
Generating Competitive Priority Strategy in Transformer Industry
Rita Ambarwati
Magister Management, Universitas Muhammadiyah Sidoarjo, Jalan Majapahit 666B, Sidoarjo, Indonesia
ritaambarwati@umsida.ac.id
Keywords: Strategy of Competition, Quality Cost Delivery Service (QCDS), Quality Function Deployment (QFD),
Analytical Hierarchy Process (AHP).
Abstract: The transformer market competition in Indonesia is getting more attractive and dynamic. This encourages
transformer manufacturers to improve competitiveness, such as quality, cost, timely delivery, and service.
Therefore, companies need to understand customer needs and choose the right competition strategy. There
are three alternative strategies to compete, cost leadership, differentiation, and focus. This research
understands the customer needs and choose the right strategy to face the competition. The design of this study
used survey and data collection through questionnaires. Data analysis methods using QFD and AHP combined
with Focus Group Discussion (FGD) implementation. QFD analysis results in the form of the house of quality
shows two major things: recommendations action for internal improvement and priority contribution value
which will be the next input analysis with AHP method. The result of AHP analysis on the priority of
contribution value in choosing an alternative strategy shows that the most appropriate strategy is
differentiation, with the company focus on its competitive advantage. Practical implications of this research,
for the management need to increase production through efficiency and cost reduction. This research develops
product development theory by digging priority customer needs as one element to determine the competition
strategy.
1 INTRODUCTION
Energy is the most important thing in human life.
Parallel with increasing the human population and
social economical increment, people’s needs of
electricity continues to increase year to year,
including the need for transformers. This condition is
in line with the government's policy to upgrade
Indonesia’s Electricity Supply to be 35,000 MW in
the next five years (Abdurrahman, 2015). Relating to
today's business competition, each company should
pay attention to competition factors, such as quality,
product features, functionality and reliability of
products, services, available stock, the company's
reputation, knowledge of sales people to their
product, and competitive prices (Fahey, 1999). The
above background explains that transformer market
competition concentrated on four main keywords
there are quality, cost, delivery, and services.
Therefore this study can answer the five competitive
forces (rival competition, newcomer threats, product
substitution threats, supplier bargaining power,
customer bargaining power), there are three generic
successful strategic approaches to outperform the
competitors: Cost Leadership, Differentiation, and
Focus on specific target markets (Porter M., 1980).
Therefore company should able to define the right
strategy.
Research related to QCDS is from Rochmoeljati,
(2006) which perform performance measurement of
supplier based on vendor performance indicator
(VPI) with the method of quality cost delivery
flexibility responsiveness at the stainless steel
company. From the result of the research, it finds that
the important supplier plate performance evaluation
system at the stainless steel company is for Quality
(0,408), Cost (0,204), Delivery (0,204),
Responsiveness (0,071), flexibility (0,112). Several
studies related to the strategy of market competition
and customer satisfaction based on AHP methods are
among others by Ocampo and Clark in An AHP-
MOLP Approach on Prioritizing Competitive
Strategies Toward Sustainable Business (Ocampo &
Clark, 2014) and research conducted by Wang, Liu,
and Ou, The Evaluation Study of Customer
Satisfaction Based on Gray–AHP Method for B2C
Electronic-Commerce Enterprise (Wang, Liu, & Ou,
2007). Ocampo and Clark research on the select
28
Ambarwati, R.
Generating Competitive Priority Strategy in Transformer Industry.
In Proceedings of the Annual Conference on Social Sciences and Humanities (ANCOSH 2018) - Revitalization of Local Wisdom in Global and Competitive Era, pages 28-35
ISBN: 978-989-758-343-8
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

strategies in their correlation competition with the
triple bottom line where the business not only focus
on the benefits alone, but rather need to pay attention
to environmental aspects and human support of
develop he business itself. The AHP and Multi Aim
Linear Programing methods used to find the optimal
correlation value of the above three focuses (Profit,
People, and Planet). In conclusion Ocampo's research
finds an alternative of business priority competitively
in terms of economic, social and environmental
dimensions. While Wang, Liu, and Ou's research
focused more on mathematical calculations by
incorporating Gray's evaluation and hierarchy
evaluation to test the level of customer satisfaction
with B2C (Business to Consumer) electronic
commerce companies. Using Gray-AHP to test
mathematical models and build a customer
satisfaction evaluation system through conditioning
the evaluation indicator system. In his research,
Wang, Liu, and Ou used 3 level criteria with each of
the 4 indicator levels. Meanwhile, research based on
the QFD method has done by Felice and Petrillo from
the University of Cassino, Faculty of Engineering,
ITALY that combines the use of QFD with AHP to
assess the customer needs (De Felice & Petrillo,
2010). De Felice and Petrillo research on filter
products from ceramic materials, so they compile
survey questions with only nine indicators, namely:
filtering power, capacity of regulating the flow,
lifetime, dimensional of specification of coupling,
product certificated, and competitive price. This
research uses QFD method to determine attribute
criteria of QCDS and AHP based market competition
to determine market competition strategy. attributes
used in this study are twenty indicators. This is due to
the level of complexity of transformer products is
much more complex.
This research problem limited: (1) The study
focuses on twenty indicators offered by Fahey, as
mentioned above (Fahey, 1999); (2) The transformer
product limited to the distribution transformer.
Referring to the research problem formulation, the
research objectives planned: understand the customer
needs and choose the right strategy in facing
transformer market competition in Indonesia. The
results expected to be useful create strategic
management science. Also, to be an input to improve
the company’s competition strategy, make
continuous improvement to improve the company's
advantage.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Product Review
A transformer is a device that transfers power
between two or more electrical circuits through
electromagnetic induction. An alternating voltage
(Vp) applied to the PRIMARY creates an alternating
current (Ip) through the primary. This current
produces an alternating magnetic flux in the magnetic
core. This alternating magnetic flux induces a voltage
in each turn of the primary and in each turn of the
SECONDARY. The transformer production process
divided into three steps, there are:
• Mechanical Process: The process of making a
tank that uses as a transformer’s body.
• Electrical Process: we call or inner transformer or
active part, the inside sub assembly parts is the
active source of the generation power or voltage
drop, and
• Final Assembly Process: The process of
combining the active part into the tank and finally
is the installation process of all transformer
accessories.
Since these 3 steps finished, whole units of the
produced transformer must follow quality test phase.
Once it passed, therefore transformer can deliver,
otherwise reworked. In addition, several service
processes that also a concern of the company are
technical training and technical services under
customer needs and demands.
2.2 Management Strategy Concept
Strategy Management is a series of managerial
decisions that determine the success of the company
in the long term (Ambarwati, et al., 2014). It
comprises three stages: strategy formulation, strategy
implementation, and strategy evaluation. Strategy
formulation includes developing the vision and
mission, identifying external opportunities and
threats, determining internal strengths and
weaknesses, establishing long-term goals, planning
alternatives, and selecting strategies to implement
(Porter M., 1987). In strategic management, corporate
management activities involved plan multiple
business units as an operational sequence (Goold,
Campbell, Alexander, 1994). Implementation
strategies require companies to set an annual goal,
create policies, motivate employees, and divide
resources so that a planned strategy can run (David,
2011). Strategy evaluation is the final stage in
strategic management. Market competition will
Generating Competitive Priority Strategy in Transformer Industry
29

dynamically follow the businesses and industry
grows. There are five forces of competition
considered: Competition rival, Competition among
similar industries; The threat of newcomers, it can be
a serious threat to old players, including in the
transformer industry; The threat of replacement
products, technological changes enable significant
threats, such as the experienced by Kodak and Nokia;
Supplier bargaining power, supplier relationship with
the customer should be a partner, and Bargaining
power of customers, customers have its own
bargaining power for suppliers and can suppress
them. Answering this competitive challenge, there are
three alternative competitive strategies, Cost
Leadership, Differentiation, and Focus (Porter M.,
1980):
Cost Leadership, this strategy guides companies
to aggressively perform efficiency, tightening
controls in cost reduction process. The principle is to
avoid costs that are not the main post of the business
process, with consistently keep the product quality,
services, and proximity to customers.
Differentiation, the second strategy is provides a
distinctive value of products and services offered,
creates something unique to customers, and is a
competitive advantage over the competitors.
Focus, This strategy is on a particular market
group. A goal is to serve a certain target well, and
every functional policy within the organization on
this strategy. A key of this strategy is the belief that
companies can reach their strategic targets more
effective or efficient than competitors playing in the
broader segment. Referring to Dr. Liam Fahey, the
competitive indicators in this study can be seen in
Appendix 1.
3 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
This study aims to understand the customer needs and
choose the right strategy to face the competition.
Locate this study is all of BCD branches in Indonesia.
This research is within a three month period is from
October to December 2017.
The research data is in two stages. First,
questionnaires distributed to 33 companies of BCD’s
customers who also bought the competitor’s
products. Questions is focuses to the level of
Customer Interests of the attributes, the level of
satisfaction on PT. BCD’s product, and the level of
satisfaction on the competitor’s product. The second
stage is discussion with the BODs and managers of
the PT. BCD to discuss the alternative options of a
strategy through pair-wise comparison matrix on the
AHP method. Respondents were 10 managers and 3
directors as organizational decision maker.
The customer satisfaction questionnaire
organized according to Fahey’s attributes. While the
data collection getting by distribution of
questionnaires through BCD’s sales team directly
visit to customer get discussion over there. Validity
and reliability test begins the data processing steps if
valid and reliable then the research continued.
4 ANALYSIS AND DISCUSSION
In this section, the author will explain the data
processing on this research by using QFD and AHP
methods.
4.1 Data Sufficiency test
For n = 33 with the error rate 0.05 where Z_ (α / 2) =
1.96 and the proportion of respondents satisfied and
not satisfied is 0.5. The number of respondents who
meet the criteria is 30 respondents while the
minimum sample size is 28 respondents. Then the
sufficiency test of the data declared has fulfilled
4.2 Validity and Reliability test
Validity test of customer satisfaction data and value
Customer Interests data on Fahey’s attributes with the
number of responded, n = 30 and α = 5%, where r
table 0.3 result from SolAnd 2.1 calculation of
correlation coefficient value for both data is valid.
The result of running SolAnd 2.1, in got that
coefficient α Cronbach declared reliable, with a value
of customer satisfaction reliability, consecutively are
BCD 0,920; TFD 0.918; And AST 0.909. While the
reliability for value Customer Interests is 0.93.
4.3 Preparation of HOQ (House of
Quality)
The steps of HOQ preparation are: First determine the
value of customer satisfaction and competitive
satisfaction performance got from the data of the
respondent’s satisfaction level of each attribute. Next,
set the goals for each attribute determined by
management. The basis of goal value, determined
from the highest level of satisfaction on each product
attribute even though it occurs on other brands
(Wijaya, 2011). The important customer interest on
attributes can take directly from the questionnaire.
The value of customer needs as to explain the value
ANCOSH 2018 - Annual Conference on Social Sciences and Humanities
30
of customer interest can be seen in Appendix 2 about
HOQ below.
Improvement ratio results from goals devided by
today’s customer satisfaction value, that is showing if
the determined goal has reached. Averages, the value
of BCD’s customer satisfaction has outperformed its
competitors, so BCD’s improvement ratio is 1, except
the brand image.
Sales point is the ability to sell the product
attributes based on management perceptions on the
value added of each attribute. Sales point setting
based on: 1.0=No Sales Point, no value added to the
product; 1.2=Medium Sales Point, there is value
added but not significant; 1.5=Strong Sales Point,
value added to the product is high.
Raw weight is the weight of an attribute,
multiplication between customer needs with
improvement ratio and sales point. While normalized
raw weight, is the value of raw weight divided by total
raw weight. This raw weight value will be useful for
calculating the contribution value when you have
determined the technical response and the numerical
value for each technical response. Contribution value
is the output of the QFD analysis seen in the house of
quality.
4.4 Technical Response and Correlation
of Technical Requirement
Generating Technical Response is the answer to the
problems of customers on each product attribute.
Technical responses can be seen in the house of
quality.
4.5 Action Priority
In choosing the priority of technical response
calculated based on value of customer interest. First
is state contribute each technical response.
Contribution value of the technical response is the
multiplication of raw weight with the relationship
value (numeric number as a differentiation to replace
the correlation code: ● = 9; ○ = 3; △ = 1).
4.6 Own Performance and Competitive
Benchmarking
Own performance is customer satisfaction value
multiple with relationship value, it is forecasting the
future customer satisfaction if the technical response
done. The competitive benchmark value is similar
methods, with own performance calculation by
change the satisfaction value using the competitor’s
customer satisfaction value, respectively. Assuming
the value of relationship is equal with BCD to the easy
compare of benchmarking purposes.
4.7 Important Action and Improvement
Target
Important Action is the numeric value from technical
response multiple with the value of customer interest.
Improvement target of the action returned to
management judgment. The important action value is
in the house of a quality image.
4.8 Priority of Improvement Action
The improvement project is impossible to do in one
short activity, but there have to be an action and step
by step, how to do? we need to prioritize the action.
The priority chosen based on the important action at
HOQ. If the priority of action organized according to
its importance action, then we will find the Figure 1
about Pareto curve as shown below:
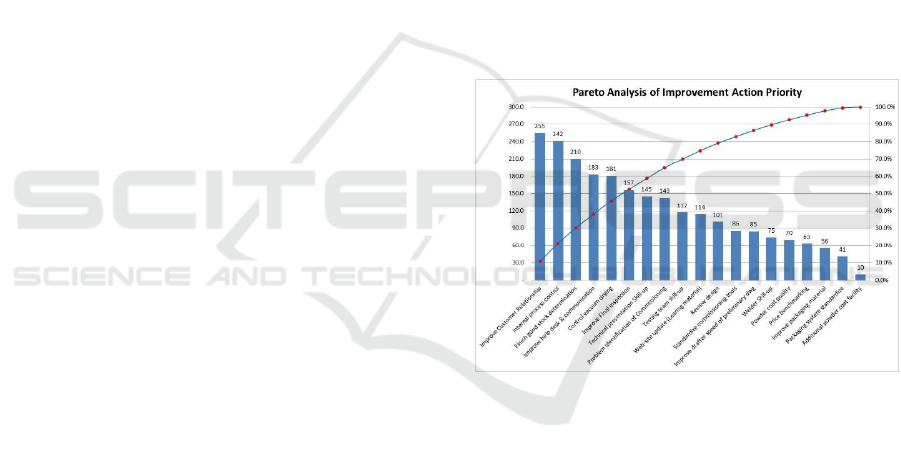
Figure 1: Pareto Analysis of Improvement Action.
4.9 Determine the Alternative Decision
Making
The first aim of this study has answered with the
results of QFD analysis and the above quality house.
To answer the purpose of the second aim, the authors
will present the result of BCD Management’s
discussion with AHP method. The output of QFD (the
contribution value) becomes an input on AHP
calculation to find out the alternative strategy.
4.10 Fair-wise comparison matrix, Eigen
Vector, Normalized Eigen Vector,
and Weight
The pair-wise comparison matrix generated by
tabulating the data into the square matrix in the
Generating Competitive Priority Strategy in Transformer Industry
31

columns and rows to the right of the diagonal. Eigen
vector, calculate by completing the pair-wise
comparison matrix on the left side of the diagonal
with the reciprocal value of the pair comparison
matrix. Weight calculation determined by
normalizing the eigen vector (by summing each
column and then dividing each cell with the sum of
each column). The weight is the right-hand column
which is the average of the sum of each line in the
normalized eigen vector (Saaty, 1993).
To be proof the consistency of assessment, by sum
the weight, if equal to 1, then we can declare that the
matrix is consistent.
4.11 Management Decision Making
Sort the weight of each alternative strategy on the
matrix, the greatest value is the best alternative value.
To determine the best competition strategy is through
discussion among managers and top management in
FGD forum by use the QFD output becomes AHP
input.
By making Pareto analysis of contribution value
priority, got 14 attributes that have over 80%
contribution. Then management selected 14 priority
to mapping the alternative strategies by pair-wise
comparison. From the results of AHP analysis we get
the weight of the alternative strategy for each attribute
can be seen in Appendix 3.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The conclusions that the authors take as the answer to
the research question are: The biggest focus of
customer attention is on the attributes of technical
services such as commissioning, technical services,
technical training, response time, and help desk.
Looking at customer satisfaction goals, almost all of
BCD’s attributes has outperformed its competitors,
except for the brand image, the competitor is superior.
Thus, BCD Management needs more serious to
improve Brand Image. Brand image becomes
important after being given a technical response by
management, although the customer places this
attribute on the order of the 16 priority interests, but
management gives the significant value for long-term
strategy, that’s why the priority of this attribute
contribution becomes second priority after
commissioning. In line with the value of
contributions from priority of customer needs, there
is eleven priority actions that need to be the concern
for PT. BCD to improved. From the results of data
analysis with AHP method, it concluded that the most
appropriate strategy to implement by PT. BCD is
Differentiation strategy by the focus on the
company's advantage. The second alternative
strategy is Cost Leadership by a focus on improving
product quality, functionality, and reliability, and an
optimizing process efficiency.
REFERENCES
Abdurrahman, S. (2015). Pemerintah Menerapkan Syarat
Ketat Dalam Menetapkan Investor Program 35.000
MW. Retrieved February 7, 2017, from
http://www.esdm.go.id/siaran-pers/55-siaran-
pers/7250-pemerintah-menerapkan-syarat-ketat-
dalam-menetapkan-investor-program-35000-mw.html.
Ambarwati, R., Hadiwidjojo, D.Z., Sudiro, A., Fatchur
Rohman, F. (2014). The Role of Multichannel
Marketing in Customer Retention and Loyalty: Study in
Emerald Bank Customer in Indonesia. Asia-Pacific
Management and Business Application. Vol. 2 No. 3.
David, F. (2011). Strategic Management, CONCEPTS
AND CASES. New Jersey: 13th Edition, Pearson
Education, Inc., Publishing as Prentice Hall.
De Felice, F., & Petrillo, A. (2010). A multiple choice
decision analysis: an integrated QFD–AHP model for
the assessment of customer needs. International
Journal of Engineering, Science and Technology, 2(9).
Fahey, L. (1999). Competitor Analysis: Out Witting, Out
Maneuvering, and Out Performing. New York City:
John Wiley & Sons, Inc. ISBN: 978-0-471-29562-4.
Goold, M., Campbell, A., & Alexander, M. (1994).
Corporate-Level Strategy: Creating Value in the Multi
business Company. New York: John Wiley & Sons.
Ocampo, L. A., & Clark, E. E. (2014). Developing a
framework for sustainable manufacturing strategies
selection. DLSU Business & Economics Review, 23(2),
115-131.
Porter, M. (1980). Competitive Strategy: Technique for
Analyzing Industries and Competitors. New York City:
The Free Press, Simon Schuster Inc., 1230 Avenue.
Porter, M. (1987, May). From Competitive Advantage to
Corporate Strategy. Harvard Business Review, p. p. 65.
Wijaya, T. (2011). Quality Service Management, Servqual
Design, QFD, and Kano: Accompanied by Application
Examples in Research Case. Jakarta: PT. INDEKS.
Rochmoeljati, R. (2006). Supplier Performance
Measurement Based on Vendor Performance Indicator
with Quality Cost Delivery Flexibility Responsiveness
Method. Journal Tekmapro.
Saaty, T. (1993). Decision Making for Leaders: The
Process of Analytic Hierarchy For Complex Decision
Making. Jakarta: PT. Pustaka Binama Pressindo.
Wang, M., Liu, P., & Ou, G. (2007). The Evaluation Study
of Customer Satisfaction Based on Gray-AHP Method
for B2C Electronic-Commerce Enterprise. Engineering
Letters, 15(1), 157-162.
ANCOSH 2018 - Annual Conference on Social Sciences and Humanities
32
APPENDIX
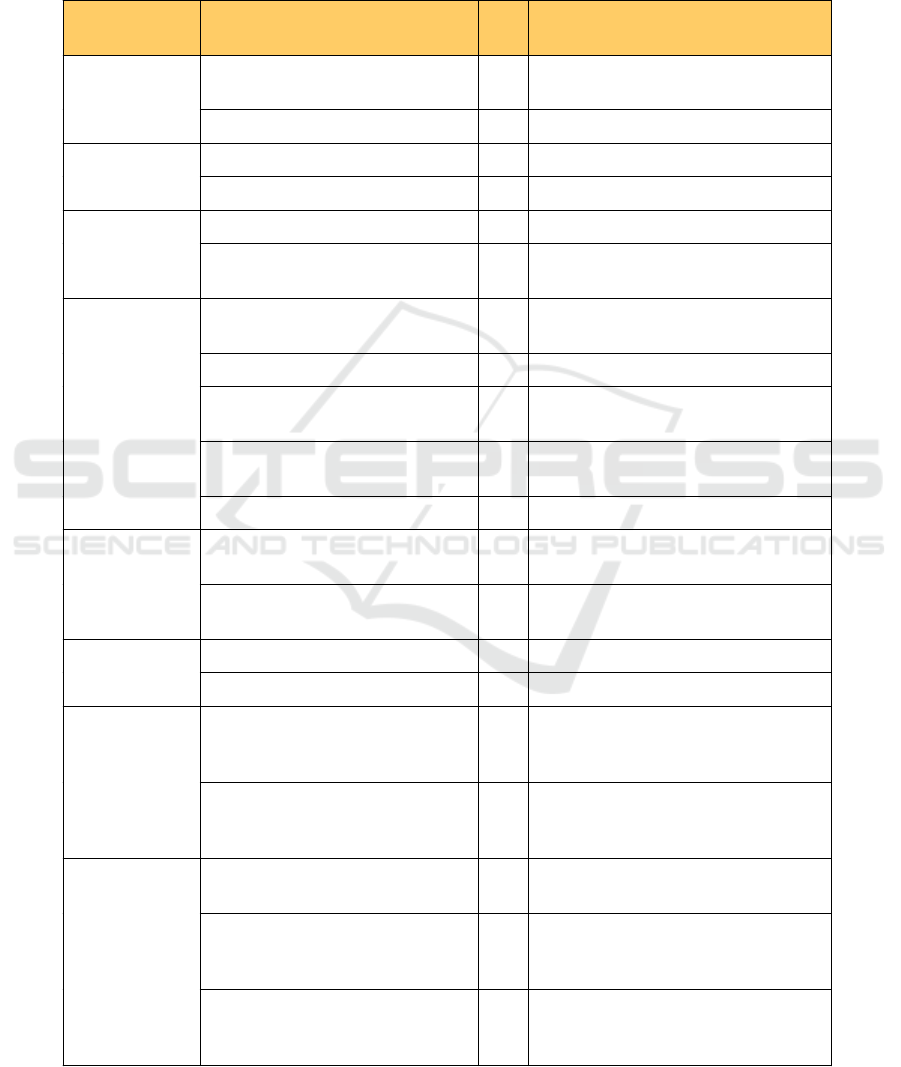
Appendix 1. The Competitive Indicators of Transformer
Kriteria
Indikator
QC
DS
Penjelasan
Quality
Q
1
Visual of transformer
Q
The visual quality of the transformer
match with customer approved design.
Q
2
Electrical test result
Q
Electrical testing result.
Features
F
1
Packaging
QD
Packanging of the transformer.
F
2
Coloring
Q
The Color of tank
Functionality
U
1
Performance
Q
The transformer can work properly
U
2
Reliability
Q
Life time of transformer in a normal
work.
Services
S
1
Commissioning
Q S
The installation process in customer
sites.
S
2
Help desk service
S
Have a contact person clearly and care.
S
3
Technical training
Q S
Company provide the knowledge
sharing.
S
4
Technical service
Q S
Ability of company to do
refurbishment.
S
5
Response time
Q S
How quick the response delivered.
Availability
A
1
Remote warehouse & stock
readiness
D
Availability of out factory warehouse
in ourder to provide available stock.
A
2
Delivery time
QD
Ability to deliver on time as per
contract.
Image and
reputation
I
1
Brand image
Q S
Image of customer perception
I
2
Quick response reputation
Q S
Reputation as per customer perception
Relationships
and sales
knowledge
R
1
Relationship with customer
Q S
The ability of the sales team to
establish good relationships with
customers.
R
2
Sales product knowledge
Q S
Sales team knowledge on the product,
such as technical, quality,
specification, etc.
Price
P
1
Quotation
C S
Q
Speed of the quotation offer according
to customer expectations
P
2
Value
C S
The price paid for the products and
services the customer receives is
worth.
P
3
Price performance
CQ
S
A price offering compared to
competitors (cheaper, more expensive,
equivalent)
Generating Competitive Priority Strategy in Transformer Industry
33
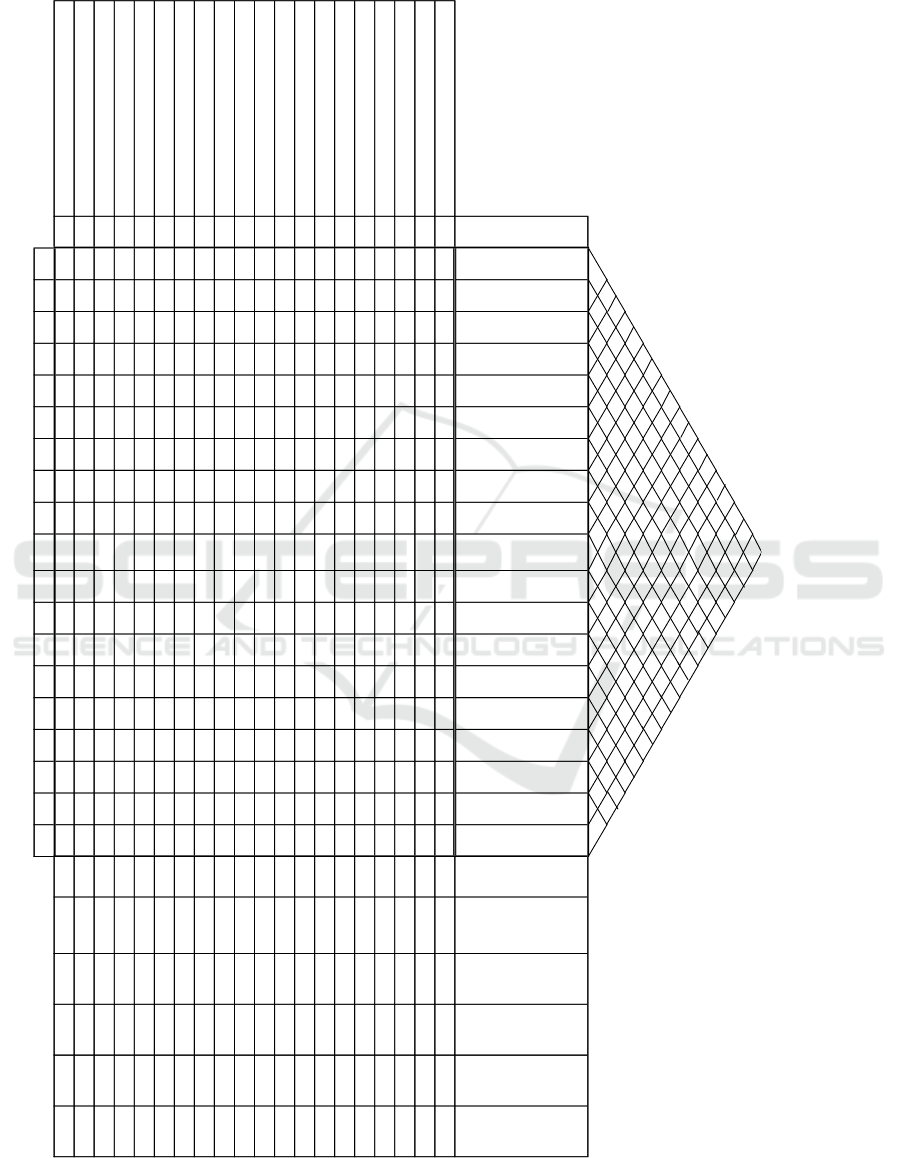
Appendix 2. House of Quality
Important to
customer
Welder Skill-up
Powder coat quality
Review design
Internal process control
Testing team skill-up
Improve packaging
material
Packaging system
standardize
Additional powder coat
facility
Improve Final
Inspection
Standardize
commissioning tools
Problem identification
of Commissioning
Technical presentation
Skill-up
Web-site update
(Learing material)
Improve help desk &
communication
Finish good stock
determination
Improve Customer
Relationship
Improve drafter speed
of preliminary dwg
Price benchmarking
Raw weight
Contribition
BCD's Customer
Satisfaction
BCD Performance
TFD Performance
AST Performance
Q1 Visual of Transformer
Secara Fisik, trafo yang kami beli telah
3.2
●
○ ● ● ― ― ― ― ● ― ― ― ― ― ― △ ― ―
3.80
152.0 4.100 164.00 148.00 129.33
Q2 Electrical test result
Hasil uji elaktrik di pabrik menyatakan trafo
4.4
― ― ○ ● ● ― ― ― ― ― ― ― ― ― ― △ ― ―
6.60
204.6 4.367 135.37 125.03 108.50
F1 Packaging
Packing tranfo saat datang di lokasi kami,
3.3
― ― △ ○ ― ● ● ― ― ― ― ― ― ― ― ― ― ―
3.92
86.2 3.967 87.27 83.60 74.07
F2 Coloring
Warna cat trafo sesuai harapan dan kualitas
3.3
― △ ● ○ ― ― ― ○ ● ― ― ― ― ― ― ― ― ―
3.33
83.3 3.933 98.33 92.50 81.67
U1 Performance
Pada saat energize trafo berfungsi baik dan
3.3
― ― ○ ● ○ ― ― ― ○ ― ― ― ― ― ― ― ― ―
4.90
132.3 4.233 114.30 102.60 95.40
U2 Reliability
Trafo telah dioperasikan selama > 10 thn dan
4.1
― △ ○ ○ ○ ― ― ― △ ― ― ― ― ― ― ― ― ―
6.15
123.0 4.033 80.67 72.67 65.33
S1 Commissioning
Technical Service team handal melakukan
4.4
― △ ― ○ ● ― △ ― ● ● ● ― ― ― ― ● ― ―
6.55
334.1 4.033 205.70 183.60 168.30
S2 Help desk service
Sangat mudah menghubungi pihak
4.1
― ― ― ― ― ― ― ― ― ― ○ △ ● ● ― ● ― ―
4.92
152.5 4.233 131.23 104.37 99.20
S3 Technical training
Maker memberi training untuk user sehingga
4.0
― ― ― ― ― ― ― ― ― ― ● ● ● ○ ― ○ ― ―
4.84
159.7 3.733 123.20 103.40 104.50
S4 Technical service
Maker sangat responsive ketika diminta
4.3
○ ― ― △ △ ― ― ― ― ● ● ― △ △ ― ○ ― ―
6.50
182.0 3.933 110.13 93.33 93.33
S5 Response time
Kecepatan response pabrikan sangat bagus,
4.1
― ― ― ― ― ― ― ― ― △ ○ ― ― ○ ● ● ― ―
6.15
153.8 3.767 94.17 84.17 78.33
A1 Remote warehouse & stock readiness
Pabrikan punya cukup stock di warehouse
3.7
― ― ― ― ― ― ― ― ― ― ― ― ― ― ● ― ― ―
4.48
40.3 3.967 35.70 32.70 28.20
A2 Delivery time
Ketepatan delivery, selama ini cukup tepat
4.0
― ― ― ● ○ ― △ ― ○ ― ― ― ― ― △ △ ― ○
6.05
127.1 3.900 81.90 76.30 67.20
I1 Brand image
Merek dagang perusahaan ini cukup terkenal
3.7
● ● ― ○ ― ○ △ ― ● △ ― ● ― ● △ ● ― ―
4.55
286.6 3.933 247.80 256.20 197.40
I2 Quick response reputation
Reputasi di pasaran pada umumnya bagus
4.1
― ― ― ― ― ― ― ― ― ― △ ― ― ● ● ● ● ―
6.15
227.6 4.000 148.00 131.97 115.93
R1 Relationship with customer
Hubungan kemitraan dengan customer pada
3.9
― ― ― ― ― ― ― ― ― ― ― ● ― ● ○ ● ○ ―
5.90
194.7 4.200 138.60 113.30 106.70
R2 Sales product knowledge
Kemampuan team sales dalam menjelaskan
4.1
― ― ― ― ― ― ― ― ― ― ― ● ● ○ ― ― ― ―
6.10
128.1 4.000 84.00 73.50 65.80
P1 Speed of Quotation
Kecepatan response saat diminta penawaran
4.0
― ― ― ― ― ― ― ― ― ― ― ― ― ― ● ― ● △
6.00
114.0 4.133 78.53 65.87 59.53
P2 Price Value
Harga yang dibayarkan untuk produk dan
3.9
― ○ ― ○ ― △ ― ― ― ― ― ― ― ― ○ ― ― ○
4.64
102.1 4.100 90.20 81.40 73.33
P3 Price performance
Harga produk yang ditawarkan cukup
4.0
― △ △ ● ― ○ ― ― ― ― ― ― ― ― ● ― ― ●
4.76 195.2 4.000 164.00 154.43 136.67
75 70 101 242 117 56 41 10 157 86 143 145 114 183 210 255 85 63
Control vacuum drying
―
●
―
―
●
●
△
―
―
―
―
―
―
―
―
―
―
―
●
●
Important Action for Improvement
181
◎
○
※
◎
◎
○
○
◎
○
×
○
○
○
○
○
○
○
○
○
○
◎
◎
◎
◎
◎
◎
◎
※
◎
◎
◎
◎
○
◎
◎
◎
◎
◎
○
ANCOSH 2018 - Annual Conference on Social Sciences and Humanities
34
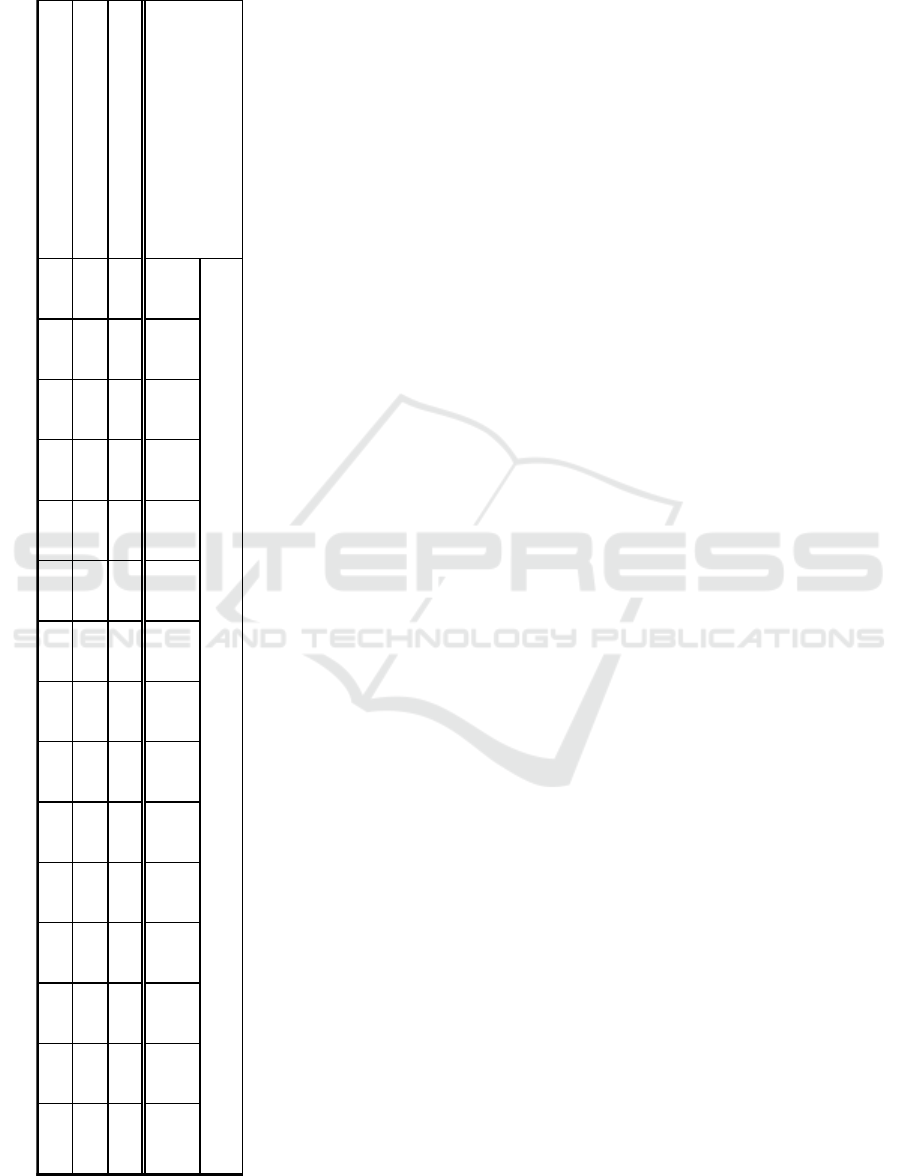
Appendix 3. Value of Weight for Priority Attributes
S1
I1 I2 Q2 P3 R1 S4 S3 S5 S2 Q1 U1 R2 A2
Sum
Cost Leadership
0.19 0.17 0.19 0.05 0.75 0.44 0.22 0.11 0.10 0.19 0.17 0.19 0.13 0.78
3.68
Differentiation
0.75 0.73 0.74 0.74 0.19 0.49 0.73 0.30 0.69 0.71 0.77 0.72 0.75 0.15
8.46
Focus
0.06 0.10 0.07 0.20 0.06 0.08 0.05 0.59 0.21 0.10 0.06 0.08 0.12 0.07
1.85
Alternatif Strategi
Value of Weight for Priority Attributes
Generating Competitive Priority Strategy in Transformer Industry
35
