
Analysis of System Design of SIPKD (Regional Financial
Management System) and SIM PAD (Locally-Generated Revenues
Management Information System) Integration in Order to Fulfill the
Need for Preparing an Accrual-Based Financial Statements
Case Study in The Provincial Government of Jakarta
Masithoh Titania and Machmudin Eka Prasetya
Magister of Accounting, Faculty of Economics and Business, Universitas Indonesia, Jakarta, Indonesia
msth.titania@gmail.com, machmudin.prasetya@yahoo.com
Keywords: Analysis of System Information Design, FAST Method, SIM PAD, SIPKD, System Integration.
Abstract: This research aims to determine the needs of information systems required by The Provincial Government
of Jakarta in related to the management of retribution revenue and other locally-generated revenues, to find
out what is required by SIM PAD and SIPKD in the framework of the management of retributions and other
locally-generated revenues, and to analyze the integration of SIM PAD and SIPKD in order to create an
integration model for the two systems in order to facilitate the preparation of accrual-based financial
statements. This research is a qualitative research with case study method at The Provincial Government of
Jakarta. The result of this research shows that the problem in managing the retribution revenue and other
locally-generated revenues is that the systems being used are not fully integrated, thus causing the reporting
of the revenues-LO, receivable, and allowance for doubtful account for retribution and other locally-
generated revenues still being done manually and not in accordance with the accrual base accounting cycle.
Therefore, this research will produce a design for integration plan within SIM PAD and SIPKD in order to
produce accurate and reliable data, in result to meet the need for accrual-based government accounting
standard implementation.
1 INTRODUCTION
2016 is a challenging year for government financial
management, especially in the case of financial
statements, as in accordance with the mandated
Government Regulation Number 71 Year 2010
(hereinafter referred to as PP 71 Year 2010) that the
deadline for accrual government-based accounting
implementation is at the time of preparation of
financial statements fiscal year 2015. Prior to 2015
government agencies are still permitted to use
Government Regulation Number 71 of 2010
Appendix II, which is cash-based toward accruals
similar to Government Regulation No. 24 Year 2005
(hereinafter referred to as PP 24/2005). The adoption
of accrual-based government accounting has had a
major impact on government financial reporting that
previously used the cash-based toward accruals,
particularly in recognition for each accrual-based
account. In addition to the issue of recognition the
number of reports should be presented also increased
from the previous 4 (four) reports into 7 (seven)
reports. The additional three new reports are
Statement of Operational Activities (LO), Statement
of Changes in Surplus Budget Balance, and
Statement of Changes in Equity.
Implementation of accrual-based government
accounting is of course a challenge for the
Provincial Government of Jakarta, the main problem
in the spotlight is the problem of information
systems. In 2017 the Provincial Government of
Jakarta has several independent systems in
accordance with their designation. These systems are
not integrated because of their development by
different work units. These stand-alone systems
make the preparation of financial statements more
difficult and longer because data from each of these
systems should be reconciled with existing data in
SIPKD as the main system of financial management
392
Titania, M. and Prasetya, M.
Analysis of System Design of SIPKD (Regional Financial Management System) and SIM PAD (Locally-Generated Revenues Management Information System) Integration in Order to Fulfill
the Need for Preparing an Accrual-Based Financial Statements - Case Study in The Provincial Government of Jakarta.
In Proceedings of the Journal of Contemporary Accounting and Economics Symposium 2018 on Special Session for Indonesian Study (JCAE 2018) - Contemporary Accounting Studies in
Indonesia, pages 392-399
ISBN: 978-989-758-339-1
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

in the Provincial Government of DKI Jakarta. In
addition to making it difficult and time consuming,
with no integration of the system the preparation of
financial statements to be incompatible with the
appropriate accounting cycle.
Two systems that become the object of this
research is SIPKD (Regional Financial Management
System) and Locally-Generated Revenues
Management Information System (SIM PAD), some
of the things underlying are:
1) Reporting of Retribution and other locally-
generated revenue-LO account and retribution
and other locally-generated receivable account,
do not go through the appropriate accounting
cycle. The revenue-LO and receivable account is
journalize only in reporting period, not at the
time of the transaction occurred and only for
account that have balance at the end of accouting
period.
2) Reporting of Retribution Revenue-LO account
and Retribution Receivable account do not use
SIPKD. as described in the preceding point, the
journal process is only made at the end of the
accounting period, so in SIPKD the data for that
account is only available during the reporting
period and is only available for accounts that
have balance at the period.
Satrio, et al (2016) in their research states that
one of the obstacles in the application of accrual-
based accounting is the problem of information
systems that do not support accrual based accouting
and not fully integrated with each other. Kusuma
(2016) also in their research stated that Constraints
in the implementation of accrual-base government
accounting standard is the preparation of financial
statement still done manually using microsoft excell
because there is no special software for accrual
based government accounting standard.
Based on these matters, this research aims to
analyze the needs of information systems required
by the Provincial Government of Jakarta related to
the management of retribution and other locally-
generated revenues and to analyze design of SIM
PAD and SIPKD integration to create an integration
model for both systems so as to facilitate the
preparation of accrual based financial statements
through the appropriate accounting cycle and
generate more reliable data.
This research will analyze current condition of
SIM PAD and SIPKD. this study does not just
extend the current finding of the information system
requirements for the needs of accrual-based
government accounting standard, but also propose
an appropriate system development model for the
needs of accrual-based governement accounting
standard in terms of retribution and other locally-
generated revenues management. In creating the
integration and development model for SIM Pad and
SIPKD researchers will use FAST Method and
middleware.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Information System
The system is one or more components that are
interconnected and interact to achieve the goal. Most
systems consist of small sub-system components
that support a large system. Each sub-system is
created to achieve one or more organizational or
company goals. While information is data that has
been prepared and processed to give meaning to
improve decision making process. Increasing the
quantity and quality of information will make users
make better decisions. (Romney and Steinbart,
2012).
Information system is an arrangement of people,
data, processes and information technology that
interact to collect, process, store, and provide as
output the inforation neededto support an
organization (Whitten and Bentley, 2007).
Organizations or companies need the help of
information systems that can assist in running
company or organization activities. Information
systems also help in management's decision-making.
this is also applies to government entities.
Permana, et al (2016) and Sophian (2016) in
their research stated information systems have a
significant influence in the implementation of
accrual-based government accounting standard. the
higher the readiness of information systems will
affect the readiness of accounting accrual-based
accounting
2.2 Middleware
Middleware is a generic term used to described
software that mediates with other software and
allows for communication between disparate
applications in a heterogeneous system (Connolly
and Begg, 2014). Hurwitz (1998) defines six main
type of middleware:Asynchronous Remote
Procedure Call (RPC), synchronous RPC,
publish/subscribe, message-oriented middleware
Analysis of System Design of SIPKD (Regional Financial Management System) and SIM PAD (Locally-Generated Revenues Management
Information System) Integration in Order to Fulfill the Need for Preparing an Accrual-Based Financial Statements - Case Study in The
Provincial Government of Jakarta
393

(MOM), Object Request Broker (ORB) and SQL-
oriented data access.
Al Jaroodi, et al (2010) stated in their paper that
currently midlleware is essential component for
almost any tipe of of distributed environment and
network applications. Starting from the hardware
infrastructure and run-time support all the way up to
the applications, middleware solutions provide
endless possibilities to support applications
requirements both functional and non-functional.
They believe that in the near future we will have
more generic middleware solutions that will provide
clean interfaces, dynamic functionalities and
adaptive operating criteria to support a wide range of
networked applications and operating environments
Al-Jaroodi, et al (2011), stated in their research that
middleware can play an important role in facilitating
the design, development and implementation of
service-oriented systems and furthermore,
middleware approaches will provision non-
functional requirements like performance,
scalability, reliability, flexibility and quality of
service (QoS) assurance.
2.3 Framework for the Application of
System Thinking (FAST)
In analyzing and designing the development and
integration of SIM PAD and SIPKD, we used the
FAST (Framework for the Application of System
Thinking) method. The Framework for the
Application of System Thinking is a compilation of
best practices found in many reference and
commercial methods. FAST is a flexible framework
to support different types of strategies and projects
(Bentley and Whitten, 2007).
The stages in the FAST methodology are as follows:
1. Scope Definition
The first phase of the FAST methodology is
scope definition, this phase has the dual function
of first answering the question "is this problem
worth calculating?", And secondly assuming the
problem is worth taking into account, it sets the
size and constraints of the project.
2. Problem Analysis
The second phase is problem analysis, in this
phase studying the current system and analyzing
the findings to give the project team a better
understanding of the problems that triggered the
project.
3. Requirement Analysis
In this phase the project team determine and
prioritizing business needs, in order to generate a
system requirements analysis report, system
analysts should be close to the user system to
identify their needs and priorities.
4. Logical Design
In this phase the project team changes the form
of business needs from the form of words to the
image form known as the system model to
validate the completeness and consistency of the
business needs.
5. Decisions Analysis
The objectives of this phase are to (1) identify
technical solution candidates, (2) analyze
solutions of candidates for feasibility tests, and
(3) recommend candidate systems as target
solutions to be designed.
6. Physical Design and Integration
The purpose of this phase is to change the
business needs (partly represented by the system
model) into physical design specifications that
will guide the development of the system.
7. Construction and Testing
There are two objectives of this phase: (1) to
build and perform system tests that meet
business needs and physical design
specifications; and (2) implementation of
interfaces between the new system and the
current system.
8. Installation and Delivery
In the last phase performed by the team is to
provide a good transition from the old system to
the new system.
9. System Operation and Maintenance
After the system operates, it is necessary to
support system (support system) continuously.
From the nine FAST stages that described above,
this study is limited to only the fourth stage of FAST
Method.
Ariyani (2014) and Firdaus (2016) in their
research using FAST methodolgy for their research,
because FAST methodology is an agile method that
provide alternatives routes and strategies to
accommodate different types of project, technology
goals, developer skills and development paradigms.
3 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3.1 Research Methods
This research is a qualitative research with a
descriptive analysis. This approach is chosen to
address the research purposes that has been
JCAE Symposium 2018 – Journal of Contemporary Accounting and Economics Symposium 2018 on Special Session for Indonesian Study
394

described about what is the requirement of
retribution and other locally-generated revenues
system that must be fulfilled by The Provincial
Government of Jakarta in order to implement the
accrual based accounting and how does the design of
integration of SIM PAD and SIPKD help The
Provincial Government of Jakarta in preparing the
accrual bases financial report more efficient and
reliable.
This research is single case study with one unit
of analysis. Object in this research is regional
finance management board (BPKD) of The
Provincial Government of Jakarta. This research
focuses on the management of retribution and other
locally-generated revenues in order fulfill the needs
for preparing an accrual based financial statement.
We took a case study of the phenomena in BPKD
Provinsi DKI Jakarta as regional finance
management board. The selection of case study
method based on problems occur in BPKD Provinsi
DKI Jakarta that requires direct involvement of
researchers in this research.
This study uses primary data sources obtained
directly from BPKD. The use of primary data
sources aims to support the objectives of this study
which are to understand how the systems works and
to propose an design of integration between the two
systems.. We used several research instrument to
support data collection process as follows:
1. Interview
We conducted interview with the revenues
division, treasury division, information system
division and accounting division. The interview
aims to obtain an understanding how SIM PAD
and SIPKD works and to obtain the information
about user requirement and expectations.
2. Document Analysis
We analyzed several internal documents in the
form of certain government accounting standard,
governor regulation about retribution and other
locally-generated revenues management, and
structure of SIM PAD and SIPKD. This method
aims to obtain an overview of accrual based
government accounting standard and the
retribution and other locally-generated revenues
management process.
3.2 Data Analysis
This study uses a deductive approach, data analysis
produce a conclusion that originated from the theory
or model or main framework used as the basis of
conclusions. We use qualitative descriptive method
to elaborate, describe and compare the data obtained
during the research. We use the data collected to
analyze the integration design of SIM PAD and
SIPKD. This analysis will generate information on
how the two systems works and what development
is needed for both systems in order to fulfill the
needs for preparing the accrual based financial
report . We also developed a design for integration
between SIM PAD and SIPKD using FAST Method.
The results of interviews, document analysis will
generate scope definition, problem analysis and
system requirement as the basis to develop the
integration design.
4 RESULT
4.1 Scope Definition and Problem
Analysis
To analyze information system needs in order to
better management of retribution and other other
locally-generated revenues and reporting in
accordance with accrual based government
accounting standards, the researchers performs
scope definition, problem analysis and system
requirement in FAST method.
In the scope definition stage, we do PIECES
framework analysis proposed by James Wetherbe
(Whitten and Bentley, 2007), it is called as PIECES,
because the letters of each of the six categories of
PIECES, the categories are Performance,
Information, Economics, Control, Efficiency and
Service. The result of the PIECES framework
analysis is the problem statement. After the scope
definition process is completed and the problem
statement and scope of system development have
been determine then the researcher performs the
problem analysis. we conduct the analysis of
problem related to the system that currently used
SIM PAD and SIPKD. The following is the
identification of the problems and consequences that
arise from the currently unintegrated SIM PAD and
SIPKD.
The following is the identification of the
problems and consequences that arise from the
currently unintegrated SIM PAD and SIPKD.
Analysis of System Design of SIPKD (Regional Financial Management System) and SIM PAD (Locally-Generated Revenues Management
Information System) Integration in Order to Fulfill the Need for Preparing an Accrual-Based Financial Statements - Case Study in The
Provincial Government of Jakarta
395

Table 1 List of Problems, Impact and Solutions
No
Problem
Impact
Solution
1
The reporting of revenues-LO
accounts, accounts receivable for
retribution and other locally-
generated revenues is done manually.
• The reporting process becomes
longer, because reconciliation is
required for each account and each
SKPD (work unit).
• The process of preparing the
financial statements is inconsistent
with the appropriate accounting
cycle.
• Unable to generate financial reports
at any time
Integrated SIM PAD with
SIPKD so that data for
revenues-LO account,
receivables and allowance for
doubtful account for
retribution and other locally-
generated revenues are
transferred from SIM PAD to
SIPKD
2
Calculation and reporting for
allowance for doubtful account
retribution and other locally-
generated revenues is done manually
using ms excel.
• The value of the account that goes
into the financial statements is
potentially miscalculated and
incorrect input
• Unable to present account
allowance for doubtful account
retributions and other locally-
generated revenues at any time
Additional menu is required
for the calculation of
allowance for doubtful
account retributions and
other locally-generated
revenues.
3
The menu for payment validation on
SIPKD does not suitable with
SIMPAD
Unable to validate payment from SIM
PAD to SIPKD
A new user interface is
required to validate payment
data with the data in bank
statement.
4
There is no database for revenues-LO
at SIPKD to accommodate the
assignment and payment data from
SIMPAD
Reporting of revenues-LO accounts is
done manually
An additional database for
revenues-LO and additional
menus in SIPKD should be
created.
4.3 Requirement Analysis
After the current problem is known and understood,
the next step is to conduct the requirement analysis
to make the system able to overcome the problem.
These requirements include the system's ability to do
the following:
1. The system can generate revenues-LRA account,
revenues-LO account, accounts receivable, and
allowance for doubtful account retribution and
other locally-generated revenues in the financial
statements of the Provincial Government of
Jakarta.
2. The system can simplify the process of preparing
financial statements from previously done with
the manual process, to be more effective and
efficient.
3. The system can generate operational reports
every month, not only during the financial
reporting period
4. The system can generate revenue report data for
retribution and other PAD more accurate and
complete
4.4 Logical Design
The integration between SIMPAD and SIPKD is
done through a middleware application in charge of
translating data from SIMPAD into a format
readable by SIPKD and then sending it to SIPKD on
daily basis. Diagram of system integration between
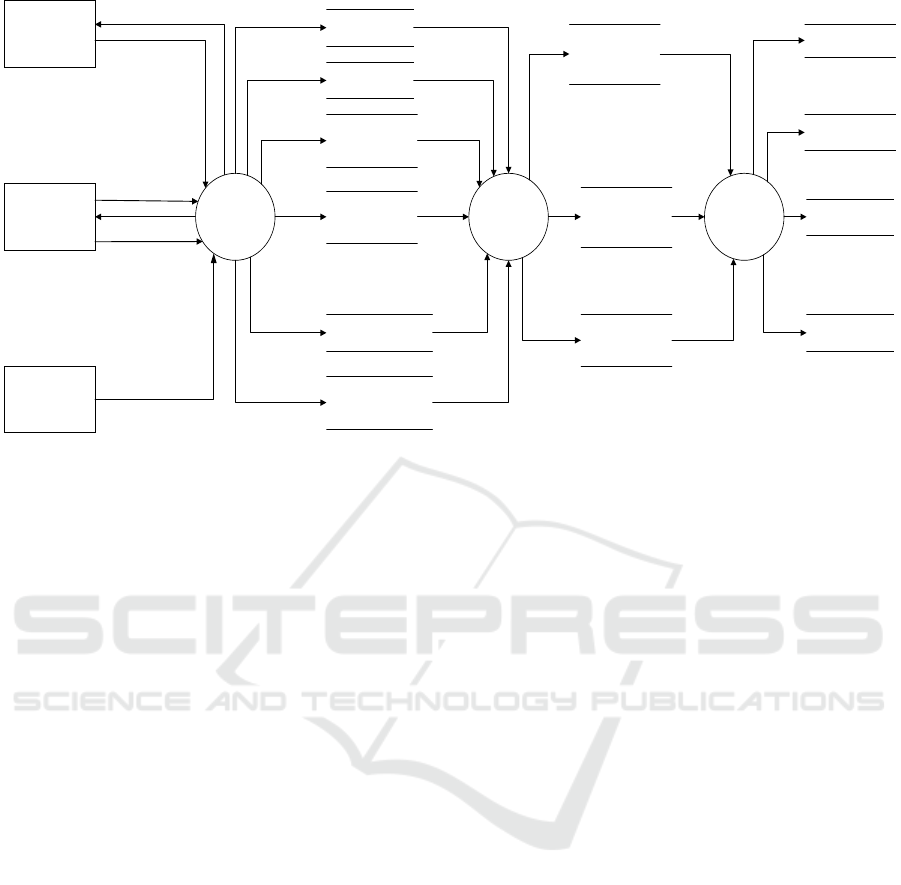
SIM PAD and SIPKD can be seen in figure 1.
JCAE Symposium 2018 – Journal of Contemporary Accounting and Economics Symposium 2018 on Special Session for Indonesian Study
396
Retribution and Other
Locally-Generated
Revenues Payer
Permit and
deposit submission
SKRD/STS
Bank
SKRD/STS Data
NTPD
Sistem Kependudukan
dan Catatan Sipil
Civil Registration Data
SIM PAD
Credit Note &
Bank Statement
Middleware
Receivable and
Allowance for Retribution
Receivable
Receivable and
Allowance for Other
Locally-Generated
Revenues Receivable
Retribution Payment After
Validation
Other Locally-Generated
Revenues Payment After
Validation
Receivable and
Allowance for Retribution
and Other Locally-
Generated Revenues
Receivable
SIPKD
Other Locally-Generated
Revenues Charge
Retribution Charge
Retribution & Other
Locally-Generated
Revenues Charge Data
Retribution & Other
Locally-Generated
Revenues Payment Data
Revenues-LO Journal
Revenues-LRA Journal
Adjustment Journal
General Ledger
Figure 1 Diagram of System Integration Between SIM PAD and SIPKD
Based on figure 1, the following is Mapping data
transfer that is done from SIMPAD to SIPKD
through middleware:
1. Data transfer from retribution charge record and
other locally-generated revenues charge record in
SIM PAD into retribution and other locally-
generated revenues charge record in SIPKD.
2. Data transfer from retribution payment record
and other locally-generated revenues payment
record in SIM PAD into retribution and other
locally-generated revenues payment record in
SIPKD
3. Data transfer from receivable and allowance for
receivable retribution record and receivable and
allowance for receivable other locally-generated
revenues record in SIM PAD into receivable and
allowance for receivable retribution and other
locally-generated revenues record in SIPKD.
In addition to integration design, we also propose
a system development both in SIM PAD and
SIPKD. Development on SIM PAD is an additional
menu and database for receivable and allowance for
receivable retribution and other locally-generated
revenues, receivable write-off process and validation
for retribution and other locally-generated revenues
payment to replace the manual input data for
payment of retribution and other locally-generated
revenues. While development in SIPKD is an
additional process which is automatic journal for
revenues-LO, revenues-LRA, receivable and
allowance for receivable account to replace manual
journal process.
4.5 Advantage of The Proposed
Integration and Development Model
The integration and development model of SIM
PAD and SIPKD that has been described has several
features that can assist The Provincial Government
of Jakarta in terms of the management of retribution
and other locally-generated revenues and reporting
in the financial statements in accordance with the
appropriate accounting cycle and more reliable
account data.
The first advantage is that there is no need to do
manual data input on retribution payments and other
other locally-generated revenues data because the
data is transferred from SIM PAD to SIPKD so as to
minimize error during input and increase efficiency
because there is no need to input one by one. The
second advantage is retribution and other locally-
generated revenues charges data generated by SIM
PAD can be transferred to SIPKD, which is
currently unavailable in SIPKD and the data can
then be used as a basis for doing a revenue-LO
journal.
Based on the first and second advantages, it
relates to the third advantage of not having to do
manual journals for revenue-LO recognition and
revenue-LRA, since the journal will be
automatically performed by the system based on the
Analysis of System Design of SIPKD (Regional Financial Management System) and SIM PAD (Locally-Generated Revenues Management
Information System) Integration in Order to Fulfill the Need for Preparing an Accrual-Based Financial Statements - Case Study in The
Provincial Government of Jakarta
397

charge and payment data of retribution and other
locally-generated revenues that have been
transferred from SIM PAD to SIPKD. Retribution
and other locally-generated charge data will serve as
the basis for revenue-LO journal, while payment
data will serve as the basis for revenue-LRA journal.
This automated journal has several advantages: time
efficiency because the journal does not need to be
done manually and one by one, minimize journal
errors that can occur in manual journals, it does not
need much human resources to do journal
considering the large number of retribution and other
locally-generated revenues transactions.
The last advantage is that there is no need to
calculate and journal the allowance for bad debts by
manual. One of the proposed developments in SIM
PAD is the addition of menus and databases for
calculation of receivables and allowance for
retribution and other locally-generated revenues
receivables. The allowance data of these receivables
will then be sent to SIPKD, which this data will
serve as the basis for SIPKD to perform adjustment
entries for allowance for retribution and other
locally-generated revenues receivables at the end of
the accounting period. This process has several
advantages that minimize miscalculation of
allowance for receivable account that has been done
manually and also the advantages of the automatic
journal as mentioned in the third advantage above.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the results of the analysis and discussion
that has been discussed in the previous section, some
conclusions obtained are as follows:
1. To meet the needs of accrual-based government
accounting standard implementation, it is
necessary to integrate the SIM PAD and SIPKD.
Such integration is required for data on
retribution and other locally-generated revenues
to flow into SIPKD and can be used in SIPKD
for accrual based financial reporting. With the
data flowing it will eliminate the manual process
that has been done so as to minimize errors that
may occur.
2. In order to integrate SIM PAD with SIPKD,
some adjustments are required to fit the
accounting needs of government-based accruals.
Such adjustments need to be made on either the
SIM PAD or SIPKD, the adjustments are as
follows:
a. There should be additional database and
menu to calculate the allowance for doubtful
account retribution and other locally-
generated revenues either on SIPKD or SIM
PAD.
b. There needs to be a new menu for validation
of retribution and other locally-generated
payment in SIM PAD to replace the current
manual validation menu.
c. There needs to be a new database in SIPKD
to accommodate the charged and payment of
retribution and other locally-generated
revenues data sent from SIM PAD.
d. It is necessary to make changes to the menus
and databases to conduct and retain revenue-
LO, revenues-LRA and allowance for
doubtful account journals.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The first author would like to acknowledge the
Provincial Government of Jakarta who supported her
study and Regional Financial Management Board
(BPKD) of The Provincial Government of Jakarta as
research subject.
REFERENCES
Bentley, Lonnie D. and Jeffrey L. Whitten. 2007. System
Analysis and Design for The Global Enterprise (7
th
Edition). New York: McGraw-Hill Companies.
Romney, Marshall B. and Paul J. Steinbart. 2012.
Accounting Information Systems (12
th
Edition). USA:
Pearson Education Limited.
Connolly, Thomas. And Begg Carolyn. 2014. Databse
System: A Practical Approach to Design,
Implementation and Management: Global Edition.
Pearson Education Limited
Peraturan Pemerintah Nomor 71 Tahun 2010 Tentang
Standar Akuntansi Pemerintahan
Peraturan Gubernur Nomor 204 Tahun 2016 Tentang
Kebijakan Akuntansi Pemerintah Daerah Khusus
Ibukota Jakarta
Peraturan Gubernur Nomor 108 Tahun 2017 Tentang
Pelaksanaan Penerimaan Pendapatan Daerah Secara
Elektronik
Peraturan Gubernur Nomor 188 Tahun 2015 Tata Cara
Pemberian Keringanan, Pengurangan dan Pembebasan
Retribusi Daerah
Peraturan Gubernur Nomor 254 Tahun 2016 Tentang
Organisasi dan Tata Kerja Badan Pengelola Keuangan
Daerah
Peraturan Daerah Provinsi DKI Jakarta Nomor 12 Tahun
2017 Tentang Organisasi Perangkat Daerah
JCAE Symposium 2018 – Journal of Contemporary Accounting and Economics Symposium 2018 on Special Session for Indonesian Study
398

Al-Jaroodi, Jameela. And Nader, Mohamed. 2011.Service
Oriented Middleware:A Survey.Journal of Network
and Computer Applications. Available at Elsevier:
www.elsevier.com/locate/jnca
Ariyani, Lidya. (2014). Analisis Sub Sistem Informasi
Rekam Media RSUD Pasar Rebo Dalam Rangka
Memenuhi Kebutuhan Sistem Jaminan Kesehatan
Nasional. Tesis, Magister Akuntansi, Universitas
Indonesia.
Firdaus, Muhammad Iqbal. (2016). Rancangan Sistem
Informasi Tilang Elektronik Terintegrasi Berbasis
Automatic Number Plate Recognition (ANPR) (Studi
Kasus Pelanggaran Jalur Bus Transjakarta). Tesis,
Magister Akuntansi, Universitas Indonesia.
Permana, Ida Bagus Gede Bayu. And Wiratmaja, I Dewa
Nyoman. 2016.Pengaruh Sumber Daya Manusia,
Komitmen Organisasi, Sistem Informasi pada
kesiapan penerapan laporan keuangan pemerintah
daerah berbasis akrual. Available at E-Jurnal
Akuntansi Universitas Udayana: www.ojs.unud.ac.id
Sophina, Mohammad Dimas. 2016. Pengaruh Kompetensi
Sumber Daya Manusia dan Sistem Informasi
Akuntansi Terhadap Penerapan Standar Akuntansi
Pemerintah Berbasis Akrual. Skripsi. Fakultas
Ekonomi. Universitas Pasundan.
Satrio, M Dimas. Yuhertiana, Indrawati. And Hamzah,
Ardi. 2016. Implementasi Standar Akuntansi
Pemerintahan Berbasis Akrual di Kabupaten Jombang.
Jurnal Akuntansi dan Keuanga Vo.18 ISSN 1411-0288
print/ISSN 2338-8137 online
Kusuma, Ririz Setiawati. 2013. Analisis Kesiapan
Pemerintah Dalam Menerapkan Standar Akuntansi
Pemerintah Berbasis Akrual.Skripsi. Fakultas
Ekonomi. Universitas Jember
http://www.jakarta.go.id/v2/news/2013/11/latar-belakang-
2013-2017#.WZ54LilLfIV. accessed on 24 Agustus
2017
http://www.beritajakarta.id/visi_misi. accessed on 24
Agustus 2017
http://bpkd.jakarta.go.id/profil. accessed on 24 Agustus
2017
Analysis of System Design of SIPKD (Regional Financial Management System) and SIM PAD (Locally-Generated Revenues Management
Information System) Integration in Order to Fulfill the Need for Preparing an Accrual-Based Financial Statements - Case Study in The
Provincial Government of Jakarta
399
