
Research on Modelling of Grate Cooler Based on Typical Operating
Conditions
Hongliang Yu
1
, Yongmei Sun
2
, Bing Huang
1
and Zheng Zheng
1
1
School of Electrical Engineering, University of Jinan, Jinan 250022
2
Shandong University of Finance and Economics, Jinan 250014
Keywords: Grate cooler pressure, Model, Typical conditions.
Abstract: In the long-term operation of grate coolers, the application of a single model to grate cooler control has
great limitations. Based on the statistical analysis of production site data and the expert experience of
cement plant operators, this paper identifies the typical working reference points for the grate coolers for
cement clinker production lines and typical operating conditions. After that, a dynamic model of the
continuous characteristics of each typical operating condition was established. Simulation results prove the
validity and practicality of the above model.
1 INTRODUCTION
The grate cooler is the main equipment for clinker
cooling and heat recovery in the sintering process of
cement clinker, and maintaining the grate cooler
pressure stability is the basis for ensuring efficient
heat exchange between the clinker of high
temperature and the air of normal temperature. The
grate cooler pressure is affected by the multi-
variables such as the grate speed, raw material
quantity, and the temperature of the material exiting
the kiln. Therefore, based on expert knowledge and
historical data analysis, this paper has determined
the typical working condition template of grate
cooler. Afterwards, a modeling study was performed
on each typical working condition with continuous
dynamic characteristics, which provided a good
basis for subsequent grate cooler pressure control[1-
3].
2 GRATE COOLER TECHNOLOGY
INTRODUCTION AND
WORKING REFERENCE
POINT DETERMINATION
2.1 Grate Cooler Technology
The main function of the grate cooler is to cool the
high temperature clinker, the high temperature
clinker calcined in the rotary kiln falls from the kiln
hood into the grate cooler, with the reciprocating
motion of the grate plate, the high temperature
clinker is distributed on the full grate bed, to form a
layer of material with a certain thickness. The high
pressure cold air blown into the plenum below the
grate cooler is quickly blown into the material layer
to cool the clinker. While cooling the clinker, the
cooling wind exchanges heat with the high-
temperature clinker and turns into hot air, This is the
secondary air and the tertiary air in cement
production. They are fed into the rotary kiln system
through a secondary air duct and a tertiary air duct
respectively. After cooling, the small pieces of
clinker can fall through the grid screen into the
conveyor, and the large pieces of clinker must be
broken into the conveyor. In the grate cooler cooling
process, the speed of cooling and the degree of
sufficient cooling are of critical importance to ensure
the quality and thermal efficiency of the clinker. In
addition, there is an important goal is to stabilize the
secondary air temperature, and the thickness of the
material layer is the key to stabilize the secondary
air temperature. If the material layer is too thick, the
cooling air cannot blow through the clinker, the
clinker cooling is uneven, and the effect is not good,
and due to too much high-temperature clinker
damage to the sampan; If the material layer is too
thin, the cooling wind will quickly blow through the
clinker, without sufficient heat exchange, resulting
in a decrease in the temperature of the second and
third air, and also affect the heat recovery for waste

heat power generation. However, in actual
production, the thickness of the material layer is
difficult to measure directly, so the pressure of the
material cooler is usually used to reflect the
thickness of the material layer, the greater the
thickness, the greater the pressure. Therefore, based
on the idea of hybrid systems, this paper establishes
a grate cooler control model based on grate cooler
pressure output.[4-5]
2.2 The Dominant Factors Affecting
the Pressure of Grate Cooler
2.2.1 Grate Speed and Grate Cooler
Pressure
The most directly controlled grate cooler pressure is
the grate speed (abbreviation: grate speed). Adjust
the speed of the propelled material by adjusting the
speed of the raft, that is, by adjusting the speed of
the grate speed to change the pressure of the cooler.
Change the pressure and stabilize it at the optimal
layer thickness. Under the condition that the cooling
material flow rate of the grate cooler remained
unchanged under the same material, the greater the
thickness of the clinker material layer, the greater
the grate cooler pressure and the need to increase the
grate speed; If the thickness of the material layer is
smaller, the pressure of the grate cooler is smaller
and the idle speed needs to be reduced. This is the
current main control technology for the grate cooler:
adjust the grate cooler pressure by idling to stabilize
the layer thickness. Therefore, the grate speed and
pressure of the grate cooler are important variables
in grate cooler modeling.
2.2.2 Balance Fan Current and Grate Cooler
Pressure
According to the introduction of the cement plant's
on-site sintering system control operator, the balance
fan, that is, the cooling fan of the grate cooler, is
very important for the control of the grate cooler,
with good real-time performance and high reference
value. For the "off the kiln skin" and other abnormal
conditions can be real-time and accurate response
and to some extent, the pressure of grate coolers is
reflected. The performance is that when the balance
fan current increases, the wind pressure increases
and the grate cooler pressure decreases. When an
abnormal operating condition occurs, the parameter
can also change significantly, and the current drop is
greater. It represents a larger kiln skin off,it need to
ensure a balanced fan speed constant. Therefore,
balancing the fan current is also very important,
which helps the operator to perform timely
operations and stabilize production.
2.2.3 Kiln Current and Grate Cooler
Pressure
The Kiln current t is also a key parameter in the
grate cooler control, which has important guiding
significance for the change of the material quantity
in the rotary kiln. At the same time, it can also
intuitively reflect the abnormal phenomena such as
“off the kiln skin” and “burning flow” in the rotary
kiln. When the kiln skin falls, the force of the kiln
body will increase instantly, so that the current of
the kiln main body will increase instantly. In
addition, when the burning flow occurs in the rotary
kiln, the current of the kiln main machine will
instantly drop, and the clinker after the burning flow
will fall into the grate cooler, and will form a large
block under the effect of cooling, so that the grate
cooler pressure will increase. Therefore, considering
the relationship between the kiln host current and the
grate cooler pressure also has certain reference
value.
2.2.4 Raw Material Quantity and Grate
Cooler Pressure
The quantity of raw material to be discharged
determines how much clinker is produced. That is, it
is determined how many clinker coolers need to be
cooled, and it is also common for the production site
to have abrupt changes in the amount of raw meal.
Therefore, it is necessary to consider the impact of
the raw material discharge amount in the grate
cooler control. When the quantity of raw material is
increased, after a certain time delay, the pressure
will increase, and vice versa. In the cement
production process, the operation of stopping the
material will often occur. Therefore, it is necessary
to take into account the sudden decrease in the
quantity of material to be discharged in order to
ensure a stable grate cooler pressure.
2.2.5 Secondary Air Temperature and Grate
Cooler Pressure
After the cooling wind blows through the clinker, it
exchanges heat with the high-temperature clinker to
form secondary and tertiary air. It is used in the grate
cooler and the rotary kiln for combustion, which is
crucial to ensure high heat recovery efficiency. At
the same time, the chiller clinker temperature is a
key indicator for the quality of clinker. The
secondary air temperature can effectively reflect the
temperature of the grate cooler clinker, which
directly affects the thermal efficiency. The higher
the secondary air temperature, the more heat is
recovered and the higher the thermal efficiency.
Therefore, there is a certain relationship between the
secondary air temperature and the grate cooler
pressure.
2.3 Grate Cooler Typical Working
Reference Point Determination
Relying on the historical data of a cement
production line in Shandong Province for statistical
analysis, combined with the expert experience of
operators, a typical working point for a grate cooler
with a daily output of 5,000 tons of cement clinker
production line can be established. As shown in
Table 1.
Table 1: Reference points for key process parameters in
grate cooler systems.
3 RESEARCH ON MODELLING
OF GRATE COOLER BASED
ON TYPICAL OPERATING
CONDITIONS
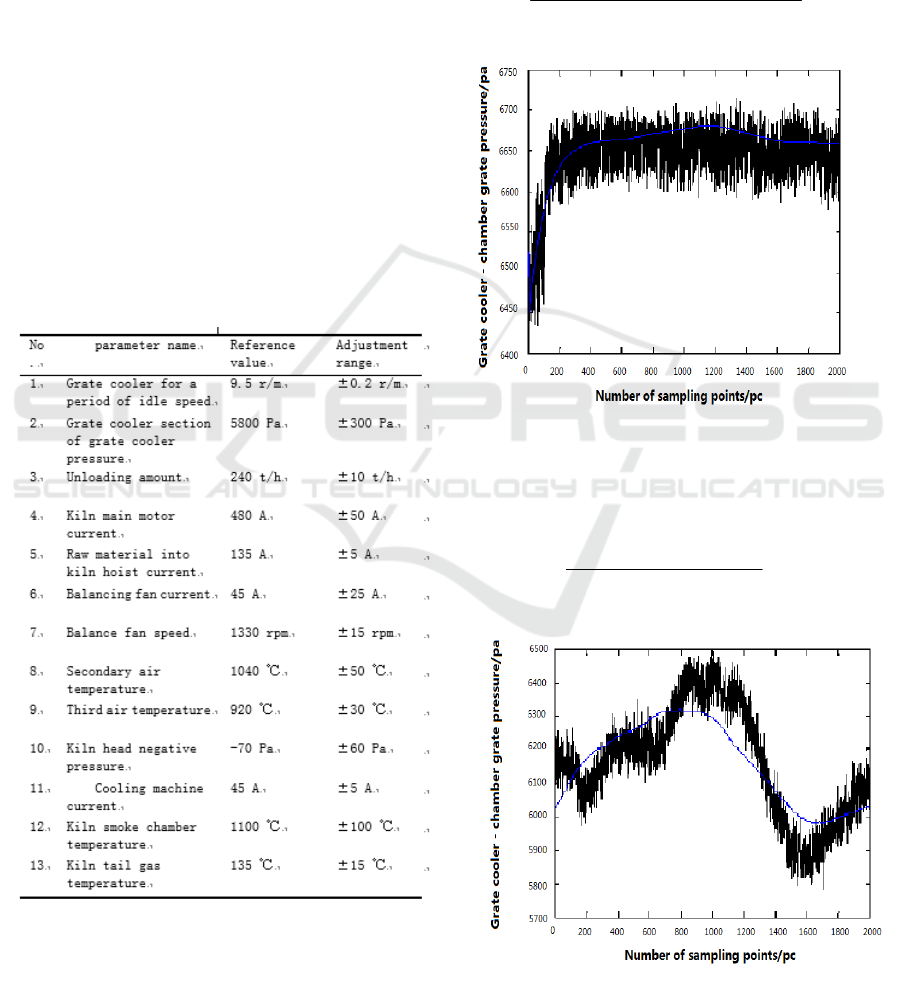
Grate speedand grate cooler pressure model:
)68.1111)(74.1111)(001.01(
64.656
)(
sss
sG
+++
=
(1)
Figure 1: grate speed and grate cooler pressure model test.
Balance fan current and grate cooler pressure
model:
)48.2541(
)10*3.11(10*97.1
)(
65
ss
s
sG
+
−
=
−
(2)
Figure 2: Balanced fan current and grate coolerpressure
model verification.

Kiln current and grate cooler pressure model:
)39.9501)(69.3551)(8.53531(
)2.51831(66.13
)(
sss
s
sG
+++
+
=
(3)
Figure 3: Kiln current and grate cooler pressure model
validation.
Input raw material quantity and grate cooler
pressure data collected into the system identification
toolbox, can get birth raw material quantity and
grate cooler pressure model(formula:4):
s
e
sss
s
sG
03.27
65
)24.1091)(45.1111(
)10*6.11(10*9.3
)(
−
−
++
−
=
(4)
Figure 4: Raw material quantity and grate cooler pressure
model verification.
Secondary air temperature and grate cooler
pressure model(formula:5):
)87.621)(17.01)(395181(
)360741(46.0
)(
sss
s
sG
+++
+
=
(5)
Figure 5: Secondary air temperature and grate cooler
pressure model verification.
The above six single input and single output
models for grate coolers obtained from the
MATLAB system identification toolbox. Entering
the verification data in the system identification
toolbox proves that the model has certain rationality.
After that, the least squares algorithm was
applied to obtain the grate speed, secondary air
temperature, and grate cooler pressure models (
formula:6):
)(32.1)1(24.0- )2(02.1-)(88.13)1(80.46
-)2(64.340.14y(n)-1)y(n13.129.22-)2(
nznznznunu
nuny
+++++
++++=+
(6)
Similarly, the quantity of raw material,
secondary air temperature and grate cooler pressure
model(formula:7):
)(.86z0-)1(84.0 )2(14.1)(25.1)1(.70u0
-)2(1.43u-0.04y(n)-1)y(n93.088.001-)2(
nnznznun
nny
++++++
+++=+
(7)
Similarly, kiln host current, secondary air
temperature and grate cooler pressure model (
formula:8):
)(.07z0-)1(27.0 )2(.19z0-)(u03.0)1(u14.0
)2(0.08u-0.10y(n)1)y(n85.078.253)2(
nnznnn
nny
+++++
+++++=+
(8
)
Similarly, Balancing fan current, secondary air
temperature, and grate cooler pressure model (
formula:9):
)(54.1)1(15.0- )2(74.1)(11.0)1(35.0
)2(03.00.17y(n)1)y(n80.007.91)2(
nznznznunu
nuny
−+++−+
++++++=+
(9)
The above-mentioned four dynamic models of
the two-input single-output of the grate cooler
obtained by the least-squares method.
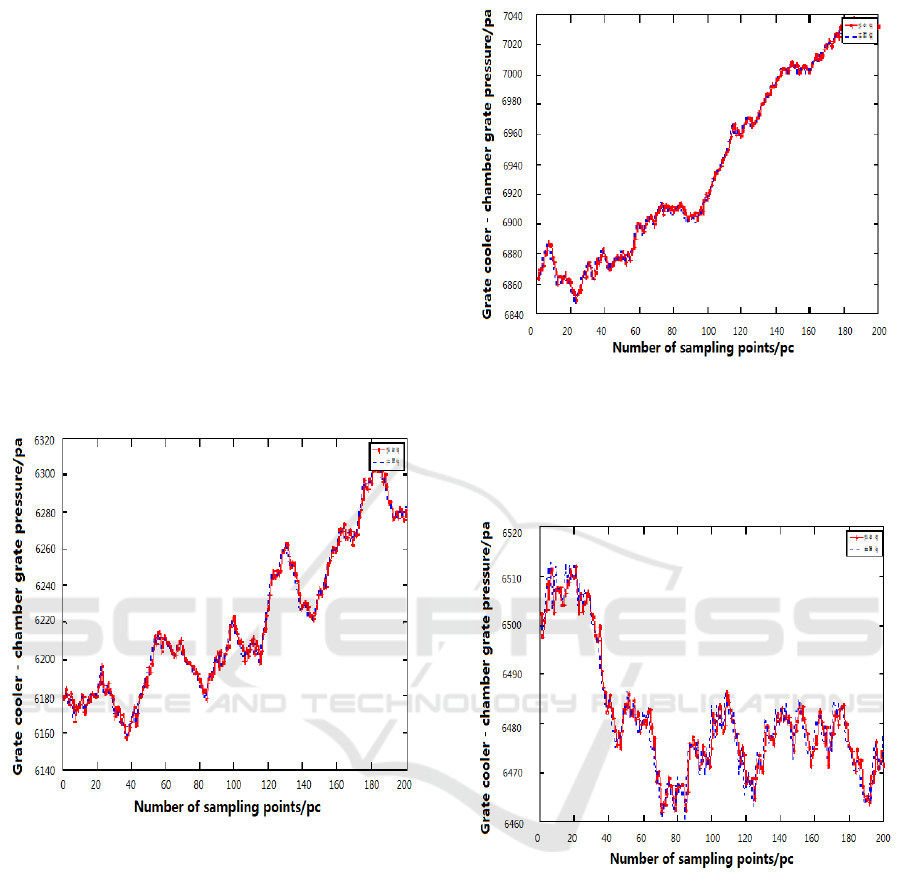
Grate speed, secondary air temperature and grate
cooler pressure model fitting curve shown in Figure
(6)
Figure 6: Grate cooler idling, secondary air temperature
and grate cooler pressure model fitting curve.
Raw material quantity, secondary air temperature
and grate cooler pressure model fitting curve shown
in Figure(7)
Figure 7: Raw material quantity, secondary air
temperature and grate cooler pressure model fitting curve.
Kiln master current, secondary air temperature
and grate cooler pressure for the grate cooler shown
in Figure(8)
Figure8: Kiln current, secondary air temperature and grate
cooler pressure for the grate cooler.
Grate cooler balance fan current, secondary air
temperature and grate cooler pressure model fitting
curve shown in Figure(9)
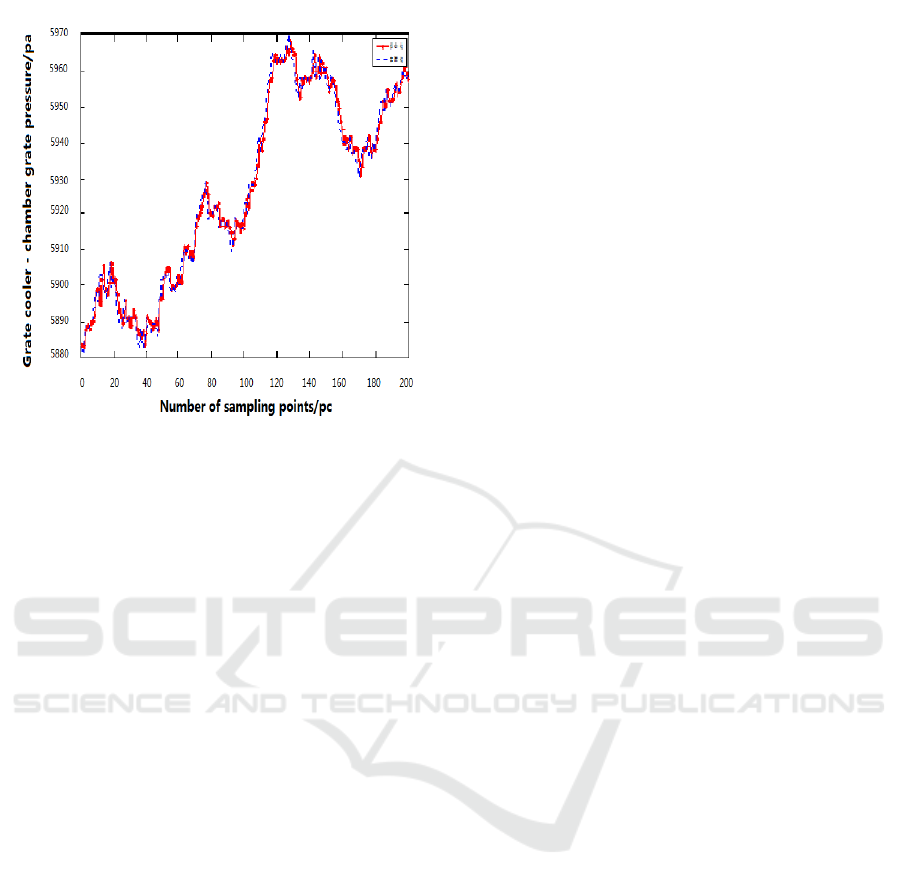
Figure9: Grate cooler balance fan current, secondary air
temperature and grate cooler pressure model fitting curve.
4 CONCLUSIONS
In the long-term operation of the grate cooler, the
application of a single model to grate cooler model
control will have significant limitations. Based on
statistical analysis of production site data and expert
experience of cement plant operators, this paper
identifies the typical operating reference points for
the clinker cooler for a 5000 t/d cement clinker
production line and typical operating conditions.
Through simulation data verification, it proves the
practicability and effectiveness of the established
model and condition identifier, and lays a good
foundation for the subsequent grate cooler model
control.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work is supported by the Sino-European SMEs
research cooperation fund project on energy
conservation and emission reduction
(SQ2013ZOC600003).
REFERENCES
1. Wu Yuqin. Application of predictive control theory
in clinker cooling process of cement clinker [D].
Jinan University, 2007.
2. Wang Xili, Wu Hongming. Hanging swing
trampoline coolers [J]. China Cement, 2005, 05: 67-
70.
3. Yang Huawei.Performance evaluation and
optimization of clinker cooler [D]. Beijing: Beijing
University of Technology, 2009.
4. Wei Wei. Modeling and Control of Cooling Process
for New Dry Cement Production [D]. Jinan: Jinan
University, 2009.
5. Guo Yan. Research and practice of clinker thickness
electrohydraulic control system for 5000t/d grate
cooler[D]. Qinhuangdao: Yanshan University, 2013.
