
Ergogenic Effects of Pop Music on Endurance Performance in Hot
Conditions among Physically Active Individuals
Eng Hoe Wee, Xiao Ying Lai and Hui Yin Ler
Tunku Abdul Rahman University College, Jalan Genting Kelang, 53300 Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
Keywords: Music, Endurance Performance, Ergogenic Effects, Hot Condition.
Abstract: Music has been reported by numerous researchers to elicit psychological, psychophysical, and ergogenic
effects. Some researchers found that music could improve endurance performance, others reported
progressive impairment in endurance performance with increasing ambient temperature. The purpose of this
study was to determine the effects of pop music on endurance performance in hot conditions (35°C) among
physically active individuals. Twenty-eight physically active subjects (14 males, 14 females, age=19.57±1.7
yrs, height= 164.8±8.3 cm, weight= 58.6±8.8 kg, VO2max = 42.5±7.7 ml.kg
-1
.min
-1
) were recruited to
participate in this randomized cross-over study: with music (WM) and no music (NM) trials. For each trial,
subjects cycled at 60 rpm for the first 20 minutes followed by maximal cycling effort in the last 20 minutes
to determine the distance achieved. The workload of 40 minutes exercise were maintained at 55% Pmax.
Heart rate (HR), oxygen uptake (VO2) and rate of perceived exertion (RPE) were recorded throughout the
experimental trials. Experimental trials were separated by at least 5 days apart. Results revealed that there
was no significant interaction between music and cycled distance [F(1, 26) = 1.372, p=0.252, ηp2=0.050].
Results also revealed that similar physiological responses (HR and VO2) and RPE were found in both WM
and NM trials. In conclusion, there is no sufficient evidence to support that pop music could enhance
endurance performance in the heat among physically active individuals.
1 INTRODUCTION
Numerous researchers studied the ergogenic aids of
music on sport performance. They reported that
music helps increased arousal, increased power
output and heart rate, delayed fatigue, and increased
exercise duration and intensity (Foster, 2010;
Karageorghis et al, 2009).
Varied results had been obtained on the effects of
music on sport performance. Atan (2013) found no
significant differences between type of music (slow
music, fast music and no music) in anaerobic power
assessments, heart rate (HR) or blood lactate.
Beaumont et al. (2014) studied music tempo on
cycling performance and revealed that fast music and
slow music had the higher average distance cycled as
compared to no music. Average HR was higher in no
music condition as compared to fast music condition
and RPE was higher in fast music condition as
compared to no music. Elisa et al. (2017) found music
at high volume did not improve physical
performance. While others (e.g. Waterhouse and
Edwards, 2009) found faster music enabled exercise
to be performed at a bigger work rate and with a
greater physiological effect and more positive
subjective responses, than did slower music.
Bigliassi et al. (2012) revealed that regardless of
the time of application (i.e., before or during
exercise), music did not affect performance and
psychophysiological parameters during the 5-km
time-trial cycling. Dyer and McKune (2013) in a
study of the effects of fast-tempo (140 bpm),
medium-tempo (120 bpm), slow-tempo (100 bpm),
and no music on well-trained cyclists, results
indicated no significant changes in performance,
physiological, or psychophysical variables. Hagen et
al. (2012) found no effect of music on 10-km cycle
time-trial performance; there were no statistically
significant differences in performance time or
physiological or psychological markers related to
music.
Another effect of listening to music is
physiological (HR, systolic and diastolic blood
pressure). Edworthy and Waring (2006) found a
significant increase in HR while listening to fast
music during exercise. Birnbaum et al. (2009)
Wee, E., Lai, X. and Ler, H.
Ergogenic Effects of Pop Music on Endurance Performance in Hot Conditions among Physically Active Individuals.
DOI: 10.5220/0006887000910097
In Proceedings of the 6th International Congress on Sport Sciences Research and Technology Support (icSPORTS 2018), pages 91-97
ISBN: 978-989-758-325-4
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
91

reported that listening to fast music decreased the
subjects’ HR and blood pressure during steady state
treadmill exercise. Conversely, Atan (2013) and
Schwartz et al. (1990) examined effects of fast music
tempo on HR and found no significant changes.
Exercise in hot conditions causes heat stress
which can be detrimental to sporting performance.
However numerous studies had reported the
mediating effects of music on sport performance in
hot conditions. In a Malaysian study (Nikol et al.,
2018) of running time-to-exhaustion for 12 runners
during the synchronous music and no music
conditions, it was reported that participants ran
significantly run longer before reaching exhaustion
while listening to synchronous music compared to
the no music condition with a main gain of 151s. On
the contrary, Tatterson et al. (2000) found in a study
comparing the performance of trained cyclist in a 30-
min time-trial, with (32°C) and without (23°C) heat
stress, reported 6.5% reduced power output.
Due to inconclusive and controversial results
from previous research, this study proposed to
investigate the effects of pop music on cycling
performance in hot conditions.
2 METHOD
2.1 Participants
Twenty-eight physically active individuals (14 males,
14 females, age = 19.57±1.7 yrs, height = 164.8±8.3
cm, weight= 58.6±8.8 kg, VO2max = 42.5±7.7 ml.kg
-
1
.min
-1
) volunteered for this study (Table 1). All
subjects were of good health and free of any chronic
health conditions through the scrutiny of Medical
Health History. They were chosen based on ACSM’s
(2014) criteria that they performed at least 30 minutes
of moderate-intensity physical activity five days per
week or 20 minutes of more vigorous activity three
days per week.
Table 1: Participants characteristics and VO
2max
parameters
(mean ± SD).
Prior to the participation, the participants
completed the Physical Activity Readiness
Questionnaire (PAR-Q), to rule out contraindications
to participation. The approval to conduct this research
was approved by the University College Ethics
Committee. In conforming to the principles of the
declaration of Helsinki of the World Medical
Association, participants were briefed on the
methods, procedures, benefits and potential risk
before signing the written consent.
2.2 Research Design
This study applied a crossover randomized
experimental design which consisted of two
experimental conditions, to test the effects of ‘With
Music’ (WM) and ‘No Music’ (NM) on endurance
cycling performance in hot conditions. After the
preliminary testing, each subject was required to
undergo two randomized-separate experimental
trials. The two experimental trials were NM in the
Hot Condition (35°C) and WM in Hot Condition
(35°C).
2.3 Music Selection
Based on the recommendation of Lopes-Silva et al
(2015) and Karageorghis et al. (1999), pop and rock
music tracks were selected for the music condition.
Fifteen pieces of pop and rock music tracks were
selected and in their original form, the tracks were
played in the tempo range of 78-144 bpm. However,
in order to control music tempo, the tempo of the
music tracks was standardized at 150 bpm. using a
computer software package (Virtual DJ v. 8; Atomic
Productions, Paris, France) as suggested by
Karageorghis et al. (2010). The subjects with music
condition listened to the music at 150 bpm through
headphones connected to a portable MP3 player set at
approximately 80 decibels as proposed by Edworthy
and Waring (2006). Each track lasted approximately
4 minutes and the track sequence was applied during
all the music conditions.
2.4 Procedure
Procedure consisted of two phases (a) Familiarization
and Preliminary Testing, (b) Experimental Trials. The
research design consisted of experimental conditions.
Each subject was tested two times under the same
laboratory conditions in a randomized manner.
Condition 1 (NM) consisted of performing warm-up
and cycling exercise without music. For condition 2
(WM) the athletes listened to music during warm-up
and while performing cycling exercise.
icSPORTS 2018 - 6th International Congress on Sport Sciences Research and Technology Support
92

2.4.1 Familiarization and Preliminary
Testing
The first phase of the research involved the Maximal
Oxygen Uptake (VO
2max
) Test. Upon the arrival of
each subject, subject’s height and weight were
measured. After which the subject was fitted onto the
cycle ergometer (Corival, Lode) and the saddle height
and reach length were measured and recorded for
subsequent experimental trials and profiling
purposes. Once the subject settled in, heart rate (HR)
and resting blood pressure (BP) were measured using
a heart rate monitor (FT4M, POLAR, Australia) and
a blood pressure monitor (Omron 1 A2, OMRON,
Japan). When the subject was sufficiently rested and
ready, the Portable Metabolic System (K4 b2,
Cosmed, Italy) was fitted. The Modified Astrand
Maximal Cycle Protocol was used in this VO
2max
test.
Submaximal oxygen uptake test was performed
before the VO
2max
test. The initial workload was 25
watts for female and 30 watts for male (Pollock et al.,
1987). Subjects were instructed to maintain 60 rpm in
every load. After 4 minutes at this initial workload,
the workload was increased in increments of 25 watts
for female and 30 watts for male. The submaximal
test ended after 4 stages of increments. Subjects were
instructed to sit and rest until they recovered to resting
heart rate. After that, subjects started on the VO
2max
test by a load that was achieved by the subject’s when
his/her HR was at 130+/-bpm in the previous
submaximal test. Subjects’ load was added 25 watts
for female and 30watts for male every 2 minutes. The
test continued until the participant was exhausted or
was no longer maintaining the pedalling frequency of
55 rpm. The data from the submaximal and VO
2max
test were used to determine the 55% P
max
for the
experimental trials.
2.4.2 Experimental Trials
Subjects were required to complete 2 experimental
trials that were conducted each week in the sports and
exercise science laboratory. All subjects were
involved in both conditions of WM in Hot Condition
(35⁰ C) and NM in Hot Condition (35⁰ C). Humidity
for both conditions were maintained at 55-65%.
After arriving at the laboratory for the
experimental trials, subjects rested for 10 minutes,
after which RHR was measured using a HR monitor.
Before the experimental trial started, the subject was
fitted with the portable metabolic system and all the
required ancillary instruments as mentioned in the
preliminary testing. In the music conditions, a
portable MP3 player was turned on after warm-up. In
the non-music conditions, headphones were
connected, but the portable MP3 player remained off
during the entire test.
Each experimental trial consisted of 40 minutes
55% of P
max
cycling which the subjects maintained 60
rpm for the first 20 minutes and followed by cycling
as fast as possible in the last 20 minutes to determine
the distance completion. Prior to each experimental
trial, subjects warmed up for 5 minutes on the cycle
ergometer at 60 rpm without resistance. HR, VO
2max
,
RPE were measured at intervals of 5 minutes during
the experimental trials and distance of completion for
the last 20 minutes were recorded. The experimental
trials were separated by at least 5 days to ensure full
recovery from previous experimental trial.
2.5 Statistical Analysis
The statistical software package “SPSS Statistics
23.0” (IBM) was used for statistical analysis. Mean
value and standard deviation for the research
parameters were calculated. T-tests were used for
comparative analyses. Two way Repeated Measures
ANOVA was used to examine the differences across
the VO
2,
HR, distance and RPE for both trials. When
significant interaction was obtained, pair-sampled t-
test was used to identify differences between mean
scores. The level of significance was set at p < 0.05.
3 RESULTS
The Two-way repeated-measures ANOVA (minutes
20 through 40) showed there was a significant
interaction between music and HR [F(1,26) = 76.698,
p<0.001, ηp
2
=0.754]. HR responses were higher in
NW trial as compared to WM trial but statistically not
significant (p>0.05). The HR values from 0 to 40
minute values are displayed in Figure 1.
Figure 1: HR Responses during WM and NM Trials.
Ergogenic Effects of Pop Music on Endurance Performance in Hot Conditions among Physically Active Individuals
93
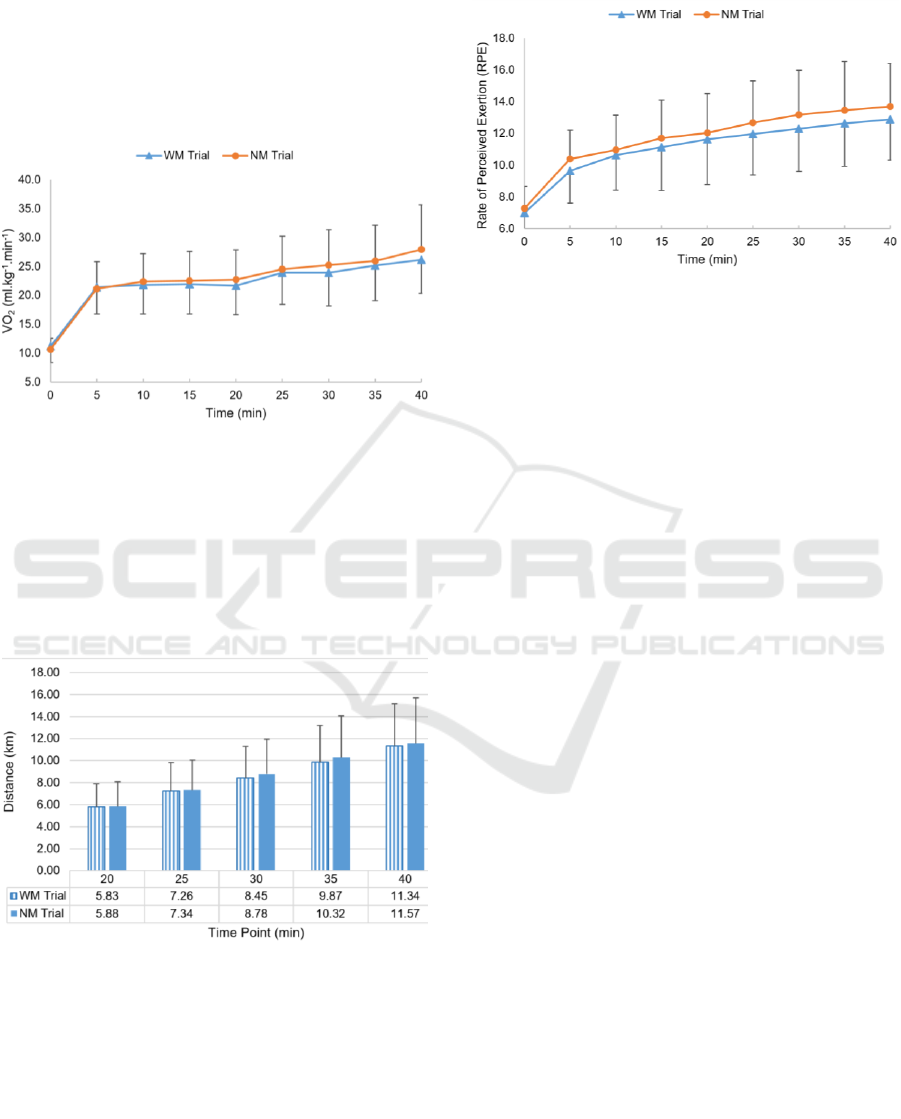
The Two-way repeated-measures ANOVA
(minutes 20 through 40) showed there was a
significant interaction between trials and VO
2
[F(1,26) = 104.836, p <0.001, ηp
2
=0.801] as NM trial
displayed an increase in VO
2max
values over time
greater than WM trial. VO
2
in NM trial was
significantly higher than WM trial at 20 min and at 40
min (p=0.041, p=0.016) respectively (Figure 2).
Figure 2: VO
2
responses during WM and NM Trials.
The Two-way repeated-measures ANOVA
showed that there was no significant interaction
between music and cycled distance [F(1,26) = 1.372,
p = 0.252, ηp
2
=0.05]. Subjects cycled the similar
distance during both experimental trials. Maximum
effort cycled distance in 20 to 40 minute values are
displayed in Figure 3.
Figure 3: Cycled distance during WM and NM Trials.
Similarly result was obtained in examining
interaction between music and RPE. The Two-way
repeated-measures ANOVA revealed no significant
interaction between music and RPE [F(1,26) =
20.406, p>0.05, ηp
2
=0.440]. Subjects of NM trials
perceived exercise to be harder as compared to the
perception of WM trials. However, the difference in
perceptions in the two trials was not statistically
significant (p<0.05). RPE values of 0 through 40
minutes are displayed in Figure 4.
Figure 4: RPE measures during WM and NM Trials.
4 DISCUSSIONS
The purpose of this study was to determine the effects
of music on endurance performance in physically
active individuals in hot condition (35°).
4.1 Effects of Music on Endurance
Performance
The Two-way repeated-measures ANOVA showed
there was no significant interaction between music
and cycled distance [F(1, 26) = 1.372, p=0.252,
ηp2=0.050]. Subjects cycled the similar distance
during both experimental trials.
Similar performance in the NM condition can be
explained by Lima-Silva et al. (2012) and Tenenbaum
et al. (2004). They reported that listening to music did
not delay fatigue on exercise performance. Similarly,
the result of this research is supported by Nakamura
et al., (2010) who found that total distance covered
during constant-load exercise performed at critical
power (207 ± 53 W) was not increased compared to
the control group, irrespective of listening to
preferred or non-preferred music. In contrast, there
was a study done by Atkinson et al. (2004), when
athletes listened to music, there was an improvement
in performance during a 10km cycling time trial
compared to no music.
According to Nakamura (2010), differences in the
findings may be due to the methodological issues
such as the differences in exercise protocols and other
aspects of age, music tempo, musical preference and
socio-cultural influences.
icSPORTS 2018 - 6th International Congress on Sport Sciences Research and Technology Support
94

4.2 Effects of Music on HR
The Two-way repeated-measures ANOVA (minutes
20 through 40) showed there is a significant
interaction between music and HR [F(1,26) = 76.698,
p=0.<0.001, ηp2=0.754] as NM condition displayed
an increase in HR values over time greater than WM
condition. HR responses were higher in NW trial as
compared to WM trial but statistically not significant
(p>0.05).
The result of this study differed from the findings
of Hagen et al. (2013). In conducting a 10-km cycle
time trial with music as ergogenic aids, Hagen et al.
found that HR were not significant different between
the music and no-music trials. The result of this study
was also in contrast to the study by Nethery (2002)
and Lopes-Silva et al. (2015) where no significant
difference in HR was found between the session with
music and without music.
Similarly Potteiger et al. (2000) reported during
20 min. of moderate intensity exercise the under
varied conditions of fast upbeat music, classical
music, self-selected music, and no music
that decrement in HR occurred in all conditions
except the NM condition.
The HR responses of WM condition were slightly
lower over time than NM trials but not significant.
This is a common notion that music serves as a
distraction from the exercise itself, and other
investigators have reported an increase in HR and
blood pressure due to stimulation of the sympathetic
nervous system when listening to music while
exercising (Birnbaum et al., 2009; Mitchell and
Wolffe, 1990; William and Michael, 1989;
Yamashita et al., 2006).
In supporting the findings of this study, Edworthy
and Waring (2006) and Thornby, Haas & Axen
(1995) revealed a significant increase in HR when
their subjects listened to fast music while exercising.
However, their studies used different exercise
protocols and different music selection processes,
which may account for the contradictory findings.
The discrepancy between our findings and previous
studies could be differences in exercise type (circuit
type resistance exercise versus treadmill or cycle),
duration, training status of the subjects, and the music
selection process (fast versus medium or low tempo).
4.3 Effects of Music on VO
2max
The Two-way repeated-measures ANOVA (minutes
20 through 40) showed there was a significant
interaction between trials and VO2 [F(1,26) =
104.836, p<0.001, ηp2=0.801] as NM trial displayed
greater VO2 values over time than WM condition.
VO2 in NM trial were significantly higher than WM
trial at 20 min and at 40 min (p=0.041, p=0.016,
respectively).
There was a 2.97% of decrement in VO
2max
mean
scores during WM Trial compared to the VO
2max
mean scores during NM Trial. The reduction of
VO
2max
is supported by Bacon, Myers &
Karageorghis (2012) who stated that VO
2max
was
lower in synchronous music compared to the slow
tempo asynchronous condition. According to Nomura
et al. (2006), a reduced of VO
2max
was because of the
cycling pedal revolution rate was synchronized with
music. Cycling pedal revolution rate synchronized
with music could enhanced coupling between the
regular muscular contractions of cycling and HR
which would improve the metabolic efficiency.
The HR response in WM trial (Figure 1) showed
the HR mean score was between 137-154 bpm after
20 minutes. This showed that music enhanced
coupling between the regular muscular contractions
of cycling and HR. Besides, Szabo, Small & Leigh
(2012) was also stated that there was an improvement
in metabolic efficiency when fast tempo music was
used during incremental exercise.
The increasing VO
2max
over time of 20 to 40
minutes
in
WM group of this study did not paralleled
the findings of Szmedra and Bacharach (1998).
Szmedra and Bacharach found VO
2max
lower in WM
trial because of a relaxing effect that music had on the
participants and it led to reducing muscle tension and
lessening the narrowing of blood vessels. This
condition had improved blood flow to the working
muscle and helped in cleaning up plasma lactate and
decreasing the production of plasma lactate which
may involve in muscle fatigue (Thomas et al., 2004).
4.4 Effects of Music on RPE
The Two-way repeated-measures ANOVA revealed
no significant interaction between music and RPE
[F(1,26) = 20.406, p>0.05, ηp
2
=0.440]. Subjects of
NM trials perceived exercise to be harder as
compared to the perception of WM trials.
The increase in RPE in WM condition of this
study is inconsistent with those of previous studies
that reported reduced RPE while listening to music.
Nethery et al. (1991), Potteiger et al. (2000), Nethery
(2002), Yamashita et al. (2006), and Dyer and
McKune (2013) reported a decrease in RPE when
listening to music while exercising. Similarly, many
other researchers (Birnbaum et al., 2009; Caria et al.,
2007, Schwartz et al., 1990) found that listening to
music had no affected any changes in RPE.
Ergogenic Effects of Pop Music on Endurance Performance in Hot Conditions among Physically Active Individuals
95

However, since this study involved WM subjects
cycling at 55% of VO
2max,
the increase in RPE in WM
condition seemed to be supported by Lopes-Silva et
al. (2014) that music could influence the RPE only at
low-to-moderate exercise intensity (<80% VO
2max
).
This was due to the fact that external stimuli such as
music would be able to compete against weaker
internal cues for attentional focus. Similarly, Bigliassi
et al. (2012) emphasised that low intensity exercise
would enhance the brain’s capability to shift its
attention from the exercise from load to external
stimuli, leading to a reduction in the rate of RPE. In
addition, in a study on the effects of known and
unknown exercise duration on RPE by Coquart et al.
(2008), it was reported that RPE was lower when the
total duration was unknown beforehand. The subjects
of WM in this study had knowledge of exercise
duration, thus external stimuli (music) could not help
subjects overcame attentional focus. This has helped
increase RPE in WM subjects. This increments in
RPE in this study is supported by Bwonley et al.,
(1995), that trained participants had higher post-
exhaustive RPE compared to untrained participants.
Pires et al. (2011) explained that the long exercise
duration (<80% VO
2max)
such as exercise duration in
this study, could affect the peripheral signals to
contribute substantially to generate RPE.
5 CONCLUSION
The results of this study revealed that pop music has
no effect on cycling performance in the heat among
physically active individuals. One possible reason
had to be the choice of music. Preferred music could
motivate and improve physical performance
(Karageorghis et al., 2011, Karageorghis et al., 2006),
influenced perceived exertion (Nakamura et al.,
2010). Thus it is suggested that more investigation on
the effects of type of music and music preference on
endurance performance in the hot conditions would
be investigated.
REFERENCES
ACSM (2014) ACSM’s Guidelines of Exercise testing and
Prescription. 9
th
ed. Philadelphia, PA, USA: Lippincott
Williams & Wilkins.
Arazi, H., Asadi, A. and Purabed, M. (2015) Physiological
and psychophysical response to listening to music
during warm-up and circuit-type resistance exercise in
strength trained men, Journal of Sports Medicine, pp.1-
6.
Atan, T. (2013) Effect of music on anaerobic exercise
performance, Biology of Sport, pp.30(1), 35-39.
Atkinson, G., Wilson, D., Eubank, M. (2004) Effects of
music on work-rate distribution during a cycling time
trial, Int J Sports Med, 25, pp.611–615.
Bacon, C.J., Myers, T.R. and Karageorghis, C.I. (2012)
Effect of music-movement synchrony on exercise
oxygen consumption, Journal of Sports Medicine and
Physical Fitness, 52(4), pp.359-365.
Bigliassi, M., Dantas, J.G., Smirmaul, B.P.C. and Altimari,
L.R. (2012) Influence of Music and Its Momnts of
Application on Performance and
Psychophysiologyogical Parameters during a 5km
Time Trial, Rev Andal Medicine Deporte, 5(3), pp.83-
90.
Beaumont, J., Deaton, M., Schowalter, M. and Van Dyk, V.
(2014) "The Effect of Music Tempo on Cycling
Performance in Female College Students". 13th Annual
Celebration of Undergraduate Research and Creative
Performance. Paper 116. Available at:
https://digitalcommons.hope.edu/curcp_13/116
[Accessed 10 Apr. 2018].
Birnbaum, L., Boone, T. and Huschle, B. (2009)
Cardiovascular responses to music tempo during
steady-state exercise. Journal of Exercise Physiology,
12(1), pp.50–57.
Brownley, K.A., McMurray, R.G. and Hackney, A.C.
(1995) Effects of music on physiological and affective
responses to graded treadmill exercise in trained and
untrained runners. International Journal of
Psychophysiology 19, pp.193-201.
Caria, M.A., Tangianu, F., Concu, A., Crisafulli, A. and
Mameli, O. (2007) Quantification of Spinning bike
performance during a standard 50-minute class,
Journal of Sports Sciences, 25(4), pp.421–429.
Coquart, J.B.J., Legrand, R., Robin, S., Duhamel, A.,
Matran, R. and Garcin, M. (2008) Influence of
successive bouts of fatiguing exercise on perceptual and
physiological markers during an incremental exercise
test. Psychophysiology, 46(1), pp.209-216.
Dyer, B. J. and McKune, A. J. (2013) Effects of music
tempo on performance, psychological, and
physiological variables during 20 km cycling in well-
trained cyclists, Perceptual and Motor Skills,
117, pp.484–497.
Edworthy, J. and Waring, H. (2006). The Effects of Music
Tempo and Loudness Level on Treadmill Exercise,
Ergonomics, 49(15), pp.1597–1610.
Elisa, A.G., Gennifer, A.F. and Jorge Alberto, A.C. (2017)
Exploring music intensity on heart rate, perceived
exertion and physical performance during sub-maximal
exercise, Revista Kronos, 16(2), pp.1-7.
Foster, C., Porcari, J.P. and Anders, M. (2010) Exploring
the effects of music on exercise intensity, ACE Certified
News, pp.1-3.
Hagen, J., Foster, C., Rodriguez-Marroyo, J., de Koning, J.
J., Mikat, R. P., Hendrix, C. R. and Porcari, J. P. (2013)
The Effect of Music on Time Trial Performance,
International Journal of Sports Physiology and
Performance, 8(1), pp.104-106.
icSPORTS 2018 - 6th International Congress on Sport Sciences Research and Technology Support
96

Karageorghis, C.I. and Priest, D.L. (2012) Music in the
exercise domain: a review and synthesis (Part I),
International Review of Sport and Exercise
Psychology, 5(1), pp.44-66.
Karageorghis, C.I., Jones, L., Priest, D.L., Akers, R.I.,
Clarke, A., Perry, J.M and Lim, H.B.T. (2011)
Revisiting the Relationship Between Exercise Heart
Rate and Music Tempo Preference, Research Quarterly
for Exercise & Sport, 82(2), pp.274-284.
Karageorghis, C.I., Priest, D.L., Williams, L.S., Hirani,
R.M., Lannon, K.M. and Bates, B.J. (2010) Ergogenic
and psychological effects of synchronous music during
circuit-type exercise, Psychology of Sport and
Exercise, 11, 551-559.
Karageorghis, C.I., Mouzourides, D., Priest, D.L., Sasso,
T., Morrish, D. and Walley, C. (2009). Psychophysical
and Ergogenic Effects of Synchronous Music during
Treadmill Walking, Journal of Sport & Exercise
Psychology, 31, pp.18-36.
Karageorghis, C. I., Jones, L. and Low, D. C. (2006)
Relationship Between Exercise Heart Rate and Music
Tempo Preference, Research Quarterly for Exercise
and Sport, 77 (2), pp.240-250.
Karageorghis, C.I., Terry, P.C. and Lane, A. M. (1999)
Development and validation of an instrument to assess
the motivational qualities of music in exercise and
sport: The Brunel Music Rating Inventory, Journal of
Sports Sciences, 17, 713-724.
Lima-Silva, A. E., Silva-Cavalcante, M. D., Pires, F. O.,
Bertuzzi, R., Oliveira, R.S. F. and Bishop, D. (2012)
Listening to Music in the First, but not the Last 1.5 km
of a 5-km Running Trial Alters Pacing Strategy and
Improves Performance, Int J Sports Med, 33(10),
pp.813-818.
Lopes-Silva, J.P., Lima-Silva, A.E., Bertuzzi, R. and Silva-
Cavalcante, M.D. (2015) Influence of Music on
Performance and Psychophysical Responses during
Moderate-Intensity Exercise Preceded by Fatigue,
Physiology & Behavior, pp.274-280.
Mitchell, J. H. and Wolffe, J. B. (1990) Neural control of
the circulation during exercise, Medicine & Science in
Sports & Exercise, 22, pp.141–154.
Nakamura, P.M., Pereira, G., Nakamura, F.Y. and Kokubun
E. (2010) Effects of Preferred and Non preferred Music
on Continuous Cycling Exercise Performance,
Perceptual and motor skills, 110, pp.257-264.
Nethery, V.M., Harmer, P.A. and Taaffe, D. R. (1991)
Sensory mediation of perveived exertion during
submaximal exercise. Journal of Human Movement
Studies, 20, pp.201–211.
Nethery, V.M. (2002) Competition between Internal and
External Sources of Information during Exercise:
Influence on RPE and the Impact of the xercise Load,
Journal Sports Medicine Phys Fitness, 42, pp.172-178.
Nikol, L., Kuan, G., Ong, M., Chang, Y-K and Terry, P.C.
(2018) The Heat Is on: Effects of Synchronous Music
on Psychophysiological Parameters and Running
Performance in Hot and Humid Conditions. Front,
Psychol (9), 1114.
Nomura, K., Takei, Y., Yoshida, M. and Yanagida, Y.
(2006) Phase – dependent chronotropic response of the
heart during running in humans, European Jrl. of
Applied Physiology, 97, pp.240-247.
Pires, F.O., Lima-Silva, A.E., Bertuzzi, R., Casarini, DH,
Kiss, M.A.P.D.M., Lambert, M.I. and Noakes, T.D.
(2011) The influence of peripheral afferent signals on
the rating of perceived exertion and time to exhaustion
during exercise at different intensities,
Psychophysiology, 48(9), pp.1284-1290.
Pollock, M.L., Foster, C., Knapp, D., Rod, J.L. and
Schmidt, D.H. (1987) Effect of age and training on
aerobic capacity and body composition of master
athletes, Journal of Applied Physiology, 62(2), pp. 725-
731.
Potteiger, J.A., Schroeder, J.M. and Goff, K.L. (2000)
Influence of Music on Ratings of Perceived Exertion
during 20 minutes of Moderate Intensity Exercise,
Perceptual and Motor Skills, 91, pp.848-854.
Schwartz, S. E., Fernhall, B. and Plowman, S. A. (1990)
Effects of music on exercise performance, Journal of
Cardiopulmonary Rehabilitation, 10(9), pp.312–316.
Szabo, A., Small, A. and Leigh, M. (1999) The effects of
slow-and fast – rhythm classical music on progressive
cycling to voluntary physical exhaustion, J Sports Med
Phys Fitness, 39, pp.220-225.
Szmedra, L. and Bacharach, D.W. (1998) Effect of music
on perceived exertion, plasma lactate, norepinephrine
and cardiovascular hemodynamics during treadmill
running, Int J Sports Med 19(1), pp.32-37.
Tatterson, A.J., Hahn, A.G., Martin, D.T. and Febbraio,
M.A. (2000) Effects of heat stress on physiological
responses and exercise performance in elite cyclists, J
Sci Med Sport. 3(2), 186-93.
Tenenbaum, G., Lidor, R., Lavyan, N., Morrow, K.,
Tonnel, S., Gershgoren A, Meis, J. and Johnson, M.
(2004) The effect of music type on running
perseverance and coping with effort sensations,
Psychology of Sport & Exercise, 5(2), pp.89–109.
Thomas, C., Sirvent, P., Perrey, S., Raynaud, E. and
Mercier, J. (2004) Relationships between maximal
muscle oxidative capacity and blood lactate removal
after supramaximal exercise and fatigue indexes in
humans, J Appl Physiol, 97(6), pp.2132-2138.
Thornby, M. A., Haas, F. and Axen, K. (1995) Effect of
distractive auditory stimuli on exercise tolerance in
patients with COPD, Chest, 107(5), pp.1213–1217.
Yamashita, S., Iwai, K., Akimoto, T., Sugawara, J. and
Kono, I. (2006) Effects of music during exercise on
RPE, heart rate and the autonomic nervous system,
Journal of Sports Medicine and Physical Fitness, 46(3),
pp.425-430.
Waterhouse, J. and Edwards, B.J. (2009) Effects of Music
Tempo upon Submaximal Cycling Performance,
Scandinavian Journal Medicine & Science in Sports,
20, pp.662-669.
William, B. D. and Michael, H. T. (1989) The influence of
preferred relaxing music on measures of state anxiety,
relaxation and physiological responses, Journal of
Music Therapy, 26, pp.168–187.
Ergogenic Effects of Pop Music on Endurance Performance in Hot Conditions among Physically Active Individuals
97
