
Device of Lymphedema Pump Therapy Based on Pressure
Pump: Design and Development
Suryani D. Astuti
1
, Deny Arifianto
2
, Dewa A.G.M. Supartha
3
, Alfian P. Putra
3
, Tri A. Prijo
1
1
Department of Physics, Faculty of Science and Technology, Universitas Airlangga, Surabaya, Indonesia
2
Post Graduate Program in Biomedical Engineering, Universitas Airlangga, Surabaya, Indonesia
3
Biomedical Engineering Study Program, Department of Physics, Faculty of Science and Technology, Universitas
Airlangga, Surabaya, Indonesia
Keywords: Pressure pump, Lymphedema pump therapy, Microcontroller
Abstract: Breast cancer is a cancer with the highest prevalence in Indonesia and one of the factors that trigger
lymphedema. Lymphedema caused by disruption of the lymph flow due to removal of some lymph nodes
during breast cancer surgery causes swelling of the upper or lower extremities. Compression pump therapy is
a therapeutic technique for controlling swelling. This research aimed to design and development of pressure
pump based on microcontroller with good performance. The lymphedema pumps were made with 3 chamber
handcuffs which had 4 variations of pressure values, i.e. 20mmHg-30mmHg, 30mmHg-40mmHg, 40mmHg-
50mmHg, and 50mmHg-60mmHg which could be selected using push button. The reading of the air pressure
value on the handcuff used the MPX5050GP pressure sensor. The air control system uses Arduino UNO
ATMega 328 microcontroller. The result of performance test of pressure sensor to output voltage showed
correlation coefficient 99.93%. The result of pressure calibration showed 99.96% linearity. The assembled
lymphedema pump had the characteristic of a chamber which was able to inflate and deflate sequentially from
distal to proximal with the mean pressure on each chamber. So, the assembled pressure pump has a candidate
as lymphedema pump therapy.
1 INTRODUCTION
Cancer is one of the main causes of death in the world,
one of them is breast cancer (Torre et al., 2015). In
2013, Indonesia has over 0.5% of breast cancer
patients, which is about 61.682 cases. Breast cancer
is one the causes that could cause lymphedema.
Lymphedema is a swelling of the upper and lower
extremities that caused by disruption of the lymph
flow. Lymphedema in breast cancer occurs in the
upper limb of the axilla due to removal of some lymph
nodes during surgery (Harris et al., 2001).
Lymphedema causes discomfort, limb dysfunction,
and morbidity (Damstra and Partsch, 2009).
Lymphedema is a chronic disease that could not be
cured. However, there are several attempts that could
be made to control swelling and reduce pain, such as
exercising, wrapping the arms or legs,
massage/Manual Lymphatic Drainage (MLD), and
pneumatic compression. Pneumatic Compression
(IPC) is a therapeutic technique using a device that
called lymphedema pump (Moseley et al., 2007). In
Indonesia, the availability of the pumps is very
limited because of the price is expensive, while every
year, the patient with lymphedema in cases of breast
cancer is increase because of this situation so many
people are not handled properly. Therefore, it is
necessary to make lymphedema pump with good
performance and reasonable price. Feldman et al
(2012) has created a Lymphedema pump by giving an
air in the handcuffs with 3 chambers sequentially
from the bottom to upper limb on the upper extremity
(distal to proximal) (Feldman et al., 2012). When the
three of chamber is already expending, the chambers
would deflate alternately. This is intended to allow
the lymph fluid to flow out of the upper limb with
lymphedema. The purpose of this research is to make
a lymphedema pumps that has controls on the air
delivery system so that the chambers could expand
sequentially from distal to proximal and deflating
alternately. Handcuff consists of three chambers. In
this device also has a pressure setting using push
button. The pressure range is within 20 mmHg to 60
Astuti, S., Arifianto, D., Supartha, D., Putra, A. and Prijo, T.
Device of Lymphedema Pump Therapy Based on Pressure Pump: Design and Development.
DOI: 10.5220/0007540502310235
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference Postgraduate School (ICPS 2018), pages 231-235
ISBN: 978-989-758-348-3
Copyright
c
2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
231
mmHg (Lee et al., 2011). There is an LCD to displays
the output of pressured that given to the patient.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
The ATMega328 pump consists of air pumps and
handcuffs. The expending handcuff would suppress
and force fluid, such as blood and lymph, out of the
pressurized area. Lymphedema pump component
consists of as follows.
2.1 Hardware
Hardware consists of air pumps, MPX5050GP sensor
circuit, solenoid valve control circuit, push button
circuit, on-off transistor circuit, LCD circuit, and
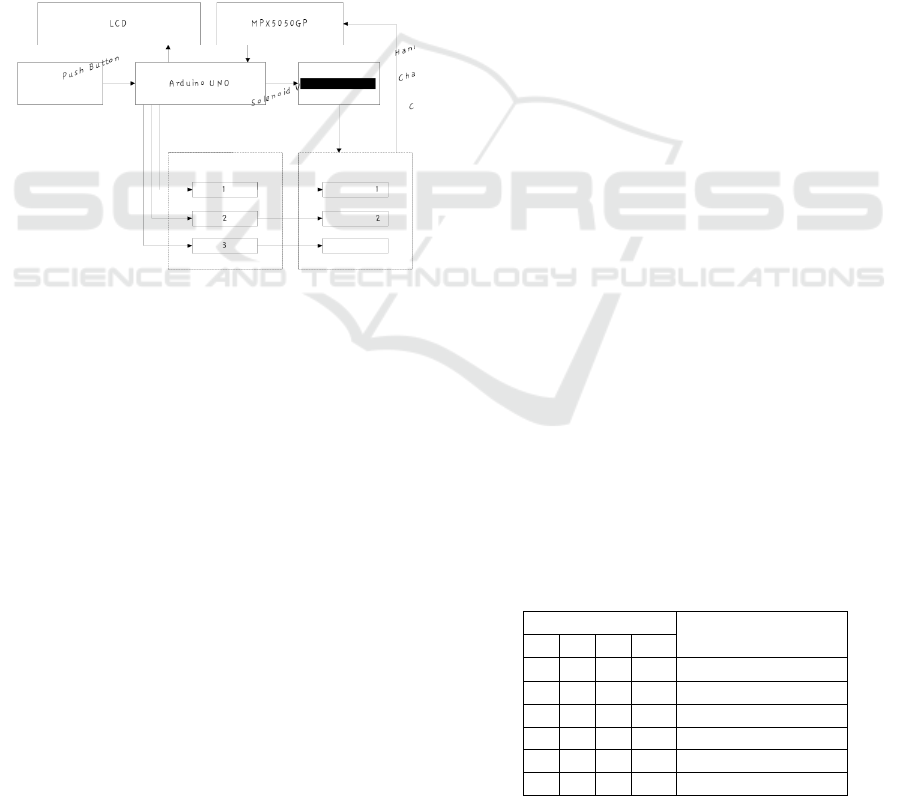
handcuff circuit. The block diagram of the
lymphedema pump is shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1: The diagram block of compression pump for
lymphedema therapy
2.1.1 Air Pump and Pressure Sensor
Lymphedema pump used air pump to compress the
air that flows in the output hole. This air pump has
same principle as the wind compressor, which
compress air so the air has a pressure than the outside
air pressure.
MPX5050GP sensor was used to detect the
changes of the air pressure by converting the pressure
into voltage. MPX5050GP sensor is a piezo-resistive
transducer consisting of a thin silicon chip, a circular
silicon diagram, and four piezo-resistors. When the
pressure is applied to the silicon, the flexural
diaphragm causes the resistance of the silicon to
change. The changeable resistor is connected to the
Wheatstone bridge so that the sensor output is
voltage. The output voltage (VO) of the Wheatstone
bridge could be obtained using Equation 2.1 (Lee et
al., 2011). The output data from MPX5050GP sensor
still in analogue voltage so it needs converting to
Analogue to Digital Converter (ADC). The digital
data is converted into pressure value using transfer
function of MPX5050GP in Equation 4 (Freescale
Semiconductor Technical Data, 2007).
V
o
=(S * P * VB) ±VOS
(1)
V
out
=V
s
* (0,018 * P + 0.04)
(2)
P
a
=((V
out
– (0.04* V
s
))/(0.018* V
s
))
(3)
P
b
=(((V
out
– (0.04* V
s
))/(0.018* V
s
))*7,5)
(4)
V
o
= output voltage (mV)
S = sensitivity (mV/V/psi)
P = pressure (Psi)
VB = input voltage in Wheatstone bridge
VOS = offset error
V
out
= voltage form ADC
V
s
= 5 Volt
P
a
= the value of the pressure measured by the
sensor (kPa)
P
b
= the value of the pressure measured by the
sensor (mmHg), 1 kPa =7.5 mmHg
2.1.2 Handcuff
A handcuff circuit server to suppress the area that has
lymphedema, which is the upper limb. The handcuff
consists of three chamber that sewn together and
connected to a solenoid valve control circuit using a
hose.
2.1.3 Solenoid Valve
This circuit has a function to manage the outflow of
air so the handcuff could be expending or deflating
just like a massaging movement. Solenoid valve
control system in form of on-off control system,
which connects or disconnects electric current in the
solenoid valve. The type of this solenoid valve is
normally open, which means the piston is open when
there is no current flow. The operation of this
solenoid valve control circuit is shown in Table 1. If
the solenoid valve is 0, the solenoid valve is open so
that the air flow out of the chamber, ad if the solenoid
valve is 1, the solenoid valve is closed so the air could
not pass through the chamber.
Table 1: The Operation of Solenoid Valve
Solenoid Valve
Water flow in
1
2
3
4
0
1
1
1
Chamber 1
1
0
1
1
Chamber 2
1
1
0
1
Chamber 3
0
1
1
0
Out Chamber 1
1
0
1
0
Out Chamber 2
1
1
0
0
Out Chamber 3
ICPS 2018 - 2nd International Conference Postgraduate School
232

Valve consists of a magnetic coil that is controlled
by an electric current. The magnetic coil would
supply an electric current and produce a magnetic
field used to driven the piston (plunger) (Whitman et
al., 2012).
2.1.4 Arduino UNO, Liquid Crystal Display
(LCD) 2x16 Character, and Transistor
Arduino UNO ATMega328 based microcontroller
board be used as PWM (Pulse Widht Modulation)
output. This lymphedema pump use arduino uno as
the air control system. The LCD has a function to
display four variation of pressure valve, which are
20mmHg-30mmHg, 30mmHg-40mmHg, 40mmHg-
50mmHg, and 50mmHg-60mmHg and also a result
from MPX5050GP sensor. The on-off transistor
circuit serve as an automatic air pump switch to
channel the air into the solenoid valve control circuit.
2.2 Software
The programing was made using Arduino software.
After the pressure value is inserted, then the pump
would release air and solenoid valve 1 was open, and
the other solenoid valve would close. The air would
fill the chamber 1. The pressure value would be
displayed on the LCD. If the air pressure on chamber
1 has reached maximum pressure, then the solenoid
valve 2 open and the other solenoid valve is closed.
Air pumps emit air and fill chamber 2 and so on.
Pressure values would be displayed on the LCD. If
the air pressure on chamber 3 has reached maximum
pressure, then solenoid valve 4 would open and
solenoid valve 1, 2, 3 would open alternately. So that
air at each chamber would come out. If the insert
voltage is stopped, the air pump would stop pumping
and the fourth solenoid valve would open.
2.3 Performance Test and Analysis
The in-air pump test was carried out by pressure
calibration by using pressure meter (manometer). The
calibration was done by counting percentage of error.
MPX5050GP sensor pressure calibration was done by
connecting MPX5050GP sensor with manometer and
pump. The sensor performance test was performed by
measuring the output voltage of the MPX5050GP
sensor. MPX5050GP sensor performance test results
were used as input to calculate the pressure of the
lymphedema pump so it could be known that the
desired pressure value is appropriate
The pressure stability test of each chamber was
performed to determine the stability of the air
pressure that could be maintained in each chamber for
35 minutes. The pressure stability test time of each
chamber refers to the Huntleigh Physician Form
where the time required for 1-time therapy is 30-120
minutes. The data collection of pressure stability test
was done every 1 minute (Huntleigh, 2001). This
study used four variations of pressure for therapy,
20mmHg-30mmHg, 30mmHg-40mmHg, 40mmHg-
50mmHg, and 50mmHg-60mmHg. The cuff used is 3
chambers. Pressure stability test of each chamber is
performed for each pressure.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Hardware
Hardware is divided into four circuit blocks, i.e. block
circuit 1 containing series of LCD and Arduino UNO,
circuit block 2 contains supply circuit, circuit block 3
contains MPX5050GP sensor circuit and on-off
transistor circuit, and circuit block 4 contains push
button circuit.
3.2 Performance Test MPX5050GP
Sensor and Pressure Calibration
MPX5050GP sensor performance test results data
were analysed using linear regression. Figure 2
showed a gradient line of 12.813. The line equation
for the best match is y=12.813x+225.12 with
correlation coefficient of 0.9993.
Figure 2: The linearity relationship of the pressure value
with the output voltage on MPX5050GP
The value of the air pressure used in this
lymphedema pump therapy is 20mmHg-60mmHg
(Lee et al., 2011). The calibration analysis of
MPX5050GP sensor pressure with pressure
calibration data manometer used a linear regression.
The best line gradient (m) was 0.955. The line
Device of Lymphedema Pump Therapy Based on Pressure Pump: Design and Development
233
equation for best match was y = 0.955x + 1.74 with
correlation coefficient of 0.9996.
3.3 Stability Test of Each Chamber
Pressure
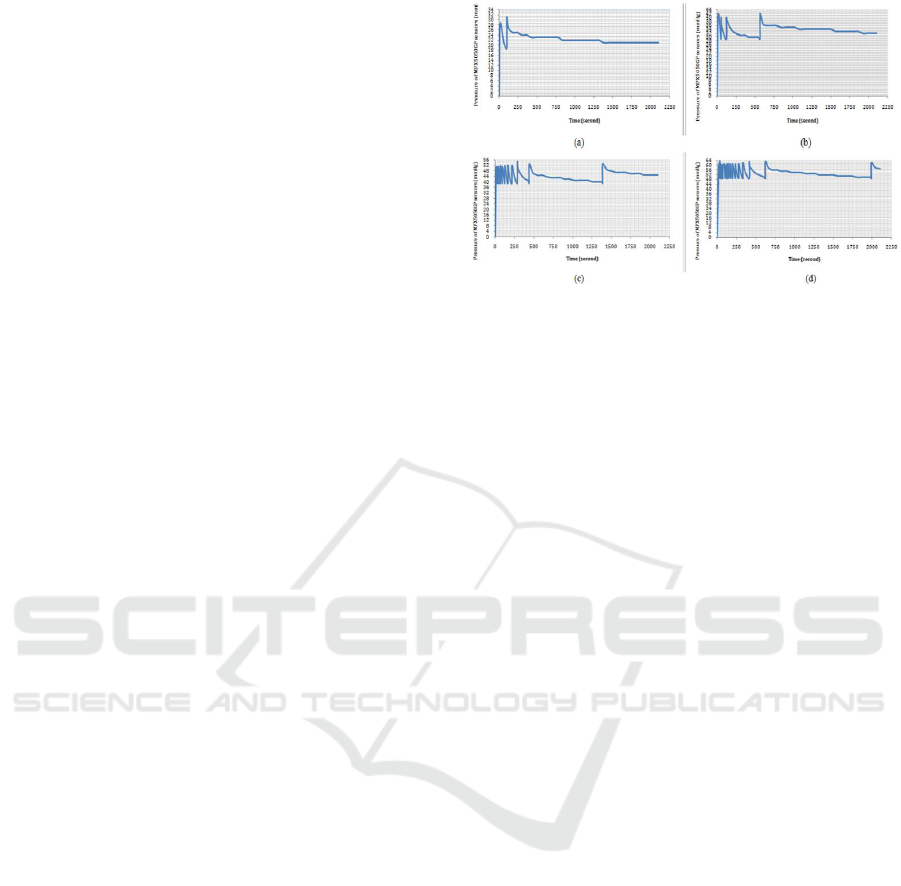
The test results of pressure stability over time in
Figure 3 shows that chamber 1 at 20mmHg-30mmHg
pressure could be fully charged after 11, 9, and 15 s
respectively. The stability of air pressure with a
minimum limit of 20 mmHg and a maximum limit of
30 mmHg could be maintained for 33’20”, 9’14” (1
st
stability) and 22’58” (2
nd
stability), and 5’9” (1
st
stability) and 24’1” (2
nd
stability) for Chamber 1, 2,
and 3 respectively. A pressure of 30mmHg-40mmHg
could be fully charged after 12, 10, and 19 seconds in
chamber 1, 2, and 3 respectively. The stability of air
pressure with a minimum limit of 30 mmHg and a
maximum limit of 40 mmHg could be maintained for
7’23” (1
st
stability) and 25’34” (2
nd
stability), 15’23”
(1
st
stability) and 13’3” (2
nd
stability), and 6’19” (1
st
stability) and 20’9” (2
nd
stability) for chamber 1, 2,
and 3 respectively. 40mmHg-50mmHg pressure
could be fully charged after 12, 12, and 19 seconds
for chamber 1, 2, and 3 respectively. The stability of
air pressure with a minimum limit of 40 mmHg and a
maximum limit of 50 mmHg could be maintained for
15’51” (1
st
stability) and 11’52” (2
nd
stability), 8’12”
(1
st
stability) and 20’9” 2
nd
stability), and for 11’17”
(1
st
stability) and 21’14” 2
nd
stability) for chamber 1,
2, and 3 respectively. 50mmHg-60mmHg pressure
could be fully charged after 16, 24, and 19 seconds
for chamber 1, 2, and 3 respectively. The stability of
air pressure with a minimum limit of 50 mmHg and a
maximum limit of 60 mmHg could be maintained for
3’21” (1
st
stability) and 24’42” (2
nd
stability), 6’51”
(1
st
stability) and 17’8” (2
nd
stability), and 7’14” (1
st
stability) and 17’44” (2
nd
stability) for chamber 1, 2,
and 3 respectively.
The assembled lymphedema pump has a pressure
value in the range of 20mmHg to 60mmHg according
to the standard pressure of the Intermittent Pneumatic
Compression (Partsch et al., 2008). Handcuff could
inflate sequentially from distal to proximal according
to the massage standard for lymphedema patients
especially lymphedema due to breast cancer surgery
and pressure on each chamber could be maintained
for more than 10 minutes (Damstra et al., 2008).
Figure 3: Stability pressure on chamber 1; (A) 20mmHg-
30mmHg pressure; (B) pressure 30mmHg-40mmHg; (C)
40mmHg-50mmHg pressure; (D) 50mmHg-60mmHg
pressure
4 CONCLUSIONS
Controlled pressure values of this device have the
same standard of the intermittent pneumatic
compression within range from 20 mmHg to 60
mmHg. The handcuff could inflate sequentially from
distal to proximal according to the massage standard
for lymphedema patients with pressure on each
chamber could be maintained for more than 10
minutes.
REFERENCES
Damstra, R.J., Brouwer, E.R., Partsch, H., 2008.
Controlled, comparative study of relation between
volume changes and interface pressure under short
stretch bandages in leg lymphedema patients. Dermatol
Surg, 34: 773-8.
Damstra, R.J. and Partsch, H., 2009. Compression therapy
in breast cancer-related lymphedema: A randomized,
controlled comparative study of relation between
volume and interface pressure changes, Journal of
Vascular Surgery, 49(5): 1256-1263.
Feldman, J.L., Stout, N.L., Wanchai, A., Stewart, B.R.,
Cormier, J.N. and Armer, J.M., 2012, Intermittent
Pneumatic Compression Therapy: a Systematic
Review, Lymphology, 45: 13-25.
Freescale Semiconductor Technical data, Integrated Silicon
Pressure Sensor on-Chip Signal Conditioned,
Temperature Compensated and Calibrated, 2007.
Freescale semiconductor inc.
Harris, S.R., Maria, R.H., Ivo, A.O., and Levine, M., 2001,
Clinical practice guidelines for the care and treatment
of breast cancer: 11, Lymphedema, cmaj,, 164(2): 191-
199.
ICPS 2018 - 2nd International Conference Postgraduate School
234

Huntleigh Physician Form, 2001. Journal of Medical
Engineering & Technology, 25(5): 230-235.
Lee, B.B., Laredo, J., Neville, R., Loose, D., 2011.
Lymphedema: A Concise Compendium of Theory and
Practice, Springer: New York, pp.11-69.
Moseley, A.L., Carati, C.J., Piller, N.B., 2007. A systematic
review of common conservative therapies for arm
lymphedema secondary to breast cancer treatment. Ann
Oncol (2007); 18:639-46.
Partsch, H., Clark, M., Mosti, G., Steinlechner, E., Schuren,
J., Abel, M., et al. 2008. Classification of compression
bandages: practical aspects. Dermatol Surg, 34:600-
605.
Torre, L.A., Bray, F., Siegel, R.L., Ferlay, J., Tieulent, J.L.,
Jemal A., Global Cancer Statistics, 2012, CA cancer J.
Clin , 65:87–108.
Whitman, B., Johnson, B., Tomczyk, J., Silberstein, E.,
2012. Refrigeration & Air Conditioning Technology,
7th ed., America: Delmar Thomson Learning USA, pp.
595-636.
Wilson, J., 2005. Sensor Technology Handbook, Oxford:
Elsevier Inc., pp.237-254.
Device of Lymphedema Pump Therapy Based on Pressure Pump: Design and Development
235
