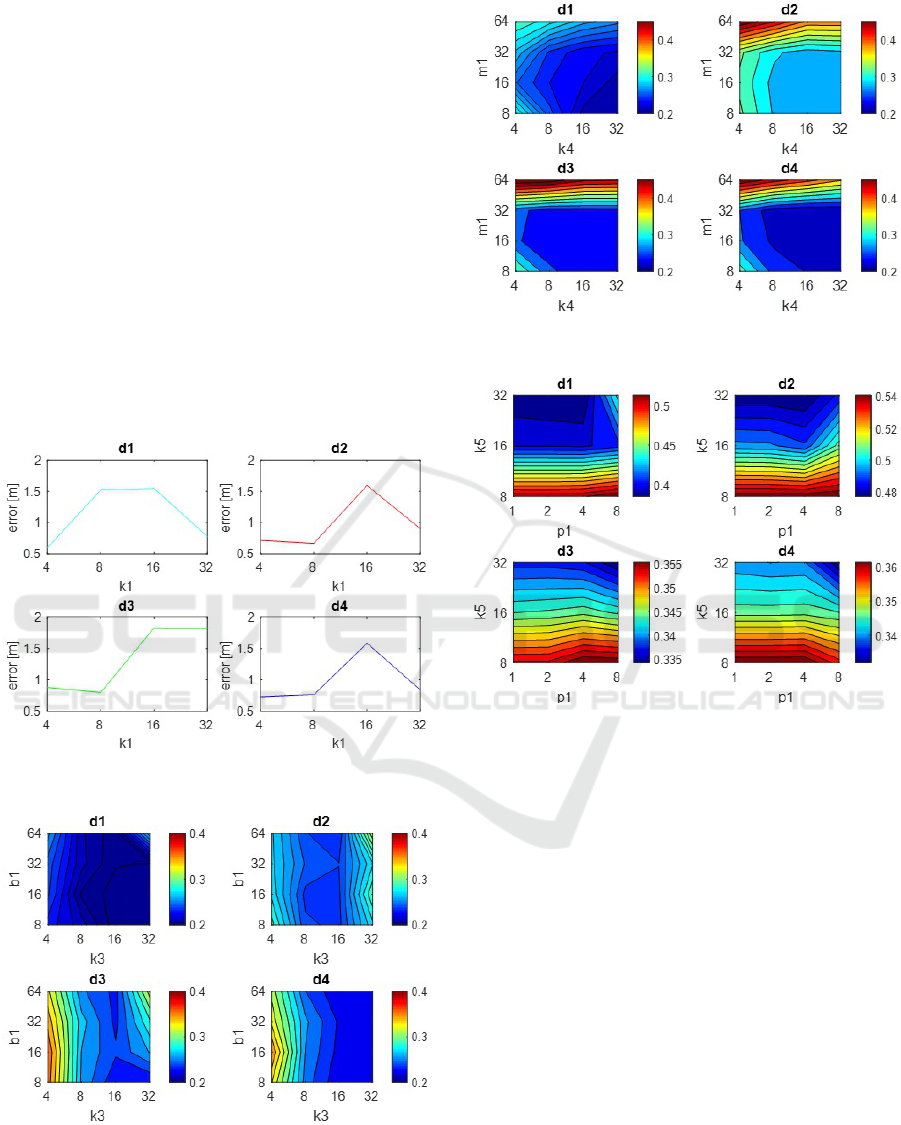
tween 0,2 and 0,6m . The best results are given with
intermediate values of k
2
and b
1
and the distance d1.
With k
2
=32, b
1
=16 and distance d1 we obtain the low-
est error, 0,189m.
About gist, the mean error is between 0,2 and 1m.
If k
3
or m
1
values are low, the error will increase and
it will not decrease significantly when the parameters
are high. In fact it will offer relatively bad results
if m
1
increases a lot; so medium values are the best
choice. The lowest error has been obtained with the
distance d1, k
3
=32 and b
1
=8, when the error is 0,21m.
The maximum error in our night proofs using gist has
been 1,37m. It has been obtained with d3, k
4
=2 and
m
1
=256. This is a relatively low error if it is compared
with the maximum error using other descriptors.
Finally, the localization error with Radon is be-
tween 0,4 and 1,8m. The lower k
4
is, the lower the
error is; p
1
has little influence in the results. When
k
4
=32, p
1
=1 and d3 the localization error is 0,3281m.
Figure 7: FS. Localization error (m) using test images from
the night dataset versus k
1
.
Figure 8: HOG. Localization error (m) using test images
from the night dataset versus k
2
and b
1
.
It is remarkable that we obtain better results when
the localization task is made at night than when it was
made on a sunny day. This could be cause because of
Figure 9: Gist. Localization error (m) using test images
from the night dataset versus k
3
and m
1
.
Figure 10: Radon. Localization error (m) using test images
from the night dataset versus p
1
and k
4
.
the large amount of walls made of by glass in Freiburg
database; and, as we work with different lighting con-
ditions, it could cause anomalies, such as brights and
reflections. But taking into account the great chal-
lenge that it suppose, the localization presents notably
good results in both states.
4.3 Computational Cost
Besides having a low error, it is important to have a
reasonable computation time. We have also studied
the computational time the process spends in order to
know if the localization can be made in real time. Fig-
ures 11, 12, 13 and 14 show the runtime needed to es-
timate the robot position with each descriptor method
and distance measure. The data are given in seconds.
FS offers the quickest results. The highest time is
0,221s when k
1
=32 and the distance d3. The time has
an exponential growth when the variable k
1
increases.
Runtimes with HOG are similar to FS ones. The
optimal result is 0.235s. When the parameters in-
Evaluating the Robustness of Global Appearance Descriptors in a Visual Localization Task, under Changing Lighting Conditions
263
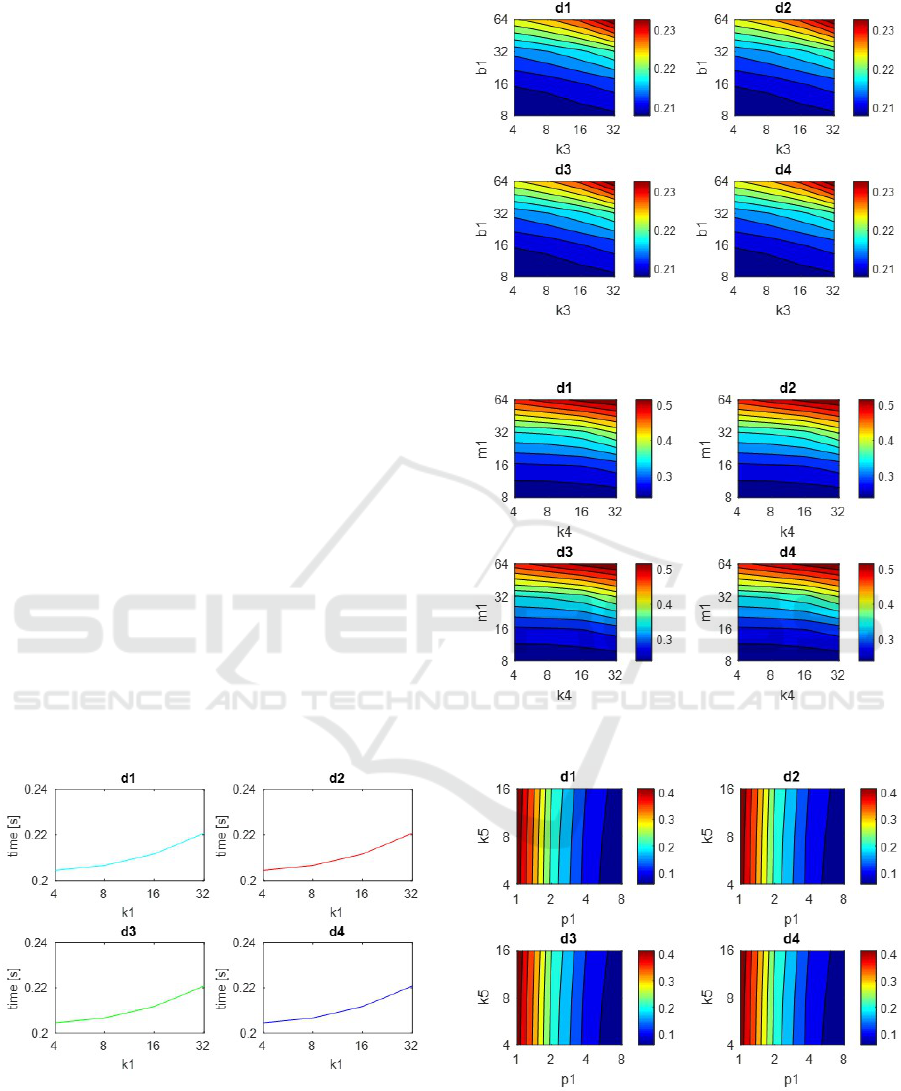
crease, the runtime increases too. b
1
has more influ-
ence so it is important not to have high values of it.
However, k
2
has less importance in the runtime.
Gist does not offer a quick runtime if it is com-
pared with other descriptors. Using gist the runtime
could be 0,537s when m
1
=64 and k
3
=32. In this case,
the parameter m
1
has a lot of importance in the time.
The quickest runtime with gist is given when m
1
=8
and k
3
=4, whose associated time is 0.2405s.
Finally, we have studied the RT runtime. We can
observe high dependence on p
1
and less importance
of k
4
. The lower p
1
, is the higher the runtime will be.
The highest time is 0,447s with p
1
=1 and k
4
=16 but
Radon could offer relatively reduced times like 0.059s
when p
1
=8 and k
4
=4.
The time spent while the program had to change
from omnidireccional images to panoramic ones is
the time which has more relevance in the results ob-
tained. So the compression process and the compar-
ison between descriptors have less importance. As
a result the experiments give us similar runtimes be-
tween Fourier and HOG and a slow runtime with gist.
The RT process does not have to change the images to
panoramic pictures so it reduces the cost of the pro-
cess, but when p
1
is low, its compression process is
slower and it has significant relevance in the RT pro-
cess. The experiments have been carried out in a PC
with a CPU Quad-Core Intel i7-700
R
at 3.60 GHz
and through Matlab
R
programming.
These results are not absolute, they will depend
of the machine which runs the process. But they
are comparable because all the calculations have been
done with the same computer.
Figure 11: FS. Localization time (s) per image versus k
1
.
5 CONCLUSIONS
This work has focused on the study of different prob-
lems in navigation tasks under illumination variations
Figure 12: HOG. Localization time (s) per image versus k
2
and b
1
.
Figure 13: gist. Localization time (s) per image versus k
3
and m
1
.
Figure 14: Radon. Localization time (s) per image versus
p
1
and k
4
.
and changes introduced by human activity, and the
robot is only equipped with an omnidireccional cam-
era. We have compared four appearance-based algo-
rithms applied to this localization task. When the im-
ICINCO 2018 - 15th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
264

ages have been described and the localization error
has been calculated a comparative evaluation has been
carried out and the computational cost has also been
studied.
On the one hand, the Fourier Signature and HOG
offer quicker results, so they constitute the most suit-
able option to do tasks in real time. On the other hand,
HOG and gist descriptors provide better accuracy in
localization tasks.
This work opens the door to new applications of
the appearance-based methods in mobile robots. As
we have shown, the appearance-based descriptors are
a suitable method to do navigation tasks. A prob-
lem is the high requirements of memory and compu-
tation time to do the database and make the neces-
sary calculations to compute the position. Once we
have tested the methods’ robustness under human ac-
tivity and changes in illumination and in the position
of some objects, the next step should be to create a
method that continuously renews the database adapt-
ing it to new lighting conditions. It can also evolve
to a system that creates more sophisticated maps to
make it possible an autonomous navigation system.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work has been supported by the Spanish Gov-
ernment through the project DPI 2016-78361-R
(AEI/FEDER, UE): “Creaci
´
on de mapas mediante
m
´
etodos de apariencia visual para la navegaci
´
on de
robots”.
REFERENCES
Berenguer, Y., Pay
´
a, L., Peidr
´
o, A., Gil, A., and Reinoso,
O. (2016). Nearest position estimation using omni-
directional images and global appearance descriptors.
In Robot 2015: Second Iberian Robotics Conference,
pages 517–529. Springer.
Dalal, N. and Triggs, B. (2005). Histograms of oriented gra-
dients for human detection. In 2005 IEEE Computer
Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern
Recognition (CVPR’05), volume 1, pages 886–893
vol. 1.
Gil, A., Mozos, O. M., Ballesta, M., and Reinoso, O.
(2010). A comparative evaluation of interest point de-
tectors and local descriptors for visual slam. Machine
Vision and Applications, 21(6):905–920.
Hoang, T. V. and Tabbone, S. (2010). A geometric invari-
ant shape descriptor based on the radon, fourier, and
mellin transforms. In Pattern Recognition (ICPR),
2010 20th International Conference on, pages 2085–
2088. IEEE.
Hofmeister, M., Liebsch, M., and Zell, A. (2009). Vi-
sual self-localization for small mobile robots with
weighted gradient orientation histograms. In 40th In-
ternational Symposium on Robotics (ISR), pages 87–
91. Barcelona.
Menegatti, E., Maeda, T., and Ishiguro, H. (2004). Image-
based memory for robot navigation using properties
of omnidirectional images. Robotics and Autonomous
Systems, 47(4):251 – 267.
Murillo, A. C., Guerrero, J. J., and Sagues, C. (2007). Surf
features for efficient robot localization with omnidi-
rectional images. In Robotics and Automation, 2007
IEEE International Conference on, pages 3901–3907.
IEEE.
Oliva, A. and Torralba, A. (2001). Modeling the shape
of the scene: A holistic representation of the spatial
envelope. International journal of computer vision,
42(3):145–175.
Oliva, A. and Torralba, A. (2006). Building the gist of a
scene: The role of global image features in recogni-
tion. Progress in brain research, 155:23–36.
Pay
´
a, L., Fern
´
andez, L., Reinoso,
´
O., Gil, A., and
´
Ubeda, D. (2009). Appearance-based dense maps
creation-comparison of compression techniques with
panoramic images. In ICINCO-RA, pages 250–255.
Pay
´
a, L., Mayol, W., Cebollada, S., and Reinoso, O. (2017).
Compression of topological models and localization
using the global appearance of visual information. In
Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 2017 IEEE Interna-
tional Conference on, pages 5630–5637. IEEE.
Pay
´
a, L., Reinoso, O., Berenguer, Y., and
´
Ubeda, D. (2016).
Using omnidirectional vision to create a model of
the environment: A comparative evaluation of global-
appearance descriptors. Journal of Sensors, 2016.
Pronobis, A. and Caputo, B. (2009). COLD: COsy Lo-
calization Database. The International Journal of
Robotics Research (IJRR), 28(5):588–594.
Radon, J. (2005). 1.1
¨
uber die bestimmung von funktio-
nen durch ihre integralwerte l
¨
angs gewisser mannig-
faltigkeiten. Classic papers in modern diagnostic ra-
diology, 5:21.
Siagian, C. and Itti, L. (2009). Biologically inspired mo-
bile robot vision localization. IEEE Transactions on
Robotics, 25(4):861–873.
Valgren, C. and Lilienthal, A. J. (2010). Sift, surf & sea-
sons: Appearance-based long-term localization in out-
door environments. Robotics and Autonomous Sys-
tems, 58(2):149–156.
Evaluating the Robustness of Global Appearance Descriptors in a Visual Localization Task, under Changing Lighting Conditions
265
