
Wearable Mind Thoughts Controlled Open Source 3D Printed Arm
with Embedded Sensor Feedback System
S. Hasan, K. Al-Kandari, E. Al-Awadhi, A. Jaafar, B. Al-Farhan, M. Hassan, S. Said and S. AlKork
College of Engineering and Technology, American University of the Middle East, Kuwait
Keywords: Robotic Arm, 3D Printer, EEG, Emotiv, Arduino, Inmoov, Prosthetic Arm, Mind Controlled.
Abstract: Number of amputees are increasing every year due to may causes such as vascular disease (54%) including
diabetes and peripheral arterial disease, trauma (45%), and cancer (less than 2%). The fields of brain
controlled and Medical applications for 3D printing are expanding rapidly and are gradually revolutionizing
the delivery of health care. Based on these two technologies, we set out to find the feasibility of a low-cost
wearable 3D printed arm to address the problem of amputation. This paper presents mind-controlled 3D
printed arm with embedded sensor feedback system. The aim of this project is to come up with a light-
weighted wireless 3D arm which can be portable, wearable and controlled using EEG headset. The given
criteria were set to be based on 3 factors: Weight, Cost and Battery Life. An open source 3D arm was printed
and controlled using an EEG headset to test the arms flexibility. The results show that the printed arm weighs
almost half of an average male arm (1.53KG). More over the Cost of the arm was considerably lower than a
surgical, prosthetic or static procedure with the deviation reaching up to a massive 8000% in the favour of the
robotic arm. The battery life is estimated to be about 0.5 to 1 day considering normal usage. Given that all
three factors fall in a reasonable range, it could be concluded that the future of 3D printed arms for amputees
is much bright, with more work to be done in the portability and mechanical design.
1 INTRODUCTION
Millions of people are suffering from disability which
prevents them from doing basic things that we take
for granted. Studies show that about 15% of the
world’s population suffers from some form of
disability (Hawking, 2011). Around 10 million of the
world’s population are amputees, and 30% of them
are arm amputees (LeBlance, 2011). Moreover, due
to many political, economic, and scientific reasons,
the overall rates of amputees and limb dysfunction
patients are increasing (NBC, 2010). People who are
suffering from amputation have difficulty to do their
daily life routine by themselves and they need assist
from others. There is a great way to help the
amputees, but they are either being incredibly
expensive and not everyone can afford, hard to install
and maintain, or it may require surgical procedures in
this case it relies on the nerves which in some cases
might be damaged. A lot of work is being done on the
lower body exoskeletons (Li, et al., 2016) (A.
Bennett, 2002). but this project focuses more on the
upper body. There has been a research done on
development of robotic arms such as the one
developed by the team in John Hopkin University
(Jeong, et al., 2000), but most of them are more
focused on the functionality rather than the real world
feasibility. The mind controlled 3D printed arm has
the potential to help amputees to preform many of
their daily activities normally (Beyrouthy, et al.,
2017), provide a better life, and improve the quality
of life. Also, it helps amputees to regain functionality
with natural control via brain waves. There are
several existing solutions such as surgical arm,
myoelectric-controlled arm, cosmetic restoration, and
bionic arm and each type has advantages and
disadvantages. One of the solutions for amputees is
having a prosthetic arm. Prosthetic arm needs to be
measured and specified to the patient needs. The
second solution is the surgical limbs, where the
patient will have a surgical operation to have a new
arm. The surgical method is considered to be very
costly. There are some problems that may happen due
to the surgical arm. For example, sometimes the
nerves may cause problem when they are damaged
totally, which could make it hard to perform surgery.
Also, the surgical method causes heart disease and
back pain in some patients. The amputees face
Hasan, S., Al-Kandari, K., Al-Awadhi, E., Jaafar, A., Al-Farhan, B., Hassan, M., Said, S. and AlKork, S.
Wearable Mind Thoughts Controlled Open Source 3D Printed Arm with Embedded Sensor Feedback System.
DOI: 10.5220/0006929701410149
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Computer-Human Interaction Research and Applications (CHIRA 2018), pages 141-149
ISBN: 978-989-758-328-5
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
141
nociceptive and neuropathic pain, due to bone and
soft tissue injury. On the other hand, the prosthetic
arm has less problems when compared to the surgical
arm. Prosthetic arm avoids many medical issues that
may happen. Table 1 shows comparison between
different arm types:
There are many techniques to control a robotic
arm. First method is to use an EEG device. The EEG
is a headset which records the brain waves when the
person is thinking of an action or implementing a
facial expression. The EEG will read signals and then
convert them to commands, to send them to the arm.
The second method is to have surgical implantation
for the person. In this method, the arm will be
connected to the person’s torso by performing
surgery. The aim of connecting the arm to the nerves
is to read the signals and then convert them to
commands. The last method is using sensors. The
sensors will be connected directly to the arm, and
would take the readings from the surroundings. Some
examples of such sensors would be EMG, gyroscope,
and accelerometer.
The objective was to implement a wireless mind
controlled 3D printed arm that can be controlled by
brain signals using an EEG headset. The EEG headset
is not only cost effective but accurate as well (
Beyrouthy, et al., 2016).In addition, the material for
building the arm had to be light-weight and high-
strength which could handle high impact while being
comfortable, as studies have shown that 64 % of the
amputees rate the comfort level of the prostheses as
fair or not acceptable (Davidson, 2002). Moreover,
the goal was to minimize the number of sensors used
i.e. to use the most important ones for preforming
normal hand activities. Also, making the 3D printed
arm wearable (Said S. et al, 2017), secure, light-
weighted, affordable, user friendly and easy to wear
and to take off. The arm was controlled via brain
signals obtained from EEG headset which is Emotiv
EPOC headset (Sayegh, F. et al, 2017). Different
mind states are captured and encoded to allow the arm
to react and execute pre-programmed series of actions
in specific cases.
Table 1: Comparison between different arm types.
Arm Type Cost Potential Flexibility Resistance
Bionic
Might cost
$36,000
Good potential especially
with the microprocessor
revolution
Depends on the
surroundings analyzing of
the processor
Optimum resistance as it
aware of its surroundings
Robotic
Might cost
$1150 - $1300
High potential with the
rise of 3D printers
Depends on the motors,
material and design
High resistance depends
on the motors
Surgical
Might cost
$10,000 -
$120,000
Very high potential
Depends on the training
and the physiotherapy
Different depending on
each case
Static
Might cost
$3,000 -$5,000
No potential Not flexible Low resistance
Prosthetic
Might cost
$10,000
Might be overshadowed by
the surgical and the robotic
limbs
Very high flexibility
because it is custom made
for each person with exact
measurements
Need less work to ensure
the best result
CHIRA 2018 - 2nd International Conference on Computer-Human Interaction Research and Applications
142

Table 2: Comparison between Different Arm Amputation Solutions.
Type Accuracy Cost Installation Degree of Control
EEG Accurate $100 750 Detachable Complete Control
Surgical
Very Accurate $10000- 120000 Permanent Complete Control
Sensors Accurate Under $100 Detachable Limited
2 STATE OF THE ART
The prosthetic technology is growing and getting
more advanced for the past years. Many companies
are developing 3D printed arms, such as Inmoov,
Open Bionics, Create O&P and e-nable.
Inmoov (Langevin, 2012) is one of the most
popular Open Source prosthetic arm, which contains
the parts for building a full robot. Building a full arm
does not require particular skills since it is easy to
learn and all the STL files are free to download. It is
also possible to adjust some parts to make it fit the
design. Inmoov requires 3D printer with at least 12 x
12 x 12 volume of printing, and filament either ABS
or PLA. Create O&P is a medical- technology
company in the orthotic and prosthetic industry
(Create O&P,2018). Create O&P arm is attractive,
light in weight, low-cost, and custom-made for each
patient. The arm is attached by using silicone
suspension sleeve. Open Bionics (Open Bionics,
2018) is a bionic company that developed an assistive
device which improve the human body. Open Bionic
is one of the most affordable bionic arms in the
market. Each arm is custom-built for patients that are
as young as nine. The arm is light-weighted,
comfortable, and breathable. The Open Bionics arm
has special sensors that detect muscle movements,
and the patient will effortlessly control it.
3 SYSTEM MODULES
The design consists of four modules: EEG Module.
Electromechanical Module, 3D Printed Arm Module
and Feedback Module.
3.1 EEG Module
First, Emotiv EPOC headset (Andrew, 2012.) reads
the signals from the brain and sends them (using
wireless communication) to USB dongle, which
connects to a PC. These signals are read by the
Emotiv Xavier software which are mapped to an
event into any combination of keystrokes. Apart from
that, a significant amount of training for different set
of actions like opening and closing hand, rotating the
wrist etc. was done which was then connected to the
keystrokes. These keystrokes are then sent to the
second module which is the electromechanical
module.
3.2 Electromechanical Module
In this module, we have XBee communication
between the PC and the Arduino UNO. We used two
XBee modules, one of them was attached to the PC
using XBee USB adapter, and the other one was
connected to the Arduino using XBee shield. Both of
the XBee modules are capable of sending and
receiving data. The first XBee module which was
connected to the PC sends the values to the XBee
module that is connected to the Arduino to perform
the movement. Based on this data, a certain arm
Wearable Mind Thoughts Controlled Open Source 3D Printed Arm with Embedded Sensor Feedback System
143
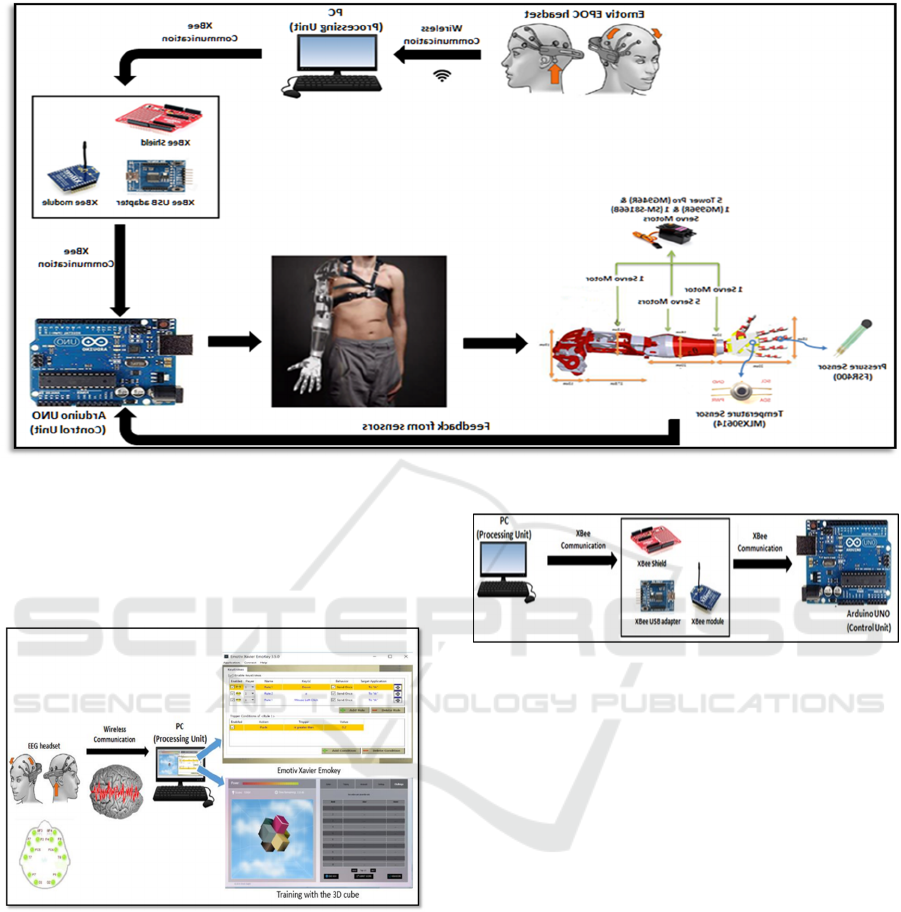
Figure 1: Mind Controlled 3D Printed Arm Design.
movement occurs. The XBee module that was
connected to the Arduino sends the sensor feedback
readings to the XBee module that was attached to the
PC to be printed on the terminal.
Figure 2: EEG Module.
3.3 3D Printed Arm Module
The third module is the 3D printed arm. In order to
create the full 3D printed arm, the open source
Inmoov design was used (Langevin, 2012). For the
testing purposes only the files for the right arm were
used Figure 4.
Figure 3: Electromechanical Module.
All the relevant parts were printed using PLA
filament and assembled with bolts, nuts and screws.
The final 3D printed arm is shown on figure 4. The
arm was designed in such a way that it remains light-
weight while maintaining high-strength. This was
important as the arm has able to handle several types
of objects with different weights.
3.4 Feedback Module
The last module is the feedback module, where the
sensors are connected to Arduino. Both the
temperature and pressure sensor were placed on the
fingers which were connected to the analog pins of
Arduino. This feedback system is important as the
person who using the arm will not have the sense of
feeling, this would help avoid any damages to the arm
from the surroundings. For the arm movements, 7
servomotors were used, 5 for the fingers, 1 for the
wrist and 1 for the elbow. All of them were connected
to the digital pins of Arduino.
CHIRA 2018 - 2nd International Conference on Computer-Human Interaction Research and Applications
144

Figure 4: 3D Printed Arm Module.
The communication between the sensors and
Arduino helps the arm to have the ability to respond
to the surroundings. The respond occurs when the arm
faces any objects. For example, if the arm wants to
hold something that is very hot, the temperature
sensor will avoid holding the object and the hand
would open. In the other case if delicate object is
being grabbed the pressure sensor would make sure
to avoid breaking the object as well as the finger
mechanism.
Figure 5: Feedback Module.
4 TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION
4.1 Hardware Overview
Using Emotiv EPOC headset, the user initiates brain
commands to control the arm. After the thinking
process, the headset will send the brain signals to the
PC, which then compares them to the training in the
Emotiv Xavier program. By using EmoKey each
signal is mapped to have its own keystroke that is
pressed while thinking of a certain action such as
push, pull, rotate. Using Arduino Ide, the signal is
processed that initiates a corresponding action by
controlling the servo motors. This data is sent to
Arduino UNO using XBee communication. Based on
certain values of the keystroke, motors are activated.
Since the user does not have the sense of feeling, a
feedback system which includes temperature sensor
and pressure sensor was added.
The temperature sensor is embedded on the finger,
so that while holding the object, the temperature
sensor will measure the temperature (at every angle).
If the temperature reading is too high for the human
skin or for the material to handle, an action will occur
to open the hand. After checking the temperature, if it
was not high then the pressure sensor checks the
pressure while holding the object. This allows the
fingers to stop at a redefined pressure. If both the
temperature and the pressure readings are safe, the
action of holding an object occurs.
Table 3: Main Hardware Components.
Component Input/output Analog/Digital
Temperature
Sensor
MLX90614
Input
Analog
Pressure Sensor
FSR400
Input Analog
Tower-Pro
MG946R Servo
Motor
Output Digital
SM-S8166B
Servo Motor
Output Digital
XBee Module
Input
Output
Analog
EEG headset
(Emotiv EPOC)
Input Analog
Wearable Mind Thoughts Controlled Open Source 3D Printed Arm with Embedded Sensor Feedback System
145
4.2 Power Consumption
The Emotiv EPOC headset uses a lithium (Li) battery
that can be used for up to 12 hours continuously when
fully charged. If the headset is fully discharged it will
take 4 hours to be fully charged.
Thus, mind controlled 3D printed arm needs
batteries that can make the arm operate for about 7 to
8 hours of continues usage. Furthermore, the arm
weight should be suitable for the person and
comfortable. Two lead Acid batteries are used
separately in order to let the arm operate for longer
time, one of them is 6V with an output current of 7Ah,
and the other one is 6V with output current 4.5Ah.
Given the table below the total ampere required to
operate the arm is added to be 3.92A. With this usage,
the arm will operate for about 2 continuous hours.
Since a person moves their arm for about 1 to 3 hours
per day on an average depending on the activity
performed, the system can work for approximately
0.5 to 1 day. We calculated the power consumption
for each component as shown in Table 4 using
Equation 1
∗
(1)
Table 4: Power Consumption Calculation.
Component Power Consumption
Arduino UNO 5V * 0.05A = 0.25 W/h
MG996R Servo Motor 5V * 0.9A = 4.5 W/h
MG946R Servo Motor 5V * 0.95A = 4.75 W/h
SM-S8166B Servo Motor 5V * 2A = 10 W/h
FSR400 Pressure Sensor 5V * 0.01A = 0.05 W/h
MLX90614 Temperature
Sensor
5V * 0.01A = 0.05 W/h
5 SYSTEM FLOWCHART
5.1 Flowchart Scenario
Step 1: The user will have the ability to initiate brain
commands to control the arm, after the thinking
process, the headset will read the signals then
compare it to the database of the Emotiv Xavier. After
that, signal processing will be performed to obtain a
corresponding action. Finally, the data will be sent to
Arduino and based on the XBee values servo motors
will be active.
Step 2: If the value of the XBee equals to 1, then
“Action 1” command occurs; thus, the user will be
able to open the hand.
Figure 6: Open Action 1.
Step 3: If the value from the XBee equals to 2,
then “Action 2” command occurs, the servo motor in
the bicep that controls the fingers will close to a
certain degree which will make the hand closes and
will help in holding the object.
Step 4: The temperature sensor is embedded on
the hand palm so that while holding the object, the
temperature sensor will measure the temperature. If
the temperature sensor reading is too high for the
human skin or for the material to handle, “Action 1”
will occur and this will open the hand.
Figure 7: Close Action 2.
Step 5: If the temperature was not high then the
pressure sensor will check the pressure of holding the
object, if pressure was detected, the servo motors will
stop at that position.
Step 6: If the result of both the temperature and
the pressure sensors are safe and the value of the
XBee equals to 3, “Action 3” will occur which will
make the hand rotate to a certain angle then “Action
1” will occur to open the hand and throw the object.
Finally, we will have a delay and after the delay
"Action 4" will occur and the hand will rotate back to
the initial position.
CHIRA 2018 - 2nd International Conference on Computer-Human Interaction Research and Applications
146

Figure 8: Rotate Action 3.
6 DESIGN CONSTRUCTION,
TESTING AND
IMPROVEMENT
The construction of the arm started with fingers. The
fingers were attached and connected to the servo
motors (MG946R). The hand was tested with the
temperature and pressure sensors. For the wrist the
MG9996R servo motor was used. The hand and the
wrist were tested with the headset with four actions,
which were close hand, open hand, rotate wrist right,
and rotate wrist left. Emokey was used to map the
signals with different keystrokes and send it to
Arduino.
Figure 9: Testing fingers' Movements with sensors
Figure 10: Emotiv Headset Training (Xavier Control
Panel).
Figure 11: EPOC Headset Testing.
The strings were re-adjusted (of the fingers) to
make sure that they move in a synchronized motion.
After completing the hand, wrist, and forearm, the
sensors were attached to the hand.
Figure 12: Testing the Arm Actions.
For the wireless communication the XBee module
was added. The XCTU program was used to start the
communication between two XBee modules, one of
the modules was attached to XBee adapter and
connected to the PC, and the other module was
attached to XBee shield that was connected to
Arduino. Both of XBee modules act as TX (sender)
and RT (receiver).
The final step was assembling the elbow and the
bicep. The SM-S8166b servo motor was used for the
elbow. The servo motor had some fitting issues, as the
Inmoov used different servo motor, which were fixed.
However, it worked fine at the end. Figure 13 shows
the final implementation of the project. After
completion of the hardware the total weight of the
arm without the battery and electronics was measured
which came out to be 1.53 KG.
Figure 13: Attaching the Arm to Mannequin.
Wearable Mind Thoughts Controlled Open Source 3D Printed Arm with Embedded Sensor Feedback System
147
7 PROJECT COST
The cost of the project is divided into two parts which
are the components (servo motors, sensors, XBee,
Arduino UNO and Emotiv EPOC headset, two Lead
Acid batteries), and the 3D printing cost. All the
required components are relatively inexpensive. The
total cost of the design is estimated to be around
$1451 as shown in Table 5.
Table 5: List of Main Components.
Components Cost
Emotiv EPOC Headset $840
Servo Motors $88
Sensors $66
3D Arm $233
Arduino UNO Microcontroller $39
XBee Communication $123
Batteries $62
Total $1451
8 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
WORK
At the completion of building the 3D printed arm and
assembling the needed sensors, the arm movements
controlled successfully using EEG headset. Thus, the
technology of brain controlled and printing 3D
materials lead up to create a wearable light-weighted
affordable arm that has feedback system. Despite
getting good results there is a lot of work still to be
done in order to make the 3D printed arm a reality.
One area to be explored is to control the arm using
facial expressions in addition to the mind control.
Facial expressions can be an alternative option for the
amputee when his mind signals cannot be detected
easily because of noises or if the user is not relaxed
and does not act normally, so the needed signals
which are muscles sensors will be detected using his
facial expressions such as smiling, blinking, looking
right and left, clenching, laughing, etc. Moreover,
Raspberry Pi as a processing unit instead of PC could
be added in order to get portable arm. Some small
additions like attaching LCD screen to the arm to
show the sensors readings could also improve the
overall user experience. Another aspect in the
improvement is the appearance of the arm which
could be greatly improved by adding silicon giving it
a more natural look.
In conclusion, the number of amputees is
increasing year by year in the world due to several
reasons such as cancer, trauma, explosions, and
diabetes. As a result, amputation prevents people
from doing their daily life activities and leads them to
depend on others. Actually, there are many solutions
in the market but they are either incredibly expensive
or require surgical procedures that relies on nerves
which in some cases might be damaged. Thus, in this
project we came up with an affordable design that can
help amputees to depend on themselves by
performing their daily routine which helps them to
raise their self-esteem and provide them with a better
life. A 3D printed arm that is controlled by brain
signals using EEG headset and equipped with most
important sensors that gives a feedback and avoid any
damaging or breaking in the arm.
Results show that the printed arm weighs almost
half of an average male arm (1.53KG). More over the
cost of the arm was considerably lower than a
surgical, prosthetic or static procedure with the
deviation reaching up to a massive 8000% in the
favour of the robotic arm. The battery life is estimated
to be about 0.5 to 1 day considering normal usage.
Given that all three factors fall in a reasonable range,
it could be concluded that the future of 3d printed
arms for amputees is much bright, with more work to
be done in the portability and mechanical design.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We would like to thank the American University of
the Middle East that gave us the opportunity to carry
out our research. We would also like to thank the
Robotics Research center for funding the project
providing us such great facilities and assistance
throughout our research.
REFERENCES
Beyrouthy, T., K Al Kork, S., Akl Korbane, J. &
Abdulmonem, A., 2016. EEG Mind controlled Smart
Prosthetic Arm. Balaclava, Emerging Technologies and
Innovative Business Practices for the Transformation of
Societies (EmergiTech), IEEE International.
A. Bennett Wilson, J., 2002. History of Amputation
Surgery and Prosthetics. [Online]
CHIRA 2018 - 2nd International Conference on Computer-Human Interaction Research and Applications
148

Andrew, 2012. Neourosky Mindwave Mobile Rewiew.
[Online] Available at: https://neurogadget.net/2012/
12/20/neurosky-mindwave-mobile-review/6611.
Davidson, J., 2002. A survey of the satisfaction of upper
limb amputees with their prostheses, their lifestyles,
and their abilities. Journal of Hand Therapy, pp. 62-70.
Hawking, S. W., 2011. World Report on disability, Geneva:
World Health organization.
NBC, 2010. Limb loss a grim, growing global crisis.
[Online] Available at: http://haitiamputees.nbcnews.
com/_news/2010/03/19/4040341-limb-loss-a-grim-
growing-global-crisis
LeBlance, M., 2011. Give Hope - Give a Hand. [Online]
Available at: Available: https://web.stanford.edu/
class/engr110/Newsletter/lecture03a-2011.html
Jeong, Y., Lee, D., Kim, K. & Park, J., 2000. A wearable
robotic arm with high for reflection capability. Osaka,
9th IEEE International Workshop on Robot and Human
Interactive Communication, pp. 411-416.
Langevin, G., 2012. Build Yours InMoov. [Online]
Available at: http://inmoov.fr/build-yours/
Li, J. et al., 2016. A Robotic Knee Exoskeleton for Walking
Assistance and Connectivity Topology Exploration in
EEG Signal. UTown, 6th IEEE RAS/EMBS
International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and
Biomechatronics (BioRob).
Said, S., AlKork, S., Beyrouthy, T. & Abdrabbo, M. F.,
2017. Wearable Bio-Sensors Bracelet for Driver’s
Health Emergency. Paris, Bio-engineering for Smart
Technologies (BioSMART),IEEE.
Sayegh, F. et al., 2017. A Wearable Rehabilitation Device
for Paralysis. Paris, Emerging Technologies and
Innovative Business Practices for the Transformation
of Societies (EmergiTech), IEEE International
Open Bionics. (2018). Hero Arm - an affordable, advanced
and intuitive bionic arm. [online] Available at:
https://openbionics.com/hero-arm
Create O & P. (2018). Create Prosthetics. [online]
Available at: https://www.createoandp.
S. K. A. Kork, I. Gowthami, X. Savatier, T. Beyrouthy, J.
A. Korbane and S. Roshdi, "Biometric database for
human gait recognition using wearable sensors and a
smartphone," 2017 2nd International Conference on
Bio-engineering for Smart Technologies (BioSMART),
Paris, 2017, pp. 1-4.
Taha Beyrouthy, Samer Al. Kork, J. Korbane, M.
Abouelela, "EEG Mind Controlled Smart Prosthetic
Arm – A Comprehensive Study", Advances in Science,
Technology and Engineering Systems Journal, vol. 2,
no. 3, pp. 891-899 (2017).
Wearable Mind Thoughts Controlled Open Source 3D Printed Arm with Embedded Sensor Feedback System
149
