
Parameter Matching and Simulation Study
on the
R
an
g
e Extender of Extended
R
an
g
e Electric Vehicles
Limian Wang
1
, Do Chen, Shumao Wang and Zhenghe Song
College of Engineering,China Agricultural University, Qinghua East Road, Haidian District Beijing,China
1
Faculty Secretary Office, Beijing Automotive Technician College, Caiyu Town, Daxing Beijng, China
wlmjt2003@126.com, {tchendu, wangshumao, songzhenghe}@cau.edu.cn
Keywords: Range extender, Parameter matching, Simulation.
Abstract: Vehicles are used more and more widely as a means of daily travelling, which has led to serious problems
such as air pollution and energy shortage. This has stimulated interests in development of electric vehicles
in many countries. In recent years, the focus of the development is geared towards extended range electric
vehicles in order to resolve the drawback from short continued driving mileage of traditional electric
vehicles. The core of the extended range electric vehicle is the range extender. The parameter matching
design for the range extender and the related power system components is carried out in the paper based on
automobile theory while the simulation study is carried out by using Cruise software.
1 INTRODUCTION
As one of the greatest achievements of modern
industrial development, vehicles have offered great
convenience for people's daily travelling. But a
large number of vehicle usages have caused a series
of negative impacts to our society, such as air
pollution, energy shortage and so on. To tackle
aforementioned problems, electric vehicle
development has attracted attentions worldwide.
However, problems residing in the core components
of electric vehicles, the technology and cost of
power battery, the poor availability of charging
stations, and the short driving range have imposed
limits on promotion and usage of electric vehicles.
This has become an imminent driving force for
performance improvement of the extended range
electric vehicle.
Extended Range Electric Vehicle (E-REV) is
mainly driven by electric power. As an electric
supplement, the range extender is composed of a
small engine and a generator, and it can make up for
the power supply of electric vehicles when the usual
mileage is exceeded. This provides an advantage
that the vehicle’s power supply does not depend on
the charging station.According to statistics, 80%
user’s daily travel mileage is less than 80km. The
number of batteries equipped with 80km in the pure
electric drive mode is greatly reduced compared
with that for vehicles with driving range of 200km.
As a result, this greatly reduces weight and cost of a
vehicle.
2 PARAMETER MATCHING OF
POWER SYSTEM RELATED
COMPONENTS
2.1 Vehicle Parameters
In this paper, an extended range electric vehicle is
selected as the study prototype, and its sample
parameters are shown in table 1 and table 2.
Table 1: The design parameters of the vehicle
Parameter name and unit Value
Curb weight m
0
(kg) 1500
Full load weight m
1
(kg) 1940
Frontal area A (m
2
) 2.2
Air resistance coefficient C
D
0.32
Rolling resistance coefficient 0.014
Tire radius r (m) 0.275
Reduction gear ratio i
g
i
0
7.9
Transmission efficiency
0.95
550
Wang, L., Chen, D., Wang, S. and Song, Z.
Parameter Matching and Simulation Study on the Range Extender of Extended Range Electric Vehicles.
In 3rd International Conference on Electromechanical Control Technology and Transportation (ICECTT 2018), pages 550-554
ISBN: 978-989-758-312-4
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

Table 2: The technical index of vehicle performance
Index name and uni
t
Technical target
Maximum speed (km/h) 130
Acceleration time (0-100km/h) (s) 13.2
Maximum climbing degree 30%
Energy consumption rate
under the pure electric mode (NEDC)
(kWh/100km)
≤15
(90km/h) Extension mileage
under the pure electric mode S
0
(km)
(DOD=70%)
≥80
(60km/h)Extension mileage
under the pure electric mode
S
1
(km)
≥80
2.2 Parameter Design of the Drive
Motor
Motor is the critical component for good power
performance of the extended range electric vehicle.
In the parameter matching process, the smallest
number of system parameters is used to meet the
dynamic requirements of the design index. The main
parameters such as the base speed n
0
, the maximum
speed n
max
, the rated power P
0
, the peak power P
max
and the peak torque N
max
need to be matched (Hu He,
2012). Prior to matching the parameters of the
driving motor, the parameters of the transmission
system have to be determined first. The motor has
the characteristic of delivering constant torque at
base speed and delivering constant power between
the base speed and the maximum speed (Dong
Xinyang, 2012), which makes it ideal to meet the
speed and torque requirements of the vehicle. As
shown in table 1, the speed ratio of the transmission
system is tentatively defined as 7.9.
2.2.1 The Base Speed n
0
and the Maximum
Speed n
max
The designed maximum speed of the drive motor
should meet the requirement as stated in this
formula:
0
max
max
377.0
ii
rn
V
g
In the formula, v
max
(km/h)
is the designed
maximum speed of the vehicle, r (m) is the tire
radius, i
g
i
0
is the total transmission ratio of the
transmission system (value of 7.9 is taken in this
paper). Values for each respective parameter are
shown in table 1 and table 2. These input values
yield results of n
max
≥ 9906r/min, and n
max
=
10000r/min.
The relationship between the maximum speed
n
max
and the base speed n
0
of the motor is defined as
below.
0
max
n
n
In the formula,
is the constant power expansion
coefficient. The greater its value, the greater the
output torque of the motor at low speed, and the
better the corresponding starting and climbing
performance of the vehicle. But it will increase the
size of the power converter if the value is too large.
The reasonable value is 2-4(Deng Chunrong, 2014).
Based on these values, 2500
≤
n
0
≤5000
is obtained.
In this paper,
is defined as 3.3, and the base speed
n
0
equals to 3300 r/min.
2.2.2 The Rated Power P
0
and the Peak
Power P
max
The power balance equation for the vehicle driving
is shown as below.
dt
du
muU
A
D
C
mgumgfu
e
P
aaa
2
15.21
sincos
3600
1
In the formula, P
e
(kW) is the drive motor power,
is the transmission efficiency, m (kg) is the vehicle
weight, g (m/s
2
) is the gravitational acceleration. is
the rolling resistance coefficient,
(°) is the slope
angle, C
D
is the air resistance coefficient, A(m
2
) is
the frontal area,
is the rotary mass conversion
coefficient, du/dt(m/s
2
) is the acceleration.
The motor demand power and the maximum
speed.
The relationship between the motor demand
power and the maximum speed must satisfy the
formula below (Yu Zhisheng, 2006).
3
maxmax
761403600
1
v
AC
v
mgf
P
D
u
The vehicle weight for the test is taken as,
m=m
0
+180kg (Wang Da, 2015). Using values from
table 1 and above vehicle weight produces P
1
=
22.3kW.
The motor demand power and the
acceleration time between 0 km/h to100km/h.
The motor power required to meet the
acceleration performance of the vehicle is stated as
below(Yu Zhisheng, 2006).
322
5
1
3
2
21000
1
fDafbf
a
a
AvCmgfvvv
t
m
P
In the formula,
is a constant with value of 1.06,
t
a
(s) is the acceleration time between 0 to 100 km/h.
v
f
(m/s) is the speed at the end of acceleration, which
equals to 12m/s.
a
is the air density, which equals
to 1.202Ns
2
m
-4
. The other parameters are same as
above. These input values yield P
2
= 74.33kW.
Parameter Matching and Simulation Study on the Range Extender of Extended Range Electric Vehicles
551

The motor demand power and the maximum
climbing degree and the corresponding
climbing speed.
Substituting the vehicle weight with full load
weight (m=m
1
), the motor power demand under the
requirements of different speed and climbing degree
of the vehicle can be obtained.
3
76140
cossin
3600
a
D
a
i
V
AC
f
mgv
P
In the formula,
is the maximum climbing
degree. v
a
is the climbing speed, which is 20km/h.
The other parameters are same as above. These input
values produce P
3
= 22.3kW.
In the design, the drive motor rated power is
usually based on P
1
, and the peak power is
determined by P
2
and P
3
as below (Xu Chengfu,
2014).
10
PP
32max
,max PPP
For the conditions of the drive motor rated power
P
0
= 25kW, and the peak power P
max
= 75kW, the
overload coefficient of the motor is 3.
2.2.3 The Rated Torque T
0
and the Peak
Torque N
max
The relationship between power, torque and speed is
stated as below.
n
P
T
9550
Using n=n
0,
the rated power P
0
and the motor
peak power P
max,
the motor rated torque T
0
from the
above formula is 79.6 Nm, and T
0
is rounded to 80
Nm. The peak torque P
max
equals to 239 Nm, and is
rounded to 240 Nm. The drive motor characteristic
parameters are shown in table 3.
Table 3: The drive motor parameters
Parameter name and unit Value
Rated power P
0
(kW)
25
Peak power P
max
(kW)
75
Rated speed n
0
(r/min)
3300
Maximum speed n
max
(r/min)
10000
Rated torque T
0
(Nm)
80
Peak torque T
max
(Nm)
240
3 PARAMETER MATCHING OF
THE RANGE EXTENDER
3.1 Generator Parameter Design
When the power drawn from the battery is
insufficient during vehicle running, the range
extender begins to work and provides energy to the
vehicle. In the paper, the range extender output
power can ensure that the vehicle runs at the
constant speed of v
c
, which is 130km/h.
mc
cD
c
RE
AvC
mgfv
P
3600
15.21
3
In the formula,
mc
is the drive motor efficiency,
and
mc
with value of 0.9 is used here. The other
parameters are same as above. Using these values
produces, P
RE
≥ 33.49kW, and this is rounded to
36kW. The parameter matching of the generator is
shown in table 4.
Table 4: The generator parameters
Parameter name and unit Value
Rated power(kW) 36
Peak power(kW) 46
Rated torque(r/min) 3000
Peak torque(r/min) 4000
3.2 Engine Parameter Design
In the paper, the generator will start working only
when the SOC of the power battery reaches the
lower limit. At this point, the battery will be
recharged and then transmits the energy to the drive
motor. In this way, the vehicle can continue to move
forward at certain speed, while the maximum power
meets the power demand of the vehicle's maximum
speed.
For the case of the speed v
c
= 130km/h, the motor
output power is calculated as follows:
kW
AvC
mgf
v
P
cD
mc
c
mc
72.31
15.213600
2
With motor efficiency
mc
of 0.9, the power
supplied to the motor by the battery is
31.72kW/0.9=35.24kW. With battery discharging
efficiency
b
of 0.95, the power of the generator
ICECTT 2018 - 3rd International Conference on Electromechanical Control Technology and Transportation
552
provided to battery charging is 35.24kW
/0.95=37.09kW. In the end, the continuous output
power of the engine is selected as 40kW.
The engine peak power P
c_max
should be
satisfied with the following formula.
gen
RE
fc
P
P
max_
max_
In the formula, P
RE_max
(kW) is the peak power of
the range extender, which is also the generator peak
power.
gen
is the generator efficiency, which equals
to 0.9. These input values yield, P
c_max
≥51.1kW.
The final selected engine parameters are shown in
table 5.
Table 5: The engine parameters
Parameter name and unit Value
Displacement(L) 1.5
Peak power(kW) 52
Maximum speed(r/min) 4200
4 PERFORMANCE
SIMULATION AND ANALYSIS
4.1 Pure Electric Mileage in the NEDC
Conditions
In the paper, Cruise is used for simulation of pure
electric driving mileage according to the NEDC
conditions. The simulation results show that the pure
electric mileage is close to 80km, which meets the
design requirements.
4.2 Drive Motor Torque under the
Pure Electric Mode
From the curve of the drive motor torque, it can be
seen that the vehicle speed trends well under the
NEDC conditions, while the drive motor executes
the energy recovery function smoothly, as shown in
figure 1.
Figure1: The curve of the drive motor torque
4.3 The Generating Torque of the
Range Extender
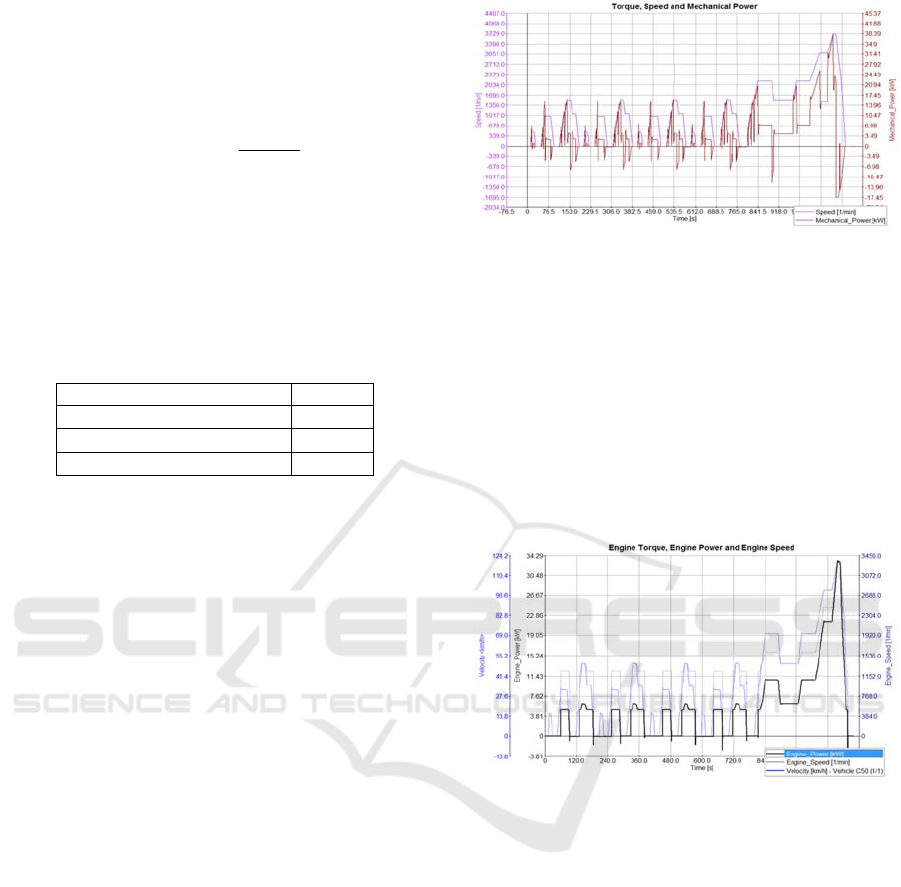
It can be seen from the curve of the range extender
torque that the range extender starts up when the
starting conditions are met and stops when the shut-
down conditions are encountered, as shown in figure
2.
Figure 2: The curve of the range extender torque
5 CONCLUSIONS
In the paper, parameter matching and design on a
prototype vehicle are carried out according to
pertinent automobile theory.
This study has demonstrated that the pure
electric driving mileage meets the design
requirements. The study further illustrated that the
drive motor can achieve good energy recovery, and
the range extender can meet the start-up and
shutdown requirements.
Parameter Matching and Simulation Study on the Range Extender of Extended Range Electric Vehicles
553

ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This paper is financially supported by the Thirteen
Fifth National Key Research and Development
Program of China (Grant No. 2016YFD0700102).
REFERENCES
Hu he. Parameters design and performance optimization of
the power system of the range extended electric
vehicle [D], Changchun, Jilin University, 2012.
Dong Xinyang. A study of control strategy design and
optimization for the powertrain of the range extended
electric vehicle [D], Hefei, Hefei University of
Technology, 2012.
Deng Chunrong. Design and study on the permanent
magnet synchronous motor used in electric vehicles
[D]. South China University of Technology, 2014.
Yu Zhisheng. Automobile theory [M]. Beijing, Machine
Press, 2006.
Xu Chengfu. Study on parameter matching and
optimization of driving system and control strategy for
Range-extended electric vehicles [D].Hefei, Hefei
University of Technology, 2014.
Wang Da, Wang Bo. Research on Driving Force Optimal
Distribution and Fuzzy Decision Control System for a
Dual-motor Electric Vehicle [A]. Chinese Control
Conference[C]. Hangzhou: Institute of Electrical and
Electronics Engineers, 2015.
ICECTT 2018 - 3rd International Conference on Electromechanical Control Technology and Transportation
554
