
Study on Evaluation Method of Surface Roughness of Wood
Processing
L Qing, Z F Li and D Xing
*
College of Material Science and Art Design, Inner Mongolia Agricultural University,
Hohhot 010018, China
Corresponding author and e-mail: D Xing, xing.dong2008@163.com
Abstract. Surface roughness is one of the important indexes for evaluating the surface
properties of materials. However, the present surface roughness evaluation of porous
materials is not a uniform standard and equipment. In this paper, a laser three-dimensional
microscope system is used to test and analyze the surface roughness of different parts of
wood with different processing methods. A fast method is proposed for the evaluation of
surface roughness of wood processing. The first step is to comprehensively consider the
evaluation site of the selected specimen; Second step is to select two steps to meet the
accuracy grade and the appropriate test mode to finish the measurement and evaluation.
1. Introduction
The surface of wood products is one of the main evaluation indexes of contact with human body and
appearance performance, it affects the function and use of wood products. The surface roughness
value is mainly used in the evaluation of superficial quality, and there are many factors affecting
surface roughness. Wood properties, processing machinery precision, processing parameters, tool
materials and tool parameters [1, 2], and other factors alone or superimposed, the shape is very
complex. The different surface roughness evaluation parameters are different, the surface roughness
formation mechanism is different, and the pipe and other timber structure caused by the pits. As a
result, the surface roughness of wood processing is composed of two parts [1, 3]
resulting from the
surface roughness formed by the processing itself and the roughness caused by the wood cell
structure. The wood structure affecting surface roughness mainly includes duct (Guincon), wood
fiber, axial thin-walled tissue, wood ray and ring, and the influence degree of tree species and
processing surface and wood structure is different[1, 3, 4, 5]. The surface shape and roughness of
wood affect the consumption, non-flammable and decoration quality of adhesives and coatings, and
the requirements of surface roughness should be taken into account when determining processing
technology and machining allowances. Therefore, many researches have been done on the surface
roughness of wood at home and abroad, and the research on the determination of surface roughness
of wood has sprouted in the 30's [6], the real beginning was the 50's [3]. The main wood surface
roughness parameters of the study[7, 8, 9], study on the mechanism of surface forming and the
influence of tree species and wood structure[3, 10, 11], study on the influence of cutting mode and
cutting parameters and roughness[12, 13], study on machined surface and suitable filtration treatment
value[14]. Research on laser online test and application[15, 16, 17], research on the relationship
Qing, L., Li, Z. and Xing, D.
Study on Evaluation Method of Surface Roughness of Wood Processing.
In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Materials, Chemistry and Engineering (IWMCE 2018), pages 83-92
ISBN: 978-989-758-346-9
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
83

between surface roughness, tactile sensation and roughness[10, 14], the effect of wood treatment
conditions on surface roughness
[18], Application of image processing method in surface roughness
measurement[19, 20, 21], Effect of surface roughness on finishing treatment[22, 23], the influence of
material on surface roughness[24, 25, 26], the study of the influence of cutting tool and tool material
on surface roughness[27, 28], basically covers various factors that affect the surface roughness of
wood processing. With the continuous improvement of people's living standard and the rapid
development of wood industry, building decoration industry and furniture industry, the surface
quality requirements and importance of wood parts are more and more high. The surface roughness
not only affects the appearance quality of wood parts, but also affects the processing technology and
production cost. However, at present, there is no special measuring equipment and the ideal
evaluation method. The measuring parameters and standard methods of surface roughness of wood
parts are developed on the basis of the standardized measurement theory of the contact needle
homogeneous materials [29, 30, 31]. The method of surface roughness measurement can be divided
into two types: contact measurement and non-contact measurement. Contact measurement mainly
refers to the stylus type measurement, this method can reproduce the surface condition of workpiece,
but it is easy to damage the surface of the workpiece, at the same time the size of probe needle
directly affects the precision of measurement, low measurement precision, and can not directly
identify the structure of wood, it is difficult to meet the requirements of modern measurement
technology. Non-contact measurement has the advantages of fast, non-contact, non-destructive and
high precision, which is paid attention to by people. The Non-contact method, represented by the
laser method with high measurement accuracy and relative measuring speed, is more suitable for the
determination of wood surface roughness. In this study, a shape measuring laser microscope system
was used to determine the surface roughness of wood with different parts, different processing modes,
different magnification and different test modes, so as to propose a method for evaluating the surface
roughness of wood processing.
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Test materials
The Elm (Ulmus rubra) and Poplar (Populus beijingensis) used in this experiment were taken from
the woodland of Yuquan District Dalai Zhuang village, Hohhot. The age of Elm is 45-48 years. The
sapwood is consisted of 6 rings; Heartwood is consisted of 41rings. The ring width distribution of
0.35-7.90mm and the average diameter of ring is about 303mm.
Poplar is of 34-37 years. The sapwood is consisted of 13 rings, while heartwood of 23. The ring
width distribution is of 0.57-9.68mm and the average diameter is of 315mm.
Pinus sylvestris was obtained from the Forest in the Ude (Ulam) region of Russia, with the age of
79-83 years. The Sapwood has about 44 rings, the heartwood is consisted about 38. The ring width is
from 0.21 to 3.65mm and the average diameter is about 310mm.
2.2. Sample processing
Each log selected two sections after the cross-section saw into a disk-wood section, the disk of wood
at intervals 90° intercept 50mmx50mmx70mm hardness test block, with 80 mesh abrasive belt
grinder sanding into a specimen. Sawing machine with rotational speed of 3600rpm rotary sawing
machines. Log cross-section saw the processing of 40mm wide rotary cutting wood section, with the
modified lathe to spin cut out the chip samples, cutting edge arc radius 0.3m [32], cutting thickness
of 0.32mm.
IWMCE 2018 - International Workshop on Materials, Chemistry and Engineering
84
2.3. Determination of roughness
2.3.1. Test Equipment. The laser microscopy system, which is produced by Keyence (KEYENCE), is
used in vk-x150 shape measurement to meet the requirements of iso4287:1997 roughness
measurement and test standards. The main characteristics of the sample is not required for the initial
processing of steam, and do not need to cut, disassembly and other processing, can directly carry out
3D measurement analysis. Compared with the traditional contact surface roughness instrument and
optical microscope, it has many advantages such as high resolution, good definition, large-area
panorama analysis, good image coherence, three-dimensional appearance and rapid acquisition of
three-dimensional shape information of sample surface. such as 10 times times the objective 200
times magnification, the field range is 1350um×1012um, Z axis measurement height range 7mm.
2.3.2. Test method. The surface roughness of the specimens of Elm, Poplar and Pinus sylvestris was
measured by the laser microscope system with VK-X150 shape, and the ring junction was selected.
The influence of wood microstructure, tree species, cutting process, magnification and test mode on
surface roughness of specimen was analyzed.
3. Results and discuss
3.1. Analysis of surface roughness
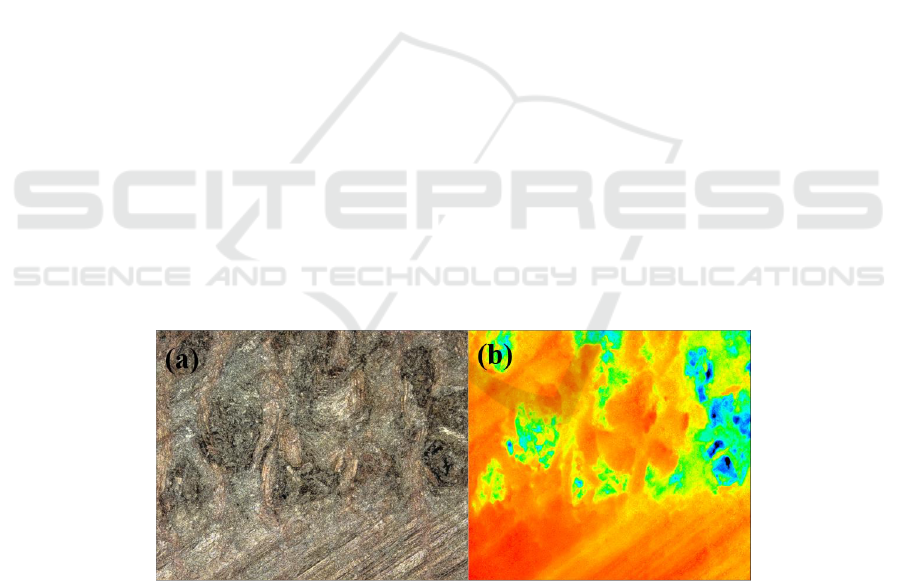
3.1.1. Determination of surface roughness. The process of measuring surface roughness of Elm cross
section sanding is an example to illustrate the method of roughness determination and evaluation.
The main image, color height image and three-dimensional image of the laser scan generated in the
following Figure 1 are measured by the shape measurement laser microscope system. Clearly see the
diameter and distribution of the Elm's pipe hole and the blockage of the abrasive powder into the pipe
hole. Choose different test locations to get different roughness values. In this experiment, the average
roughness value (Ra) was used to evaluate the roughness of machined surface under various test
conditions.
Study on Evaluation Method of Surface Roughness of Wood Processing
85

Figure 1. The three kinds of test charts for the transverse section of elm Sanding. (a): main image
(laser + color); (b): height image; (c) 3D image.
The surface roughness values of the large parts of the wood structures, which are affected by the
structure of the pipe and other timber structures, are measured by the line roughness measurement
function, as shown in Figure 2 below. According to the laser scanning, color height and
three-dimensional topography, the structure of the wood structure is clearly separated, and the
suitable evaluation site can be selected. Select the stylus mode to obtain the measuring value of the
stylus surface roughness.
3.1.2. Comparison of surface roughness of different parts. Wood is a naturally growing biomass
material, which is mainly embodied in its three facets. Therefore, in the case of elm, the surface
roughness values of the three sections and different test conditions of elm sanding are shown in
Figure 3. The location of the selected rings of the determination site takes into account both the early
and late materials. It is shown from the figure that the roughness of the three-cut section of Elm
Wood is the cross section of the diameter section and the chord plane. This is the diameter of the duct
and wood rays and other tectonic effects more prominent as a result, the chord section of the tube and
wood rays on the shallow, cross section of the main pipe hole pits, to some extent by the abrasive
powder blocking. The roughness of the duct, which does not contain (less) on each section, is
obviously less than that of the surface roughness of the large part of the structure, and the roughness
of the three sections is close to the cross section. The diameter and cross section of the structure
impact of the wood fiber is more dense homogeneous, while the string on the surface of the reverse
and the consequent sanding of the impact of roughness. The pits of the pipe holes are clearly seen in
Figure 1 and 2.
IWMCE 2018 - International Workshop on Materials, Chemistry and Engineering
86

Figure 2. Sketch map of transverse test position and roughness curve of Elm wood in sanding
process.
3.1.3. Influence of different measuring modes on surface roughness. The stylus mode of the selected
shape measurement laser microscope system is measured to obtain the surface roughness value under
the contact needle mode of the Elm three-section. Compared with the corresponding laser
measurement, it is shown that in Figure 3, the roughness measured in the stylus mode is less than the
surface roughness value of the laser test, which is the result of the laser scanning to the more
microscopic part. Increase or decrease rate within 4%.
Figure 3. Surface roughness comparison of three sections and different test conditions of Elm
sanding.
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
Cross section Radial Section Tangential
Section
Roughness of machined
surface /µm
With vessel
With vessel stylus model
Without vessel
Study on Evaluation Method of Surface Roughness of Wood Processing
87
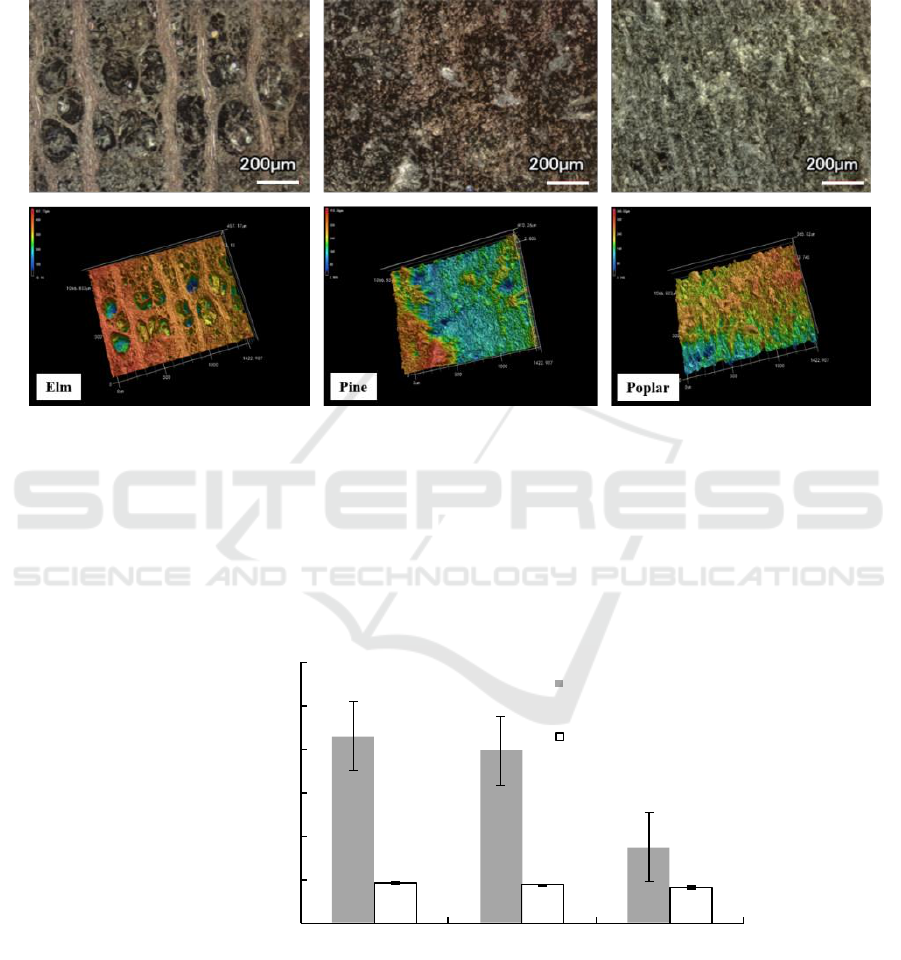
3.2. Comparison of surface roughness of specimens of different species
The laser scanning and three-dimensional images of three kinds of wood specimens are shown in
Figure 4 as follows, as far as possible to select the ring junction area. The different and
concave-convex uneven structure of the surface structure are clearly seen in the two graphs.
Figure 4. Comparison of laser scanning and three-dimensional structure of three kinds of timber in
cross section sawing (200 times amplification).
Further testing of the surface roughness of the small part of the wood structure and the influence
of the roughness of the structure on the large parts show that in Figure 5, the roughness of the
microstructure of the wood cell tissue was significantly greater than that of the small part, and the
roughness value was obviously different. The roughness value is elm, pine and Poplar, but the
roughness value tends to be close to the effect of small structure, and the effect of tree species is not
significant.
Figure 5. Comparison of roughness of three kinds of wood sawn cross-section.
3.3. Analysis of different machining methods and surface roughness
The cutting, sanding and turning plane of the poplar specimen 200 times times magnified laser
scanning picture and three-dimensional image picture as shown in Figure 6, the two kinds of pictures
are not difficult to see the surface of the sawing wood burr, observed that the sanding surface
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
Elm Pine Poplar
Machined surface
roughness(Ra)/m
Wood structure with
high impact
Wood structure with
low impact
IWMCE 2018 - International Workshop on Materials, Chemistry and Engineering
88
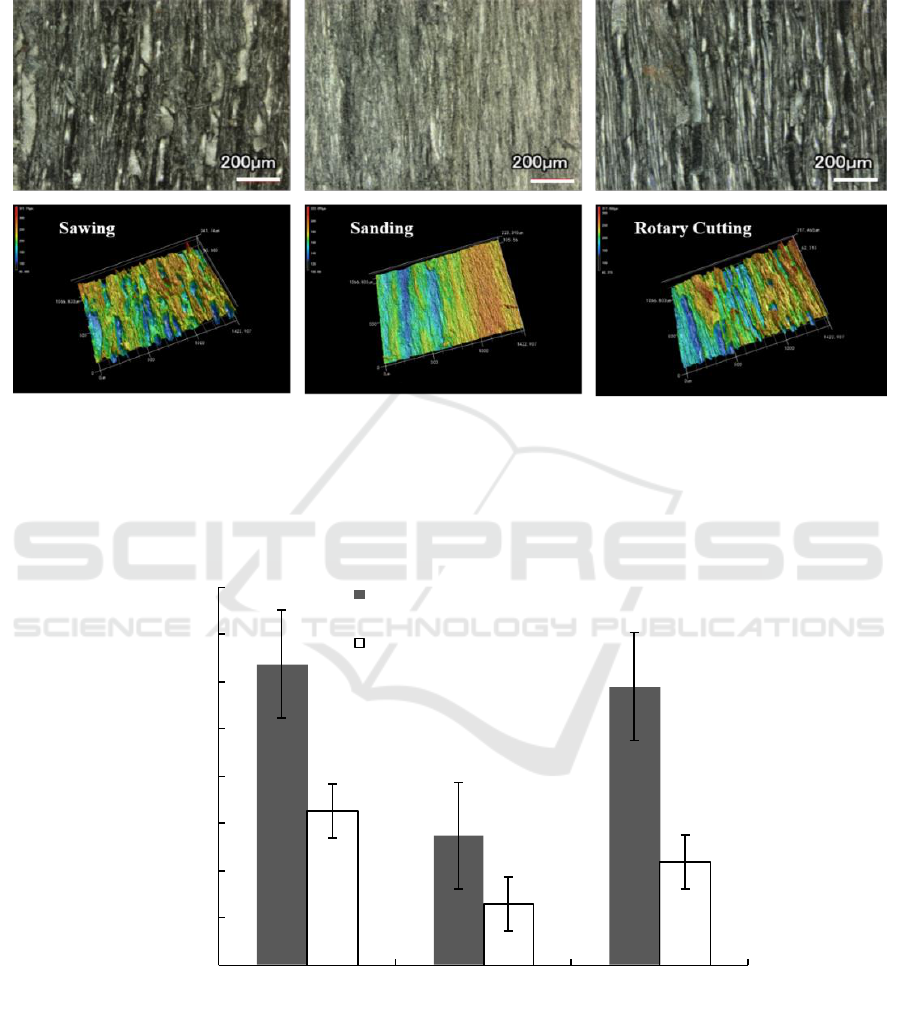
structure is not clear. The surface structure and uneven distribution are clearly seen on the sawing and
rotating plane.
Figure 6. Comparison diagram of 200 times of different cutting process of poplar specimen.
Further testing the surface roughness of the parts with large influence on the wood structure and
the roughness values of the parts with little influence on the wood structure show that in Figure 7, the
surface roughness of the slice are close, and the surface roughness of the sanding process is
obviously small.
Figure 7. The change of machining mode and surface roughness of Poplar.
3.4. Magnification and surface roughness
Selecting the Poplar and elm pecimens for example, the laser scanning microscopic structure of the
different magnification ratios of the tangential cutting of the chord plane is shown in Figure 8 below.
It is difficult to evaluate the roughness of the machined surface, especially when the elm duct and the
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
Sawing Grinding Rotary cutting
Machined surface roughness(Ra)/µm
Wood structure with
high impact
Wood sturcture with low
impact
Study on Evaluation Method of Surface Roughness of Wood Processing
89

wood rays take up the whole surface of the microscopic structure such as the specimen tube, the
wood ray and the grain hole.
Figure 8. Comparison of microstructure of Poplar and elm specimens with different magnification.
It is shown that the roughness value of the parts with large influence on the surface roughness of
the wood structures and the roughness of the wood structure is less than that in Figure 9. The
variation tendency and size of the roughness value of the small part of wood structure are very close
to that of tree species. It is not difficult to see that the structure of wood has a great influence on the
roughness, and the influence of wood structure must be taken into account in the determination and
evaluation. The influence of wood structure on the roughness of large parts is very different, the
bigger the surface roughness of poplar wood is, the more the positive and decreasing relationship is.
However, the roughness of elm wood structure affects large parts with the increase of magnification
and then tends to a certain value, it is difficult to evaluate the processing surface roughness when the
magnification is large. The appropriate magnification must be selected, and the test results show that
the magnification ratio of elm wood is 200 and that of poplar wood magnification 400 is advisable.
Figure 9. Magnification and surface roughness variation.
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
0 200 400 600 800 1000 1200
Surface roughness (Ra)/µm
Magnification
Poplar with high wood structure impact
Poplar with low wood structure impact
Elm with high wood structure impact
Elm with low wood structure impact
IWMCE 2018 - International Workshop on Materials, Chemistry and Engineering
90

4. Conclusions
To Elm, Poplar wood for testing materials, different parts, different magnification, different cutting
methods and different test mode to determine the surface roughness and impact of wood processing,
the following conclusions are drawn:
1. Surface roughness value due to different processing methods, with the improvement of
processing accuracy and reduce. In the test range, the influence of wood structure on the roughness
values of different sections of Elm is the cross section and the cross section of the chord plane, and
the cross section of the wood structure affects the hourly chord plane. The effect of wood structure on
roughness is particularly obvious, and the influence of different parts and wood structure must be
considered when evaluating surface roughness.
2. The same tree species, the same section, sanding surface roughness is significantly lower than
sawing and cutting surface roughness, sawing and cutting surface roughness value is close.
Magnification has obvious effect on tree species and cut, but the influence of wood structure on the
hours is not significant.
3. The factors affecting the surface roughness of wood processing are considered, and the
two-step method for measuring the surface roughness of wood is proposed. The first choice of the
selected wood products such as tree species, different sections, wood structure and processing
methods to determine the evaluation site, and then consider the test mode method and equipment
accuracy, selected to meet the determination of the requirements of the method to complete the wood
processing surface roughness measurement and analysis.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under grant no.
31460170.
References
[1] Banshoya K, Okumura S, Hattori N and Murase Y 2007 Wood Science Series(6)-Cutting
Processing (The Second Edition) (in Japanese) M. Ootushi Kaiseisha Press p59-62
[2] Costes J P, Ko P L and Ji T 2004 Orthogonal cutting mechanics of maple: modeling a solid
wood-cutting process J. Journal of Wood Science 50(1) 28-34
[3] Okumura S and fujiwara Y 2007 Roughness evaluation of machined surfaces of wood
MOKUZAI GAKKAISHI Vol. 53 No.4 p173-179(in Japanese)
[4] Zhao G J 1992 Scientific research on the woody environment in thecircle of forest product
research in Japan J. World Forestry Research 5(4) 53-57
[5] Cheng J Q 1985 Wood science M. Beijing China Forestry Publishing House
[6] Zhang L J, Zhang L P and Meng Q J 2000 Elementary discussion onpresent situation and
development trend of timber surface roughnessdegree in the world J. Forestry Machinery
and Woodworking Equipment 28(6) 7-9
[7] Gurau L, Mansfield-Williams H and Irle M 2013 The influence of measuring resolution on the
subsequent roughness parameters of sanded wood surfaces J. European Journal of Wood
and Wood Products 71(1) 5-11
[8] Hiziroglu S 1996 Surface roughness analysis of wood composites: a stylus method J. Forest
Products Journal 46 67-72
[9] Fujii Y, Yoshizane M and Okumura S 1997 Evaluation of surface roughness by various
parametersI Relationships between several roughness parameters and tactile roughness
MOKUZAI GAKKAISHI Vol.43 No.7 p574-579
[10] Li J, Dong Y K and Liu Y X 1991 Timber, human and environment J. Furniture (6) 8-10
[11] Wang M Z, Wang J Y and Li L 2005 Roughness and roughness sense of wood surface from
different machining processes Journal of Beijing Forestry University Vol.27 No.1 p14-18
Study on Evaluation Method of Surface Roughness of Wood Processing
91

[12] Azemović E, Horman I and Busuladžić I 2014 Impact of planing treatment regime on solid fir
wood surface J. Procedia Engineering 69 1490-1498
[13] Hendarto B, Shayan E and Ozarska B 2006 Analysis of roughness of a sanded wood surface J.
International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology 28(7-8) 775-780
[14] Fujiwara Y, Fujii Y, Sawada Y and Okumura S 2004 Assessment of wood surface roughness :
comparison of tactile roughness and three- dimensional parameters derived using a robust
Gaussian regression filter J Wood Sci. Vol.50 No.1 p35-40
[15] Wilkowski J, Rousek M and Svoboda E 2013 Analysis of the influence of cutting parameters
on surface roughness of milled wood based on Taguchi techniques J. Journal of Urology
166(6) 2087-2090
[16] Han Y J and Chiaki T 2005 Quantitative measurement of surface roughness of wood by laser
displacement sensor SCIENTIA SILVAE SINICAE Vol.41 No.6,Nov.,
[17] Long Q, Hideyuki Y and Shiro O 2009 Optimization of Veneer Cutting of Sugi I.MOKUZAI
GAKKAISHI Vol.55 No.6 p.331-338
[18] Emilia-Adela S and Salim H 2014 Evaluation of hardness and surface quality of different
wood species as function of heat treatment J. Materials and Design 62 416-423
[19] Zhong Z W, Hiziroglu S and Chan C T M 2013 Measurement of the surface roughness of
wood based materials used in furniture manufacture J. Measurement 46(4) 1482-1487
[20] Akbulut T and Ayrilmis N 2015 Effect of compression wood on surface roughness and surface
absorption of medium density fiberboard J. Silva Fennica 40(1) 161-167
[21] Ispas M, Gurau L and Campean M 2016 Milling of Heat-Treated Beech Wood (Fagus
sylvatica L.) and Analysis of Surface Quality J. Bioresources 11(4) 9095-9111
[22] Richterk, Feist W C and Knaebe M T 1995 The effect of surfaceroughness on the performance
of finishes. Part1. Roughnesscharacterization and stain performance J. Forest Products
Journal 45(7 8):91-97
[23] Chang F Y and Wu Z H, 2016 Effect of the Roughness on the Quality of NAno-modified
Lacquer Painting Film Furniture Vol.37 No.2
[24] Lemaster R L and Bellfc 1996 The use of an optical profilometer tomeasure surface roughness
in medium density fiberboard J. ForestProducts Journal 46(11 12) 73-78
[25] Hiziroglus 1996 Surface roughness analysis of wood composite: Astylusmethod J. Forest
Products Journal 46(7 8) 67-72
[26] Jiang Z H, Yu W J and Ye K L 2001 Analysis of bamboo surfaceroughness by stylus method J.
China Wood Industry 15(5) 14-16
[27] Beer P, Djouadi M A and Marchal R 1999 Inflence of knife-surfaces modification with hard
coatings on the peeling wood process J. Journal of Materials Processing Technology
(92~93) 264-268
[28] Faga M G and Settineri L 2006 Innovative anti-wear coatings on cutting tools for wood
machining J. Surface & Coatings Technology 201 3002-3007
[29] GB/T1031-2009 2009 Geometrical product specifications (GPS) - Surface texture: Profile
method - Surface roughness parameters and their values S. Beijing Standards Press of
China
[30] GB/T12472-2003 2003 Geometrical product specifications (GPS) - Surface texture: Profile
method - Surface roughness parameters and their values for wooden pieces S. Beijing
Standards Press of China
[31] GB/T3505-2009 2009 Geometrical product specifications (GPS) - Surface texture: Profile
method - Terms, definitions and surface texture parameters S. Beijing Standards Press of
China
[32] Qing L, Hideyuki Y and Shiro O 2010 Optimum Roundness of Tool Edge in Veneer Cutting of
Sugi MOKUZAI KOGYO Vol.65, No.3, p.113-118
IWMCE 2018 - International Workshop on Materials, Chemistry and Engineering
92
