
Aqueous Solution of Ammonium Persulfate Assisted
Electrochemical Exfoliation of Graphite into Graphene
D X He, W D Xue and R Zhao
*
Institute of Applied Electrochemistry, School of Materials And Energy,
University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu 610054,
PR China
Corresponding author and e-mail: R Zhao, ruizhao@uestc.edu.cn
Abstract. Mass production of high-quality graphene sheets is essential for their further
practical application. Here a facile electrochemical method was carried out to produce bulk of
graphene. Ammonium persulfate (APS) aqueous solution was applied as the electrolyte and
successfully exfoliated the graphite into graphene. The method here shows great promise for
the synthesis of bulk graphene with high quality.
1. Introduction
With the dramatic development of graphene producing and its applications, low-costs, high-quality
and mass production of graphene have been the major challenges and limitations for its further
development. Many excellent graphene preparation strategies have been developed respect to
different requirements and applications. Mechanical exfoliation methods came up with its first
discovery. There is a big step from adhesive tape assisted micromechanical cleavage [1] to sonication
assisted liquid-phase exfoliation [2-3]. They provide feasible means for producing graphene with low
number of defects, but still with an insufficient yield. Chemical vapor deposition (CVD) emerged as
a popular method for the growth of graphene with high quality [4]. However, the costs and
production restricted its further application in industry. With bulk scale production and solution-
processable property,graphene oxide (GO) which produced by the modified Hummer’s method has
been developed as one most available method especially for synthesizing graphene-based composites
materials [5]. But the low quality (most of the graphene are few layers) and environment pollution
problem are still the key limitations.
In recent years, electrochemical exfoliation of graphene or graphene oxide have been explored as
an efficiency strategy to achieve the goal. For example, GO had been achieved with good quality and
high yield via a two-step electrochemical intercalation and oxidation approach using ammonium
sulphate and sulfuric acid as the electrolyte [6]. Furthermore, apply ammonium sulphate [7] or (2, 2,
6, 6-tetramethylpiperidin-1-yl) oxyl (TEMPO) [8] as electrolyte had also been proved to be the ideal
methods to directly produce graphene.
In this study, in the presence of aqueous ammonium persulphate (APS) solution, the
electrochemical exfoliation of graphene was successfully carried out. Few layers graphene was
produced with high quality, low-cost, environment friendly and high efficiency.
658
He, D., Xue, W. and Zhao, R.
Aqueous Solution of Ammonium Persulfate Assisted Electrochemical Exfoliation of Graphite into Graphene.
In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Materials, Chemistry and Engineering (IWMCE 2018), pages 658-662
ISBN: 978-989-758-346-9
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
2. Experimental details
Commercial graphite foil (Gee graphite LTD) with a thickness of 0.5 mm was used directly as the
working electrode. The electrochemical process was carried out with a Pt mesh counter electrode and
a DC power supply (BK PRECISION 1688B). A length of about 30 mm of the graphite ribbon was
immersed into aqueous ammonium persulphate (0.1 M, ≥98%, Aldrich) electrolyte and a constant
voltage (10 V) was applied for 5 minutes. The products were washed with water for several times
and dried in the vacuum oven.
The morphology of the powder was characterized by using a transmission electron microscope
(TEM, Philips CM20). The Raman spectra were obtained by using a Raman spectrometer (inVia,
Renishaw) equipped with a λ=532 nm laser. FTIR (Fourier Transform Infra-Red) Spectroscopy was
used to determine the chemical functional groups of the sample. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy
(XPS) was performed with a Kratos Axis Ultra X-ray photoelectron spectrometer; the curve fitting
was accomplished by CasaXPS software. The samples for atomic force microscope (AFM, JPK
Instruments) and optical microscope (Nikon Eclipse LV100ND microscope) characterization were
prepared by drop casting of the graphene ethanol solution on a Si/SiO
2
wafer.
3. Result and discussion
Electrochemical exfoliation of graphite has been widely used to rapidly producing graphene. Many
organic or inorganic solution have been proved to be good candidates as the electrolyte [7-9]. Here
we firstly applied APS aqueous solution as the electrolyte. The output can be readily increased
through continuous production.
(a)
(b)
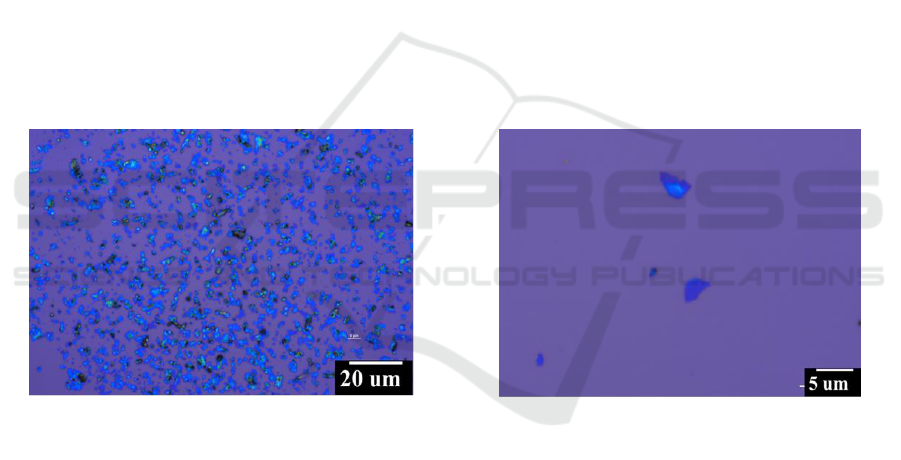
Figure1. (a) and (b) Optical image of the sample under different magnification.
Optical microscope was firstly carried out to roughly evaluate the quality of the products.[10] The
optical contrast differences between the substrates and the 2D nanosheets with different layer
numbers can be readily and reliably observed. As shown in Figure 1a, hundreds nanosheets are
observed in the optical image and more than 95 % showed purple in contrast with the substrate,
indicating that these flakes were few layers graphene. Furthermore, comparing with the related
references [11], the optical contrasts of high-magnification optical microscope image in Figure 1b
showed that most of them are under 6 layers, indicating the high quality of the products. Besides, the
black sheets within the field should be the graphite.
Aqueous Solution of Ammonium Persulfate Assisted Electrochemical Exfoliation of Graphite into Graphene
659
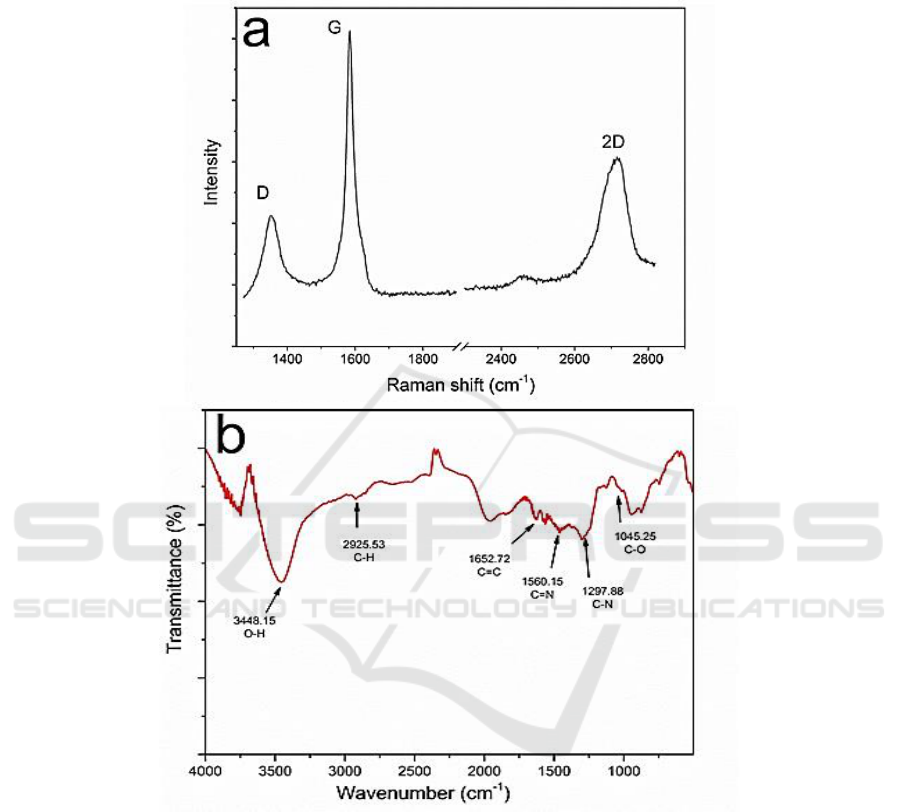
Figure2. (a) Raman spectra characterization of the graphene. (b) FTIR characterization of the
graphene.
Raman spectra and FTIR spectra characterizations were carried out later to obtain more
information about its fundamental structures. As shown in Figure 2a, the two typical peaks at around
1354 cm
−1
and 1585 cm
−1
refer to the disorder-induced D band and crystalline graphitic G band,
respectively. Briefly, the 2D peak at 2716 cm
−1
is the D-peak overtone, the intensity ratio of I
2D
/I
G
is
about 0.5 and indicating the few layers structure of the graphene. That also matches well with the
conclusion we obtained from the optical images in Figure 1.
Furthermore, the fast exfoliation process promoted it with low defects which mainly came from
the functional groups (Figure 2b). More details obtained from the XPS indicated that the C/O ratio is
as high as 17.4 and better than most of the related works [12]. TEM was applied to further analyze
the characteristics of the graphene sheets. As shown in Figure 3a, the thin layers were uniformly
IWMCE 2018 - International Workshop on Materials, Chemistry and Engineering
660
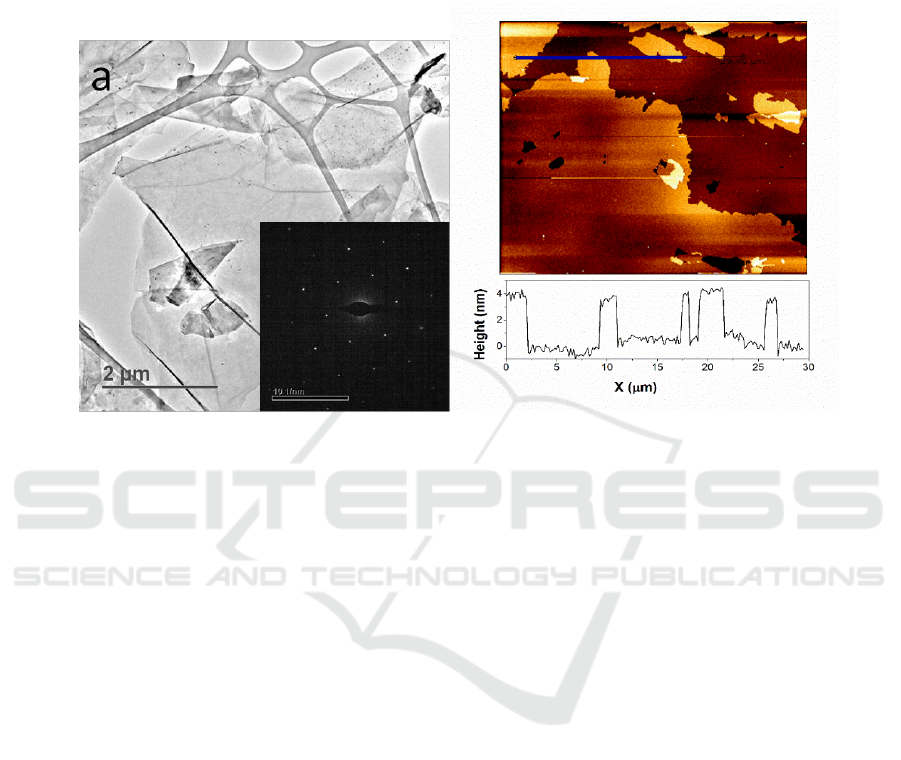
distributed on the substrate. The inset selected-area electron diffraction (SAED) of the thin layer
shows the typical 6-fold symmetry of grapheme [6]. The thickness of the layer can be further
confirmed with AFM analysis. As shown in Figure 3b, the thin flakes were uniformly distributed and
a thickness value of about 3 nm was observed.
Figure 3.(a) typical TEM image of the graphene layer (inset is the corresponding SAED); (b) AFM
image of the graphene layer.
The mechanism of the electrochemical exfoliation process has been recognized as: (i) the bias
voltage results in the electrolysis of water and the radicals oxidize the edge or grain boundaries of the
graphite (
); (ii) the hydrolysis of APS occurs in the water (
,
,
), and the sulfate ions
(SO
4
2-
) and water intercalate in between the graphite layers; With a continuous exfoliation process,
these two steps synergetic work on exfoliating the layers.[9] Finally, bulk of graphene was obtained.
4. Conclusions
Herein, APS aqueous solution was used for the first time as the electrolyte to synthesize graphene.
The graphene was produced with low cost, environment-friendly and high quality. Most of the flakes
are blow 4 nm thick and with low ratio of defects. The result presented herein provided an alternative
method for producing graphene powder with large-scale.
References
[1] Novoselov A A F K S, Geim A K, Morozov S V, Jiang D, Zhang Y and Dubonos S V 2004
Science (80-. ) 306 666
[2] Lotya M, Hernandez Y, King P J, Smith R J, Nicolosi V, Karlsson L S, Blighe F M, De S, W
Zhiming, McGovern I. T, Duesberg G S and Coleman J N 2009 J Am Chem. Soc. 131 3611
[3] Nuvoli D, Valentini L, Alzari V, Scognamillo S, Bon S B, Piccinini M, Illescas J and Mariani
A 2011 J. Mater. Chem. 21 3428
[4] Li X, Cai W, An J, Kim S, Nah J, Yang D, Piner R, Velamakanni A, Jung I, Tutuc E, Banerjee
S K, Colombo L and Ruoff R S 2009 Science (80-. ) 324 1312
[5] Botas C, Álvarez P, Blanco P, Granda M, Blanco C, SantamarRía, Romasanta L J, Verdejo R,
López-Manchado M A and Menéndez R 2013 Carbon N. Y. 65 156
Aqueous Solution of Ammonium Persulfate Assisted Electrochemical Exfoliation of Graphite into Graphene
661

[6] Cao J, He P, Mohammed M A, Zhao X, Young R J, Derby B, Kinloch I A, Dryfe R A W 2017
J. Am. Chem. Soc., jacs. 7b08515
[7] Parvez K, Wu Z S, Li R, Liu X, Graf R, Feng X, Mullen K 2014 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136, 6083
[8] Yang S, Brüller S, Wu Z S, Liu Z, Parvez K, Dong R, Richard F, Samorì P, Feng X, Müllen K
2015 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 137 13927
[9] Parvez K, Yang S, Feng X, Müllen K, Synth. Met.2015, 210 123
[10] Ni Z H, Wang H M, Kasim J, Fan H M, Yu T, Wu Y H, Feng Y P and Shen Z X 2007 Nano
Lett. 7 2758
[11] Li H, Wu J, Huang X, Lu G, Yang J, Lu X, Xiong Q and Zhang H 2013 ACS Nano.7 10344
[12] Pei S and Cheng H M 2012 Carbon N. Y. 50 3210
IWMCE 2018 - International Workshop on Materials, Chemistry and Engineering
662
