
Determination of Total Specific Migration of Acrylic Acid and
Acrylic Esters in Food Contact Materials
Meng Qing
1
, Honzhen Zhang
1
, Qingyun Xia
1
and Bohen Huang
1
1
Vkan Test and Certification Co., Ltd, Tianta yi Road Kaitai Avenue, Guangzhou, China
Keywords: Acrylic acid and acrylic esters, Total specific migration, Gas chromatography mass spectrometry (GC -
MS), Food contact materials (FCMs).
Abstract: In this study, we selected a total specific migration indicator including 12 acrylic acid and acrylic esters, i.e.
SML (T) 22 from national food safety standard. After comparison, methyl acetate was selected as the
extracting agent, which was applicable for the treatment of acidic and aqueous simulants. The HP -
INNOWAX polarity column was applied to separate the 12 compounds and the solvent. The GC - MS was
utilized for qualitative and quantitative analysis with optimization of extraction duration, temperature
program, scanning mode as well as the carrier gas flow rate and the sampling volume. The 12 acrylic
compounds present good separation in 12 minutes, and the analytical duration is greatly shortened. The
linearities in different simulants range from 0.047 mg/L to 11.43 mg/L, while the detection limits are from
0.009 mg/L to 0.666 mg/L. The actual products analysis shows that the recoveries are between 81.2% and
81.2%, and the RSDs (n = 6) are within 5.15%. This developed analysis method is fast, economical, non-
toxic, with low detection limit, high precision and high accuracy. It has good applicability and is easy to
promote to use.
1 INTRODUCTION
Acrylic acid and acrylic esters are volatile with
serious odor, and have certain nerve toxicity and
reproductive toxicity. They can contaminate the
atmosphere and the water (Wang et al., 2002), and
are also significantly harmful to human body. Thus
the world health organization's international agency
for research on cancer has listed acrylic acid and its
esters as carcinogens in category 2 or 3. At the
international level, such as the European Union
(European Commission, 2011), as well as the Japan
(Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, 2011) has
issued regulations to limit those monomer residues.
Chinese National Health and Family Planning
Commission (NHFPC) together with Food and Drug
Administration has also announced a series of FCMs
related national food safety standards in 2017 (see
the national food safety standards bulletin No.15 of
2016).
According to GB 4806.6 2016 (NFHPC, 2016),
GB 9685-2016 (NFHPC, 2016), the total specific
migration limit indicator [SML (T) 22], quantified in
acrylic acid containing 12 species of acrylate
monomers, 1 species of poly-acrylic acid salt and 1
species of acrylic polymer is limited to under 6
mg/kg. Nowadays all the common FCMs on the
market such as resin, plastic, paint and coating,
paper, ink, adhesives, etc., should meet the national
standard limit requirement. Content determination of
acrylic acid and its esters first started from the
production in chemical industry process, monomer
residue from textile production, air pollution and
waste liquid pollution (Gu et al., 2002; Shi et al.,
2003; Liu et al., 2013a; Liu et al., 2011b; Shentu et
al., 2008), and were mainly carried out by using gas
chromatography (GC) analysis method. Wang
Jianling et al. (Wang et al., 2016; Dong et al., 2013;
Ma et al., 2013) separated 12 acrylic monomers in
GC instrument with non-polar chromatographic
column and carried out the detection of migration
content for water-based FCMs simulants. Lai Ying
and Lin Rui (Lai et al., 2015) using a purge and trap
sampling method, solved the direct sampling
problem of water-based simulants in gas
chromatography, while the shortcoming is that the
acrylic acid could not be trapped. Li ying and Li
Chengfa (Li et al., 2014a; Li et al., 2015b; Li et al.,
2016c;), respectively utilized the solid-phase micro-
extraction-GC-MS method, the head space GC-FID
method, and the high performance liquid
chromatography (HPLC) method to determine a

variety of acrylate and methyl acrylate migration,
but these methods require complex operation, and
qualitative ability are poor. Moreover the general LC
is unable to separate geometric isomers with similar
polarity.
Due to the bigger differences of polarity and
boiling point between the 12 acrylic monomers and
the existence of isomers, it is difficult to separate
them in a single method. From home and abroad, a
mature analysis method which can directly separate
Chinese regulatory acrylic esters and can be used to
determine the total specific migration has not yet
been reported. We separated the 12 compounds and
the solvent by polarity column with the GC - MS,
and optimized the extraction time, temperature
program, scan mode and sampling volume, carrier
gas flow rate, etc.. The method presents feasible and
precise characteristics in determining 12 acrylic acid
and acrylic esters so as to calculate the total specific
migration limit thereafter.
2 TEST
2.1 Instruments and Reagents
GC - MS instrument: Japan Shimadzu GC - MS
QP2010 – plus.
Electronic balance: Switzerland Mettler, 0.1 mg,
XS – 204.
Whirlpool extraction apparatus: Germany IKA,
Vortex Genius 3.
Ultrapure water purification system: American
Millipore, Milli - Q.
Methyl acrylate (> 99.7%, Aladdin), acrylic acid
(> 99.5%, Aladdin), butyl acrylate (> 99%, Aladdin),
benzyl acrylate (> 97%, Aladdin), iso - propyl
acrylate (> 95%, International Laboratory USA); n -
propyl acrylate (> 95%, Alfa Aesa), ethyl acrylate (>
99.5%, Dr. Ehrenstorfer GmbH), n - butyl acrylate
(> 99.5%, Dr. Ehrenstorfer GmbH), sec - butyl
acrylate (> 95%, Chem Service), n - octyl acrylate (>
95%, Chem Service), hydroxyl ethyl acrylate (>
99.5%, Chem Service), tert - butyl acrylate (>
99.5%, Aike import packing). Methyl acetate
reagent is of chromatography grade, and the rest
reagents are of analysis grade.
2.2 Analysis Conditions
2.2.1 GC Conditions
The polar chromatographic column with
polyethylene glycol (PEG), HP - INNOWAX (30m
× 0.25mm × 0.50μm) is adopted. The Injection port
temperature (T
injec
) is 220 ºC, the interface
temperature (T
inter
) is 250 ºC, and ion source
temperature (T
ion
) is 230 ºC. Carrier gas for high
purity helium (He, purity is more than 99.999%) is
used, and the carrier gas flow rate is 1.8 ml/min.
Sampling volume is 1μL with splitless injection
mode. Solvent delay: in pure water and acid
simulation is of 4.5 min; in ethanol simulation is of
6.2 min.
Programmed temperature: the initial temperature
is 40 ºC, then maintain it for 5 min; after that rise the
temperature at a rate of about 20 ºC / min to 70 ºC;
then warm at a rate of about 40 ºC / min to 180 ºC,
finally at a rate of about 20 ºC / min to keep the
temperature for 1 min at 220 ºC.
2.2.2 MS Conditions
Adopt both the full scan (SCAN) and the select ion
scan (SIM) at 5.1 ~ 7.0 min as well as 10.6 ~ 11.0
min for data collection, while only the full scan
Table 1: Characteristic ions of 12 acrylic acid and acylate monomers
(SCAN) mode for the rest of testing duration. SCAN
range: m/z 25 - 200. Quantitative ions are shown in
Table 1.
2.3 Preparation of Calibration Solution
Weighed respectively 0.100 g standard solution of
acrylic acid and acrylic esters in a 10 ml volumetric
flask, and filled methyl acetate to the volume to
obtain the mixed standard stock solution at the
concentration level of 10000 mg/L. Continued to
dilute step by step with methyl acetate to
concentrations of 0.5, 1.0, 5.0, 10.0, 20.0, 50.0
mg/L.
Prepared five different blank simulants of 4%
acetic acid, water, 10% ethanol, 20% ethanol, 50%
ethanol according to the requirements of GB
5009.156 2016. Measured out 6 copies, 4mL of each
simulants above into 10 mL centrifugal tubes, and
respectively added 0.5, 1.0, 5.0, 10.0, 20.0, 50.0
mg/L mixed standard solutions of 0.4 mL, and
produced a series standard working solutions of
0.05, 0.10, 0.50, 1.00, 2.00, 5.00 mg/L with 6
duplicate samples each. The extraction procedure
was according to step 2.4 extraction operation.
2.4 Total Specific Migration
2.4.1 Migration Test Conditions
Conditions are selected in accordance with GB
31604.1-2015. Considering method detection limit
applicability, the more gentle migration test
conditions are selected as the migration incubating at
40 ºC for 2h.
2.4.2 Food Simulants Selection
In order to analyze as much food simulants as
possible, the 4%acetic acid, pure water, 10%
ethanol, 20% ethanol, 50% ethanol were chosen. Fat
simulant was not considered due to the solvent
influence in baseline separation.
2.4.3 Extraction Operation
Move 4.0 mL migrating solutions or standard
working solutions in 10 mL centrifugal tubes with
plug. To the centrifugal tube respectively add 0.5 g
sodium chloride and 4 mL methyl acetate, and add 1
mL saturated sodium sulfate for 50% ethanol
simulant only, then extract all by vortex (1500
g/min) for 5 min. Carefully take the supernatant
fluid after stratification for 2 min. Samples are ready
to be analyzed with GC – MS after filtration by
0.45μm filter membrane.
2.4.4 Calculation of Total Specific Migration
Total specific migration based on acrylic acid is the
summation of specific migration of 14 target
compounds; this paper provides the specific
migration analysis method of 12 species of acrylic
compounds.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS
3.1 Extraction Operation
3.1.1 Selection of Extractant
As there are 12 target compounds containing many
different species as acid, ester, hydro-ester, benzene
ester co-existing in the analysis system, and the
acrylic acid is highly acidic, the solubility for target
compounds must be considered as well as the
immisciblity for liquid-liquid extraction process
between extraction agent and aqueous water, which
actually leave very few options of the solvents.
Small molecule esters and ethers with medium
polarity or weak polarity may be applicable in
theory. After test, methyl acrylate (which possesses
the minimum polarity in the 12 monomers) can only
be separated with methyl acetate solvent, and is
unable to be separated with such medium polar
solvent as ethanol, ethyl ether, methyl tert - butyl
ether, and is susceptible to be interfered by ethyl
acetate. Moreover, in non-polar solvents such as n-
hexane and isooctane, poor baseline separation
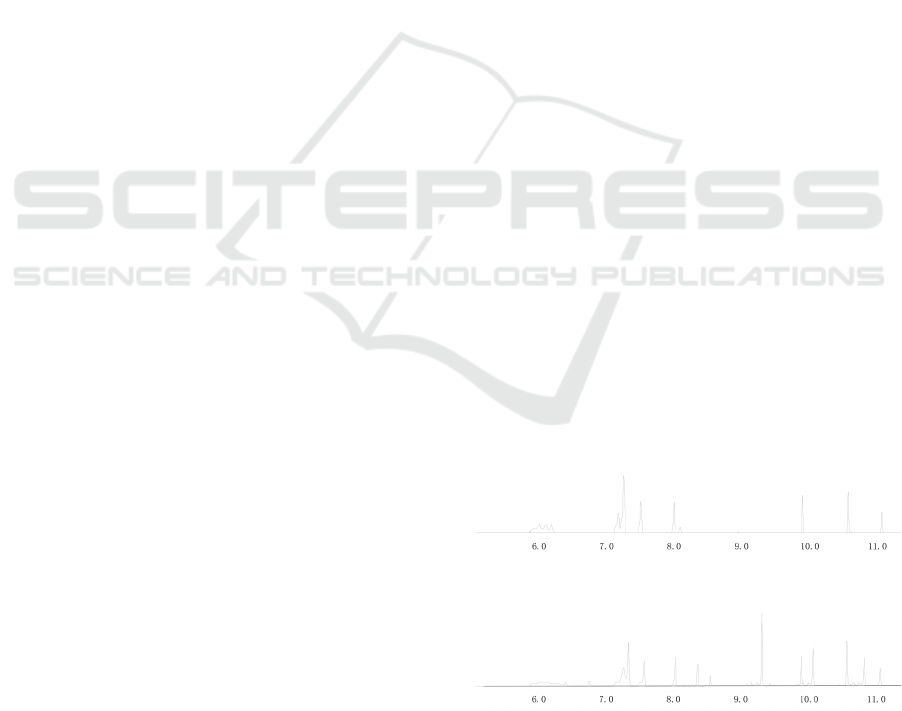
effect is shown (seen in Figure 1 to Figure 2).
Ultimately, methyl acetate is chosen as the
extraction solvent for tests thereafter.
Figure 1: Separation of acrylates in hexane.
Figure 2: Separation of acrylates in iso - octanet.

3.1.2 Optimization of Extraction Duration
Take each of 4 ml 4% acetic acid simulant for 6
copies into 10 ml centrifugal tubes with plugs, add
0.4 mL standard solution at the concentration of 10
mg/L, then add 4 ml of methyl acetate, sodium
chloride 0.5 g. Respectively extract for 1 min, 2 min,
5 min, 10 min to determine the average response.
The results show that the response growth of 12
monomers is no longer obvious after 5 min;
therefore extraction time is selected as 5 min for test.
3.2
Instrumental Optimization
Separations of three chromatographic columns are
investigated. GC temperature program and MS
scanning mode were given intensive optimization to
achieve rapid qualitative and quantitative. Besides,
sampling volume and carrier gas flow rate were also
given appropriate consideration. Sampling volume at
splitless injection mode is 1 μL since higher volume
would cause detector saturation. On the premise of
separation, carrier gas flow rate can be set as higher
as possible to achieve faster outflow. After
optimization, chromatograms of mixed standard
solutions of the 12 acrylic monomers are showed in
Figure 3-1 to Figure 3-6, in which the Figure 3-1 to
Figure 3-5 are the SIM m/z 55 graph of acrylic
monomers, and in which the Figure 6 is the SIM m/z
72 graph of acrylic acid. Since methyl acrylate
cannot be separated from ethanol, data of methyl
acrylate is not collected in ethanol simulants.
3.2.1 Chromatographic Column Selection
This paper tested three chromatographic columns to
separate 12 target compounds. They are respectively
column AT SE - 54 (30m × 0.32mm × 0.50μm),
column DB - WAX (30m × 0.25mm × 0.25μm) and
column HP - INNOWAX (30m × 0.25mm ×
0.50μm).
Firstly, target compound methyl acrylate
possesses very weak polarity as well as low boiling
point, and is unable to reach the baseline separation
in non-polar chromatographic column AT SE - 54
even with almost all sorts of solvent. Secondly,
target compound acrylic acid and hydroxyl ethyl
acrylate both present weak responses at AT SE – 54
column maybe is because of stronger polarity, and
peak tailing are obvious at the same time. Based on
the above, a polar chromatographic column with
thicker stationary phase liquid membrane of 0.5μm
HP – INNOWAX is selected.
3.2.2 GC Temperature Program
The peak of target methyl acrylate is different at
different initial column temperature. Because of its
low boiling point and weak polarity, its responses
reduce gradually with the rising initial temperature
Figure 3-1: 12 Acrylate monomers in 4% acetic acid.
Figure 3-2: 12 Acrylate monomers in water.
Figure 3-3: 11 Acrylate monomers in 10% ethanol.
Figure 3-4: 11 Acrylate monomers in 20% ethanol.
Figure 3-5: 11 Acrylate monomers in 50% ethanol.
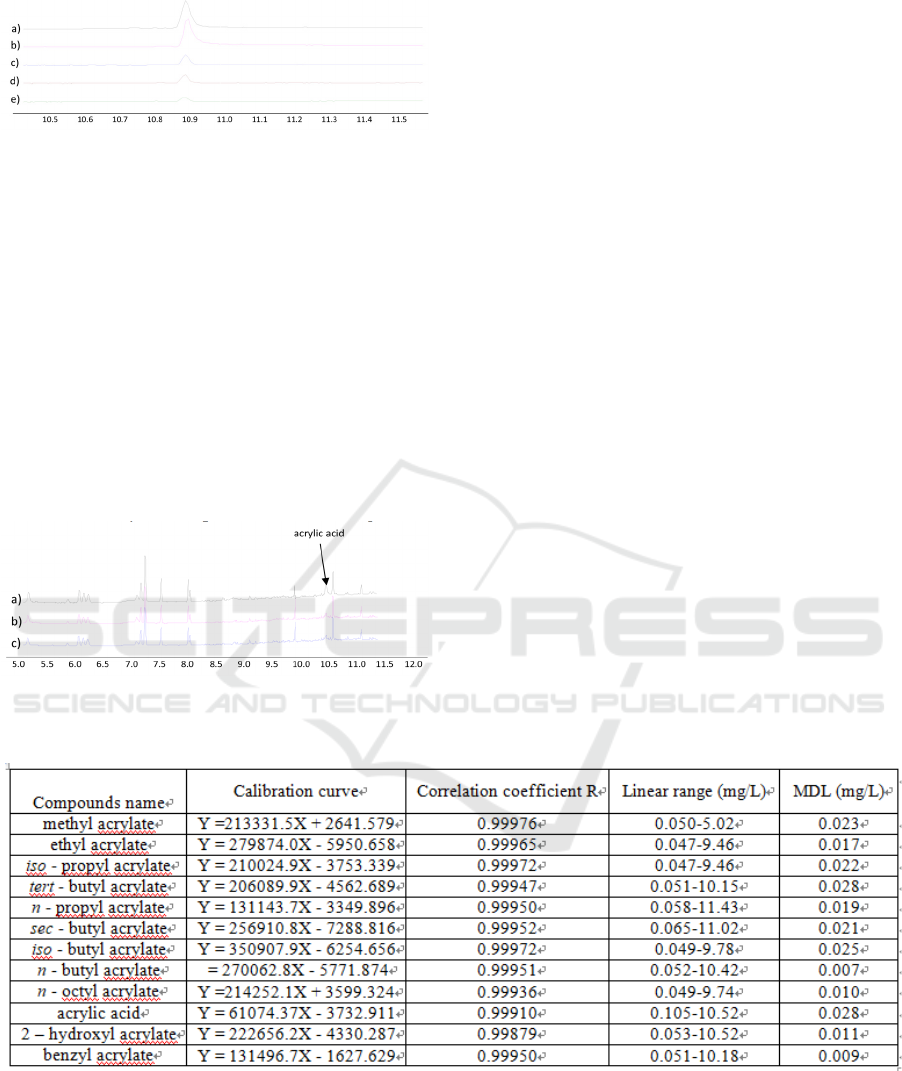
Figure 3-6: Acrylic acid in five different simulants.
Number 1-12 represent the corresponding compounds in
Table 1. a) acrylic acid in 4% acetic acid, b) acrylic acid in
10% ethanol, c) acrylic acid in 20% ethanol, d) acrylic
acid in 50% ethanol, e) acrylic acid in aqueous.
despite the same other conditions, and there is even
no outflow when temperature is 60 ºC above. Finally
the initial temperature is set at 40 ºC. For ethyl
acrylate, iso - propyl acrylate and tert - butyl
acrylate, it is more difficult to separate them, thus a
lower rate of warming is adopted at their outflow.
Last but not the least, T
injec
, T
ion
and T
inter
have
influence on acrylic acid response, results show that
when T
injec
is 220 ºC, T
ion
is 230 ºC and T
inter
is 250
ºC, a clearer acrylic acid peak is observed (Figure 4).
Figure 4: GC temperature optimization
a) T
injec
= 220 ºC, T
ion
= 230 ºC, T
inter
= 250 ºC
b) T
injec
= 180 ºC, T
ion
= 230 ºC, T
inter
= 250 ºC
c) T
injec
= 180 ºC, T
ion
= 200 ºC, T
inter
= 250 ºC
3.2.3 MS Scan Mode
The vast majority of the acrylate targets in this test
system is of high sensitivity, so single SCAN mode
is adopted. However, for targets outflow at low
temperature and the acrylic acid, sensitivity can be
relatively low, so simultaneously adopting SCAN
and SIM mode to collect data is recommended.
3.3 Linearity and Detection Limit
The linear ranges and the detection limits of 12
acrylic monomers in different simulants are
examined. As shown from Table 2 to Table 6, the
vast majority of the monomers in their
corresponding linear range show a correlation
coefficient of above 0.998. Method detection limits
(MDL) in the calculation of 10 times the signal-to-
noise ratio (10 S/N), are between 0.009 ~ 0.666
mg/L. It can be concluded that 50% ethanol
stimulant has a greater matrix influence, although
the detection limit could still meet the total amount
requirement of under 6 mg/kg.
Table 2: Calibration curve and MDL of 12 acrylic monomers in 4% acetic acid simulant.
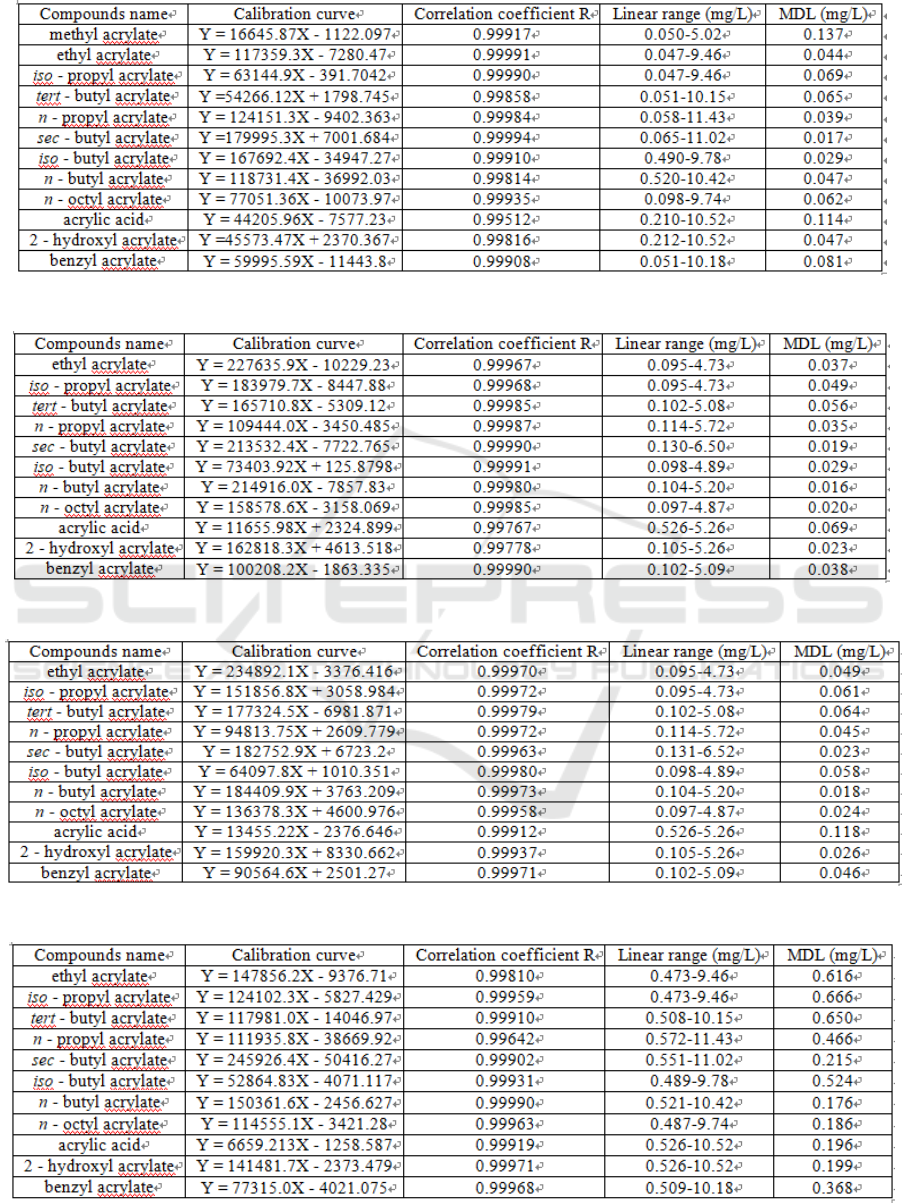
Table 3: Calibration curve and MDL of 12 acrylic monomers in aqueous simulant.
Table 4: Calibration curve and MDL of 11 acrylic monomers in 10% ethanol simulant.
Table 5: Calibration curve and MDL of 11 acrylic monomers in 20% ethanol simulant.
Table 6: Calibration curve and MDL of 11 acrylic monomers in 50% ethanol simulant.

3.4 Recovery and Precision
A plastic lid of ABS material is used to incubate
with the five food simulants under 40 ºC,
respectively for 2 h. Then take each the migrated
solutions of 4 ml, and add respectively 0.10, 1.0, 5.0
mg/L mixed standard solution extract according to
the extraction operation in step 2.4. Six duplicate
samples at three concentration levels were required.
Recovery and precision at the three levels were then
tested. Results show that the recovery rate of acrylic
acid and esters in both acid and water simulants
ranges in 81.2% ~ 108.3%, while the relative
standard deviation (RSD, n = 6) of which is within
5.15%.
4 CONCLUSIONS
The National Food Safety Standard involved limit
indicator [SML (22)], a total specific migration
calculated by acrylic acid contains 12 acrylic
monomers, which are rather difficult to quantify by a
single system due to their large differences of
physical and chemical properties. In fact common
LC column cannot separate the four butyl acrylate
isomers. In this study, with the most commonly used
GC-MS in the testing laboratories, we establish aan
instrumental analysis method for determination
migration with acid and aqueous food simulants.
This method has the characteristics of rapidity and
non-toxicity, with low detection limit and high
precision. But in some simulants containing large
amount of ethanol, the methyl acrylate peak is
significantly hindered by residual ethanol solvent.
Another conclusion maybe deduced from the results
as well, that is the ethanol also has different degree
of influence on other monomers’ outflow.
Subsequently, attempt of multiple liquid-liquid
extraction will be made to possibly reduce the
ethanol residual for improved GC analysis; or study
of using headspace sampling will be continued to
explore probably reduced interference of high
concentrations of ethanol simulants.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This article was supported by Vkan Test &
Certification co., LTD. and the funding of science
and technology projects plan B from China Electric
Apparatus Research Institute (project NO:
SBRV2017054), which herewith acknowledge with
best thanks.
REFERENCES
1. Wang, Z., Yin, Y., Chen, S., Fu, X., Xie, X., and Duan,
S. (2002). Acrylic acid and acrylic ester of acute
toxicity to aquatic organisms. Journal of Jinan
University (Natural Science And Medicine Edition),
pages 75-80.
2. European Commission. (2011). Commission
regulation (EU) No 10/2011 on plastic materials and
articles intended to come into contact with food.
Official Journal of the European Union, pages 15(1):
1-89.
3. Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare. (2011).
Specifications and Standards for Foods, Food
Additives, etc. Under the Food Sanitation Act
(Abstracts) 2010. Japan External Trade Organization,
pages 1-186.
4. The national health and family planning commission
of the People's Republic of China. (2016). GB 4806.6-
2016, National Food Safety Standard, Food contact
plastics and resins. Standards Press of China (to
appear), Beijing, China .
5. The national health and family planning commission
of the People's Republic of China. (2016). GB 9685-
2016, National Food Safety Standard, Food Contact
materials and products using additives standard.
Standards Press of China, pages 1-384, Beijing,
China .
6. Gu, H., and Shi, Y. (2002). Determination of acrylic
acid and its ester compounds from the atmosphere by
gas chromatography. Chemical Analysis and Meterage,
pages 28-29.
7. Shi, C., Luan, S., and Wu, X. (2003). Determination of
acrylic acid and methyl sulfonic acid content in the
waste liquid by ion chromatography. Analytical
Instrumentation, pages 34-36.
8. Liu, C., Wang, L., Yang, J., Chen, Y., and Li, P.
(2013a). High performance liquid chromatography
method and application for seawater acrylic acid. Acta
Oceanologica Sinica, 35(01):172-176.
9. Liu, D., Chen, X., Wu, M., Li, S., and Dai, Y. (2011b).
A headspace gas chromatography - mass spectrometry
method in determination of adhesives residual
monomer of acrylic esters. Chinese Journal of
Chromatography, 29(12):1179-1182.
10. Shentu, X., and Zhang,W. (2008). Determination of
residual monomer acrylic esters in coatings. Dyeing
and Finishing, pages 33-35.
11. Wang, J., Guan, X., and Liu, T. (2016). GC-MS
Determination of 12 methacrylates migrated from
plastics in contact with foods to aqueous simulants.
Physical Testing and Chemical Analysis Part B:
Chemical Analysis, 52(07):809-814.
12. Dong, Q., Lin, R., Lai, Y., Lin, H., Lin, W., Huang, L.,
Ge, X., Lai, T., and Chen, W. (2013). Determination

of migration of methyl methacrylate in sunflower oil
simulants. Journal of Food Safety and
Quality ,4(04):1067-1071.
13. Ma, M., Qing, J., Zhou, Y., Zhou, Y, and Shen, J.
(2013). Head-space GC determination of residual
amount of monomer in products of
polymethylmethacrylate. Physical Testing and
Chemical Analysis Part B: Chemical Analysis,
49(12):1486-1488+1492.
14. Lai, Y., Lin, R., Lin, W., Ge, X., Dong, Q., and Huang,
Z. (2015). Determination of 16 monomers amount of
migration and migration risk investigation in food
contact materials acrylic resin. Chinese Journal of
Analytical Chemistry, 43(10):1573-1579.
15. Li, Y., Li, C., Chen, X., Liang, F., Bai, S., Liao, W., Li,
Y., and Sun X. (2014a). Determination of five kinds of
acrylate monomers migrated from plastic food-
contacting materials by SPME with GC/MS. Plastics
Science and Technology, 42(01):115-119.
16. Li, Y., Li, C., Sun, X., Chen, X., Chen, Z., Sun, D.,
and Wu, S. (2015b). Gas chromatography
determination of migration of 12 monomers in food
contact materials. Packaging Engineering, 36(11):36-
41+50.
17. Li, C., Li, Y., Liao, W., Chen, X., Sun, X., Li, Y.,
and Bai S. (2016c). Determination of migration
amounts of acrylate monomers by high performance
liquid chromatography in food contact materials.
Journal of Food Safety & Quality, 7(01):322-330.
