
A Wireless Sensor Network as a Living Lab for the Development of
Solutions for IoT and Smart Cities
Jorge Arturo Pardiñas-Mir, Luis Rizo-Dominguez and Luis Eduardo Pérez-Bernal
Department of Electronics, Systems and Informatics, ITESO University, Periférico Sur 8585, 45604, Tlaquepaque, Mexico
Keywords: Wireless Sensor Networks, Internet of Things, Living Lab.
Abstract: As internet connectivity and digital solutions spread all over, it has become necessary to have the possibility
of experimenting and developing solutions for the Internet of Things (IoT) into a laboratory with similar
conditions as those of the big scale application. Living Labs are a solution for such a need and in this paper
we present the implementation of a living lab based on a wireless sensor network (WSN) aimed to help the
learning of this technology by giving the opportunity of experimenting and developing solutions. The WSN
works primarily on the ZigBee protocol but, being an educational and developing tool, it also permits to add
devices working in other protocols like WiFi, 3G and Sigfox, that we have already experienced. The system
includes the possibility that the collected data be kept into an internet server and be able to be displayed to
users through a mobile application.
1 INTRODUCTION
As internet connectivity and digital solutions spread
all over, it has become necessary to have the
possibility of teaching, research, and develop
solutions for the Internet of Things (IoT) into a
laboratory with similar conditions as those of the real
big scale application. This need has been identified in
the scientific community, so several efforts have been
invested in that direction. We think that despites the
many meanings given to the term “Living Lab”, for
example in (Del Vecchio et al., 2014), (Vicini et al.,
2013), and (Tang and Hämäläinen, 2012) among
others, it is adequate to describe such a kind of
facility, as defined by (Eriksson et al., 2006): “a user-
centric research methodology for sensing,
prototyping, validating and refining complex
solutions, in multiple and evolving rea life contexts”.
In (Chin and Callaghan, 2013) it is argued that
Internet-of-Things is a perfect platform for teaching
computer science and it proposes a Living Lab
approach based on combining concepts taken from
iCampus, Smart Box ad Pervasive-interactive-
Programming (PIP). They show that their methods
have a good potential for introducing students to
programming in a way that is simple and motivating.
An experiential learning program, Living Lab,
which provides real world experience in all aspects of
information technology to students, is presented in
(Justice and Do, 2012). It helps students to develop
modern technological skills, effective oral and written
communications skills, and the ability to perform well
in teams. The development of a wireless sensors and
controllers network for training students in
Automation is described in (Katsaounis et al., 2014).
This is a chance for students to keep in touch with a
small-scale implementation of a hybrid network. An
educational platform for promoting awareness of lake
environmental protection is presented in (Wang et al.,
2016). It is based on Internet of Things and wireless
sensor network technologies, monitoring water
quality of lakes and providing data analysis of lake
pollution.
In this paper, we describe our approach to the
implementation and launching of a Wireless Sensor
Network (WSN) as a support for teaching and
research on issues related to the Internet of Things. It
has the aim of also being a “Living Lab” allowing the
development and testing of solutions under real
conditions that facilitate its implementation in a larger
scale. This project is not focused on a particular
course, but it allows experiencing many topics related
to the internet of things. Students can use the system,
for example, to develop the final project of a sensor
course, or to demonstrate the operation of a
microcontroller that performs some function within
the network. There are students involved in
Pardiñas-Mir, J., Rizo-Dominguez, L. and Pérez-Bernal, L.
A Wireless Sensor Network as a Living Lab for the Development of Solutions for IoT and Smart Cities.
DOI: 10.5220/0006915103030308
In Proceedings of the 15th International Joint Conference on e-Business and Telecommunications (ICETE 2018) - Volume 1: DCNET, ICE-B, OPTICS, SIGMAP and WINSYS, pages 303-308
ISBN: 978-989-758-319-3
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
303

application projects related to sensor networks and
mobile applications. Some of the topics that this
framework allows to study are the four core
technologies normally embodied in currently IoT
systems: embedded computing, sensors, networking,
and cloud computing (Dickerson, 2017). The
teaching of these technologies are mainly aimed to
students of the following bachelor programs:
Electronic Engineering, Computer Systems
Engineering, Information Security and Network
Engineering, and Engineering in Service Companies.
Our system was developed based on the
monitoring of environmental conditions of the
university campus, taking into account the main
technical subjects required in learning and working
with Internet of Things projects. On the one hand, a
wireless network has been developed that monitors
the temperature and humidity of the soil in different
points of the campus gardens. This goal took into
account the university needs related to maintaining in
good health the gardens and trees of the campus. The
collected information is placed in the hands of the
university authorities for analysis and undertake of
appropriate action. On the other hand, independent
wireless nodes have been added that communicate
directly with the system, bypassing the wireless
network, to provide information on specific aspects
or to allow the use of a different technology.
The architecture of the implemented system and the
description of the elements related to the management
of collected data, its storage and availability on the
Internet was presented in (Perez et al., 2015). This
paper focuses on the development and
experimentation of the wireless sensor network and
its communication with the system.
Section 2 describes the architecture of the system
as a whole. Section 3 presents the network
development and section 4 describes some tests and
results. Finally, the conclusions include some ideas
about future work.
2 SYSTEM’S ARCHITECTURE
The Living Lab System for the Development of
Solutions for IoT and Smart Cities is a system
operating in a university campus, aimed to measure
mainly environmental variables of the campus. The
system is composed of 3 main elements, Figure 1: the
wireless sensor network, the acquisition and storage
internet service and the information retrieval service.
The wireless sensor network is in charge of
collecting the data through several sensor
nodes around the campus. The first series of
installed nodes has the capability of
measuring soil’s temperature and moisture.
This information is sent from each node to the
network coordinator who, acting as a
gateway, send the data to the system server in
internet.
The acquisition and storage of data on the
web, is an internet service being in charge of
the system server. It keeps track of each node,
stores the collected information in a database,
and it also manages everything related to the
network, like adding and deleting nodes,
sensor variables to be measured, and
assigning a location to each node.
The retrieval of information is the server’s
section providing real time data collected by
the nodes. It also allows generating data
reports. The data can be consulted and
displayed through a web page or through a
mobile application via internet.
Figure 1: Elements of the system.
The information system design also allows having
independent nodes sending its data directly to the
server, without belonging to the wireless network,
allowing testing special sensor nodes configurations
or new sensor technologies.
The university campus, where the system is
installed, has a surface of over 41 hectares of which
22 are green areas: gardens and trees. It is a polygon
with approximately 530 meters wide and 715 meters
long. It exists at the campus over 3,000 trees of about
280 species. In the first stage of development of our
system, the wireless network was installed in a
delimited area, allowing easily ensuring and
monitoring its operation. The system is then a
laboratory the size of the campus, with a network of
sensors and an information system in operation. The
system allows to easily experiencing topics related to
the internet of things in an integrated manner:
embedded systems, sensors, powering and energy
consumption in sensors, use of communication
systems for sensors, web services, front-end, back-
end, and cloud computing. The services related to the
information systems have already been described in
(Perez et al., 2015), while in this paper we will focus
in describing the wireless sensor network, its
operation, experiments and results.
WINSYS 2018 - International Conference on Wireless Networks and Mobile Systems
304
3 WIRELESS SENSOR
NETWORK DEVELOPMENT
The wireless network was developed with an initial
application target: measuring humidity and
temperature of soil, under the requirements of the
university office in charge of campus facilities. In this
way, we would achieve first the objective of working
with a real application. At the same time, its
development took into account the possibility of
having an easily growing network and of being
compatible with different technologies. Taking this as
a starting point, it was determined to divide the
development of the network into 3 parts: the choose
of the technology, the architecture of the network and
the sensors to be used.
3.1 Base Technology
It was decided to use a well-known technology as the
basis of the network, which would make it possible to
operate a network of sensors easily and reliably. This
would allow to add new elements little by little and to
try new technologies later. The chosen technology
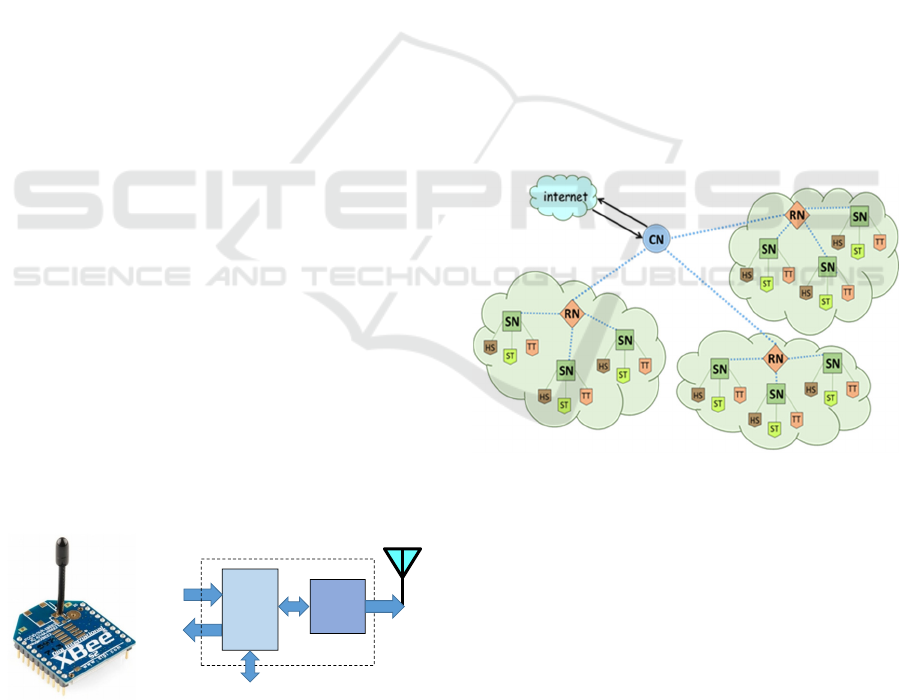
was the XBee sensor modules from Digi
International, which communicate via the ZigBee
protocol working at the ISM 2.4 GHz band, Fig 2.
Among the features of these modules are being
specifically configurable for activities related to
sensing, like defining the inputs and outputs and the
sampling time. There is available a Pro version with
high transmission power (50mW -17dBm-) and high
receiver sensitivity (-102 dBm) focused on network’s
coordinators and routers and a low power version
with less transmission power (2 mW -3 dBm-) and a
smaller receiver sensitivity (-96 dBm) focused on end
devices. These modules have the possibility of
defining 4 analog inputs and 4 digital input/outputs.
The communication with the module is made through
a serial UART.
Figure 2: XBee ZigBee module physical aspect and block
diagram.
3.2 The Sensor Network
As it is known, a ZigBee network is formed with a
single network coordinator (CN) that controls the
network, routers nodes (RN) that create the links
between all elements in the network and end or
sensor nodes (SN), which are tasked with taking
samples periodically and transmit them to the
network. The implemented WSN uses the two
different ZigBee modules in the network according
to the functions of the nodes. In the case of sensor
nodes, the low power module version is used while
for the routers and coordinator nodes the high power
version is installed instead. The network is
organized in 3 zones, each one with a router in
charge of many sensor nodes. Each router in turn
communicates directly to the network coordinator or
to another router if it is within its range. Fig. 3 shows
the block diagram of such an architecture, where
HS, ST, and TT are the end devices measuring
humidity of the soil, soil temperature and tree
temperature respectively. The latter is a sensor not
yet implemented. The ZigBee protocol allows the
nodes to create automatically the needed links to
form the network.
Figure 3: Topology of the implemented WSN.
3.3 The Sensor Nodes
Each sensor node comprises an XBee low power
version module, working as an end device, a soil
temperature sensor and a humidity soil sensor. We
choose sensors aimed to be applied in real
environments in order to obtain a reliable and useful
behaviour. We selected the Vegetronix THERM 200
and VH400 respectively, shown in Fig. 4. They
output an analog voltage proportional to the
temperature and moisture. Each node is powered by a
3.7 volt battery, which is recharged through a solar
cell. A 3.7V-5V converter powers the sensors. Some
nodes are additionally powered by night. The node is
μC
Tx/Rx
A/D ins
D outs
XBee
serial
A Wireless Sensor Network as a Living Lab for the Development of Solutions for IoT and Smart Cities
305

configured to take samples around each 30 minutes,
send it to the router and return to a low activity state
(sleep) until next sampling. The data is transmitted to
the sensor network into a ZigBee frame, which in the
XBee implementation is a 0x92 API frame. One
version of the implemented sensor node is shown in
Fig. 5.
Figure 4: Soil’s moisture and temperature sensors.
Figure 5: The Sensor Node.
3.4 The Gateway
The gateway is composed of a microcontroller and a
Zig-Bee coordinator. The data arriving from the end
devices to the routers is transferred to the network
coordinator. The microcontroller analyses the
received frame and extracts the voltage values
corresponding to the temperature and moisture’s
sensors. These values are converted to the
corresponding temperature and moisture units and
they are placed in the format of a new frame,
recognizable by the system server. A first version of
the Gateway was developed with an Arduino
microcontroller board, using a WiFi shield, Fig. 6. It
was preferred to use WiFi technology to have greater
versatility in the position of the gateway, and increase
the possibilities of experimentation.
Figure 6: The Gateway architecture.
4 RESULTS
4.1 Installation Tests
The installation and operation of the Wireless Sensor
Network was carried out experimenting with different
positions of nodes and distances between them. The
sensor nodes were installed at ground, between the
trees. It was found that a good distance to avoid losing
any frame was in general a maximum of 30 meters. It
is good to remember that the sensor nodes transmit
with a maximum power of 2 mW (3 dBm) and have a
Figure 7: Received power vs distance between the network
coordinator and one router.
Figure 8: The Wireless Sensor Network Architecture.
WINSYS 2018 - International Conference on Wireless Networks and Mobile Systems
306
receiver sensitivity of -96 dBm. On the other hand,
range tests were made between routers and the
coordinator, both of them transmitting with a
maximum power of 50mW (17dBm) and with a
receiver sensitivity of -102 dBm. Here the distance to
locate routers apart from the coordinator was found to
be around 150 meters. Fig. 7 shows the results of one
of the tests. The final location of nodes into the
network at the test stage is shown in Fig. 8.
4.2 Monitoring of Environmental
Variables
As said before, being the first job of our system to
behave as a Living Lab, the network was designed to
serve the campus authorities to collect environmental
data concerning the health state of gardens and trees
of the campus. With this information, the office in
charge of the campus facilities will have the
possibility of taking actions to improve, for example,
the irrigation system. Additionally to the temperature
and moisture of soil, we have added to the system, as
required by the same office, two different kind of
sensors. One device, a Waspmote Libelium Plug &
Play!, measuring some air pollution gases and
connecting to the ZigBee network. The second device
measures some variables related to the water quality
of the campus water treatment plant. It connects
independently to the internet server through WiFi.
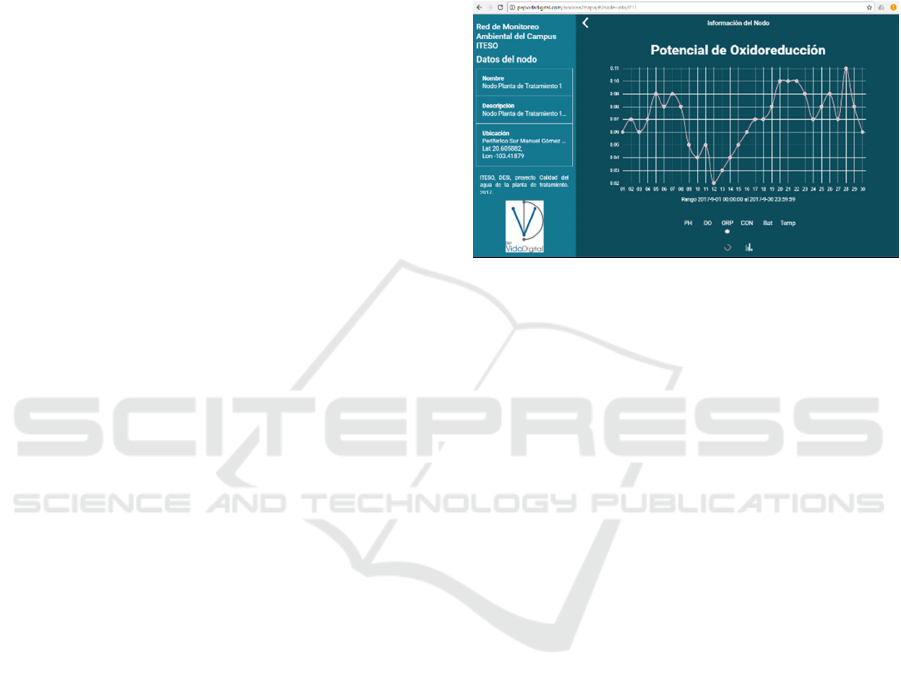
Figure 9 illustrates, as an example, the web
information page showing the graphic of the
Oxydation Reduction Potential values of water,
collected during September 2017.
4.3 Learning Laboratory
As a Learning Laboratory, our system has helped in
the development of training experiences for students
in their last year of engineering, in different technical
areas. This work has been done under real application
conditions. Some of the tasks carried out by the
students have been:
Design and implementation of a voltage
converter card for analog sensors.
Programming a ZigBee-WiFi Gateway
using the Waspmote device from Libelium.
Programming a SigFox enabled sensor node
based on the Freescale (NXP) KL43Z.
Addition of functions to the server’s data
reception service, such as the automatic time
stamping of the received frames and
improvement of graphics display.
Improvement of network management tools.
Some of these activities allowed some students to
participate in a project to install a wireless sensor
network in a forest. The objective is to monitor,
within a limited area, the variables that can show the
improvement of soil characteristics. In this project,
we have collaborated with professors from other
areas, such as chemical engineering and
environmental engineering.
Figure 9: Example of webpage showing Oxydation
Reduction Potential values of water.
5 CONCLUSIONS
This paper presents a wireless sensor network that is
part of a system acting as a Living Lab. It helps at the
same time the development and learning of
technology solutions for IoT and Smart Cities under
an easy manageable scale but with similar conditions
as the application implemented at full scale. The
WSN platform was implemented successfully,
allowing the collection of useful data for the care of
the campus gardens. It is ready for experimenting new
technologic approaches or new products. It has
helped students to experience and learn about these
technologies. The system makes it easy to add a new
technology sensor, or to test a new topology, for
example. In the short term, the next steps in the
development of the system are to increase the number
of sensor nodes, to expand the network coverage, and
to give the Gateway more intelligence for doing more
local processing.
REFERENCES
Chin, J., Callaghan, V., 2013. Educational Living Labs: A
Novel Internet-of-Things Based Approach to Teaching
and Research. In 2013 9th International Conference on
Intelligent Environments, Athens, 2013.
Del Vecchio, P., Elia, G., Ndou, V., Secundo, G., Specchia,
F., 2014. To what extent the practice on living labs
A Wireless Sensor Network as a Living Lab for the Development of Solutions for IoT and Smart Cities
307

match with the theoretical framework? The case of
VINCENTE Living Lab for the creation of technology
entrepreneurship. In 2014 International ICE
Conference on Engineering, Technology and
Innovation (ICE), Bergamo.
Dickerson, S. J., 2017. A comprehensive approach to
educating students about the internet-of-things. In 2017
IEEE Frontiers in Education Conference (FIE),
Indianapolis, IN, 2017, pp. 1-7.
Eriksson, M., Niitamo, V. P., Kulkki, S., Hribernik, K. A.,
2006. Living labs as a multi-contextual R&D
methodology. In 2006 IEEE International Technology
Management Conference (ICE), Milan, 2006, pp. 1-8.
Justice, C., Do, L., 2012. IT experiential learning: The
Living Lab. In Frontiers in Education Conference
(FIE), Seattle, WA., 2012.
Katsaounis, G., Tsilomitrou, O., Manesis, S., 2014. A
Wireless Sensors and Controllers Network in automa-
tion a laboratory-scale implementation for students
training. In 22nd Mediterranean Conference on Control
and Automation, Palermo, 2014, pp. 1067-1073.
Pérez L., Pardiñas-Mir J., Guerra O., de la Mora J.,
Pimienta M., Hernández N., Lopez M., 2015. A
Wireless Sensor Network System - For Monitoring
Trees’ Health Related Parameters in a University
Campus. In Proceedings of the 12th International
Conference on Wireless Information Networks and
Systems, ISBN 978-989-758-119-9, pages 42-47.
Tang, T., Hämäläinen, M., 2012. Living lab methods and
tools for fostering everyday life innovation. In 2012
18th International ICE Conference on Engineering,
Technology and Innovation, Munich, 2012, pp. 1-8.
Vicini, S., Bellini, S., Sanna, A., 2013. User-Driven Service
Innovation in a Smarter City Living Lab. In 2013
International Conference on Service Sciences (ICSS),
Shenzhen, 2013, pp. 254-259.
Wang, W., Liu, Y., Guo, Y., Jian, P., 2016. An Educational
Platform for Promoting Awareness of Lake
Environmental Protection with Live Monitoring
Technology. In 2016 International Conference on
Educational Innovation through Technology (EITT),
Tainan, 2016, pp. 238-241.
WINSYS 2018 - International Conference on Wireless Networks and Mobile Systems
308
