
Key Technology for Constructing Mobile System of Water
Purification System in Eutrophic Lakes and Reservoirs
Li Lin
1,2,*
, Min Wu
1,2
, Xianqiang Tang
1,2
, Liangyuan Zhao
1,2
and Qingyun Li
1,2
1
Basin Water Environmental Research Department, Changjiang River Scientific Research Institute, Wuhan 430010, China;
2
Hubei Provincial Key Laboratory of River Basin Water Resources and Eco-Environmental Sciences, Wuhan 430010,
China.
Email: linli1229@hotmail.com.
Keywords: Eutrophication water, mobile water purification system, micro-current electrolysis, microporous aeration,
adsorption
Abstract: The present paper proposes the treatment technology of mobile water purification system for in-situ
treatment in lake and reservoir eutrophication water. This system was composed of water purification unit,
mainly including adsorptions unit, microporous aeration unit, micro-current electrolysis unit, instruction
control unit, water quality on-line detection unit and power supply unit. The goal of excessive nutrient
reduction and harmful algal blooms control could be achieved by nitrogen and phosphorus removal by
adsorptions unit and microporous aeration unit, and algal inhibition by micro-current electrolysis unit. The
optimal dosage of adsorption material, in-situ adsorption time, aeration intensity, current density,
electrolytic time and other technical parameters were achieved by the experiment of adsorption,
microporous aeration and micro-current electrolysis using high-performance adsorbents, optimal aeration
way and electrode material. Finally, the present study prospects the way to improve the water purification
performance and enhance the operation management of mobile water purification system was discussed
according to the experimental results and subsequent practical application. Overall, the technology of
mobile water purification system is a new and effective technology for eutrophication treatment and will
provide solutions for prevention and control of nutrient overloading and algae blooms.
1 INTRODUCTION
Widespread eutrophication in the lakes or reservoirs
has become one of the most serious environmental
problems. The proportions of eutrophication lakes or
reservoirs were 41%, 61% and 77% in 1970s, 1980s
and 1990s respectively (Ma and Li, 2002). The
water quality survey of lakes during 2007-2010
showed that 85.4% shallow lakes exceeded the
eutrophication criteria, in which 40.1% were severe
eutrophication (Yang et al., 2010). Eutrophication
deteriorated the water quality and caused water
resource scarcity crisis, which decreased water
utilization efficiency and capability of safe water
supply. Eutrophication weakened the supporting role
of water resource for the social development and the
national economy greatly (Lin et al., 2015).
The prevention of eutrophication includes algae
control and excess nutrients (e.g., nitrogen and
phosphorus) reduction. For algae control, the
traditional methods include removing algae by
machinery or chemical method (Zhu et al., 2016).
For the reduction of excess nutrients, clean water
dilution, absorption and cleanup by plants are the
common methods. Those technologies for algal
control are usually time and energy consuming.
Reduction of excess nutrients typically requires
supporting of water diversion construction project or
vegetation restoration project. Water diversion
project wastes much clean water, while the
efficiency of vegetation restoration project is low.
Above all, under the condition of controlling
external pollution source, choosing suitable
technologies to decrease ammonia and phosphorus
concentration is the most important issue for solving
eutrophication in lakes and reservoirs.
Eutrophication in lakes and reservoirs usually
occurs in the bay of lakes and branch of reservoirs
176
Lin, L., Wu, M., Tang, X., Zhao, L. and Li, Q.
Key Technology for Constructing Mobile System of Water Purification System in Eutrophic Lakes and Reservoirs.
In Proceedings of the Inter national Workshop on Environment and Geoscience (IWEG 2018), pages 176-181
ISBN: 978-989-758-342-1
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

with slow flow. It is very hard to purify water by
pumping water from the water body. In this study,
we built a mobile water purification system, which
integrated the traditional water treatment
technologies such as adsorption and microporous
aeration, and new technology such as micro-current
electrolysis technology for nutrients reduction and
algae control. This mobile water purification system
can move on the surface of lakes and reservoirs and
purify the water body continuously. It will provide
new solutions and technical support for
eutrophication in lakes and reservoirs.
2 KEY TECHNOLOGY FOR
CONSTRUCTING MOBILE
WATER PURIFICATION
SYSTEM
2.1 Construction and Work Principle
of the System
The mobile water purification system consists of a
mobile float platform, water treatment unit
(absorption unit, microporous aeration unit, and
micro-current electrolysis unit), water quality on-
line detection unit, instruction control unit and
power supply unit, etc (Figure 1). Mobile float
platform is made as a ship. The standard absorption
unit and micro-current electrolysis unit is set on the
deck of the ship. Microporous aeration unit arranged
below the absorption unit and micro-current
electrolysis unit. Water quality on-line detection unit,
instruction control unit and power supply unit are
supporting systems for the mobile water purification
system, which are used for controlling and
managing the whole system.
The work principles of mobile water purification
system are shown in Figure 2. Based on the results
from water quality on-line detection unit and
analysis the water quality, absorption unit, micro-
current electrolysis unit and microporous aeration
unit began to work. The system moved on the
surface of the water body, and the water treatment
units worked together. Then oxygen concentration in
the water was increased, and nitrogen and
phosphorus in water were absorbed, and the algal
growth was inhibited by micro-current electrolysis
unit. When the water quality of the treated water
meets the requirements, the system enters the new
target area. In the whole process of water treatment,
the operation parameters of micro-current
electrolysis unit and microporous aeration units
were controlled by instruction control unit, the
moving direction and speed for the system were
controlled by power supply unit.
Figure 1: Side view and bottom view of mobile water
purification system
Figure 2: Sketch of circuit connection for mobile water
purification system.
2.2 Key Technical Difficulties
The treatment effects of mobile water purification
system are depending on the function of the
absorption unit, micro-current electrolysis unit and
microporous aeration unit. According to the working
principle of the mobile water purification system, it
Key Technology for Constructing Mobile System of Water Purification System in Eutrophic Lakes and Reservoirs
177
is necessary to solve the key technical difficulties by
experiments.
(1) Performance and technical parameters of
mobile adsorption
In view of the water quality characteristics for
eutrophication waters, the selection of adsorption
materials for high efficiency and low concentration
of nitrogen and phosphorus is the key technical
difficulties. The optimal dosage of the adsorption
material, adsorption time and service life were
important operation factors which are needed to be
studied.
(2) Performance and technical parameters of
microporous aeration unit
For in-situ microporous aeration unit, aeration
intensity, aeration time are the key parameters
needed to be explored.
(3) Inhibited algal growth performance and
technical parameters for micro-current electrolysis
Based on the results of inhabited algae by micro-
current electrolysis, the selection of electrode
materials was the key difficulty, whereas the
appropriate current density and electrolysis time are
the key parameters needed to be studied.
3 EXPERIMENTAL STUDY FOR
CONSTRUCTING MOBILE
WATER PURIFICATION
SYSTEM
Experiments were carried out using natural lake
water, pH for lake water was 8.0. The initial
ammonia and total phosphorus concentration were
controlled as 3.0 mg/L and 0.5 mg/L by adding the
nutrient of nitrogen and phosphorus, respectively.
Mobile adsorption, microporous aeration and micro-
current electrolysis were used for water purification,
which make relevant water quality indicators to
meet the V class of water standards (ammonia
concentration lower than 2.0 mg/L, total phosphorus
concentration lower than 0.2mg/L) of national water
environmental quality standard in China (GB 3838-
2002) (in reference).
3.1 Mobile Adsorption
Phosphorus is the limiting factor for water
eutrophication (Tang et al., 2014). Our study results
showed that the adsorption capacity of activated
alumina was better than that of zeolite (including
natural, acid modification, ion modification),
manganese sand and ceramsite by indoor
experiments (data not shown).
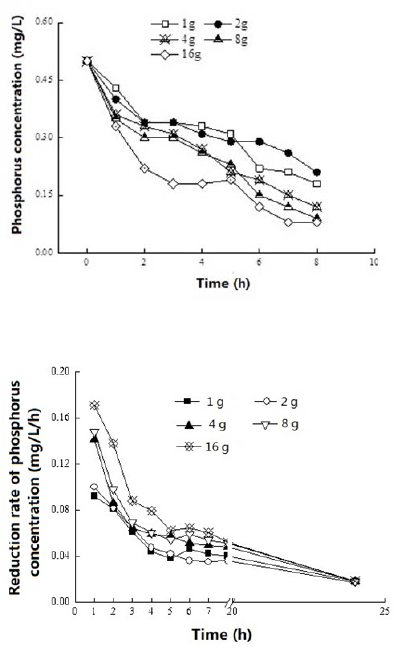
Figure 3 shows phosphorus adsorption mass for
activated alumina. With the different dosages of
activated alumina including 1 g/L, 2 g/L, 4 g/L, 8
g/L and 16 g/L, the removal efficiency of
phosphorus were 64%, 58%,76%, 82% and 84%,
respectively. When the dosage of activated alumina
was 8 g/L, the phosphorus removal rates haven’t
increased with dosages of activated alumina. When
the dosage of activated alumina increased from 8
g/L to 16 g/L, the increasing extent of adsorption
rate decreased. With the same initial concentration,
the phosphorus will diffusion into the surface of
activated alumina and absorbed by activated alumina.
Considering the phosphorus removal effect and the
phosphorus adsorption capacity per unit mass of
activated alumina, 8g/L activated alumina was
selected for the mobile water purification system.
Figure 3: Phosphorous concentration variations with time.
Figure 4: Average decrease rate of phosphorus
concentration.
IWEG 2018 - International Workshop on Environment and Geoscience
178

Figure 4 shows the average decrease rate of
phosphorus concentration. The average decrease rate
was calculated based on concentration difference
divided by time difference. The decreasing rates of
phosphorus concentration were comparatively
consistent with different dosages of active alumina.
The rate of the first 2 h was high, then decreased. At
the end of the experiment, the decrease rate of
phosphorus concentration was 0.018 mg/L/h. From
the experiment results, 2 h was selected as the
optimum time for mobile water purification system.
3.2 Microporous Aeration
Ammonia is one of the most important indexes to
reflect the eutrophication status of the water body.
High concentration of ammonia in eutrophic water
can lead to damage to the organism. Aeration
technology is suitable for treating water polluted by
ammonia. The ammonia removal efficiency and the
cost between micro-nano aeration equipment and
microporous aeration equipment were compared in
this study. It is found that the microporous aeration
equipment can be used in situ and treat large amount
of water. Therefore, it is more suitable for mobile
water purification system, whereas the aeration time,
strength and effective time of dissolved oxygen were
studied.
Figure 5 shows the effect of microporous
aeration time on removal of ammonia nitrogen. The
initial concentration of ammonia was 3.0 mg/L,
which was inferior to V class standard of surface
water. The initial pH of natural water was 8.01 and
the aeration intensity was 0.5 kg/cm
2
. The results
showed that microporous aeration time had a certain
effect on ammonia nitrogen removing. The effect of
ammonia removal increased significantly at first 4 h.
Figure 5: Effect of microporous aeration time on ammonia
removal.
Figure 6 shows the effect of microporous
aeration intensity on removal of ammonia nitrogen.
With the same experimental condition, the ammonia
removal efficiency increased with aeration intensity,
the removal efficiency of aeration with 1.0 kg/cm
2
was higher than that with 0.5 kg/cm
2
and 0.2 kg/cm
2
.
In order to decrease energy consumption and avoid
sediment disturbing, 0.5 kg/cm
2
was chosen for
aeration equipment.
Figure 6: Effect of aeration intensity on ammonia removal.
3.3 Micro-Current Electrolysis
Controlling algae growth is the most effective way
to prevent eutrophication. Micro-current electrolysis
technology uses micro-current to make the algae
inactivate, which inhibited algae growth in their
early stages of production, and then prevent the
occurrence of algae bloom (Lin et al., 2015). In
order to apply micro-current electrolysis technology
to mobile water purification system effectively, the
key technical parameters such as electrode materials,
current density, electrolysis time and electrode
effective range were studied.
In order to know whether the remaining algae
cells had the potential to survive and grow, the algal
solution after electrolysis were poured to a 100 mL
conical flask with a gauze stopper, and put into an
illumination incubator to culture. Samples were
taken from the conical flask at 0, 2, 4, 6, 8 and 15
days. Control samples with no electrolysis were also
exposed to the same conditions as the test samples.
OD
680
of algal solution samples which was used as
the indirect index of cell viability of algal solution
was measured. Chlorophyll fluorescence parameters
Fv/Fm was used to determine the photosynthetic
activities of algae (Lin et al., 2015).
Key Technology for Constructing Mobile System of Water Purification System in Eutrophic Lakes and Reservoirs
179
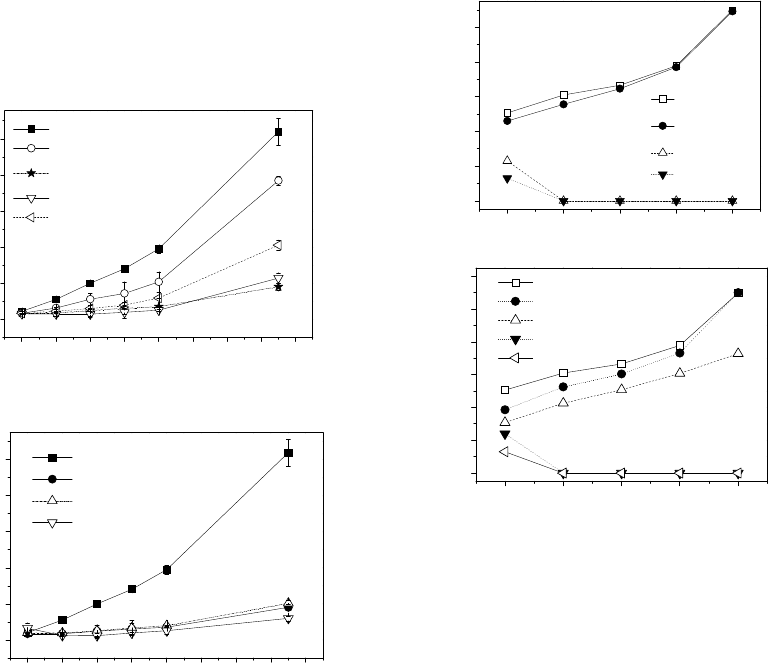
Figure 7 shows the effect of different anode and
cathode materials on algal control by micro-current
electrolytic. Under conditions of 100 mL algae
solution with 1×10
6
cells/mL, electrode working
area of 2.5 cm×5.5 cm, electrolysis plate spacing of
4 cm, electrolysis current density of 20 mA/cm
2
, and
electrolysis time 10 minutes, 4 kinds of anodes
materials include RuO
2
/Ti, Pt/Ti, stainless-steel and
IrO
2
/Ti were chosen by experiments. The results
showed that anode materials had a great influence on
the inhibition of algae, while the effect of cathode
materials was small. RuO
2
/Ti and stainless steel
were selected as the anode and cathode materials,
respectively. Active substances produced by
electrolysis played an important role for inhibition
of algae (Xu et al., 2014). Based on our study, the
height, width and pitch of the electrode plate are
suggested to be 50 cm, 20 cm and 2 cm respectively
for mobile water purification system.
0246810121416
0.0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0
OD
680
Time (d)
control sample
IrO
2
/Ti
RuO
2
/Ti
Pt/Ti
stainless steel
0246810121416
0.0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0
OD
680
Time (d)
control sample
stainless steel
Zn
graphite
Figure 7: Effect of different anode (left) and cathode (right)
materials on algae suppression by micro-current
electrolytic (OD
680
is the optical densities at 680nm of
algal cell solution).
Figure 8 shows the effects of different current
densities (left) and electrolysis time (right) on
chlorophyll fluorescence parameters Fv/Fm. The
algae inhibition experiment was carried out with 45
L algae solution (cells density was 5×10
4
cells/mL),
electrode work area was 50 cm×15 cm, and the
spacing between two electrodes was 2 cm. The
experiment results showed that algal inhibition
increased with the current density, algae cell was
completely inactivated with current density above 9
mA/cm
2
. Therefore, the suitable current density was
9~12 mA/cm
2
for inhibition algae growth using the
mobile water purification system. And 2 h was the
suitable electrolysis time.
02468
0.0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
Electrolysis time: 2h
Fv/Fm
Time (d)
Control
6 mA cm
-2
9 mA cm
-2
12 mA cm
-2
02468
0.0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
Current density:12 mA cm
-2
Fv/Fm
Time (d)
Control
0.5 h
1 h
1.5 h
2 h
Figure 8: Effects of different current densities (left) and
electrolysis time (right) on chlorophyll fluorescence
parameters Fv/Fm.
4 CONCLUSIONS
The eutrophication lakes and reservoirs were
relatively closed and with very low flow rate. The
mobile water purification system which was an in-
situ treatment technology was built for this kind of
water body. The goals of reduction of nitrogen and
IWEG 2018 - International Workshop on Environment and Geoscience
180
phosphorus nutrients and algal control can be
achieved by using adsorption, aeration and micro-
current electrolysis.
Focused on the function units and key
technologies of the system, the adsorption, aeration,
micro-current experiment under moving conditions
were carried on, which used activated alumina,
microporous aeration and RuO
2
/Ti anode and
stainless-steel cathode, and obtained important
technical parameters as follows:
(1) With 0.5 mg/L initial concentration of
phosphorus, the optimum amount of activated
alumina for adsorbing phosphorus was 8 g/L under
moving conditions, the optimum adsorption time
was 2 h.
(2) Under 3 mg/L initial concentration of
ammonia nitrogen, the optimum treatment time of
microporous aeration was 4h, the optimum aeration
intensity was 0.5 kg/cm
2
.
(3) With 50 cm height and 2 cm spacing of
electrode plate and consisted of RuO
2
/Ti anode and
stainless-steel cathode, the optimum current density
of micro-current electrolysis system is 9~12 mA/cm
2
,
and the electrolysis time was 2 h.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
This work was supported by the National Natural
Science Foundation of China (Grants 51309019),
Young Elite Scientist Sponsorship Program by
CAST (Grant 2015QNRC001), Technology
Demonstration Project of the Ministry of Water
Resources of China (SF-201602), and State-level
Public Welfare Scientific Research Institutes Basic
Scientific Research Business Project of China
(CKSF2017062/SH).
REFERENCES
GB 3838-2002. National water environmental quality
standard in China.
Lin L, Appiah-Sefah G, Li M 2015 Using a laser particle
analyzer to demonstrate relationships between wind
strength and Microcystis colony size distribution in
lake Taihu, China [J] Journal of Freshwater Ecology
30 425
Lin L, Feng C, Li QY, et al. 2015. Effects of electrolysis
by low-amperage electric current on the chlorophyll
fluorescence characteristics of Microcystis aeruginosa
[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 22
14932.
Ma JA, Li HQ 2002 Talking about the eutrophication of
water bodies in rivers and lakes at home and abroad [J]
Resources and Environment of Yangtze River (in
Chinsese) 11 575
Tang XQ, Wu M, Dai XC, et al. 2014 Phosphorus storage
dynamics and adsorption characteristics for sediment
from a drinking water source reservoir and its relation
with sediment compositions [J] Ecological
Engineering 64 276.
Xu Y, Peng H, Yang Y, et al. 2014. Cumulative
eutrophication risk evaluation method based on a
bioaccumulation model [J]. Ecological Modelling 289
77
Yang GS, Ma RH, Zhang L, et al. 2010 Lake status,
major problems and protection strategy in China [J]
Journal of Lake Science 22 799
Zhu W, Zhou, X, Chen H, Gao L, Xiao M, Li M 2016
High nutrient concentration and temperature alleviated
formation of large colonies of Microcystis: Evidence
from field investigations and laboratory experiments [J]
Water Research 101 167
Key Technology for Constructing Mobile System of Water Purification System in Eutrophic Lakes and Reservoirs
181
