
Autonomous Vehicle Steering Wheel Estimation from a Video using
Multichannel Convolutional Neural Networks
Arthur Emidio T. Ferreira
1
, Ana Paula G. S. de Almeida
2
and Flavio de Barros Vidal
1
1
Department of Computer Science, University of Brasilia, Brazil
2
Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Brasilia, Brazil
Keywords:
Multichannel Convolutional Neural Networks, Vehicle Steering Wheel Estimation, Autonomous Vehicles.
Abstract:
The navigation technology in autonomous vehicles is an artificial intelligence application which remains un-
solved and has been significantly explored by the automotive and technological industries. Many image pro-
cessing and computer vision techniques allow significant improvements on such recent technologies. Using
this motivation as a basis, this work proposes a novel methodology based on Multichannel Convolutional
Neural Networks (M-CNN) capable of estimating the steering angle of an autonomous vehicle, having as only
input images captured by a camera attached to the vehicle’s frontal area. We propose five Convolutional Neural
Network architectures: 1-channel, 2-channel and 3-channel in the convolution step. Based on the performed
tests using a public video dataset, it is presented a quantitative comparison between the proposed models.
1 INTRODUCTION
Nowadays, autonomous driving and navigation
technology in autonomous vehicles is an artificial in-
telligence application that has drawn great attention
with the popularity of intelligent vehicles. In these
application areas, unsolved issues still remain and
have been significantly explored by the automotive
and technological industries, due to the potential im-
pact that such innovation will bring in the near future
(Pomerleau, 1989; Thrun et al., 2006; Thorpe et al.,
1988).
Over the last decades, many works have approa-
ched this theme: In 1989, (Pomerleau, 1989) descri-
bed the construction of an autonomous vehicle based
on artificial neural networks. The proposed network is
responsible for providing guidance to the vehicle and
the architecture of the network consists of a classical
artificial neural network (ANN) with a single interme-
diate layer, containing 29 neurons fully connected to
the input units.
Many works involving ANN in autonomous vehi-
cle applications can be found in the vast litera-
ture available. However, a lot has changed since
the advent of new network architectures. With the
rise of deep learning, Convolutional Neural Net-
works (CNN) have improved the image comprehen-
sion tasks by learning more discriminative features,
allowing an useful development on several systems,
including autonomous vehicles (Wang et al., 2018).
We will describe a small sample of the numerous
applications of these networks architectures as fol-
lows: in (Chen et al., 2015) it is proposed an autono-
mous navigation system called DeepDriving based on
CNN. The speed, acceleration, brake and steering an-
gle are computed from the CNN output values, which
are then used as input to an algorithm that describes
the control logic of the vehicle.
The works of (Bojarski et al., 2016) and (Bojarski
et al., 2017) propose a CNN called PilotNet capable
of estimating the steering angle of a vehicle. In or-
der to observe the features extracted by PilotNet, a
deconvolution-based algorithm (Zeiler et al., 2011) is
used. It finds regions of the image that have the hig-
hest levels of activation in the maps produced by the
convolution layers of the network. The PilotNet net-
work was tested in a car and was able to carry out a
15 minute journey in urban area without human inter-
vention by 98% of the time.
Finally, in this work we propose a novel approach
to construct new models based on Multichannel Con-
volutional Neural Networks (M-CNN) that are capa-
ble of estimating the steering angle of a vehicle given
only a set of images from its frontal view, which is
a task that many autonomous vehicle systems must
solve.
To reach this main objective, the sections of this
work are divided as follows: Section 2 describes in
Ferreira, A., Almeida, A. and Vidal, F.
Autonomous Vehicle Steering Wheel Estimation from a Video using Multichannel Convolutional Neural Networks.
DOI: 10.5220/0006920605170524
In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics (ICINCO 2018) - Volume 2, pages 517-524
ISBN: 978-989-758-321-6
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
517
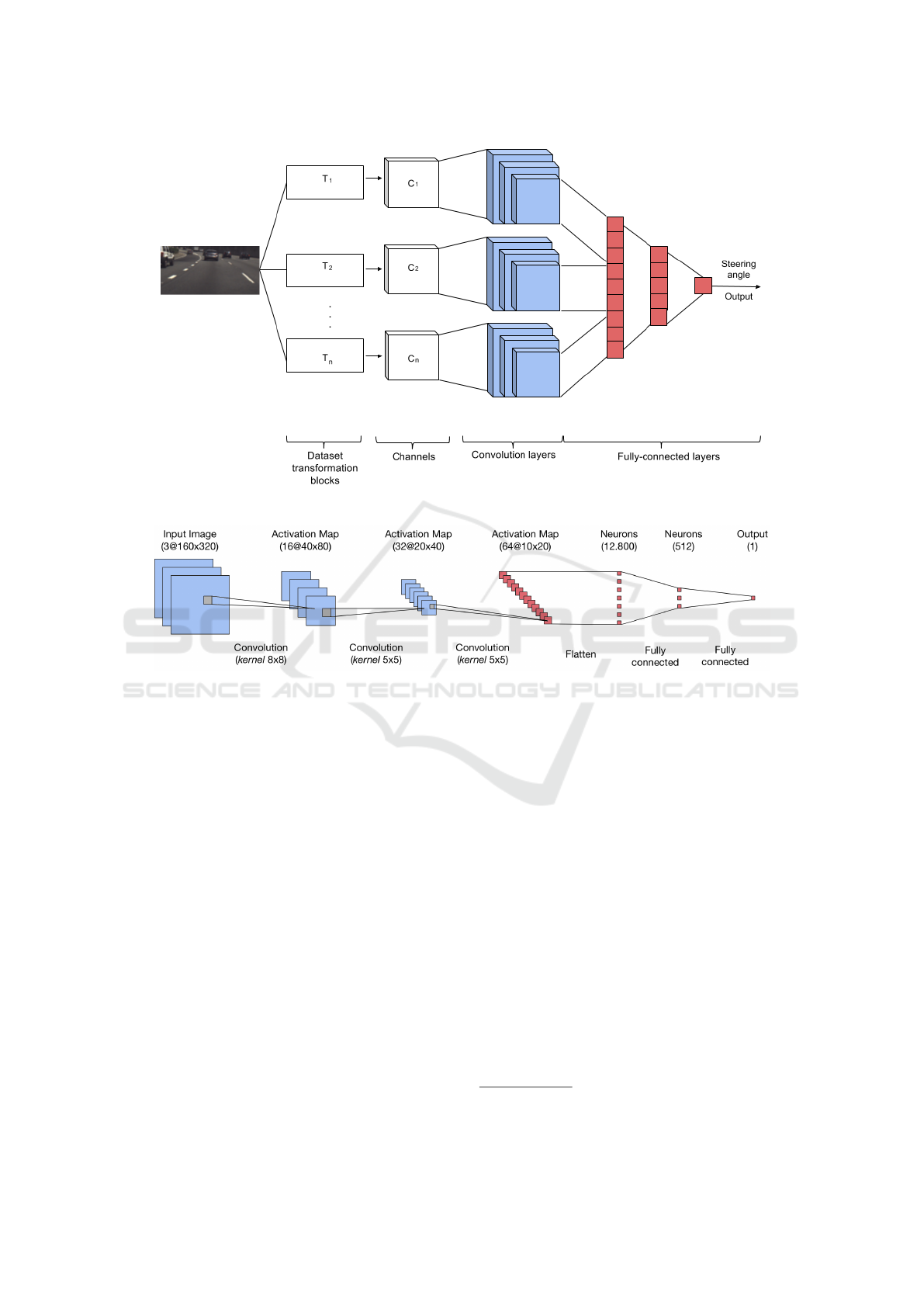
(a) Proposed M-CNN architecture.
(b) Base CNN architecture diagram.
Figure 1: Details of the proposed M-CNN architecture.
details the proposed methodology. In Section 3 the
results are shown and discussed. Section 4 is dedica-
ted to conclusions and further works.
2 PROPOSED METHODOLOGY
As seen in the related works presented in Section 1,
artificial neural networks have presented promising
results in the construction of many parts of autono-
mous vehicles systems. Hence, in this work we pro-
pose a novel method based on multichannel convolu-
tional neural networks capable of estimating a vehi-
cle’s steering angle using only information from real
traffic video scenes. In this specific case, the develo-
ped system receives as input a collection of RGB ima-
ges captured using a dash cam placed inside the vehi-
cle and outputs the estimated steering angle at the gi-
ven instant, meeting the requirements of autonomous
vehicles.
2.1 Dataset
Based on the proposed methodology, illustrated on Fi-
gure 1-(a), a dataset provided by the comma.ai organi-
zation
1
is used. The dataset is composed of 11 videos
with a 320x160 pixels resolution, variable duration
and captured in a 20Hz frequency using a dash cam
installed inside the vehicle (i.e. Acura ILX 2016),
capturing frames of its frontal vision while driving
during day and night periods, usually on a highway.
In total, the dataset is composed of 522,434 frames,
resulting in approximately 7 hours of recording time.
For the purposes of this work, the only information
that was taken into account was the video frames (in
RGB format) and the steering angle values. The steer-
ing angle is given in degrees and corresponds to the
rotation angle of the vehicle’s steering wheel. Every
angle value present in the dataset belongs to the inter-
val [−502.3, 512.6].
1
The dataset is made available on the CC BY-NC-SA
3.0 license.
ICINCO 2018 - 15th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
518

2.2 CNN Architecture
According to (Goodfellow et al., 2016), CNNs are
specialized artificial neural networks that process in-
put data with some kind of spatial topology, such as
images, videos, audio and text. Also in (Goodfellow
et al., 2016), an artificial neural network is conside-
red convolutional when it has at least one convolution
layer and receives a multidimensional input (also re-
ferred as a tensor) and applies a series of convolutions
using a set of filters. In addition to convolution layers,
CNNs are usually composed of other types of layers.
2.2.1 Multichannel CNNs
Multichannel CNNs (M-CNNs) are commonly adop-
ted when some sort of parallel processing of the input
data is desired. Such streams can eventually merge
into one in the latter layers of the network.
In recent works (Baccouche et al., 2011; Ji et al.,
2013), it is common for the point of concatenation to
be present before the first fully connected layer of the
network, that is, the parallel processing is concentra-
ted between the convolution layers. Action recogni-
tion, for example, is a problem that has been explored
with M-CNNs due to the difficulty of traditional CNN
in handling temporal information from input videos.
It is proposed in (Karpathy et al., 2014) a multi-
channel methodology capable of generating labels of
the main action in a video. In (Karpathy et al., 2014),
a 2-channel CNN is proposed, each channel receiving
two frames of the input video. Another advantage of
using M-CNNs is also highlighted by (Karpathy et al.,
2014) and it consists in reducing the dimensionality
of the network input, which helps to decrease the pro-
cessing time.
2.2.2 Architecture
The objective of the proposed approach is to basically
solve a regression problem: estimate the steering an-
gle given a set of images. Therefore, this work uses
as base a preexisting single channel CNN architecture
proposed by the comma.ai organization, described by:
Figure 1-(b) presents the diagram of the base
CNN. In more details, the network contains 13 lay-
ers and has 6,621,809 parameters to be learned. In
topological order, the layers are described by:
1. Normalization: an image in the RGB format is
given as input to the CNN, such that the value of
every pixel belongs to the interval [0, 255]. The
first layer of the network is responsible for nor-
malizing the pixel values to range [−1, 1]. Thus,
the following operation is executed:
w
0
=
w
127.5
− 1 (1)
Output dimension: 3 × 160 × 320
2. Convolution Layer (CONV): the parameters of
the first convolution layer are present in Table 1.
Table 1: Parameters of the first convolution layer.
N
o
of kernels Kernel dimension Stride 0-padding
16 8 × 8 4 × 4 2
Output dimension: 16 × 40 × 80
3. ELU
Output dimension: 16 × 40 × 80
4. Convolution Layer (CONV): the parameters of
the second convolution layer are present in Table
2.
Table 2: Parameters of the second convolution layer.
N
o
of kernels Kernel dimension Stride 0-padding
32 5 × 5 2 × 2 2
Output dimension: 32 × 20 × 40
5. ELU
Output dimension: 32 × 20 × 40
6. Convolution Layer (CONV): the parameters of
the third convolution layer are present in Table 3.
Table 3: Parameters of the third convolution layer.
N
o
of kernels Kernel dimension Stride 0-padding
64 5 × 5 2 × 2 2
Output dimension: 64 × 10 × 20
7. Flatten: flattens the input data. For example, if
the input has a 100x42 dimension, the output will
be a R
4200
vector. This step is done so that the spa-
tial information learned through the convolution
steps can be transferred to fully-connected layers.
Output dimension: 1 × 12, 800
8. Dropout: the dropout layer was originally propo-
sed by Srivastava et al. (Srivastava et al., 2014),
and it is used as a form of regularization to pre-
vent the occurrence of overfitting. This layer is
used just in the training phase, and its operation
consists in setting a value of 0 for each unity with
a probability of p.
Dropout probability: 20%
Output dimension: 1 × 12, 800
Autonomous Vehicle Steering Wheel Estimation from a Video using Multichannel Convolutional Neural Networks
519

9. ELU
Output dimension: 1 × 12, 800
10. Fully-connected layer (FC)
Output dimension: 1 × 512
11. Dropout: as in the previous dropout layer, it is
used only in the training step.
Dropout probability: 50%
Output dimension: 1 × 512
12. ELU
Output dimension: 1 × 512
13. Fully-connected Layer (FC): the last layer of the
CNN is fully connected with the 512 units from
the previous layer. It outputs h ∈ R, which con-
sists in the vehicle’s steering angle at the moment
the input image was captured.
Output dimension: 1 × 1
2.3 Proposed Architectures
From the base architecture presented in Subsection
2.2.2, this work proposes the construction of two
CNNs composed of multiple input channels, as shown
in Figure 1-(a). The motivation behind the idea is to
observe the impact that M-CNNs have in solving the
supervised problem of estimating a vehicle’s steering
angle, incorporating temporal and spatial information
obtained by the camera.
Following the original CNN architecture descri-
bed in Figure 1-(b), we propose a multichannel model
that processes the inputs in different channels until the
last ELU layer. In other words, the outputs of the last
ELU layers from each channel are concatenated and
are passed as input to the first fully connected layer.
2.4 Developed Models
After defining the dataset and the CNN architectures,
we now propose a framework used to generate all mo-
dels trained from scratch that are able to receive a set
of input images captured in a given instant by a vehi-
cle’s dash cam and output an estimation of the steer-
ing angle in such moment.
The proposed framework primarily consists in
modifying the original dataset to allow the multichan-
nel networks to be trained. Afterwards, 5 distinct ty-
pes of models are trained. Lastly, the trained models
can be tested and evaluated. More details about these
models are described in Section 2.4.2.
2.4.1 Dataset Preparation
The base CNN proposed by comma.ai has a single in-
put channel. Given that the methodology of this work
proposes the usage of M-CNNs (C1 for channel 1, C2
for channel 2 and C3 for channel 3), the original da-
taset (for future references, we will denote the origi-
nal dataset as BASE 1) had to be adapted, generating
four more versions of datasets. All these generated
datasets were inspired in the work developed by (Kar-
pathy et al., 2014) and are described as follows:
• BASE 2: original frame (C1) + frame subsampled
in 50% (C2).
• BASE 3: original frame (C1) + central region of
the image in original scale (C2).
• BASE 4: original frame (C1) + frame subsampled
in 50% (C2) + central region of the image in ori-
ginal scale (C3).
• BASE 5: frame subsampled in 50% (C1) + central
region of the image in original scale (C2).
Notice that the central region takes a 50% portion
of the original frame.
2.4.2 Training Models
Five different models were trained, each one used one
of the dataset versions presented in Section 2.4.1 and
are described as follows:
Model 1 (trained with BASE 1): In this model, the
original single channel CNN is used. This is done
for comparison with the other proposed models as a
reference model.
Model 2 (trained with BASE 2): The second model
uses the two-channel CNN architecture. In one chan-
nel it receives the original image and in the other one
it receives the same frame subsampled in 50%. He-
reby, we can observe how the CNN behaves with the
input given in different scales.
Model 3 (trained with BASE 3): The third model
uses the two-channel CNN architecture. In the first
channel it receives the original image and in the se-
cond channel it receives the original image’s central
ROI. Based on this model, we can observe how the
neural network can react when receiving a region of
the frame that probably contains objects closer to the
vehicle and that are present in the same road lane.
Model 4 (trained with BASE 4): The fourth model
uses the three-channel CNN architecture. The ob-
jective behind this model is to observe whether the
neural network can produce better results if the ad-
ditional information provided in models 2 and 3 are
ICINCO 2018 - 15th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
520

given as input at the same time, combined with the
original frame.
Model 5 (trained with BASE 5): The fifth model
uses the two-channel CNN architecture and it was ba-
sed on the idea of multi-resolution CNNs proposed by
Karpathy et al. (Karpathy et al., 2014), which introdu-
ces two input channels: fovea and context. The fovea
channel receives the central ROI of the input frame
in original resolution (resulting in a 160x80 ROI in
our dataset). The context channel receives the image
subsampled in 50% (also containing a 160x80 reso-
lution in our dataset). Thereby, the dimensionality of
the CNN input is halved, which can present a better
performance in terms of training time. Therefore, the
fifth model is proposed to observe the impact on how
M-CNNs can cause when receiving input with infor-
mation loss.
3 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
This section presents the results obtained based on the
datasets and CNN architectures detailed in the met-
hodology. The GPU used for training the proposed
models was an NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1070 and all
models were developed using the TensorFlow (Abadi
et al., 2015) and Keras (Chollet et al., 2015) frame-
works.
The performed experiments correspond to the
tests of the five models presented in the previous
section. Each model was trained in 200, 350 and 500
epochs, such that the epoch size is 10,000 examples.
Each training session with N epochs was repeated 3
times and each time the dataset was randomly partiti-
oned in training/validation/test subsets, following the
70/15/15 proportion schema.
Given that the proposed CNNs output the steering
angle using raw image data as input, it is crucial that
the model’s accuracy is correctly evaluated. All va-
lues presented in this section correspond to the error
that each trained model had for their corresponding
test set. The error is calculated between the estima-
ted vehicle’s steering angle and the ground truth angle
obtained with an internal sensor, which is provided by
the database.
The error measurement generally used to evaluate
the prediction of numerical values is the root of the
mean squared error (RMSE), which is described by:
RMSE =
s
1
n
n
∑
i=1
(y
i
− y
0
i
)
2
(2)
where n corresponds to the number of predictions, y
i
equals to the ground truth angle of the i-th example
and y
0
i
is the predicted steering angle given by the
CNN’s output. Thus, the lower the RMSE is, the gre-
ater is the model’s generalization capacity. In order
to enable the comparison between models trained un-
der different combinations of subsets, the normalized
form of the RMSE (NRMSE) was chosen. It is evalu-
ated in Equation 3:
NRMSE =
RMSE
y
max
− y
min
(3)
where y
min
and y
max
correspond to the lowest and gre-
atest angle values observed in the test set, respecti-
vely.
The values described in Table 4 shows the average
of the obtained NRMSE errors and the lowest values
for each epoch are highlighted. The graph presented
in Figure 2 shows the average of the obtained NRMSE
errors.
Table 4: Average test errors of all trained models.
200 350 500
Model 1 0.057548 0.047214 0.048096
Model 2 0.040906 0.046397 0.047917
Model 3 0.048535 0.038011 0.047673
Model 4 0.047513 0.046985 0.051179
Model 5 0.048974 0.051207 0.052770
3.1 Discussion
Based on the results obtained for each model present
in Figure 2, it is observed that the NRMSE values for
the multichannel models are similar between each ot-
her. However, it can be observed that the proposed
models have better performance when compared to
the reference model (i.e. Model 1). It is possible to
notice that the Model 3 trained for 350 epochs presen-
ted an average NRMSE of 0.038010, 7.07% less than
the second best model (i.e. Model 2 trained for 200
epochs).
Figures 3-(a) up to (e) show how the estimated an-
gles compare to the ground truth on some test videos.
It can be seen that the predicted angles are likely to
match the direction from the ground truth. Additio-
nally, it is observed that the models output subtle va-
riations in the steering wheel. Through the test charts,
it is also noted that the error is more expressive at the
beginning and end of the tests. This is due to the fact
that in the used database, the ends of the videos corre-
spond to the moment of entry and exit of the vehicle
inside a garage, an event that implies a great variation
in the steering angle.
On average, the models trained for 500 epochs did
not bring improvements in the results. Thus, it is ex-
Autonomous Vehicle Steering Wheel Estimation from a Video using Multichannel Convolutional Neural Networks
521

Figure 2: Average test errors of all trained models.
(a) (b) (c)
(d) (e) (f)
Figure 3: Figures (a) up to (e) show predicted outputs for models 1 up to 5 respectively trained for 200 epochs. In (f) it is
shown the training error variation of Model 5 trained for 500 epochs.
pected that the model should suffer from overfitting
when trained with more epochs, losing its capacity
for generalization. For example, notice in Figure 3-
(f) the training error of Model 5 trained for 500 epo-
chs. It can be seen that the error does not significantly
decrease after 200 epochs.
Finally, it is possible to perform a qualitative eva-
luation of the proposed models, following the idea
described in (Karpathy et al., 2014), by visualizing
the activation maps given as output by one of the con-
volution layers. Hence, Figure 4-(b) shows 16 acti-
vation maps produced by the first convolution layer
from Model 1 trained for 200 epochs, given the frame
on Figure 4-(a) as input to the network.
With the activation maps in Figure 4-(b), it is ob-
served that the filters from the first convolution layer
highlight the lane marks. In other words, the CNN
was able to detect the presence of visual elements in
the scene without being previously programmed to
perform such task. By finding the lane marks (Figure
4-(b)), it is possible that the network was able to learn
that the vehicle should keep itself between them while
estimating the steering angles.
4 CONCLUSIONS AND FURTHER
WORKS
This work proposes a methodology based on M-CNN
that is able to estimate the steering angle of a vehicle
ICINCO 2018 - 15th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
522

(a) Frame corresponding to the activation maps.
(b) Activation maps produced by the first convolution layer.
Figure 4: Activation maps from Model 1 trained for 200 epochs.
using only videos as input. As seen in Section 3, it
is possible to observe that the third proposed model
trained with 350 epochs obtained a lower NRMSE
when compared to the others, including the single
channel as reference model. Specifically in this mo-
del, it can be seen that M-CNNs provide significant
improvements in their use in autonomous vehicle ap-
plications. The performance of the best model was
approximately 7% better than the reference model.
Furthermore, the fifth model presents results simi-
lar to the others, showing that it was capable of main-
taining robustness even when receiving an input with
reduced dimensionality.
Future works may include the addition of explicit
space-time information during the training stage, cre-
ating new versions of datasets and training models,
exploring how M-CNNs architecture respond to this
information. Also, new datasets and more complex
situations must be tested to validate the approach.
REFERENCES
Abadi, M., Agarwal, A., Barham, P., Brevdo, E., Chen, Z.,
Citro, C., Corrado, G. S., Davis, A., Dean, J., De-
vin, M., Ghemawat, S., Goodfellow, I., Harp, A., Ir-
ving, G., Isard, M., Jia, Y., Jozefowicz, R., Kaiser,
L., Kudlur, M., Levenberg, J., Man
´
e, D., Monga, R.,
Moore, S., Murray, D., Olah, C., Schuster, M., Shlens,
J., Steiner, B., Sutskever, I., Talwar, K., Tucker, P.,
Vanhoucke, V., Vasudevan, V., Vi
´
egas, F., Vinyals, O.,
Warden, P., Wattenberg, M., Wicke, M., Yu, Y., and
Zheng, X. (2015). TensorFlow: Large-scale machine
learning on heterogeneous systems. Software availa-
ble from tensorflow.org.
Baccouche, M., Mamalet, F., Wolf, C., Garcia, C., and Bas-
kurt, A. (2011). Sequential deep learning for human
action recognition. In International Workshop on Hu-
man Behavior Understanding, pages 29–39. Springer.
Bojarski, M., Testa, D. D., Dworakowski, D., Firner, B.,
Flepp, B., Goyal, P., Jackel, L. D., Monfort, M., Mul-
ler, U., Zhang, J., Zhang, X., Zhao, J., and Zieba,
K. (2016). End to end learning for self-driving cars.
CoRR, abs/1604.07316.
Bojarski, M., Yeres, P., Choromanska, A., Choroman-
ski, K., Firner, B., Jackel, L. D., and Muller, U.
(2017). Explaining how a deep neural network trai-
ned with end-to-end learning steers a car. CoRR,
abs/1704.07911.
Chen, C., Seff, A., Kornhauser, A. L., and Xiao, J. (2015).
Deepdriving: Learning affordance for direct percep-
tion in autonomous driving. CoRR, abs/1505.00256.
Autonomous Vehicle Steering Wheel Estimation from a Video using Multichannel Convolutional Neural Networks
523

Chollet, F. et al. (2015). Keras. https://github.com/fchollet/
keras.
Goodfellow, I., Bengio, Y., and Courville, A. (2016). Deep
Learning. MIT Press.
Ji, S., Xu, W., Yang, M., and Yu, K. (2013). 3d convolu-
tional neural networks for human action recognition.
IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine
intelligence, 35(1):221–231.
Karpathy, A., Toderici, G., Shetty, S., Leung, T., Sukthan-
kar, R., and Fei-Fei, L. (2014). Large-scale video
classification with convolutional neural networks. In
CVPR.
Pomerleau, D. A. (1989). Alvinn: An autonomous land
vehicle in a neural network. In Touretzky, D. S., editor,
Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems
1, pages 305–313. Morgan-Kaufmann.
Srivastava, N., Hinton, G., Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I.,
and Salakhutdinov, R. (2014). Dropout: A simple way
to prevent neural networks from overfitting. J. Mach.
Learn. Res., 15(1):1929–1958.
Thorpe, C., Hebert, M., Kanade, T., and Shafer, S. (1988).
Vision and navigation for the carnegie-mellon navlab.
10(3):362 – 373.
Thrun, S., Montemerlo, M., Dahlkamp, H., Stavens, D.,
Aron, A., Diebel, J., Fong, P., Gale, J., Halpenny,
M., Hoffmann, G., Lau, K., Oakley, C., Palatucci, M.,
Pratt, V., Stang, P., Strohband, S., Dupont, C., Jen-
drossek, L.-E., Koelen, C., Markey, C., Rummel, C.,
van Niekerk, J., Jensen, E., Alessandrini, P., Bradski,
G., Davies, B., Ettinger, S., Kaehler, A., Nefian, A.,
and Mahoney, P. (2006). Stanley: The robot that won
the darpa grand challenge. Journal of Field Robotics,
23(9):661–692.
Wang, Q., Gao, J., and Yuan, Y. (2018). Embedding struc-
tured contour and location prior in siamesed fully
convolutional networks for road detection. IEEE
Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems,
19(1):230–241.
Zeiler, M. D., Taylor, G. W., and Fergus, R. (2011). Adap-
tive deconvolutional networks for mid and high level
feature learning. In 2011 International Conference on
Computer Vision, pages 2018–2025.
ICINCO 2018 - 15th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
524
