
Correlative Study between Ground Motion Parameters and
Geological Hazards Distribution in Bailong River Basin
Aiguo Wang
1,2,*
Daoyang Yuan
1,2
, Bo Zhang
1,2
and Wengui He
1,2
1
Lanzhou Institute of Seismology, China Earthquake Administration, Lanzhou, Gansu, China
2
Seismology Bureau of Gansu Province, Lanzhou, Gansu, China
Email: waguo2008@163.com
Keywords
: Correlative study, ground motion parameters, geological hazards distribution, Bailong River Basin
Abstract: Bailong river basin is located at the north-east margin of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. It is a high seismic intensity
region with a frequent occurrence of earthquakes and also a geo-hazards developed regions with intensive
landslides and debris flows. Based on comprehensive isoseismal lines of historical earthquakes and the
result of ground motion parameters zoning, the deterministic zoning of seismic intensity (I) and peak ground
acceleration (PGA) in Bailong river watershed were given. For each zone of seismic intensity and PGA, the
number of landslides and debris flows and some geological hazard statistical parameters such as hazard
number, hazard develop rate, and the density of hazard occurrence were calculated and analyzed. The
results show that there was a positive correlation between the geological hazard statistical indices and
seismic intensity and PGA value. Higher the seismic intensity (I) and PGA value, larger the geological
hazard statistical indices in a seismic zone. Using a logarithmic function method, the fitting functions
between the hazard occurrence density of landslides and debris flows and the value of seismic intensity or
PGA value were obtained with a high fitting degree, which can be applied as reference of geological
hazards evaluation for the similar geologic environment.
1 INTRODUCTION
As a branch of Yangtze River, Bailong river is
located in the northeast margin of Qinghai-Tibet
Plateau and also the north section of the north south
seismic belt, where active tectonics is well
developed and many large historic earthquakes
occurred (Figure 1). For large areas the river flows
through high mountains and deep valleys with high
seismic intensity. Complicated geology structure and
unique landform make the Bailong river basin one of
the regions with most severe debris-flow and
landslide damages in China (Meng et al., 2013).
According to the investigation data, more than
80% of the landslides in Wudu County in Bailong
river basin related to earthquake and the large
earthquake of Ms8 in 1879 played a crucial role in
the aggravated water and soil loss and development
of landslide and debris-flow in the last 100 years in
the middle reaches of Bailong river (Tang, 1992). In
the night of Aug. 7, 2010, torrential rainfall in
Zhouqu County triggered a devastating mudslides
which caused heavy casualties and property losses
including 1463 dead and 302 missing (Zhang and
Zhang, 2011). The mudslides blocked Bailong River
and a dangerous barrier lake formed. Research
shows that the Wenchuan Ms8 earthquake in 2012
weakened the mountain slopes, which is the main
cause of the extraordinary serious natural calamity
together with half year’s drought and subsequent
strong rainfall. So seismic action influences and
strongly controls the geological hazard in Bailong
River basin (Tang, 1992; Zhang and Zhang, 2011;
Chang et al., 2014; Ma et al., 2014).
To study the relationship between seismic action
and geological hazard, the deterministic zoning of
seismic intensity (I) and peak ground acceleration
(PGA) in Bailong river watershed were given
according to comprehensive isoseismal lines of
historical earthquakes and the result of ground
motion parameters zoning. Based on statistics of the
hazard indices of landslide and debris-flow in
different seismic zoning area, the relationship
between seismic action and geological hazard
distribution was discussed and the relation curves
were fitted, which can be a reference to the statistics,
assessment and forecast of geological disasters in
similar geologic settings.
440
Wang, A., Yuan, D., Zhang, B. and He, W.
Correlative Study between Ground Motion Parameters and Geological Hazards Distribution in Bailong River Basin.
In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Environment and Geoscience (IWEG 2018), pages 440-444
ISBN: 978-989-758-342-1
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

Figure 1: The regional seismotectonic map of Bailong
River Basin and distribution of geological hazards. (the
yellow region is Bailong River Basin).
2 SEISMIC ZONING
As the distribution of geological hazards is a
cumulative result of long-time seismic geological
action and the time span is much longer than the
historic earthquake cycle of seismic zones, the
correlative study between hazard distribution and
seismic effect should be based on long-term seismic
action -- i.e. deterministic seismic zoning based on
tectonic activity study, which can be determined by
the maximum historical earthquake method and
seismo-tectonic method (Hu, 1999).
The historic earthquake records and modern
seismic activities show that the earthquakes
controlling the distribution of maximum seismic
intensity in Bailong River basin mainly include the
earthquake Ms7-71/4 in -186A.D. west to Wudu,
earthquake Ms63/4 in 1537 near Minxian,
earthquake Ms8 in 1654 South to Tianshui,
earthquake Ms8 in 1879 south to Wudu, earthquake
Ms7.2 in 1976 near Songpan and Pingwu,
earthquake Ms5.9 in 1987 north to Diebu (Figure 1)
and Wenchuan Ms8 earthquake in 2008.
Summarizing these earthquakes’ records and
isoseismal lines (Yuan et al., 2007; Zheng et al.,
2007; Yuan et al., 2017; Yuan et al., 2014; Hou,
1989; Xing and Xu, 2011), the comprehensive
isoseismals of historical earthquakes can be obtained
by determining the maximum seismic intensity
suffered from all the history earthquake for each
place.
Seismic ground motion parameter zonation uses
probability method (Hu, 1999), which has an overall
consideration of seismogenic structure, potential
earthquake capacity, historic earthquake and elapsed
time, etc. Paleo-earthquake research revealed that
the earthquake recurrence period is about hundreds
to thousands years (James, 2009), so the seismic
ground motion parameters under exceeding
probabilities of 0.01% can be seem as the
deterministic seismic parameters based on tectonic
activity study.
By using the results of the division of potential
seismic source areas, ground motion attenuation
relationship and seismic activity parameters adopted
in the latest version of seismic zoning map of China
(GB18306-2015, 2015), the distribution of seismic
intensity (I) and horizontal peak ground acceleration
(PGA) under exceeding probabilities of 0.01% in
Bailong River Basin were calculated. Combining
with the comprehensive isoseismals of historical
earthquakes above, the deterministic zoning map of
seismic intensity I and PGA in Bailong river basin
were achieved. Figure 2 shows the zoning results
and also the distribution of landslides and debris
flows.
Figure 2: The deterministic zoning map of seismic
intensity I and PGA in Bailong River basin.
Correlative Study between Ground Motion Parameters and Geological Hazards Distribution in Bailong River Basin
441
3 GEOLOGICAL HAZARD
STATISTICAL INDICES
There are many factors influencing the occurrence of
seismo-geological hazard (Chen et al., 2013; Qi et
al., 2009). Aiming at the correlations between
ground motion parameters and geological hazards
distribution in Bailong River Basin, this study used
the following geological hazard statistical indices.
• Hazard Number DA
ji
DA
ji
means the hazard number of category or
data section j (such as I or PGA value) to factor i
(such as landslide or debris flow) in the research
area.
• Hazard Develop Rate R
ji
The definition of R
ji
is
AA
DADA
R
ji
ji
ji
=
(1)
Where A is the area of study region, A
ji
is the
area of category or data section j to factor i, and DA
is the total hazard number.
• Density of Hazard Occurrence
ji
ρ
Density of hazard occurrence means the hazard
number in unit area, i.e.
jijiji
ADA=
ρ
(2)
Where A
ji
is the area of category or data section j
to factor i, and DAji is the hazard number of
category or data section j to factor i in the research
area.
For each seismic intensity zone and horizontal
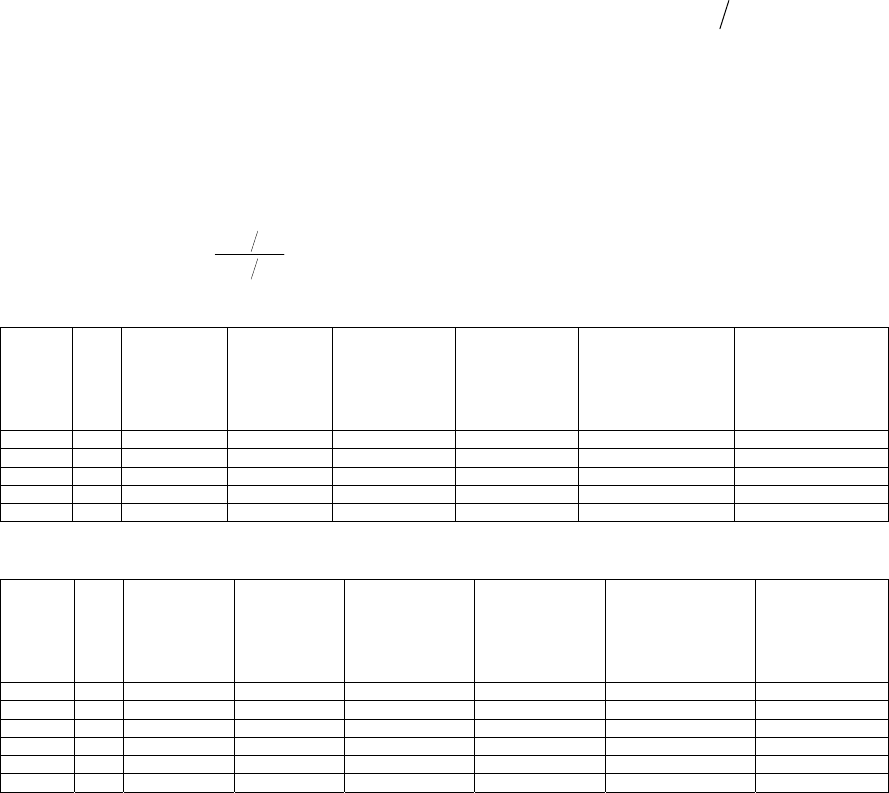
PGA zone, Table 1 and Table 2 list the above three
indices calculated separately.
Table 1: Geological hazard statistical indices in different seismic intensity zone.
Seismic
intensity
Area
/Km
2
Landslide
number DA
j1
Debris-flow
number DA
j2
Landslide develop
rate
1j
R
Debris-flow
develop rate
2j
R
Density of Landslide
Occurrence
1j
ρ
Density of Debris-flow
Occurrence
2j
ρ
8 4546 25 83 0.264 0.496 0.0055 0.0183
9 9515 186 245 0.938 0.699 0.0195 0.0257
10 5533 164 361 1.422 1.772 0.0296 0.0652
11 1184 58 76 2.351 1.743 0.0490 0.0642
Su
m
20778 433 765
Table 2: Geological hazard statistical indices in different PGA zone.
Seismic
intensity
Area
/Km
2
Landslide
number DA
j3
Debris-flow
number DA
j4
Landslide develop
rate
3j
R
Debris-flow
develop rate
4j
R
Density of Landslide
Occurrence
3j
ρ
Density of Debris-
flow Occurrence
4j
ρ
0.3g 1608 2 0.060 0.0012
0.4g 6086 78 117 0.615 0.923 0.0128 0.0192
0.5g 5874 129 179 1.054 1.462 0.0220 0.0305
0.6g 3830 123 264 1.541 3.308 0.0321 0.0689
0.7g 3382 101 205 1.433 2.909 0.0299 0.0606
Su
m
20778 433 765
4 CORRELATIVE STUDY
Figure 3 shows the statistical relationships between
ground motion parameters and geological hazards
statistical indices. The figures indicate that the
hazard number DA relates to area of zone as same
as ground motion parameters I and PGA. Except
PGA zone 0.7g due to epicenter magnitude
saturation in seismic risk assessment, Landslide
develop rate R has positive correlation with seismic
intensity (I) and PGA value, higher I and PGA
value, larger R in a seismic zone. Debris-flow
develop rate R has also positive correlation with I
and PGA value, but obviously influenced by other
factors meanwhile. Hazard occurrence ρ of
landslide and debris-flow has more consistent
positive correlations with ground motion parameters
I and PGA. Well correlative relations show that the
seismic action in Bailong River basin greatly
influences and controls the occurrence and
distribution of landslide and debris-flow.
IWEG 2018 - International Workshop on Environment and Geoscience
442
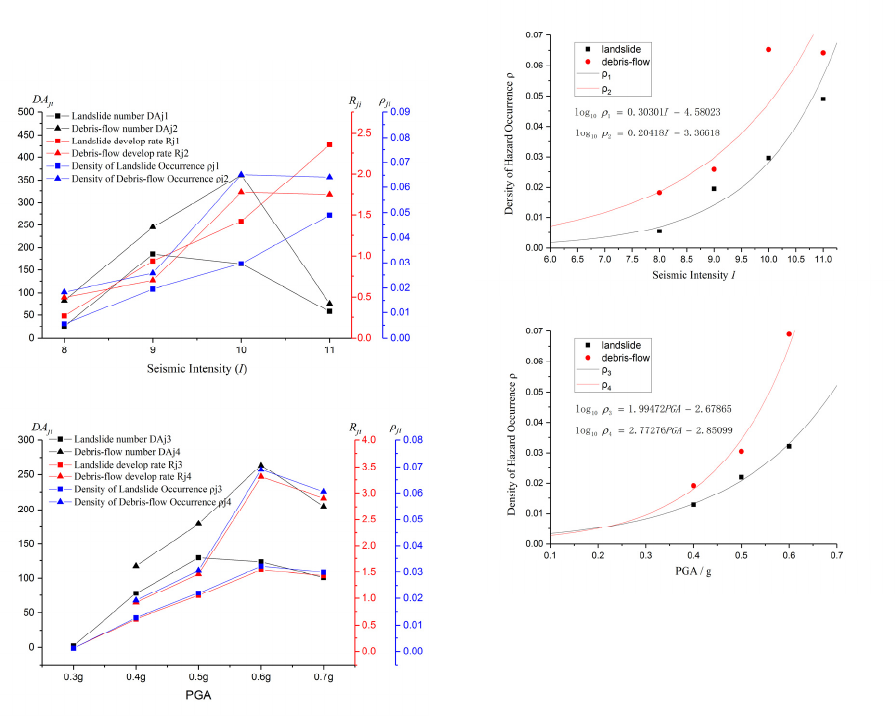
Comparing the results of the three indices,
density of hazard occurrence ρ can show the
correlative relationship between ground motion
parameters and geological hazards better. Refer to
the relation between seismic energy and seismic
parameter I and PGA, the logarithmic function was
adopted to fit the relation between density of
landslide and debris flow occurrence and seismic
parameter I and PGA, separately. Figure 4 shows
the fitting curves and original scattered data and the
fitting equations as following.
Figure 3: Statistical relationship between ground motion
parameters and geological hazards statistical indices.
Fitting equation between seismic intensity I and
density of landslide occurrence is as:
58023.430301.0log
110
−= I
ρ
R=0.963 (3)
Fitting equation between seismic intensity I and
density of debris flow occurrence is as:
36618.320418.0log
210
−= I
ρ
R=0.938 (4)
Fitting equation between PGA and density of
landslide occurrence is as:
67865.299472.1log
310
−= PGA
ρ
R=0.995 (5)
Fitting equation between PGA and density of
debris flow occurrence is as:
85099.277276.2log
410
−= PGA
ρ
R=0.987 (6)
In Equation1, Equation 2, Equation 3 and
Equation 4, R is the correlation coefficient.
These equations can be used to evaluate the
landslide and debris-flow hazard around Bailong
river or for the similar geologic environment region.
Figure 4: The fitting curves between density of hazard
occurrence and I and PGA.
5 DISCUSSION AND
CONCLUSIONS
Bailong River basin belongs to high seismic
intensity region with frequent occurrence of
earthquakes and also regions with most severe
debris-flow and landslide damages in China. The
developments of landslide and debris flow hazard
are well related to seismic action. The results show
that there is a positive correlation between the
geological hazard statistical indices and seismic
intensity (I) and PGA value in Bailong River basin,
higher I and PGA value, larger the geological hazard
Correlative Study between Ground Motion Parameters and Geological Hazards Distribution in Bailong River Basin
443
statistical indices in a seismic zone. The fitting
equations also show that density of landslide and
debris flow occurrenceρ and seismic parameter I
and PGA have well logarithmic relationship.
The main causes of widely developed landslide
and debris flow hazards in Bailong River basin are
not only the active geology structures and strong
earthquake activities but also the steep and high
topography, weak and broken rock stratum,
intensive rainfall, sharp river cutting, lower
vegetation coverage and unreasonable human
engineering activities (Tang, 1992). This research
discussed only the relation between earthquake
intensity and geological hazard distribution, and
ignored the scale and time of the landslides and
debris flows, which is not extremely scientific and
rational. Anyway the well positive correlation and
fitting equations between the geological hazard
statistical indices and seismic intensity (I) and PGA
can be applied as reference of geological hazards
evaluation around Bailong river basin or for regions
with similar geologic environment.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors would like to thank Prof. Jinzhu Ma for
providing the landslide and debris flow data. This
research was financially supported by the
Earthquake Science and Technology Spark Plan
Project of Chinese Earthquake Administration
(XH16036) and National Natural Science
Foundation of China (41572197).
REFERENCES
2015 General Administration of Quality Supervision,
Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of
China, China National Standardization Management
Committee. Seismic ground motion parameters
zonation map of China (GB18306-2015) 3
Chang Zhiyang, Wang Jian and Bai Shibiao, et al. 2014
Appraisal of active tectonic in bailongjiang basin
based on dem data Quaternary Sciences 34 292
Chen Guan, Meng Xingmin and Qiao Liang, et al. 2013
Distribution, characteristics, and associated influential
factors of the geohazards induced by minxian-
zhangxian earthquake on 22 july, 2013, Gansu, China
Journal of Engineering Geology 21 750
Hou Zhenqing 1989 The Diebu earthquake of M=5.9 on 8
Jan. 1987 Earthquake Research in China 5 71
Hu Lvxian 1999 Technical course of seismic safety
evaluation 205
James P, Mc Calpin 2009 Paleoseismology, 2
nd
Ed 19
Ma Jin-hui, Tian Fei and Chen Lu 2014 Relative
importance analysis of debris flow factors based on
dominance analysis: a case study of the Bailongjiang
Basin in China Journal of Lanzhou University
(Natural Science) 50 722
Meng Xingmin, Chen Guan and Guo Peng, et al. 2013
Research of landslides and debris flows in Bailong
river basin: progrss and prospect Marine Geology &
Quaternary Geology 33 1
Qi Shengwen, Xu Qiang and Liu Chunling, et al. 2009
Slope instabilities in the severest disaster areas of 5.12
Wenchuan earthquake Journal of Engineering
Geology 17 39
Tang Yongyi 1992 The effect of neotectonic movement
on formation of landslide and debris flow in southern
Gansu Journal of Lanzhou University (Natural
Science) 28 152
Xing Huilin and Xu Xiwei 2011 M8.0 Wenchuan
Earthquake 149
Yuan Daoyang, Lei Zhongsheng and He Wengui, et al.
2007 Textual research of wudu earthquake in 186
B.C. in Gansu province, China and discussion on its
causative structure Acta Seismologica Sinica 29 654
Yuan Daoyang, Lei Zhongsheng and Wang Aiguo 2017
Additional textual criticism of southern Tianshui M8
earthquake in Gansu Province in 1654 China
Earthquake Engineering Journal 39 509
Yuan Daoyang, Lei Zhongsheng and Yang Qingyun, et al.
2014 Seismic disaster features of the 1879 southern
Wudu M8 earthquake in Gansu province Journal of
Lanzhou University (Natural Science) 50 611
Zhang Wangfeng and Zhang Fenglin 2011 Introspection
of urban geological hazard prevention from the debris
flow disaster in Zhouqu County Gansu Science and
Technology 27 53
Zheng Wenjun, Lei Zhongsheng and Yuan Daoyang, et al.
2007 Textual Reasearch on the Historical Data of the
1573 AD Minxian Earthquake in Gansu Province and
Disscussion on Its Seismogenic Structure Earthquake
Researchin China 23 75
IWEG 2018 - International Workshop on Environment and Geoscience
444
