
Strategy of Improvement Effort in Traffic Accidents
Nur Khalimatus Sa'diyah
and Umi Enggarsasi
Faculty of Law Universitas Wijaya Kusuma Surabaya, Jl. Dukuh Kupang XXV/ 54, Surabaya, Jawa Timur, Indonesia
nurkhalimatus@yahoo.com, umienggarsasinohan@gmail.com
Keywords: Traffic Accidents Prevention, Traffic violations, Minimize Traffic Accident, Traffic Accident.
Abstract: Traffic is one means of community communication that plays an important role at national development.
One of the things faced in Traffic is an accident. This problem generally occurs when the means of
transportation, both in terms of roads, vehicles, and other supporting facilities have not been able to keep up
with the existing developments in the community. The purpose, to prevent traffic accidents, and to analyze
the prevention efforts to increase accidents in jurisdictions Regional police. The method used is empirical
juridical approach, Research with interviews and data retrieval, this research was conducted at the East Java
Regional Police of the Republic of Indonesia. The results: The efforts that have been done in preventing the
increasing of accidents in Regional police is with the prevention effort to reduce the accident caused by
several factors causing the accident traffic through 3 approaches, pre-emtive, preventive, and repressive.
With the prevention efforts it can minimize the number of accidents that occur in Indonesia.
1 INTRODUCTION
In the complexity of human daily life, it is not far
from transportation, Transportation is a very
important and strategic media to accelerate the
economy, strengthen the unity of the nation and
unity also can affect life of the nation and state
(Hartini, 2012). One of the problems in
transportation is traffic accidents. This problem
generally occurs when transportation, both in terms
of roads, vehicles, and other supporting facilities
have not been able to keep up with the existing
developments in the community. Economic growth
and large population lead to increased activities
mosly cause of course increase the need for
transportation equipment, both personal and public.
Traffic accidents many losses. As a result of traffic
accidents in the form of damage to public facilities
and caused people died. This increasingly complex
traffic conditions with the increase in the number of
motor vehicles both the two-wheelers and four
wheels directly or not participate in the increase in
the number of incidents of traffic accidents.
Descriptions of the accidents by the police were
used to identify individuals who had displayed risky
traffic behavior contributing to or causing an
accident; evidence of offending was based on a
register of contacts with police (Marianne et al.,
2001). In developed countries, traffic accidents are
the most cause of death for all age groups, except for
very old ones. This phenomenon is now experienced
by developing countries. General observations
indicate that the level of traffic accidents increases
with the increase in vehicle ownership levels. The
safety level here is measured by the number of
victim accidents. Behind the benefits of traffic, there
are also various issues related to the use of the
highway. The number of road users every day,
cannot escape the traffic problems. One of the
problems in traffic is called traffic accident.
Accidents can occur due to negligence of the driver
himself. The results showed that heavy traffic
volume, speeding, narrow lane width, larger number
of lanes, urban roadway sections, narrow shoulder
width and reduced median width increase the
likelihood for accident involvement (Mohamed,
2000). Efficiently police performance needs to be
understood. In law enforcement by the Traffic
Police, the existence of a community center police
depends on the conduct of its members. (Romli,
2005). The basic job of the Traffic Police is to keep
an eye on traffic. Keep an eye on traffic, helping to
keep the road transport system and efficiently. If a
person is allowed to use the road as they please,
what happens is mess. If the road system is defective
and undetected and unreported, it may disrupt the
activity for the traffic rider. Therefore, the task of
traffic control is basically to provide a system for
people who share the road to travel with low levels
Sa’diyah, N. and Enggarsasi, U.
Strategy of Improvement Effort in Traffic Accidents.
In Proceedings of the Annual Conference on Social Sciences and Humanities (ANCOSH 2018) - Revitalization of Local Wisdom in Global and Competitive Era, pages 181-185
ISBN: 978-989-758-343-8
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
181
of annoyance, delays and hazards. To achieve this
goal, the police with the authority and knowledge
must patrol the streets, not only detect problem spots
and problem makers, but also to be immediate and
alert in providing emergency assistance to the
community (Andrew, 2011). The increasing volume
of private vehicles, especially the type of motorbike
on the highway and not accompanied by the addition
of adequate road access to accommodate the number
of vehicles at this time negatively impact for all road
users, traffic jams and high accident rates is
evidence of the negative impact of the number of
vehicles passing thatch on the highway, especially
when people start and do their activities. The traffic
function as the circulatory function in the human
body. Similarly, with traffic. The safety, order and
smoothness of unsafe and non-current and
inefficient and efficient traffic will bring difficulties
for the community. Geographical Information
System (GIS) technology has been a popular tool for
visualization of accident data and analysis of hot
spots in highways. Many traffic agencies have been
using GIS for accident analysis. Accident analysis
studies aim at the identification of high rate accident
locations and safety deficient areas on the highways.
So, traffic officials can implement precautionary
measures and provisions for traffic safety (Saffet et
al., 2008).
Traffic accidents during the last 10 months were
January-October in 2016 based on detik.com the
number of accidents during January to October 2016
data entered as many as 19,354 traffic accident,
deaths (MD) 4,826 people, injured weight (LB)
1,422 people and minor injuries (LR) 24,657 people
and material loss more than Rp 25 billion.
Based on data from Directorate of Traffic East Java
Regional police of the Republic of Indonesia
regarding the number of traffic accident numbers
from January to May 2017: (Dadang, 2017).
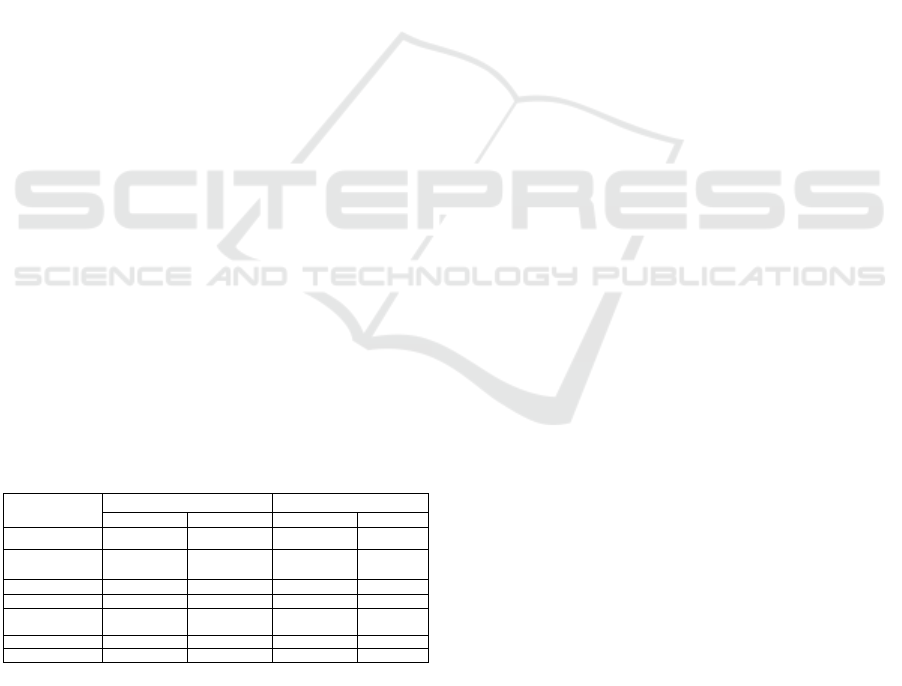
Table 1: Traffic accidents Data (Period Jan - May 2017).
DESCRIPTION
Year
TREND
2016
2017
Numbers
%
2
3
4
5
6
TRAFFIC
ACCIDENT
a. accident
8.898
9.925
1.027
11,54
b. died
2.316
2.029
-287
-12,39
c.serious injuries
621
558
-63
-10,14
d.minor injuries
11.193
13.068
1.875
16,75
e. survivors
11.750.854.000
12.563.235.000
812.381.000
6,91
The purpose, to prevent traffic accidents, and to
analyze the prevention efforts to increase accidents
in jurisdictions Regional Police. Based on the
background, the problem which raised is: How is
Strategy by Traffic Police Officer to prevention in
minimalize traffic accidents?
2 METHODS
The research method used is empirical juridical
approach, with primary and secondary data, and
qualitative analysis presented descriptively.
Research with interviews and data retrieval, the
research was conducted at Directorate of Traffic
East Java Regional police of the republic of
Indonesia, Metropolitan city police, and regency
police.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Efforts made by East Java Regional
Police to Reduce Causes of Traffic
Accidents
In the occurrence of traffic accidents must be caused
by several factors that cause traffic accidents. Traffic
violation is one of the factors causing traffic
accidents. In 2015 Regional police of the republic of
Indonesia organizes 11 programs to reduce the
factors causing traffic accidents in this case is to
reduce the number of traffic violations in order to
press the number of traffic accidents. The 11
programs are as follows.
CCTV (Circuit Closed Television), Second
Program, Strategy Bus and Truck Violation
Program, that is strategy and effort to prevent traffic
violation and potential of traffic accident caused by
bus or truck driver. Implemented with law
enforcement against violators and retraining for
violent bus and truck drivers, the third program,
Safety Riding East Java (Coaching Clinic), a
program aimed at the general public in order to
increase awareness and skills to safe driving. This
activity was conducted in seven distric and city
model in East Java, the fourth Program,
POLANTASKU Sahabatku Program, the program to
provide traffic knowledge early to make closer
traffic police with children. Thus, formed a culture
of orderly traffic in children. The program is held
with Semeru puppet stage, park then, and zebra
cendikia bus, the fifth Stop and Go Program, which
is controlling road users to obey traffic signals with
traffic light appeals, through banner installation,
distribution of leaflets, The sixth, PKS and Duta
Lantas Competition Program, a program to attract
students and students to have knowledge and insight
into traffic, The seventh program, MMS PEKA
(Traffic Safety Traffic), is a program that invites the
public to provide information about traffic violations
that occur through multimedia message service
(mms) and sent to the number of adm 3934.
ANCOSH 2018 - Annual Conference on Social Sciences and Humanities
182

Furthermore, there will be action against the
violation. It is also a form of service using social
media to provide public information disclosure,
Eighth Program, Super Lantas (Surabaya Pioneer of
Cross-Strait Safety). An innovation program from
Satlantas Polrestabes Surabaya, to print pioneering
traffic safety agencies in Surabaya. Its activities
socialize Law number 22 of 2009 in schools, modern
dance competition, cheerleader, super quiz then,
super yell and then test drive in the village visited,
the ninth program is the Mudik Bersama Program.
Inviting people to go home together and going home
early. Which are accommodated by certain agencies
that aim to minimize traffic accidents, the tenth
program, as part of an effort to encourage the
company to be sensitive to traffic safety, the
eleventh Program is the ISQ Road Safety Program, a
program to build emotional and spiritual
intelligence. Road users, officers or policemen as
well as other bikers.
In 2016 To reduce the number of traffic
accidents, Directorate of Traffic (Ditlantas) Regional
police of the republic of Indonesia held an operation
with the password "Sympathetic Semeru 2016". The
operation was held for 21 days. This operation is
more prioritize to coach the user of the vehicle.
Based on the results of the analysis conducted in
Directorate of Traffic Regional police of the republic
of Indonesia, mentioned several ways or efforts to
prevent or reduce the factors causing traffic
accidents that is in two ways namely preemptife and
preventive (Dadang, 2017).
How to pre-emptive cover such as the
implementation of binluh, put banners, leaflets and
brochures in strategic places in the traffic area with
the theme of traffic safety or driving and also the
implementation of enterprising patrols in places
prone to jam and accidents. While preventive ways
include for example helping the road users, directing
the pedestrian to cross in the places that have been
determined and also Enhancement of law
enforcement in the form of stationary or mobile
raids with the target of violations that have the
potential to cause traffic accidents through tickets or
rebuke (ibid).
The innovations to reduce the factors causing
traffic accidents that have been done by some
regency police are: SIS-KALDU (Integrated
Accident Handling System) at Directorate of Traffic
Tuban, and PECEL BAKAR (Inspection of Laka
Victim Accident at Home / Hospital) at Directorate
of Traffic Madiun.
3.2 Efforts to Minimize the Risk of
Traffic Accidents
To be able to perform the application of traffic law
must have a component for traffic interaction can
occur as follows: Human as user: Humans as users
can act as drivers or pedestrians who under normal
circumstances have different abilities and alertness
(reaction time, concentration etc.). These differences
are still influenced by physical and psychological
conditions, age and sex and external influences such
as weather, street lighting and layout; Vehicles:
Vehicles used by drivers have characteristics related
to speed, acceleration, deceleration, dimensions and
payloads that require sufficient traffic space to be
able to maneuver in traffic; Road: The road is a
trajectory planned for motorized vehicles and non-
motorized vehicles including pedestrians. The road
is planned to be able to accelerate traffic and able to
support the load of vehicle can be safe, so can
reduce the number of traffic accidents.
Poisson and negative binomial (NB) models
have been used to analyze traffic accident
occurrence at intersections for several years. There
are however, limitations in the use of such models.
The Poisson model requires the variance-to-mean
ratio of the accident data to be about 1. Both the
Poisson and the NB models require the accident data
to be uncorrelated in time. Due to unobserved
heterogeneity and serial correlation in the accident
data, both models seem to be inappropriate. A more
suitable alternative is the random effect negative
binomial (RENB) model, which by treating the data
in a time-series cross-section panel, will be able to
deal with the spatial and temporal effects in the data
(Hoong and Mohammed, 2003).
In the application of traffic law required amature
concept and can be organized well so that the
implementation of the law carried out can run
smoothly. The author tries to describe the
application of the author of the analysis in Article
245 of Law Number 22 Year 2009 on Traffic and
Road Transport, which is with the following
concept: Traffic management: Traffic management
includes planning, controlling, and controlling
activities. Traffic management is aimed at safety,
security, regularity, and traffic smoothness, and is
doing by: Efforts to increase road, segment, and / or
road network capacity; Prioritizing certain types of
vehicles or road users; Adjustment of travel demand
to a certain level of service taking into account intra-
and inter-modal alignment; Determination of traffic
circulation, prohibition and / or order for road users.
(Andrea, 2013).
Traffic planning activities: Traffic planning
activities include inventory and service level
Strategy of Improvement Effort in Traffic Accidents
183

evaluation. The purpose of the inventory, to know
the level of service on each segment of roads and
intersections. The purpose of service level in this
provision is the faculty of road and intersection to
accommodate traffic while keeping in mind the
speed and safety factor, determining the level of
service. In determining the level of service, by
taking into account: the general plan of road
transport network, the role, capacity, and
characteristics of roads, road class, traffic
characteristics, environmental aspects, social and
economic aspects. Determination of the problem
solving of traffic, the preparation of plans and
program implementation of its embodiment. The
purpose of the plan and the program of embodiment
in this provision include the following:
determination of the desired level of service on each
segment of roads and intersections, the proposed
traffic rules to be fixed on each road and
intersection, the proposed procurement and
installation as well as the maintenance of traffic
signs road markers, traffic signaling equipment, and
road user control and safety devices, proposed
activities or actions both for the purpose of drafting
proposals and extension to the public.
Traffic control activities, the activity of
determining the traffic policy on a particular
network or road segments. including in the
definition of traffic policy stipulation in this
provision, as, the arrangement of traffic circulation,
the determination of maximum and / or minimum
speed, road prohibition, prohibition and / or
command for road users.
Activities of traffic control: Monitoring and
assessment of the implementation of the traffic
policy. Monitoring and assessment activities are
intended to determine the effectiveness of these
policies in order to support the achievement of a
predetermined level of service. Included in the
monitoring activities shall include, as, inventory of
traffic policies applicable to roads, number of
violations and corrective actions that have been
taken for the violation. Included in the assessment
activities include the determination of assessment
criteria, service level analysis, violation analysis and
proposed corrective actions; Corrective action
against the implementation of the traffic policy.
Corrective action is intended to ensure the
achievement of defined service level objectives.
Included in corrective action is a review of wisdom
if in its implementation creates an unwanted
problem (Ibid)
Traffic control activities: Provision of direction
and guidance in the implementation of traffic policy.
The provision of guidance and guidance in this
provision shall be the stipulation or provision of
guidelines and procedures for the purposes of the
implementation of traffic management, in order to
obtain uniformity in their implementation and can be
implemented as appropriate to ensure the
achievement of the level of service that has been
established; Providing guidance and counseling to
the public regarding the rights and obligations of the
community in the implementation of traffic policy.
Accident size can be expressed as the number of
involved vehicles, the number of damaged vehicles,
the number of deaths and/or the number of injured.
Accident size is the one of the important indices to
measure the level of safety of transportation
facilities. Factors such as road geometric condition,
driver characteristic and vehicle type may be related
to traffic accident size. However, all these factors
interact in complicate ways so that the
interrelationships among the variables are not easily
identified (Ju-YeonLee et al., 2008).
3.3 Strategy Against East Java Police
Efforts in Preventing Increased
Traffic Accidents
Preemtive Activity, Implementation, installing
banners, leaflets and brochures in strategic places in
the traffic accidents area of vulnerable then with the
theme of traffic safety or driving; Implementation of
enterprising patrols in traffic jam and traffic
accidents areass, tourist areas and implement
proactive arrangements and patrols on roads to assist
road users, direct and assist road crossings in
designated areas to prevent traffic jams and traffic
accidents; Perform engineering traffic in places
often to jam or traffic accidents then by using
separator (broken barbell), shock band to minimize
the occurrence of traffic accidents (Dadang, 2017).
Preventive Activities: Implementing openly and
proactively the gamers and patrols on the roads to
assist road users, directing road crossings to cross
the specified places to prevent accidents and
minimize the fatality of casualties due to traffic
accidents; Enhancement of law enforcement in the
form of stationary and mobile raids with the target of
violations that have the potential to cause a traffic
accident through a speeding or a reprimand; Carry
out joint inspection activities with Transportation
Agency with the target of Bus vehicle about the
goodness of the vehicle and the load; Priority
handling traffic accidents then resulted by using
ADR (Alternative Dispute Resolution) method
which prioritizes the problem solving by mediating
between parties involved traffic accidents then until
the achievement of an agreement for the settlement
is poured into a statement; Handling of traffic
accidents ranging from TP-TKP, though crime scene
to the investigation of Traffic accident cases
ANCOSH 2018 - Annual Conference on Social Sciences and Humanities
184

conducted procedurally, proportionally and
professionally in order to achieve legal law.
Repressive Activities (Law Enforcement): The
repressive activities to solve the violations and
traffic accidents are as follows: Ticket: Tickets are
evidence of violation. the ticketing function itself is
an invitation to traffic offenders to attend a court
hearing, as well as a proof of the seizure of goods
confiscated by the police from offenders;
Foreclosure: The seizure is done because the driver
of the vehicle does not carry or have the documents
of the completeness of the vehicle and the driver's
license (SIM); Warning: A reprimand is committed
to a motorist who commits an offense but promises
not to commit another offense. Done by making a
written statement that it will not infringe.
The effort is expected to solve the problem and
also bring peace to the community, although in this
case it basically cannot eliminate the violation
directly but can give warning to those who have
committed violation by society or victim.
Furthermore, prioritizing the handling of traffic
accidents caused in material loss by using ADR
(alternative dispute resolution) method that
prioritizes problem solving by mediating between
parties involved traffic accidents then until the
achievement of an agreement for the settlement
which is poured into the statement also includes
repressive action. Handling of Traffic Accidents
from TP-TKP, TKP to Traffic Accident
investigation conducted procedurally, proportionally
and professionally in order to achieve legal law;
4 CONCLUSIONS
Strategy for the improvement effort that has been
done in preventing the increase of traffic accidents
in Regional Police of the republic of Indonesia in
East Java area by doing prevention with 3
approaches as follows: Pre-emtive Approach
(installing banners, and leaflets), Preventive
Approach (Implementing openly and proactively the
gamers and patrols on the roads to assist road users),
and Repressive Approach (Ticket, Foreclosure, and
Warning).
REFERENCES
Andrew R. C., 2011. Penegakan Hukum Lalu Lintas,
Nuansa. Bandung.
Andrea R. S., 2013. Penegakan Hukum Dalam
Mewujudkan Ketaatan Berlalu Lintas (Artikel Skripsi),
Lex Crimen Vol. II/ 7/November/2013
Dadang, D., 2017. Data from Directorate of Traffic East
Java Regional police of the republic of Indonesia.
Hartini, R., 2012. Hukum Pengangkutan di Indonesia,
Citra Mentari. Malang.
Hoong, C. C., Mohammed, A. Q., 2003. Applying the
random effect negative binomial model to examine
traffic accident occurrence at signalized intersections,
Accident Analysis & Prevention, Volume 35, Issue 2,
March 2003, Pages 253-259.
Ju-YeonLee, Jin-HyukChung, BongsooSon, 2008.
Analysis of traffic accident size for Korean highway
using structural equation models, Accident Analysis &
Prevention, Volume 40, Issue 6, November 2008,
Pages 1955-1963.
Marianne, J., Robert, W., Reinier, T., 2001. Crime and
Risky Behavior in Traffic: An Example of Cross-
Situational Consistency, Journal of Research in Crime
and Delinquency (JRCD), Volume: 38 issues: 4,
page(s): 439-459.
Mohamed A. Abdel-Aty, 2000. Modeling traffic accident
occurrence and involvement, Accident Analysis &
Prevention, Volume 32, Issue 5, September 2000,
Pages 633-642.
Romli, A., 2005. Teori dan Kapita Selekta
KRIMINOLOGI, Refika Aditama. Bandung.
Saffet, E., Ibrahim, Y., Tamer, B., Mevlut, G., 2008.
Geographical information systems aided traffic
accident analysis system case study: city of
Afyonkarahisar, Accident Analysis & Prevention,
Volume 40, Issue 1, January 2008, Pages 174-181.
Strategy of Improvement Effort in Traffic Accidents
185
