
Static Balance Performance and Sensory Integration Abilities of
Children with Dyslexia and Developmental Coordination Disorder
M. Nunzi
2
, F. Sylos Labini
3,4
, A. Meli
2
, S. Baldi
2
, D. Tufarelli
2
and C. Di Brina
1
1
Department of Mental Health (Child Neuropsychiatry), ASL of Viterbo, Italy
2
ENT Rehabilitation Unit, San Raffaele Pisana Scientific Institute Tosinvest Sanità, Via della Pisana, Rome, Italy
3
Laboratory of Neuromotor Physiology, IRCCS Fondazione Santa Lucia, Rome, Italy
4
Center of Space BioMedicine, University of Rome Tor Vergata, Rome, Italy
Keywords: Dyslexia, Developmental Coordination Disorder, Sensory Organization Test, Balance.
Abstract: Introduction: Postural dysfunctions are described in Developmental Disorders: the static balance deficit is
one of the major features of Developmental Coordination Disorder (DCD) and is reported in Dyslexic
Children. With computerized dynamic posturography (CDP) balance can be assessed objectively. The
primary aim of this study was to assess the postural function in DCD and Dyslexic in comparison with a
Control Group (CG) using CDP.
Subjects and Methods: Forty-seven children (29 males e 18 females) were assessed using all the six
conditions of the Sensory Organizing Test (SOT). 18 CG children (mean age 9.66 ± 1.96 years), 15
Dyslexic children (mean age 9.78 ± 1.09 years) and 14 DCD children (mean age 8.35 ± 1.79 years) were
included.
Results: DCD had poorer balance measured with the SOT score in every condition (p<0.05) except in SOT
3 (p= n.s.) compared to the CG. Dyslexic children had a good postural control compared to the CG, except
in SOT 5 (p = 0.02).
Conclusions: CDP showed that the DCD group had, as expected, a poorer balance than DD and CG. It is
possible to differentiate Dyslexics from the CG only in SOT 5, indicating that the postural disturbance of
this group is probably of primarily central vestibular origin. The somatic-sensory input had the same
influence on balance function in the three groups.
1 INTRODUCTION
The sensory integration is a physiological process in
selecting and combining appropriate sensory
information from somatosensory, visual and
vestibular systems. The Sensory Organization Test
(SOT) of the Computerized Dynamic Posturography
(CDP), is an objective measure of sensory
integration during balance performances. SOT
evidences more data and information than clinical
tests, using an objective analysis of balance function
(Nashner, 1997).
SOT analysis can help to identify the cause of
instability and the patient’s balance strategies
(Nashner, 1997; Prieto et al., 1996). But few studies
adopt CDP on Developmental Disorders in children.
Balance problems are described in children with
Developmental Dyslexia (DD) and Developmental
Coordination Disorder (DCD): whereas balance
impairment is a common feature and a "core"
symptom in DCD (Fong and Tsang, 2012), few
studies have investigated whether deficits in
multisensory integration may contribute to poor
standing balance in children with DCD
(Deconinck
et al., 2008). Geuze (2005) claims that under normal
conditions, static balance control is not a problem
for these children. For the majority of them, this
problem seems not to be due to greater dependence
on vision.
Moreover experimental studies resulted in the
general conclusion that DCD children had deficits in
standing balance control in conditions that included
reduced (in particular visual and vestibular) or
conflicting sensory signals (Fong and Tsang, 2012),
showing more postural sway in either one-legged
(Geuze, 2005) or two-legged stance (Przysucha and
Taylor, 2004). Converging evidence indicates that
cerebellar dysfunction contributes to the motor
problems of children with DCD. Objective
measurements confirmed these results evidencing, in
150
Nunzi, M., Labini, F., Meli, A., Baldi, S., Tufarelli, D. and Brina, C.
Static Balance Performance and Sensory Integration Abilities of Children with Dyslexia and Developmental Coordination Disorder.
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Computer-Human Interaction Research and Applications (CHIRA 2018), pages 150-155
ISBN: 978-989-758-328-5
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reser ved

a small sample of DCD, an altered pattern in the
SOT (Inder and Sullivan, 2005).
Literature on balance control in DD is
inconclusive: motor performance difficulties in DD
are attributed to a disorder in visual processing
(Stein and Walsh, 1997), in rapid information
processing (Tallal et al., 1993), and some studies
reported a postural control impairment and a
cerebellar deficit (Fawcett and Nicolson, 1999).
Nicolson et al. (1999), reported motor coordination
and balance deficits in dyslexic children population.
Other authors suggested that the balance impairment
was not strictly correlated with dyslexia but also
with other types of developmental disorders ( such
as comorbidity with Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity
Disorder (ADHD) (Raberger and Wimmer, 2003).
These opposite findings in the literature on the
argument could be influenced by differences in the
assessing processes: the use of different tasks in
evaluating balance, such as measuring the balance
only on the right or left foot (Stoodley et al., 2005),
the use of subjective measures of postural control
(Fawcett and Nicolson, 1999) and the evaluation of
dyslexic children only in the "eyes open" condition
(Moe-Nilsen et al. 2003).
The aim of this study was to assess postural
control of a DCD sample through the objective
measure of CDP, and to compare their balance
performances with DD children without co morbid
attention deficits and with a matched CG.
2 METHODS
Forty-seven children participated in the study. All
participants demonstrated adequate familial
environment, middle socio-economic status and
Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children Revised
over 90. No child had attention-deficit disorder,
epilepsy, mental retardation, cerebral palsy,
psychiatric disorders, or other neurological signs,
congenital malformations, or phoniatric alterations,
neither peripheral vestibular disorder and inner ear
disease as referred by the anamnesis and the clinical
evaluation. Subjects were divided in three groups: a
control group (CG) of 18 children (mean age 9.66 ±
1.96 years), a group of 15 dyslexic children (DD)
(mean age 9.78 ± 1.09 years) and a group of 14
DCD children (mean age 8.35 ± 1.79 years). The
diagnosis of DD and DCD was done according to
DSM-IV criteria. Children included in the DCD
group scored below the 15th percentile on the total
impairment score on the Movement-ABC
standardized test. Written informed consent to
participate in the study was obtained by parents of
all children. The study was approved by the IRCSS
San Raffaele, Hospital of Rome Pisana, Institutional
Internal Review Board. Postural control function
was assessed by SMART EquiTest 8.0 (NeuroCom
Int., Inc., Clackamas, OR, USA) instrument, using
static and dynamic CDP. This instrument has been
adopted as the only method to isolate the functional
contributions of vestibular inputs, visual inputs,
somato-sensory inputs, central integrating
mechanisms, and neuromuscular system outputs for
postural and balance control (Black, 2001) and the
instrument meets the testing standard for CDP set by
the American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head
and Neck Surgery and the American Academy of
Neurology. All subjects were evaluated using the
Sensory Organization Test (SOT) of Dynamic
Posturography (Equitest© Neurocom). The SOT
analyses the postural control and the contributions of
different sensory systems to balance control during 6
conditions, each test condition was examined three
times for 20 seconds with a 20-second break
between tests. Six different conditions (A-F) were
used in order to examine the subject’s balance
control performance under different sensory
conditions that we will call C1, C2, C3, C4, C5, C6
(Table 1, Table 2).
The force plate and visual surround are “sway
referenced” so that they can move to follow the
anterior-posterior sway of the subject. The six
conditions of the SOT are called Equilibrium Scores
(ES), that are obtained by comparing the maximum
anterior-posterior CoG displacements to a theoretical
maximum displacement. The ES ranges between 0
and 100. Lower ES indicate increased body sway
peak-to-peak amplitudes. The score of “0” was
recorded if the subject falls, touches, or gripes
reference for protecting. Nobody sway results in a
perfect score of “100.” The Composite Equilibrium
Score (CS) is a synthetic index of equilibrium and is
a mean value from the scores of all six conditions.
The CS is evaluated as a weighted average of one
subject’s equilibrium scores from six conditions of
the SOT: CS={ES(1)+ ES(2) +3[ES(3)+ ES(4)
+ES(5)+ ES(6)]}/14.
Statistical Analysis. We used one-way ANOVA to
evaluate differences between groups in mean
Composite Score, Condition Scores and in Sensory
Analysis Scores. We performed the multiple
comparison of the means using the post-hoc Tukey-
Kramer test. Pearson correlation coefficients were
used to analyze the relationship between age and
Condition Scores. Reported results are considered
significant for p < 0.05.
Static Balance Performance and Sensory Integration Abilities of Children with Dyslexia and Developmental Coordination Disorder
151

Table 1: Sensory input conditions during SOT.
Sensory condition description
Accurate Sensory
Sensory loss
Sensory conflict
C1. (A) Eyes open, fixed support
Visual, vestibular,
somatosensory
None
None
C2. (B) Eyes closed, fixed support
Vestibular, somatosensory
Visual
None
C3. (C) Eyes open, sway-referenced visual
surround
Vestibular, somatosensory
None
Visual
C4.(D) Eyes open, sway-referenced
platform
Visual, vestibular
None
Somatosensory
C5. (E) Eyes closed, sway-referenced
platform
Vestibular
Visual
Somatosensory
C6.(F) Eyes open, sway-referenced visual
surround and platform
Vestibular
None
Visual, somatosensory
Table 2: Six conditions (A–F) of SOT.
Figure 1: Composite Score and Condition Scores. Average (+SD) composite and condition scores across different groups
(Control: control group, DD: children with Developmental Dyslexia, DCD: children with Developmental Coordination
Disorder). Asterisks denote significant (Tukey-Kramer post-hoc test p < 0.05) differences.
3 RESULTS
The data showed significant differences in the
results of SOT among groups (p-value < .001)
(Fig.1); the 40% of DD children and 93% of DCD
children had a lower CS, than the mean value of CG.
The results of our CG were similar to that reported
in literature (Steindl et al., 2006).
The DD group had scores similar to control
values in all conditions, except for condition 5.
The mean C5 score of DD was similar to the
mean C5 score of DCD group and was significantly
CHIRA 2018 - 2nd International Conference on Computer-Human Interaction Research and Applications
152
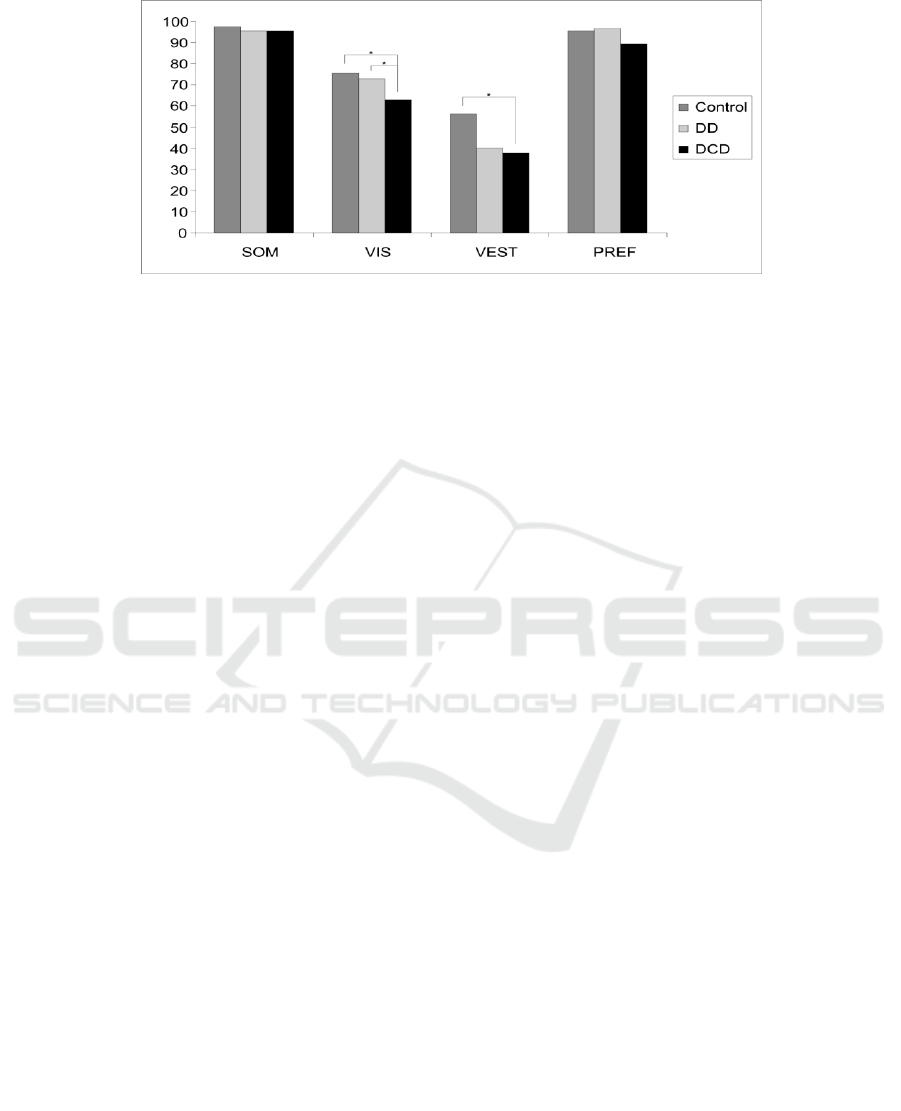
Figure 2: Sensory Analysis of Control group, DD and DCD groups. Asterisks denote significant (Tukey-Kramer post-hoc
test p < 0.05) differences.
poorer than control group (p-value = .020).
Furthermore, 53% of DD children had a lower score
in condition 5 than control children. The DCD
children had significantly worse results than the
other two groups in all conditions (p-value < .05)
except for Condition 3. In this condition there were
no significant differences among groups (p-value =
.524)
Moreover, 71% of DCD children had a lower
score in condition 5 than control group. Correlations
between age and condition scores were not found
(Pearson correlation coefficient < .60). The results of
sensory analysis showed that the somato-sensory
input had the same influence on balance function in
the three groups. Nevertheless in the DCD children
the use of visual and vestibular information in
maintaining balance was significantly less efficient
than controls. The DD children had a similar result
to DCD group for the vestibular afference, but a
normal use of visual information in maintaining
equilibrium (Fig.2).
4 DISCUSSION
Our results showed balance performances and
different sensorial patterns in two different groups of
children with Developmental Disorders. The
strategies of DD and DCD groups, during balance
tasks, were different from those adopted by CG. We
found a significantly lower balance control of DCD
group than other groups in upright standing
condition (condition 1 and condition 2), even if their
poorer performances were in tasks with sway-
platform (condition 4, condition 5 and condition 6).
These findings are consistent with previous literature
reporting a larger dependency of DCD children on
vision and difficulties in integrating visual and non-
visual information (Wann et al., 1998). Our DCD
children perceived a sway visual surround as a
negligible input in maintaining balance, their scores
were normal in conditions with visual reference
sway (condition 3). This result indicated a normal
ability to discriminate a destabilizing visual input,
which is a cortical function. Geuze (2005) found that
an improvement in conflicting sensory inputs can
occur with eyes open. It seems that the unavailability
of an important sensory information such as visual-
perception can influence the quality of postural and
balance control in DCD Children. Postural control
problems may possibly be associated with
difficulties to re-weight sensory information in
response to environmental demands (Deconinck et
al., 2008).
In summary, we observed poorer static postural
control ability in children with DCD compared with
Controls and the vestibular system failed to
effectively integrate sensory information of
insufficient and/or inaccurate visual or somato-
sensory perception, thus leading to loss balance.
However in the visual conflict they could maintain
balance (condition 3).
Our DD children showed significant impairment
of balance control with increasing task difficulty
(i.e., reduction or conflict of sensory inputs) which is
consistent with others findings: some motor
impairment in relatively complicated balance tasks
(dual-tasks) and in presence of conflicting sensory
inputs (Huxhold et al., 2006). Balance performances
of our sample showed that DD children had a normal
composite score. Balance function in DD group was
better than DCD group, however in DD children we
found higher incidence (53%) of poor balance
performances in complex tasks (condition 5). The
poor balance performance of DD children in this
task is associated with the visual exclusion and to
grounding on vestibular information (somato-
sensory conflict); DD children had a lower
Static Balance Performance and Sensory Integration Abilities of Children with Dyslexia and Developmental Coordination Disorder
153

performance with eyes closed. These findings are in
contrast with findings from other authors reporting
lower balance performances of dyslexic children in
eyes open tasks (Moe-Nilssen et al., 2003; Stoodley
et al., 2005) or normal postural stability in both
conditions (Brown et al., 1985). A possible
explanation of these differences can resides in the
balancing task proposed by these authors. It is well
established that postural stability is task dependent
(Cho and Kamen, 1998).
The stance position with eyes open could be too
easy for DD children; these tasks may not be able to
evidence balance control impairment in patients with
a normal somato-sensory and visual afferents. These
children in fixed surface with eyes open condition
use information from somato-sensory and visual
systems to maintain upright position.
Ramus and colleagues, who found evidence of
impaired balance control in dyslexic children,
related it to an altered vestibular pattern (Ramus et
al., 2003). Our data similarly indicated poor
vestibulo-spinal postural control.
Several studies evidenced the activity of
cerebellum and basal ganglia in sensory-motor
integration function and in learning, furthermore,
their role is still unclear (Waber et al., 2004).
5 CONCLUSION
In conclusion, this study, in accordance with
previous reports, provided evidence suggesting that
DCD and Dyslexic children have impaired postural
stability compared to children of similar age.
The small sample size is the main limitation of
this study and these findings could be explored
further with a larger sample. In agreement with the
hypothesis of sensori-motor deficit in DD and DCD,
these children could suffer of a sensory multimodal
integration difficulties.
REFERENCES
Black, F.O. (2001) What can posturography tell us about
vestibular function? Ann NY Acad. Sci; 942: 446-464.
Brown B., Haegerstrom-Portnoy G., Herron J., Galin D.,
Yingling CD., Marcus M. (1985) Static postural
stability is normal in dyslexic children. J Learn
Disabil; 18(1): 31-34.
Cho CY, Kamen G (1998) Detecting balance deficits in
frequent fallers using clinical and quantitative
evaluation tools. J Am Geriatr Soc 46:426–430.
Deconinck F.J.A., De Clercq D, van Coster R, Oostra A,
Dewitte G, Savelsbergh GJR, Cambier D, Lenoir M.
(2008) Sensory contributions to balance in boys with
developmental coordination disorder. Adapt Phys Act
Q.;25(1):17–35.
Fawcett A.J., Nicolson R.I. (1999) Performance of
Dyslexic Children on Cerebellar and Cognitive Tests.
J Motor Behav; 31(1): 68-78.
Fong, S.S., Tsang W.W., Ng G.Y..(2012) Altered postural
control strategies and sensory organization in children
with developmental coordination disorder. Human
Movement Science., 31: 1317-1327.
Geuze, R.H. (2005).Postural control in children with
developmental coordination disorder. Neural
Plasticity. Vol. 12, No. 2-3.
Huxhold, O, Li, SC, Schmiedek, F, Lindenberger,
U.(2006) Dual-tasking postural control: aging and the
effects of cognitive demand in conjunction with focus
of attention. Brain Res Bull.; 69:294–305.
Inder J.M., Sullivan S.J. (2005) Motor and postural
response profiles of four children with developmental
coordination disorder. Pediatr Phys Ther; 17(1): 18-
29.
Moe-Nilssen, R., Helbostad, J.L., Talcott, J.B.,
Toennessen, FE. (2003) Balance and gait in children
with dyslexia. Experimental Brain Research; 150(2):
237-244.
Nashner L.M., Posturographic Testing. In: Kartush JM,
Jacobson GP, Newman CW editors, Handbook of
Balance Function Testing. Clifton Park, NY: Thomson
Delmar Learning, 1997.
Nicolson RI., Fawcett AJ., Berry EL., Jenkins IH., Dean
P., Brooks DJ. (1999) Association of abnormal
cerebellar activation with motor learning difficulties in
dyslexic adults. Lancet; 353(9165): 1662-1667.
Prieto TE, Myklebust JB, Hoffmann RG, Lovett EG,
Myklebust BM. Measures of postural steadiness:
differences between healthy young and elderly adults.
IEEE trans biomed eng 1996; 43(9): 956-966.
Przysucha EP., Taylor MJ.(2004)Control of stance and
Developmental Coordination Disorder: The role of
visual information. Adapt Phys Activ Q; 21: 19-33.
Ramus F., Pidgeon E., Frith U.(2003) The relationship
between motor control and phonology in dyslexic
children. J Child Psychol Psyc; 44(5): 712-722.
Raberger T. & Wimmer H. (2003) On the
automaticity/cerebellar deficit hypothesis of dyslexia:
balancing and continuous rapid naming in dyslexic
and ADHD children. Neuropsychologia; 41(11): 1493-
1497.
Stein J., Walsh V. (1997) To see but not to read; the
magnocellular theory of dyslexia. Trends Neurosci;
20: 147-152.
Steindl R., Kunz K., Schrott-Fischer A., Scholtz AW.
(2006) Effect of age and sex on maturation of sensory
systems and balance control. Dev Med Child Neurol;
48: 477-482.
Stoodley, C.J.,Fawcett, A.J., Nicolson, R.I.,Stein, J.F.
(2005) Impaired balancing ability in dyslexic children.
Exp Brain Res, 167: 370–380.
CHIRA 2018 - 2nd International Conference on Computer-Human Interaction Research and Applications
154

Tallal P., Miller S., Fitch RH. (1993) Neurobiological
basis of speech: a case for the preeminence of
temporal processing. Ann NY Acad Sci; 682: 27-47.
Waber DP., Forbes PW., Wolff PH., Weiler MD.(2004)
Neurodevelopmental characteristics of children with
learning impairments classified according to the
double-deficit hypothesis. J Learn Disabil ; 37(5):
451-461.
Wann J.P., Mon-Williams M., Rushton K. Postural control
and co-ordination disorders: The swinging room
revisited. Hum Movement Sci 1998; 17: 491-513.
Static Balance Performance and Sensory Integration Abilities of Children with Dyslexia and Developmental Coordination Disorder
155
