
A Preliminary System for the Automatic Detection of Emotions based on
the Autonomic Nervous System Response
Asier Salazar-Ramirez
1
, Raquel Martinez
1
, Andoni Arruti
1
, Eloy Irigoyen
2
, J. Ignacio Martin
1
and Javier Muguerza
1
1
Dept. of Computer Architecture and Technology, University of the Basque Country (UPV/EHU),
Donostia-San Sebasti
´
an, Spain
2
Dept. of Automatic Control and Systems Engineering, University of the Basque Country (UPV/EHU), Bilbao, Spain
Keywords:
Emotion, Film Clip, ECG, GSR, Finite State Machine.
Abstract:
People’s life quality is being improved thanks to the advances in medicine and to the promotion of health.
One of the pillars for having a healthy life is to know and to take care of the emotions of oneself. Due to
the close relationship between the emotions and the responses of the autonomic nervous system, the aim of
this work is to study and detect the physiological patterns produced by two of the basic human emotions:
surprise and contentment. The work presents a preliminary system that processes and analyzes two non-
invasive physiological signals (the galvanic skin response and the heart rate variability) and that uses a finite
state machine for the detection of the activation of the sympathetic nervous system. The work also presents
the experimental procedure that was designed in order to elicit different emotions in laboratory conditions.
The F-score results obtained for the correlation of the analyzed emotions and the physiological patterns were
F
1
=1.00 and for surprise and F
1
=0.94 for contentment.
1 INTRODUCTION
Nowadays, there is an increasing concern among in-
formatics engineering research groups about applying
technical knowledge to systems that allow the im-
provement of people’s life quality. Besides, there
are medical groups that look for technological solu-
tions in order to improve the diagnostical processes
through the automatic detection of certain patholo-
gies that currently are only detected empirically. In
addition, entities from the social spheres request the
development of tools that help people with autonomy
problems recover their independence, as due to any
kind of disability they might be in danger of social
exclusion. Therefore, the ensemble of these three dis-
ciplines converges in a common objective that is to
help people that suffer from any kind of disease or
disability.
Being able to detect automatically certain psycho-
physiological patterns permits to improve human-
computer interaction (Soegaard and Dam, 2013). Mo-
reover, detecting these patterns can also be useful for
helping understand how people suffering from au-
tism or brain paralysis feel, if something pleases them
or if they are suffering any kind of pain, among ot-
her things ((Rice et al., 2015),(Johnson and Picard,
2017),(Giusiano et al., 1995),(Carcreff et al., 2018)).
The affective computing is the discipline that stu-
dies and develops systems and devices in order to re-
cognize, interpret, process and stimulate human emo-
tions (Picard, 2010). Within its fields of study, a re-
levant subject consists on identifying how people re-
act emotionally when facing certain specific events.
The intention of identifying these reactions is to help
the previously mentioned collectives to improve their
communication with the environment, their perso-
nal autonomy and their life quality. When an in-
dividual lives any positive or negative situation his
organism produces a psycho-physiological response
that produces subsequently an emotion ((Cannon,
1935),(Schachter and Singer, 1962),(Kreibig, 2010)).
Due to this reaction, monitoring the physiological va-
riables of the body is one of the methods that enable
the detection of these emotional changes.
When facing any stimuli, the physiological re-
sponse of the body is controlled by the Central
Nervous System and the coordination that this sy-
stem applies between the Autonomic Nervous Sy-
stem (ANS), the Endocrine System, the Immunolo-
gic System. . . The ANS, through its two components,
46
Salazar-Ramirez, A., Martinez, R., Arruti, A., Irigoyen, E., Martin, J. and Muguerza, J.
A Preliminary System for the Automatic Detection of Emotions based on the Autonomic Nervous System Response.
DOI: 10.5220/0006900600460052
In Proceedings of the 6th International Congress on Neurotechnology, Electronics and Informatics (NEUROTECHNIX 2018), pages 46-52
ISBN: 978-989-758-326-1
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

which are the Sympathetic Nervous System (SNS)
and the Parasympathetic Nervous System (PNS), is
the system responsible of balancing the organism.
The “fight or flight” theory ((Cannon, 1935), (Porges,
2001)) poses that the peripheral physiological signals
that are regulated by the SNS are the ones that pro-
vide information on the arousal or activation of the
brain. On the other hand, the PNS is related to the
relaxation of the body as mention (Cacioppo et al.,
2007), (P
´
erez-Lloret et al., 2014) and (Benedek and
Kaernbach, 2010). The peripheral physiological sig-
nals that are regulated by the ANS are various: the
cardiac rhythm, the respiration, the sweating, the cor-
poral temperature, the diameter of the eye pupils, the
brain activation, etc.
In order to further study the relationship between
emotions and the physiological signals, the research
team designed an experiment where, in laboratory
conditions, seven of the basic emotions were indu-
ced in the participants while their physiological sig-
nals were being collected. The chosen eliciting sti-
mulus was the visualization of video clips. The phy-
siological signals that were acquired were the cardiac
activity and the sweating as they can be registered
by non-invasive means. Nevertheless, despite seven
emotions were induced during the experiment, only
two of them were taken to the study presented in this
article as they are the ones that have the clearest rela-
tionship with the SNS: surprise and contentment.
Finally, after the experimental part was finished
and the physiological signal database had been regis-
tered, the research group used the finite state machine
(FSM) developed in (Martinez et al., 2017) to detect,
classify and rate the activation of the SNS.
This work presents the study of the physiological
patterns of the SNS that are related to the emotions
of surprise and contentment. In order to do so, an
experiment was done where some of the biosignals of
the participants were collected while emotions were
being induced on them by means of projecting video
clips. Later, those biosignals would be analyzed by
the FSM in order to detect the reactions on the SNS
of the two mentioned emotions.
2 MATERIALS AND METHOD
In order to study the relationship between emotions
and the physiological changes, the research team de-
signed an experiment for inducing certain emotional
states in the participants sitting it. During the expe-
riment the electrocardiogram (ECG) and the swea-
ting of the participants, also called galvanic skin re-
sponse (GSR), were collected. The stimulus chosen
to elicit those emotions was the visualization of video
clips, which is a method validated in several research
works ((Gross and Levenson, 1995),(Martinez et al.,
2009),(Gilman et al., 2017)).
2.1 Participants
A total of 32 subjects, aged between 21 and 35
(mean=26 y SD =3.1), participated voluntarily in the
experiment (7 male and 25 female). All the partici-
pants were students or workers of the university.
2.2 Materials
The set of video clips that were used to elicit the emo-
tions in the laboratory was an adaptation to the Spa-
nish population (Martinez et al., 2009) of the audi-
ovisual database published by (Gross and Levenson,
1995). The adaptation consists on using the database
of (Gross and Levenson, 1995) updating it with more
recent video clips and adding clips showing real life
stories and situations, being all of them adapted to the
Spanish culture. The new audiovisual database, va-
lidated in different Spanish cities, proposes the use
of 20 films that can be used to induce the following
seven basic emotions: contentment, amusement, dis-
gust, fear, surprise, sadness and anger.
Specifically, the database contained three clips for
each emotion but for contentment, that had only two:
for amusement, “When Sally met Harry”, “Bote” and
“Concejal”; for anger, “Cry Freedom”, “El bola” and
“Te doy mis ojos”; for fear, “Shining”, “The Ring”
and “The Ring 2”; for sadness, “Champ”, “Omayra”
and “Nasija”; for surprise, “Capricorn one”, “La
monja” and “El orfanato”; for disgust, “Autopsy”,
“Pink Flamingos”, “Hostel”; and finally, for content-
ment, “Dolphin”, and “BBC”. The films have last be-
tween 32 and 214 seconds (M=256, SD=71).
2.3 Assessment Instruments
The assessment of the emotional responses of the
participants was done by collecting their impressions
through two questionnaires already validated by the
psychological community in the existing literature.
The first questionnaire, designed by (Gross and Le-
venson, 1995), is the Post film Questionnaire (PFQ).
This survey is used to assess the capacity of each clip
for eliciting each of the emotions. In addition, the
PFQ also collects information on whether the subjects
had previously seen the clip or not. The second que-
stionnaire is the Self-Assessment Manikin and it is
used to assess the emotions from a dimensional point
of view or paradigm (Lang, 1980).
A Preliminary System for the Automatic Detection of Emotions based on the Autonomic Nervous System Response
47
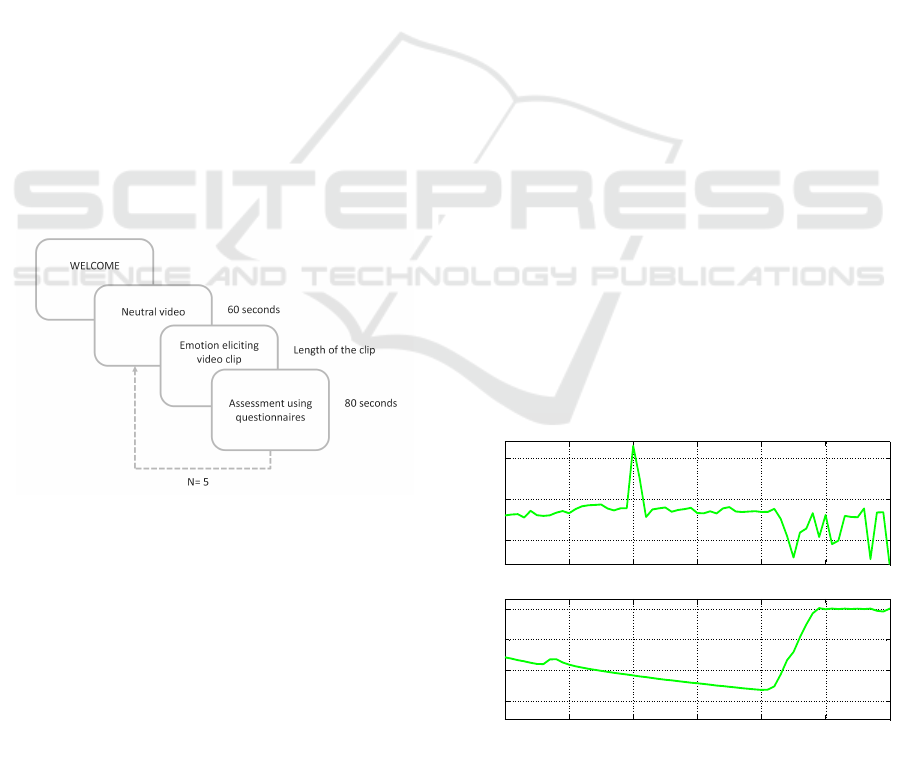
2.4 Procedure
All the sessions of the experiment took place in the
audiovisual projection room of the university, asses-
sing the emotional responses and collecting the phy-
siological signals to be studied from two participants
per sessions. Prior to starting the test the participants
received an explanation on the objective and the pro-
cedure of the experiment, the documentation they had
to fulfill, the questionnaires and the physiological sig-
nals that were going to be collected. In addition, the
participants were explained that the experiment had
passed all the requirements of the ethical committee
of the university and that all their privacy rights were
preserved and that all the laws related to these experi-
mental procedures were being respected.
Despite being 20 clips, not all of them were used
in every experiment; the clips were divided in 6 diffe-
rent projection sets, using 5 of clips in each of those
sets. At the beginning of all the projections a wel-
come message was displayed on the screen (15 se-
conds). After the welcome video the same sequence
was repeated five times, being this sequence compo-
sed of a neutral video (60 seconds), the emotion elici-
ting clip and a message asking the participants to ful-
fill the corresponding questionnaires in paper format
(80 seconds). The sequence followed in the experi-
ment is shown graphically in Figure 1.
Figure 1: Temporal sequence of the projections of the clips
during the experiment.
The data acquisition system used to collect the
physiological signal was the BIOPAC MP150. The
sweating was measured through the galvanic skin re-
sponse (GSR) and SS3LA gel electrodes were used
on the participants non-dominant hand to collect the
signal. In addition, the cardiac activity was studied by
analyzing the electrocardiogram (ECG) and to collect
it the three terminals of the SS2LB electrodes were
placed on the chest of the participants.
2.5 Psycho-physiological Analysis
The design of the experiment was to aiming to eli-
cit anger, sadness, contentment, fear, surprise, amu-
sement and disgust. Due to the complexity of identi-
fying certain emotions from the physiological signals,
this work has only studied those emotions that present
a clear and specific physiological pattern, which are:
contentment, related to the sympathetic inhibition sta-
tes, and surprise, related to activation states.
The physiological patterns associated to the acti-
vation of the SNS correspond to the acceleration of
the cardiac rhythm and to an increase of the sweating.
On the other hand, those changes related to its inhibi-
tion are the relaxation of the cardiac rhythm and the
decrease if the sweating.
As previously mentioned, the signals collected du-
ring the experimentation were the ECG and GSR.
Anyway, as the only indicator of heart activity to be
used was the cardiac rhythm, during the phase of ana-
lysis the researchers decided to use the Heart Rate
Variability (HRV) instead of using the ECG itself.
The HRV is the signal that provides information of
the time changes between each heartbeat of the ECG
(Thayer et al., 2010). Thus, when the cardiac activity
accelerates the time between heartbeats decreases and
so does the HRV. On the contrary, if the heart beats
relaxed then the time intervals between heartbeats get
greater and it produces bigger HRV values.
On the one hand, Figure 2 depicts the evolution
of the physiological variables when, during the pro-
jection of one of the clips, a participant in the experi-
ment gets eventually shocked (marked with SS). On
the other hand, Figure 3 shows how the physiological
variables tend to relax during the projection of a clip
corresponding to contentment.
780 790 800 810 820 830 840
0.5
1
1.5
SS
HRV
SURPRISE
780 790 800 810 820 830 840
7
8
9
10
Time (s)
GSR
SS
Figure 2: Physiological signals for surprise.
NEUROTECHNIX 2018 - 6th International Congress on Neurotechnology, Electronics and Informatics
48
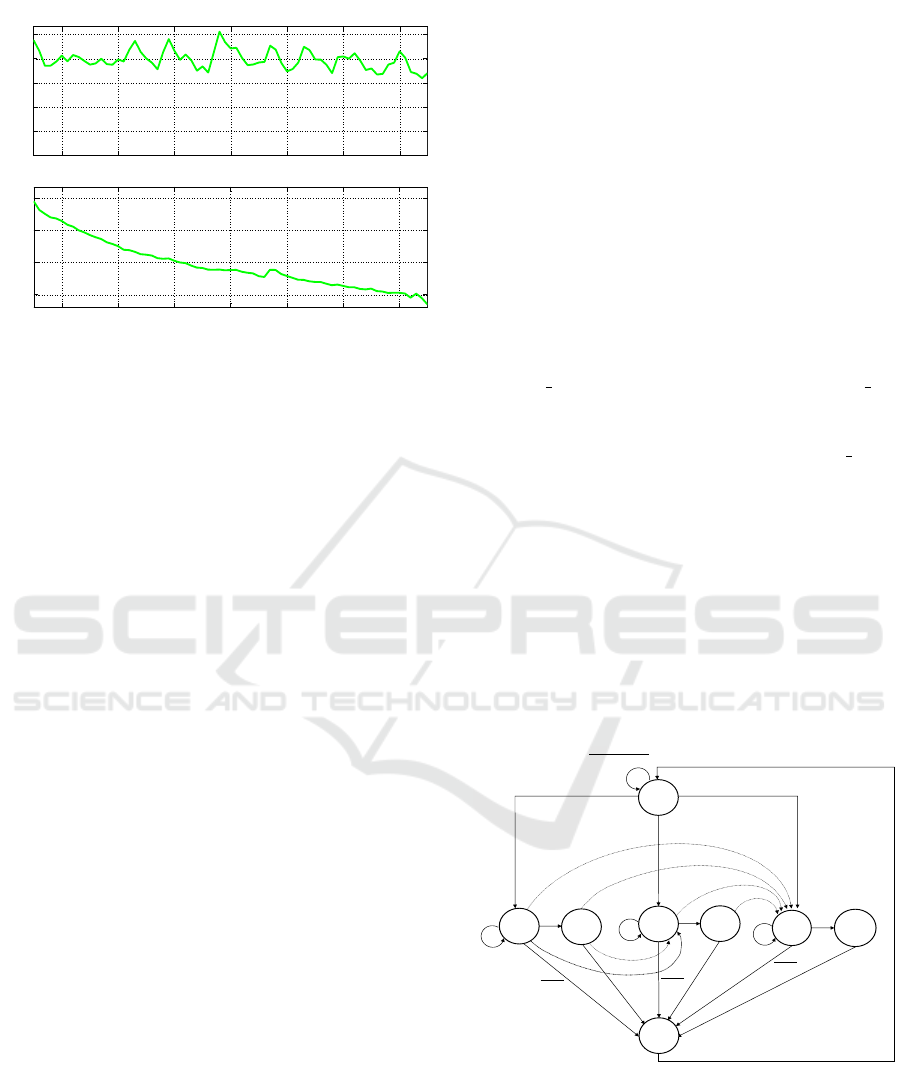
290 300 310 320 330 340 350
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
1.2
HRV
CONTENTMENT
290 300 310 320 330 340 350
3.4
3.6
3.8
4
Time (s)
GSR
Figure 3: Physiological signals for contentment.
Analyzing Figure 2 it can be seen that there is an
increase in the GSR and a big decrease in HRV in
the moment of the shock happens. Looking at Figure
3 it can be seen that the reaction to the contentment
clips is opposite to what happened in Figure 2, there
is a clear decrease of the GSR and the cardiac rhythm
remains stable.
2.6 Automatic Detection of the
Emotional States
The identification of emotions by the automatic de-
tection of physiological change patterns was done
using the system designed by (Martinez et al., 2017).
The detection system is a finite state machine (FSM)
that detects, rates and classifies the arousal of the
SNS. When the FSM detects a SNS arousal it rates it
depending on its intensity: Low Alert, Medium Alert,
High Alert. In addition, if the activation lasts for lon-
ger than 3 iterations, then the system changes its clas-
sification from alert to stress: Low Stress, Medium
Stress or High Stress. Therefore, the output of the
FSM can vary within seven states, one for the absence
of arousal and six for activation states. The numerical
outputs of the FSM for the classified states labels are
the following: 0= No Arousal, 1=Low Alert, 2=Low
Stress, 3=Medium Alert, 4=Medium Stress, 5=High
Alert and 6=High Stress.
In order to analyze the signal throughout the
whole experiment the researchers chose a sliding win-
dow approach where the window had a width of 20
seconds and slided using 5 second steps. The charac-
teristics of the physiological signals that were used as
inputs for the FSM were the slopes of both GSR and
HRV signals, the multiplication of the two slopes be-
tween them and the amount of consecutive windows
computed by the machine for the detected state.
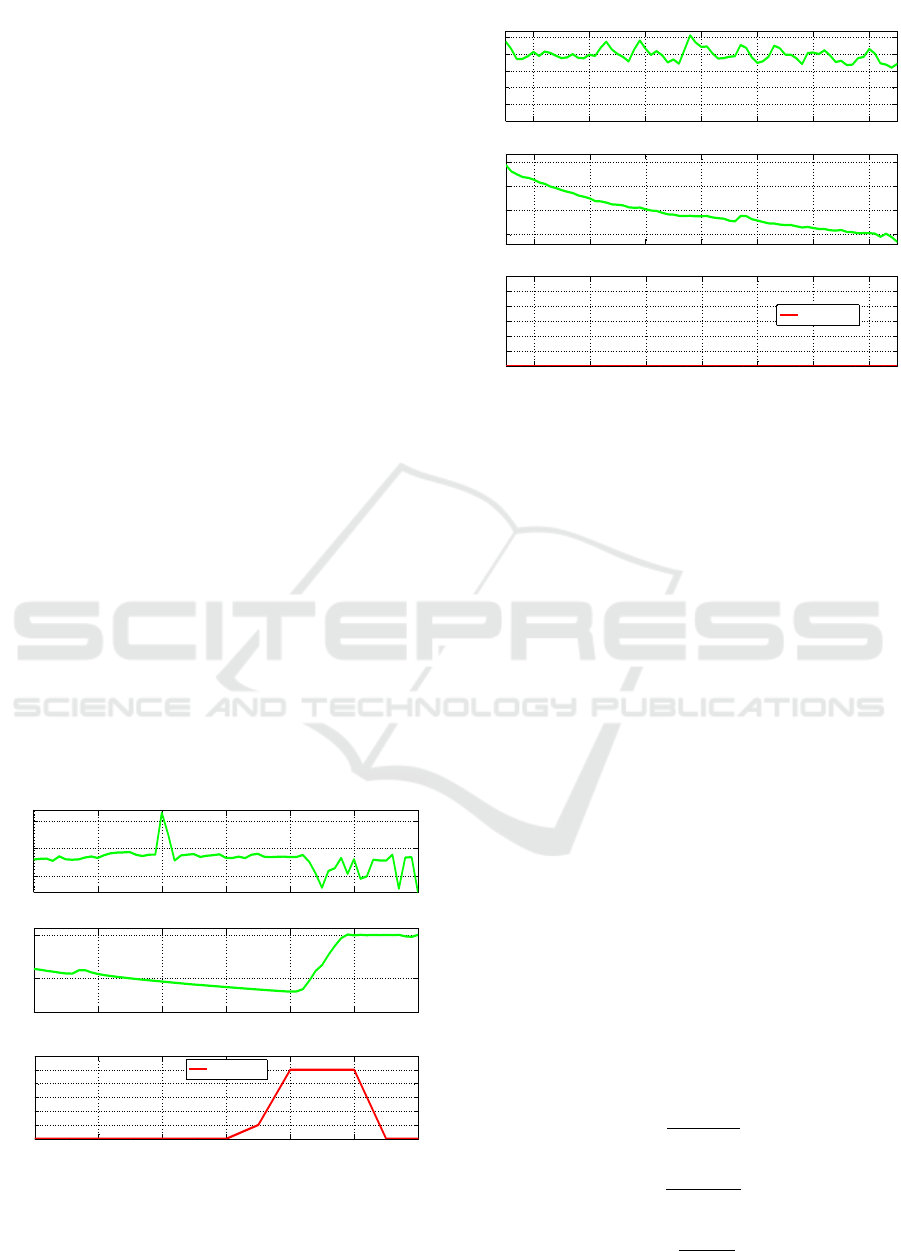
Despite the FSM is further explained by (Martinez
et al., 2017), Figure 4 provides a graphic explanation
on how it works. Each of the circles of Figure 4 stand
for one of the seven classified levels of stress, being
0 the default state. If the subject eventually suffers a
SNS arousal, then a transition condition is triggered
and it makes the FSM change its state. For instance,
if the activation was not very intense, Activation Re-
sponse 1 (AR1) would trigger taking the FSM from
state 0 to state 1 (Low Alert). In the same way, if the
activations were medium or high then AR2 and AR3
would trigger and the states would change to state 3
and 5 respectively.
Once one of the alarm states has been reached, the
FSM starts checking whether the values of physiolo-
gical signals are maintained for the following itera-
tions: (S AR condition). On the one hand, if S AR
is not fulfilled then the machine goes back to its de-
fault 0 state. On the other hand, if after three win-
dow sliding iterations (n=3, i.e., 15 seconds) S AR is
still true, then n=3 condition is triggered and the FSM
changes its output from alarm state 1, 3 or 5 to the
corresponding stress state 2, 4 or 6 respectively. Af-
ter that happened, in the next iteration the machine
would go back to the default 0 state and would wait
there until a new activation happened. Anyway, if the
machine was in an alarm or stress state and an acti-
vation of greater intensity took place, then the ma-
chine would move from the current state to a higher
intensity alarm state. For example, if the current state
was 1 or 2 and AR2 happened, then the FSM would
change to state 3.
4
6
5
0
1
2
0
3
(AR1,AR2,AR3)
AR1
AR2
AR3
AR3
AR3
AR3
AR3
S_AR
n=3
n=3
n=3
AR2
AR2
S_AR
S_AR
S_AR
S_AR
S_AR
Next
Next
Next
Figure 4: State transition diagram of the FSM.
A Preliminary System for the Automatic Detection of Emotions based on the Autonomic Nervous System Response
49
3 RESULTS
This section presents the results obtained from the use
of the FSM on the physiological signals collected in
the experiments as inputs. As previously mentioned,
the emotions that were studied were surprise and con-
tentment. For the clips targeting surprise, in the in-
stant of the shock, the physiological signals should
experiment an increase of the sweating and a decrease
of the HRV, being them correlated to a medium-high
level of arousal. The adaptive function of the surprise
is to warn the body that something not expected is ta-
king place. Because of that, it is the shortest of all the
emotions and it is immediately followed by the emo-
tion produced after the assimilation of what is happe-
ning in the new event (Verduyn and Lavrijsen, 2015)
. As it is a short emotion that does not necessarily re-
main during the time, the output of the FSM for this
emotion can be either alert or stress depending on its
duration. On the other hand, when the subject visuali-
zes the clip for contentment tends to relax and there is
no SNS activation. Thus, looking to the physiological
signals, the GSR decreases and the HRV remains at
the same values or increases. This reaction gives evi-
dence that there is no sympathetic activation, hence
the output of the FSM is equal 0.
Figure 5 and Figure 6 illustrate both the physio-
logical signals of a participant of the experiment and
the output of the FSM for the signals collected in the
projections. In the case of Figure 5 the signals de-
picted correspond to surprise. On the other hand, Fi-
gure 6 depicts those signals collected during the clip
for contentment.
780 790 800 810 820 830 840
0.5
1
1.5
SS
HRV
SURPRISE
780 790 800 810 820 830 840
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
Time (s)
FSM
AROUSAL
780 790 800 810 820 830 840
8
10
GSR
SS
SS
Figure 5: The physiological signals and the output of the
FSM during the clip of surprise.
In order to determine the degree of success of the
290 300 310 320 330 340 350
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
1.2
HRV
CONTENTMENT
290 300 310 320 330 340 350
3.4
3.6
3.8
4
GSR
290 300 310 320 330 340 350
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
Time (s)
FSM
AROUSAL
Figure 6: The physiological signals and the output of the
FSM during the clip of contentment.
detection system, the researchers have analyzed the
outputs of the detection system during the projections
of the clips targeting surprise and contentment. For
surprise, it is considered as a positive result if in the
moment of the shocking images the system’s output
was 3, 4, 5 or 6 corresponding to Medium Alert, Me-
dium Stress, High Alert or High Stress respectively.
Consequently, a positive result for contentment would
be when the system gives an output of no activation,
i.e., the output equals 0.
Table 1 shows the results that have been obtai-
ned in the research. The columns reflect the results
obtained in the following way: Manual Label stands
for the amount of clips labeled by the researchers for
each emotion; True Positive (TP) stands for the states
correctly detected by the FSM; False Negative (FN)
stands for the cases in which the algorithm should
have detected a state but did not do it; False Posi-
tive (FP) represents the cases where the algorithm has
detected certain states without them being previously
labeled for that state. The performance of the system
has been estimated using Precision (P), Recall (R) and
the F-Score (F
1
), whose calculation formulas are pre-
sented in equations (1), (2) and (3) respectively. The
best possible score for these indicators is 1 and the
worst is 0.
P =
T P
T P + FP
(1)
R =
T P
T P + FN
(2)
F
1
=
2 · P · R
P + R
(3)
NEUROTECHNIX 2018 - 6th International Congress on Neurotechnology, Electronics and Informatics
50

Table 1: Statistical results of the automatic detection.
Emotion
Manual
Label
FSM
TP FN FP Precision Recall F
1
Contentment 19 17 2 0 1.00 0.89 0.94
Surprise 9 9 0 0 1.00 1.00 1.00
As shown in Table 1, the results for surprise achie-
ved a Precision of 1.00, a Recall of 1.00 and a F
1
score
of 1.00. For contentment the results obtained were
1.00 for Precision, 0.89 for the Recall value and 0.94
for the F
1
. Therefore, considering the performance
rates obtained by the algorithm, it can be said that the
combination of the chosen signal characteristics and
the FSM results in a valid system for detecting the
emotional states of surprise and contentment.
Anyway, it is not a trivial issue to recognize and
to classify an specific emotion. Due to this reason
several authors prefer to classify grouped by clus-
ters. For example, (Canento et al., 2011) achieved
80%, 70% and 70% success rates using the leave one
out cross validation methodology with a k-NN clas-
sifier in order to distinguish between positive and ne-
gative, positive and neutral and neutral and negative
emotions respectively. Other authors prefer to clas-
sify emotions in a dimensional manner paying at-
tention to valence and arousal. This is the case of
(Kim and Andr, 2008) who presented a novel scheme
of emotion specific multilevel dichotomous classifi-
cation that achieved success rates of 95% and 70%
for subject-dependent and subject-independent emo-
tion classification respectively. Finally, (Soleymani
et al., 2015) presented an specific emotion classifica-
tion distinguishing between fear, sadness, frustration,
happiness, please and satisfaction. The classification
was done using an artificial neural network and due to
the complexity of the classification the network achie-
ved an accuracy of 55.8%.
Thus, it seems clear that the success rates decre-
ase quickly as the classification gets more emotion-
specific. The FSM presented in this work has only
been used to classify between two specific emotions
and so, despite it has been proved to be effective for
this certain problem, it would be recommendable to
expand the study to other emotions and see how it per-
forms as the classification gets more complex.
4 CONCLUSIONS
The aim of this work was to study the response of the
SNS during the elicitation of emotions through the
interpretation of physiological signals. Specifically,
two of the seven basic emotions have been taken to
analysis, surprise and contentment for being directly
related to ANS activation and inhibition respectively.
The research team developed an experiment to induce
the studied emotions in laboratory conditions while,
at the same time, the sweating and the cardiac activity
of the subjects was collected. The stimulus chosen
to elicit the emotions was the visualization of audio-
visual clips. The chosen clips elicited both content-
ment and surprise to the participants. Anyway, the
clips only elicited surprise as long as the subjects had
not previously seen the clip, as pointed by (Martinez
et al., 2009).
The physiological signals collected during the ex-
periment were used as inputs of an algorithm that
detects and classifies the activation of the SNS. The
signals confirmed that the SNS got active when the
participants were surprised by the clip and as a con-
sequence the output of the FSM gave values of me-
dium or high alert or stress. When the subjects felt
that the abnormal or hazardous sensation was over the
activation of the SNS stopped, giving confirmation to
what posed by (Schachter and Singer, 1962) . On the
contrary, during the visualization of the clips of con-
tentment the physiological signals responded accor-
ding to the pattern of inhibition of the ANS (Cacioppo
et al., 2007) and, because of it, the output of the FSM
was 0 which corresponds to the ANS not being active.
The results obtained from the performance analy-
sis (F-score) of the FSM were F
1
=1.00 and F
1
=0.94
for surprise and contentment respectively, and so the
algorithm gets validated as a useful tool for the study
of the activation of the SNS.
As a future approach the researchers propose the
study of other emotions in order to see their relations-
hip with the ANS. To do so, it would be necessary
to expand the amount of used physiological signals,
including to the study signals as the respiration, the
photoplethysmography or the encephalography.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was partially supported by the Depart-
ment of Education, Universities and Research of the
Basque Government under Grant IT980-16 and by
the Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness of
A Preliminary System for the Automatic Detection of Emotions based on the Autonomic Nervous System Response
51

the Spanish Government and the European Regio-
nal Development fund- ERFD (PhysComp project,
TIN2017-85409-P).
REFERENCES
Benedek, M. and Kaernbach, C. (2010). Decomposition of
skin conductance data by means of nonnegative de-
convolution. Psychophysiology, 47(4):647–658.
Cacioppo, J. T., Tassinary, L. G., and Berntson, G. (2007).
Handbook of psychophysiology. Cambridge: Cam-
bridge University Press.
Canento, F., Fred, A., Silva, H., Gamboa, H., and Loureno,
A. (2011). Multimodal biosignal sensor data handling
for emotion recognition. In Sensors, pages 647–6507.
IEEE.
Cannon, W. (1935). Stresses and strains of homeosta-
sis. The American Journal of the Medical Sciences,
189(1):13–14.
Carcreff, L., Gerber, C. N., Paraschiv-Ionescu, A., Cou-
lon, G. D., Newman, C., Armand, S., and Aminian,
K. (2018). What is the best configuration of wearable
sensors to measure spatiotemporal gait parameters in
children with cerebral palsy? Sensors, 18(2):394.
Gilman, T. L., Shaheen, R., Nylocks, K. M., Chapman, J.,
Flynn, J. J., and Coifman, K. G. (2017). A film set for
the elicitation of emotion in research: A comprehen-
sive catalog derived from four decades of investiga-
tion. Behavior research methods, 49(6):2061–2082.
Giusiano, N., Jimeno, M. T., Collignon, P., and Chau, Y.
(1995). Utilization of a neural network in the elabo-
ration of an evaluation scale for pain in cerebral palsy.
Methods of Information in Medicine, 34(5):498–502.
Gross, J. and Levenson, R. (1995). Emotion elicitation
using films. Cognition & emotion, 9(1), 9(1):87–108.
Johnson, K. T. and Picard, R. W. (2017). Spring: Customi-
zable, motivation-driven technology for children with
autism or neurodevelopmental differences. In Procee-
dings of Interaction Design and Children (IDC’17).
ACM.
Kim, L. and Andr, E. (2008). Emotion recognition based
on physiological changes in music listening. IEEE
Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intel-
ligence, 30(12):2067 – 2083.
Kreibig, S. D. (2010). Autonomic nervous system acti-
vity in emotion: a review. Biological Psychology,
84(3):394–421.
Martinez, R., Irigoyen, E., Arruti, A., Martin, J. I., and Mu-
guerza, J. (2017). A real-time stress classification sy-
stem based on arousal analysis of the nervous system
by an f-state machine. Computer methods and pro-
grams in biomedicine, 148:81–90.
Martinez, R., Irigoyen, E., Lopez de Ipi
˜
na, K., Asla, N., and
Garay, N. (2009). Dise
˜
no de un gestor de emociones
para la mejora de un tutor inteligente dirigido a la in-
tegraci
´
on de personas con discapacidad intelectual. In
Congreso Internacional de Inteligencia Emocional.
P
´
erez-Lloret, S., Diez, J., Dom
´
e, M. N., Delvenne, A. A.,
Braidot, N., Cardinali, D. P., and Vigo, D. E.
(2014). Effects of different “relaxing” music styles
on the autonomic nervous system. Noise and Health,
16(72):279–284.
Picard, R. W. (2010). Affective computing: from laughter
to ieee. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing,
1(1):11–17.
Porges, S. W. (2001). The polyvagal theory: phylogenetic
substrates of a social nervous system. International
Journal of Psychophysiology, 42(2):123–146.
Rice, L. M., Wall, C. A., Fogel, A., and Shic, F. (2015).
Computer-assisted face processing instruction impro-
ves emotion recognition, mentalizing, and social skills
in students with asd. Journal of Autism and Develop-
mental Disorders, 45(7):2176–2186.
Schachter, S. and Singer, J. E. (1962). Cognitive, social, and
physiological determinants of emotional state. Psy-
chological review, 69(5):379–399.
Soegaard, M. and Dam, R. F. (2013). The encyclopedia
of human-computer interaction. Interaction Design
Foundation.
Soleymani, M., Pantic, M., and Pun, T. (2015). Multimodal
emotion recognition in response to videos. In Interna-
tional Conference on Affective Computing and Intelli-
gent Interaction (ACII), pages 491–497. IEEE.
Thayer, J. F., Yamamoto, S. S., and Brosschot, J. F. (2010).
The relationship of autonomic imbalance, heart rate
variability and cardiovascular disease risk factors. In-
ternational Journal of Cardiology, 141(2):122–131.
Verduyn, P. and Lavrijsen, S. (2015). Which emotions last
longest and why: The role of event importance and
rumination. Motivation and Emotion, 39(1):119–127.
NEUROTECHNIX 2018 - 6th International Congress on Neurotechnology, Electronics and Informatics
52
