
In Vitro Test Bench with Intelligent Behavior to Ventricular Assist
Devices
Jeferson Cerqueira Dias
1
, Jônatas Cerqueira Dias
1
, Marcelo Barbosa
1
, Diolino José Santos Filho
1
,
Fabrício Junqueira
1
, Paulo Eigi Miyagi
1
, Jose Roberto Cardoso
2
1
Department of Mechatronics Engineering and Mechanic Systems,
University of São Paulo - USP, Prof. Luciano Gualberto Avenue, 380, São Paulo, Brazil
2
Department of Energy Engineering and Electrical Automation,
University of São Paulo - USP, Prof. Luciano Gualberto Avenue, 380, São Paulo, Brazil
Keywords: Intelligent Behavior, Test Bench, Ventricular Assist Device, Reliability, In Vitro Test.
Abstract: The abstract The Ventricular Assist Device (VAD) is a mechatronic device used to treat patients with heart
failure who are able to use them in short- and long-term strategies. However, with increasing population
longevity, long-term use has been intensified. Thus, the development of resources that improve the
robustness and reliability of these devices is justified. This work proposes an in vitro test bench with
intelligent behaviour that through a systematic of protocols for the collection, treatment and monitoring of
reliability data, coming from standard curves of monitored variables, such as: flow, pressure, vibration,
rotation, density, viscosity and temperature, provides a decision support system with user friendly interface
for verification, validation and certification of VAD. The proposed method is descriptive of an in vitro test
bed model for VAD that considers the use of Petri net for validation of the dynamic behaviour in front of
the variables and a decision support system based on big data analytics technology with extraction of dada,
which subsidizes intelligent behaviour. The proposed model is consistent with the bibliographic base and its
validation. The Petri net allows confirming its application in the decision making, with intelligent
behaviour, from the data mining.
1 INTRODUCTION
In the last twenty years we have witnessed a
technological evolution in the development of
products and processes, from consumer goods to
industrial automation systems. One of the most
determining characteristics observed in this evolution
is artificial intelligence, although there is no common
definition among researchers. We can describe
intelligence as the ability to understand events in the
surrounding environment and to process information
rationally in order to react to events in this
environment (Flyn, 2009; Khalfa, 1995).
Over the years, this characteristic has been
moving towards consumer products, something
perceived in 1991 by Mark Weiser, considered the
forerunner of ubiquitous computing, of which
technology is present everywhere (present in objects
such as clothing labels , switches, pens, among
others), but it is transparent to the user (Weiser,
1991). These technologies enable physical products
to be filled with intelligence, sensitivity, and
communication skills. This creates a new product
category called "Smart Products" (Mühlhäuser,
2007; Sharma, et al., 2017; Kuhn et al., 2018) that is,
systems that behave rationally (Russell; Norvig,
2013).
This evolution is based on the microelectronics
with the recent innovations in microchips, allowing
to create smaller sensors that through computers,
control actuators, allowing, thus, to create
mechanisms of intelligent mechatronic systems.
The development of mechatronic devices
encompasses the design that combines: mechanical
structures with electronic control circuits (Silva,
2005). Over the years, these devices have become
smarter, utilizing optical resources, renewable
energy, computer science, automated control and
other disciplines, as well as new software
technologies, internet of things (IoT), robotics and
manufacturing integrated by computer (Atoche and
Marrufo, 2011).
Dias, J., Dias, J., Barbosa, M., Filho, D., Junqueira, F., Miyagi, P. and Cardoso, J.
In Vitro Test Bench with Intelligent Behavior to Ventricular Assist Devices.
DOI: 10.5220/0006849101270134
In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics (ICINCO 2018) - Volume 1, pages 127-134
ISBN: 978-989-758-321-6
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
127

This article proposes the use of this technological
evolution in the study of Ventricular Assist Devices
(VAD), since according to the World Health
Organization in 2016 of the 38 million deaths per
year, classified as "non-transmissible", 17.5 million
(46%) were cardiovascular diseases. Of these, 7.4
million were coronary heart disease and 6.7 million
strokes (World Health Organization, 2016) and a
growth of more than 23.6 million of these diseases is
planned for 2030 (Mozaffarian et al., 2016).
Cardiovascular mortality rates remain the leading
cause of death worldwide (Nichols et al., 2015).
The implantation of a VAD has proven to be a
successful option for the treatment of patients with
heart failure, that is, it can be implanted to ensure
that the patient can wait until a heart transplant, and
in this case, this practice is known as "a bridge to the
transplant”, or when the patient has a high rejection
rate for the transplant, the device is implanted as a
permanent solution and in this case this practice is
known as "destiny therapy" (Murala and Si, 2017)
(Healy et al., 2016) (Drakos et al., 2010). One of the
issues that has intensified the use of these devices as
target therapy is the imbalance between the number
of donors and the number of recipients for heart
transplantation (Christie et al., 2012).
The increasing longevity of patients transplanted
with VADs as a target therapy recently (Goldstein
et al., 2018) (Cowger et al., 2018) justifies the
development of features that improve the robustness
and reliability of these devices. In this sense, there
are several approaches that can be used for
implantable medical devices, ISO standards, ASTM
standards, in vivo animal study, cadaver study,
among others, as well as specific methods such as
the characterization and demonstration of reliability
(Zhang; Jiang, 2017). Guidelines for validation
procedures have also been developed for the reliable
procedure for validating medical devices. The
accelerated tests used as tools to verify the
correctness of the manufacturing of electronic
components and microelectronics are a good option
to obtain and prove reliability data (Valis; Vintr;
Koucky, 2010) (Evans; Sinha, 2018).
For ventricular assist devices some research has
been developed, such as the use of an in vitro
hemolysis test bench for development evaluation
and safety regulation to check the
hemocompatibility of medical devices such as
VADs that have contact with blood (Olia et al.,
2017). To model the arterial and pulmonary
hemodynamic behavior of the circulatory system
was developed by (Mueller et al., 2017) a bench of
tests that presented good results for reproduction of
the system. For a total heart without valves,
compatible with pediatric population, was presented
by (Tozzi et al. 2017) a bench of tests that presented
encouraging results, despite issues related to
durability, and the need for confirmation of results
with in vivo test. The bench test to simulate in vitro
conditions of biomedical metal alloys for implants of
devices made by (Ijaz et al., 2017) demonstrated
satisfactory results for fatigue resistance of Ti-Nb-Zr
alloys when compared with Ti alloys.
Improving the reliability of VADs allows a
constant search, however, the absence of failure data
from the device or its components for a performance
analysis is a gap that can be improved with an in
vitro test bed of VADs. This work within a control
hierarchy proposes the testing and monitoring of
devices with a continuous collection of context data,
which will be analyzed and treated against reference
correlation curves of variables (pressure, flow,
vibration, temperature, viscosity, density , rotation,
and power) that will allow us to identify the
description of the occurrence of failures from which
the system transfers the information to a cloud
knowledge base for analysis of standards according
to Big Data Analytics technologies. With this
information an intelligent module based in Artificial
Intelligence (AI) can readjust the set-up variables by
adjusting the control to a safe state of operational
functionality. Allied to this system a remote
operator, with support for decision making, can also
monitor and analyze the level of system failure and
operate from a smart device.
In this prospective work will be used the
modeling of an in vitro test bench for VAD in Petri
net to represent its behavior and for validation of the
model.
2 TEST BENCH
This work’s proposed test bench is composed by two
tanks (T1 and T2) that are responsible for the storage
of the fluid that travels through the system. The fluid
is transported from tank T1 to tank T2. The transport
is carried out from a pump (B1), which imposes
energy on the system. During the test bench
operation process, sensors are used to collect the
main variables involved in the system (Figure 1).
Sensors collect fluid pressure at tank outlet T1,
engine speed M1 from pump B1, pump vibration
B1, electric motor current M1 from pump B1, fluid
pressure at pump outlet B1, fluid flow at outlet of
the pump B1, the temperature of the fluid at the
outlet of the pump B1, the position of the motor M2
ICINCO 2018 - 15th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
128

Figure 1: VAD In vitro Test Bench Process Diagram and
Instrumentation.
of the valve V1, the electric current in the motor M2
of the valve V1 and the pressure of the fluid at the
inlet of the tank T2.
To perform, the test bench has an M1 motor
responsible for the rotation control of the pump B1
and an M2 motor responsible for the position control
of the valve V1 that allows the flow control of the
fluid. To collect the data emitted by the sensors and
impose the new references to the actuators, a
communication manager is necessary for distribution
of the information.
3 PROPOSED CONTROL
SYSTEM
In the development of the proposed control system,
it is approached the concept that the test bench does
not have an on-board control and monitoring system.
In this way, the control system acts on a remote
server that collects information from the test bench
sensors for monitoring information on mobile /
desktop devices.
The information that travels from the test bench
to the supervision is carried out from the concept of
Publish / Subscribe (Sonawala et al, 2017). This
communication approach is characterized by the
asynchronous exchange of events between devices
and applications that make up the system, so the
applications need to receive a certain type of event
subscribers that is originated by another application
and event publisher. The main characteristics of
publish / subscribe communication are to eliminate
the direct coupling between the applications and to
allow the selective dissemination of information
based on the interests of the system (Lopes, Bock
and Gómez, 2017).
The actuating commands for parameterization of
the Set Ups, the motor rotation (M1) of the pump
(B2) and the position of the motor (M2) of the valve
(V1) are performed by two agents: a) from a mobile
/ desktop, in this case the user interferes directly in
the event management and b) by the AI module,
which searches through the learning and the patterns
identified by the Big Data Analytics module, the
best conditions of Set Up of the control variables to
allow the greater life of devices (VADs) under test.
The information system performs all demand
processing to inform the local communication
manager that replicates the data to the local control
system reference. For monitoring, the
communication manager is responsible for reading
the data emitted by the sensors from the test bench
and publishing them from the physical event
manager to the collection and storage processes in
the database.
To access information about test bench
operation, users can: require the performance and
requests data directly from the user interface, request
query information from the Big Data Analytics and
AI modules, and in vitro make operational decisions
through the mobile / desktop module (Figure 2).
Figure 2: Architecture of proposed control.
All collection, storage, monitoring, and
command features are centralized in the use-case
manager. This module is responsible for controlling
the information demanded by sensors, actuators,
users and AI. Below is a representation of the
proposed control architecture.
4 SYSTEM MODELING
Petri nets are tools that use mathematical models and
graphics that apply to a system that, by its
In Vitro Test Bench with Intelligent Behavior to Ventricular Assist Devices
129

characteristics, allows modeling of system behavior,
as well as graphical visualization, synchronization,
parallel data processing and observation of
competing systems (Murata, 1989). These
characteristics allow to follow the variations of the
dynamic behavior of the modeled system, which in
this case will be the test bench.
Petri nets have been used in various applications,
for example, to model complex biological systems
of yeast cell cycles based on multisite
phosphorylation (Herajy; Liu; Heiner, 2018),
modelling and analysis of traffic signal priority
control systems (An et al., 2018) in accidents, in the
cascade analysis for vapor cloud explosions of
flammable fuels (Zhou; Reniers, 2017),
interoperability test bench model for embedded train
control system (Yuan et al., 2010), and, approach for
the evaluation of the reliability of the final elements
of the Instrumented Security System with time-
dependent failure rates (Wu et al., 2018).
5 METHOD
The research has a theoretical and quantitative
descriptive methodological approach, since it aims
to discover the existence of associations and
correlations between variables (Mattar, Oliveira and
Motta, 2014) and prospective in the timeline
(Fontenelles et al., 2009) when a method of
experimentation is proposed by means of in vitro
models. Modeling through the Petri net completes
the In vitro model, allowing the simulation of the
process in a computational model of a real system,
conducting experiments with this model with the
purpose of understanding and validating its behavior
(Centeno, 1996).
On the other hand, the technical procedures,
related to the method, are the application of the Petri
net to model the dynamic behavior of the variables
of the VADs in tests, obtaining the behavior of faults
by deviations when compared to the standard curves
of these variables (pressure, flow, vibration,
temperature, viscosity, density, rotation and energy).
Decision making is based on maintaining the
longevity of the life of the device being tested, in
which two agents can act: a) an AI module that is
based on machine learning and b) a human assistant.
5.1 Data Colleting and Handling
The "context" information source (Wan, 2009) of the
assisted device is connected to the sensors in the
"Test Bench", from which it transfers this
information to a real-time cloud knowledge base.
This knowledge base is handled by a standards
analyzer for knowledge discovery using Big Data
Analytics technologies.
In this paper "context" is any information that
can be used to characterize the situation of an entity
(object of interest), it is also known as sentient
computing (Andrade, 2015). Thus, an entity can be a
person, a place, or an object that is considered
relevant to the interaction between a user and an
application, including the user and the applications
themselves (Schilit; Adams; Want, 1994).
5.2 Data Analysis
The Big Data Analytics’ approaches to pattern
discovery are based on: (i) Descriptive Analysis -
Real-time understanding of events so that immediate
decisions can be made. The descriptive analysis
works with data history, crossing information with
the objective of generating a clear and precise
panorama of the relevant themes for the present
moment, without necessarily relating it to past or
future patterns (Marquesone, 2016). (ii) Diagnostic
Analysis: Its objective is to understand the relation
of cause and effect (Who, When, How, Where and
Why) perceived over time and its possibilities. It
works based on the collection of data related to a
certain subject, crossing information in order to
understand which factors influenced the current
result (Marquesone, 2016). (iii) Predictive Analysis:
Known for "predicting" the future, we use data
mining: statistical and historical data to know future
trends (Marquesone, 2016). (iv) Prescription
Analysis: Very confused with the predictive
analysis, the prescriptive analysis works with the
same logic, but with different objectives. While
predictive analysis identifies future trends, the
prescriptive outlines the possible consequences of
each action. It is a way of defining which choice will
be most effective in a particular situation
(Marquesone, 2016).
6 SYSTEM MODELLING
The modeling developed for the system uses a
systematic and refinement approach. Using a
combination of the work of Villani (2004) to
perform the modeling of the supervisory control and
monitoring system of the test bench (Figure 3). In
step 1, fluid flow modeling is performed by the
bench of tests to characterize the dynamics of the
test bench (Villani et al., 2004).
ICINCO 2018 - 15th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
130
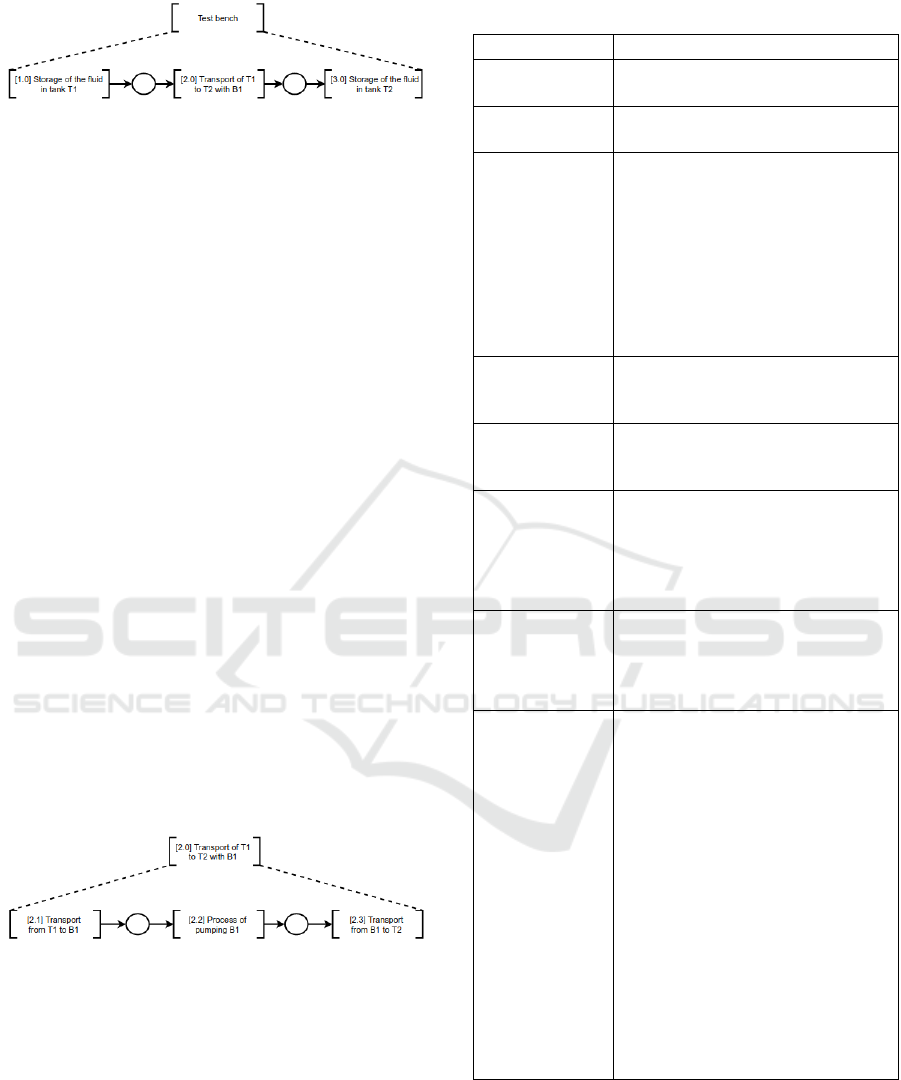
Figure 3: PFS model of the test bench.
In step 2 all desired functionalities are described
for the control and monitoring system of the test
bench (Villani et al., 2004). In step 3, the
implementation strategies of the control system are
described, so it is specified how the system should
behave for each use case. In step 4, the modeling
procedures begin by performing the modularization
of the system components. In step 5, the component
models for analysis are integrated. In step 6, the
models are analyzed from the main properties of
Petri nets.
6.1 Step 1: Modeling Material Flows
This step aims to define the boundaries of the test
bench that will be controlled by a command and
monitoring control system. This model is built on
PFS (Product Flow Schema), which is based on the
concept of successive refinement (Villani et al.,
2004). For more information on PFS modeling and
successive refinement, it is recommended to read
Miyagi (1988).
The activities of [Storage of the fluid in tank T1]
and [Storage of the fluid in tank T2] are detailed in
Figure 4 so that no further refinement is required.
For the activity [Transport of T1 to T2 with B1], one
can drill down to another level.
Figure 4: Activity Detail [Transport of T1 to T2 with B1].
From this model it is possible to highlight the
dependencies and inputs and outputs of the
operational process of the test bench.
6.2 Step 2: Definition of Use Cases
1. The system agents (user and AI) can
parameterize the flow reference flowing
through valve V1 and pump motor rotation
reference B1.
Table 1: Assignment of features for each control device.
Devices
Activities
Sensors
-Publish value collected to the
communication manager
Actuators
-Receive new reference from the
communication manager
Communication
Manager
-Receive value collected from the
sensors
-Receive new physical event manager
reference;
-Publish value collected from sensors
to the physical event manager;
-Publish new reference received by
the physical event manager to the
actuators;
Physical Event
Manager
-Direct publication and receipt of the
use case manager and communication
manager;
Use Event
Manager
-Direct publication and receipt of the
mobile / desktop devices and use-
case manager;
Mobile / desktop
device
-Request data from the sensors stored
in the database;
-Amply new reference to actuators;
-Measure new sensor value limits;
-Receive alert for abnormal values;
Database
-Save data collected from sensors;
-Save sensor limit value;
-Store new actuators reference;
-Consult stored values of the sensors;
Use case
manager
-Receives value collected in the
sensor of the physical event manager,
validates the measured value to
ensure that it is within the accepted
limits of the standard curve of pump
B1 and stores in the database;
-Receives new reference value from
the actuators of the event manager,
stores it in the database and publishes
it to the physical event manager;
-Receives new threshold value from
the sensors of the event manager and
stores it in the database;
-Receive request to query the sensor
data in the database of the event
manager and publish the data in the
event manager;
2. System agents (user and AI) can
parameterize a pressure value limit on
sensors PT1, PT2 and PT3, vibration on
sensor VT1, rotation on sensor ST1,
electric current on sensors IT1 and IT2,
temperature on sensor TT1 and the FT1
sensor.
In Vitro Test Bench with Intelligent Behavior to Ventricular Assist Devices
131

3. System agents (user and AI) can monitor
the pressure values in the PT1, PT2 and
PT3 sensors, vibration in the VT1 sensor,
rotation in the ST1 sensor, electric current
in the IT1 and IT2 sensors, temperature in
the TT1 sensor and flow in the FT1 sensor.
4. The supervisory system collects the
pressure values on the sensors PT1, PT2
and PT3, vibration on the VT1 sensor,
rotation on the sensor ST1, electric current
on the sensors IT1 and IT2, temperature on
the sensor TT1 and flow on the sensor FT1
and stores in the bank data.
6.3 Step 3: Specification of Control
Strategies to Be Modeled
From the proposed control architecture, we identify
mobile / desktop devices, use case manager,
communication manager, database, test bench,
physical event manager and event manager. Table 1
specifies the assignment of functionality for each
device.
6.4 Step 4: Construction of
Components
From the control strategies (step 3) and proposed
control architecture, the modelling procedures are
started. For each device specified in the strategies
there will be a Petri net. In this way, integrating the
devices according to their needs, one must build the
Petri net models of the mobile / desktop device, use
case manager, database, event manager, physical
event manager and communication manager.
The final goal of device integration can be seen in
Figure 5.
Figure 5: Interactions of the supervisory control.
6.5 Step 5: Integrated Component
Modelling
In the integrated modeling, the component models
are combined to perform the Petri nets verification
from their properties for each of the system use
cases: collection, validation and storage of the
sensor data.
6.6 Step 6: Analysis of Models
The analysis of the models is performed for each of
the use cases, so that the properties of the mark
diagram are evaluated, it is verified if the modelled
Petri net is limited, safe, alive and bootable.
7 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The research sought to analyse the automation of a
test bench, using resources: modelling of dynamic
behavior, through the Petri net; to provide intelligent
behavior with the use of AI and machine learning, in
face of the changes of the monitored variables; as
well as the use of diagnostic and prognostic features
in Big Data Analytics technology for data analysis
and treatment.
From the analysis of the properties of the models
and simulations performed in the validation of each
of the specified use cases for the control system, it is
identified that the proposed system meets the
functional requirements according to the model
properties checks. However, it requires simulation
tests for adjustments in the predictive and diagnostic
model, which still causes conflicts with the user's
decision regarding the adjustments made by the AI
model.
8 CONCLUSIONS
The purpose of this work is to explore the benefits of
the introduction of intelligent control systems,
applied to a test bench of ventricular assist devices
(VAD), allowing to these “in test” devices the
greatest possible longevity of use, at the same time
in which the behavior variations are identified,
observing the changes in the dependent variables,
while controlling the independent ones, by means of
the set-up change of these variables.
The final result obtained is: a knowledge
database containing: a) failure data and respective
behaviors over time, allowing intelligent control to
ICINCO 2018 - 15th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
132

predict future consequences, from tests of new
devices; b) a set of improvements that can be applied
to the design of new devices, allowing more durable
devices; c) refinement of a learning system as it
continually evaluates the test results, compared to
the designs of each device, e.g. device with such
design characteristics as: structure, form of
construction, materials used, among others, have
tendencies of behavior, which can lead to a set of
predictive actions; d) the subsidy and experience for
the elaboration of a new challenge, of a robotic
device (VAD) that can, depending on the construct-
ion project, use this knowledge base to provide
longevity of use of its resources and limitations,
consequently creating longevity of its host.
A robotic VAD could have adaptive and resilient
behavior, being flexible without the need to be
reprogrammed, since robots are designed to be able
to perform various tasks based on simple
programming (Niku, 2013).
With these elements, it can be concluded that the
control system for control and monitoring of the test
bench provides significant gains for the detailed
study of the operation of VADs. With the collection
of more flexible information and interfaces it is
possible to carry out analysis and data collection that
help in the continuous improvement of these
devices.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors thanks FAPESP, CNPQ e CAPES for
supporting this research.
REFERENCES
An, Y. et al. (2018) ‘Hierarchical Colored Petri Nets for
Modeling and Analysis of Transit Signal Priority
Control Systems’, Applied Sciences, 8(1), p. 141. doi:
10.3390/app8010141.
Andrade, L. A. de (2015) Jogos Digitais, Cidade e
(Trans)mídia: A Próxima Fase. Curitiba: Editora
Appris.
Atoche, A. C. and Marrufo, O. P. (2011) ‘“Nuevas
Tendencias en Sistemas Mecatrónicos”’, Ingeniería,
15(2).
Cassandras, C. G. and Lafourtune, S. (2008) Introduction
to Discrete Event Systems. Boston: Springer US.
Centeno, M. A. (1996) ‘An introduction to simulation
modeling’, Winter Simulation Conference, pp. 15–22.
doi: 10.1109/WSC.1996.873255.
Christie, J. D. et al. (2012) ‘The registry of the
international society for heart and lung transplantation:
29th adult lung and heart-lung transplant report -
2012’, Journal of Heart and Lung Transplantation.
Elsevier Inc., 31(10), pp. 1073–1086. doi: 10.1016/
j.healun.2012.08.004.
Cowger, J. A. et al. (2018) ‘Quality of life and functional
capacity outcomes in the MOMENTUM 3 trial at 6
months: A call for new metrics for left ventricular
assist device patients’, Journal of Heart and Lung
Transplantation. Elsevier Inc., 37(1), pp. 15–24. doi:
10.1016/j.healun.2017.10.019.
Drakos, S. G. et al. (2010) ‘Risk Factors Predictive of
Right Ventricular Failure After Left Ventricular Assist
Device Implantation’, American Journal of
Cardiology. Elsevier Inc., 105(7), pp. 1030–1035. doi:
10.1016/j.amjcard.2009.11.026.
Evans, J. W. and Sinha, K. (2018) ‘Applications of
fracture mechanics to quantitative accelerated life
testing of plastic encapsulated microelectronics’,
Microelectronics Reliability. Elsevier, 80(October
2017), pp. 317–327. doi: 10.1016/j.microrel.2017.10.
022.
Flyn, J. R. (2009) O que é Inteligência? Além do efeito
Flyn. Porto Alegre: Editora Artmed.
Fontenelles, M. J. et al. (2009) ‘Metodologia da pesquisa
científica: diretrizes para a elaboração de um protocolo
de pesquisa 1’.
Goldstein, D. J. et al. (2018) ‘Impact of age, sex,
therapeutic intent, race and severity of advanced heart
failure on short-term principal outcomes in the
MOMENTUM 3 trial’, Journal of Heart and Lung
Transplantation. Elsevier Inc., 37(1), pp. 7–14. doi:
10.1016/j.healun.2017.11.001.
Healy, A. H. et al. (2016) ‘Predictors of 30-day post-
transplant mortality in patients bridged to
transplantation with continuous-flow left ventricular
assist devices - An analysis of the International
Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation Transplant
Registry’, Journal of Heart and Lung Transplantation.
Elsevier, 35(1), pp. 34–39. doi: 10.1016/j.healun.
2015.07.007.
Herajy, M., Liu, F. and Heiner, M. (2018) ‘Efficient
modelling of yeast cell cycles based on multisite
phosphorylation using coloured hybrid Petri nets with
marking-dependent arc weights’, Nonlinear Analysis:
Hybrid Systems. Elsevier Ltd, 27, pp. 191–212. doi:
10.1016/j.nahs.2017.09.002.
Ijaz, M. F. et al. (2017) ‘Novel Electrochemical Test
Bench for Evaluating the Functional Fatigue Life of
Biomedical Alloys’, Jom. Springer US, 69(8), pp.
1334–1339. doi: 10.1007/s11837-017-2375-x.
Khalfa, J. (ed.) (1995) A Natureza da Inteligência: uma
visão interdisciplinar. São Paulo: Fundação Editora
Unesp.
Kuhn, M. F. et al. (2018) ‘A Novel RFID-Based Strain
Sensor for Wireless Structural Health Monitoring’,
Journal of Nondestructive Evaluation. Springer US,
37(2), p. 22. doi: 10.1007/s10921-018-0475-3.
Lopes, G., Bock, E. and Gómez, L. (2017) ‘Numerical
Analyses for Low Reynolds Flow in a Ventricular
Assist Device’, Artificial Organs, 41(6), pp. E30–E40.
In Vitro Test Bench with Intelligent Behavior to Ventricular Assist Devices
133

doi: 10.1111/aor.12776.
Marquesone, R. (2016) Big Data - Técnicas e tecnologias
para extração de valor dos dados. São Paulo: Editora
Casa do Código. Available at: http://forum.casado
codigo.com.br/.
Mattar, F. N., Oliveira, B. . and Motta, S. L. S. (2014)
Pesquisa de Marketing: metodologia, planejamento,
execução e análise. 7th edn. Edited by Elsevier. Rio de
Janeiro.
Mozaffarian, D. et al. (2016) Heart disease and stroke
statistics-2016 update a report from the American
Heart Association, Circulation. doi: 10.1161/CIR.00
00000000000350.
Mueller, N. et al. (2017) ‘Design of a right ventricular
mock circulation loop as a test bench for right
ventricular assist devices’, Biomedical Engineering /
Biomedizinische Technik, 62(2). doi:
https://doi.org/10.1515/bmt-2016-0104.
Mühlhäuser, M. (2007) ‘Smart Products: An Introduction’,
Smart Products: An Introduction, (AmI 2007
Workshops), pp. 158–164. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-
85379-4.
Murala, J. and Si, M. (2017) ‘Mechanical circulatory
support for the failing functional single ventricle’,
Translational Pediatrics, 6(1), pp. 59–61. doi:
10.21037/tp.2016.10.09.
Murata, T. (1989) Petri Net: Properties, Analysis and
Applications, Petri Net Theory. Chicago: IEEE.
Nichols, M. et al. (2015) Australian Heart Disease
Statistics 2015, Australian Heart Disease Statistics.
Available at: https://www.heartfoundation.org.au/
images/uploads/publications/RES-115-Aust_heartdise
ase_statistics_2015_WEB.PDF.
Niku, S. B. (2013) Introdução à robótica: análise,
controle, aplicações. Rio de Janeiro: LTC.
Olia, S. E. et al. (2017) ‘A Reusable, Compliant, Small
Volume Blood Reservoir for In vitro Hemolysis
Testing’, Artificial Organs, 41(2), pp. 175–178. doi:
10.1111/aor.12724
Russell, S. and Norvig, P. (2013) Inteligência Artificial.
São Paulo: Elsevier Ltd.
Schilit, B. N., Adams, N. and Want, R. (1994) ‘Context-
aware computing applications’, Proceedings of the
1994 First Workshop on Mobile Computing Systems
and Applications, pp. 85--90. doi:
10.1109/MCSA.1994.512740.
Sharma, R., Singh, P. and Singhal, A. (2017) ‘Two
different authentication protocol for RFID credit card
security’, Journal of Engineering and Applied
Sciences, 12(22), pp. 6006–6012.
Silva, C. W. de (2005) Mechatronics An Integrated
Approach. New York: CRC press.
Sonawala, N. M., Tank, B. and Patel, H. (2017)
‘Implementation of MQTT protocol in Context with
Industry 4 . 0’, 4(4), pp. 260–67.
Tozzi, P. et al. (2017) ‘An original valveless artificial
heart providing pulsatile flow tested in mock
circulatory loops’, International Journal of Artificial
Organs, 40(12), pp. 683–689. doi: 10.5301/ijao.50
00634.
Valis, D., Vintr, Z. and Koucky, M. (2010) ‘Accelerated
test used as a tool for manufacturing correctness
check’, in Bris, R., Martorelli, S., and S., G. S. & (eds)
Reliability, Risk and Safety: Theory and Applications -
Bris. London: CRC press, pp. 807–811.
Villani, E. et al. (2004) ‘Object oriented approach for cane
sugar production: Modelling and analysis’, Control
Engineering Practice, 12(10), pp. 1279–1289. doi:
10.1016/j.conengprac.2004.04.011.
Wan, K. (2009) ‘A Brief History of Context’, Journal of
Computer Science, 6(2), pp. 33–43.
Weiser, M. (1991) ‘The Computer for the 21st Century’,
Scientific American, pp. 94–104. doi: 10.1038/scien
tificamerican0991-94.
World Health Organization (2016) ‘world health statistics
monitoring health for the sdg s’.
Wu, S. et al. (2018) ‘Reliability assessment for final
elements of SISs with time dependent failures’,
Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries.
Elsevier, 51(October 2017), pp. 186–199. doi:
10.1016/j.jlp.2017.12.007.
Yuan, L. et al. (2010) ‘Modeling of an interoperability test
bench for the on-board system of a train control
system based on Colored Petri Nets’, WIT
Transactions on the Built Environment, 114, pp. 271–
280. doi: 10.2495/CR100261.
Zhang, H. and Jiang, M. (2017) ‘An Integrated Approach
for Implantable Medical Devices Fatigue Reliability
Prediction’, pp. 0–5.
Zhou, J. and Reniers, G. (2017) ‘Petri-net based cascading
effect analysis of vapor cloud explosions’, Journal of
Loss Prevention in the Process Industries. Elsevier
Ltd, 48(October 1989), pp. 118–125. doi:
10.1016/j.jlp.2017.04.017.
ICINCO 2018 - 15th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
134
