
Using Flexible Time Scale to Explore the Validity of Agent-based
Models of Ecosystem Dynamics: Application to Simulation of a Wild
Rodent Population in a Changing Agricultural Landscape
Jean Le Fur
1
and Moussa Sall
2
1
Institut de Recherche pour le Développement (IRD), Centre de Biologie pour la Gestion des Populations (CBGP),
Campus Baillarguet, CS 30016, F-34988 Montferrier-sur-Lez, France
2
Dépt. Informatique, Univ.G.Berger/Saint-Louis Sénégal and lab. IRD-BIOPASS, Campus Bel-Air, Dakar, Senegal
Keywords: Agent-based Model, Time Scale, Rodent, Discrete Time Simulation, Sensitivity Analysis.
Abstract: Identifying parameters value is a major issue in model engineering. In discrete time agent-based models,
time step is an important one as it determines the frequency at which agents realize their activity step. This
parameter is commonly defined as a fixed constant during the model design stage. In particular cases, this
may lead to biases as it may be sometimes difficult to determine if agents efficiently realize their activity
step once each 1, 2 seconds, hour or the like. A simulation model of a rodent population has been used to
study the effect of using a flexible time scale on its outcomes. Three types of processes have been
considered as time dependent in the model, environment sensing, movement and life cycle (maturity,
gestation…). A time step sensitivity analysis constitutes the principal result of this study. For the widest
range of time step values, model’s behaviour is unrealistic and bound to algorithms artefacts. A very small
range of time steps leads to simulation of a perennial rodents’ population. Biases bound to variable time step
implementation are discussed. Using flexible time scale approach proved efficient to get insight into the
model’s behaviour and fruitful clues to assess agents’ processes frequency in the actual ecosystem.
1 INTRODUCTION
Agent-based models are recognized as powerful
approaches to formalize ecological processes (White,
2016; Fu and Hao, 2018). This formalism is wide-
spread in social systems modelling (Squazzoni, 2010),
whether animal or specifically human systems, as it
can make emerge organization patterns out of agents’
interaction (Whitley, 2016). As for other models, one
important focus must be put in agent-based models on
calibration of parameters used to describe the
simulated populations (Stanilov, 2011). Indeed,
following Watts (2016), an agent-based model whose
parameters are not conveniently fitted may be useless,
even with a good representation of its agents’ logic.
Several directions are proposed in the literature
to simulate agent-based models with a particular
distinction between discrete time and discrete events
simulation (Buss et al., 2010). Among these
alternatives, discrete time simulations are widely
used (Railsback et al., 2017) as they constitute a
practical and easier to implement approach (Floudas
et al., 2004) to formalize concrete systems, be them
natural (Singh et al, 2018), social (Sauser et al.,
2018) or economical (Ponomarenko et al., 2018). In
discrete time simulations, agents are sequentially
allowed to perform one cycle of activity each given
time step. As a general rule, parameters calibrations
are realized for a fixed time step uniformly
incremented (Al Rowaei et al., 2011). Recent work
on this question put forward the significant impact
that using a fixed time step could have on the
outcomes of such type of models (Buss and Rowaei,
2010, Kuo, 2015). Indeed, one cycle usually implies
agents’ decision processes about their environment
such as perception-deliberation-execution in a PDE
scheme (Ferber and Müller, 1996) or Belief-Desire-
Intention in a BDI scheme (Caillou et al., 2017).
Whatever the scheme however, it is often difficult, if
possible, to determine if one agent has to process the
selected scheme once each second, two seconds,
minute, hour, day or the like.
In this study we are interested in configuring a
classical agent-based model of a rodent population
in the wild. The aim is to evaluate the optimal time
step duration to fulfil the need of the model’s
objective, that is to say, make evolve a perennial
population in a changing landscape. Beyond the
Fur, J. and Sall, M.
Using Flexible Time Scale to Explore the Validity of Agent-based Models of Ecosystem Dynamics: Application to Simulation of a Wild Rodent Population in a Changing Agricultural Landscape.
DOI: 10.5220/0006912702970304
In Proceedings of 8th International Conference on Simulation and Modeling Methodologies, Technologies and Applications (SIMULTECH 2018), pages 297-304
ISBN: 978-989-758-323-0
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
297

model design with its environment, agents’
behaviour, etc., we designed the model so as it could
be run at various time scales in order to determine
the convenient time step necessary for this purpose
and thereafter use the model accordingly.
The article is first devoted to the presentation of
the model and the approach used to implement a
flexible time scale. The use case is then described
along with the simulation protocol and its associated
time-scale sensitivity analysis. The results section
presents the outcomes of the model for a range of
time steps used. Results and the method used to
formalize time scale changes are then discussed
before concluding on perspectives and possible
improvements.
2 MODEL AND USE CASE
DESCRIPTION
2.1 General Model Overview
The general model used is described in Le Fur et al.
(2017). It is coded in Java using the Repast
Simphony Platform (North et al., 2005). It is a
combination of three connected class hierarchies;
one for substrates at different spatial aggregation
levels, one for genes and genomes that define
agents’ life traits (age at maturity, gestation length,
max age, …) and one to describe agents’ behaviours;
the latter being a compound of moving, reproduction
and social behaviours mechanisms.
The model is implemented using the so-called
‘mechanistically rich’ approach (De Angelis and
Mooij, 2003, Topping et al., 2010) combining abiotic,
trophic, physiological, behavioural, social,
demographic and environmental mechanisms, all
being formalized in the most parsimonious way. The
expected outcome of this approach is to formalize the
dependency of each underlying causal chains to gain
an insight into the overall complex patterns observed
in the natural environments within which agents
evolve. The ‘mechanistically rich’ approach leads to
simulation models producing complex patterns that
cannot be systematically interpreted but that can be
studied by modifying the model’s logic or parameters.
Environment is simulated using a discrete grid
where substrate within each cell can be characterized
and modified (road, crop, house, hedge …). It is
superimposed with a continuous space where agents’
moves and sensing can be computed precisely.
Within the use case presented, cells formalize a
heterogeneous agricultural landscape with fields of
different kinds such as corn, rape, meadow, alfalfa…
(
Figure 2). Each field characteristic is modified
through time by simulated agricultural practices
(sowing, mowing, growing, ploughing…) which
leads to modify the interest or danger of each cell for
the simulated rodent agents. Moreover, each year,
the nature of each field may be modified so as to
simulate crop rotations that are usual in this type of
environment. Agents hence are submitted to a
perpetually changing environment which influences
their distribution or population size.
Agents are individual rodents bearing different
statuses (mature, immature, male, female, pregnant,
weaning, etc.); they evolve in the domain fulfilling
several desires such as foraging, reproduction,
fleeing, suckling... Foraging agents react to their
environment by selecting and moving to the area for
which they perceive themselves to have the highest
affinity. They select a destination (or choose to
remain where they are) on the basis of their
physiological state, location, and the perception of
their surroundings. This is taken into account in the
model using a ‘perception-deliberation-decision-
action’ scheme (e.g., Ferber, 1999).
In this study, the decision process of the rodent is
limited to aiming to a selected destination and
interacting with its target once arrived. Agent’s
speed, sensing radius and deliberation processes
affect its response to its environment (Figure 1). A
controller schedules the agents’ steps and manages
the seasonal fluctuation of the landscape.
Update physiological status
If current place is dangerous or overloaded
Flee (remove target, select an aim and move at high speed)
Else
If already gets target (other relative, burrow system, crop)
If arrived
Process target (eat, suckle, mate, enter burrow…)
Update 'cognitive’ status (target, desire)
Else
If moving target re-compute target’s position
Move towards target
Else
Perceive objects within sensing area
Select desire (forage, reproduction, none, spawn, suckle)
Elaborate set of alternatives
(deliberate out of perceived objects given desire)
Select target (out of possible alternatives
(closest+random)
If target found
Compute target position
Move towards target
Else wander (choose random aim and move)
Grow older (increment age)
Check death (age dependent death probability)
Figure 1: simplified pseudocode for the processes
performed by each rodent agent during one time step.
Bold: sub-models not detailed here; italics: comments on
the corresponding sub-model; underlined: processes
involving time-scale dependency.
SIMULTECH 2018 - 8th International Conference on Simulation and Modeling Methodologies, Technologies and Applications
298

2.2 Use Case Description
A theoretical domain is used as a support for
simulation. The simulated space mimics one real
situation encountered in the French Poitou-
Charentes region (e.g.,
46°16'9.91"N 0°24'26.07"W),
an area colonized by the rodent species simulated.
It is a square of 53x53 cells of 7.48 m side
representing one 15.72 ha area. Various types of
crops are arbitrarily disposed in the domain as well
as human habitation, road and a motorway.
Rodents reproduce from April to October,
during this period, reproduction prevails on
foraging. When male mature agents perceive
mature females they mate; females then produce
offspring’s after a gesta-tion length (mating latency
and weaning are also formalized). Burrow systems
are the third spatial entity considered. They are dug
by female rodent agents and disappear within a
week when they are empty. Burrow systems thus
exist for limited periods of time; they are located in
both the discrete and continuous space in which the
agents move.
A common simulation output is presented on
Figure 2. Rodents distribute themselves through
time depending on the reproduction season and the
evolution of the field statuses. They usually
preferentially occupy perennial fields of meadow
or alfalfa as well as roadside verges or field borders
as described in the literature (e.g., Briner et al.,
2005, Topping et al., 2010). Population size (
Figure
2 middle) shows a seasonal fluctuation with births
occurring during the reproduction season. Mortality
peaks occur when ploughing happens in a crop
occupied by a colony of rodents. At a yearly scale,
population may undergo acute decline (e.g., year 7)
leading to either population collapse or restoring.
Mean dispersal (
Figure 2 bottom) remains steady
and fits with the observed vital domain of this
species (Quéré and Le Louarn, 2011), maximum
dispersal fluctuates at a value near the simulated
domain side with less dispersal for females which
remain more sedentary because of their childcare
activity.
2.3 Time Scale Mechanisms Involved
Three major categories of processes are bound to the
time scale used and vary accordingly to the time step
chosen for simulation. The first involves the duration
of each phase of the rodent life cycle (weaning,
maturity, gestation length, etc.); the second concerns
agents’ sensing:
Figure 2: standard simulation outputs of the studied use
case - common vole rodents in a fragmented agricultural
landscape. Top: snapshot of the population distribution
within the simulated domain; middle, population size and
birth/death rates; bottom: evolution of mean and
maximum dispersal within the period (simulation time
step: 3hours).
♂♂
immature mature
♀♀♀
immature mature pregnant suckli ng dispersing burrow
system
0
200
400
600
800
1000
1200
0%
10%
20%
30%
40%
50%
60%
birth rate (%) death rate (%) Population size (right axis)
0
50
100
150
200
250
meters
meanFemaleDispersal meanMaleDispersal
maxFemaleDispersal maxMaleDispersal
Using Flexible Time Scale to Explore the Validity of Agent-based Models of Ecosystem Dynamics: Application to Simulation of a Wild
Rodent Population in a Changing Agricultural Landscape
299

Agents have a sensing area encompassing any
object or agent (substrate nature, relatives, burrow
systems) perceptible within one time step. It is
defined as a fixed circle with a parameterized radius
(e.g., Jia et al., 2018) corresponding to the vital
range of this type of animal (Quéré and Le Louarn,
2011). The sensing area moves with the agent and is
computed precisely from the continuous space
coordinates. The radius value is declared in m/day
and is adjusted to the time step (or tick) scale used
by converting it into m/tick or cell/tick depending on
the behaviour mechanism involved in rodent’s
activity.
The third category of process depending on
time scale is the common speed of the agent which
is also expressed in m/day and converted into
m/tick. For a given time step, the rodent speed is
fixed except in cases where either its current place
has exceeded the cell or burrow system carrying
capacity or if it arrived in a dangerous area (e.g.,
road, motorway…). In such cases the rodent flees
from its current place at a speed four times its
normal speed until it reaches a place that is not
overloaded.
2.4 Flexible Time-scale Implementation
To ensure the integrity of the multiple scales units
and conversions dealt with and secure model’s
verification, we have first suffixed most methods or
properties names with the units that characterize
them (e.g., meter, day, cell, tick, gramPerDay).
Time and space conversion is realized using an
extension of the standard java Gregorian calendar
which constitutes the time reference within the
model. This class manages both a time amount and
a time unit (e.g., 3+hours). We also plugged a
converter class providing all the necessary utilities
to operate the needed conversions between time
step units and universal units managed by the
calendar. This permits conversion of speeds and
sensing spheres depending of the time or space
units in the continuous space and within the grid
(e.g., meter per day into meter per tick or into grid
cells per tick).
2.5 Simulation Conditions and
Sensitivity Analysis Performed
The rodent population is initialized with 400
individuals and 50 burrow systems representing a
pioneer population density of 25 ind./ha.
Simulations are run using time steps ranging (i) from
5 min to 90 min each 5 min, (ii) from 90 min to 48
hours each 10 min and (iii) from 48 hours to 9 days
each 30 min. Two constraints are imposed to stop
simulations. The first correspond to a maximum of
three years simulation duration, giving a one-year
cycle to allow the model to escape from initial
conditions and two supplementary yearly cycles
with similar cyclic patterns. Simulations are stopped
at the beginning of the reproduction season where
rodents’ population is at its lowest. The second stop
condition is triggered when either a maximum
population of 6.000 individuals evolving within the
domain is reached, that is a signature of a pullulating
population, or when no female remains, hence
signing a collapsing population. Two indicators are
selected to study the effect of changing time step,
the first one is the duration of the simulation; either
max allowed time or population life before collapse.
The second is the size of the population at the end of
the simulation
3 RESULTS
Depending on the initial parameter values the
simulated population may persist a few days to
several centuries before collapsing. In the current
model the latter case is rare and the population often
collapses in the complex environment within which
it evolves. This is expressed in Figure 3 where the
time step values tested almost always result in the
early extinction of the population, except for small
tick values.
The range of values used in this sensitivity
analysis is intentionally larger than the supposed
realistic range of time step values; this makes it
possible to highlight the artefactual behaviours
related to the model function and the simplification
that it brings. Thus, the right of the graph shows an
increase in the lifetime of the population as the
time step increases with a phase transition at a time
step of 190 hours leading to a plateau. In those
extreme situations from 20 to 190 hour per time
step, the increase in the population life span is
related to the increase in rodent speed and
perception that allows them to reach their target
more and more quickly during a single cycle (as of
a time step equals to 63 hours, rodents acquire a
complete perception of the domain at each tick).
Detailed simulations observed there indicate a
boundary conditions effect that becomes
preponderant with a significant rodent density
observed abutting the limits of the domain.
SIMULTECH 2018 - 8th International Conference on Simulation and Modeling Methodologies, Technologies and Applications
300
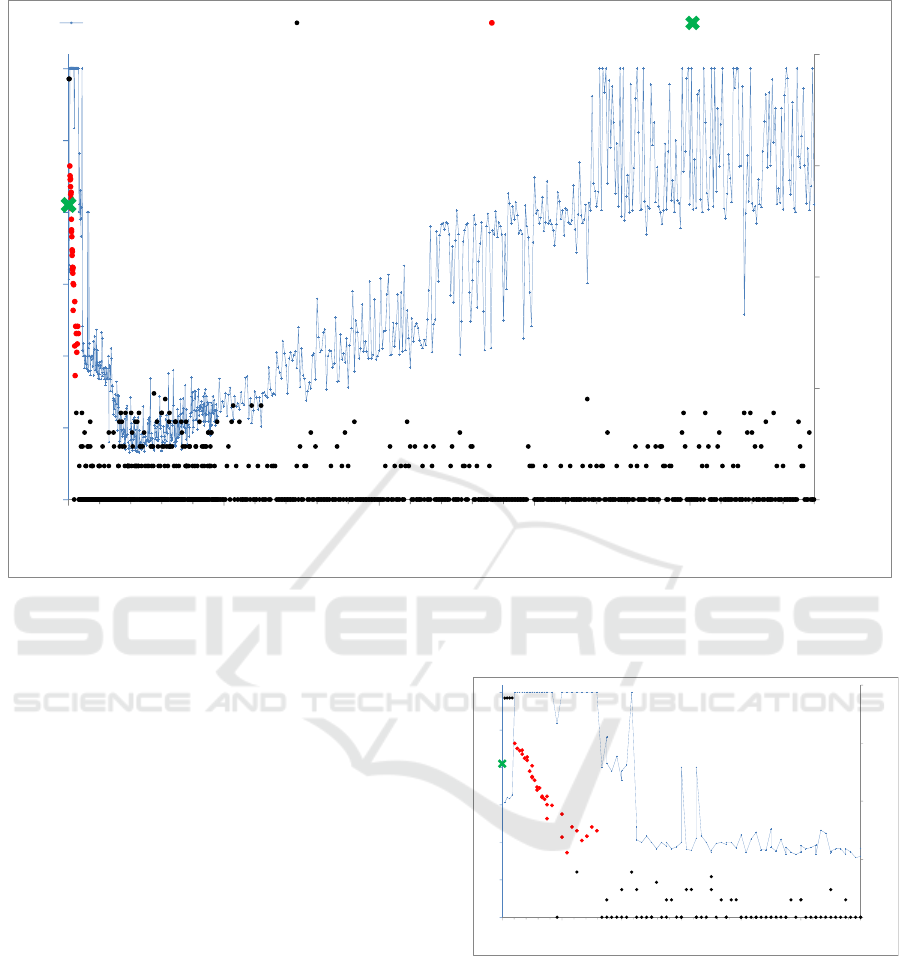
Figure 3: Selected output indicators of the time step sensitivity analysis. Dots: population size at the end of the simulation;
dotted line: duration of the simulation. Simulations are stopped when the rodent population collapses, when it exceeds 6.000
individuals (proliferation), or when the duration reaches 3 years.
The last plateau to the right of the figure starts at
the time step 190 hours when rodents acquire a
speed per tick allowing them to traverse the whole
domain modelled during a single time step. At this
stage, any target is instantly reached. However, this
functionality does not allow the population to persist
and in this value range no population is viable. The
observed outputs indicate high mortality peaks
during the winter season. These peaks are attributed
to the non-optimal positioning of rodents related to
their excessive displacements.
For much shorter time steps (Figure 4),
simulations indicate a range of tick values (in red)
that enables a sustainable population over the
medium term (i.e., beyond the period presented
here). Within this interval, the population remains at
a sufficient level to resist the hazards of its
environment. This range of values also reflects the
adequate frequency of agents’ deliberation/execution
process. It lies in this case between 25 minutes and 3
hours with optimal value at about 45 min
corresponding to an almost steady population (see
illustration on Figure 2).
Figure 4: Sensitivity analysis outputs for small values of
the time step: focus on the extreme left part of Figure 3;
same caption used.
It can be also noticed that within this interval, the
more the time step increases, the more the dynamics
of the population deteriorates with a smaller and
smaller size at the end of the simulation. This
phenomenon can be attributed to a less efficient
adaptation of the virtual population to its simulated
environment. It can be also interpreted as a bias
related to the method used for computing the
1
10
100
1 000
10 000
-
0.5
1.0
1.5
2.0
2.5
3.0
050100150200
Time step (hour)
Simulation length (year) Population size (log) Perennial population Initial population
1
10
100
1 000
10 000
-
0.5
1.0
1.5
2.0
2.5
3.0
024681012
Time step (hour)
Using Flexible Time Scale to Explore the Validity of Agent-based Models of Ecosystem Dynamics: Application to Simulation of a Wild
Rodent Population in a Changing Agricultural Landscape
301

rodents’ sensing area according to the time step,
which will be discussed in the next section.
For very small tick values (5 to 20 min), the
observed phenomenon is a rodent outbreak. Detailed
observation of each of these simulations (not
figured) suggests that, using these small tick values,
rodents’ moves remain very limited from one time
step to another. The burrow systems then constitute
foci where rodents maintain themselves in dense
groups that reproduce intensely. In addition, when
burrows are established in stable areas, resident
populations may be less subject to the hazards of the
environment than when they move further.
4 DISCUSSION
Performing a sensitivity analysis of the model on a
wide range of time scales provided two types of
insights. On the one hand it permitted to get better
understanding of the model function and limitations.
On the other hand it provided a mean to infer a
reasonable range of validity from the logic of the
modelled processes, such as here the frequency of
decision/action processes performed by rodents over
a period of time and leading to a perennial
population in a given environment. The valid range
of frequency here suggests that rodents in the wild
would perform a deliberation process from each 3
min to each 3 hours. To our knowledge, this value is
not accessible to experimentation or sampling.
However, it could constitute a clue to estimate the
order of magnitude of the cognitive activity that
these small animals realize in their environment.
Nevertheless, these results have to be considered
with caution and as only indicative since they come
from a single parameter sensitivity analysis, that is,
all other things being equal otherwise. It is almost
certain that the model is also sensitive to numerous
other aspects such as the spatial resolution or the
initial conditions imposed. Changing values for
these parameters would be susceptible to modify the
resulting optimal time scale that rose out of the
analysis. Multi-criteria sensitivity analysis (e.g.,
Saltelli et al., 2004) would therefore be necessary to
get more confident insight into the model’s
potential.
Simulations indicated large variation of the
selected indicator outputs; the population life time
and size. In an ideal scheme, the expected outcome
of such analysis would be that the simulated
population dynamics and indicator values would
remain unchanged whatever the time scale chosen.
Some contexts permits to reach such objective.
These occur when relationships between time
dependent parameters and time scale are linear. This
was here the case for life traits parameters such as
gestation, weaning duration, ageing.... Changing
time scale did not change the rodent agents’ life
cycle whatever the time step chosen. Kuo et al.
(2012) developed an epidemiological stochastic
agent-based model where probabilities could be
adjusted relative to time scale. In this case also, their
study led to almost reproducible results whatever the
time scale chosen. When however relationships
between time step and time-dependent parameters
are not linear, discrepancies appear and increasing
biases occur with increasing changes in time steps.
This is particularly the case here for time scaling
of agents’ perception area. Little literature was
found on formalization of agents' perception area.
Jia et al. (2018) used sensing circle radius as the
parameter defining the perception area of an agent.
This parameter was also used in this study to define
the agents’ sensing area and perform the conversion
from one time scale to the other. In a fixed time step
context, this approach is indeed the more logical and
straightforward. However, in a multi-time-scale
context, where sensing area must be scaled as a
function of time, it is not clear if this approach
comes out as a satisfactory solution. Geometry
calculations made before this study indicate that, in
the case of a straight line movement, the cumulated
area perceived by a rodent during several small time
steps is greater than that of a circle corresponding to
the area perceived on a larger time step equivalent to
the sum of the previous ones. At the same time, if
one considers that the rodent does not usually move
in a straight line but in an erratic or semi-erratic
trajectory such as in Lévy flight’s (Chechkin et al.,
2008), as it is the case during foraging, this travelled
area then decreases and converges toward the same
order of magnitude than the integrated circle.
In any case therefore, the area actually perceived
depends on the detail of the agent’s trajectory. It is
indeed logical that the perception area computed at
any timescale depends on the simulated trajectories
of rodents. Since these trajectories are moreover
themselves dependent on time and objects, changing
time scale produces biases in the model outcome
that may be difficult to reduce.
5 CONCLUSION
Exploitation of the model output at different time
scales proved valuable to better understand the
model potential, limitation and functioning. This
SIMULTECH 2018 - 8th International Conference on Simulation and Modeling Methodologies, Technologies and Applications
302

approach also provided a better insight on the
plausible range of activity of rodents in the wild
such as the frequency at which they should react to
their environment by mean of the perception/
deliberation scheme, within the limitation of such
simplified model.
This work also raises question on the best way to
formalize sensing. In this domain, comparative study
of different means to formalize time-dependent
perception, for example by using a surface, a radius,
or making agents’ sensing area a time-independent
parameter, would help improving modelling of
ecosystem-dependent agents.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to thank S. Corso for his
contribution to the question of perception
formalization; J.P. Quéré, B. Gauffre, K. Berthier for
their expertise on the bio-ecology of the common
vole, P.A. Mboup for his implementation of the
space and time-scale converter, and S. Le Fur for
English verification. We gratefully acknowledge
support provided by CEA-MITIC (The African
Centre of Excellence in Mathematics, Computer
Science and ICT).
REFERENCES
Al Rowaei, A. A., Buss, A. H., and Lieberman, S., 2011.
The effects of time advance mechanism on simple agent
behaviors in combat simulations. Proc. Winter
Simulation Conference: 2431-2442.
Balci, O., 1998. Verification, Validation, and Accreditation.
Proc. Winter Simulation Conference: 41-48.
Briner, T., Nentwig, W. and Airoldi, J.P., 2005. Habitat
quality of wildflower strips for common voles (Microtus
arvalis) and its relevance for agriculture. Agriculture,
Ecosystems and Environment 105:173–179
Buss, A., Al Rowaei, A., 2010. A comparison of the
accuracy of discrete event and discrete time. Proc.
Winter Simulation Conference: 1468-1477.
Caillou, P., Gaudou, B., Grignard, A., Truong, C. Q. and
Taillandier, P., 2017. A Simple-to-use BDI architecture
for Agent-based Modeling and Simulation. Advances in
Social Simulation 2015:15-28.
Chechkin, A., Metzler, R., Klafter, J. Gonchar, V., 2008.
Introduction to the Theory of Lévy Flights. In R.
Klages, G. Radons, I.M. Sokolov (Eds), Anomalous
Transport: Foundations and Applications, Wiley-VCH,
Weinheim.
DeAngelis, D. L., Mooij, W. M., 2003. In praise of
mechanistically rich models. In: Canham, C. D., Cole, J.
J., Lauenroth, W. K. (Eds.), Models in Ecosystem
Science. Princeton University Press, Princeton, New
Jersey, pp. 63–82.
Ferber J., 1999. Multi-agent systems: an introduction to
distributed artificial intelligence, Addison-Wesley
Reading.
Ferber, J. and Müller, J. P., 1996. Influences and reaction: a
model of situated multi agent systems. Proc.
International Conference on Multi-Agent Systems
(ICMAS-96): 72-79.
Floudas, C. A., and Lin, X., 2004. Continuous-time versus
discrete-time approaches for scheduling of chemical
processes: a review. Computers & Chemical
Engineering, 28(11): 2109-2129.
Fu, Z., Hao, L., 2018. Agent-based modeling of China’s
rural-urban migration and social network structure.
Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications:
1061-1075.
Jia, J., Chen, J., Chang, G., Wen, Y., and Song, J., 2009.
Multi-objective optimization for coverage control in
wireless sensor network with adjustable sensing radius.
Computers & Mathematics with Applications, 57(11-
12), 1767-1775.
Kuo, C. T., Wang, D. W., and Hsu, T. S., 2012. A Simple
Efficient Technique to Adjust Time Step Size in a
Stochastic Discrete Time Agent-based Simulation. In
Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on
Simulation and Modeling Methodologies, Technologies
and Applications - Volume 1: SIMULTECH: 42-48.
Le Fur, J., Mboup, P.A., and Sall, M., 2017. A Simulation
Model for Integrating Multidisciplinary Knowledge in
Natural Sciences. Heuristic and Application to Wild
Rodent Studies. Proc. 7th Internat. Conf. Simul. And
Model.Method., Technol.and Applic. (Simultech),
Madrid, july 2017: 340-347.
North, M. J., Howe, T. R., Collier, N. T., Vos, J. R., 2005.
The Repast Simphony Development Environment. In,
Proc. Agent 2005 Conference on Generative Social
Processes, Models, and Mechanisms:13-15.
Ponomarenko, A., and Sinyakov, A., 2018. Impact of
Banking Supervision Enhancement on Banking System
Structure: Conclusions Delivred by Agent-Based
Modelling. Bank of Russia Working Paper Series
wps19, Bank of Russia.
Quéré, J.P. and Le Louarn, H., 2011. Les rongeurs de
France: faunistique et biologie. Quae ed., Paris, ISBN:
978-2-7592-1033-6, 312p.
Railsback, S., Ayllón, D., Berger, U., Grimm, V., Lytinen,
S., Sheppard, C., and Thiele, J., 2017. Improving
execution speed of models implemented in NetLogo.
Journal of Artificial Societies and Social Simulation,
vol. 20, no. 3. doi:10.18564/jasss.3282
Saltelli, A., Tarantola, S., Campolongo, F., Ratto, M., 2004.
Sensitivity Analysis in Practice. Wiley, New York.
Sauser, B., Baldwin, C., Pourreza, S., Randall, W., and
Nowicki, D., 2018. Resilience of small-and medium-
sized enterprises as a correlation to community impact:
an agent-based modeling approach. Natural Hazards,
90(1): 79-99.
Singh, K., Ahn, C. W., Paik, E., Bae, J. W., and Lee, C. H.,
2018. A Micro-Level Data-Calibrated Agent-Based
Using Flexible Time Scale to Explore the Validity of Agent-based Models of Ecosystem Dynamics: Application to Simulation of a Wild
Rodent Population in a Changing Agricultural Landscape
303

Model: The Synergy between Microsimulation and
Agent-Based Modeling. Artificial life: 128-148.
Squazzoni, F., 2010. The impact of agent-based models in
the social sciences after 15 years of incursions. History
of economic ideas: 197-233.
Stanilov, K., 2012. Space in agent-based models. In Agent-
based models of geographical systems: 253-269).
Springer, Dordrecht.
Topping C. J., Høye T. T. and Olesen C. R., 2010. Opening
the black box – development, testing and documentation
of a mechanistically rich agent-based model. Ecological
Modelling 221 (2) 245-255.
Watts, J., 2016. Scale Dependency in Agent-Based
Modeling: How Many Time Steps? How Many
Simulations? How Many Agents?. Uncertainty and
Sensitivity Analysis in Archaeological Computational
Modeling, Springer, Cham.: 91-111.
White, A. A., 2016. The sensitivity of demographic
characteristics to the strength of the population
stabilizing mechanism in a model hunter-gatherer
system. In Uncertainty and Sensitivity Analysis in
Archaeological Computational Modeling, Springer,
Cham.: 113-130.
Whitley, T. G., 2016. Archaeological simulation and the
testing paradigm. In Uncertainty and Sensitivity
Analysis in Archaeological Computational Modeling
Springer, Cham.: 131-156.
SIMULTECH 2018 - 8th International Conference on Simulation and Modeling Methodologies, Technologies and Applications
304
