
Research on Glass Fiber Reinforced Plastic Head Cover of High-
Speed Train
Chunmian Chen
Hunan Railway Professiona1 Technology College, Zhuzhou,Hunan, China
Keywords: High-speed train; head cover; glass fiber reinforced plastic; stiffeners.
Abstract: The role of the high-speed train head cover was discussed in this paper. According to the actual situation of
the train operation, comparing the theoretical calculation to experimental analysis, the calculation load of
the high-speed train head cover was confirmed, strength and mode calculation on the glass fiber reinforced
plastic head cover by using ANSYS software were performed, and the result was analyzed in order to
provide some reference for future work.
1 INTRODUCTION
The high-speed train head cover is the part at the
front of the train that covers the coupler, which is
closed during normal operation constitutes a
streamlined shape to ensure the aerodynamic
performance of the train. In the case of a shunting
operation, rescue, and double-linking, the head cover
of the vehicle needs to be opened to expose the
mounting and operating space for the lifting hooks
and the lifting rods of the coupler.
At present, many kinds of high-speed trains
produced in China have adopted streamlined car
body. If the head cover adopts a fixed structure,
disassembly and storage are inconvenient. China has
already conducted research on the automatic
opening and closing head cover and has applied it to
production
[1]
. However, there are also
imperfections. It is necessary to conduct in-depth
research on the structural design of the head cover in
order to achieve the desired results.
2 PROBLEM ANALYSIS
During train operation, the air resistance is
proportional to the square of the speed. When the
train speed reaches 200km/h, the air resistance
accounts for more than 70% of the total running
resistance. The aerodynamic load on the head cover
at the front end of the train head is more
complicated.
In order to ensure the aerodynamic performance
of the train, the head cover and supporting
mechanism of the head of the locomotive must meet
the following requirements: (1)The head cover itself
should have a certain strength and cannot be
destroyed by steady state pressure or transient
pressure wave impact; (2) Under the action of wind
load, the head cover itself cannot produce large
deformations that affect aerodynamic performance,
nor can they cause unexpected opening and closing
actions; (3) The support mechanisms of the head
cover should have sufficient support/self-locking
capability and resistance to wind pressure.
There are no specific standards and
specifications as reference for the complex wind
load that the train. To solve the above problems, it is
necessary to rely on the combination of theoretical
calculation and experimental analysis to determine
the calculation load of the head cover. On this basis,
the ANSYS was used to theoretically calculate the
strength and natural frequency of the head cover
under certain load conditions, and the basic
structural form and size range of the head cover
were determined based on the calculation results.
Which will provide institutions for designing of
opening and closing mechanism of the head cover.
3 LOAD SOURCE AND BASIS
In order to obtain good aerodynamic performance,
the shape of the train head cover is a freeform
surface. Its mathematical expression is:
(1)
In the formula: x, y, and z are positional
parameters.
During the operation of a high-speed train, the
actual load on the head cover mainly comes from the
surface pressure caused by air resistance, and the
surface pressure changes with time. That is to say,
during the running of the train, the actual load
received at a certain point on the head cover needs to
be expressed by a four-variable functional
relationship:
(2)
In the formula: t is the time parameter.
If the load in the calculation process according to
its actual stress, the calculation process will be
extremely tedious. While use the FLUENT to
simulate the load of the high-speed train head flow
field at speed 200km/h, compared with the dynamic
real vehicle test, found that the error is small, the
accuracy meets practical requirements, can be used
as the calculated load[2]. Therefore, assuming that
the surface pressure of the train does not change
with time, this paper uses the aforementioned
calculation results as the source of the load data, and
converts it into a load with a running speed of 300
km/h using the Bernoulli equation [3]. The
conversion formula is as follows:
2
300
300
2
200
200
2
1
2
1
ρνρν
PP
C
P
==
(3)
In the formula:
P
C
- pressure coefficient;
ρ
- the density of air;
200
ν
,
300
ν
— train speed,
200
ν
= 200km/h,
300
ν
= 300km/h;
200
P
,
300
P
,—surface pressure experienced at
train speeds of 200km and 300km.
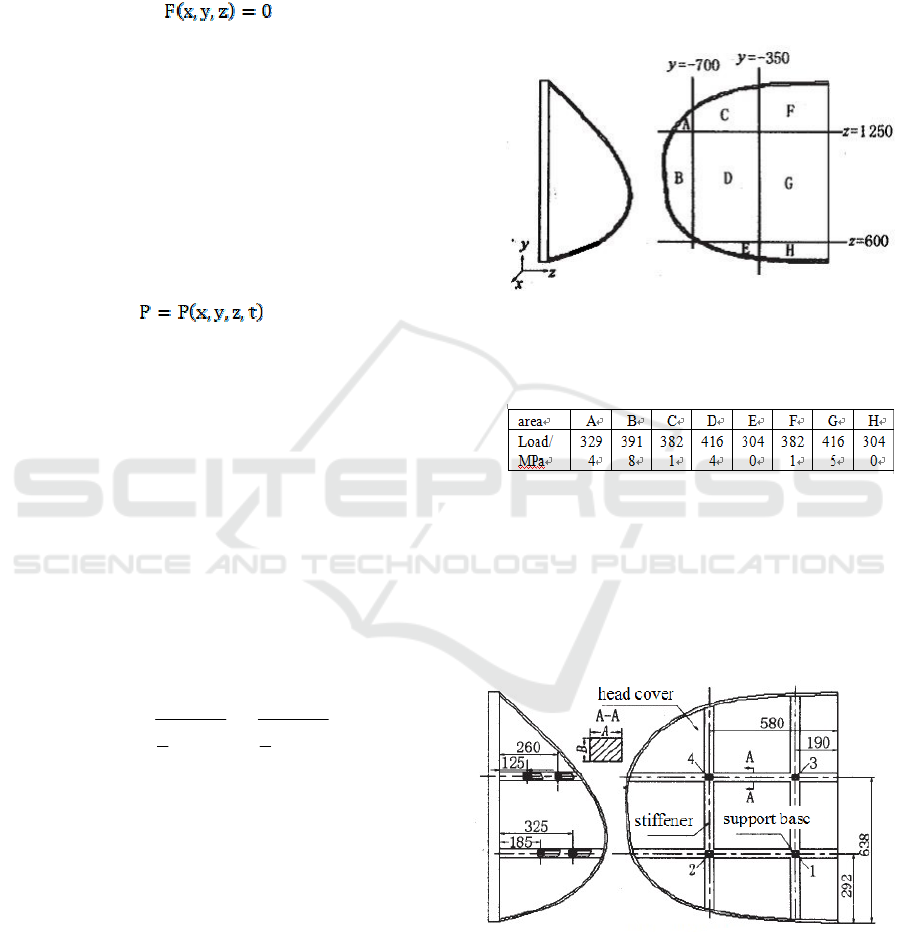
In order to simplify the calculation, in the actual
analysis, the head cover is divided into 8 pieces
along the horizontal plane and a certain section of
the longitudinal section to load. In the place where
the curvature changes smoothly, the blocks are
sparse; in the places where the curvature is more
severe, the blocks are dense. Take the pressure value
at one point in each block as the surface pressure
value of the entire block. And fully consider the
fluctuation of the load caused by the speed change,
the selection of all data complies with the principle
of safety and conservation. Figure 1 shows the block
diagram along the coordinates of the head cover.
Fig.1 Block of head cover and its surface load.
Table 1 Block Loading Data Table.
The loads in this calculation are the distributed
loads applied to the surface of the head cover. All
the loads are added to the finite element model
(nodes and units). The head cover and the opening
and closing mechanism are connected by four
supporting seats (as shown in Fig. 2), and each of
the six degrees of freedom of each support base is
restrained.
Figure 2. Head Cover Structure.

3 HEAD COVER INTRODUCTION
3.1 Selection of Head Cover Material
The material of the head cover must ensure that it
has sufficient strength and rigidity; the free curved
surface is difficult to process using conventional
methods, so the material used to manufacture the
head cover must have excellent processing
properties. Glass fiber reinforced plastic, commonly
known as fiberglass, it has so many advantages
ensure that the free-form-shaped head cover can be
manufactured at a lower cost. Therefore, FRP is
used as the material of the head cover in this
calculation.
The different types of glass fiber reinforced
plastic and its fiber winding methods have a great
influence on the physical properties of FRP
materials. Considering the particularity of the
working environment of the vehicle head cover, this
calculation proposes the physical properties that
should be possessed by the head cover and the
parameters used in the calculation [4]:
Density/kg•m-3 1.8×103
Tensile strength/MPa ≥80
Quasi-static compression modulus ≥ 10
Dynamic compression modulus/GPa ≥15
Elastic Modulus/GPa 10
Poisson's ratio 0.4
3.2 Head Cover Structure
In this calculation, the thickness of the head cover
shell is 10 mm, and the four Q235 steel stiffeners are
connected to the head cover via the opening and
closing mechanism support bases fixedly (see Figure
2). The role of stiffeners is to increase the stiffness
of the head cover.
4 CALCULATION MODEL
The calculation model includes two parts: head
cover and stiffeners. The model is built using solid
modeling. The head cover is plate shell elements
(Shell 63) and the stiffeners are beam elements
(Beam 188). The grid is divided into free meshes.
The discrete data of the finite element model are as
follows: Shell63 and Beam188 have 543 and 96
cells, and the total number of cells is 639.The total
number of nodes is 679.
5 CALCULATION CONTENTS AND
RESULTS
In this calculation, the head cover was subjected to
strength analysis and modal analysis.
The corresponding calculation results are shown in
Table 2, Table 3 and Table 4.
Table 2 Calculation results of counterforce and counter-
torque.
Note: Fx, Fy, and Fz represent the counterforce along
the x-axis, y-axis, and z-axis respectively; Mx, My, and
Mz represent the counter-torque around the x-axis, y-axis,
and z-axis respectively.
Table 3 Displacement and stress change with the cross
section of the stiffeners.
Table 4 Modal calculation results when the cross section
of the stiffeners is 40mm ×12mm (sixth-order natural
frequency).
When the cross section size of the stiffeners is
changed, the results of the modal calculations varies
very small, so only the modal calculation results of
40mm×12mm are calculated here.

6 CALCULATION RESULTS
ANALYSIS
From Table 2, it can be seen that during the
operation of the train, the head cover is subjected to
a force of 2974.7N in the direction of the wind, so
the head cover itself should have sufficient strength.
The torque in the height direction of the support base
1 reaches 117.43N·m, which requires that the
influence of this factor on the operation of the head
cover should be fully taken into consideration when
designing the support mechanism, the movement
mechanism and the locking mechanism of the head
cover.
As long as the value of the surface load and the
position of the restraint do not change, the bearing
reaction force will not change; but the change in the
cross section size of the stiffeners has little effect on
the modal calculation results, so this is mainly based
on the results of the displacement and stress,the
cross section size of the stiffeners was determined.
This is also the reason why only the stiffeners cross
section size of 40mm×12mm was calculated in the
modal analysis. From the calculation results, it can
be seen that the first-order natural frequency of the
head cover is 52.595 Hz, and the natural frequency
of the general high-speed motor car body is not
bigger than 20 Hz[5], so the head cover does not
generate resonance with the car body.
In view of the current literature on the
calculation of FRP materials, from the perspective of
safety, the safety factor of 4 is used in this
calculation, that is, the allowable stress [σ] = 20MPa
for FRP materials. From Table 3, it can be seen that
the maximum stress reaches 54.722MPa, which
greatly exceeds the allowable stress of FRP
materials and is very unsafe. Therefore, it must be
reinforced. When the cross section thickness was
changed from 8 mm to 10 mm, the maximum
translational displacement vector and the maximum
stress were all reduced significantly. When the
thickness was changed from 10 mm to 12 mm or
more, the change was not significant. When the
cross-sectional area is equal, the greater the height of
the stiffeners, the more significant the effect of
reducing the stress concentration. Based on the
above results and taking into account the weight of
the head cover, it is more appropriate for this type of
head cover to use a cross section size of 40 mm×12
mm. If you want to better ensure the safety of train
operations, the cross section size of the stiffeners can
be 40mm × 14mm, 40mm × 16mm or even 40mm ×
20mm.
With regard to the aging problem of glass fiber
reinforced plastics, various countries are conducting
research, but no obvious results have yet been
obtained. Therefore, the question of the service life
of glass fiber reinforced plastic head cover needs
further study. For different shapes of the head cover,
the distribution of the head flow field is not the same
and the loads are not the same. Therefore, the shape
and distribution of the stiffeners are also different.
The requirements for the support structure of the
head cover are also different. These need to be given
specific analysis during the design process.
REFERENCES
1. Nie Yonghong. Design of Automatic Opening and
Closing Mechanism for the Head Cover of
Streamlined Vehicle Head., 2002. Electric
Transmission for Locomotives, 2002 (4): 22-24.
2. Central South University., 2003. Train Aerodynamic
Vehicle Test Study and Assessment Report. Changsha:
Central South University
3. Anderso,J.D., 2010. Fundamentals of Aerodynamics,
Aviation Industry Press. Beijing
4. Dong Junguo., 2000. Practical Materials Handbook,
Mechanical Industry Press, Beijing
5. Wang Yali., 2001. Analysis of response of random
track irregularity to high-speed motor car. Changsha:
Central South University.
