
Analysis of the Effect of Public E-Health Service Quality on the
Creation of Public Value
Case Study: PMR Hospital Surabaya City
Ria Rizki Wardani
1
, Erma Suryani
1
1
Magister Manajemen Teknologi Informasi, Institut Teknologi Sepuluh November, Surabaya, Indonesia
Key
words: Customer Satisfaction, Service Quality, E-Health, Public Value, and Partial Least Square (PLS)
Abstract: Utilization of information technology becomes very important role because it has been proven that by using
information technology, effectiveness, efficiency in doing a faster process is achieved. With the existence of
fast and quality health service is expected to increase public value in society. Quality of service could be
obtained from customer satisfaction which is formed by customer perception. One of the emerging areas of
health by adopting information technology is E-Health. E-Health Innovation in Indonesia is spearheaded by
the Surabaya City Government with the aim of making it easier for people to come to the community health
centre (Puskesmas) and hospitals to register online, both new patients and old patients. Thus, no longer long
queues occur and the patient could estimate the time to come to the targeted health facility. Enthusiastic
people of Surabaya in utilizing E-Health online registration system is high enough to spur other private
health agencies to apply a similar system. PMR hospital located in Surabaya City is an international private
hospital that has implemented a similar system. But in reality the system has not been able to create
maximum public value in accordance with hospital expectations. This study is aimed at analysing the
influence of service quality online registration system E-Health Hospital PMR Surabaya city to maximize
the creation of public value. The research method used in this research was descriptive quantitative
approach. Data collection of respondents for quantitative research would be taken in Surabaya City area
based on respondents by using E-Health online registration application. The sampling technique used in this
research was the questionnaire survey using partial least square data analysis (PLS). The number of samples
in this study was 100 respondents. The result showed that E-Health had positive and significant effect to
Public Value with original value sample estimate of 0.267 and t-test result obtained by t-count (3.036) > t-
table (1.96). This means that if the better E-health, then the Public Value was increasing. Recommendations
of research results indicate that there is an improvement in the system by building or adding a service and
system criticism survey system and suggestions on the online registration application of the Surabaya City
PMR Hospital.
1 INTRODUCTION
Rohman (2008) Public services is a service or giving
to public the form of the use of public facilities, both
services and non-services, which are performed by
public organizations in this case a government.
Public service is a must for the state or government
to serve its citizens. Public services are not easy to
do and many countries fail to do good public
services for their citizens, Rohman (2008). The
failure and success of a public service can be
determined by the services quality or services
provided by the public service.
One area of public service is health. Each
healthcare service institution is required to create a
competitive advantage in the face of new
competitors engaged in the same service agency that
must have the ability to develop strategic choices in
order to adapt to a dynamic environment. Health
field is a public service that needs to be improved in
terms of service quality. The aim is to develop the
implementation of quality, transparent, easy, cheap,
fast, fair, and fair public service delivery to all
people in order to support the public interest.
In Indonesia the use of information technology
for the health sector has been regulated in Law no.
36 of 2009 on health, where to organize effective
220
Wardani, R. and Suryani, E.
Analysis of the Effect of Public E-Health Service Quality on the Creation of Public Value.
DOI: 10.5220/0007540402200226
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference Postgraduate School (ICPS 2018), pages 220-226
ISBN: 978-989-758-348-3
Copyright
c
2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
and efficient health efforts required information and
health services conducted through the system
information and through cross-sector. E-health is
one of the innovations undertaken to overcome these
obstacles. According to Wickramasinghe and
Goldberg (2004) that E-Health or electronic health,
which is essentially driven by the use of information
and communication technologies in health has the
potential to transform the health industry worldwide
in terms of infrastructure, cost and quality of service.
The enthusiasm of Surabaya society in utilizing
the online registration system is high enough to spur
other private health agencies to implement similar
systems. PMR hospital located in Surabaya is an
international private hospital selected by the
researcher. PMR hospitals have utilized the E-Health
service-based E-Health website but it is not yet
optimal, as evidenced by the visits of patients who
are admitted to PMR hospitals either directly
registering or through online registration through
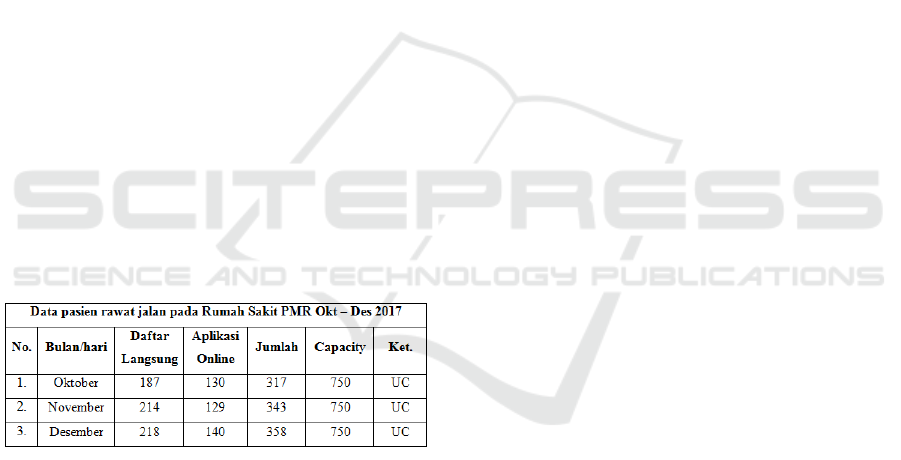
websites tend to be quiet or under-capacity (UC). As
preliminary information, PMR hospital has 25 polies
ready to serve outpatients with a maximum capacity
of patient per 25 to 30 patients per day. This
indicates that PMR Hospital with the service
capacity provided has not met the target customer
with maximum. The following is the data obtained
by the researcher for the last 3 (three) months based
on the patient visit in PMR Hospital Surabaya.
Table 1.1: Data on patient visit in PMR Hospital 2017.
Source: Internal data of PMR Hospital visitors’
statistics (2017)
Benefit to be gained by PMR Hospital by
improving service quality is able to create maximum
public value. The technique used in this study is
non-probability sampling, where all elements of the
population do not have the same opportunity or
opportunity to be a member of the research sample
and the type of non-probability sampling used in this
study is purposive sampling that is sampling
technique based on criteria and the characteristic of
the specified sample. Data collection used direct
survey method with questionnaires instrument. For
further analysis, used Partial Least Square (PLS)
method and analysis technique. PLS was chosen by
the researchers with the consideration that PLS is a
powerful analytical method because it can be applied
to any data scale, does not require many assumptions
and the sample size does not have to be large. PLS is
a more appropriate approach for predictive purposes,
especially in conditions where indicators are
formative.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
Service quality is closely related to the customer
epuasan k are believed to be major factors that
significantly impact customer value. Customer was
believed to be a significant impact on the increase in
revenues. This becomes something that is important
for profit-seeking companies.
Some studies conclude that customer satisfaction
does not have a significant impact on customers,
customers also have no significant impact on
corporate profits. The theories used in this study
include from various literature journals, guidebooks
of quality Partial Least Square (PLS), online
media, as well as one of the object of One Hospital
which became the research place. In this case the
health agency company which is the object
of research is PMR Hospital in Surabaya city .
2.1 Quality of Service
Kotler & Keller (2009) state that service quality is
the totality of features and characteristics of products
or services that are capable of satisfying the stated or
implied customer requirements.
A qualified
company is a company capable of delivering its
products or services to meet or exceed customer
expectations.
From the definition of service quality can be
concluded that the quality of service is all forms of
activities undertaken by the company to meet
consumer expectations.
Service in this case is
defined as services or services delivered by the
owner of services in the form of ease, speed,
relationship, ability and hospitality addressed
through the attitude and nature in providing services
for customer satisfaction.
2.2 Public Service
Gronross (2013) states that service is an activity or
a series of activities that are invisible (not palpable)
that occur as a result of interaction between
consumers with employee or other things provided
by the company service providers intended to solve
consumer or customer problems.
Analysis of the Effect of Public E-Health Service Quality on the Creation of Public Value
221

Ratminto and Atik Septi Winarsih (2006)
conclude that public service or public service is as
any form of service, either in the form of public
goods or public services which in principle is the
responsibility and implemented by government
agencies in central, regional, and in the environment
of State-Owned Enterprises, in an effort to meet
the needs of the community as well as in the
implementation of the provisions of the laws and
regulations.
2.3 Public Value
Customers have the same needs, but the wish of
each customer is different. This causes the
customer's perception of the product or service
offered by the company will give different value in
customer's eyes. Value is something that is
individual because something that is valuable to
someone is not necessarily valuable to
others. Sometimes customers value a product or
service based on the merits of the product or service,
but in another situation the customer judges a
product or service based on the employee's service
or friendliness in serving the customer regardless of
the benefits of the product or service.
The public value / customer value is a level of
satisfaction determined when a customer sees more
value from a product and the service performance
received from a process of purchasing a product or
service (Lupiyoadi, 2006). The more value to
customers given by a product or service is a
customer's answer to determine his
choice. On basically the customer is looking for the
greatest value provided by a product or service.
2.4 E-Health
E-Health is an internet application or other related
technology in the healthcare industry that aims to
improve access, efficiency, effectiveness, and
quality of medical and business processes, involving
the organization of medical services (hospitals or
clinics), medical practitioners (physicians or
therapists) laboratories, pharmacies, insurance, and
patients as consumers. Solutions on offer
E-
Health
including products, systems and services,
for example
, health information, electronic medical
records, drug purchasing services, communication
systems between users, and other information on
disease prevention, diagnosis, treatment, health
monitoring and lifestyle management.
E-Health can be seen from corporate or corporate
solutions in the health sector
that involves support of
all aspects of government structure, such as
hospitals, health centers, health offices,
pharmaceutical industries, higher education (health-
related), and polyclinics.
If E-Health is fully
supported by the population and community
administration within the scope of the region, city,
province, or national, then E-Health will be a future
application in order to optimize the public health
system.
2.5 Relationships between Variables
Theory as the Basis of the
Hypothesis
There are three types of relationships between
variables, namely symmetrical relationships, causal
relationships, and interactive relationships (mutual
influence). To find the relationship between two
variables or more is done by calculating the
correlation between the variables that will look for
the relationship. Correlation is a number that shows
the direction and strength of the relationship
between variables or more. This means expressed in
the form of a positive or negative relationship, while
the strength of the relationship is expressed in the
magnitude of the correlation coefficient.
The relationship of two or more variables is
positive, if the value of one variable is increased, it
will increase the other variable, and vice versa. If the
value of one variable is lowered, it will decrease the
other variable. The relationship of two or more
variables is stated as negative, if the value of one
variable is increased, it will decrease the value of the
other variable, and vice versa. If the value of one
variable is lowered, it will increase the value of
another variable.
2.6 Partial Least Square (PLS) Method
Partial Least Square (PLS) is an alternative method
of estimating models to manage Structural Equation
Modeling (SEM). The PLS design was made to
overcome the limitations of the SEM method. In the
SEM method requires large data, no missing values,
must be normally distributed, and should not have
multi-collinearity, whereas in PLS use a distribution
free approach where data can be distributed in a
certain way. Besides that, PLS can also be used on a
small number of samples.
Yamin and Kurniawan (2009) say that PLS is
used to determine the complexity of the relationship
ICPS 2018 - 2nd International Conference Postgraduate School
222

of a construct and other constructs, as well as the
relationship of a construct and its indicators. PLS is
defined by two equations, namely the inner model
and the outer model. The inner model determines the
specification of the relationship between the
construct and its indicators. The extract is divided
into two, exogenous and endogenous. Exogenous
extract is the cause of the constituent, which is not
affected by other constructs. Exogenous extracts
give effect to other constituents, while endogenous
extracts are the extracts described by exogenous
compounds. Endogenous extract is the effect of
exogenous constructs.
According to Gahazali (2006) that PLS method
has its own advantages including: data does not have
to be multivariate normally distributed (indicators
with category scale, ordinal, interval until the ratio
can be used on the same model) and the sample size
does not have to be large.
3 METHOD
The form of this research was descriptive
quantitative research. This research was conducted
by distributing questionnaires to the community,
especially the people who have been treated
outpatient to the hospital in Surabaya City and
conical to the respondent who registered online E-
Health at PMR Hospital Surabaya City.
Figure 3.1: Conceptual Model.
The population in this study was the community
or hospital patients who have done outpatient
treatment. The sample to be used in this study was
the community or patients who registered either
directly or online for outpatient treatment of the
hospital.
Data collection methods in the study used the
instrument in a questionnaire (Arikunto, 2002).
Questionnaires were a number of written questions
that were used to obtain information from
respondent.
The data analysis method was used Smart PLS
software that run with computer media. PLS (Partial
Least Square) was a variance-based structural
equation analysis (SEM) that could simultaneously
perform testing of measurement models as well as
structural model testing. The measurement model
was used for validity and reliability test, while the
structural model was used for causality test
(hypothesis testing with prediction model).
Figure 4.1: Model of Construct Research Structure.
4 RESULT
The results of data processing by using
Smart PLS software tools, obtained the output of the
model of loading factor construction structure that
would explain the relationship between construct
service quality, E-Health, and public value which
was shown in Figure 4. 1 following:
Analysis of the Effect of Public E-Health Service Quality on the Creation of Public Value
223
4.1 The results of Validitas dan
Reliabilitas
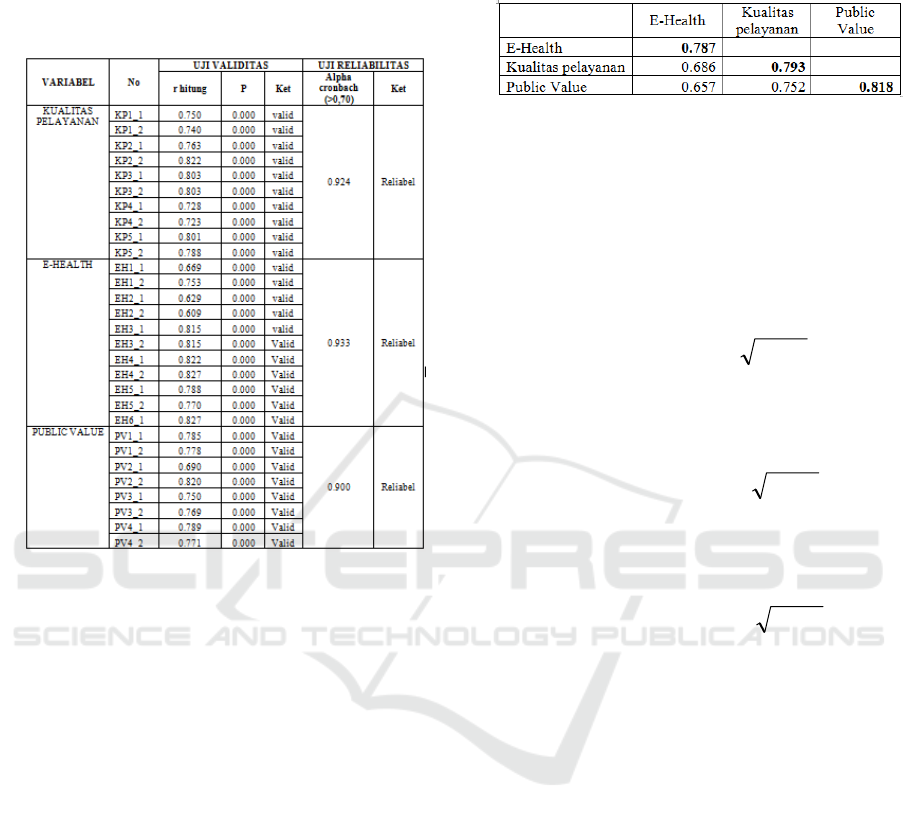
Table 4.1 Test Results Validity and Reliability.
Based on Table 4.1, it was known that all queries in
the questionnaire had r counts greater than r table
and the probability value was less than 0.05 (p <
0.05). Thus all questions were declared valid. The
result of reliability test in Table 4.1 stated that the
four variables were reliable. This is evidenced by the
value of Cronbach Alpha was greater than 0.7.
4.2 Discriminant Validity
In testing discriminant validity could be in two
ways, among others:
1. The root of AVE was to know the correlation
between constructs
Testing the validity of the indicator of
the Average Variance Extract (AVE) root
value was compared with the correlation
between constructs with other
constructs. The following values of AVE
and correlation between constructs could be
seen in Table 4.2 below.
Table 4.2: AVE Values & Correlations between
Constructs.
Description: The value in bold is the root value of
AVE.
Source: Primary data processed, 2018
The result of the test was satisfied, if the AVE
root was greater than the correlation between
constructs with other constructs. From Table 4.9,
shows that the AVE root value was higher than the
value of correlation among other constructs. More
details can be explained as follows:
a. AVE roots value (
AVE
) E-Health
construct equal to 0,787 higher than
correlation between E-Health with
service quality 0,686, and Public value
0,657.
b. AVE roots value (
AVE
) service
quality construct equal to 0,793 higher
than correlation between service
quality with E-Health 0,686, and
Public value 0,752.
c. AVE roots value (
AVE
) Public
value construct equal to 0,818 higher
than correlation between Public value
with E-Health 0,657, and service
quality 0,752.
Based on the above results, it appeared that the
AVE root value was higher than the value of
correlation among other constructs. This showed that
the constructs in the estimated model meet the
criteria of high discriminant validity, meaning that
the data analysis results were acceptable. It was
because the values that describe the relationship
between constructs develop and the AVE root value
had a value greater than the correlation value
between constructs.
2. Correlation construct with indicator itself
Discriminant validity testing in this way
was said to be valid if the construct
correlation value with its own indicator was
greater than that of other constructs and all
construct correlation values with its own
indicator and other constructs indicates a
positive value.
From the results of processing
ICPS 2018 - 2nd International Conference Postgraduate School
224
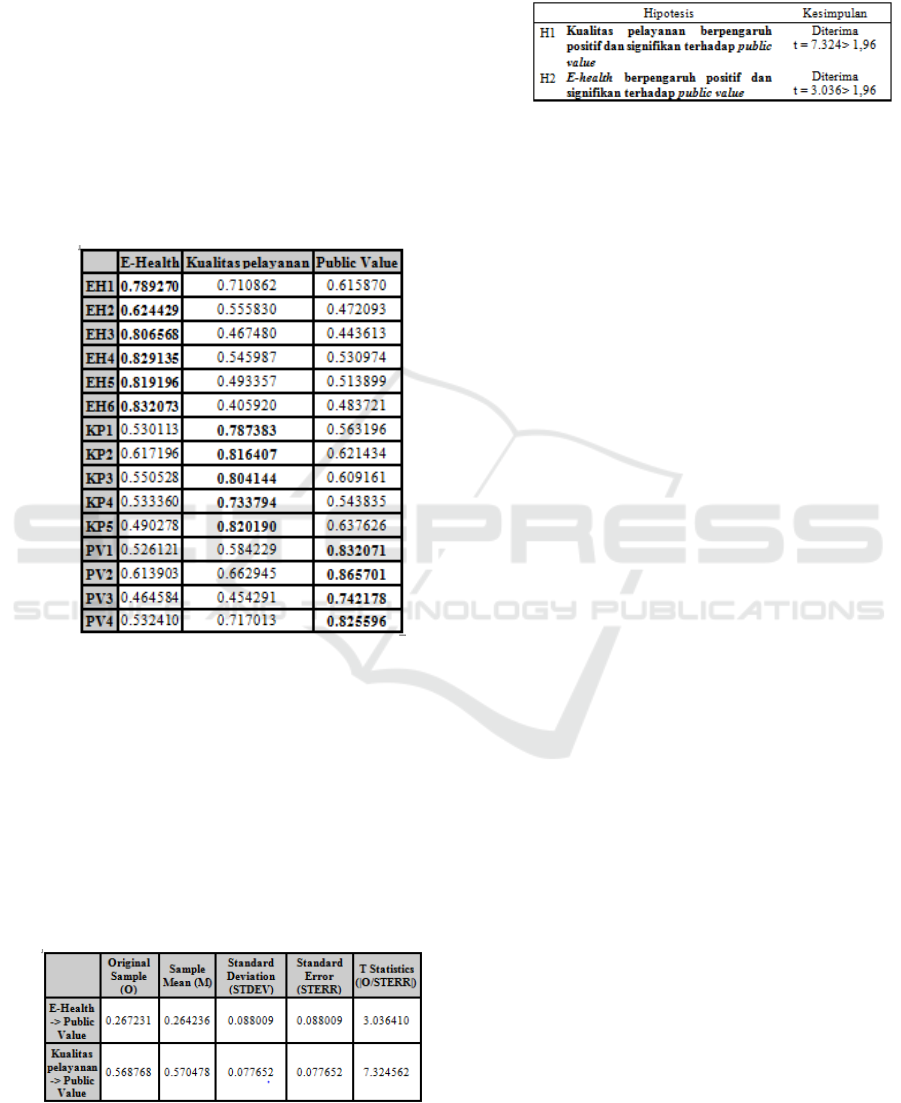
data presented on the table cross loading
could be seen that the requirements have been
met so that all constructs in the model were
estimated to meet the criteria discriminant
validity was good meaning the results of data
analysis can be accepted.
The result of an analysis of the correlation
of the construct with its own indicator or
construct correlation with other indicators
could be presented in
Table 4.3 parts of the
following cross loading.
Table 4.3: Correlation Value of Constructs with Indicator
(Cross Loading).
Description: EH = E-Health;
KP = Quality of service;
PV = Public Value
Data Source: Primary data processed, 2018
4.3 Direct Effect Analysis
The results of testing the direct effects of
each of these research variables could be seen
in Tabe 4.4.
Table 4.4: Hypothesis Test Influence.
Data Source: Primary data processed, 2018
The results of hypothesis testing could
be summarized briefly in Table 4.5 following.
Table 4.5: Hypothesis Testing Results.
Source: Primary data processed, 2018
Results if the data above could be known
in the test of each hypothesis that had been
proposed, namely:
1. Hypothesis Testing 1:
H1: Service quality had positive and
significant effect to Public Value
In test of hypothesis 1 obtained by
original value sample estimate equal
to 0,568 value proves service quality
had positive effect to Public Value
which result also reinforced from
result of t test which obtained by t-
count value (7,324) > t-tabel (1.96).,
So, it could be said that was
significant influence service quality
against Public Value.
So, it could be concluded that was
the service quality had a positive and
significant effect on Public Value,
meaning if the quality of service was
better, then the Public Value was
increasing.
Thus, the first hypothesis
was acceptable.
2. Hypothesis Testing 2:
H2: E-health had a positive and
significant effect on Public Value
In test of hypothesis 2 obtained
original value sample estimate equal
to 0,267 value prove E-health had
positive effect to Public Value which
result also reinforced from t test result
obtained by tcount (3.036) > t-table
(1.96), so it could be said there was
significant influence E-health
to
Public Value.
So, it could be concluded that E-
Health had a positive and significant
effect on Public Value, meaning that if
the E-health was better, then the
Public Value was increasing.
Thus,
the second hypothesis was acceptable.
Analysis of the Effect of Public E-Health Service Quality on the Creation of Public Value
225

5 CONCLUSION
Based on the results of the research and discussion
above, the conclusion of this study was the service
quality had a positive and significant effect on the
Public Value with the original sample estimate value
of 0.568. Then, the result of t-test obtained t-count
(7,324) > t-table (1.96). This means that if
the service quality was better, then the Public Value
was increasing. E-Health had a positive and
significant effect on Public Value with original value
sample estimate of 0.267 and t-test result obtained
by t-count (3.036) > t-table (1.96). It means that if
E -Health is better, then the Public Value is
increasing. Recommendations of research results
indicate that there is an improvement in the system
by building or adding a service and system criticism
survey system and suggestions on the online
registration application of the Surabaya City PMR
Hospital. This study only identifies the factors that
influence the quality of service in terms of the use of
E-Commerce, namely E-Health in increasing public
value. It is expected that in further research to better
identify other factors that has not been explored yet
in the study.
REFERENCES
Alford, J. and O' Flynn, J. (2009), "Making sense of public
value: concepts, critiques and emergent meanings",
International Journal of Public Administration, Vol.
32, pp. 171-91.
Arbuckle, James L, 1997, Amos 7.0 User's Guide.
Chicago, IL: SPSS Inc.
Arikunto, S. 2010. Prosedur penelitian : Suatu Pendekatan
Praktik. (Edisi. Revisi). Jakarta : Rineka Cipta.
Chang, Shu-Chun. Et. Al. 2012. Evaluation of Satisfaction
and Repurchase Intention in Online Food Group-
Buying, Using Taiwan as an Example.British Food
Journal, Vol. 116 Iss 1 pp. 44 – 61
Fandy Tjiptono, dan Gregorius Chandra. 2011. Service,
Quality and Satisfaction (ed 3). Yogyakart: Andi.
Ferdinand, Augusty. 2005. Structural Equetion Modeling
dalam Penelitian Manajemen. edisi 3. BP. UNDIP
Goss, Sue. 2001. Making Local Governance Work:
Network, Relationship and the Hair, J.F.J., Anderson,
R.E., Tatham, R.L. & Black, W.C. (1998).
Multivariate Data. Analysis, 5th edition, Upper Saddle
River: Prentice Hall.
Indrajit R. E dan Pranoto, R. D. 2002. Konsep Manajemen
Supply Chain. Grasindo, Jakarta.
Indrajit, 2004.Electronic government (strategi
pembangunan dan pengembangan sistem pelayanan
publik berbasis teknologi digital).Yogyakarta: ANDI.
Inpres Nomor 3. 2003. Depkominfo, “Instruksi Presiden
Republik Indonesia No.3 Tahun 2003 Tentang
Kebijakan Dan Strategi Nasional Pengembangan E-
Goverment,” 2003
Kaihatu, T. 2008. Analisa Kesenjangan Kualitas
Pelayanan dan Kepuasan Konsumen Pengunjung plaza
Tunjungan Surabaya.UK Petra. Surabaya.
Karunasena, 2011. Measuring the public value of e-
government: a case study from Sri Lanka. The current
issue and full text archive of this journal is available at
www.emeraldinsight.com/1750-6166.html Vol. 5, Iss.
1
Kelly, G., Mulgan, G. and Muers, S. (2002), "Creating
public value: an analytical framework for public
service reform", Cabinet Office, London, available at:
www.cabinetoffice.gov.uk (accessed 5 September
2008).
Kheng, Lo Liang., Mahamad, Osman., Ramayah. T. 2010.
The Imapcat Of Service Quality On Custemer Loyalty:
A Study Of Banks In Penang, Malasysia. International
Journal Of Marketing Studies Vol. 2, No. 2;
November 2010
Kotler, Philip, dan Kevin Lane Keller. 2009. Manajemen
Pemasaran Jilid 1, edisi Ketiga Belas, Terjemahan Bob
Sabran, MM. Jakarta: Penerbit Erlangga.
Leboeuf, Ph. D. Michael. 2010. Memenangi dan
Memelihara Pelanggan Seumur Hidup (Rahasia
Sukses Bisnis Sepanjang Masa). Cet- Ke 4. Jakarta:
Pt. Tangga Pustaka
Moore, M. H. (1995), Creating Public Value: Strategic
Management in Government, Harvard University
Press, London.
Nana Syaodih Sukmadinata. (2006). Metode Penelitian
Tindakan. Bandung: Remaja Rosda Karya
Nasution, M. N., 2001. Manajemen Mutu Terpadu (Total
Quality Management), Jakarta: Ghalia Indonesia.
Ndou, V. (2004). E-government for developing countries:
opportunities and challenges. The Electronic Journal
on Information Systems in Developing Countries 18
(1), 1-24.
Rush, Christine, 2015. Retaining public value and public
law value in outsourcing. International journal of
organization theory and behavior, 18 (1), 105-132
Schiffman, Leon & Kanuk, Leslie., L. 2008. Consumer
Behavior 7 Th Edition (Perlilaku Konsumen.
Jakrata:Pt:Indeks
Sosiawan, Edwi Arief. 2008. Kajian Teoritis Komunikasi
Virtual (Internet dalam perspektif komunikasi).
Sugiyono. 2010. Metode Penelitian Bisnis (Pendekatan
Kuantitatif, Kualitatif, dan R&D). Bandung: Alfabeta.
Sugiyono. 2012. Metode Penelitian Kuantitatif Kualitatif
dan R & D. Bandung: Alfabeta.
Try, D. and Radnor, Z. (2007), "Developing an
understanding of results-based management through
public value theory", International Journal of Public
Sector Management, Vol. 20 No. 7, pp. 655-7
ICPS 2018 - 2nd International Conference Postgraduate School
226
